Microbio Species
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
New
Card Sorting
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
1
New cards
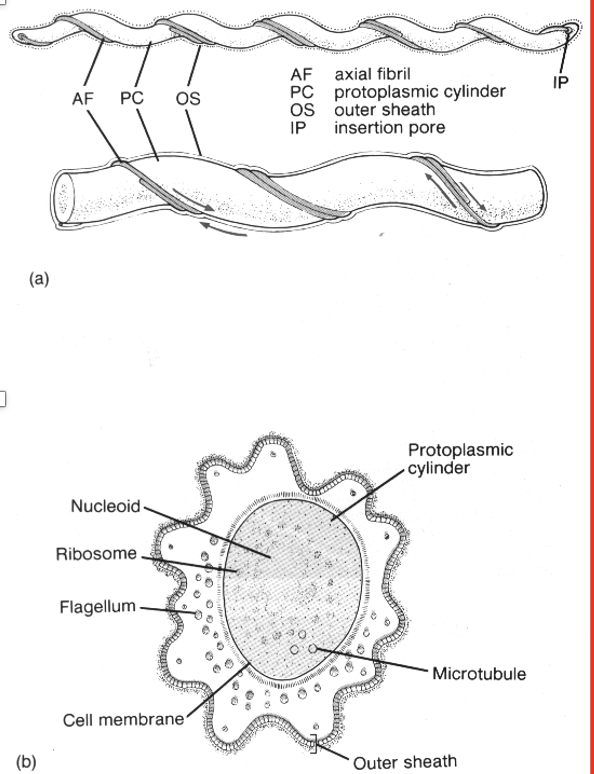
Spirochaetes
\
* Hydrobacteria
* Have axial filaments instead of flagella. They are microaerophilic and slow-growing. They are shaped like a corkscrew.
* Gram negative
* Ex: Treponema pallidum: causes syphilis, sexually transmitted
* Hydrobacteria
* Have axial filaments instead of flagella. They are microaerophilic and slow-growing. They are shaped like a corkscrew.
* Gram negative
* Ex: Treponema pallidum: causes syphilis, sexually transmitted
2
New cards
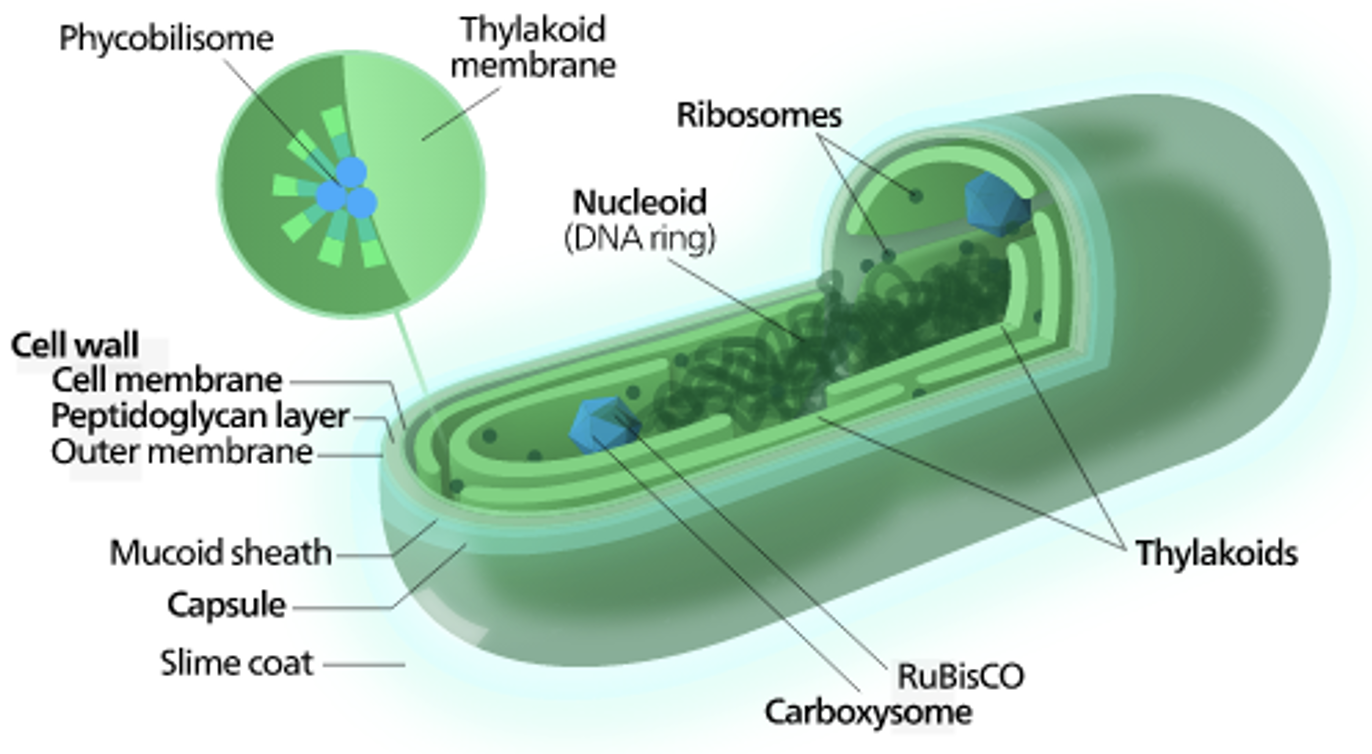
Cyanobacteria
* Terrabacteria.
