(MICROECONOMICS) - Elasticity (copy)
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Why We Study Elasticities?
Elasticity examines the responsiveness of consumers or producers to a change in a variable in the marketplace.
how much one factor changes in response to a change in a different factor.
Helps consumers + produces know how to set prices accordingly
Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)
A measure of the responsiveness of the quantity of a good demanded to changes in its price.
PED formula
PED = (Percentage change in Quantity) / (Demanded Percentage change in Price)
PED = (% ΔQuantityDemanded) / (% ΔPrice)
PED = ((Qf-Qi) / (Pf - Pi)) x (Pi / Qi)
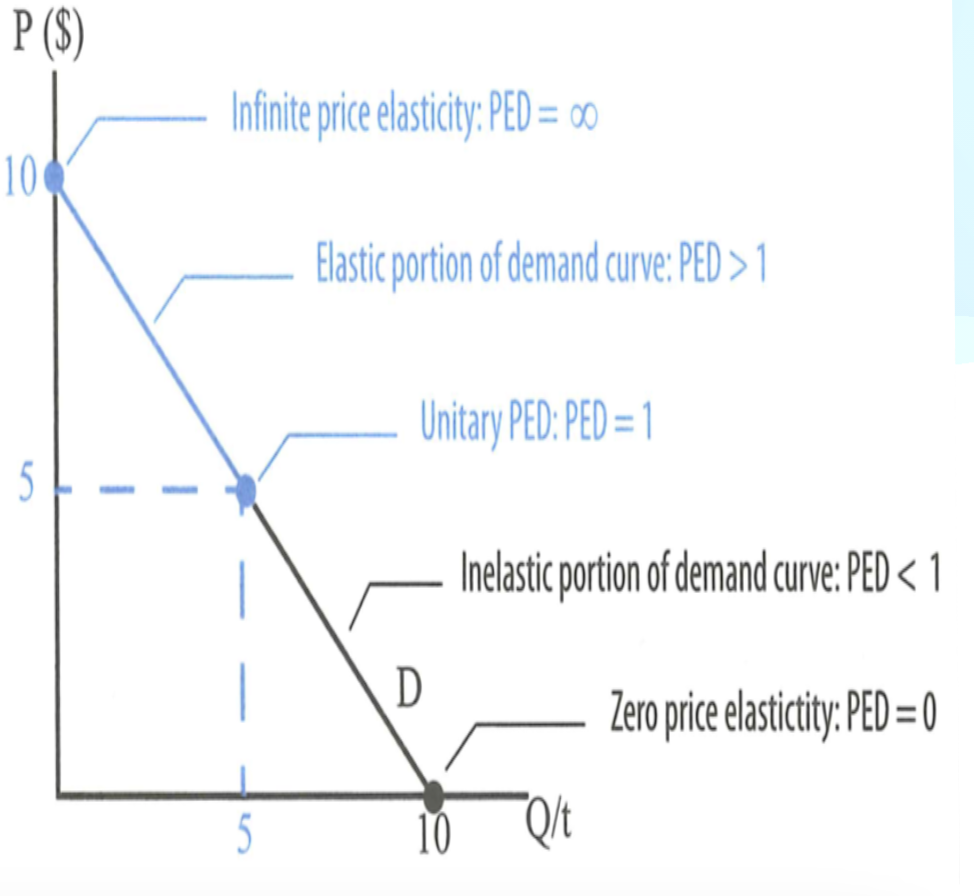
Signs & values of PED
Always look at absolute value of PED: IPEDI
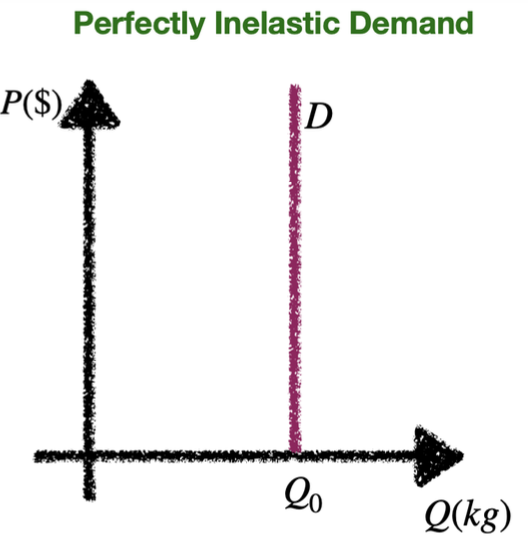
PED = 0: Perfectly inelastic demand
0 < PED < 1: Inelastic demand
