BCH Week 1 - Lec 4 - Acids and Bases
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
what type of bonds do water molecules form with one another? what are the characteristics?
water molecules form hydrogen bonds with one another
each water molecule can bond with 4 others, creating a lattice structure, and is why water is so fluid
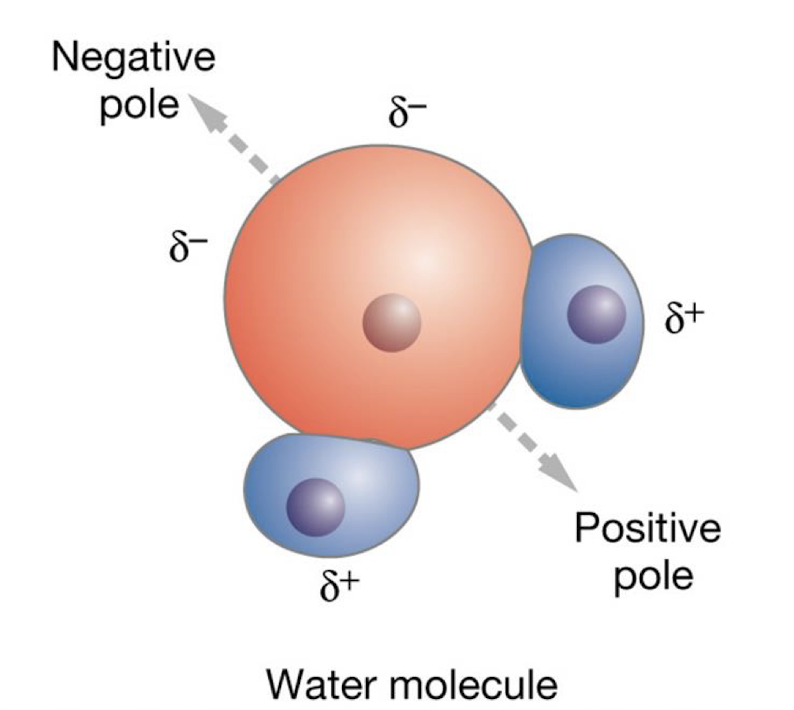
what is the chemical structure of water, and what bonds keep the atoms together?
H-O-H
held together by polar covalent bonds - excellent solvent for polar solutes
water is the main ____ in the body
water is the main solvent in the body
a solution is a solute dissolved in a solvent
solvent surrounds solute → forms a solvation shell
what is water good at dissolving? and what is solubility?
water is good at dissolving polar (hydrophilic) molecules because “like dissolves like”, and is poor with non-polar (hydrophobic)
solubility refers to the ease with which a solute dissolves
describe the dissociation of water
in very small amounts, water undergoes auto ionization and dissociates into H+ and OH-
in pure water, the concentration of H+ is 1×10^-7 M
H2O < — > OH- + H+
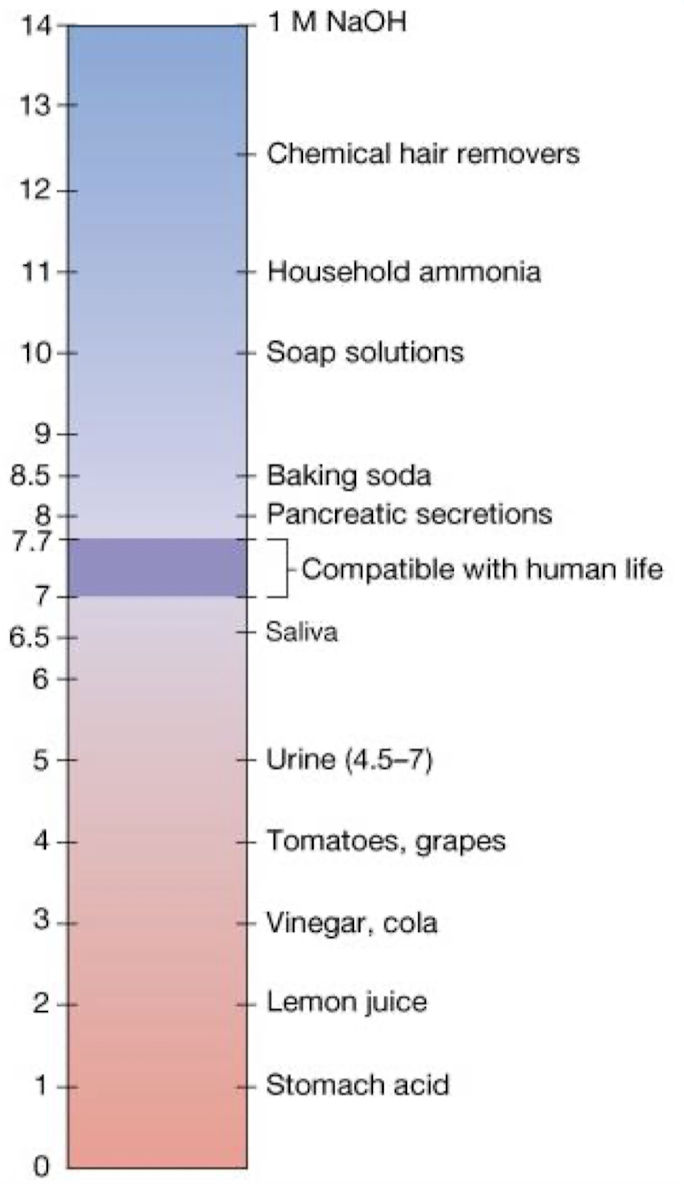
what is pH? what is the pH of water? what does it mean when the pH is less or more than the pH of water?
pH is a log scale used to measure the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution
