History of Graphic Art
1/108
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Landin is unhinged, but we love him
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
Victorian Design — Dates
1820s to the 1900s
Victorian Design — What was it a response to?
Industrialization
Victorian Design — Named after…
Queen Victoria, who reined from 1838-1901
Victorian Design - Key Invention that helped it thrive
Koenig’s letterpress in 1810 and lithography
Victorian Design — Fashion of the Time
Corsets
Sexual repression
English power and prestige!
Formal, stuffy, upperclass clothing
Charles Dana Gibson
Known for “_____ Girls” sketches
Linework!
Key artist of the Victorian Design era
Victorian Design — Typography Features
Personalized type styles (lithography allowed for it)
Letterpress needed to compete — created bigger, louder typefaces
Key Type Styles of the Victorian Design Era
Fatfaces; slab serifs (1815); Clarendon (Robert Besley, 1845); ornamental tuscan/tuscan antique; 3D typefaces (like fatface); Caslon; Pearl outline; reversed Egyptian Italic (1828)
What was the first sans serif? Who popularized it? What era was it from?
Two Lines English Egyptian; Figgins; Victorian Design Era
Photography in the Victorian Era
The Camera Obscura
The Daguerrotype (1839)
Joseph Niépce
Produced the first photograph from nature
Louis Daguerre created what, when?
The Daguerrotype, a popular alternative to oil painting, in 1839
The process could run up to $1-2,000 in current money
George Eastman
Created the Kodak camera (film) in 1901
Eadweard Muybridge is known for…
The “Horse in Motion” in 1878
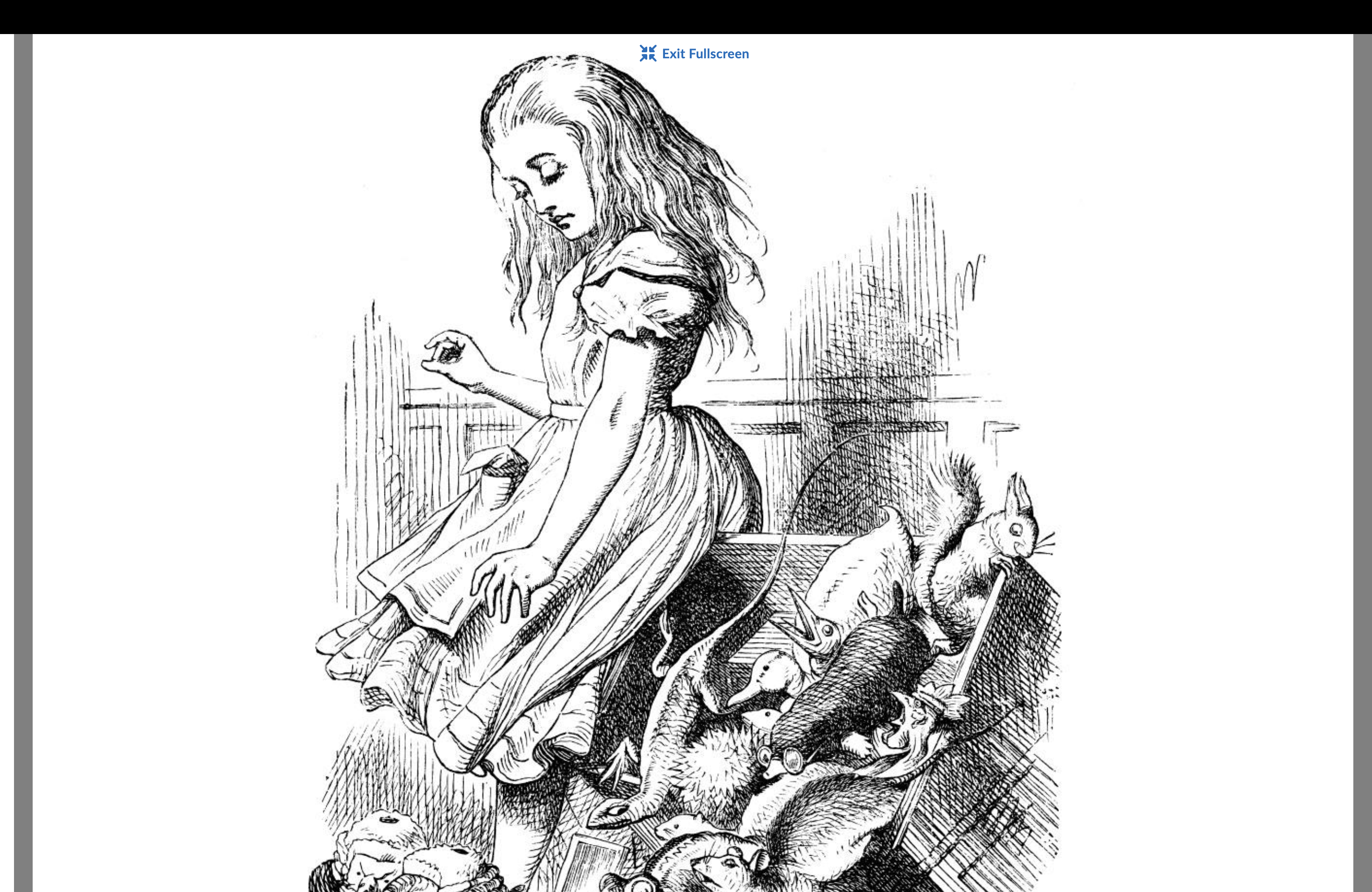
John Tenniel (1820-1914)
Illustrator in the Victorian Era
Known for Alice in Wonderland

Randolph Caldecott (1846-1886)
Illustrator in the Victorian Era
Hey Diddle Diddle (look at slides)
Beatrix Potter (1866-1943)
Illustrator in the Victorian Era
Peter Rabbit (1902)
Kate Greenaway
Illustrator in the Victorian Era
Breaks away from cluttered/ornamental look but keeps its sentiment
(Look at slides for art)

Thomas Nast (1840-1902)
American Illustrator in the Victorian Era
Political satire
High contrast
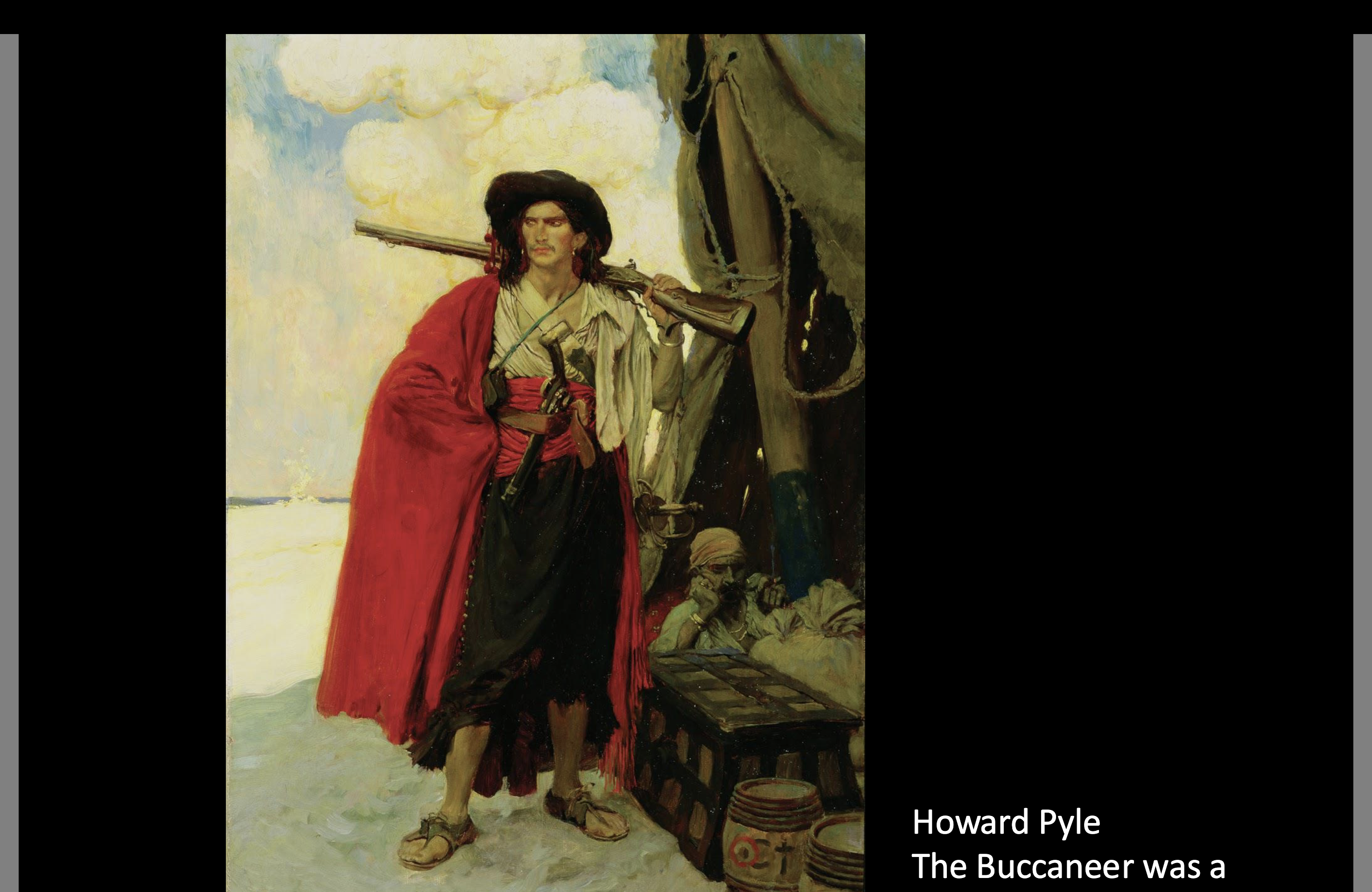
Howard Pile (1853-1911)
American Illustrator in the Victorian Era
