final exam apk2100c ahlgren UF PART 1
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
cells
smallest living units in the body
cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm
three main structural components of any cell
function o plasma memrane
-protective barrier
-cellular communication via receptor proteins
-regulates movements on substances in and out
fluid mosaic model
describes the dynamic nature of the cell membrane and its fluidity;
-bilayer of lipid molecules with embedded proteins
-tails line up end to end
-most abundant lipids are phospholipids (polar head, nonpolar tail), but theres cholesterol, glycolipisds, and diff kinds of proteins which help with memrane transport
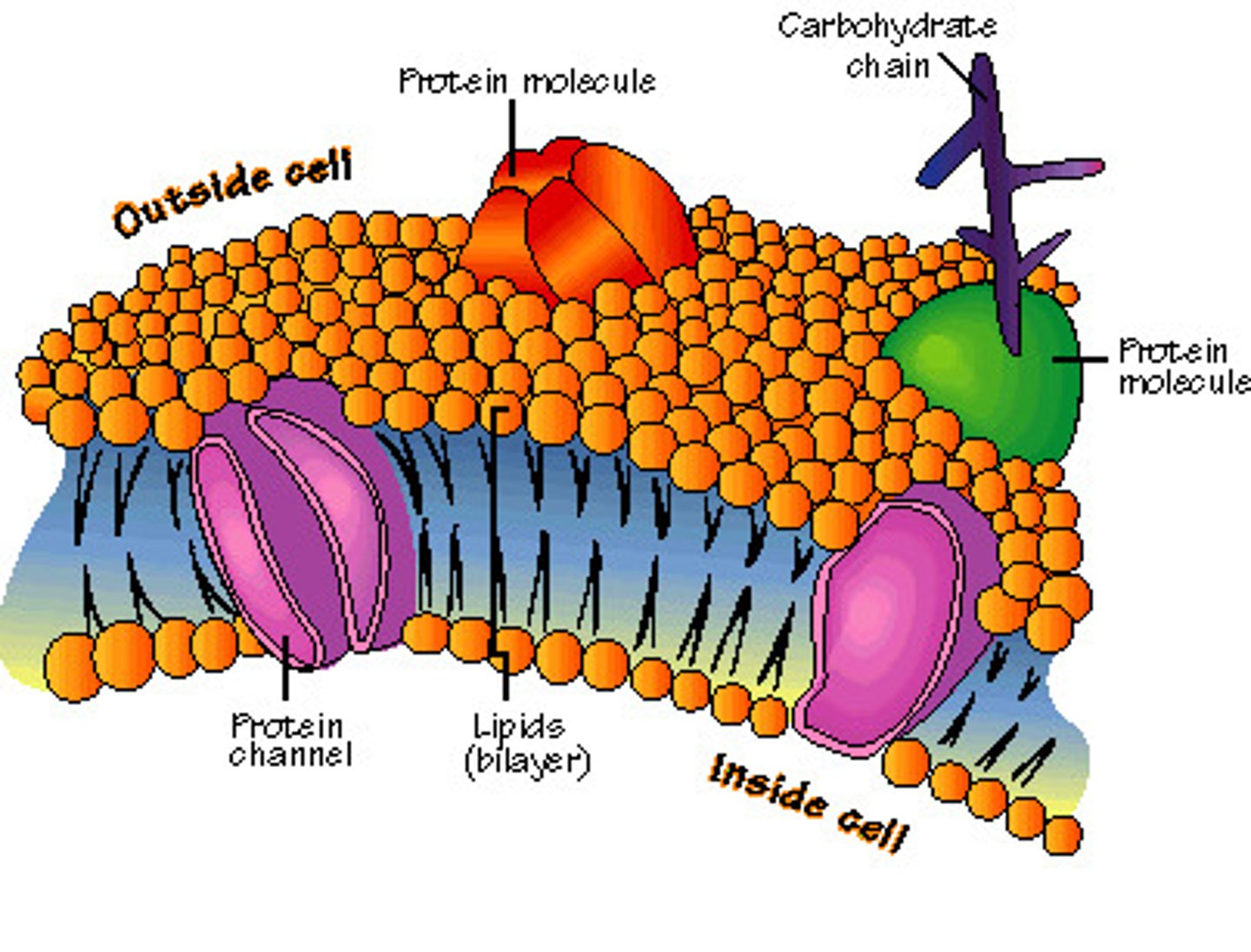
Phospholipids
what makes up most of the plasma memrane
Cholesterol
structural integrity of the plasma memrane thats in the lipid tails of bilayer
Glycolipids
assist in cell recognition and adhesion to other cells and is found in the outermost layer of bilayer
desmosomes, tight junctions, gap junctions
three kinds of membrane junctions
Tissue
group of cells that perform similar function + extracellular matrix
extracellular matrix
component of a tissue that gives it its consistency
-provides structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells
-includes: proteins, minerals, salts, lipids
Epithelium
primary tissue that COVERS body surfaces and LINES body cavities
-its cells are arranged in sheets,
-also forms glands
connective tissue
primary tissue
-form and function vary widely but all of these contain a large amount of extracellular matrix
-function: *support, holding tissue fluid, protection from disease*
muscle tissue
consists of myocytes
-*brings about most kind of body movements*
nervous tissue
forms the main component of the nervous organs (brain, spinal cord, and nerves)
---*regulates and controls body functions*
epithelial tissue is named based off
the number of layers of cells + the shape of cells on the apical surface
connective tissue
what is the most abundant and diverse type of tissue
collagen, elastic, reticular
three types of fiber in CT
skeletal, cardiac, smooth
three types of muscle
neurons and neuroglia
types of cells present in nervous tissue
tissues
skin is an organ because it consists of many _____ working together for a common function
epidermis (epithelial) and dermis (connective tissue)
two layers of the skin and what they consist of
Hypodermis, has adipose tissue
what isn't a part of the skin and why?
