Oropharyngeal & Swallowing System
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Prognathic jaw
underbite
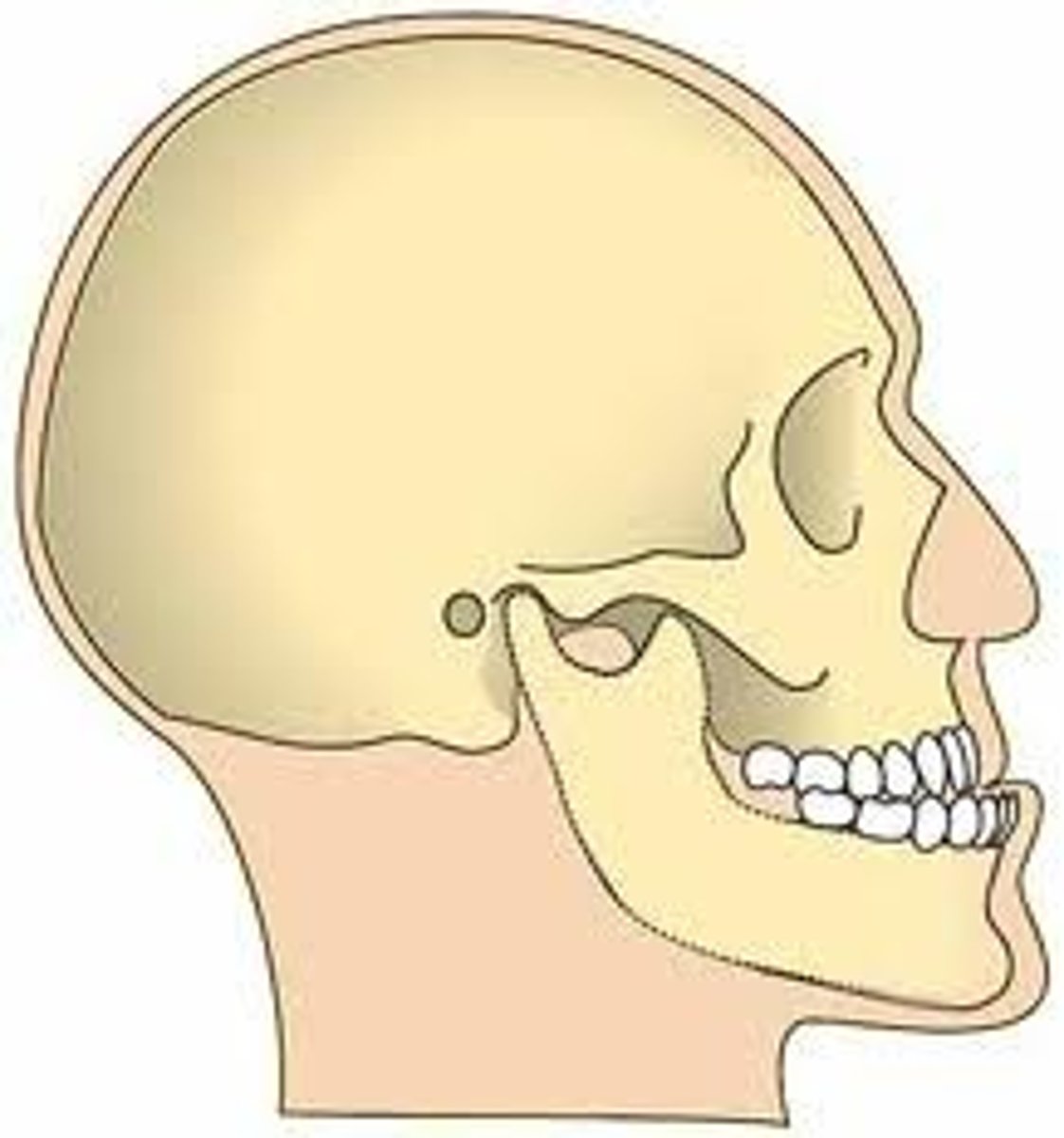
Retrognathic jaw
overbite

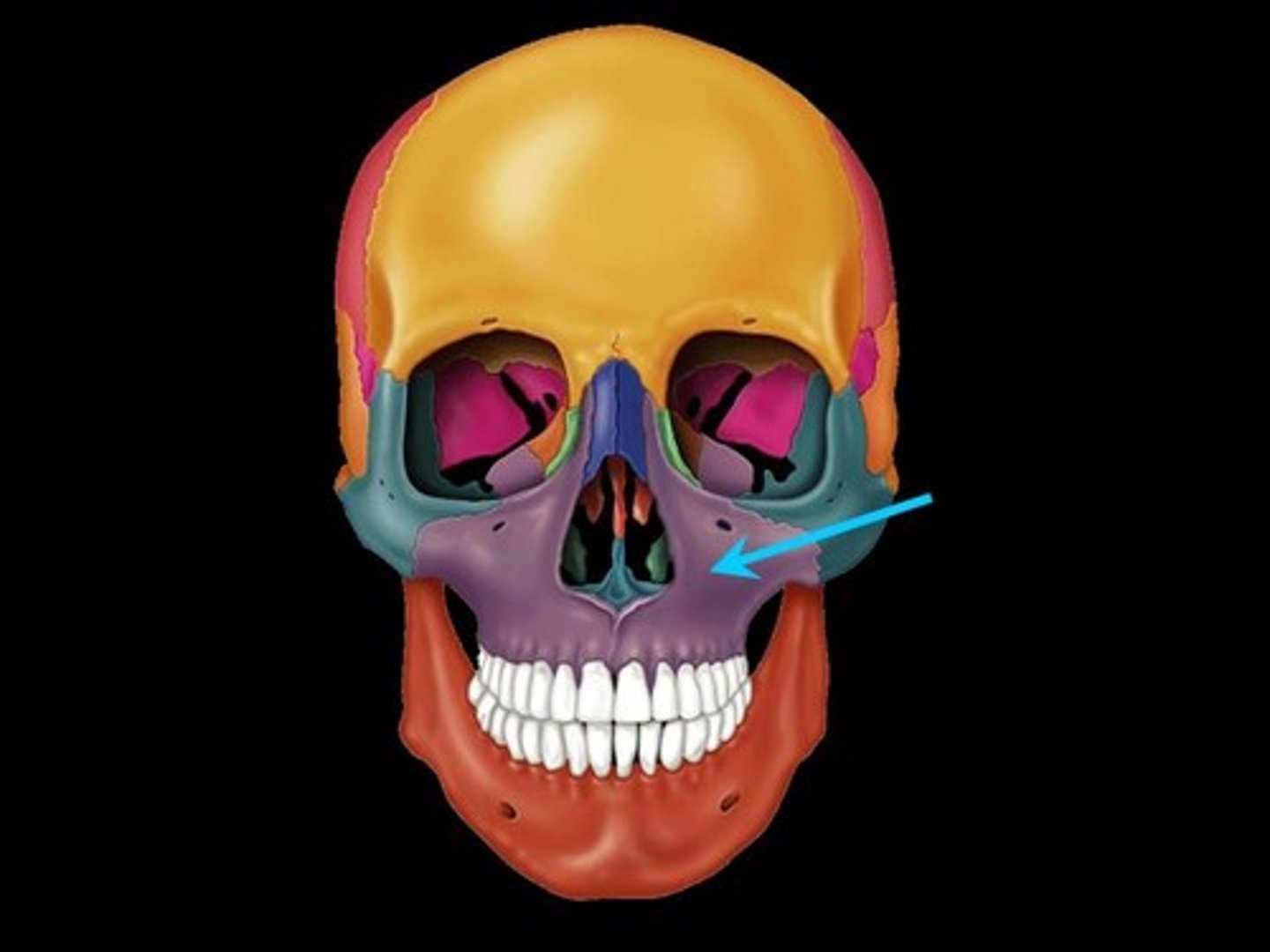
Maxilla
upper jaw
temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
the joint between the temporal bone and the mandible
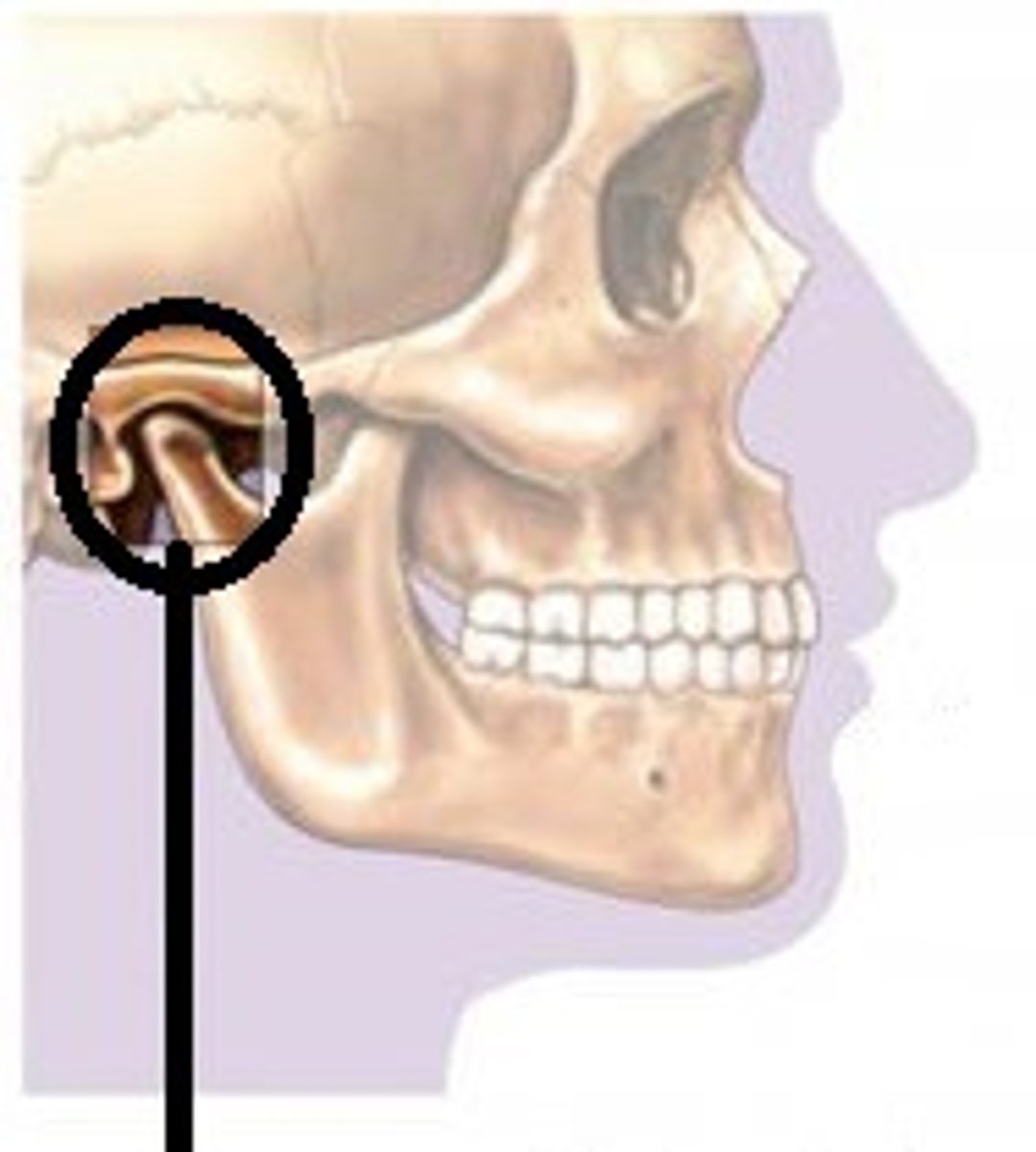
TMJ movements
Upward and downward
Forward and backward
Side to side