Colliers Weekly and other publications

NC Wyeth (1882-1911)
American Illustrator in the Victorian Era
Treasure Island
Robinhood
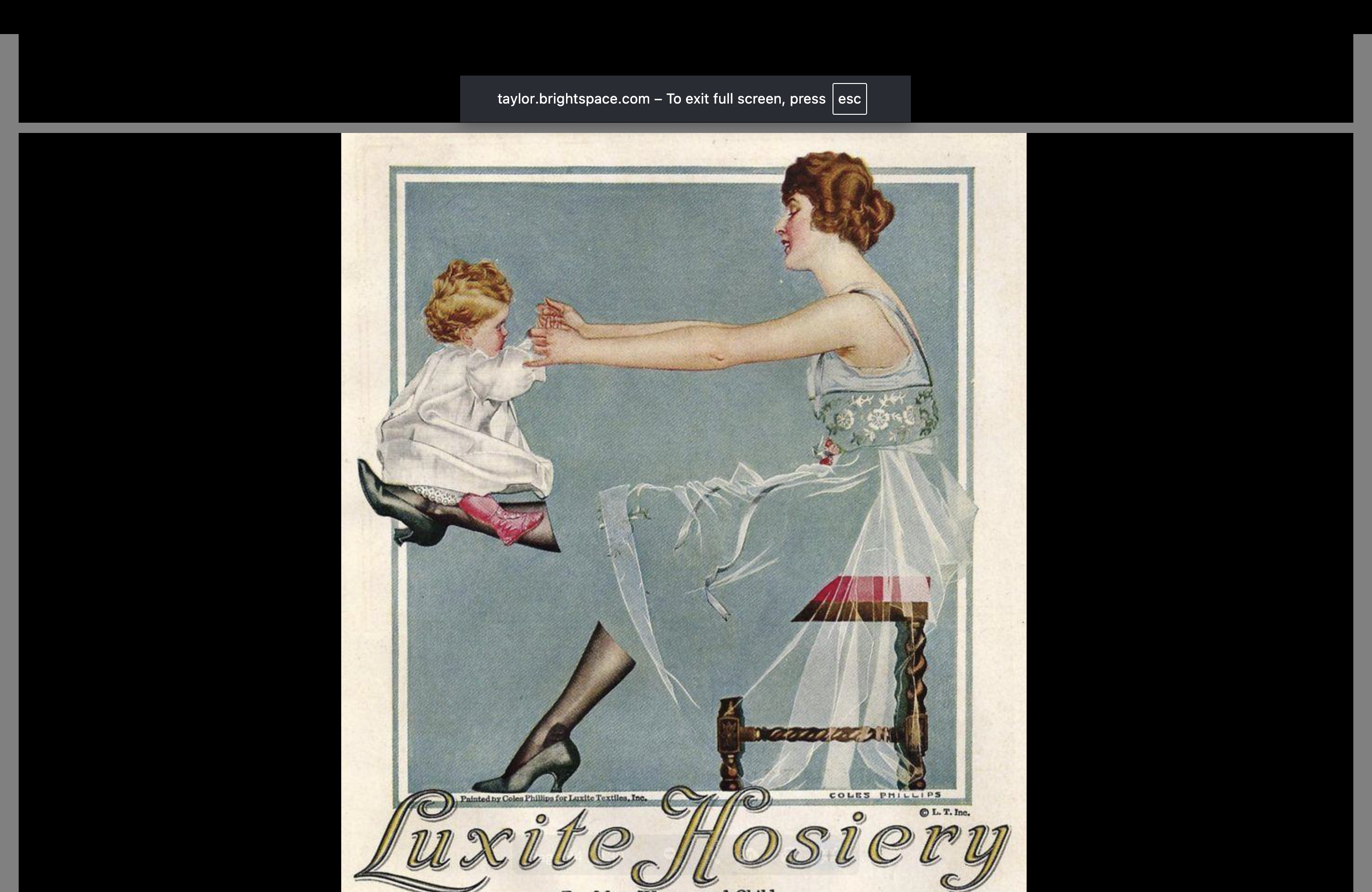
Coles Phillips
American Illustrator in the Victorian Era
Negative space usage
Posters and Cards in the Victorian Era — Key Things
Patriotism in American Victorian design
Focus on pictures over type
Chromatic lithography allowed for color
“Kitch” art
What is “Kitch” art?
Artwork created in the 19th century…cheesy, predictable, overly decorative
The Downsides of the Victorian Era
The family unit is more and more divided
Using sexual figures to sell products
Nude photography
Racism…those of African descent were portrayed in a demeaning way
Starvation in Ireland while England was prospering from their exports
Arts and Crafts Movement — Dates
1880 to 1920 (1914 in England due to WWI)
Arts and Crafts Movement — A response to…
Victorian Era art as well as a response to the industrial revolution (kids in dangerous workplaces and terrible working conditions)
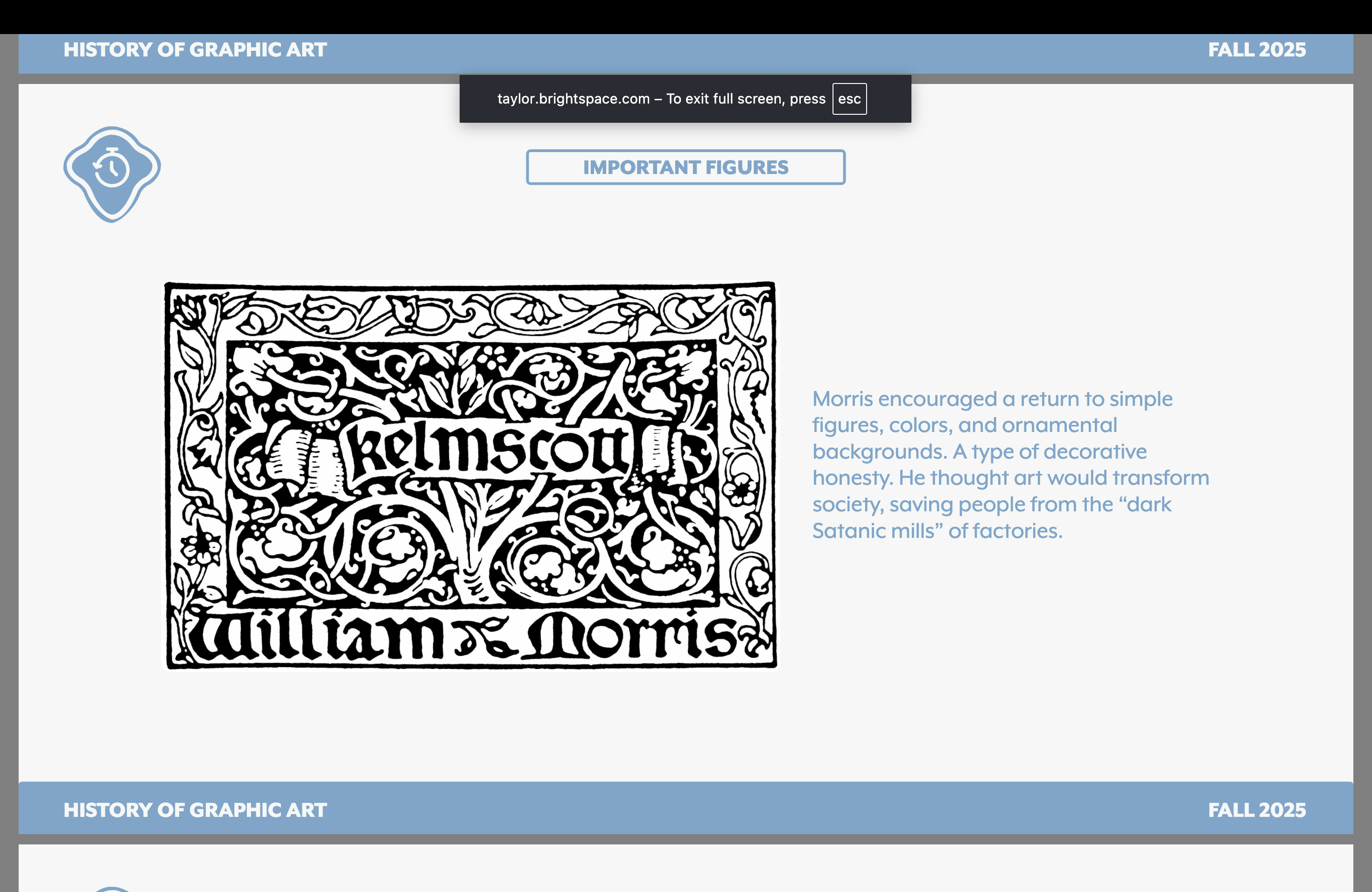
William Morris
Founder of the Arts and Crafts movement (?)
