Week 1: Research process, selecting a topic/research question
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 4:31 PM on 9/16/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
1
New cards
2 types of scientific methods to generate knowledge about health:
Epidemiology and biostatistics
- this course is a blend of both
- this course is a blend of both
2
New cards
Types of health research
Clinical
Population
Biological (basic medical)
Population
Biological (basic medical)
3
New cards
Clinical research
ways to prevent, diagnose, and treat health issues that affect individuals and families
4
New cards
Population research
focuses on the health outcomes and the determinants of health in groups of humans - populations
5
New cards
Biological research
looks at changes at human cellular level that can be related to health outcomes
6
New cards
the 5 steps of the research process:
1. Identify a study question
2. select a general study approach
3. design the study and collect data
4. analyze data
5. Write and share a report about the findings
2. select a general study approach
3. design the study and collect data
4. analyze data
5. Write and share a report about the findings
7
New cards
Demography
study of human populations, therefore used in population health research
8
New cards
Exposure, disease/outcome, population (ED/OP)
Exposure:
A personal characteristic (socioeconomic status), environmental encounter or intervention that might change the likelihood of developing a health condition
Disease/ Outcome:
An observed event such as the presence of disease in a participant study
Population: A group of individuals, communities or organizations with identifiable similar characteristics
A personal characteristic (socioeconomic status), environmental encounter or intervention that might change the likelihood of developing a health condition
Disease/ Outcome:
An observed event such as the presence of disease in a participant study
Population: A group of individuals, communities or organizations with identifiable similar characteristics
9
New cards
Standard of health Research: PICOT
P: patient or population group and problem that will be studied
I: Intervention that will be tested
C: What will the intervention be compared to, Control group?
O: Outcome of interest?
T: Timeframe for follow-up?
I: Intervention that will be tested
C: What will the intervention be compared to, Control group?
O: Outcome of interest?
T: Timeframe for follow-up?
10
New cards
A good research question must be:
A real question
Testable
Generalizable
Purposeful
Testable
Generalizable
Purposeful
11
New cards
Sequential vs Independent Objectives
Sequential:
Chronological list of actions that will achieve the main goal
Independent:
Related but independent objectives. When one objective is not achieved, it will not prevent successful completion of the other objectives
Chronological list of actions that will achieve the main goal
Independent:
Related but independent objectives. When one objective is not achieved, it will not prevent successful completion of the other objectives
12
New cards
SMART
Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic, Timely
13
New cards
Theoretical framework
a set of established models in the published literature that can inform the components and flows of the conceptual framework for a new research study
14
New cards
Lalonde's model
First modern Western government doc to propose the health field look beyond the biomedical health care system
proposed health field = human biology + environment + lifestyle + health care organization
proposed health field = human biology + environment + lifestyle + health care organization
15
New cards
Evans and Stoddart Model
Provides a broad conceptual framework for considering the factors that influence health in a community
16
New cards
Eco-social model: The big picture
Macrosystem
Exosystem
Mesosystem
Microsystem
The individual: sex, age, health
Exosystem
Mesosystem
Microsystem
The individual: sex, age, health
17
New cards
conceptual model
the model a researcher sketches using boxes and arrows to illustrate the various relationships that will affect the study
18
New cards
Protective factor
a factor that reduces a person's potential for harmful behavior
19
New cards
nonmodifiable factor
a risk factor for a disease that CANNOT be changed through health interventions. e.g. age -> cannot be reduced.
20
New cards
Modifiable risk factors
a risk factor that CAN be avoided or mitigated
21
New cards
3 levels of prevention
1. Primary
2. Secondary
3. Tertiary
2. Secondary
3. Tertiary
22
New cards
primary prevention
Efforts to prevent an injury or illness from ever occurring. e.g. nutritious diets, exercise
23
New cards
Secondary prevention
Early identification of potential illness, providing treatment, and conducting activities that prevent worsening health status. e.g. early detection and treatment of diabetes
24
New cards
tertiary prevention
Actions, such as immediate and effective medical treatment, that are taken after illness, injury, or abuse occurs and that reduce the harm or preventing disability.
25
New cards
Comorbidity
the co-occurrence of two or more disorders in a single individual
26
New cards
Hypothesis
An informed assumption about the likely outcome of a well-designed investigation that can be tested using scientific methods. Should also be falsifiable
27
New cards
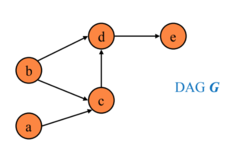
Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)
uses nodes and arrows to illustrate hypothesized pathways
28
New cards
Feasibility acronym: FINER
F: Feasible
I: Interesting
N: Novel
E: Ethical
R: Relevant
I: Interesting
N: Novel
E: Ethical
R: Relevant