Photosynthesis
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Pages 1-4 in notes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Producers
Organisms that make their own food to provide their own energy
also called autotrophs
Some don’t use light, but instead cause chemical reactions which provide heat for energy (these use chemosynthesis)
Photosynthesis
Process where energy from the sun is converted to chemical energy, stored in high energy sugar molecules
like glucose
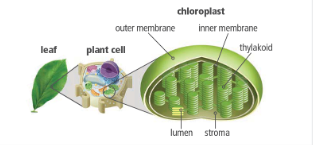
Chloroplast
Organelle in plant cells where photosynthesis occurs
specifically a leaf cell
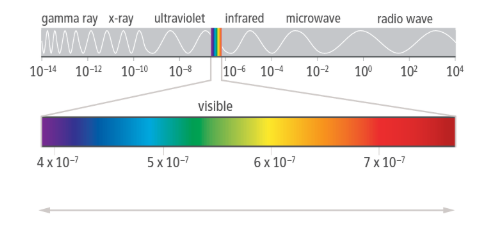
Chlorophyll
Pigment that absorbs light at a specific wavelength
absorbs light energy
Absorbs some wavelengths of light and reflects others
Why leaves appear green
Consumers
Organisms that cannot produce their own food
need to obtain it through consumption (eating/drinking)
Structures used for photosynthesis (large to small)
Leaf
Plant Cell
Organelle (chloroplast)
Thylakoid (stacks of disks)
Chlorophyll
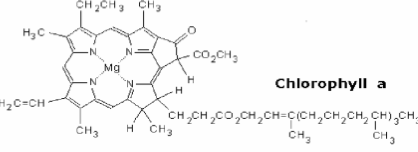
Chlorophyll A
violet and orange
H3C
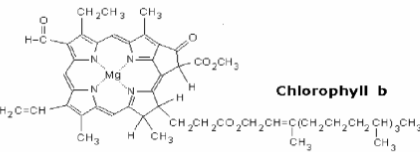
Chlorophyll B
Blue and yellow
H-C=O
Types of molecules Photosynthesis utilizes to store energy
ATP (which becomes ADP after being used)
NADPH (which becomes NADP+ after being used)
Light Dependent Reactants
Sunlight
NADP+
ADP
Light Dependant products
NADPH
ATP
Both are energized forms
First Step of Light Dependent Reactions
Energy absorbed from sunlight
photosystem II has chlorophyll b, which absorbs sunlight and transfers that energy to elections, which leave and go to the ‘electron transport chain’
Second Step of Light Dependent Reactions
Water molecules split
Enzymes break down water molecules — electrons from the water molecules replace the ones that have left the chlorophyll — oxygen is released as a waste product
Third Step of Light Dependent Reactions
Hydrogen ions transported
Electrons are moved along the thylakoid membrane — used to pump hydrogen ions from low concentration to high concentration (active transport)
Fourth Step of Light Dependent Reactions
Energy absorbed from sunlight
Photosytem I has chlorophyll a, which absorbs sunlight and transfers that energy to electrons
Fifth Step of Light Dependent Reactions
NADPH produced
Electrons from photosystem I provide energy to NADP+ — creates NADPH
Sixth Step of Light Dependent Reactions
Hydrogen ion diffusion
H+ ions diffuse (high to low concentration, passive transport_ through the ATP synthase protein (why its diffusion_, which uses that movement to add a phosphate group to ADP
Light Independent Reactants
NADPH
ATP
Light Independent Products
Sugar (glucose)
First Step of Light Independent Reactions
Carbon Dioxide Added
A CO2 molecule is added to an existing 5-carbon molecule — creates a 6 carbon molecule
Second Step of Light Independent Reactions
3-Carbon molecules formed
6-carbon molecule splits, forming 2 groups of 3 carbon molecules that are rearranged
Uses ATP and NADPH as energy
Third Step of Light Independent Reactions
3-carbon molecules exit
One 3-carbon molecule exit the cycle
Once it happens twice, the two molecules that have excited can create a 6-carbon sugar molecule (glucose)
Fourth Step of Light Independent Reactions
3-Carbon molecules recycled
5 groups of 3 carbon molecules are rearranged into 3 groups of 5-carbon molecules that will stay in the cycle
used energy from ATP
Not adding or removing any molecules
Allows the cycle to restart