Dermis
the majority of the vascularization in the integumentary tissue is in the
keratinized epidermal cells
what type of cells are hair and nails made of
sebaceous glands
glands that produce an oily substance called sebum
chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
list the hierarchy of structural organization in the body
Ipsilateral
same side
Contralateral
opposite side
Ventral
front side of the body, ventral
dorsal
back side of body, fin
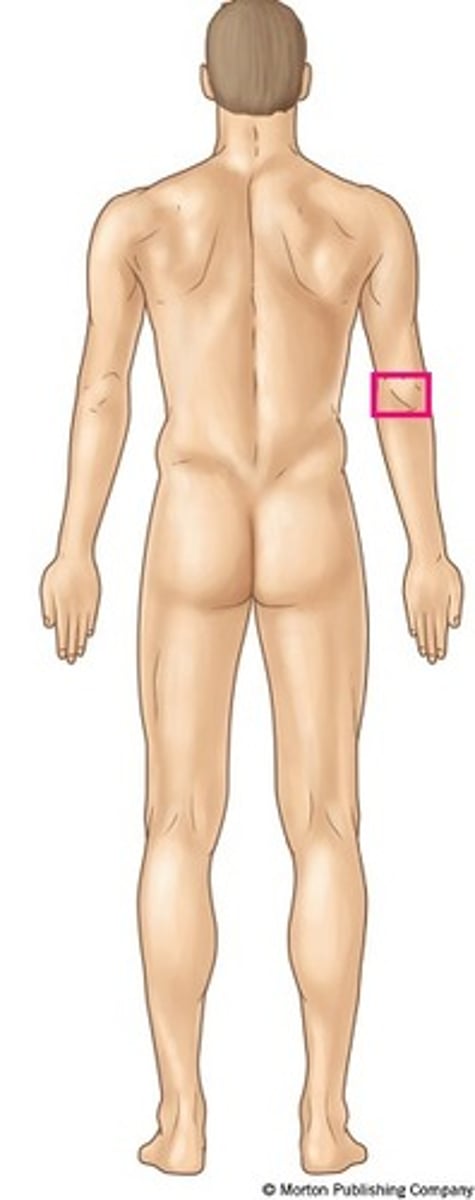
Olecranal
back of elbow
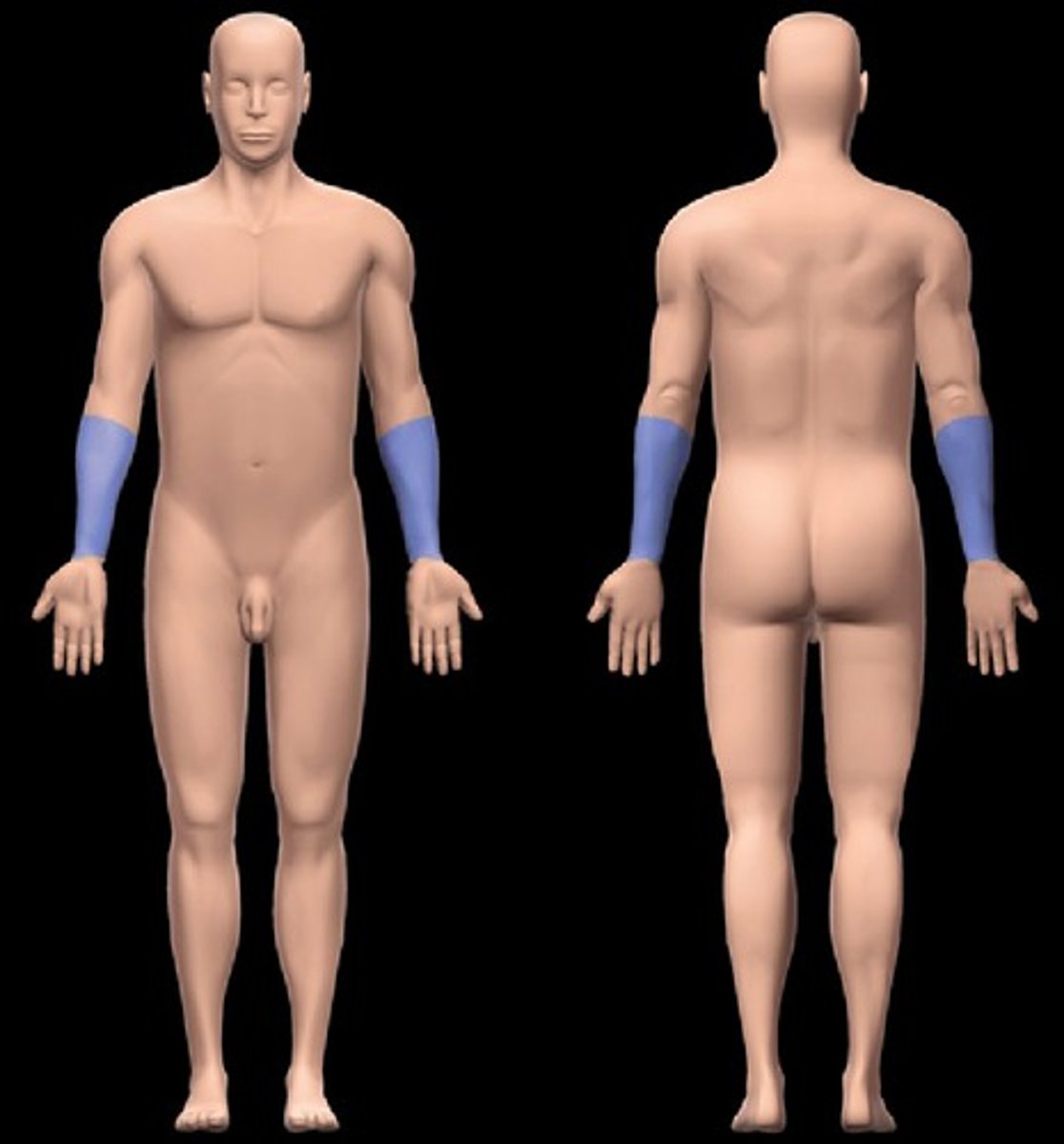
Antebrachial
pertaining to the forearm
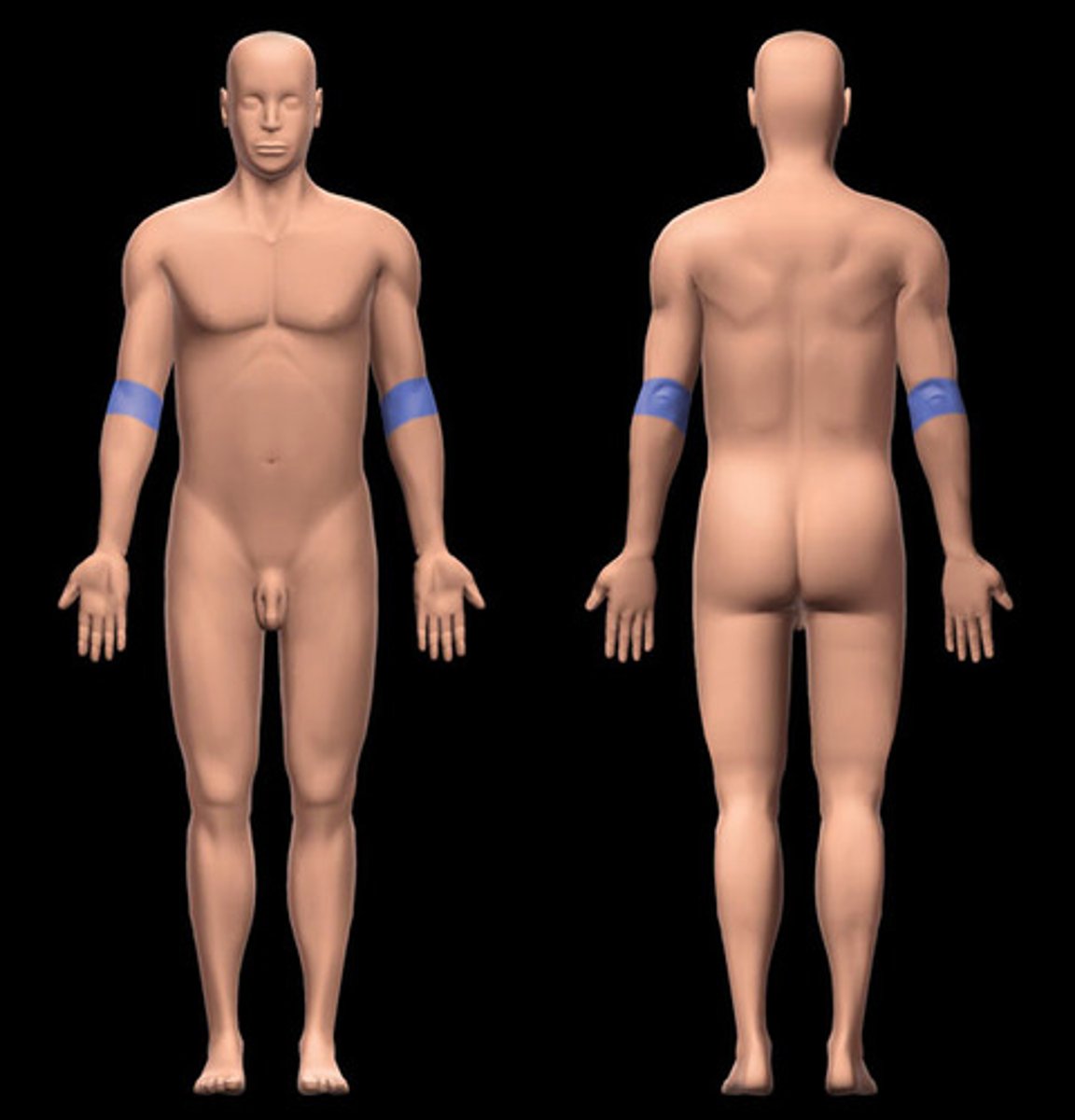
Antecubital
front of elbow
manus
hand
Pollex
thumb
Crural
shin
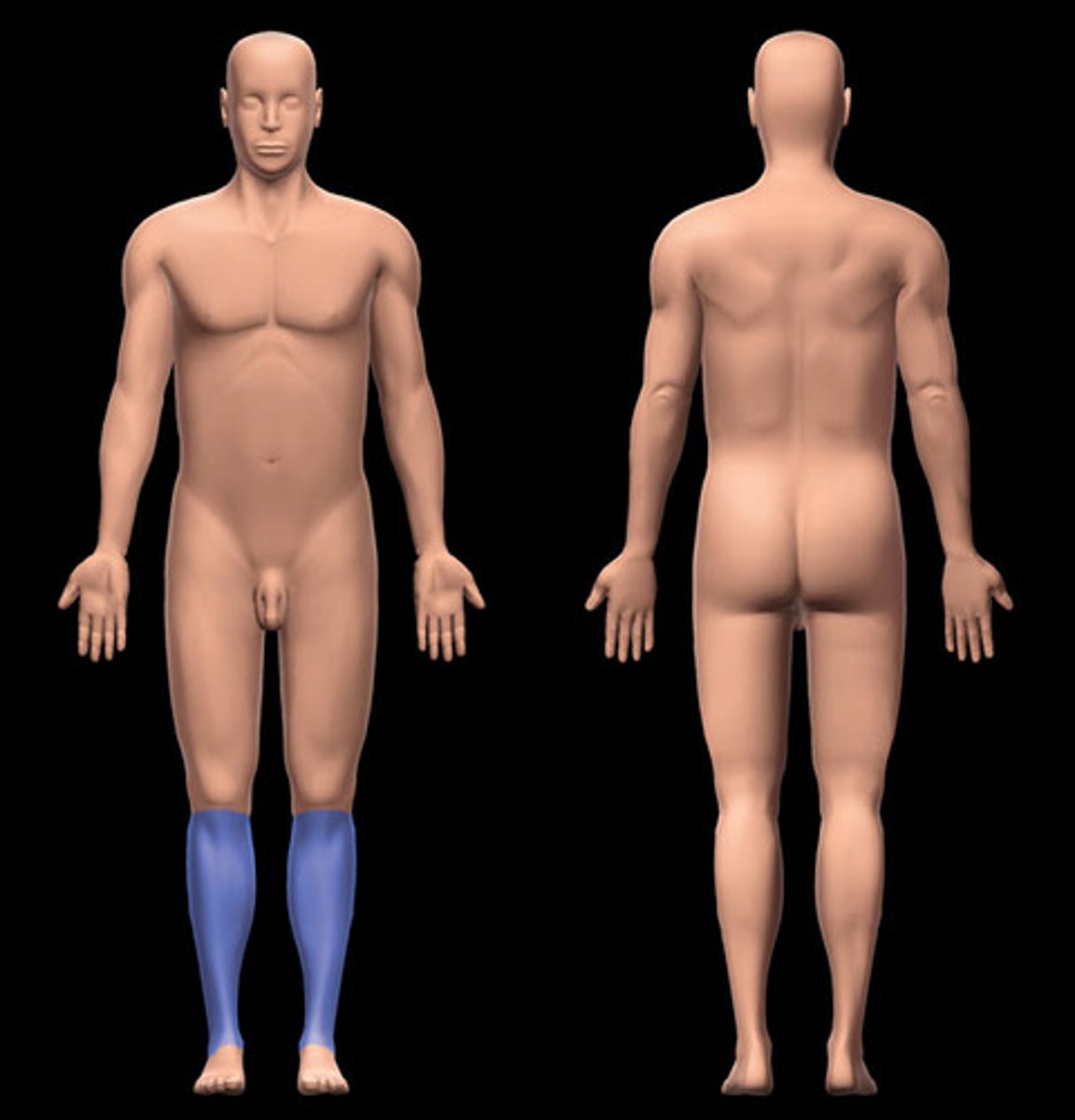
Sural
calf
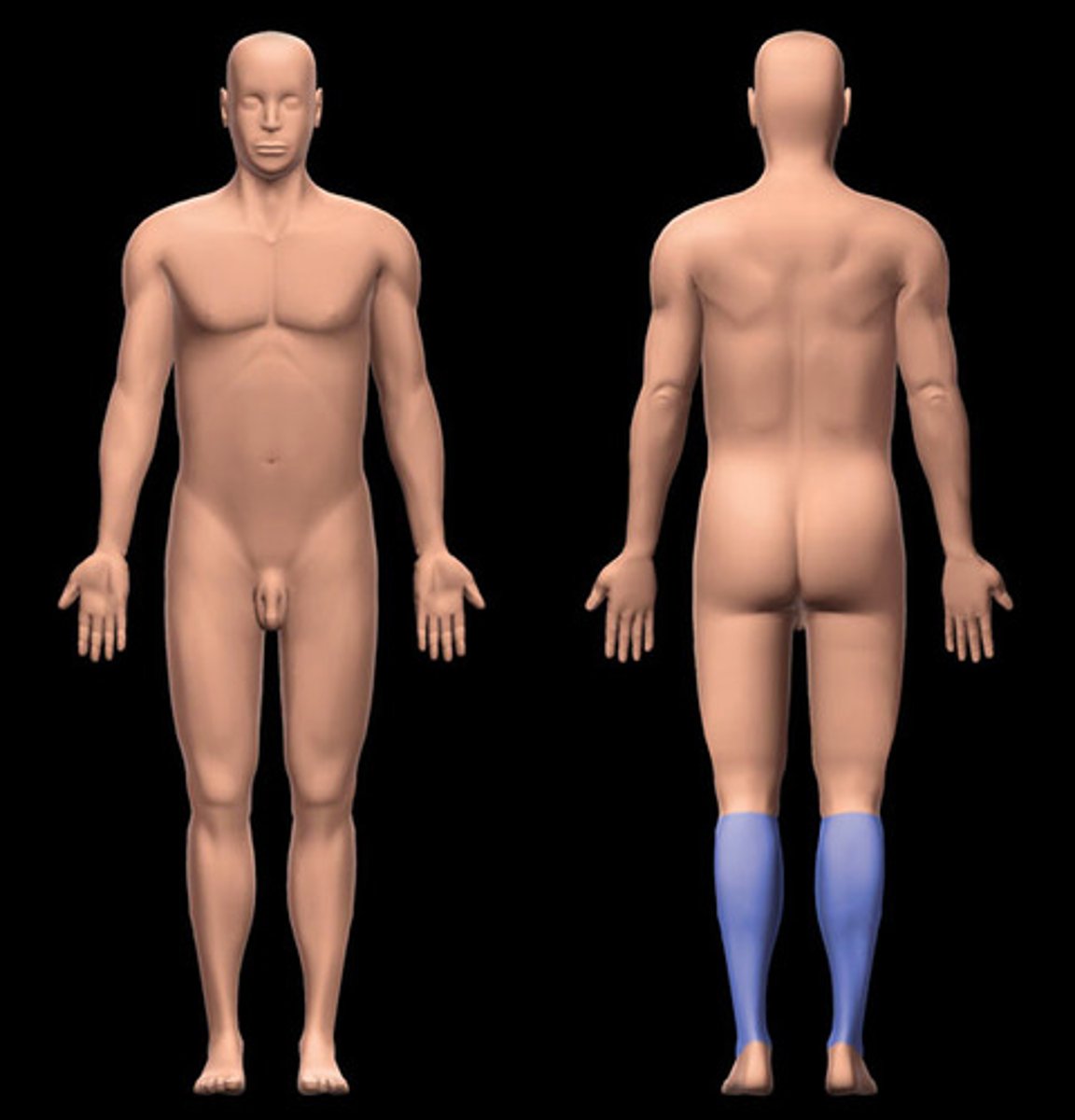
hallux
big toe
spinal cord + cranial cavity
what is in the dorsal body cavity?
