Ch5 Microeconomics Year 2 Term 1
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Elasticity
A general concept used to quantify the response in one variable when another variable changes.
elasticity of A with respect to B
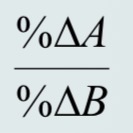
Price of elasticity demand
This is the degree of responsiveness of a change in quantity demanded as a result of a unit change in price
Price of elasticity demand
The ratio of the percentage of change in quantity demanded to the percentage of change in price; measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in price.
price elasticity of demand formula
% change in quantity demanded / % change in price
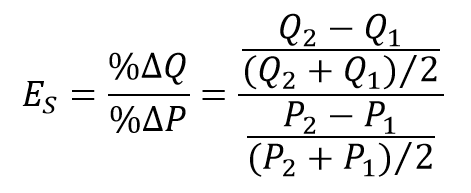
Perfectly Inelastic Demand
Demand in which quantity demanded does not respond at all to a change in price.
Perfectly Elastic Demand
Demand in which quantity drops to zero at the slightest increase in price.
A good way to remember the difference between the two perfect elasticities is

Perfectly Inelastic Demand Curves
Price elasticity of demand is zero.
Perfectly Elastic Demand Curves
A tiny price increase drives the quantity demanded to zero.
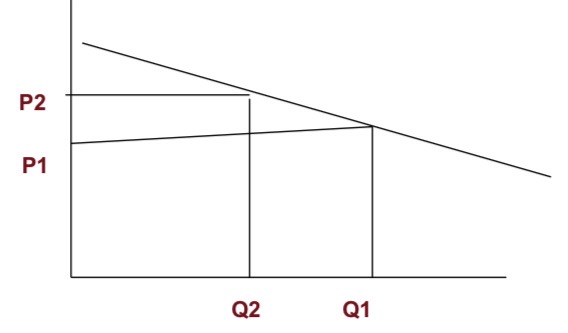
Elastic demand
A demand relationship in which the percentage change in quantity demanded is larger than the percentage change in price in absolute value (a demand elasticity with an absolute value greater than 1).
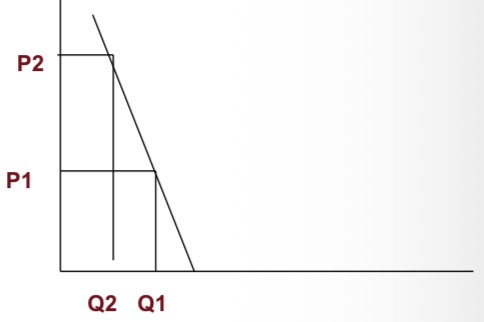
Inelastic demand
Demand that responds somewhat, but not a great deal, to changes in price. Inelastic demand always has a numerical value between zero and 1.
unitary elasticity
A demand relationship in which the percentage change in quantity of a product demanded is the same as the percentage change in price in absolute value (a demand elasticity of 1).
Elastic demand graph
Inelastic demand graph
Unitary demand graph
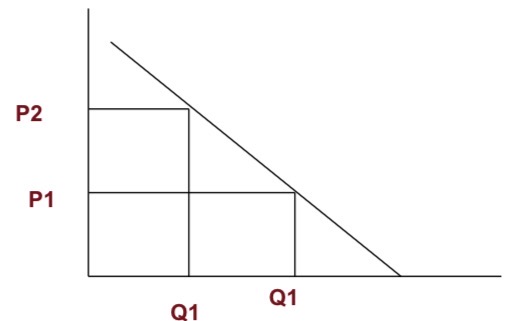
Calculating Elasticities -Calculating Percentage Changes
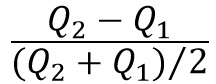
percentage change in price
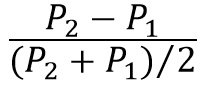
calculating elasticity in ratio of percentages
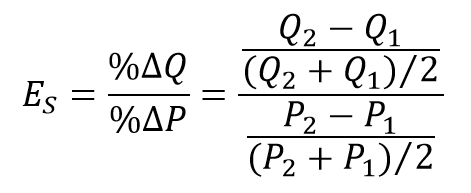
Midpoint formula
A more precise way of calculating percentages using the value halfway between P1 and P2 for the base in calculating the percentage change in price and the value halfway between Q1 and Q2 as the base for calculating the percentage change in quantity demanded.