PED = 1: Unit elastic demand
1 < PED < ∞: Elastic demand
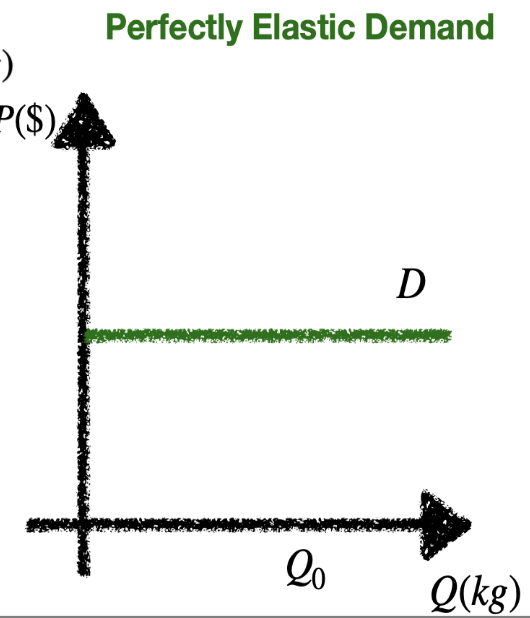
PED = ∞: Perfectly elastic demand
High PED
Demand is elastic: greatly influenced by price changes (high responsiveness)
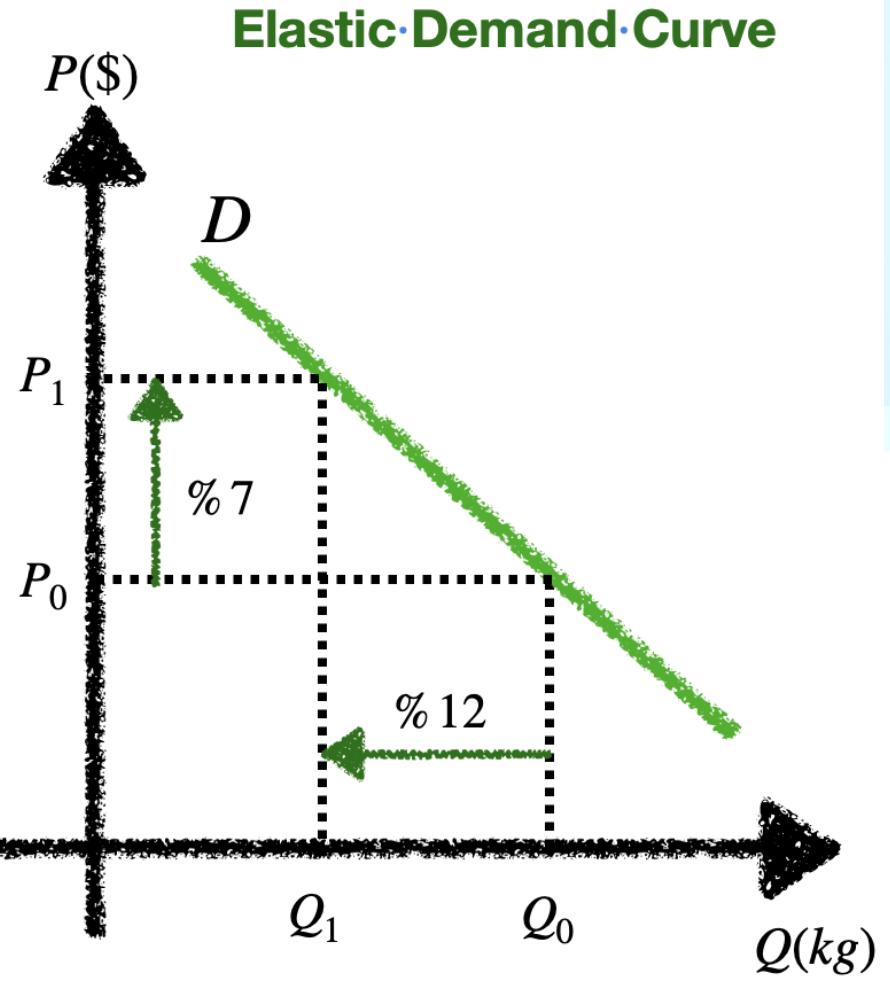
Low PED
Inelastic: demand stays the same regardless of price change (low responsiveness: consumer needs it)
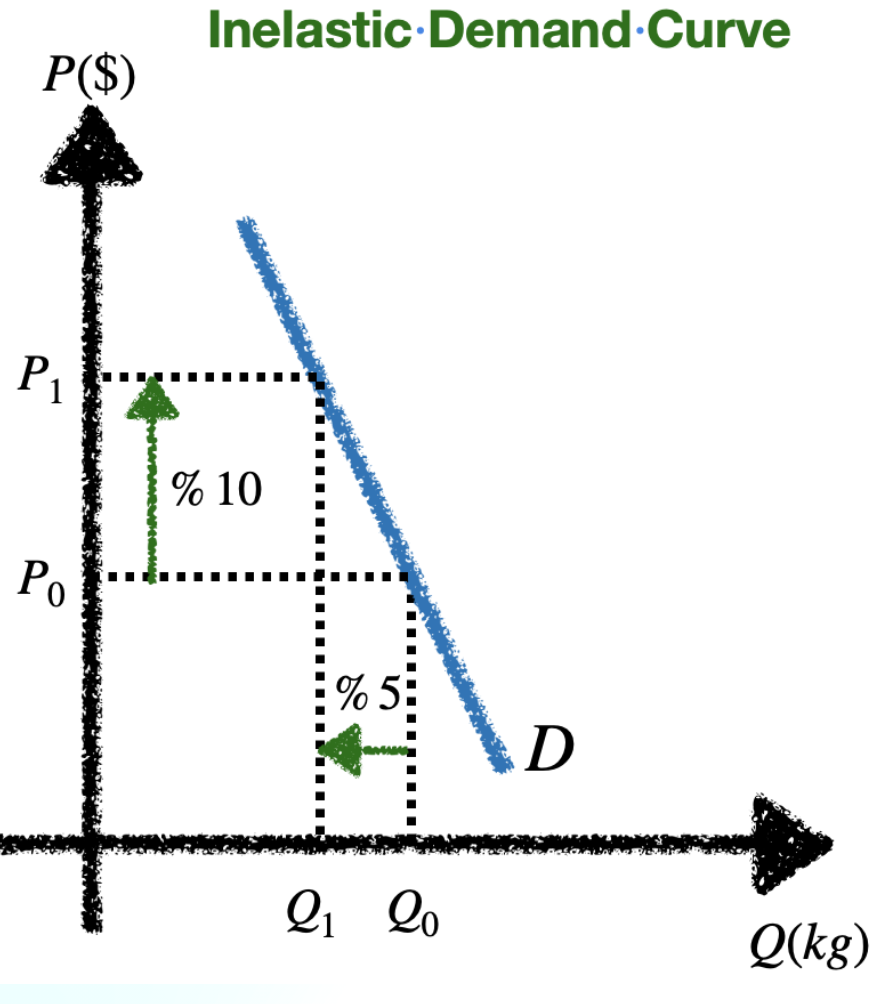
Shrinkflation
Producers reducing the size, quantity, or weight of a product while keeping the same price
Elasticities on a demand curve
Elasticity varies not only between different goods, but also along the demand curve for any specific good portrayed using a straight- line demand curve.
Perfectly inelastic demand diagram
Perfectly elastic demand diagram
6 Determinants of PED
Number of Substitutes
Most substitutes = more elastic
e.g. coffee barely has good substitutes, however, any coffee shop has many substitutes
