EARTH SCIENCE LAB STUDY GUIDE
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/127
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:28 PM on 11/29/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
1
New cards
Aerial photographs
important tools for studying earth's surface
2
New cards
stereogram
Overlapping images that allow you to see the earth's surface in 3D
3
New cards
Satellites
are used to study phenomena such as volcanic eruptions, hurricanes, and oil spills
4
New cards
satellites
help identify hidden features on earth's surface and in remote locations
5
New cards
topographic map
is a two dimensional flat representation of a three dimensional land surface
6
New cards
topographic maps show
-hills, valleys, streams, lakes, rivers, slopes, gullies, mountains
-elevations and depressions of hills and mountains
roads, buildings, parks
-elevations and depressions of hills and mountains
roads, buildings, parks
7
New cards
Quadrangle
is a rectangular section of the Earth’s surface that is bound by lines of latitude at the top/bottom and lines of longitude along the sides
8
New cards
Latitude
north / south
9
New cards
longitude
east / west
10
New cards
Prime meridian
GREENWICH, ENGLAND
11
New cards
Contour lines have
equal lines of elevation
12
New cards
Relief is
the difference in elevation between landforms (difference between the highest point and lowest point on the map)
13
New cards
Gradient is
the measurement of the steepness of a slope (finding the steepness of an incline or decline)
-Amount of rise or fall of points a and B divided by the
distance between points A and B
-Amount of rise or fall of points a and B divided by the
distance between points A and B
14
New cards
A topographic profile
is a cross section that shows the elevation and slopes along a given line
15
New cards
Vertical exaggeration
is larger than the horizontal scale of the map
-Divide the horizontal ratio scale by the vertical ratio scale
-Divide the horizontal ratio scale by the vertical ratio scale
16
New cards
Valley
low lying land bordered by higher ground
17
New cards
hill
rounded elevation of land- a mound
18
New cards
ridge
linear or elongated elevation or crest of land
19
New cards
closed depression
low point/area in a landscape from which surface water cannot drain, contour lines with hachure marks
20
New cards
steep slope
closely spaced contour lines
21
New cards
gentle slope
widely spaced contour lines
22
New cards
PLSS
public land service system
23
New cards
GPS
global positioning satellite
24
New cards
UTM
Universal Transverse Mercator grid
25
New cards
Agents of Earth
water, wind, glacier, creatures
26
New cards
water cycle
Precipitation, evaporation, transpiration, runoff, infiltration
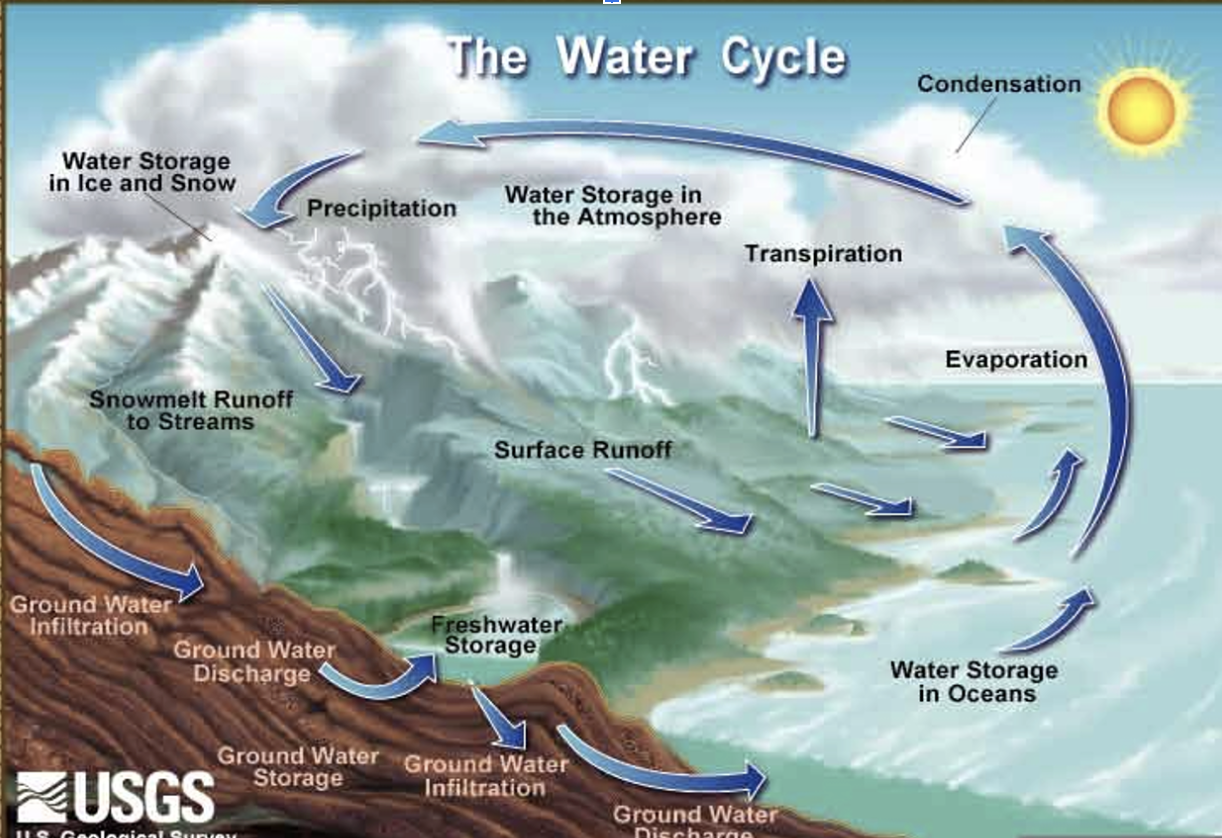
27
New cards
Infiltration
rain that falls on the ground and is absorbed, runoff happens when there is no more room for absorption
28
New cards
Rivers and streams
are responsible for creating erosion and deposition
29
New cards
An example of a stream valley
GRAND CANYON
30
New cards
Ground water fully soaks the soil in the
zone of saturation
31
New cards
Water table
Upper surface of the saturated zone
32
New cards