the actual Midpoint formula
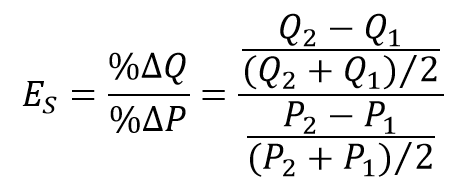
Point Elasticity
A measure of elasticity that uses the slope measurement.
We have defined elasticity as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price. We can write this as…
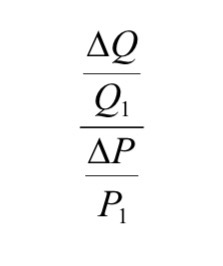
Where ∆ denotes a small change and Q1 and P1 refer to the original price and
quantity demanded.
This can be rearranged and written as
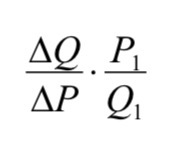
is the reciprocal of the slope.
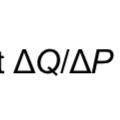
Availability of Substitutes
Perhaps the most obvious factor affecting demand elasticity is the availability of substitutes.
The Importance of being unimportant
When an item represents a relatively small part of our total budget, we tend to pay little attention to its price.
The Time Dimension
The elasticity of demand in the short run may be very different from the elasticity of demand in the long run. In the longer run, demand is likely to become more elastic, or responsive, simply because households make adjustments over time and producers develop substitute goods.
Point Elasticity Changes Along a Demand Curve
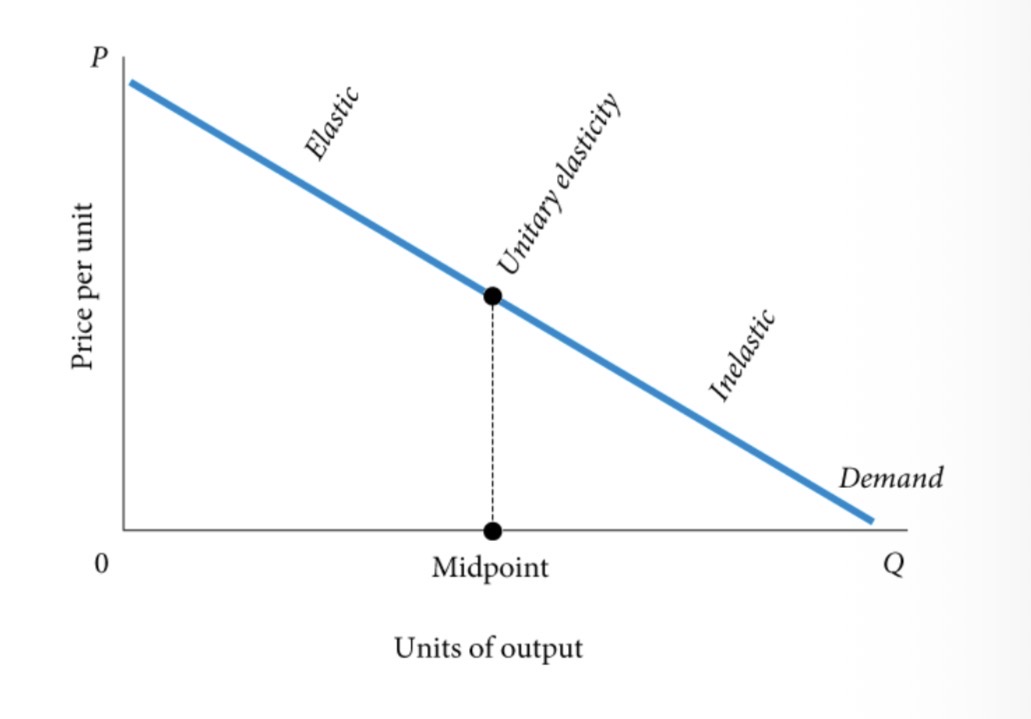
Total Revenue(TR)
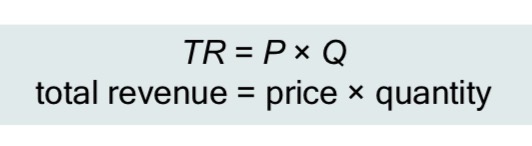
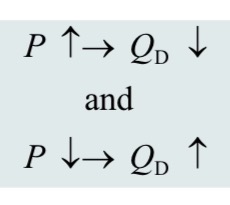
effects of price changes on quantity demanded:
