Electrophilic Addition of Halogens to Alkenes
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What is an electrophile?
A species which is strongly attracted to electrons because it is electron-deficient.
Electrophiles are usually…
Positively charged.
This means they have the ability to accept a lone pair of electrons.
What is a nucleophile?
A species which is strongly attracted to positive charge.
Nucleophiles are usually…
Negatively charged.
How do nucleophiles react?
Nucleophiles react by donating a lone pair of electrons to an electron-deficient species to form a covalent bond.
Do halogen molecules have permanent dipoles?
No.
Halogens are non-polar molecules.
Explain why electrophiles are attracted to the C=C double bonds in alkenes.
The C=C double bond is a region of high electron density.
Electrophiles are attracted to electrons.
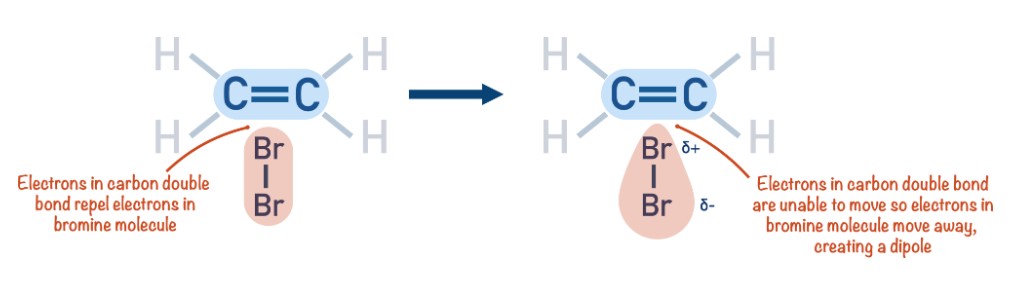
Describe what happens when a halogen molecule (bromine) approaches the C=C double bond in an alkene molecule(ethene).
As the bromine molecules approaches the ethene molecule, the high electron density of the C=C double bond repels the electron pair in the bromine molecule.
This induces a dipole in the bromine molecule.
The bromine atom nearest to the double bond exhibits a partially positive charge (δ+). This positive atom acts as the electrophile.
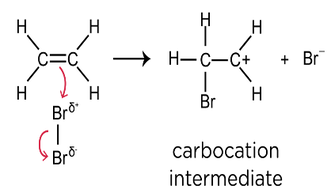
Describe what happens when a dipole has been induced in the halogen (bromine) molecule.
The C=C double bond breaks.
The bromine atom with a partially positive (δ+) charge is attracted to the region of high electron density of the double bond.
This causes a bond to be formed between this delta positive bromine atom and one of the carbon atoms in the double bond, causing the double bond to break.
A carbocation is formed.
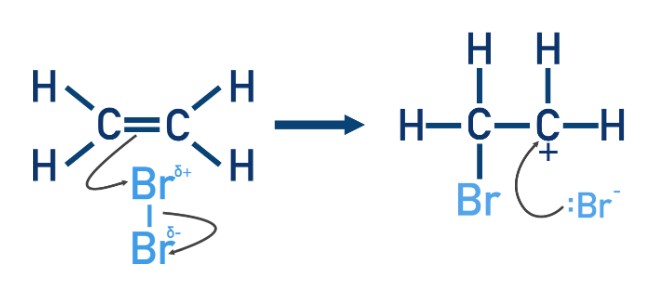
What happens to the electrons in the bromine molecule when a bond is formed between the partially positive bromine atom and one of the carbon atoms in the double bond?
Electrons from the Br-Br bond move to the partially negative bromine atom, leaving a bromide ion with a lone pair of electrons.
This is an example of heterolytic bond fission.
What is heterolytic bond fission?
When the covalent bond breaks unevenly, and one of the bonded atom receives the shared pair of electrons.
What is a carbocation?
A carbocation is a positively charged carbon ion formed by the loss of a bonding electron.
This means there are 3 covalent bonds instead of 4.
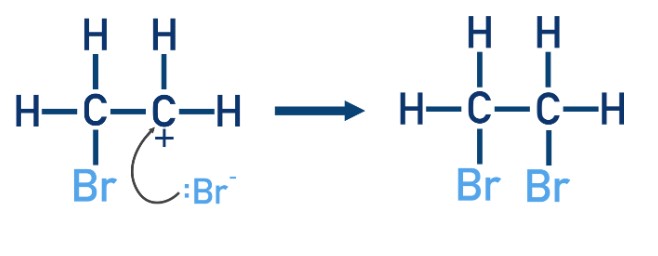
Describe what happens after a carbocation is formed.
The bromide ion with a negative charge approaches the carbocation and forms a covalent bond with it by donating its lone pair of electrons.
The product formed is 2-dibromoethane.