ventral body cavity
thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities
median (midsagittal) plane
Cuts the body into left and right planes
motion: forward and backward
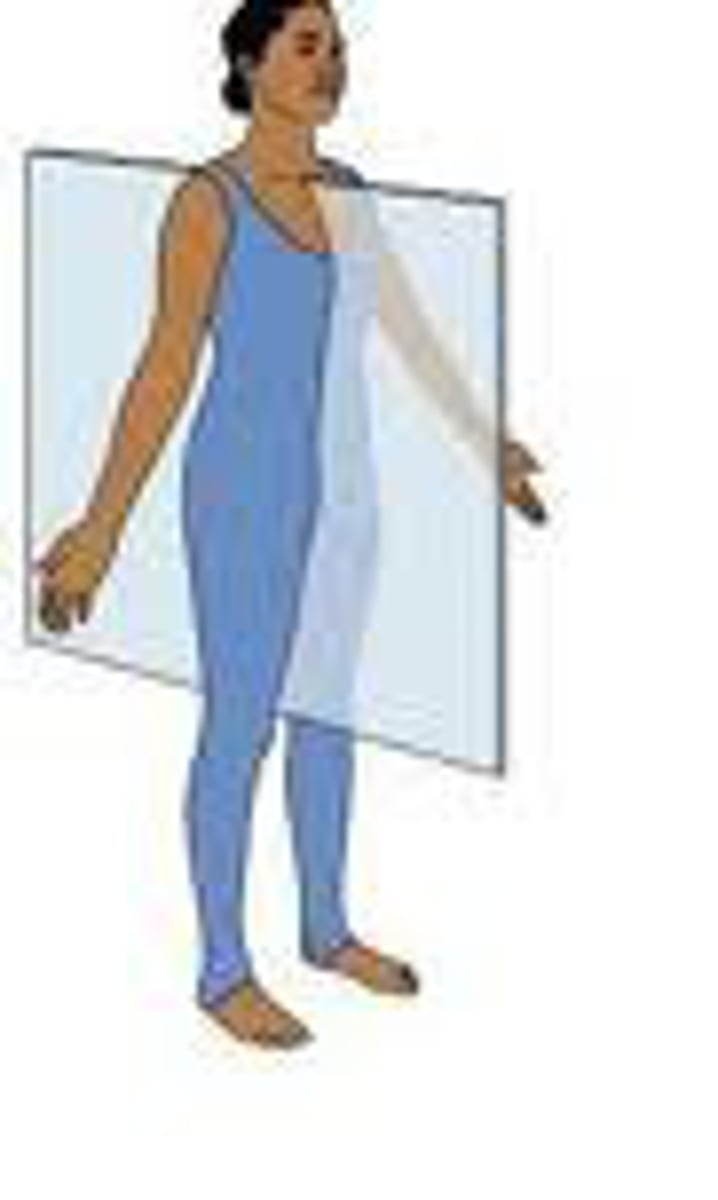
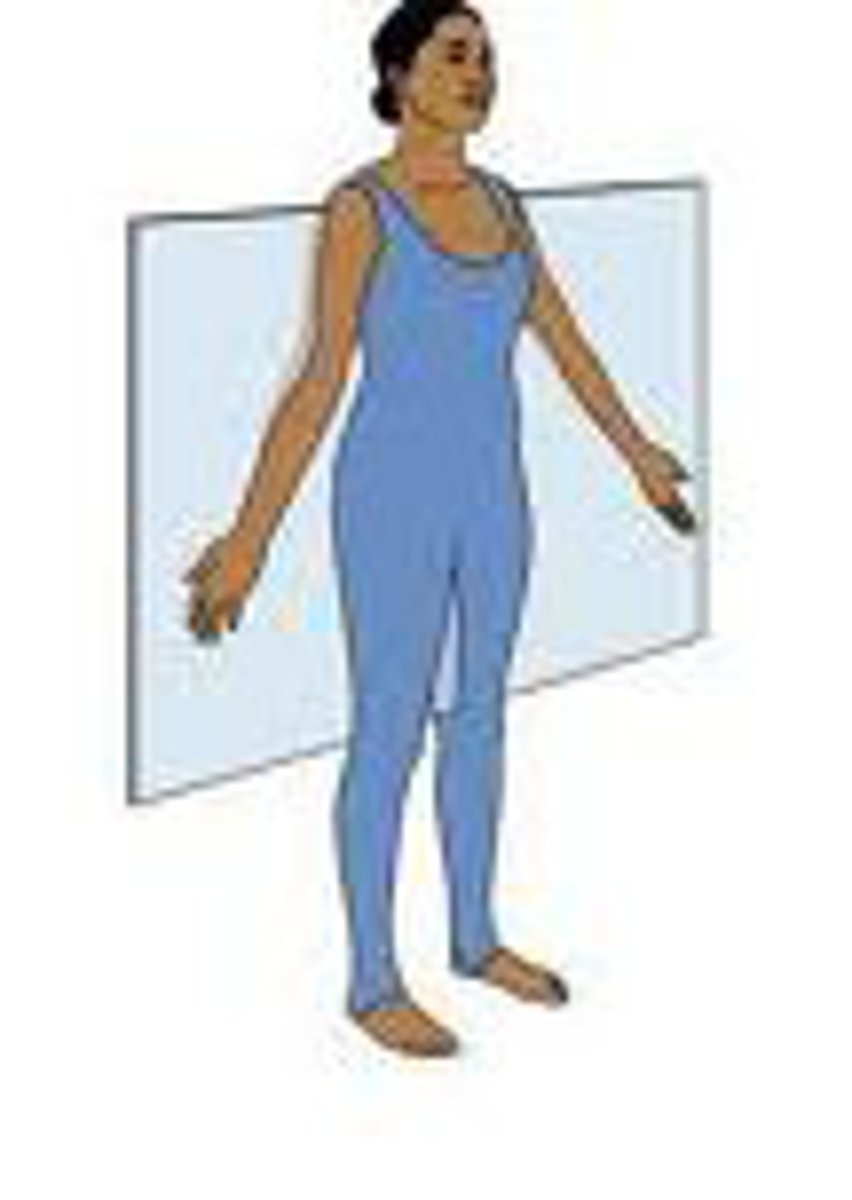
frontal (coronal) plane
vertical plane dividing the body or structure into anterior and posterior portions
motion: towards or away from the midline, lateral side to side movements

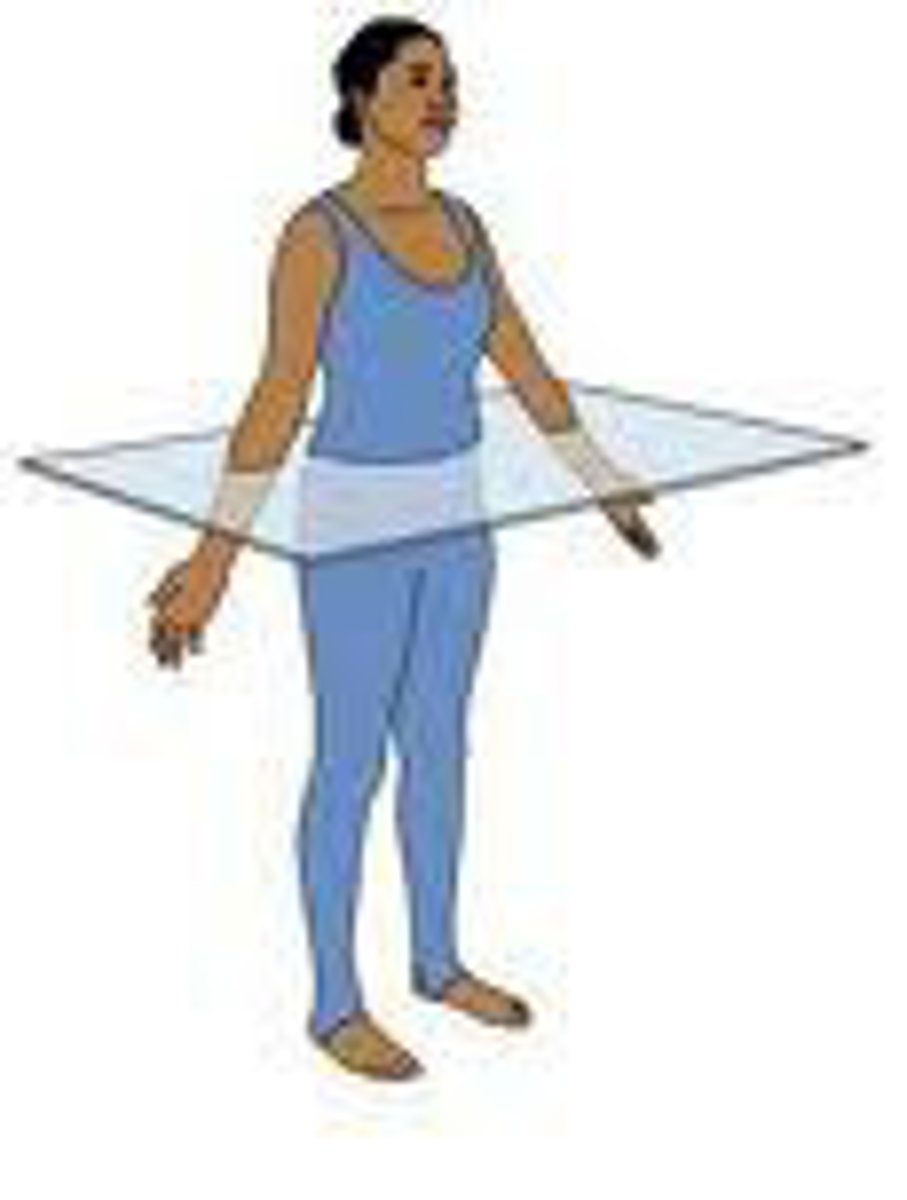
transverse plane
divides the body into superior and inferior parts
motion: rotation
Cilia
fingerlike projections that help *move* things
Microvili
projections that increase the cell's surface area
-microfilaments make up their core
Flagella
motile projection that has a tail, uses their whip like motions to move an entire cell
plasma membrane
A selectively-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of the cells
Ribosomes
produce proteins, protein synthesis
-near rough ER and mitochondria
Rough ER
produces proteins, has ribosomes attached
Smooth ER
metabolizes lipids and stores calcium (in some cells)
-no ribosomes attached
Golgi apparatus
packages proteins for use either within or outside the cell
-uses transport vesicles to send out the modified products received from ER
Lysosomes
sacs of hydrolytic enzymes that break down large molecules
-acts like intracellular digestion
Mitochondria
makes energy in form of ATP
-double memrane
-cristae ----name of inner memranes
Peroxisomes
removes toxic wastes by using special enzymes oxidase and catalase
--oxidase : breaks down free radicals into hydrogen peroxide (BAD)
--catalase: neutralizes hydrogen peroxide and turns it into water
Cytoskeleton
supports the cell shape and produces movements
Centrioles
Located near the nucleus and help to organize cell division
Centrosome
microtubule organizing center consisting of two centrioles
- where cilia and flagella are formed
Nucleus
directis the operation of the cell
-double layer
--outside layer: pushes outward that helps develop the ER
--inside layer: houses chromatin and dense packed protein RNA; ribosomes are born here
covering
one word function for epithelial tissue
support
one word function for connective tissue
Movement
one word function for muscle tissue
control (and communication)
nervous tissue one word function
special features of epithelium
-high cellularity -- lots of cells, almost no extracellular matrix
-polarity -- one side is diff from the other