* Chloroplasts came from these. Oxygenic photosynthesis with aerobic lifestyle. They are capable of nitrogen fixation.
* Phycobilisomes: light harvesting antenna. (not membrane bound)
* Can produce cyanotoxins.
* Gram negative
* Chloroplasts came from these. Oxygenic photosynthesis with aerobic lifestyle. They are capable of nitrogen fixation.
* Phycobilisomes: light harvesting antenna. (not membrane bound)
* Can produce cyanotoxins.
* Gram negative
3
New cards
Pseudomonas (genus)
* Gram -
* Sp. Pseudomonas aeruginosa - A human opportunistic pathogen: infects airways, urinary tract, buns, wounds, blood infection
* Sp. Pseudomonas syringae - water in host plants freeze at night. artificial snow
* Sp. Pseudomonas aeruginosa - A human opportunistic pathogen: infects airways, urinary tract, buns, wounds, blood infection
* Sp. Pseudomonas syringae - water in host plants freeze at night. artificial snow
4
New cards
Staphylococcus (genus)
* Gram +
* Round cells, grape-like clusters. Common in soil, many are pathogens.
* Sp. S aureus - Localized or disseminated skin infections
* Can secrete exotoxins
* Round cells, grape-like clusters. Common in soil, many are pathogens.
* Sp. S aureus - Localized or disseminated skin infections
* Can secrete exotoxins
5
New cards
Streptococcus
* Gram +
* Sp. S. pyrogens - mild skin infections / necrotizing fascitis
* Sp. S. pneumoniae - pneumococcal infection
* Sp. S. sanguinis - dental caries, endocarditis
* Sp. S. thermophiles - dairy products
* Sp. S. pyrogens - mild skin infections / necrotizing fascitis
* Sp. S. pneumoniae - pneumococcal infection
* Sp. S. sanguinis - dental caries, endocarditis
* Sp. S. thermophiles - dairy products
6
New cards
Mycoplasma
* A.k.a Tenericutes
* Resistant to penicillin. susceptible to osmotic stress. Detergents. Facultative anaerobic. Rely on the host bc their citric acid cycle is incomplete
* (neither gram +/-, no cell wall)
* Sp. M. pneumoniae - severe atypical pneumonia
* Sp. M. genitalium -genital infection
* Resistant to penicillin. susceptible to osmotic stress. Detergents. Facultative anaerobic. Rely on the host bc their citric acid cycle is incomplete
* (neither gram +/-, no cell wall)
* Sp. M. pneumoniae - severe atypical pneumonia
* Sp. M. genitalium -genital infection
7
New cards
Clostridium
* Gram +
* Sp. C. perfringens/C. histolyticum - invasive species, exotoxin producers, also produce many extracellular hydrolyses. Necrosis, Gas gangrene
* Sp. C. tetani - low invasively; produces toxin-tetanospasmin - Tetanus: painful muscular spasms, respiratory failure
* Sp. C. botulinum - Botulism: ingestion with food - toxin causes flaccid paralytic disease. the most potent toxin.