John Ruskin
…
William Morris
Planted seeds for the arts and crafts movement
Inspired by gothic forms…believed content should drive design choices. Content is key!
Believed in the total artist — a triangle of art/design/craft — and artist studios and workshops!
Known for his wallpaper designs
Arts and Crafts Movement — Key Features
Simple figures
Simple colors
Simple ornamental (nature-inspired) backgrounds
Study the differences between Victorian and Arts and Crafts art and what makes them differ from each other
…
The Arts and Crafts Movement
Stained glass windows were a big part of…what movement?
The Golden Typeface came out of…what movement?
The Arts and Crafts Movement
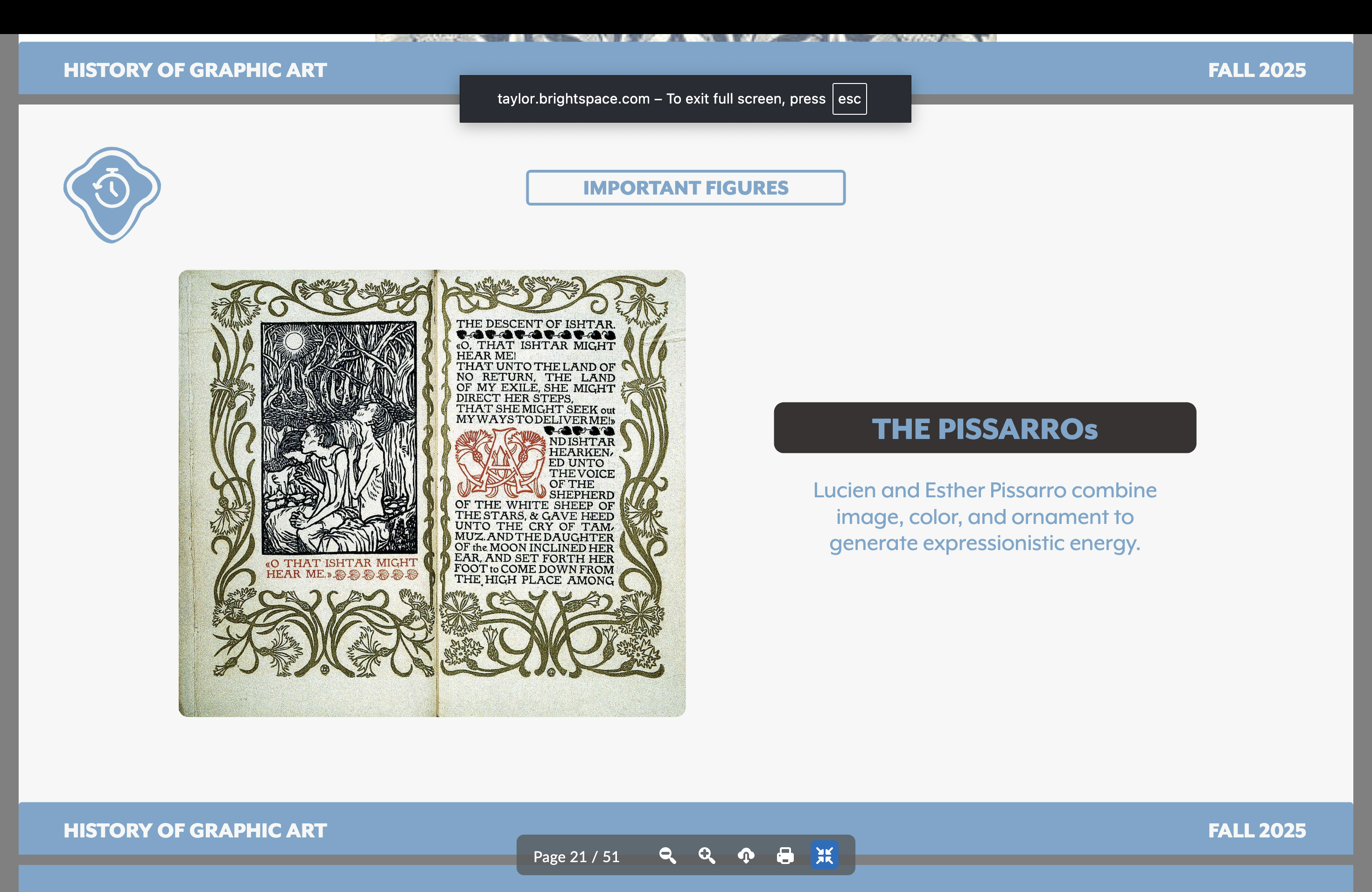
Lucien and Esther Pissarro
Artists of the Arts and Crafts Movement
Expressionistic energy!
