Chapter 1: History of Chemistry
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Who is Antoine Lavoisier?
Created law of conservation of mass
mass is neither created or destroyed
combustion involves oxygen
Joseph Proust
1) Law of Definite Proportions
the proportion by mass of the elements in a specific compound is always the same
ex: in water, the mass of oxygen is always eight times the mass of water.
John Dalton
1) Law of Multiple Proportions
When two elements combine with each other to form more than one compound, the weights of one element that combine with a fixed weight of the other are in a ratio of small whole numbers.
2) Atomic Theory Postulates
3) Created a periodic table organized by atomic mass but most were wrong
John Dalton’s Atomic Theory
Elements are made of atoms
Atoms of a given element are identical
The atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element
Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds
A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms
Atoms are indivisible by chemical processes. That is atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. A chemical reaction simply changes the way atoms are grouped together.
Which of Dalton’s postulates were wrong
1) Atoms are indivisible
protons, electrons, neutrons exist
2) Atoms of a given element are identical
isotopes = different amount of neutrons
Avogadro
Equal volumes of different gases under the same temperature and pressure contain the same # of molecules
22.4 L in 1 mol
Cannizzaro
Discovered approx values of atomic masses
JJ Thomson
Cathode Ray Tubes
When high voltage applied to a tube, a cathode ray is produced
Cathode ray emerges from negative electrode
repelled by the negative pole of an applied electric field
He theorized ray was a stream of negatively charged particles called electrons
Discovered the electron
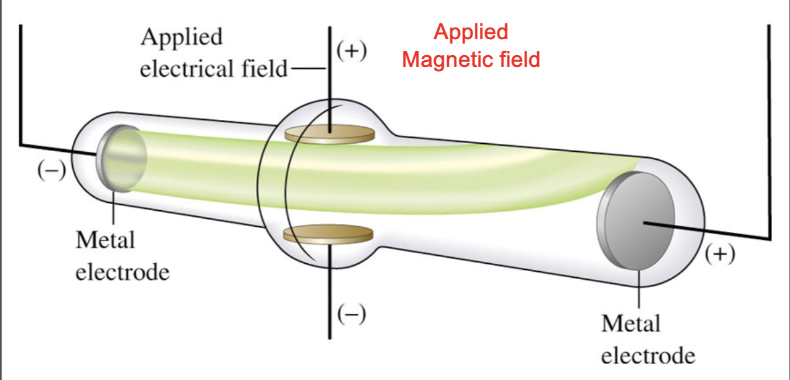
Charge to mass ratio of an electron
Charge/mass = e/m = -1.76 × 10^8 C/g
e = charge on the electron in coulombs (C)
m = electron mass in grams
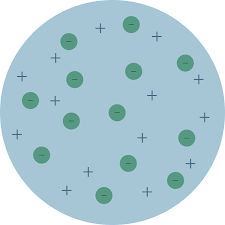
Plum Pudding Model
1. JJ Thomson
2. An atom is electrically neutral. It has no charge.
3. + charges and - charges are equal.
4. An atom is made out of a sphere of + charges with -negatively charged electrons embedded in it.
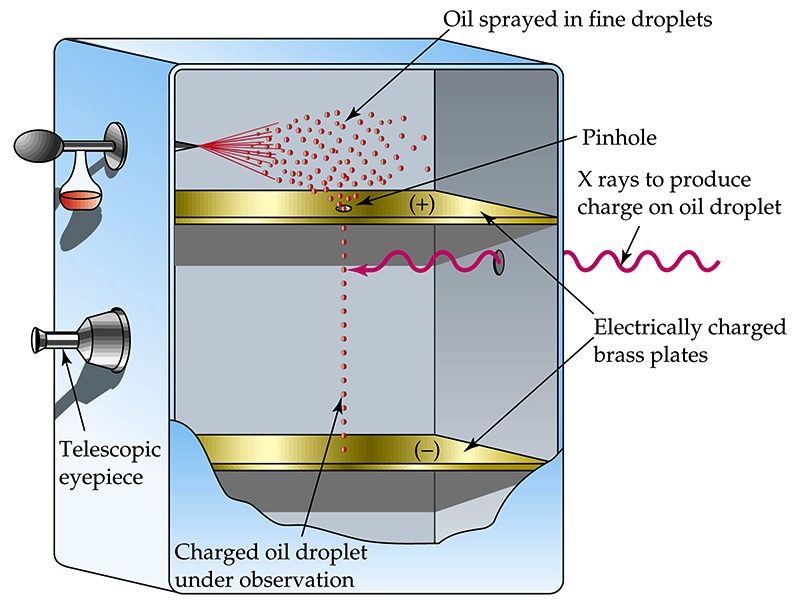
Robert Millikan
Charged Oil Drop Experiment
determined magnitude of electron charge
(Mass of drop x gravity) = (electric field x charge)
Mass of an electron
9.1 × 10^-31 kg
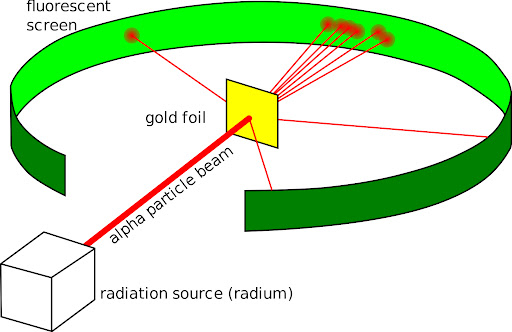
Ernest Rutherford
Shot alpha particles at a thin sheet of metal foil
He expected α particles to travel through foil
However many alpha particles were deflected or reflected
Deflections caused by a center of concentrated positive charge in the atom
Discovered the nucleus
Electrons equal the number of _____
protons, in neutral atoms
Isotope
different amount of neutrons
Mass number
neutrons + proton
top number on element notation
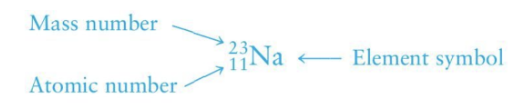
Atomic number
number of protons
bottom number on element notation
top number on periodic table
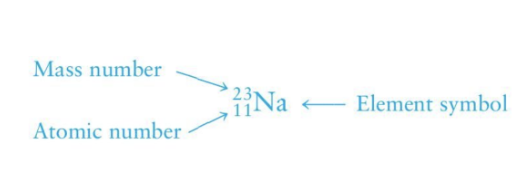
Chemical behavior determined by _____
electrons
Chadwick
Neutrons exist, no charge, isotopes exist
Isotope - different amt of neutrons