* Sp. C. perfringens/C. histolyticum - invasive species, exotoxin producers, also produce many extracellular hydrolyses. Necrosis, Gas gangrene
* Sp. C. tetani - low invasively; produces toxin-tetanospasmin - Tetanus: painful muscular spasms, respiratory failure
* Sp. C. botulinum - Botulism: ingestion with food - toxin causes flaccid paralytic disease. the most potent toxin.
8
New cards
Bacillus
* Gram +
* Sp. B. subtilis - non-pathogenic. industrial application: protease and amylase
* Sp. B. cereus - food poisoning
* Sp. B. anthracis - anthrax. affects all mammals. Pasteur developed vaccine.
* Sp. B. thuringiensis - Bt toxin: kills insects! used in making Bt-producing GMO crops (corn)
* Sp. B. subtilis - non-pathogenic. industrial application: protease and amylase
* Sp. B. cereus - food poisoning
* Sp. B. anthracis - anthrax. affects all mammals. Pasteur developed vaccine.
* Sp. B. thuringiensis - Bt toxin: kills insects! used in making Bt-producing GMO crops (corn)
9
New cards
Listeria
* Gram +
* Sp. L. monocytogenes -foodborne pathogen. Causes meningitis in newborns.
* Sp. L. monocytogenes -foodborne pathogen. Causes meningitis in newborns.
10
New cards
Vibrio
* Gram -
* Sp. V. Cholerae - Cholera: exotoxin, spreads with contaminated water
* , shaped
* Sp. V. Cholerae - Cholera: exotoxin, spreads with contaminated water
* , shaped
11
New cards
Salmonella
* Gram -
* Sp. S. enterica Sbsp. enterica-
* Enteritis: Contaminated food. Intestinal inflammation.
* Typhoid fever. Endotoxins act on the vascular and nervous system. Increased permeability and decreased tone of the blood vessels. Upset thermal regulation, vomiting, and diarrhea.
* Sp. S. enterica Sbsp. enterica-
* Enteritis: Contaminated food. Intestinal inflammation.
* Typhoid fever. Endotoxins act on the vascular and nervous system. Increased permeability and decreased tone of the blood vessels. Upset thermal regulation, vomiting, and diarrhea.
12
New cards
Actinobacteria (Actinomycetota)
* gram +
* 3 classes: Actinomycetales, Frankiales, Bifidobacteria
* Family: Streptomycetaceae