-support by connective tissue
-avascular
-nervous innervation- but no blood vessels
-high regenerative capacity
-basement membrane: helps epithelium *stick* and has some CT
tight junctions
tightly seals epithelium together and prevents leakage
Desmosomes
anchoring junctions
-holds cells together that are under mechanical stress
gap junctions
communicating junctions allow ions and small molecules to pass from one cell to the next for intercellular communication
Squamous
flat cells
Cuboidal
generally the same size all the way around
Columnar
elongated cell, nucleus gravitates towards the basal side
simple epithelium
one layer of cells
stratified epithelium
means that theres two or more layers
simple squamous epithelium
single layer of flattened cells with disc shaped central nuclei
--bird eye
simple cuboidal epithelium
single layer of cubelike cells with large spherical central nuclei
-looks mostly the same in size, height, depth, and width
simple columnar epithelium
single layer of TALL cells with ROUND to OVAL nuclei
-some cells bear cilia
-can have goblet cells
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
single layer of cells at DIFFERING HEIGHTS, some not reaching the free surface
-nuclei is seen at diff levels
-can have cilia and goblet cells
- *she only shows CILIA on this type of tissue*
stratified squamous epithelium
thick membrane composed of several layers
-basal cells are cuboidal or columnar, and surface cells are flattened (squamous)
stratified cuboidal epithelium
two or more layers of cubelike cells
stratified columnar epithelium
several cell layers
-basal cells usually cuboidal
-superficial cells elongated and columnar
general arrangement of all types of CT
-unicellular
-lots of extracellular matrix
collagen fibers
provides flexibility and *tensile* strength
-largest diameter and strongest of the CT fibers
-tensile strength -- like a rope, strength along its long axis; has little parts that make it strong bc of all of its compartments
elastic fibers
*recoil* -able to go back to its original way
Flexible and "stretchy" fibers that add elasticity to tissue
reticular fibers
smallest but still strong
*strength in tiny parts* that help to *support*
-doc A says to think of *pantyhose* - the threads are super small but bc of the way they're connected to each other, it helps make strong sheets
skeletal muscle
A muscle that is attached to the bones of the skeleton and provides the force that moves the bones.
