Calcium Homeostasis
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
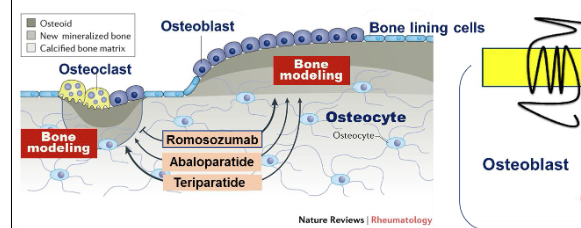
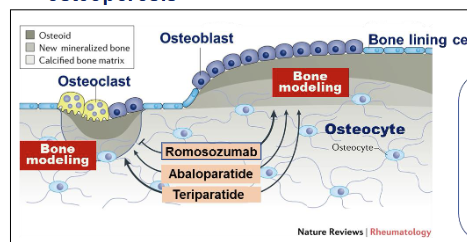
Describe bone remodeling
Physiological process - old bone is removed by osteoclasts
New bone formed by osteoblasts
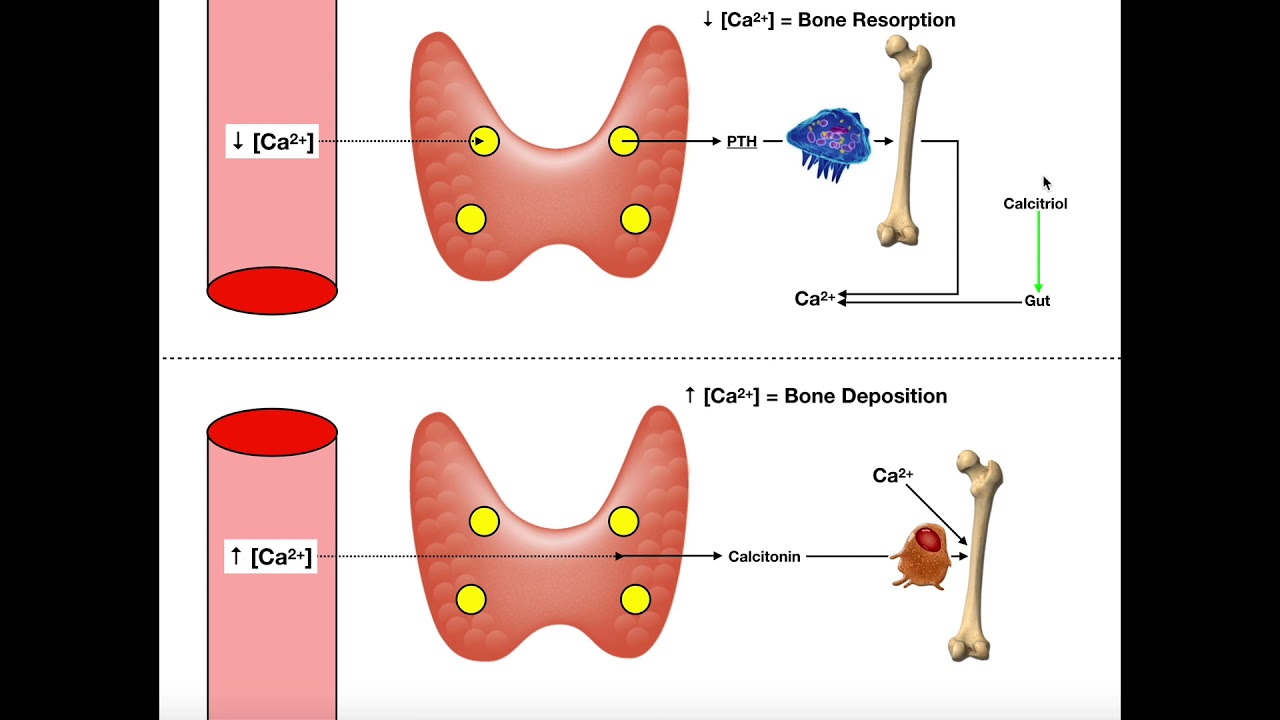
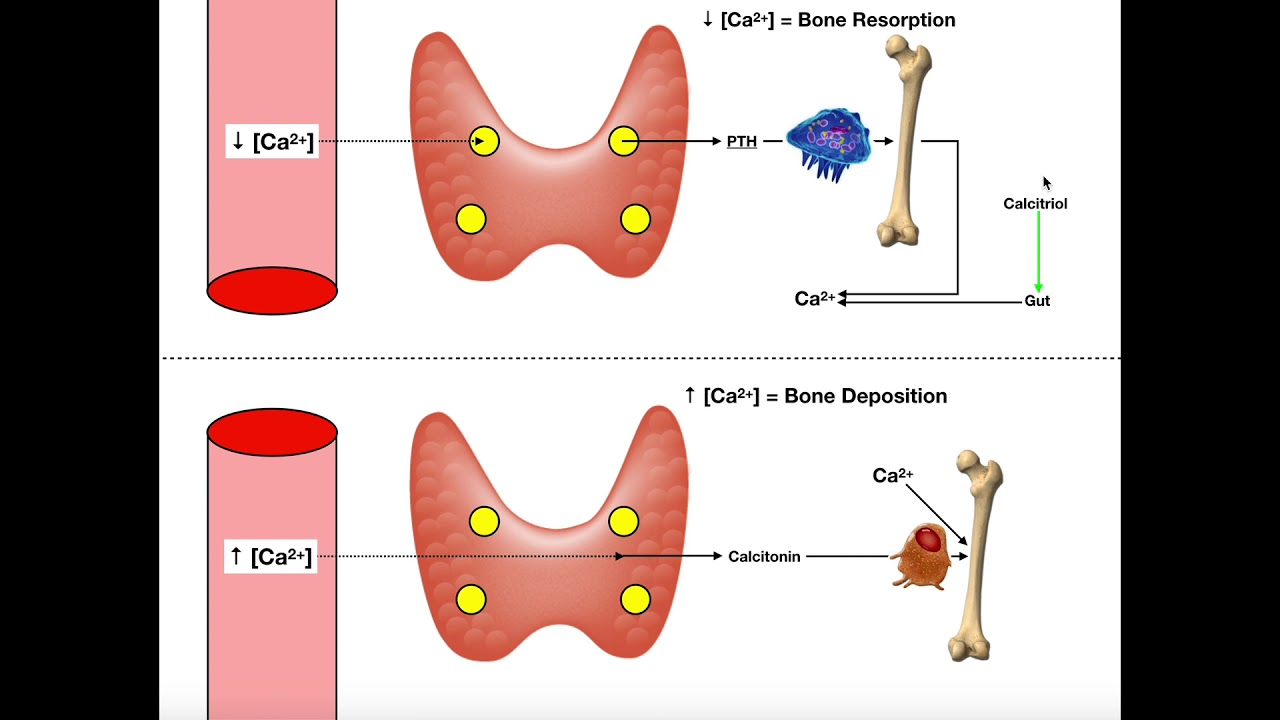
Difference between PTH and Calcitonin
PTH - acts on osteoblasts - activation of mature osteoclasts - increases calcium
Calcitonin - strongly inhibits bone-resorbing activity of osteoclasts - calcium decreases

Name 4 antiresorptive agents
Calcitonin
Bisphosphonates
Denosumab
Estrogens/SERMs

What is a calcimimetic agent?
Cinacalcet
Name 3 anabolic agents?