Complements (Joint Demand)
Elasticity of 1 good is influenced by elasticity of other good (both inelastic or elastic)
Proportion of Income
Change in price of car VS toothpick (for rich VS poor person)
Luxury or Necessity
Luxury not needed VS necessity needed
Addictive or not
Addicted consumers = inelastic (need that good)
Time to respond
People won’t change immediately → need time to find substitute/not immediately see price change
Applications of PED
Revenue of a firm
Taxes imposed:
Flat rate tax
Applies same rate to all taxpayers regardless of income
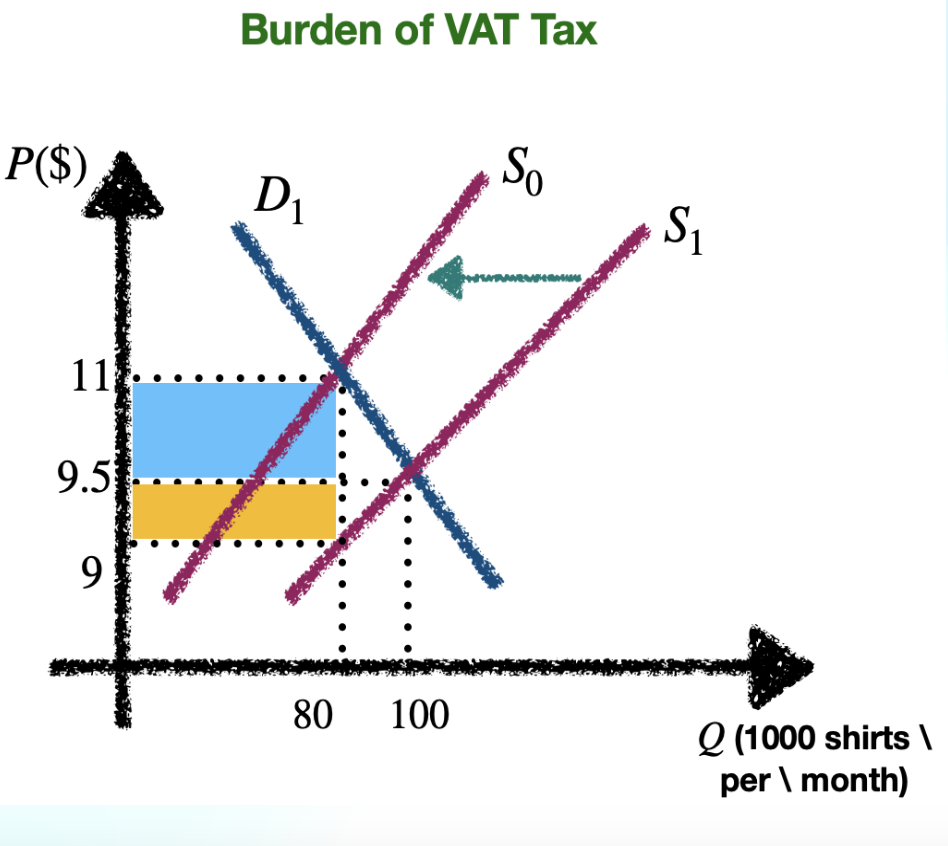
Ad valorem tax (VAT)
based on value of good
tax is percentage of sale value of good
Indirect tax
imposed on manufacturers & service providers
Cross elasticity of demand (XED)
Measures the relative sensitivity of a change in the quantity demanded of Good X with respect to a change in the price of Good Y.