The unsaturated zone has pores that are mainly filled
AIR
33
New cards
Ground subsidence
is when ground water is removes and sediments and grains become compressed and the pores collapse so the land surface cracks and sinks
34
New cards
desert
arid
35
New cards
steepe
semiarid
36
New cards
desert covers ___% of earths surface
30%
37
New cards
alluvial fans
form as streams deposit sediments at a base of a mountain
38
New cards
playa lake
temporary feature that evaporates or infiltrates the ground in the center of a basin
39
New cards
bajadas
union of alluvial fans
40
New cards
playa
dry, flat lake bed
41
New cards
pediment
broad sloping bedrock surface, covered by thin layer of sediment
42
New cards
inselburg
continued erosion, leaving nearly flat surface dotted with isolated peaks
43
New cards
Sand dunes ripple because
of wind
44
New cards
Glacier forms
when yearly snow falls exceeds quantity of ice lost by melting
45
New cards
Valley and alpine glaciers form
on mountains and flow down through valleys
46
New cards
Ice sheet
is larger than a glacier and flows in all directions
47
New cards
GREENLAND
NORTHERN HEMISPHERE
48
New cards
ANTARCTICA
SOUTHERN HEMISPHERE
49
New cards
cirque
is a amphitheater shaped basin at the head of a glaciated valley
50
New cards
arete
is a narrow knifelife ridge that separates two adjacent glaciated valleys
51
New cards
horn
is a pyramid like peak
52
New cards
hanging valley
U shaped valley
53
New cards
Glacial drift
all glacial sediments
54
New cards
Till
is unsorted sediments deposited directly by a glacier
55
New cards
Moraines
are layers of till that form on outer margins of glaciers
56
New cards
Stratified drift
is sorted and deposited by glacial meltwater
57
New cards
drumlin
looks like an inverted spoon
58
New cards
kettle lake
lake depressions formed when blocks of ice become lodged in ground
59
New cards
eskers
are sinuous ridges made of sand/gravel deposited from meltwater near glacier terminus
60
New cards
tarn
is a small lake occupying a cirque
61
New cards
Paternoster lakes
is a chain of small lakes that occupy basins formed by glacial erosion
62
New cards
radioactive isotopes
-is used to calculate the ages of rocks
-emit particles from their nuclei that cause radiation
-The rate of decay is the half-life, the time it takes for half of the parent isotope to decay
-emit particles from their nuclei that cause radiation
-The rate of decay is the half-life, the time it takes for half of the parent isotope to decay
63
New cards
Original horizontality
bedding originally deposited in horizontal sheets
64
New cards
lateral continuity
beds extend laterally out in all directions until pinched out by reaching edge of deposition basin
65
New cards
superposition
is the oldest layers at the bottom of sequence, youngest layers at the top
66
New cards
Inclusions
are a clast included in another rock must be older than the rock it is in
67
New cards
Cross cutting
is any feature that cuts through a body of rock is younger than the rock
68
New cards
conformable beds
Layers of rock that have been deposited without interruption
69
New cards
unconformity
represents a long period of time where no deposition occurred
70
New cards
Angular unconformity