The Pre-Raphaelites were also known as…
The Brotherhood
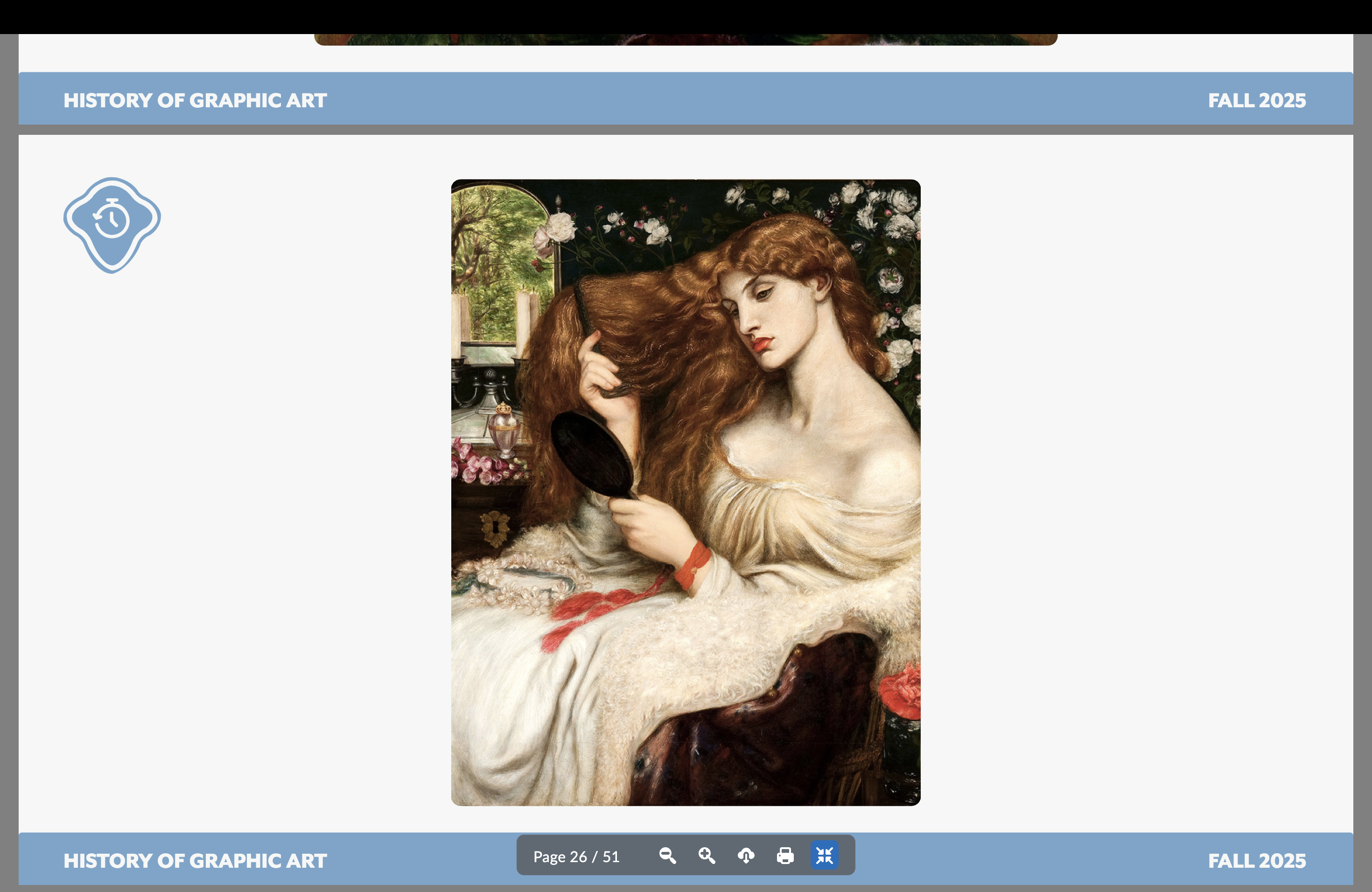
Dante Gabriel Rossetti
A member of The Brotherhood/Pre-Raphaelites
Morris’ wife was his muse and ended up having an affair w/ him
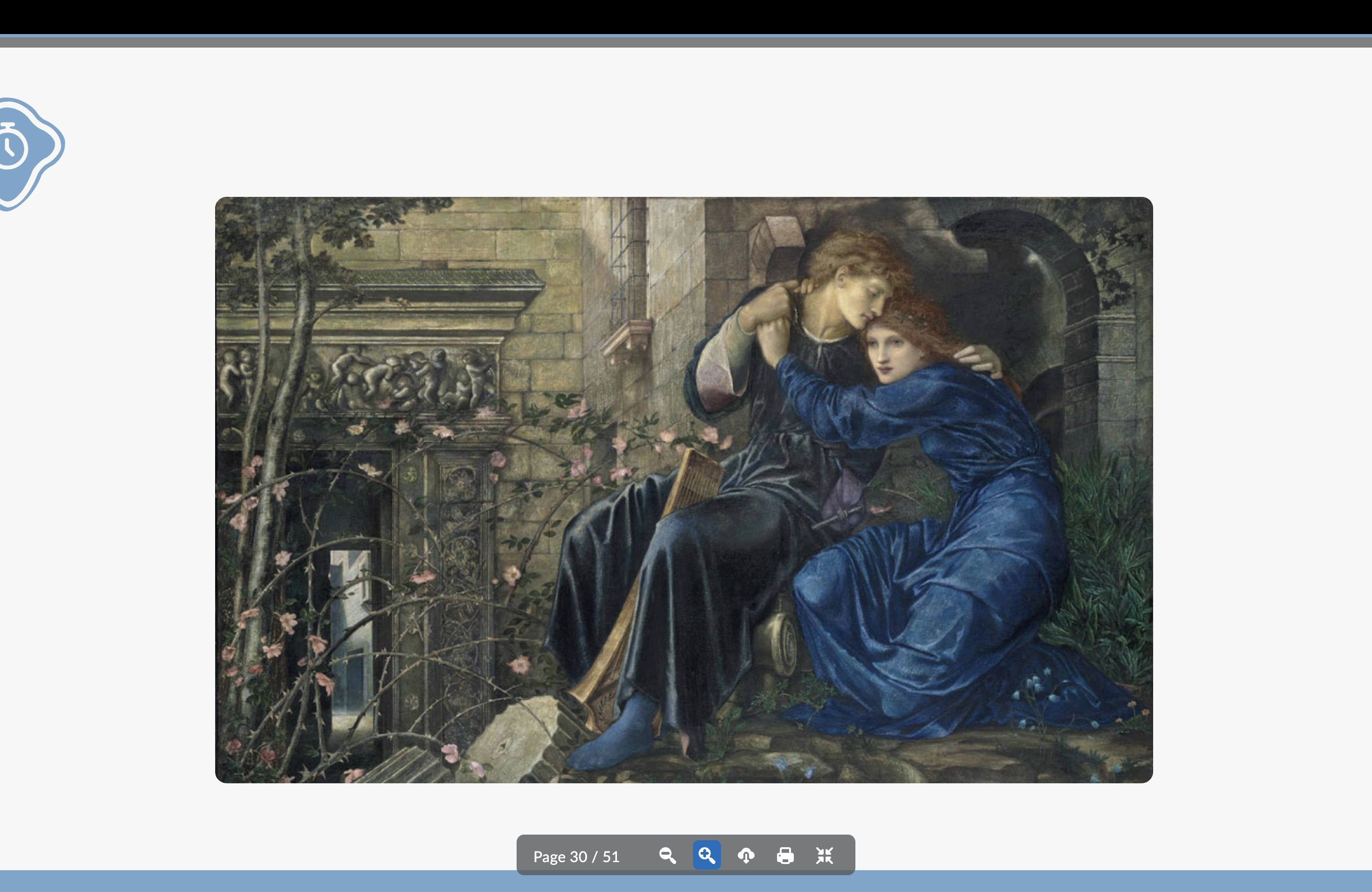
Edward Burne Jones
A member of The Brotherhood/Pre-Raphaelites
Moody, dreamlike work
John William Waterhouse
-Add from slides-