Closeness of substitutes & relevance of complements
XED formula
XED = (Percentage change in Quantity Demanded of Good X) / (Percentage change in Price of Good Y)
XED = (%ΔQuantityDemanded X) / (% ΔPrice Y)
XED = ((Qxf-Qxi) / (Pyf - Pyi)) x (Pyi / Qxi)
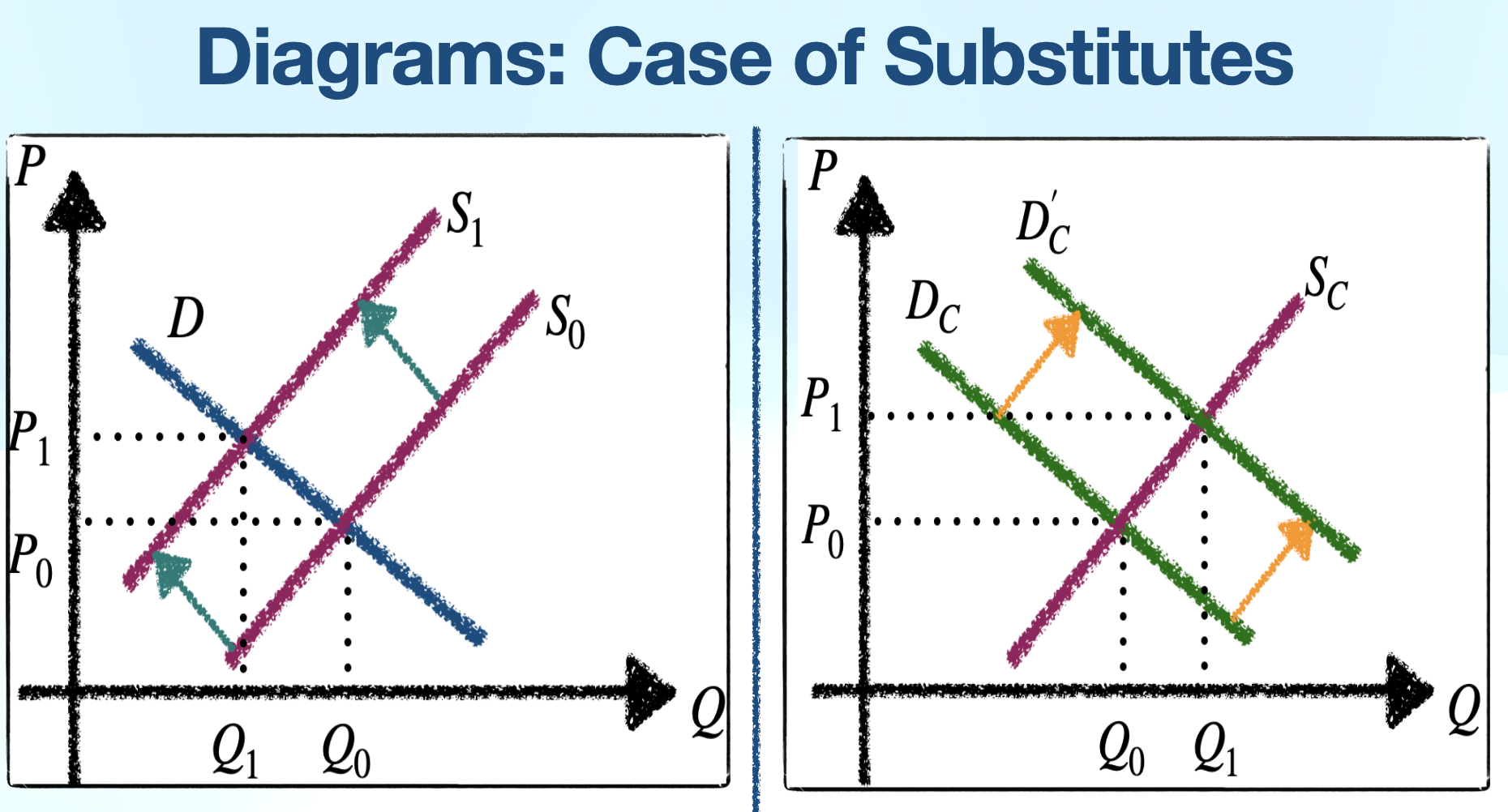
XED > 0
Substitute goods:
proportional: price x increases = demand y increases