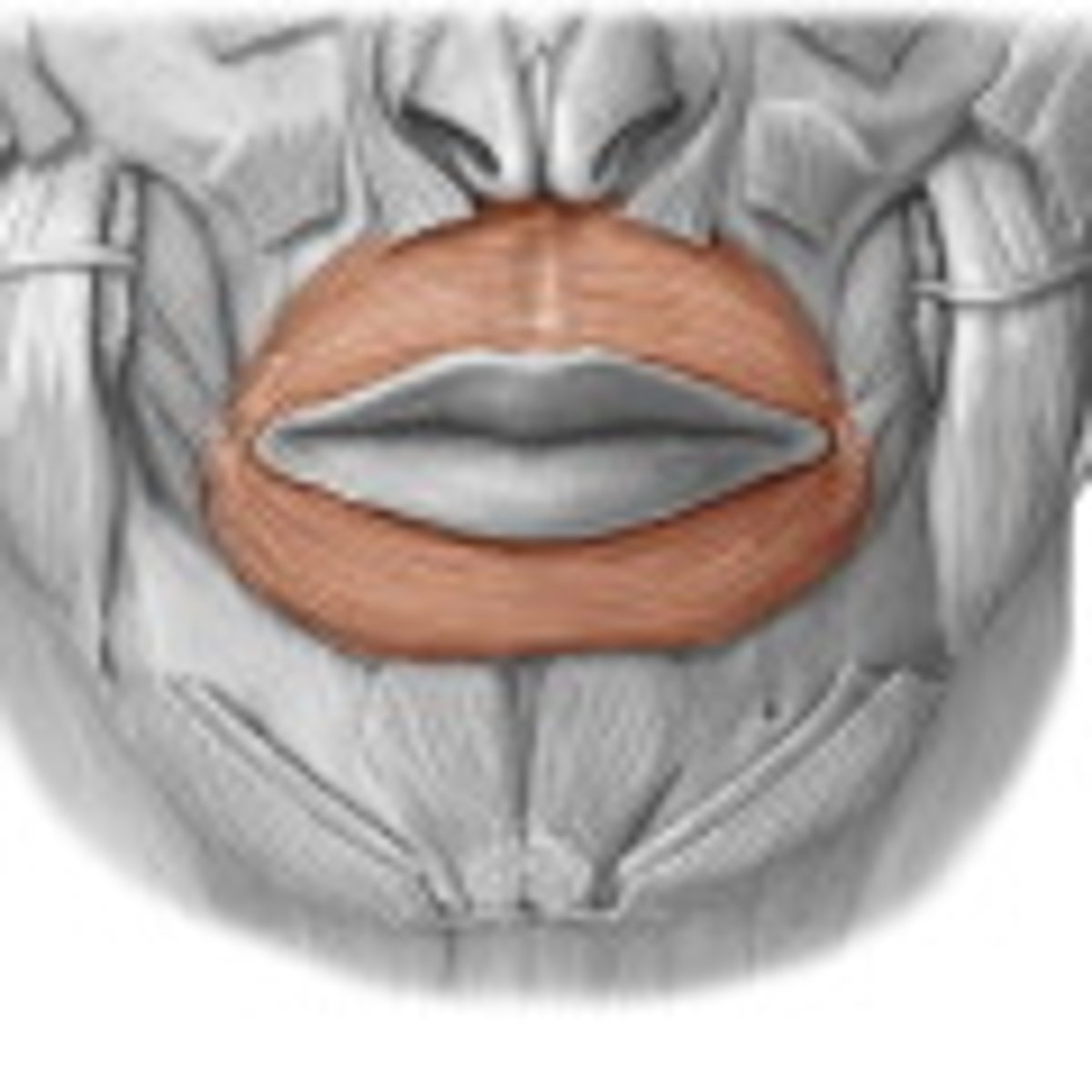
Orbicularis oris muscle
Muscle around the mouth that closes the lips
Buccinator
compresses cheek
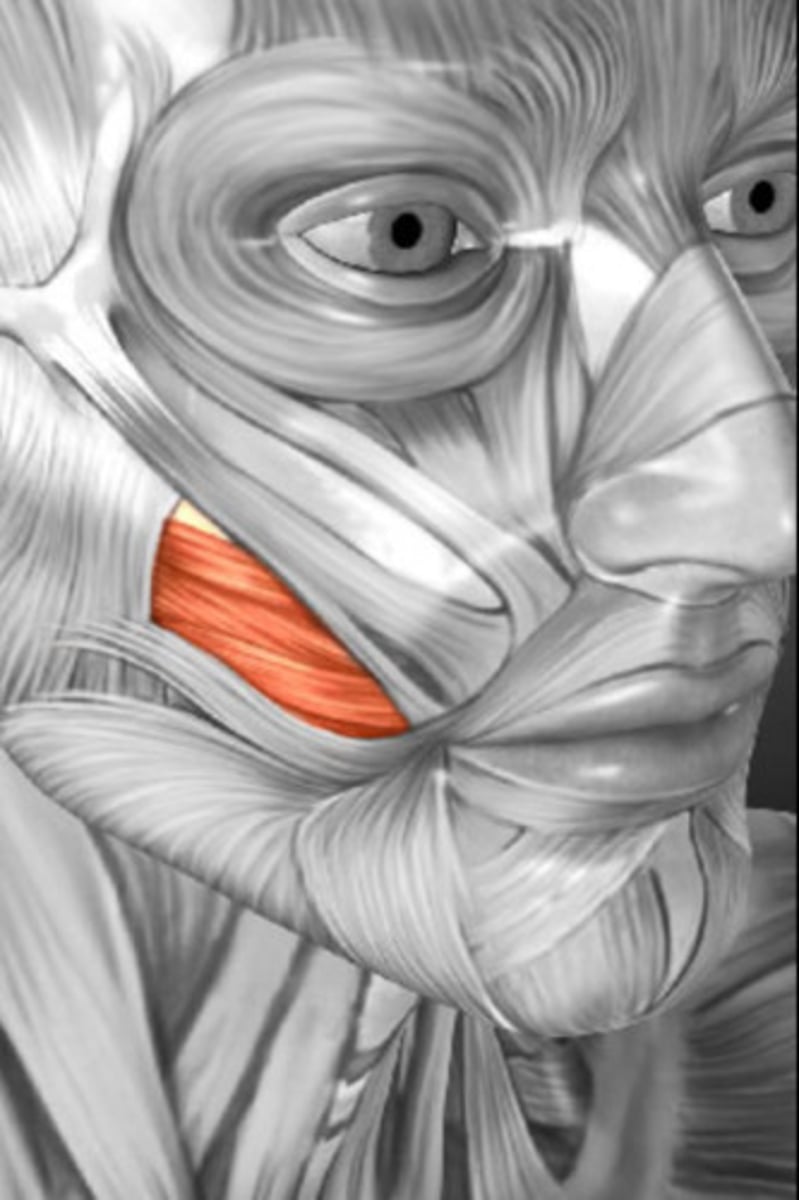
Risorius
Draws corner of mouth laterally (laughter)
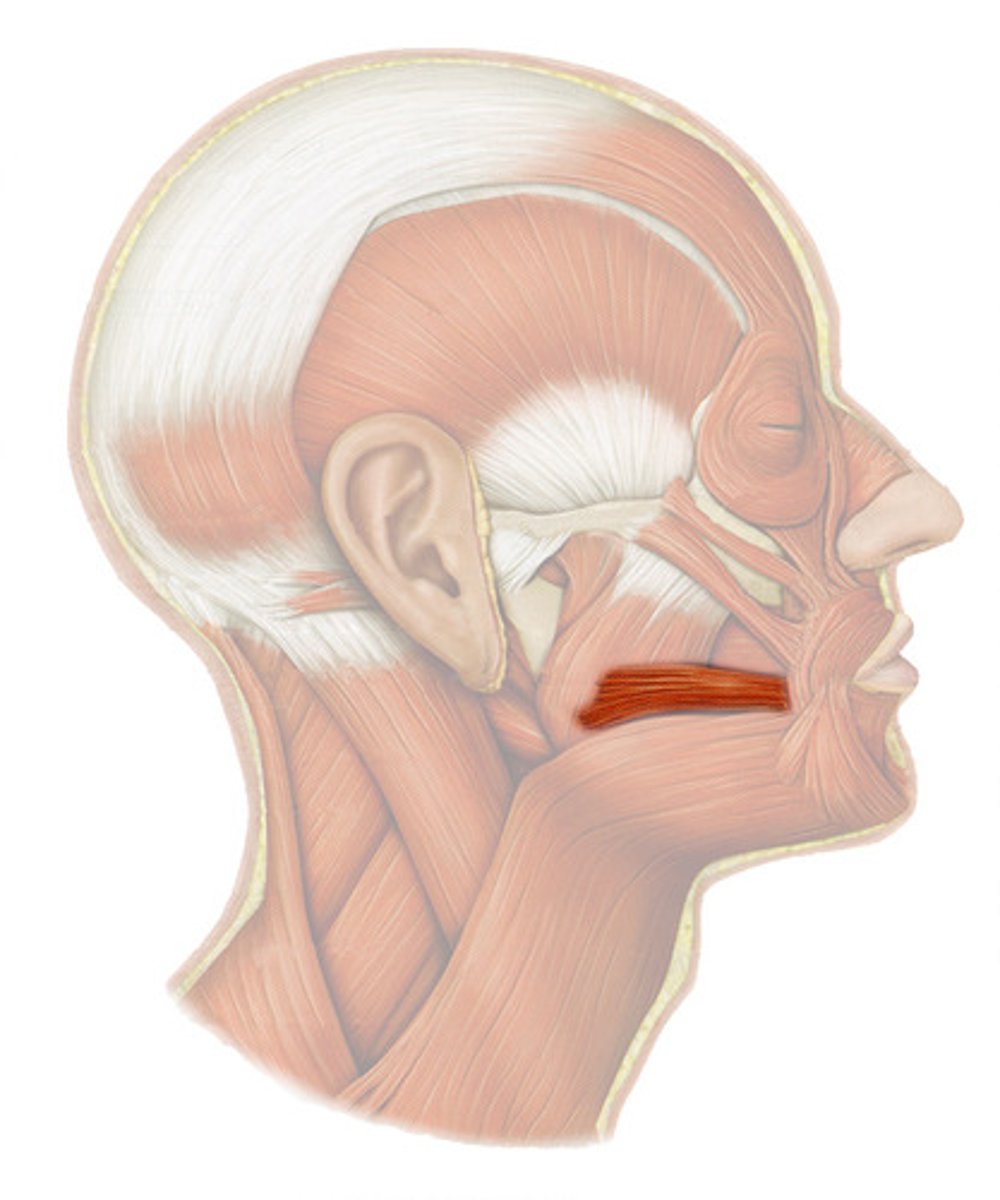
Levator anguli oris
elevates corner of mouth
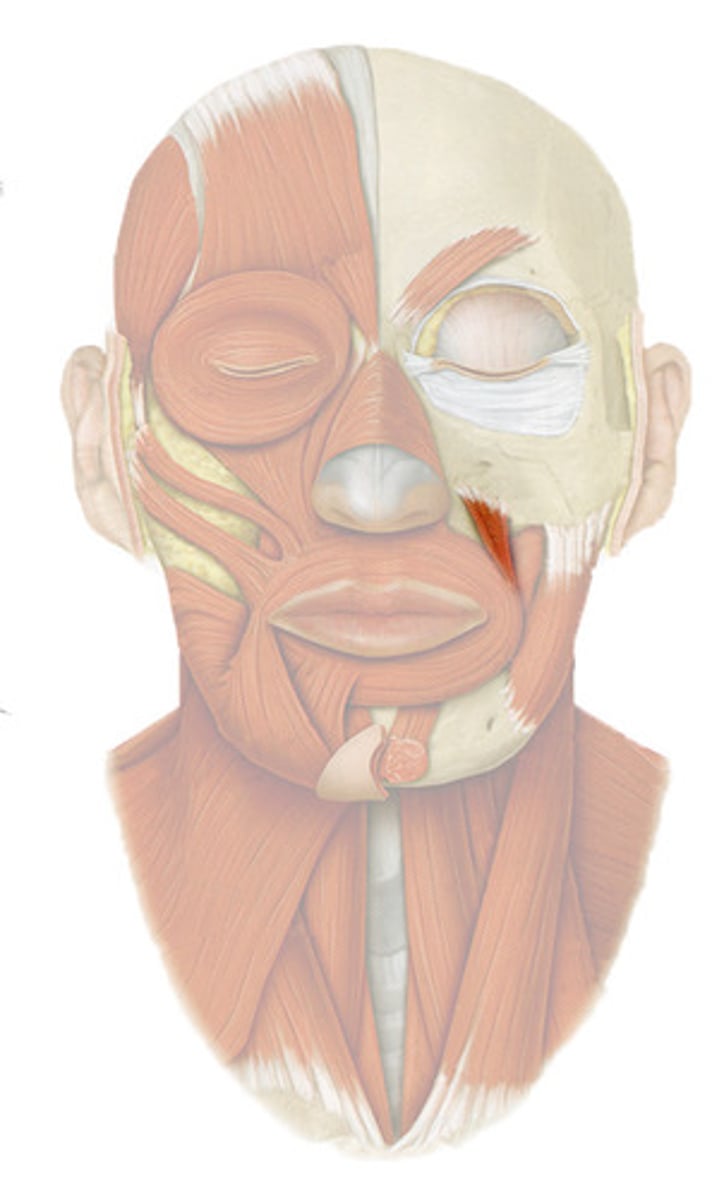
Depressor anguli oris
depresses corner of mouth
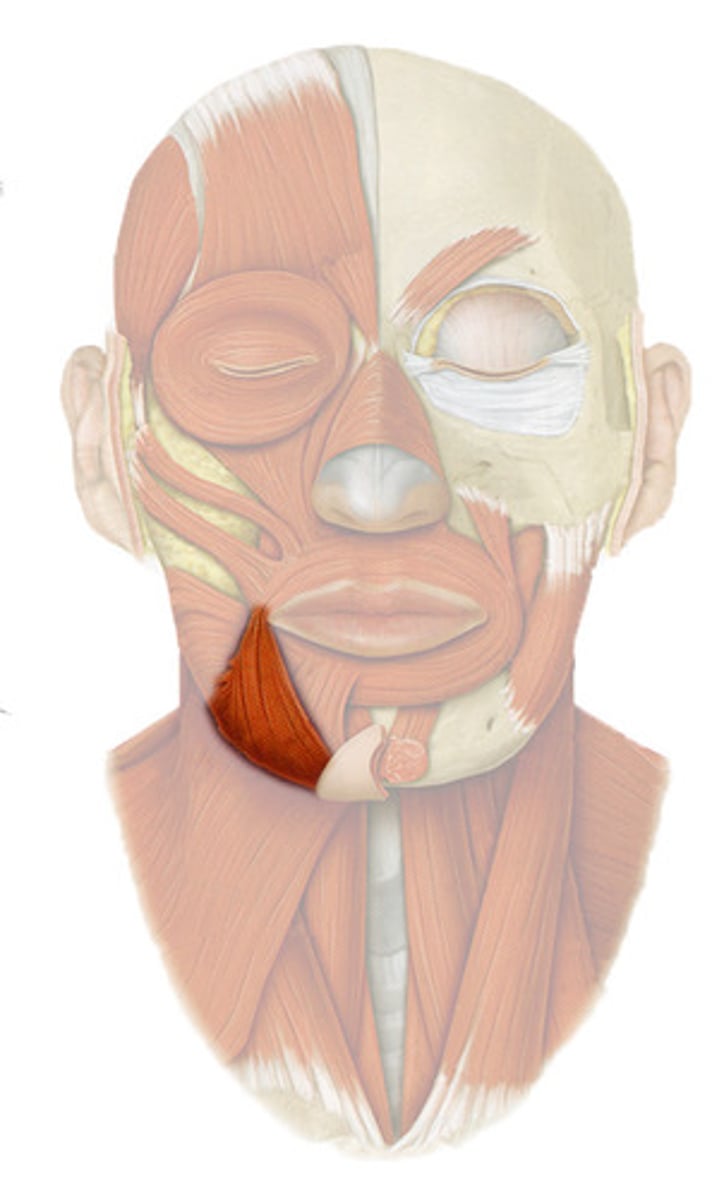
Levator labii superioris
elevates upper lip