The Century Guild Hobby Horse — Key Things
Part of the British side of the Arts and Crafts Movement
A collection of work published quarterly as a journal
Medieval preoccupation of the movement
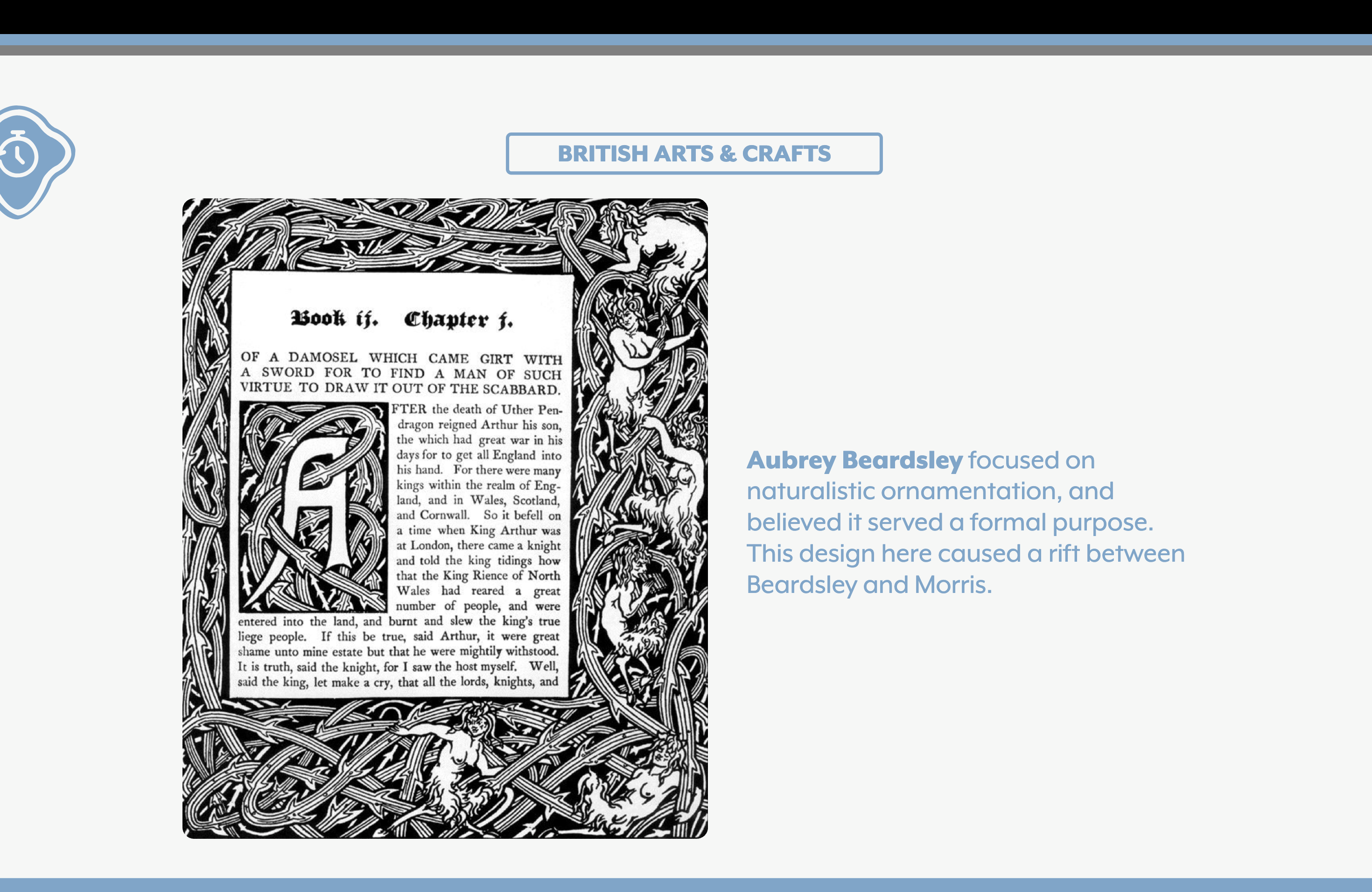
Who caused a rift in the arts and crafts movement and believed in art for pleasure, unlike Morris?
Aubrey Beardsley
What was a big deal in the British Arts and Crafts movement?