Larger value XED = greater substitutability: more similar
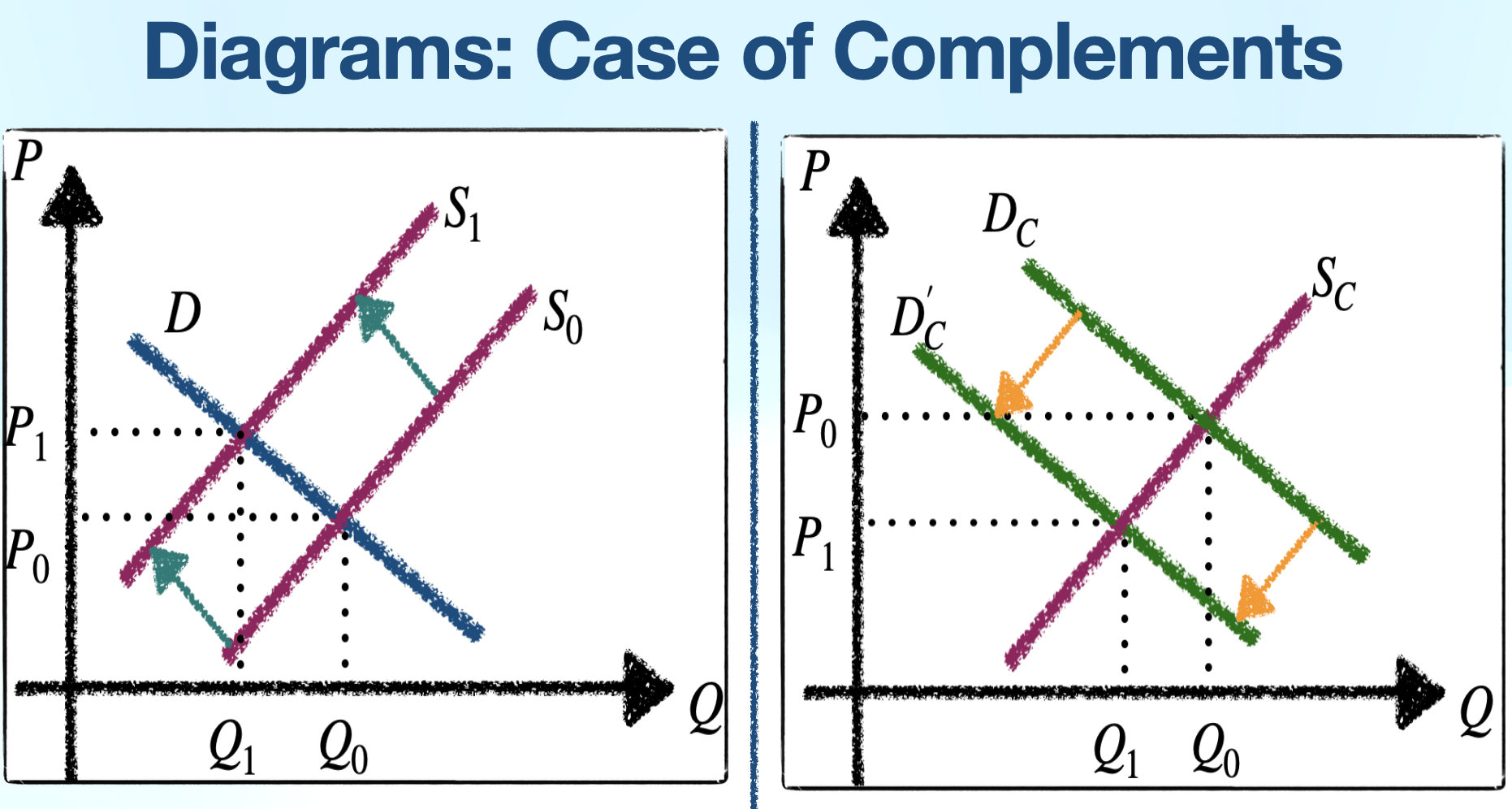
XED < 0
Compliment goods:
Inverse: price x increases = demand y decreases
Larger absolute value of XED = more complimentary
XED = 0
If cross-price elasticity of demand is zero (XED = 0) or close to zero, this means that two products are unrelated or independent of each other.
