Ortho Exam 2 - Lecture 13
1/22
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Ductility
During tensile test to fracture, measure of how much the material elongates permanently form initial gauge length
Percent elongation
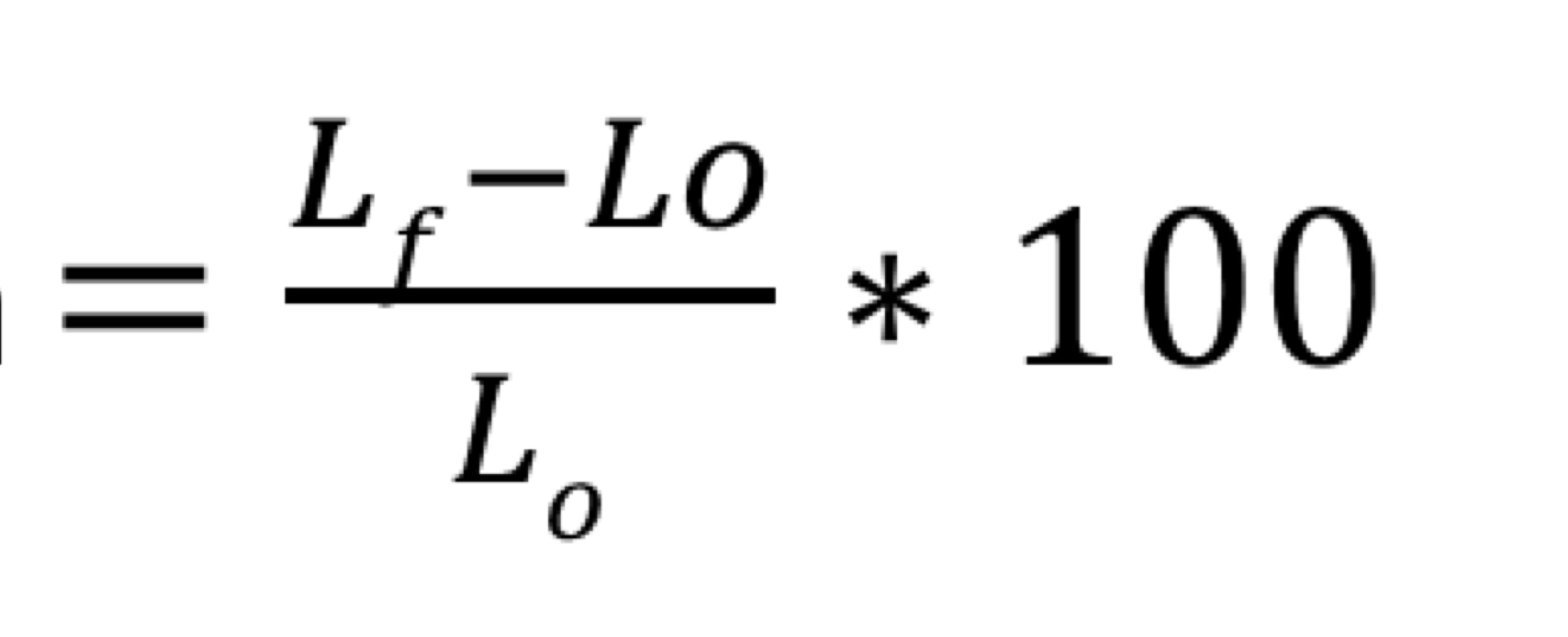
Ductile material
Will stretch and yield prior to actual fracture, causing noticeable decrease in cross sectional area of fractured region
Brittle material
Will fracture suddenly with little or no change in cross sectional area of fractured region
Ductile or brittle material more favorable for implants if they fail?
In general, more ductile fracture is desirable to give us a warning prior to fracture
What’s more common, fatigue failures or static over load? Why? Where does it occur?
Fatigue fractures due to multiple (cyclic) loading of material. Occurs at service loads at or below the maximum predicted stress levels expected during function. Always begins at flaw or crack
3 stages of fatigue fracture
Crack initiation
Crack propagation
Fracture - associated with crack growth instability
What is fatigue life drastically reduced by
The presence of flaws
(Crack initiation State is reduced or completely eliminated)
What primarily causes crack growth?