Furniture Design (look at images)
Walter Crane
Arts and Crafts Movement illustrator
The first mass-market, in-color work for kids
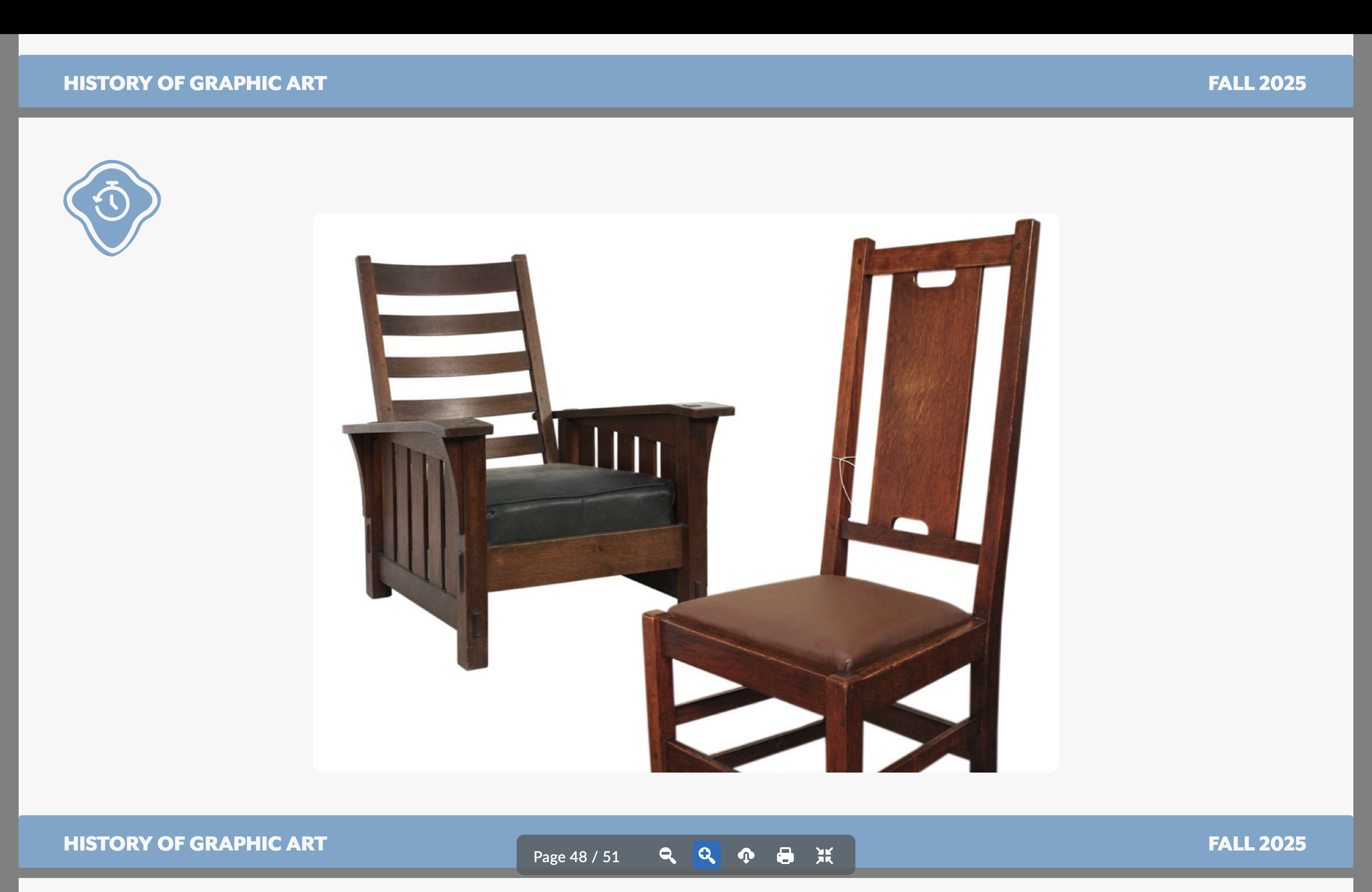
Gustav Stickley
American Arts and Crafts Movement
Focused on forms and materials that make for simplicity, individuality, and dignified work
Furniture designs! Very functional and simplistic
Structured type with some ornamentation (typical of American A&C Movement)
Art Nouveau — Dates & When/Why it Ended
1890 to 1914
Ended when WWI started
Art Nouveau — Cultural Backdrop
Industrialization
What signifies the beginning of Art Nouveau?
“Wren’s City Church” title — Henry A. Mackmurdo

Alphonse Mucha
Key Art Nouveau artist
“Art communicates a spiritual message”
Contrasts practical purpose in Arts n’ Crafts
More shading…luscious fabric, hair, framing
What inspired the Art Nouveau movement?
Ukiyo-e prints — Japanese art
French Rococco — Sensual and dreamlike
Nature/natural aspects
Symbolist movement — against realism