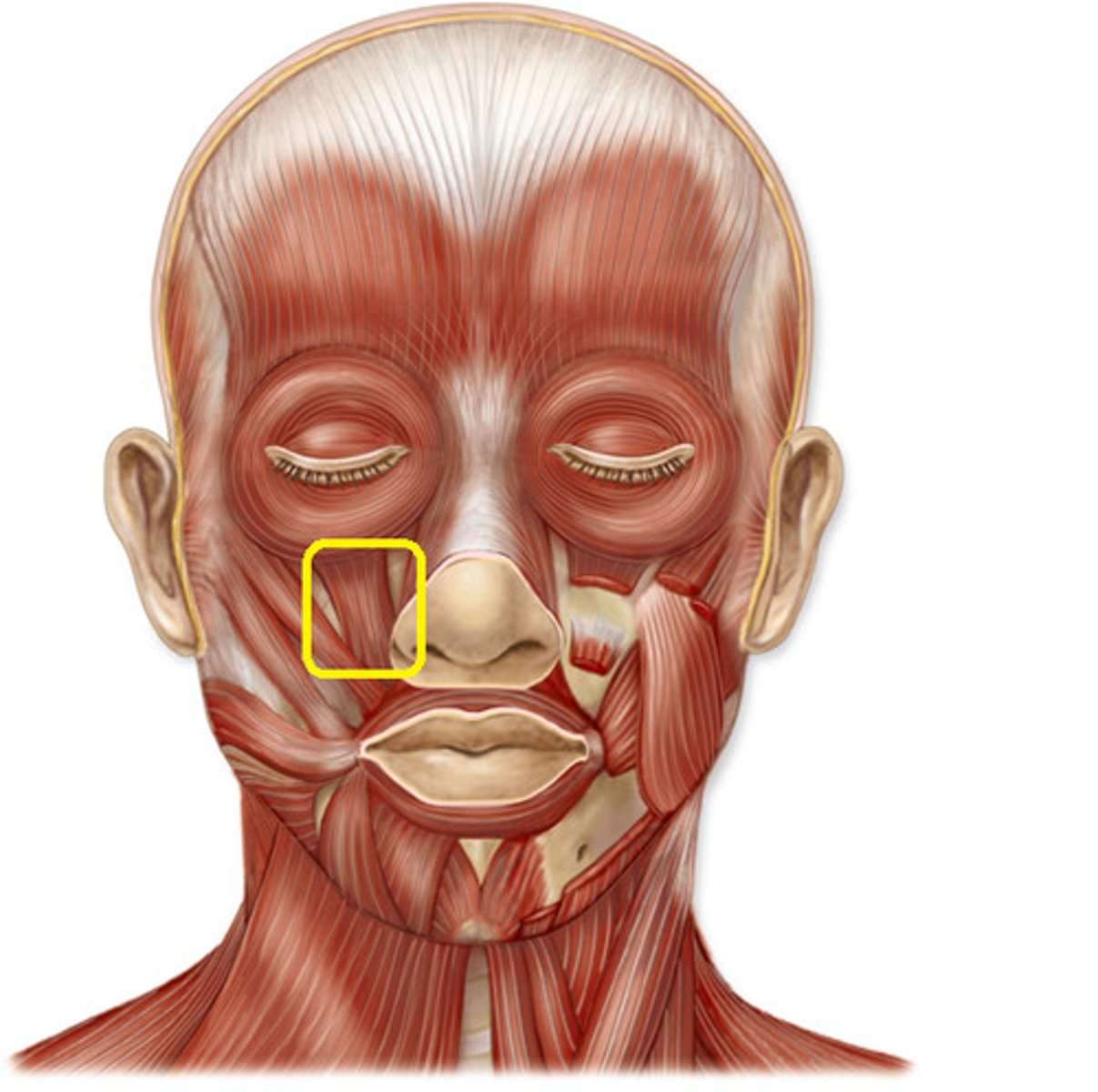
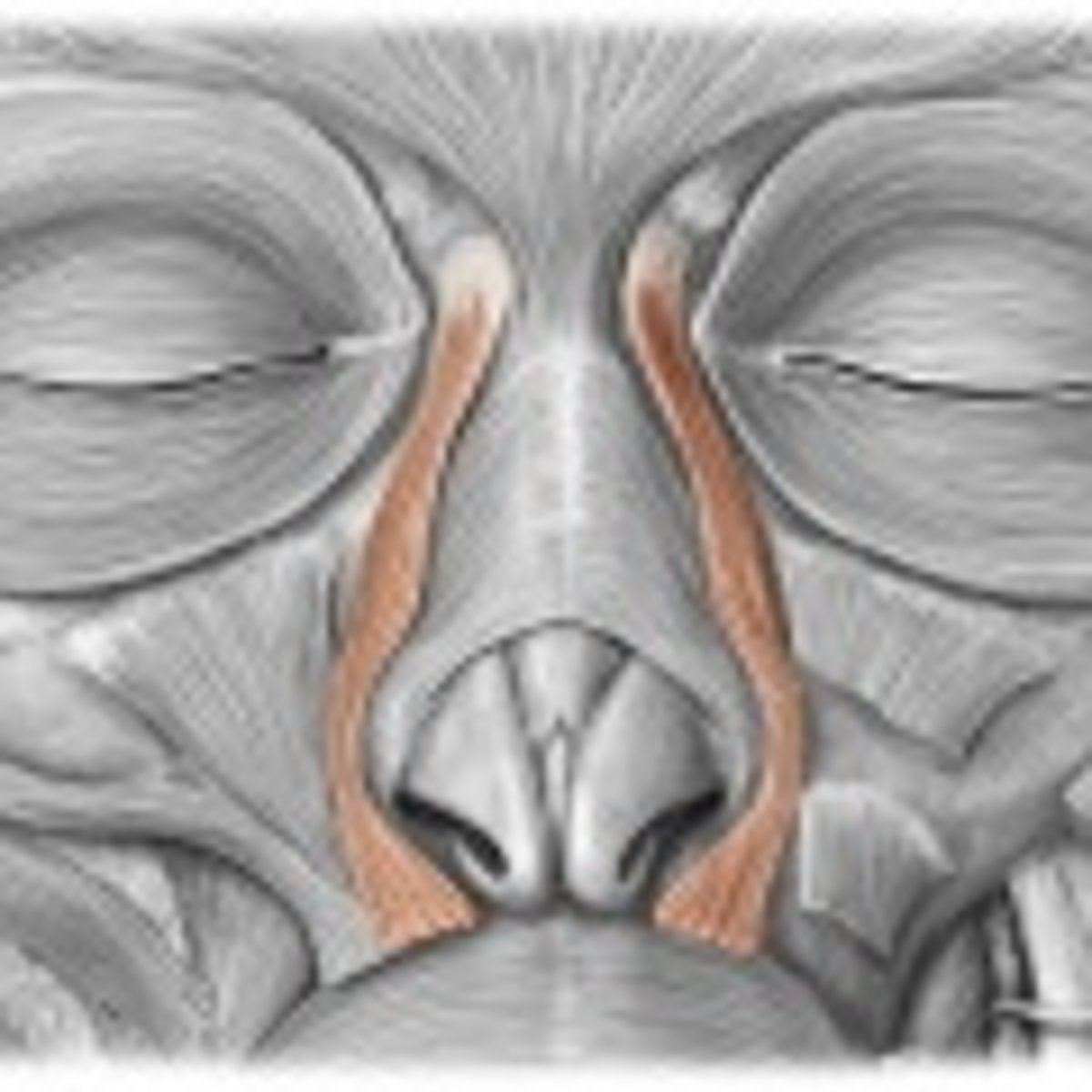
Levator labii superioris alaeque nasi
elevates upper lip
Zygomatic minor
elevates upper lip
Zygomatic major
Elevates upper lip
depressor labii inferioris
depresses lower lip
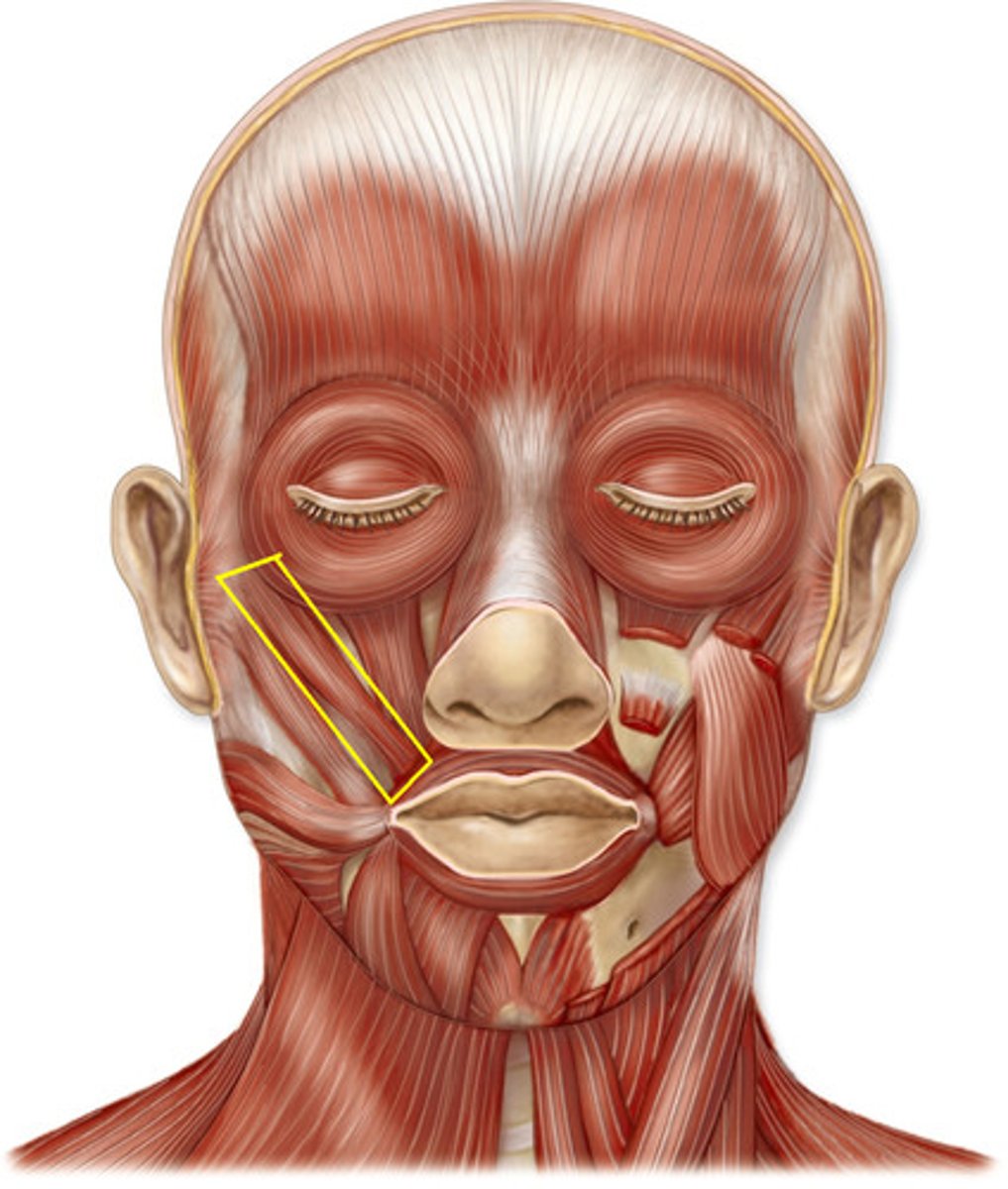
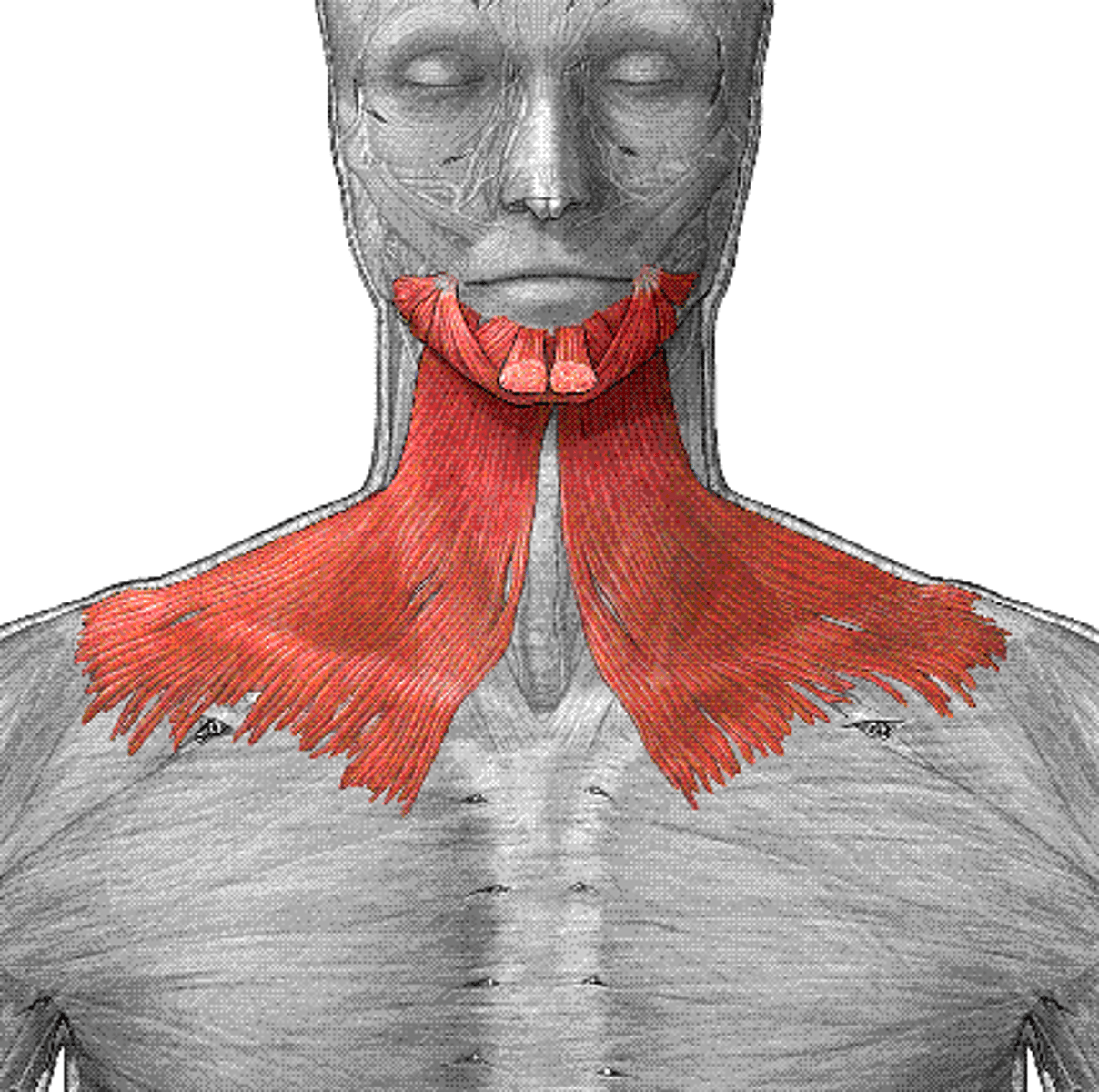
Platysma
Depresses the lower lip and mandible; tenses neck skin
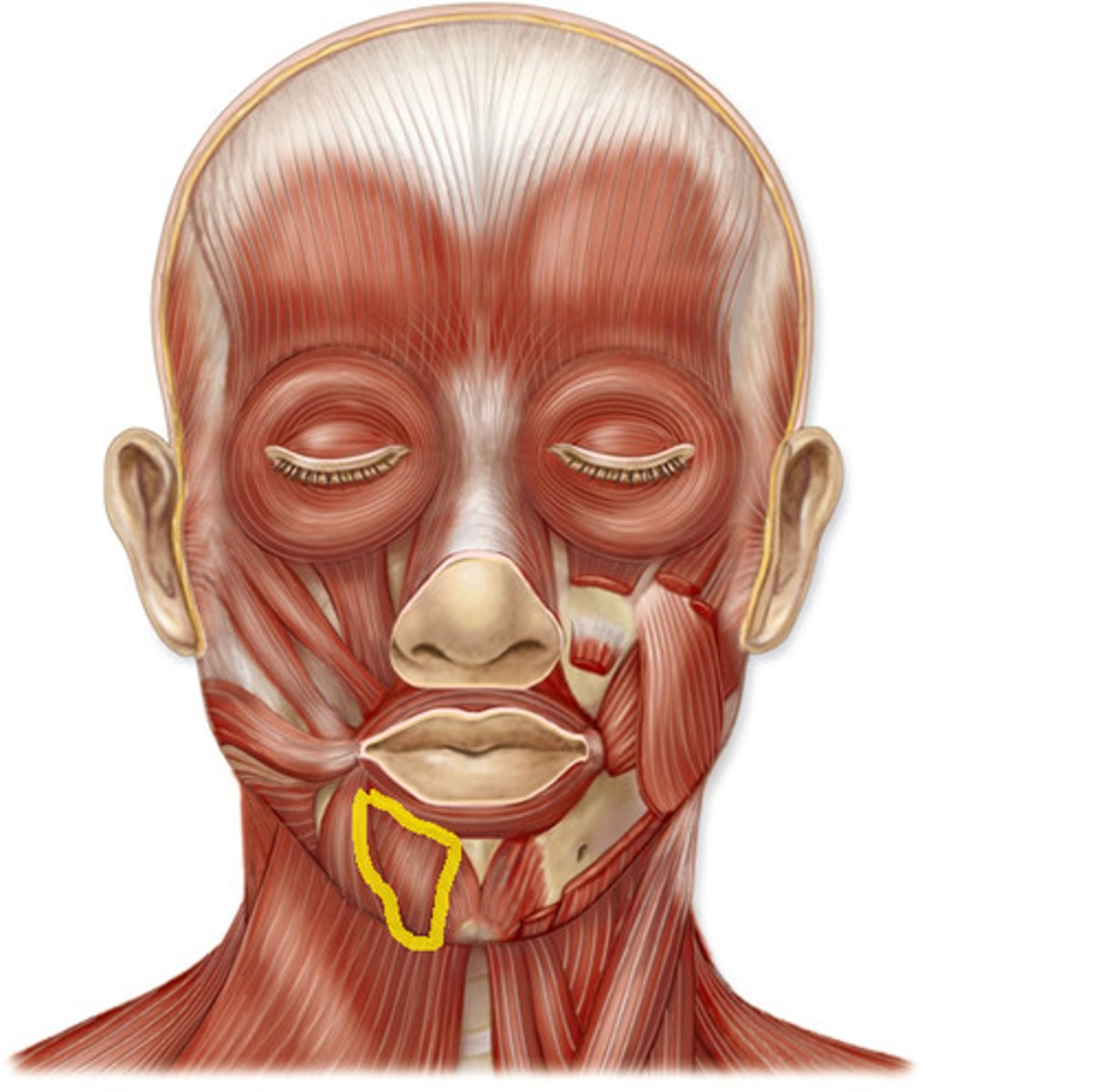
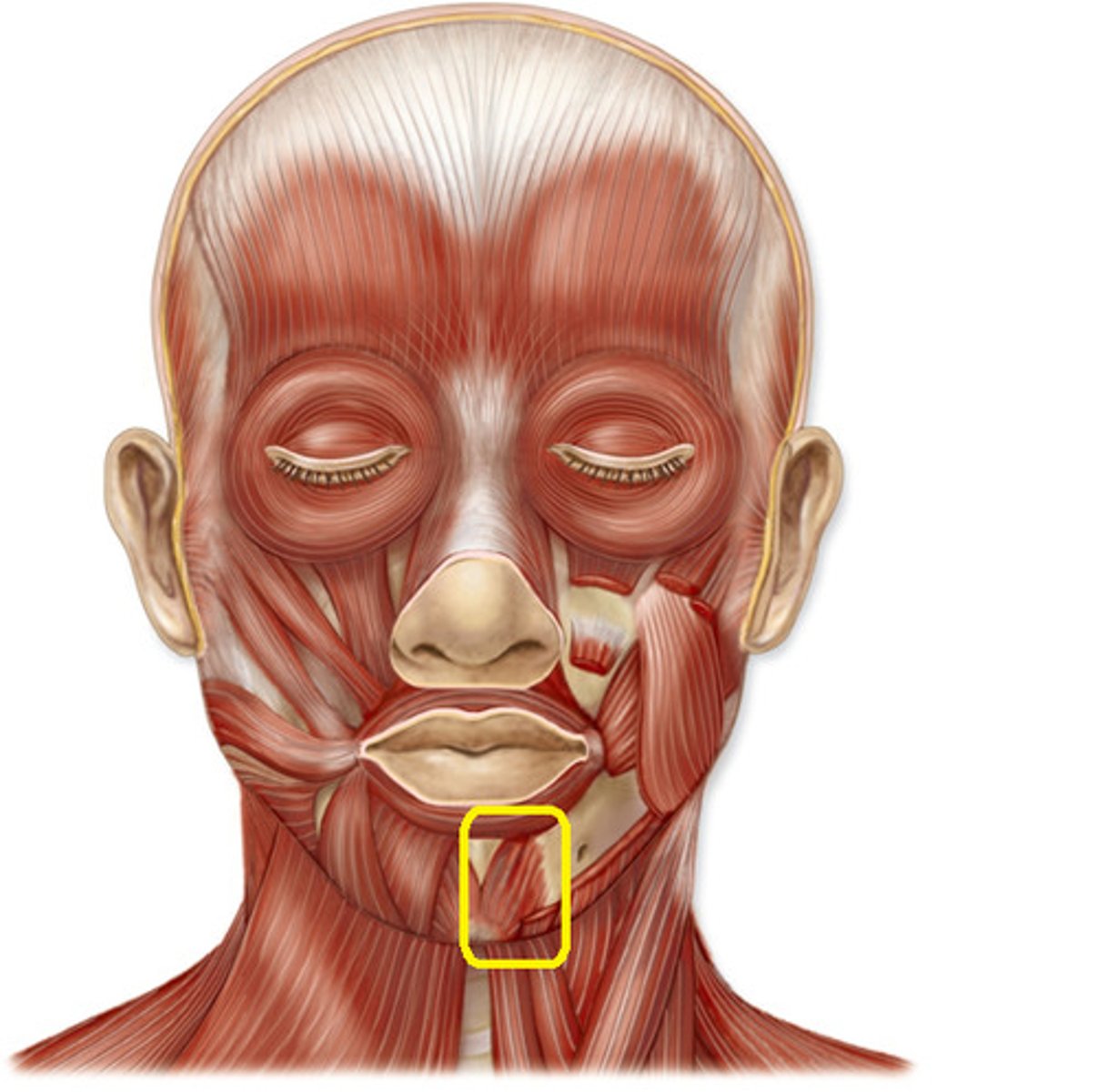