Cyclic tensile stresses
Describe Mode 1 of Basic Modes of Crack Displacement
Mode 1 - opening or tensile mode
crack surface move directly apart
Requires Mode 1 Stress Intensity Factor K(1)
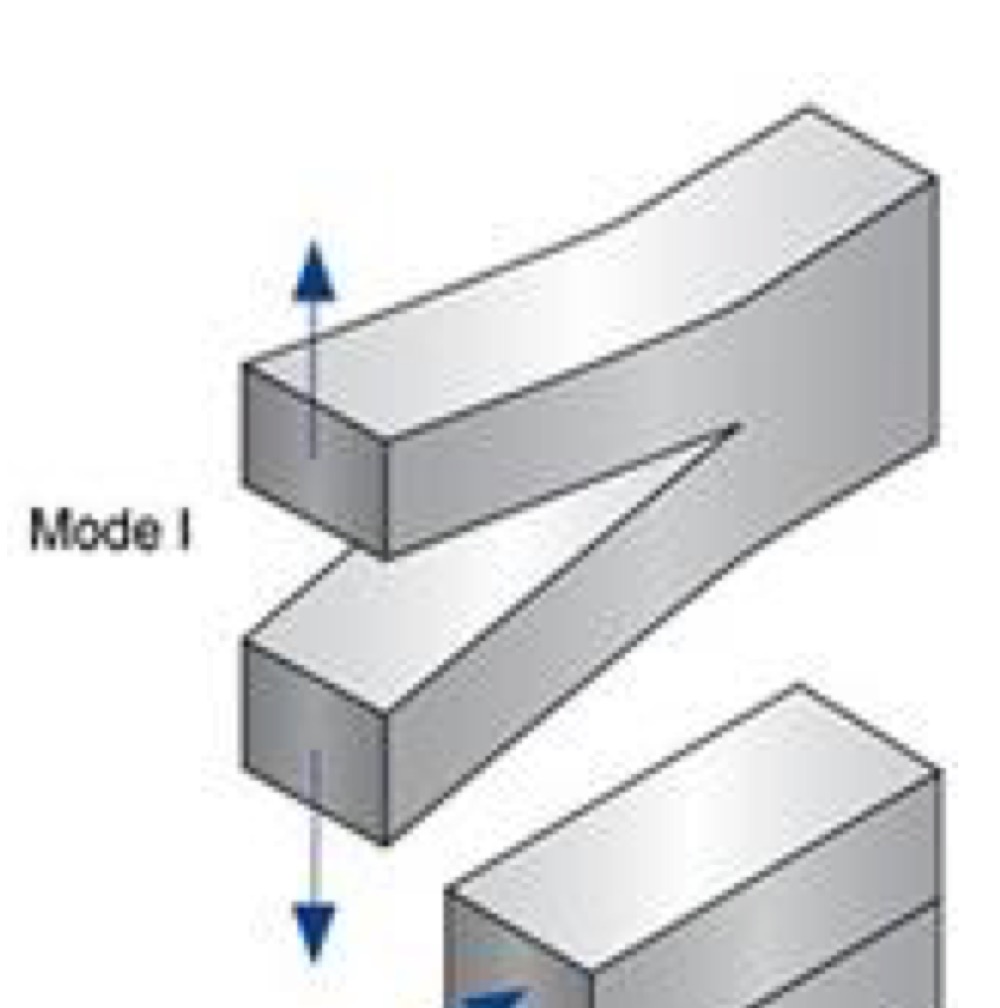
Critical stress
Stress required for crack propagation in a brittle material

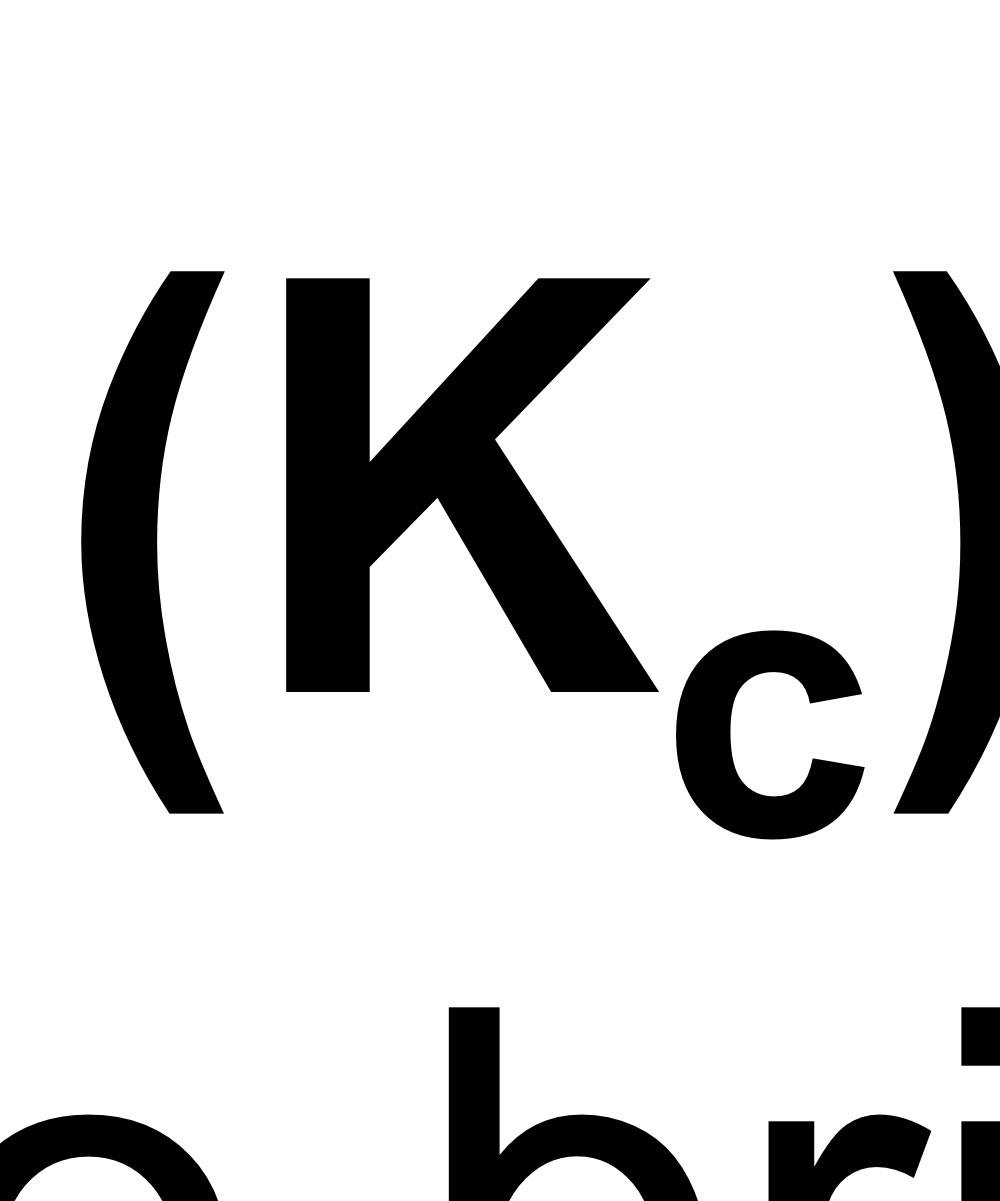
Fracture toughness
A property that is a measure of a material’s resistance to brittle fracture when a crack is present
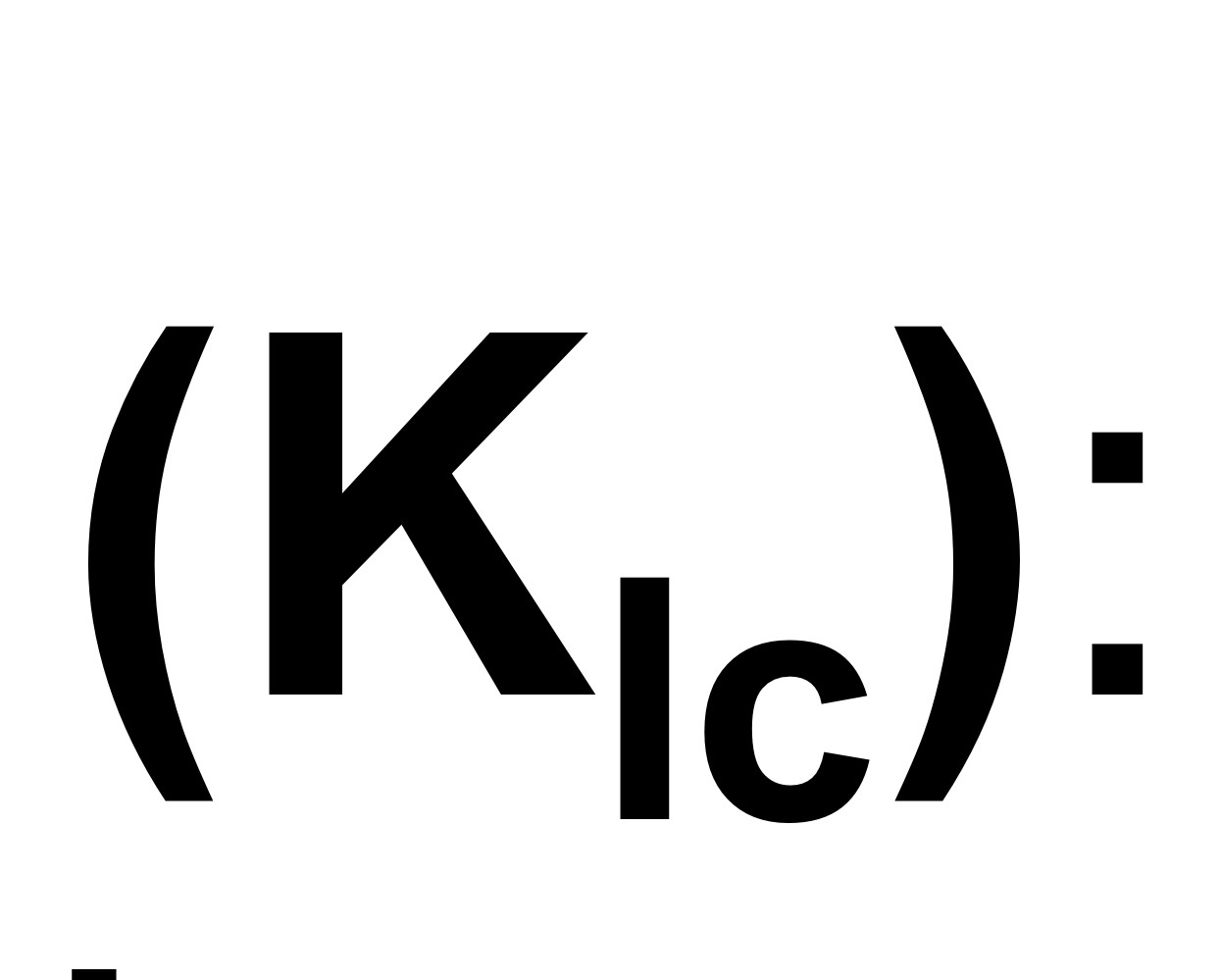