* 5 genus: Nicorida, Corynebacterium, C. dipheriae, Mycobacterium, Frankiales, Bfidobacteria
* 3 classes: Actinomycetales, Frankiales, Bifidobacteria
* Family: Streptomycetaceae
* 5 genus: Nicorida, Corynebacterium, C. dipheriae, Mycobacterium, Frankiales, Bfidobacteria
13
New cards
Mycobacterium
* Aerobic bacteria
* Pathogens: M. tuberculosis, M. leprae (leprosy)
* Thick cell wall (hydrophobic: mycolate layer + peptidoglycan layer). Low growth rate
* Pathogens: M. tuberculosis, M. leprae (leprosy)
* Thick cell wall (hydrophobic: mycolate layer + peptidoglycan layer). Low growth rate
14
New cards
Chlamydiae
* Gram - (no peptidoglycan wall)
* Steals ATP from host cell
* Sp. C. trachomatis - eye disease and sexually transmitted chlamydia
* Sp. C. pneumoniae- pneumonia
* Sp. C.-phila psicarri- psittacosis (birds with white coats)
* Steals ATP from host cell
* Sp. C. trachomatis - eye disease and sexually transmitted chlamydia
* Sp. C. pneumoniae- pneumonia
* Sp. C.-phila psicarri- psittacosis (birds with white coats)
15
New cards
Bacteroidetes
* Gram -
* B. ruminicola - ferments starch and pectin in rumen, produces hydrogen gas and CO2
* B. fragilis - causes infection if in bloodstream
* B. ruminicola - ferments starch and pectin in rumen, produces hydrogen gas and CO2
* B. fragilis - causes infection if in bloodstream
16
New cards
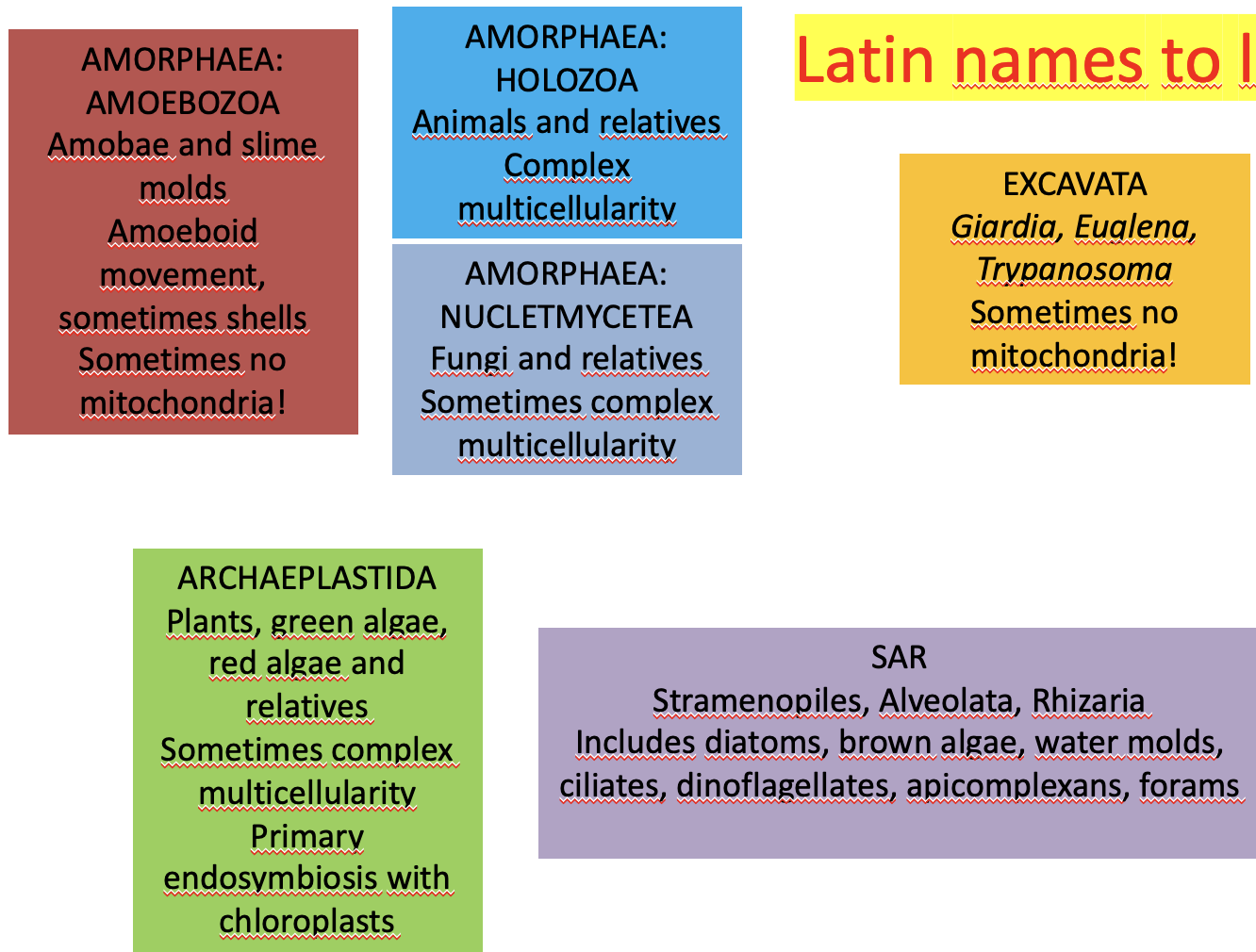
The six main groups of Eukaryotes
* Excavata
* Euglena
* Giardia
* SAR
* Diatoms
* Dinoflagellates
* Archeaplastida
* Plants
* green + red algae
* Amorphea
* Amoebozoa: amoeba, slime molds
* Holozoa: animals, relatives
* Nucletmycetea: fungi, relatives
* Euglena
* Giardia
* SAR
* Diatoms
* Dinoflagellates
* Archeaplastida
* Plants
* green + red algae
* Amorphea
* Amoebozoa: amoeba, slime molds
* Holozoa: animals, relatives
* Nucletmycetea: fungi, relatives
17
New cards
The diversity of Alveolata, including details of one microbe infecting humans
* Eukaryotes belonging to the TSAR group and they include ciliates (such as Paramecium) and Apicomplexa.