Teriparatide
Abaloparatide
Romosozumab

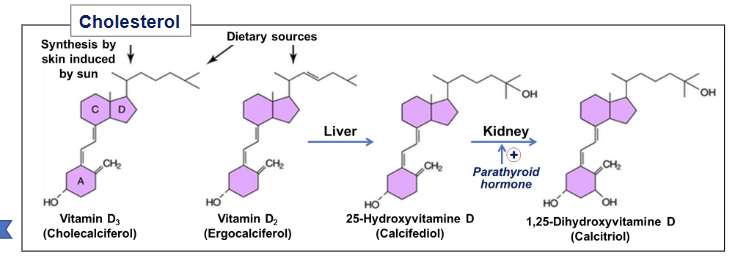
Describe the pathway of maturation of vit D
Calcitriol enhances calcium absorption in intestines/kidneys, bone resorption, and inhibits PTH
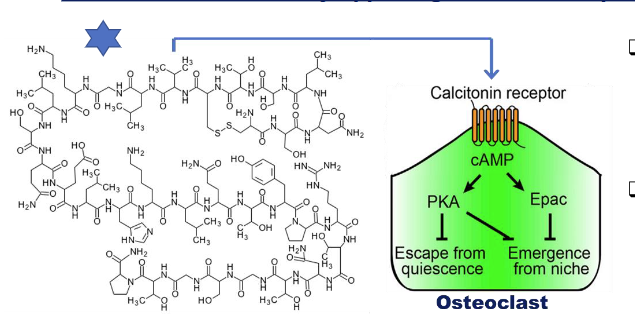
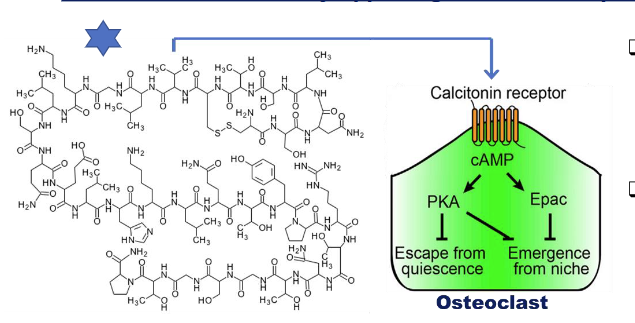
The main function of _________ is to lower blood calcium levels by inhibiting bone resorption and increases calcium excretion through the kidneys
Calcitonin - reduces blood calcium by opposing PTH
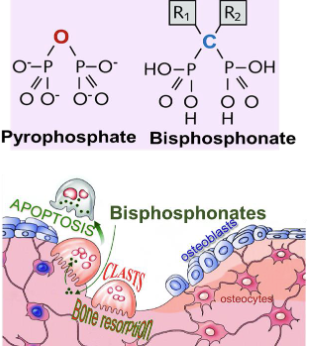
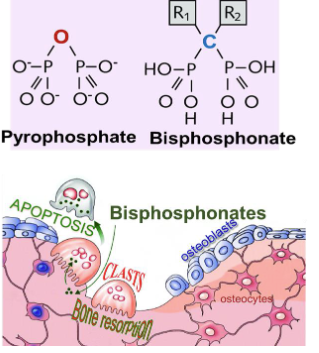
Bisphosphonates are used to treat hypercalcemia. They are ________ analogues - inhibit osteoclastic bone resorption
Pyrophosphate analogues
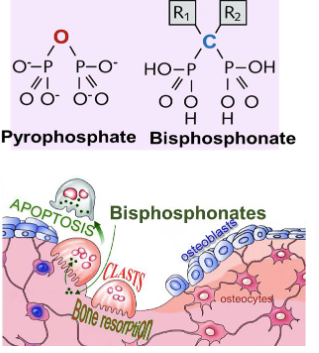
MED CHEM of bisphosphonates - what does R1 and R2 do?
R1: OH group - binding to bone is enhanced
R2: Determines drug’s effects on binding to hydroxyapatite
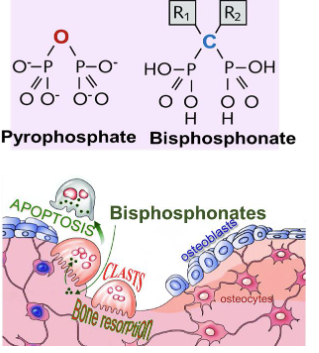

What are the two types of bisphosphonates? Name some examples?
Simple bisphosphonates
Etidronate and Clodronate
Nitrogen-containing
Risedronate, alendronate, ibandronate, zoledronate

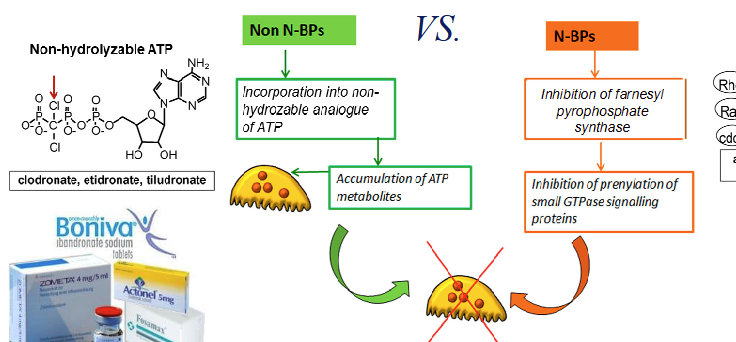
Which of the following is not correct…
Bisphosphonates are pyrophosphate analogues
Non nitrogen bisphosphonates can be metabolized to non-hydrolyzable ATP
Alendronate structurally belongs to non-nitrogen containing bisphosphonates
Nitrogen containing bisphosphonates target osteoclast farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase
Alendronate is a nitrogen containing bisphosphonate
What is the difference between bisphosphonates and denosumab MOA?