Plain strain fracture toughness
Fracture toughness under Mode 1 type crack propagation

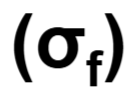
Fracture Strength
corresponds to stress, at fracture under a tensile load, that is “tensile strength”

fracture threshold
below stress. Kio corresponds to zero crack velocity. Slow of sub-critical crack growth
Total Life Approach
assumes the component is initially free of any flaws that are sufficiently sized for growth
fatigue failure due to crack nucleation and subsequent growth
majority of component life is spent in nucleation
Test Type for TLA: Stress-based test
measures conditions for failure over range of stress amplitudes and mean stresses
unnotched subject to cyclic loading, generates S-N fatigue plots, determines high cycle fatigue behavior
Design for fatigue resistance is centered on
stress-based testing
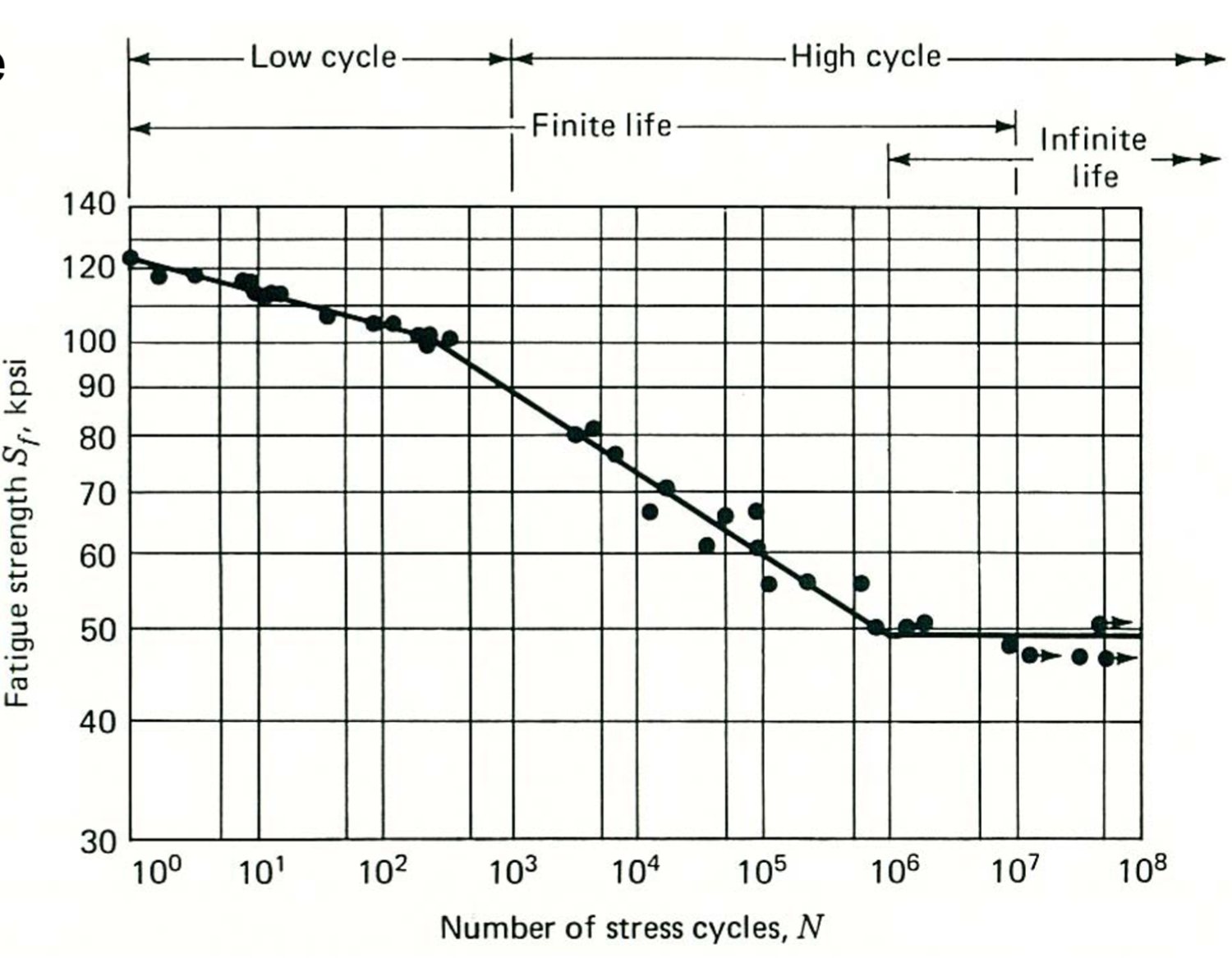
Stress Amplitude Cycle Curve
S-N curve, the relationship between applied stress and expected life, used to determine fatigue life
S = cyclic stress range
N = number of cycles to failure
Fatigue failure
failure at a point below the ultimate strength secondary to repetitive loading
Endurance Limit
maximal stress under which an object is immune to fatigue failure, regardless of number of cycles. Much lower than yield stress or ultimate tensile stress
Goodman Line
provides ability to predict life at any stress ratio
points below the relevant Goodman line represent longer life
Modified Goodman Line
endurance limit to yield stress
below the modified goodman line = safe zone