Mentalis
protrudes lower lip
Mandibular depressors
digastricus, mylohyoid, geniohyoid, platysma, Lateral Pterygoid
Mandibular elevators
masseter, temporalis, medial pterygoid
superior longitudinal
elevates tongue tip
Inferior longitudinal
depresses tongue tip
Transverse muscle of tongue
narrows tongue
Vertical muscle of tongue
flattens tongue
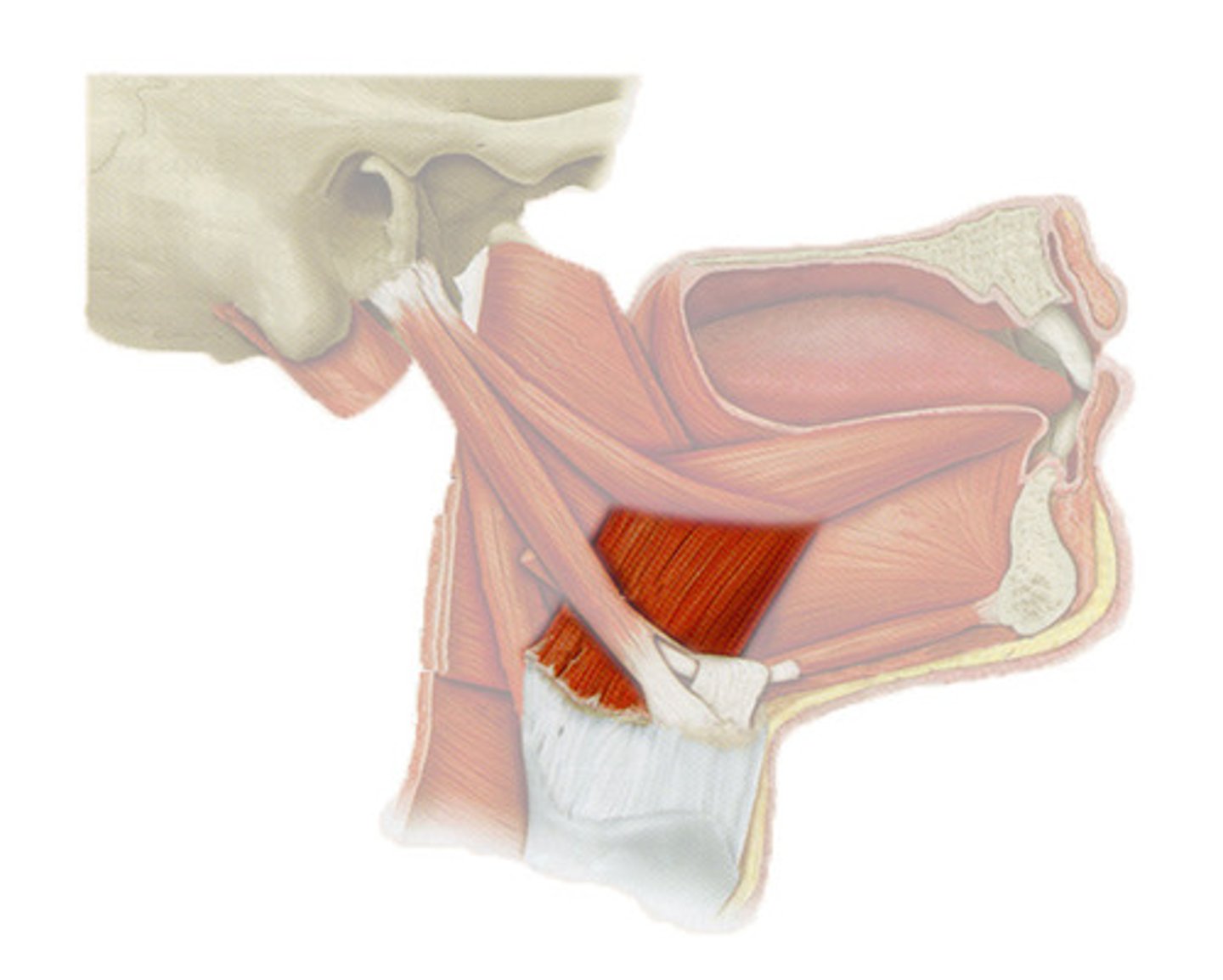
Genioglossus
depresses and protrudes tongue
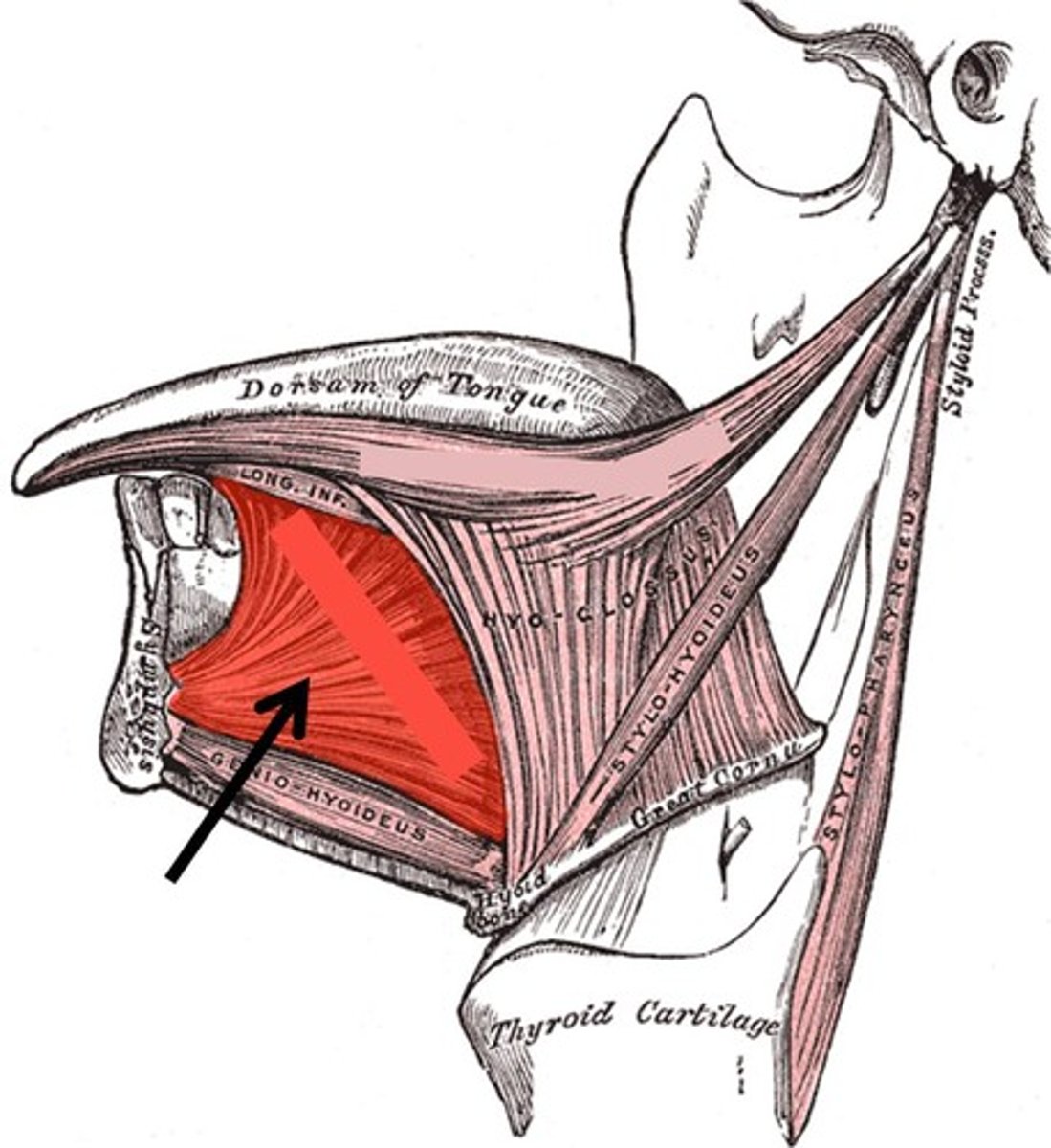