is when adjacent beds are at an angle
71
New cards
disconformity
is a gap in rock record representing a period of erosion rather that deposition
72
New cards
Nonconformity
is younger sedimentary rocks overlying older metamorphic or igneous rocks
73
New cards
Fossils
are important tools for determining geological history and prehistoric environments
74
New cards
PETRIFICATION
internal pores/caveties of an organism are filled with precipitated mineral matter
75
New cards
CAST
the space once occupied by dissolved shell or other structure is filled with mineral matter
76
New cards
IMPRESSION
a replica of an organism left in fine-grain sedimentary rock
77
New cards
Carbonization
preservation that occurs when fine sediments encase a delicate plant or animal forms and leaves a residue of carbon
78
New cards
Amber
hardened resin of ancient trees that preserved delicate organisms such as insects
79
New cards
indirect evidence
traces of prehistoric life but not the organism itself
80
New cards
oceanography
Study of the physical and biological aspects of the ocean
-Ocean covers 71% of earth’s surface
-Ocean covers 71% of earth’s surface
81
New cards
Ocean Basins:
Pacific
Atlantic
Arctic
Indian
Southern
Atlantic
Arctic
Indian
Southern
82
New cards
ocean basins form
where two tectonic plates diverge from one another
83
New cards
Continental shelf
flooded extension of continent, submerged surface that extend from the shoreline toward the ocean basin
84
New cards
Continental slope
the seaward edge of the continental shelf; a relatively steep zone that marks the boundary of continental crust and oceanic crust
85
New cards
Seamounts
are remnants of extinct volcanic activity
86
New cards
Bathymetry
mapping the ocean floor using sonar
87
New cards
Physical properties of the ocean
Salinity- amt of dissolved salts in water
Temperature
Density of seawater is influenced by salinity and temperature
Surface currents are primarily driven by prevailing global winds
Deep ocean currents are primarily driven by a gradient in water density
WHERE DO SURFICIAL WATERS SINK?
88
New cards
waves
is vibratory motion of water particles around their mean positions
89
New cards
currents
are unidirectional movement of a body of water
90
New cards
tides
are regular fluctuations in local sea levels which occur as a result of the moon’s gravitational pull on the Earth
91
New cards
Waves transfer energy from
one place in the ocean to another; most ocean waves derive energy from wind
92
New cards
Wave height
vertical distance between trough and crest
93
New cards
wavelength
horizontal distance between two crests
94
New cards
crest
water particles are at their highest point
95
New cards
trough
water particles at their lowest point
96
New cards
waves are ______ as they approach shoreline
refracted
97
New cards
Deposited sediments
accumulate to form beaches, spits,a nd baymouth bars
98
New cards
Breach drift
occurs when an uprush of water an angle to the shoreline causes sediments to move in a zigzag pattern along the beach
99
New cards
Longshore current
occurs when turbulent water in the surfzone moves in a zigzag motion, parallel to shore
100
New cards
Two coasts
US PACIFIC and US ATLANTIC