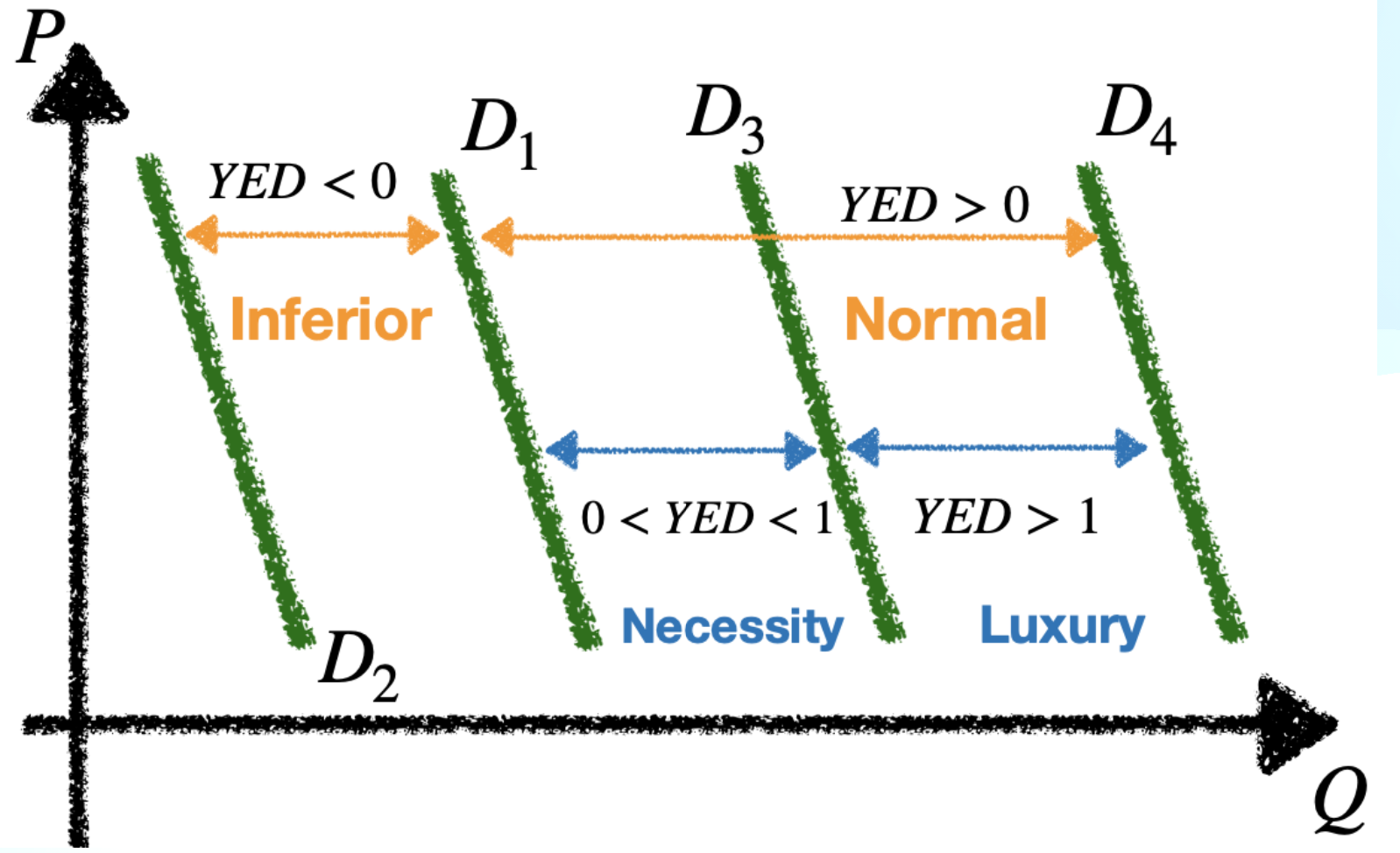
Income elasticity of demand (YED)
Measure of the responsiveness of demand to changes in income, and involves demand curve shifts.
YED formula
YED = Percentage change in Quantity / Demanded Percentage change in Income
YED = (% ΔQuantityDemanded) / (% ΔIncome)
YED = XED = ((Qf-Qi) / (Yf - Yi)) x (Yi / Qi)
YED > 0
The good is normal: income increases = demand increases
YED < 0
The good is inferior: income increases = demand decreases
Numerical value of YED
0 < YED < 1: income inelastic demand, e.g. necessities
YED > 1: Income elastic demand, e.g. luxury goods
YED & producers
If national income increases,
goods/services with elastic demand will increase
goods/services with inelastic demand will decrease
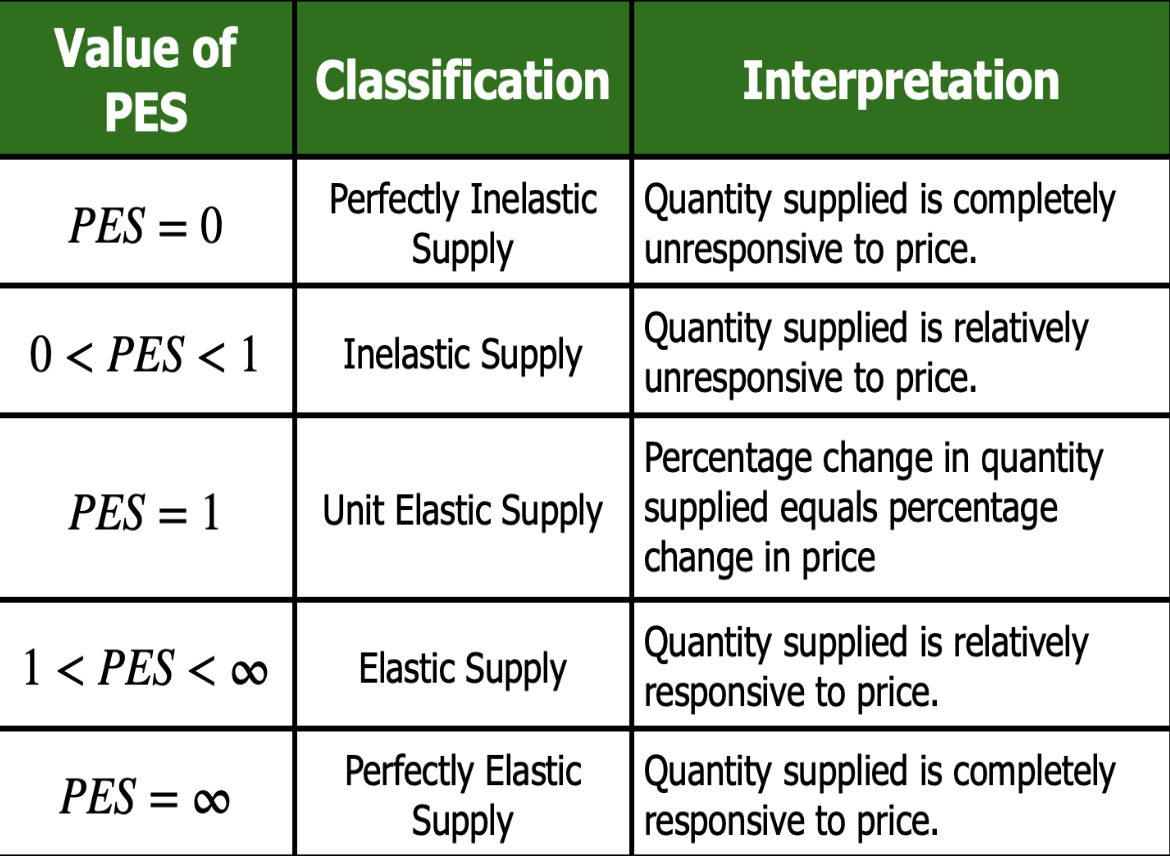
Price elasticity of supply (PES)
A measure of the responsiveness of the quantity of a good supplied to changes in its price.