Bisphosphonates typically provide persistent antiresorptive effect after discontinuation, while denosumab’s bone turnover is quickly reversible with discontinuation - transient rebound
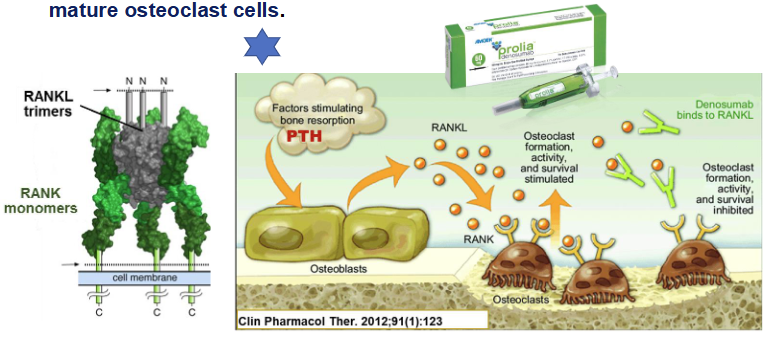
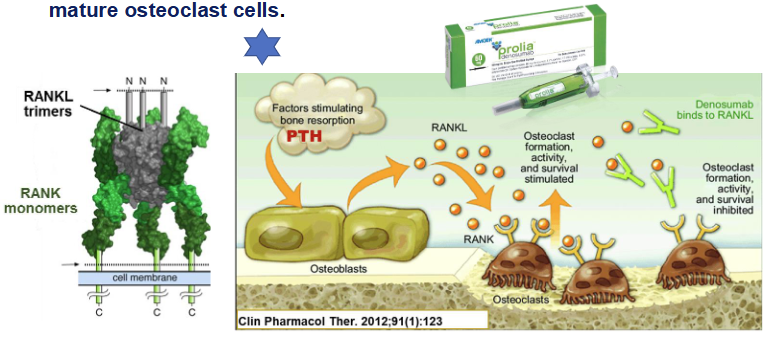
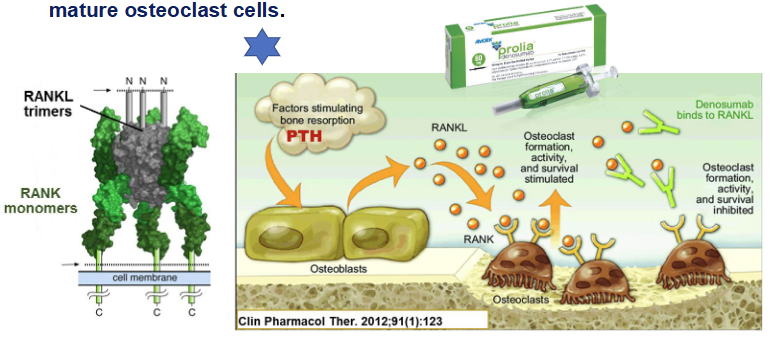
How does denosumab work?
Human monoclonal antibody
Works as a RANK ligand INHIBITOR (inhibits RANKL-RANK)
Prevents development of osteoclasts → prevents bone resorption
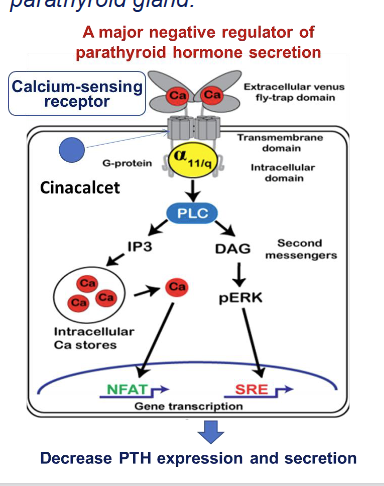
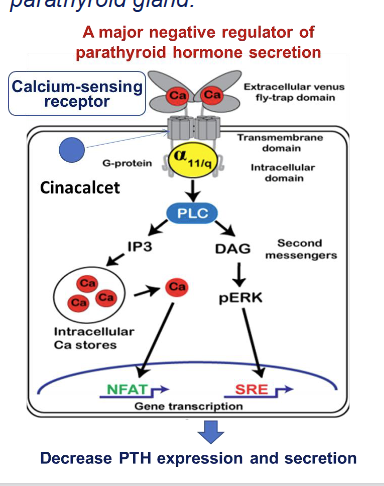
What is cinacalcet and how does it work?