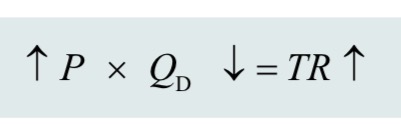
effect of price increase on a product with inelastic demand:
effect of price increase on a product with elastic demand:
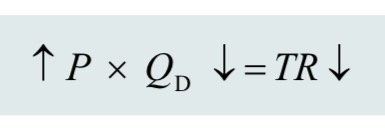
effect of price cut on a product with elastic demand:
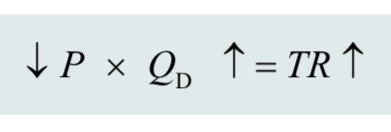
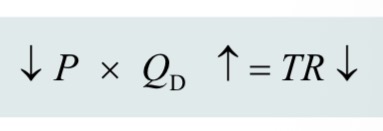
effect of price cut on a product with inelastic demand:
income elasticity of demand
A measure of the responsiveness of demand to changes in income.
income elasticity of demand formula
inferior good (-ve)
normal good (+ve)
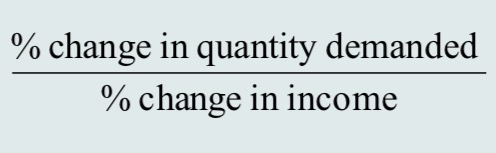
cross-price elasticity of demand
A measure of the response of the quantity of one good demanded to a change in the price of another good.
cross-price elasticity of demand formula
complimentary (-ve)
substitute (+ve)
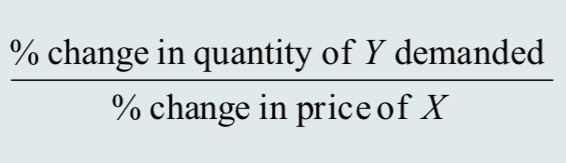
elasticity of supply
A measure of the response of quantity of a good supplied to a change in price of that good. Likely to be positive in output markets.
elasticity of supply formula
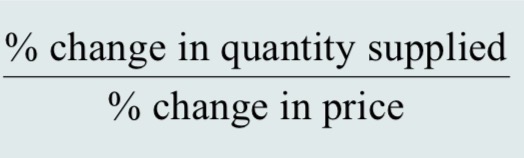
elasticity of labor supply
A measure of the response of labor supplied to a change in the price of labor.
elasticity of labor supply formula
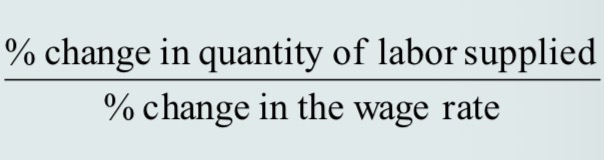
Increase in demand caused to change in equilibrium price. Thus. supply must be…
perfectly elastic (fill)