PES formula
PES = ((Percentage change in Quantity Supplied) / (Percentage change in Price)) × 100
PES = ((%ΔQuantitySupplied) / (% ΔPrice)) ×100
PES = ((Qf-Qi) / (Pf - Pi)) x (Pi / Qi)
Values of PES
PES = 0: Perfectly inelastic supply
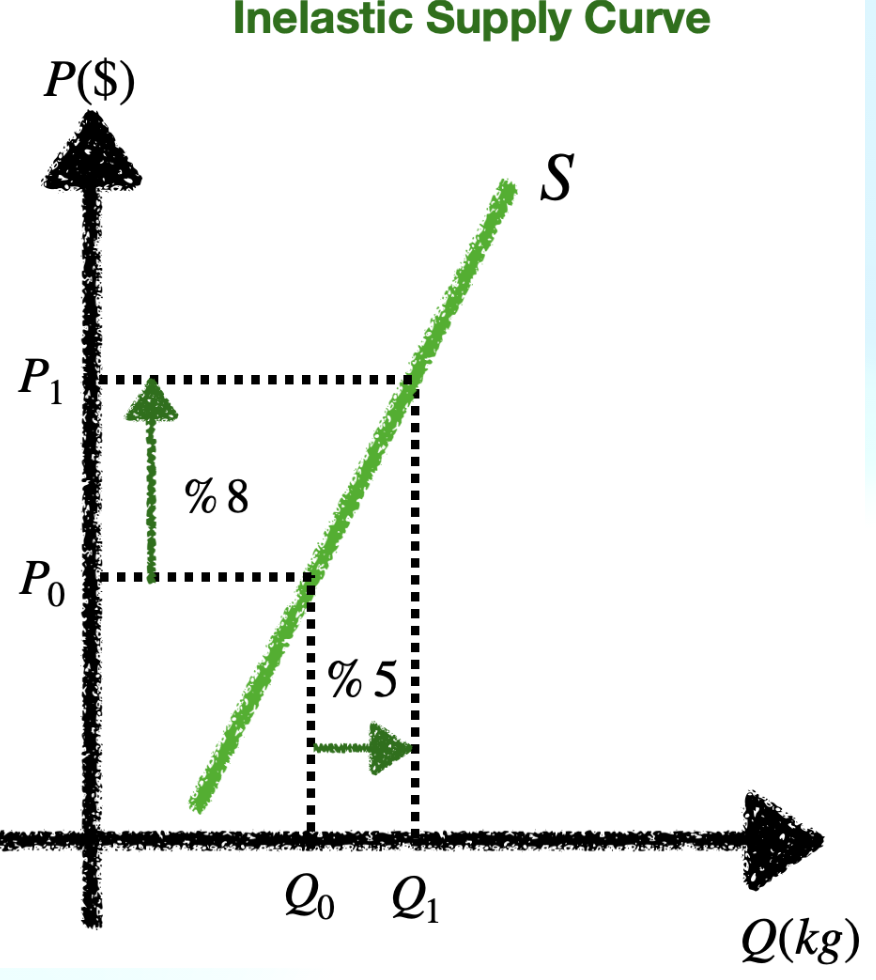
0 < PES < 1: Inelastic supply
PES = 1: Unit elastic supply
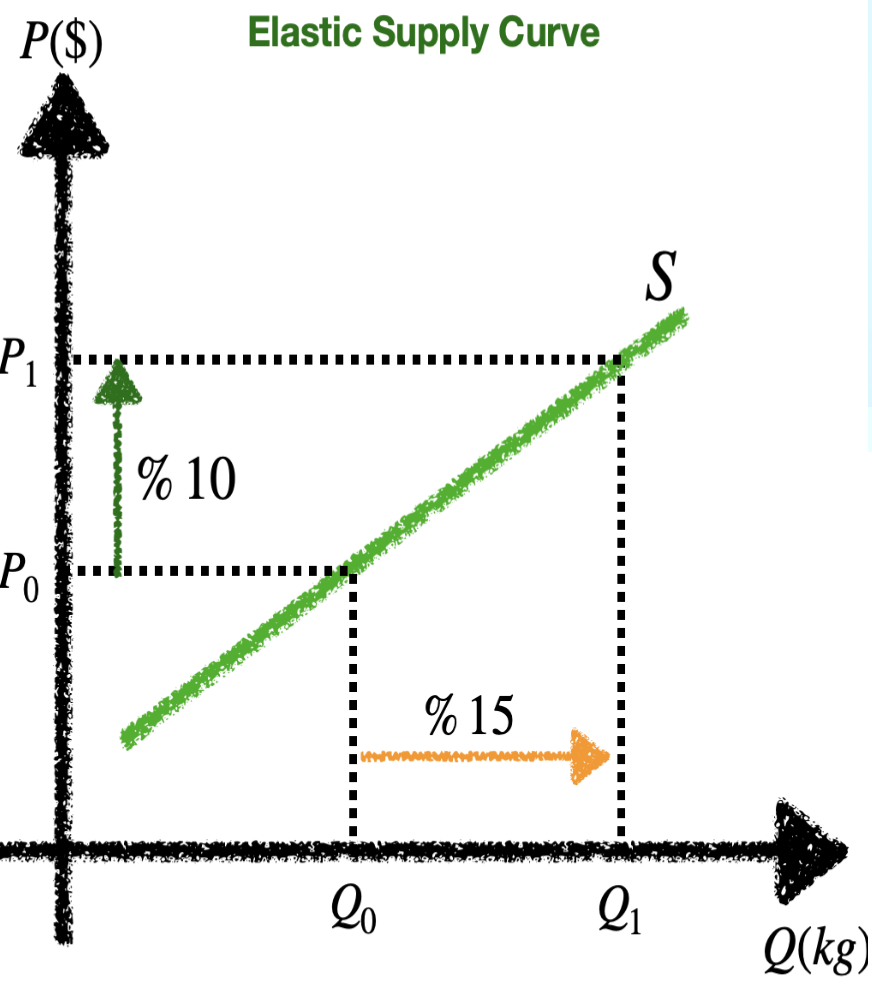
1 < PES < ∞: Elastic supply
PES = ∞: Perfectly elastic supply
Inelastic supply curve
Elastic supply curve