pH = -log [H+]
pH of pure water is 7 - equal [OH-] and [H+]
every unit lower than 7 = 10 fold increase in H+ ion number
every unit greater than 7 = 10 fold decrease in H+ ion number
![<ul><li><p>pH is a log scale used to measure the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution</p><ul><li><p>pH = -log [H+]</p></li></ul></li><li><p>pH of pure water is 7 - equal [OH-] and [H+]</p><ul><li><p>every unit lower than 7 = 10 fold increase in H+ ion number</p></li><li><p>every unit greater than 7 = 10 fold decrease in H+ ion number</p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d3cd7060-2f0e-4245-8901-1fe9c2c7437b.png)
what are acids and bases?
molecules that can donate a proton are acids, and those that can accept them are bases
strong acids - how do they behave in water? what happens to the pH when when added to a solution?
strong acids ionize completely in water and donate their H⁺
i.e. HCl —> Cl- + H⁺
adding a strong acid to solution increases H⁺ concentration, causing pH to decrease
strong bases - how do they behave in water? what happens to the pH when when added to a solution?
strong bases also ionize completely in water and donate their OH⁻
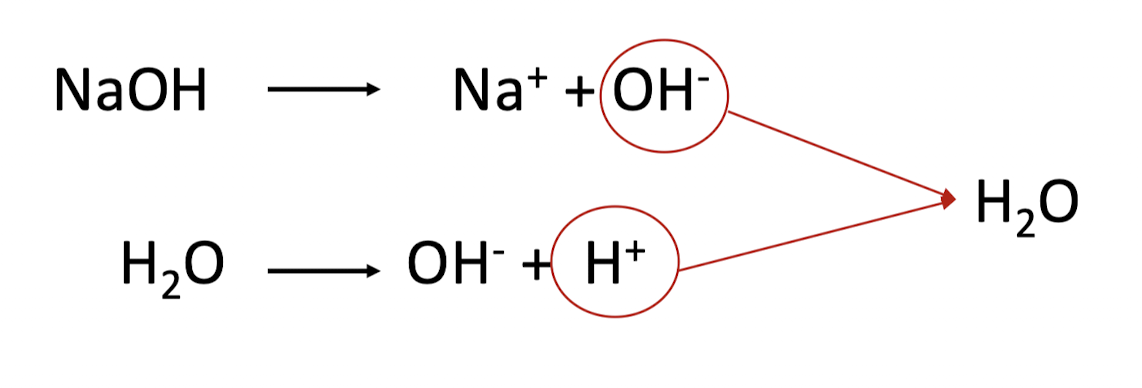
adding a strong base to solution increases OH⁻ concentration, causing pH to increase