* Toxoplasma (from alveolata, apicomplexa) is a human pathogen that is commonly transmitted by cat fecal matter to humans. It causes fevers and muscle pain and can damage the central nervous system. For pregnant women toxoplasmosis can be fatal for the fetus.
* Toxoplasma (from alveolata, apicomplexa) is a human pathogen that is commonly transmitted by cat fecal matter to humans. It causes fevers and muscle pain and can damage the central nervous system. For pregnant women toxoplasmosis can be fatal for the fetus.
18
New cards
An important Excavata pathogen or parasite (choose from Trypanosoma, Leishmannia)
* Leismannia cause Leishmaniasis. The vector for this pathogen are sand flies.
* Trypanosoma: T. brucei or T. cruzi.
* T. brucei: fatal human sleeping disease. Vector: tse-tse fly
* T. cruzei: Chagas disease. Vector: kissing bugs.
* Trypanosoma: T. brucei or T. cruzi.
* T. brucei: fatal human sleeping disease. Vector: tse-tse fly
* T. cruzei: Chagas disease. Vector: kissing bugs.
19
New cards
Main groups of Ascomycota
* Pezizomycota
* Black yeast
* Lichens
* Truffles (Tuber spp.)
* Morels (Morchella spp.)
* Erhot fungi (LSD) etc
* Taphrimycota
* Schizosaccahromyces pombe
* Taphrina
* Saccharomycetota
* Saccharomyces ceravisiae
* Candida
* Black yeast
* Lichens
* Truffles (Tuber spp.)
* Morels (Morchella spp.)
* Erhot fungi (LSD) etc
* Taphrimycota
* Schizosaccahromyces pombe
* Taphrina
* Saccharomycetota
* Saccharomyces ceravisiae
* Candida
20
New cards
Filoviridae
* -ssRNA virus
* Ebola virus (bat reservoir)
* Marburg virus
* Ebola virus (bat reservoir)
* Marburg virus
21
New cards
Paramyxoviridae
* -ssRNA virus
* Measles virus (diarrhea, ear infection, pneumonia)
* Mumps virus
* Measles virus (diarrhea, ear infection, pneumonia)
* Mumps virus
22
New cards
Orthomyxoviridae
* -ssRNA virus
* Influenza virus
* Influenza virus A: infects humans, other mammals, and birds, andcauses all flu pandemics
* Influenza virus B: infects humans and seals
* Influenza virus C: infects humans, pigs, and dogs
* Influenza virus D: infects pigs and cattle
* Influenza virus
* Influenza virus A: infects humans, other mammals, and birds, andcauses all flu pandemics
* Influenza virus B: infects humans and seals
* Influenza virus C: infects humans, pigs, and dogs
* Influenza virus D: infects pigs and cattle
23
New cards
HIV
* Retrovirus
* ssRNA-RT
* Caused AIDS (immunodeficiency syndrome)
* ssRNA-RT
* Caused AIDS (immunodeficiency syndrome)
24
New cards
Coronaviridae
* +ssRNA
* Includes SARS-CoV-2, SARS, and MERS
* SARS: Severe acute respiratory syndrome (from bats, no cases since 2004)
* MERS: Middle East respiratory syndrome (from bats)
* SARS-CoV-2: Easy transmission, Asymptomatic transmission
* Includes SARS-CoV-2, SARS, and MERS
* SARS: Severe acute respiratory syndrome (from bats, no cases since 2004)
* MERS: Middle East respiratory syndrome (from bats)
* SARS-CoV-2: Easy transmission, Asymptomatic transmission
25
New cards
SARS-CoV-2 structure
* +ssRNA
* four structural proteins:
* S (spike), E (envelope), M (membrane), and N (nucleocapsid) proteins
* four structural proteins:
* S (spike), E (envelope), M (membrane), and N (nucleocapsid) proteins
26
New cards
Flaviviridae
* -ssRNA
* Ebola (zika) virus
* Vector is mosquito
* Ebola (zika) virus
* Vector is mosquito
27
New cards
Poxviruses
* dsDNA
* Variola virus - smallpox
* Vaccina virus - Active constituent of the vaccine for smallpox
* Cowpox virus - The first smallpox vaccine by Jenner
* Variola virus - smallpox
* Vaccina virus - Active constituent of the vaccine for smallpox
* Cowpox virus - The first smallpox vaccine by Jenner
28
New cards
Herpesviruses
* dsDNA
* HSV-1 (herpes simplex virus 1) - orolabial herpes
* HSV-2 (herpes simplex virus 2) - genital herpes
* varicella zoster virus: chickenpox and shingles
* Lipid envelope
* HSV-1 (herpes simplex virus 1) - orolabial herpes
* HSV-2 (herpes simplex virus 2) - genital herpes
* varicella zoster virus: chickenpox and shingles
* Lipid envelope
29
New cards
Chytridiomycota
* Bd fungus: which is responsible for the worldwide decline of amphibians.
