Cell Division (PP #5)
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
mutation
_______ - change in the sequence of DNA nucleotides
no
Are mutations always a bad thing?
meiosis, mitosis
________ produces gametes, ________ produces cells for the rest of the body
more cells will have the mutation
What happens when a mutation occurs earlier in development?
the mutations can’t be passed on to offspring
What happens if mutations are showing up in cells that will never be apart of meiosis?
DNA replication
mutations can often occur during _____ _________, which occurs before mitosis and meiosis
transition mutation
________ ________ - purine replaced by a different purine; pyrimidine replaced by a different pyrimidine (HINT: mutation occurring at the DNA level)
transversion
__________ - purine replaced by a pyrimidine; pyrimidine replaced by a purine (HINT: mutation occurring at the DNA level)
2
How many rings do purines have?
1
How many rings do pyrimidines have?
histones
________ help compact the DNA
silent mutation
_______ ________ - triplet encodes same amino acid (HINT: mutation is occurring at the protein level)
synonymous mutation
_________ ________ - codon specifies different but functionally equivalent amino acid (HINT: mutation is occurring at the protein level)
synonymous mutations
________ ________ will not alter protein function in many cases
missense mutation
_______ _________ - codon specifies a different and nonfunctional amino acid (HINT: mutation is occurring at the protein level)
nonsense mutation
________ ________ - codon signals chain termination; changing from a regular codon to a termination codon (HINT: mutation is occurring at the protein level)
nucleic acids
RNA and DNA are both types of _______ _______
silent mutation
What is a type of neutral mutation?
silent mutation
_______ ______ - a base has been altered in an mRNA codon, but the new base still codes for the same amino acid
protein
when a gene mutation happens it means there was a change in one or more DNA bases, therefore, a new _______ can be produced
substition
_______ - the wrong base is matched (HINT: type of gene mutation)
insertion
_______ - an extra base (or bases) are added in (HINT: type of gene mutation)
deletion
_______ - a base is removed (HINT: type of gene mutation)
deletions, insertions
when it comes to gene mutations, ________ and ________ are considered especially dangerous because bases are read in groups of 3, so if the number of bases increasess/decrease, the total has changed and it might not read the right 3
duplication
________ - extra copies of genes are generated (HINT: type of chromosomal mutation)
deletion
________ - some of the genetic material breaks off (HINT: type of chromosomal mutation)
inversion
_______ - a broken chromosome segment gets inversed (reversed) and put back on the chromosome
translocation
_______ - a fragment from one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome (HINT: type of chromosomal mutation)
mitosis
________ - a type of cell division done by most of your body cells
chromatids
_______ - strands of replicated chromosome
null mutation
_______ ________ - results from proteins that are nonfunctional (ex. not the right shape, etc)
leaky mutation
______ _______ - the active site has a harder time binding to the substrate, so we are seeing less of the enzymatic result
meiosis
________ - a process that contributes to genetic variety, doesn’t make body cells, it makes sperm and egg cells (gametes)
prophase 1
What phase of meiosis does this describe:
the chromosomes will condense and thicken, lining up with their homologous pairs
crossing over occurs
homologous chromosomes
________ ___________ - chromosomes that are approximately the same size and contain the same type of genes in the same locations
crossing over
________ ______ - the chromosomes are lined up with their homologous pairs and are able to transfer their genetic information between each other
metaphase 1
What phase of meiosis does this describe:
the chromosomes are in the middle, just like in mitosis, however, since the chromosomes are in pairs it’s not a single line
anaphase 1
What phase of meiosis does this describe:
the chromosomes are pulled away by the spindle fibers
telophase 1
What phase of meiosis does this describe:
there are two newly formed nuclei and meiosis 1 is ended with two new cells
cytokinesis
__________ follows telophase 1
prophase 2
What phase of meiosis does this describe:
no homologous pairs or crossing over, spindles are starting to form in each cell
metaphase 2
What phase of meiosis does this describe:
the chromosomes are lined up in the middle, this time in a single line
anaphase 2
What phase of meiosis does this describe:
the chromatids are pulled away by the spindle fibers
telophase 2
what phase of meiosis does this describe
the nuclei reform, the two cells are ready to divide, creating 4 cells
cytokinesis
________ follows telophase 2
transition
What DNA level mutation is this image an example of?
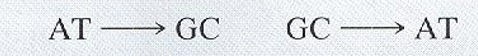
transition
What DNA level mutation is this image an example of?

transversion
What DNA level mutation is this image an example of?

transverison
What DNA level mutation is this image an example of?
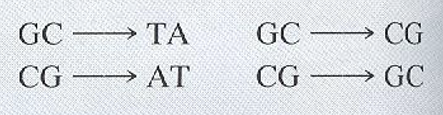
silent mutaiton
What protein level mutation is this image an example of?
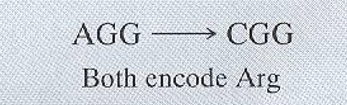
synonymous mutation
What protein level mutation is this image an example of?

nonsense mutation
What protein level mutation is this image an example of?

unequal crossover
_______ ________ - sister chromatids are not lined up right during crossover, so they are not at the same nucleotide regions during cross over
translocation
_______ - crossover between not homologs
interstitial deletion
What type of chromosomal mutation is this?
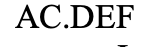
terminal deletion
What type of chromosomal mutation is this?
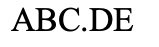
duplication
What type of chromosomal mutation is this?
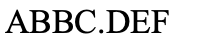
tandem duplication
What type of chromosomal mutation is this?
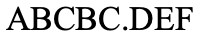
reverse duplication
What type of chromosomal mutation is this?
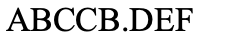
paracentric inversion
What type of chromosomal mutation is this?
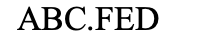
pericentric inversion
What type of chromosomal mutation is this?
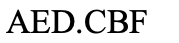
translocation
What type of chromosomal mutation is this?