Styloglossus
retracts and elevates tongue
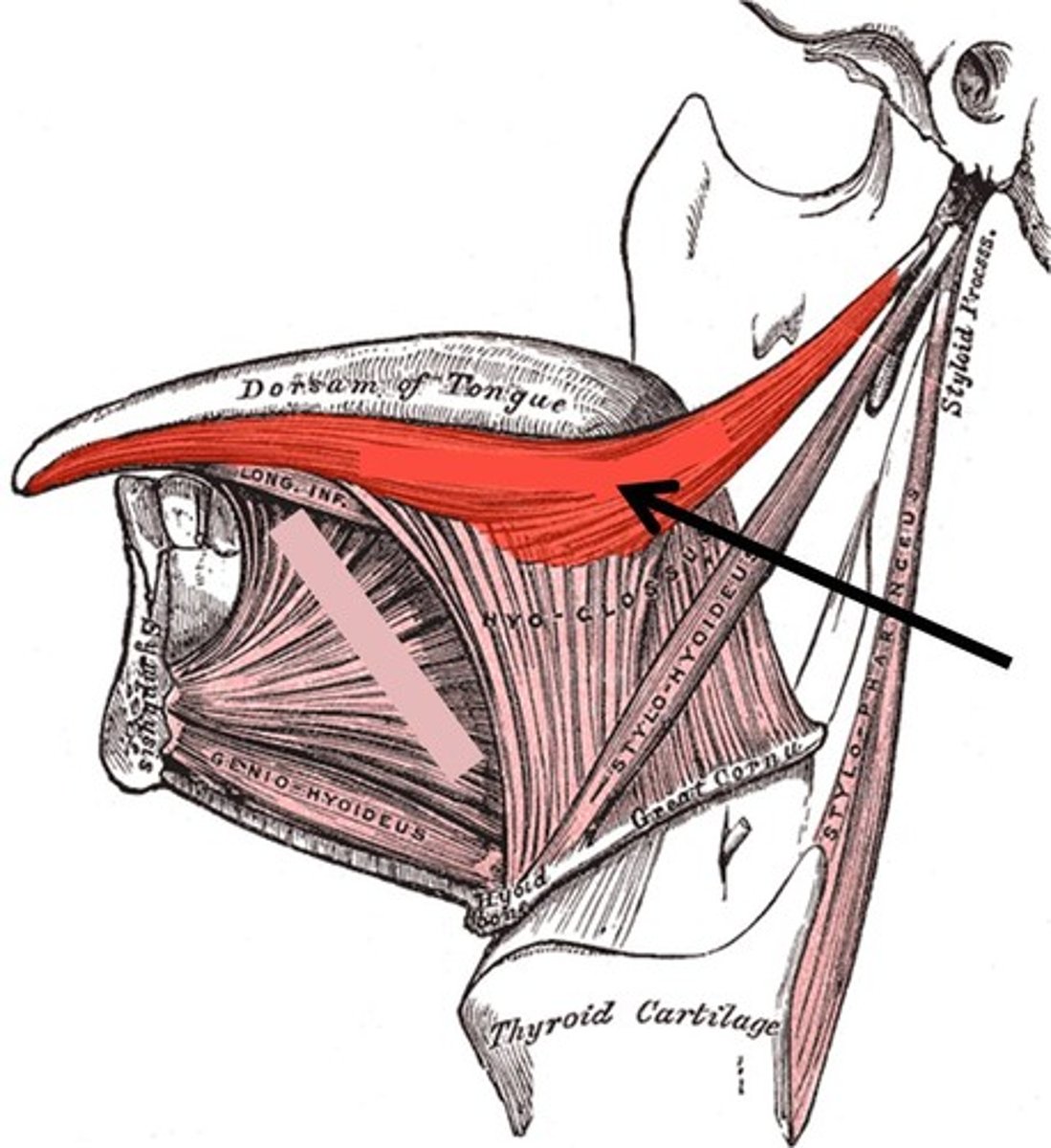
Palatoglossus
elevates posterior part of tongue
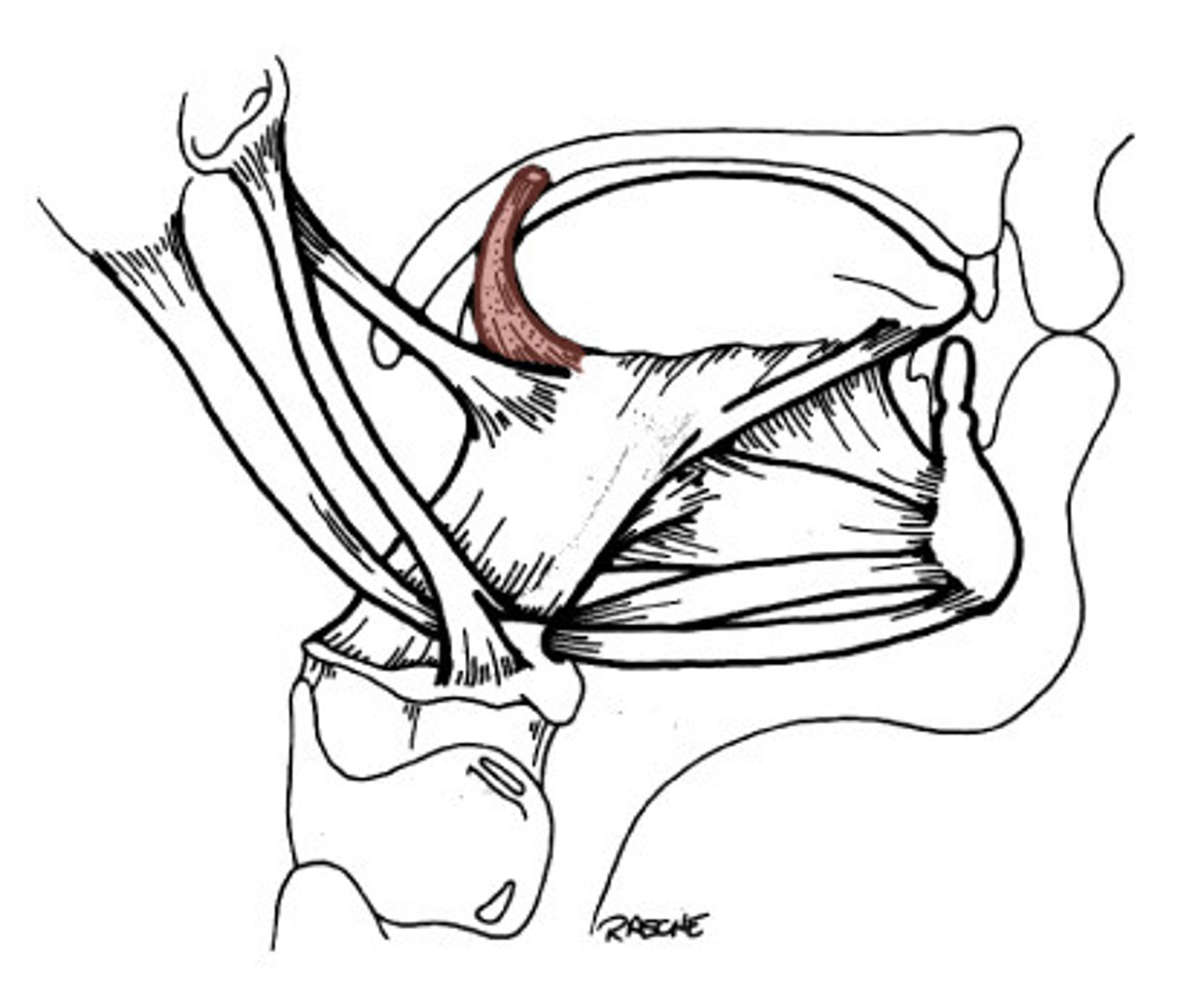
Hyoglossus
depresses and retracts tongue
Central Control Theory
There is a master control mechanism that dictates the muscle movements which are produced in a timely and accurate way
Dynamic/action theory models
Coordinative structures (muscles which work together to achieve a goal) enable system to adapt to changes. Many possible solutions exist to achieving a certain trajectory
Forward coarticulation
An articulatory feature of a phoneme is apparent during the production of a later occurring phoneme
backward coarticulation
upcoming sound can influence the preceding sound
Phonological disorder
impaired comprehension of the sound system of a language and the rules that govern the sound combinations
Articulation disorder
Difficulty producing speech sounds and speech sound sequences
deglutition
process of swallowing
Feeding
placement of food in the mouth; manipulation of food in the oral cavity prior to the swallow
Cricopharyngeal muscle
Relax and opens the UES when food approaches the esophagus
Oral preparatory stage
the stage in which food is prepared for swallow
Oral transport stage
the stage of swallow in which the bolus is transmitted to the pharynx
Pharyngeal stage
involuntary passage of bolus through pharynx into esophagus
esophageal stage
the stage of swallow in which food is transported from the upper esophageal region to the stomach
Dysphagia complications
-Aspiration pneumonia
-Dehydration
-Weight loss
Videofluoroscopic Swallow Study (VFSS)
-radiological procedure
-assesses oral, pharyngeal, and upper esophageal anatomy and stages of swallowing
-detects problems related to head/neck positioning
-helps identify compensatory techniques to minimize risk of aspiration