* Synchytrium fungus: which is responsible for warts on potatoes.
* Synchytrium fungus: which is responsible for warts on potatoes.
30
New cards
Main groups of Basidiomycota
* Agarymycotina:
* tremellomycetes (jelly fungi)
* agaricomycetes (mushrooms, puffballs, polypores).
* Includes edible species, species used in fungiculture and toxic species.
* Puccinomycota: plant rust. Complicated life cycle.
* Ustilaginomycotina: smut fungi. Corn smut is edible.
* Includes malassezia which can infect humans and cause hypo or hyperpigmentation on skin. It is yeast-like in nature.
* tremellomycetes (jelly fungi)
* agaricomycetes (mushrooms, puffballs, polypores).
* Includes edible species, species used in fungiculture and toxic species.
* Puccinomycota: plant rust. Complicated life cycle.
* Ustilaginomycotina: smut fungi. Corn smut is edible.
* Includes malassezia which can infect humans and cause hypo or hyperpigmentation on skin. It is yeast-like in nature.
31
New cards
Reproduction of molds
* Asexual reproduction: by vegetative spores (conidia), through mycelial fragmentation, or through budding/fission in yeasts.
* Deuteromycota: only able toreproduce asexually
* Deuteromycota: only able toreproduce asexually
32
New cards
Sexual reproduction of molds
* Have mating types (heterothallic fungi)
* hyphae of two colonies fuse together
* some do not (homothallic fungi).
* Ascomycota use hooks
* hyphae of two colonies fuse together
* some do not (homothallic fungi).
* Ascomycota use hooks
33
New cards
Spore dispersal
* Puffballs- mechanical dispersal
* bird's nest fungi - use falling water drops
* stinkhorn- Attract insects for disperal
* bird's nest fungi - use falling water drops
* stinkhorn- Attract insects for disperal
34
New cards
Aspergillosis
\
* Invasive pulmonary disease. Immunosupressed individuals are susceptible. The fungus grew drug resistanve bc of the use of “azoles” pesticide. There are several types of aspergillosis.
* Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis: Aspergillus causes cavities in lungs
* Invasive pulmonary disease. Immunosupressed individuals are susceptible. The fungus grew drug resistanve bc of the use of “azoles” pesticide. There are several types of aspergillosis.
* Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis: Aspergillus causes cavities in lungs
35
New cards
Blastomycosis
* Normally Blastomyces dermatitidis decomposes dead vertabrates. Some species are becoming pathogenic. Yeast infection that is similar to flu or pulmonary infection.
36
New cards
Histoplasmosis
* Histoplasmosis- Skin infections. Associated with the droppings of a bird species and bats.
37
New cards
Cryptococcosis
* Cryptococcal meningitis, encephalitis, Pulmonary cryptococcosis. Can survive intracellularly in macrophages. Most infections originally affceted HIV patients.
38
New cards
Candidiasis
* Yeasts, many species also for pseudohyphae. Opportunistic pathogens that may infect mucosae or even cause bloodstream infection. Some may live in humans without causing symptoms.
39
New cards
Coccidiosis
* Yeast infectious form. Valley fever (a type of pneumonia). May also disseminate and cause skin infections. Creates a mass that can mimic lung tumor.
40
New cards
Species of microbes utilized in biotechnology, their importance
* Actinobacteria: Streptomyces
* Complex secondary metabolism, useful in biotechnology
* Can produce Antibiotics: neomycin, streptomycin.
* Complex secondary metabolism, useful in biotechnology
* Can produce Antibiotics: neomycin, streptomycin.