perfectly elastic supply curve
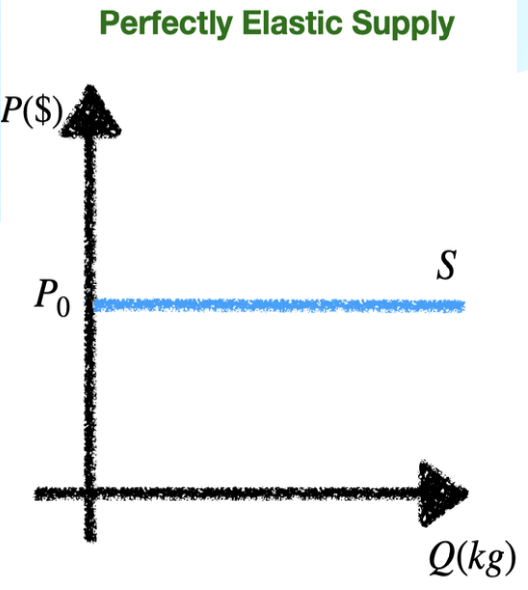
perfectly inelastic supply curve
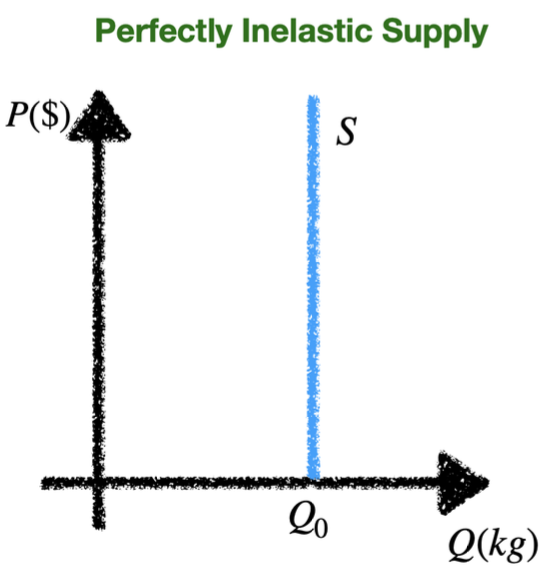
Determinants of PES
Length of time
Amount of time producers have to adjust output in regards to price changes
Mobility of factors of production
Ease/speed firms can shift resources/production (easier to move capital)
Spare (unused) capacity of firms
How much a firm can produce without needing to expand inventory
Ability to store stocks
Buffer stocks