-*voluntary and involuntary*
-striated that are perpendicular to things, multicellular
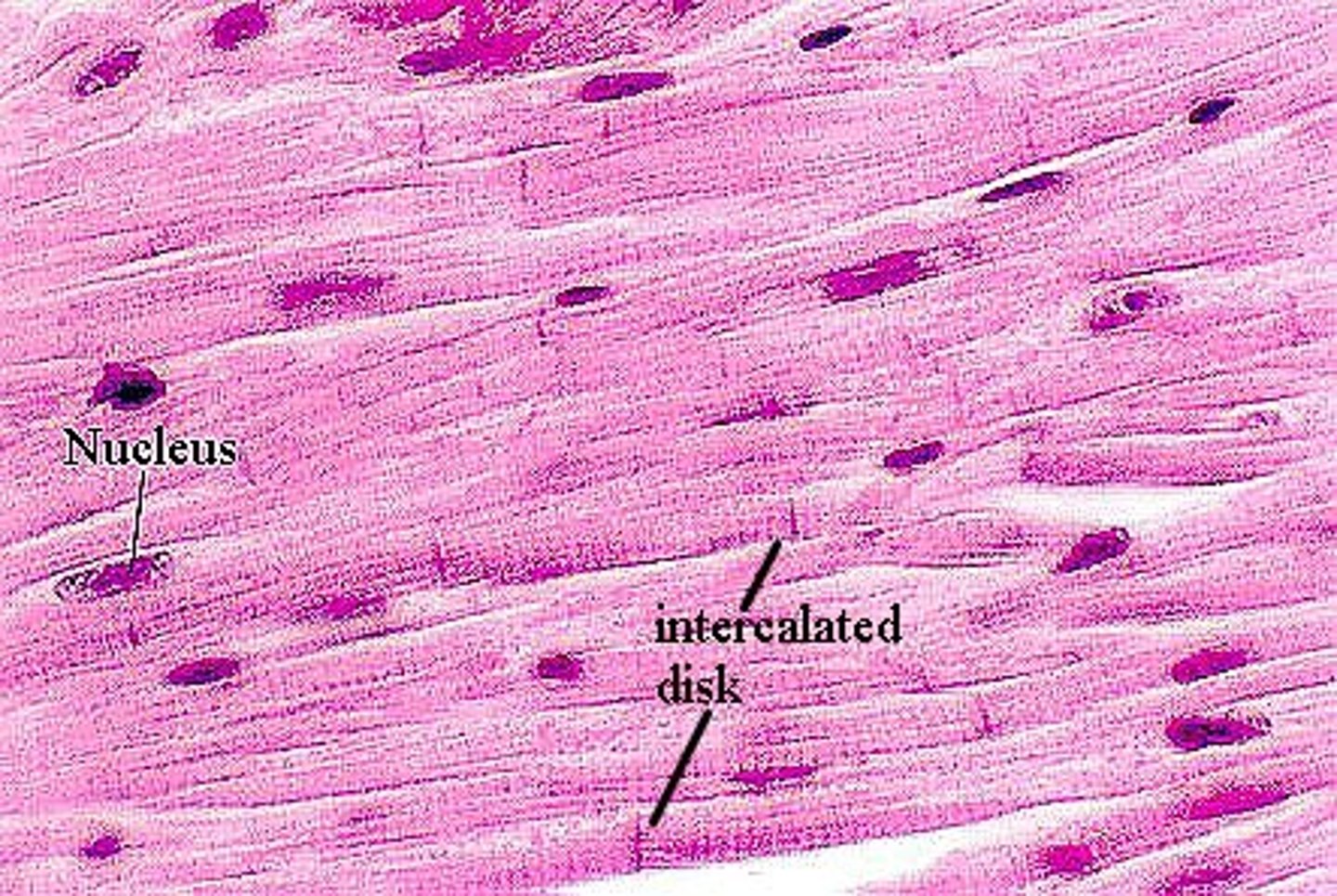
cardiac muscle
only in heart
-striated, unicellular
-function: move blood in cardiovascular system
-involuntary
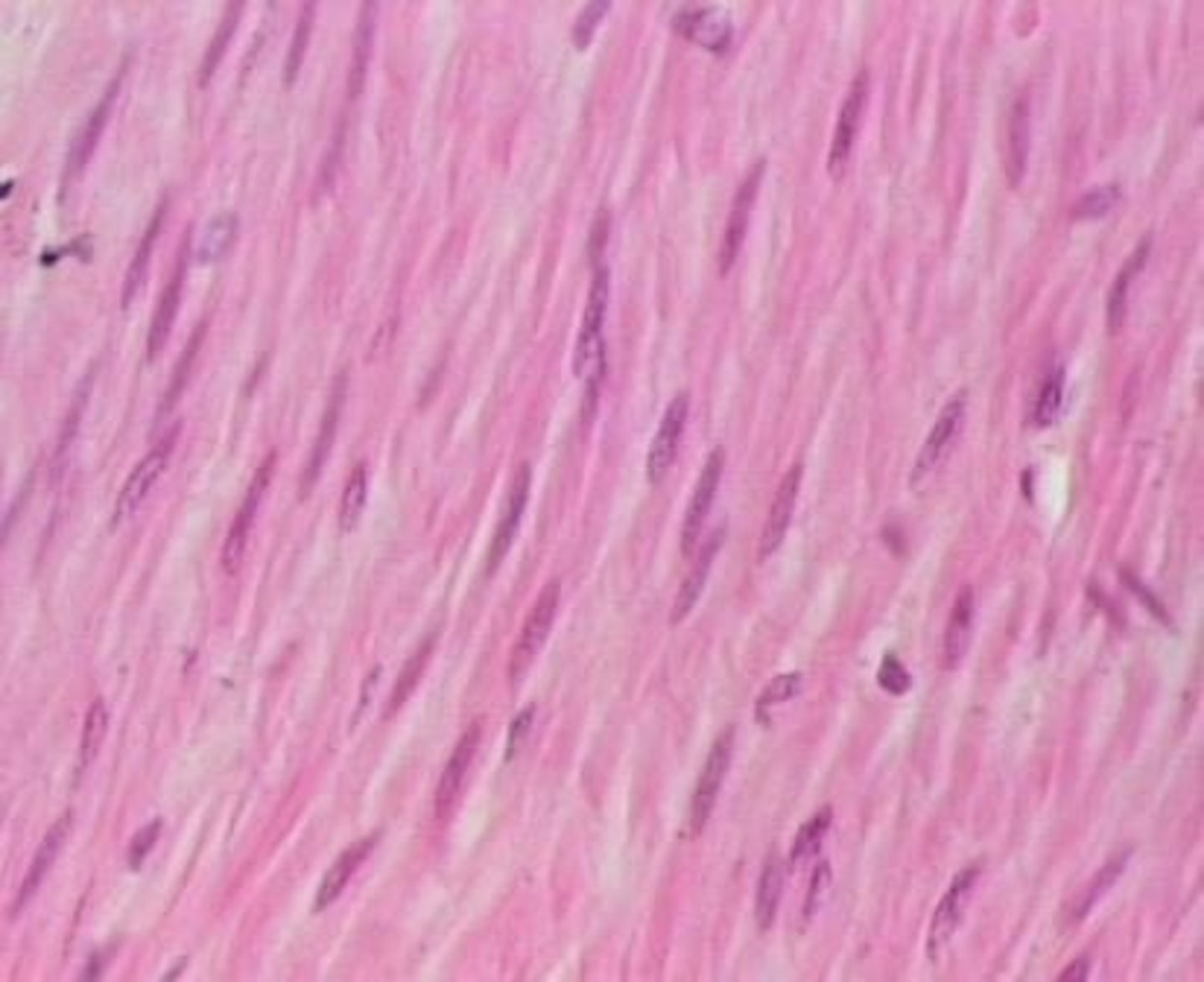
smooth muscle
Involuntary muscle found inside many internal and hollow organs of the body
-involuntary
skeletal tissue
what tissue is in this pic
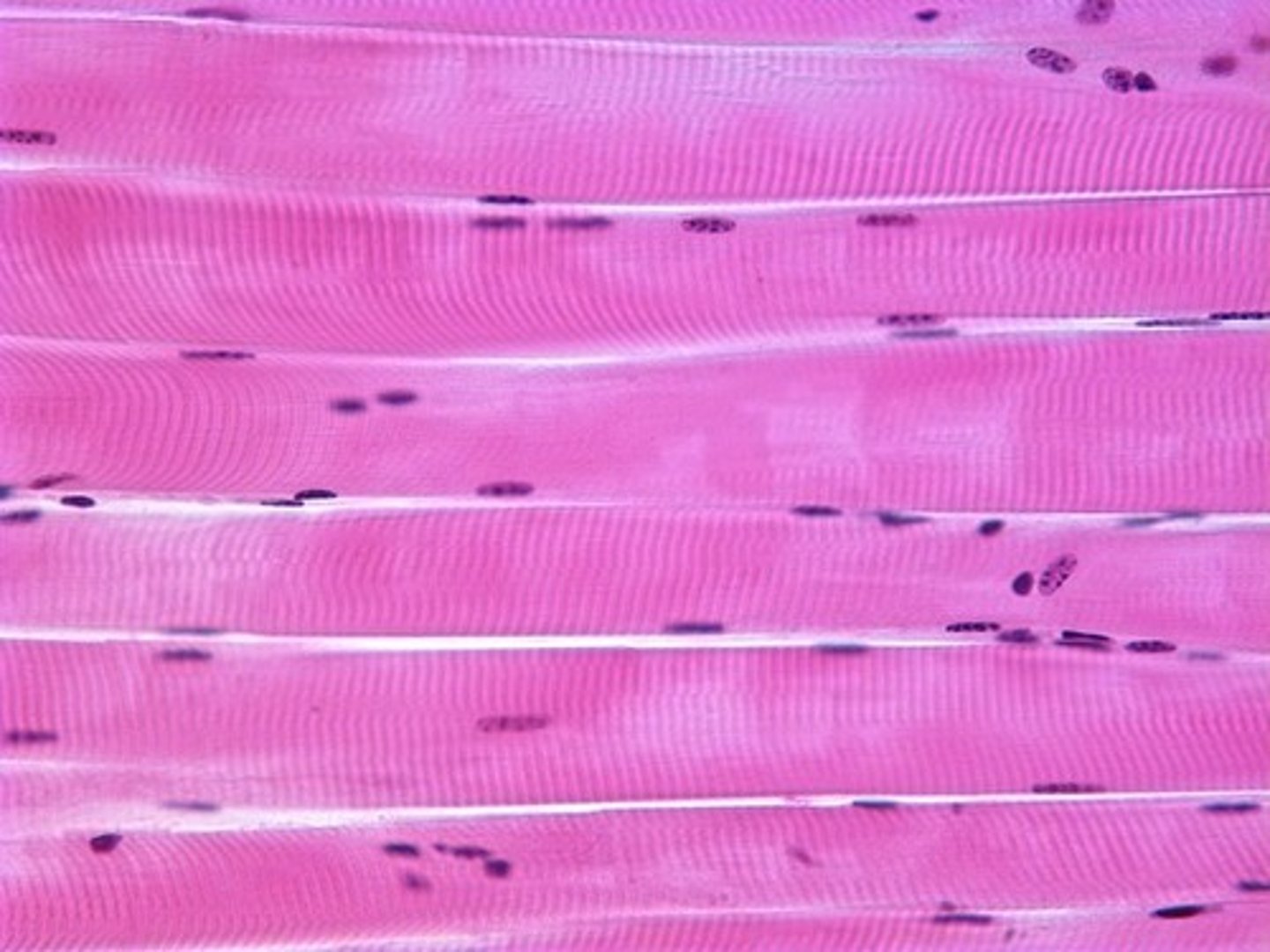
cardiac tissue
what tissue is this? *hint, look for intercalated discs*