Cinacalcet mimics the action of calcium
Allosterically activates the calcium sensing receptor
Reduces PTH → decrease serum calcium levels
Used to treat hyperparathyroidism (CKD/dialysis)
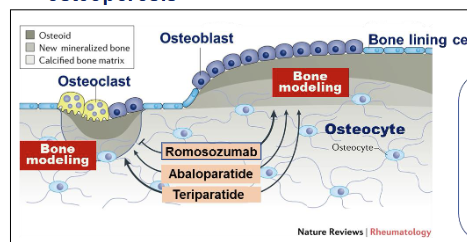
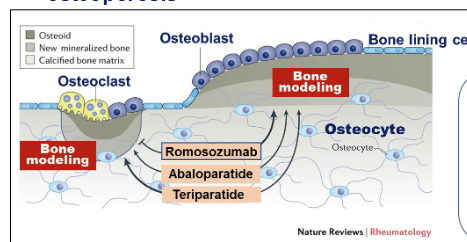
Romosozumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody - how does it work?
Increases bone formation by osteoblasts AND decreases bone resorption by osteoclast
Works against sclerostin
Inhibits genesis of osteoblasts as a WNT signaling inhibitor
Decreases bone formation
Romosozumab opposes this mechanism
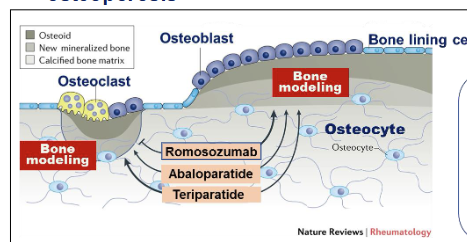
What are PTH analogue drugs?
Teriparatide = recombinant PTH
Abaloparatide = parathyroid hormone-related protein analog
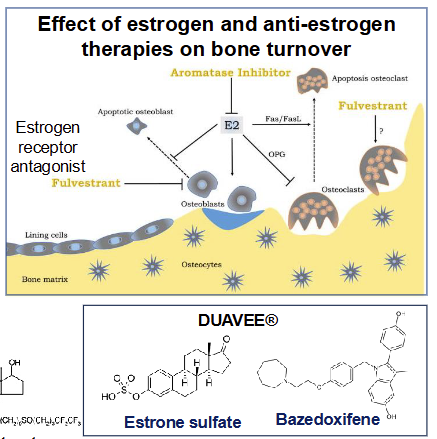
Bazedoxifene and raloxifene are both _____________ used to treat _______________ and prevent fractures in postmenopausal women
Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMS)
Treats osteoporosis
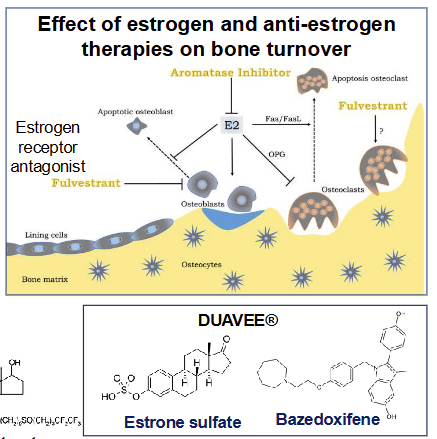

SERMs work by mimicking the effects of _________ (hormone) on __________, without stimulating the ______ or ______
Mimics estrogen on bones
Does NOT stimulate uterus or breast tissue
Reduces the risk of invasive cancers at high risk

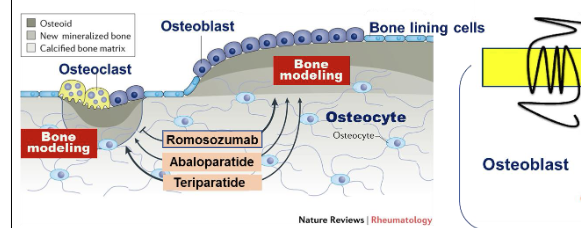
What is the difference between an anabolic and antiresorptive therapy?
Antiresorptive = slow bone remodeling and reduce bone loss
Anabolic = stimulate bone formation