smooth muscle tissue
what tissue is this? *hint: has a lot of nuclei and a cigar appearance (tapers at the end)*
connective tissue
identify this tissue
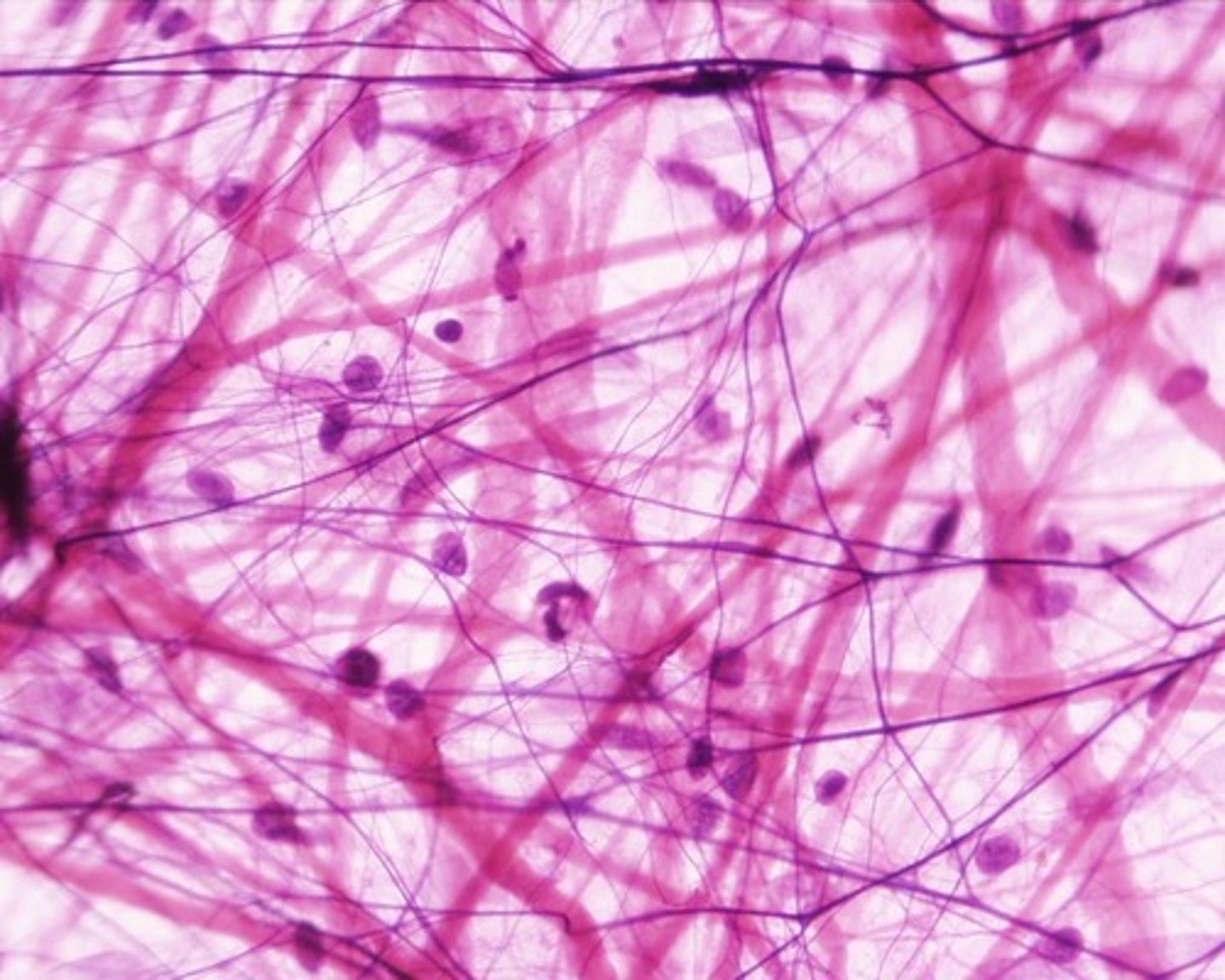
nervous tissue
identify this tissue
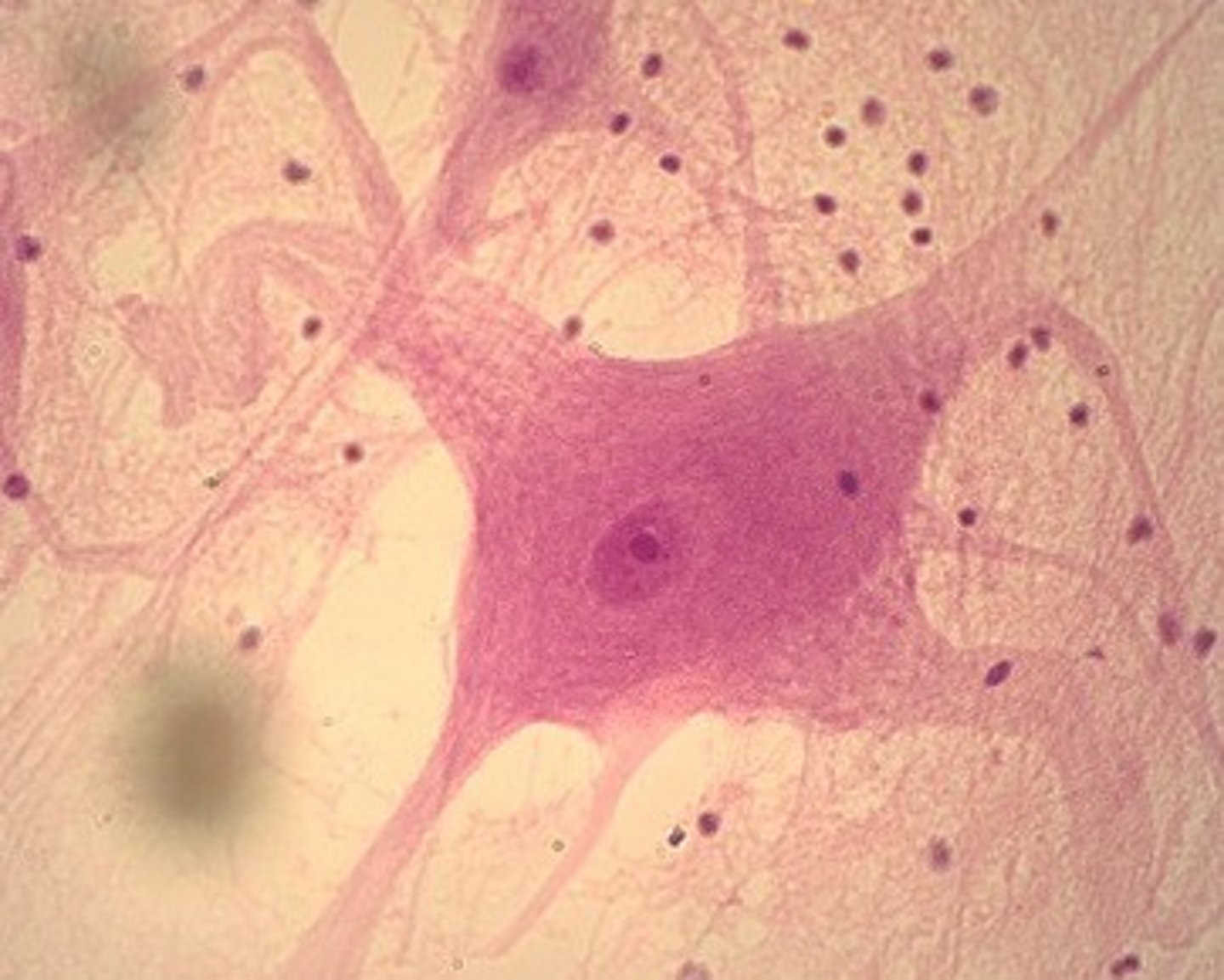
neuron and neuroglia
types of cells present in nervous tissue
skin = organ because...
consists of many tissues working together for a common function
avascular
is the epidermis vascular or avascular?
Come Lets Get Some Bluberies
mnemonic that helps to remember the epidermal layers (superficial to deep)
-corneum
-lucidum (2)
-granulosum
-spinosum
-basale
4, 5
thin skin has __ epidermal layers, thick skin has __
Dermis
-composed of dense irregular CT
-contains blood, lymphatic and nerves
-has papillary and reticular layer
epithelial
general type of tissue associated with epidermis
connective tissue
general type of tissue associated with dermis
loose connective tissue
general type of tissue associated with hypodermis
soles of feet and palms of hands
sebaceous glands are found everywhere except