Celtic art — curving/organic lines
Asymmetrical layouts/type
Nouveau is the first ____ design style because of its influence on _____
complete; culture
Antony Gaudi
Art Nouveau artist
La Sagrada Familia
Architecture
Furniture
Curvilinear forms
Jules Cheret
The father of the modern poster
Art Nouveau key artist

Henri deToulouse-Lautrec (book pg. 32)
Posters — Known for usage of strong black
Art Nouveau artist
Eugene Grasset
Art Nouveau artist
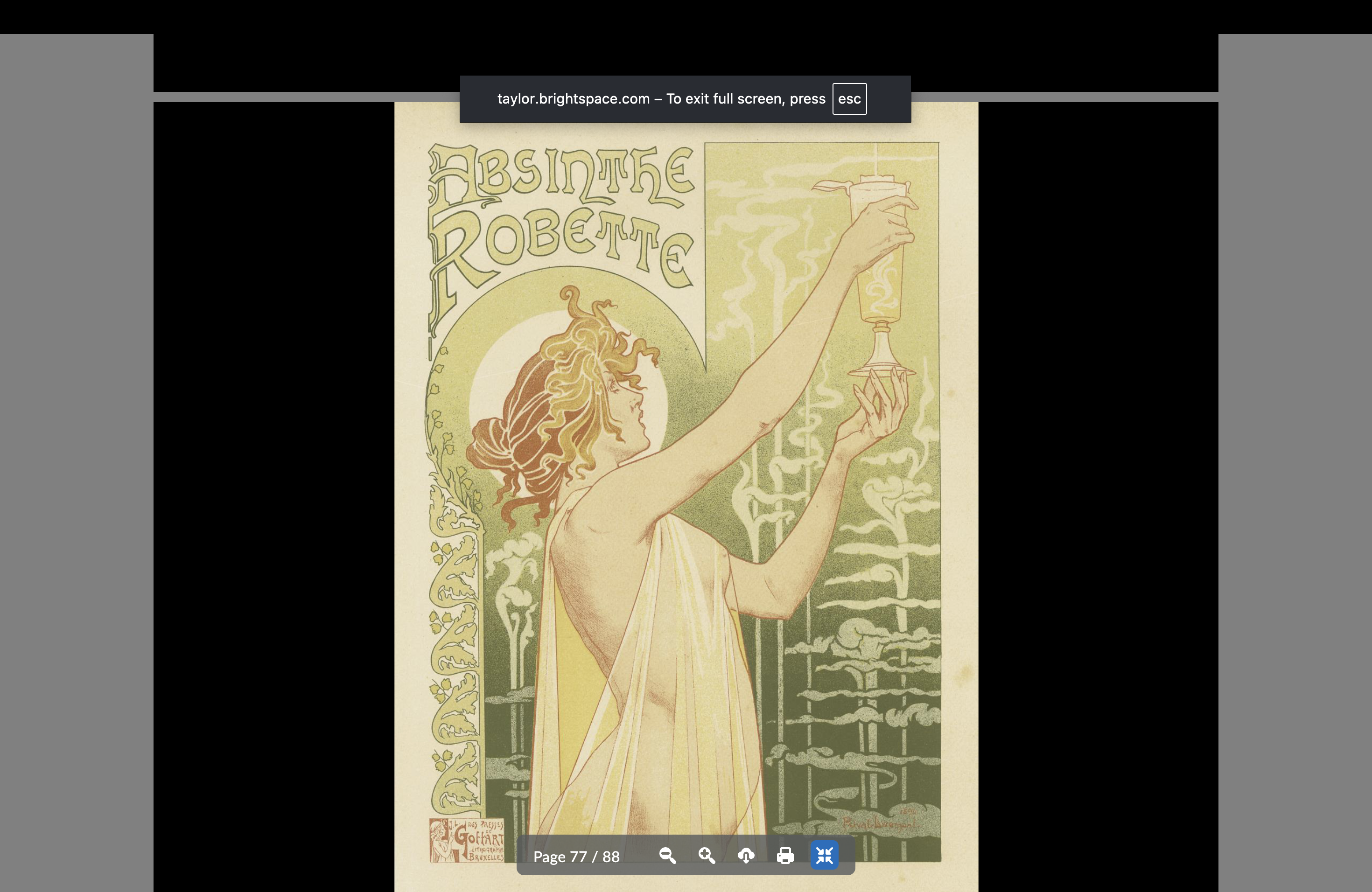
Henri Privat Livemont
Absinthe — popular drink that people blamed all their problems on
White outlines and exotic type, frames and dress
Orientalism
Key art nouveau artist
Jean de Paleologue (PAL)
More watery…no black outlining (usually)
Key art nouveau artist

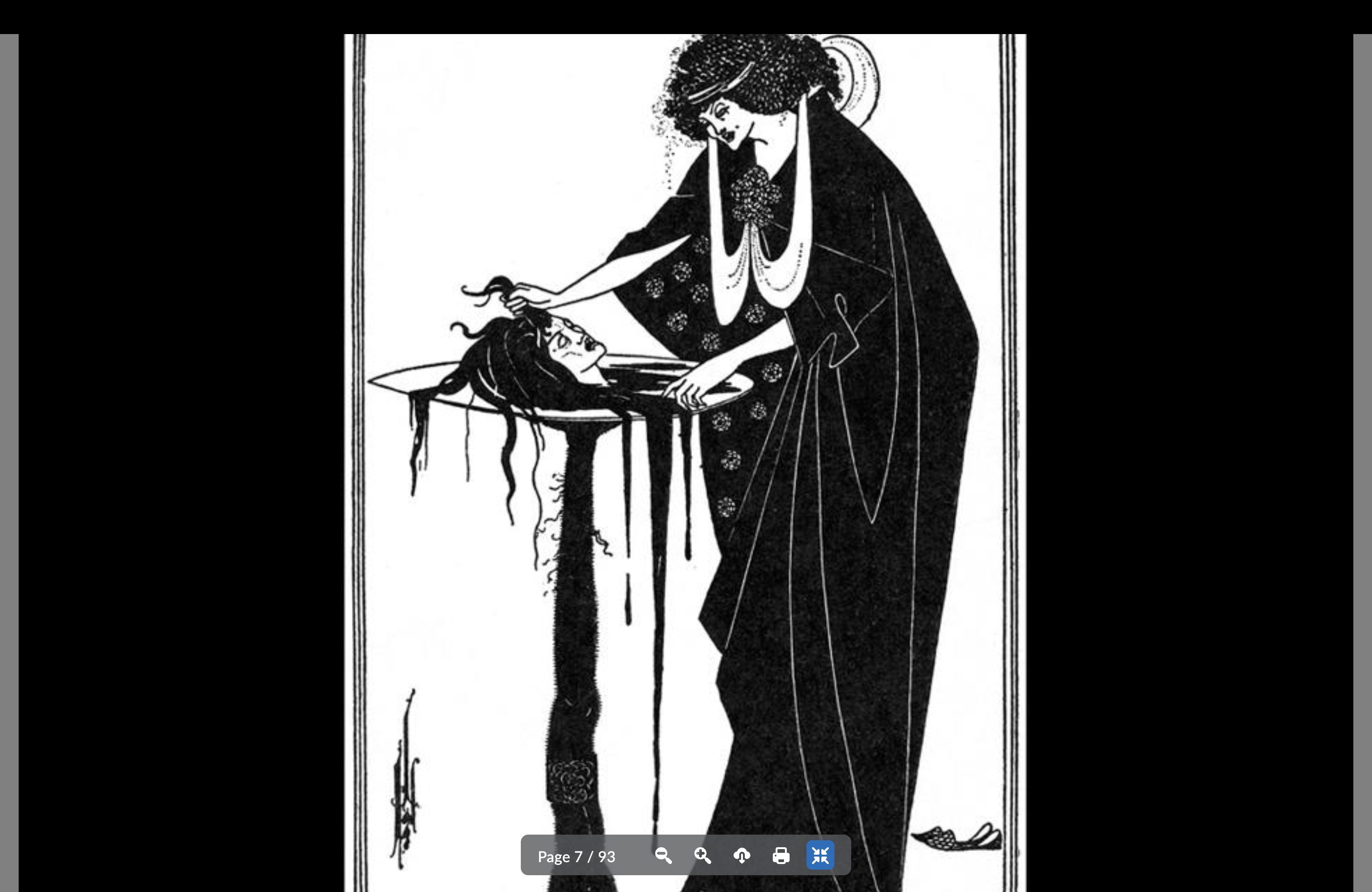
Aubrey Beardsley
Black and white style
Not a friend of the arts n’ crafts movement
More harsh/dramatic/horror
Key art nouveau artist

36 multiple choice; 22-ish identification Qs (work of art, who did it, what era is it from)
Exam Qs
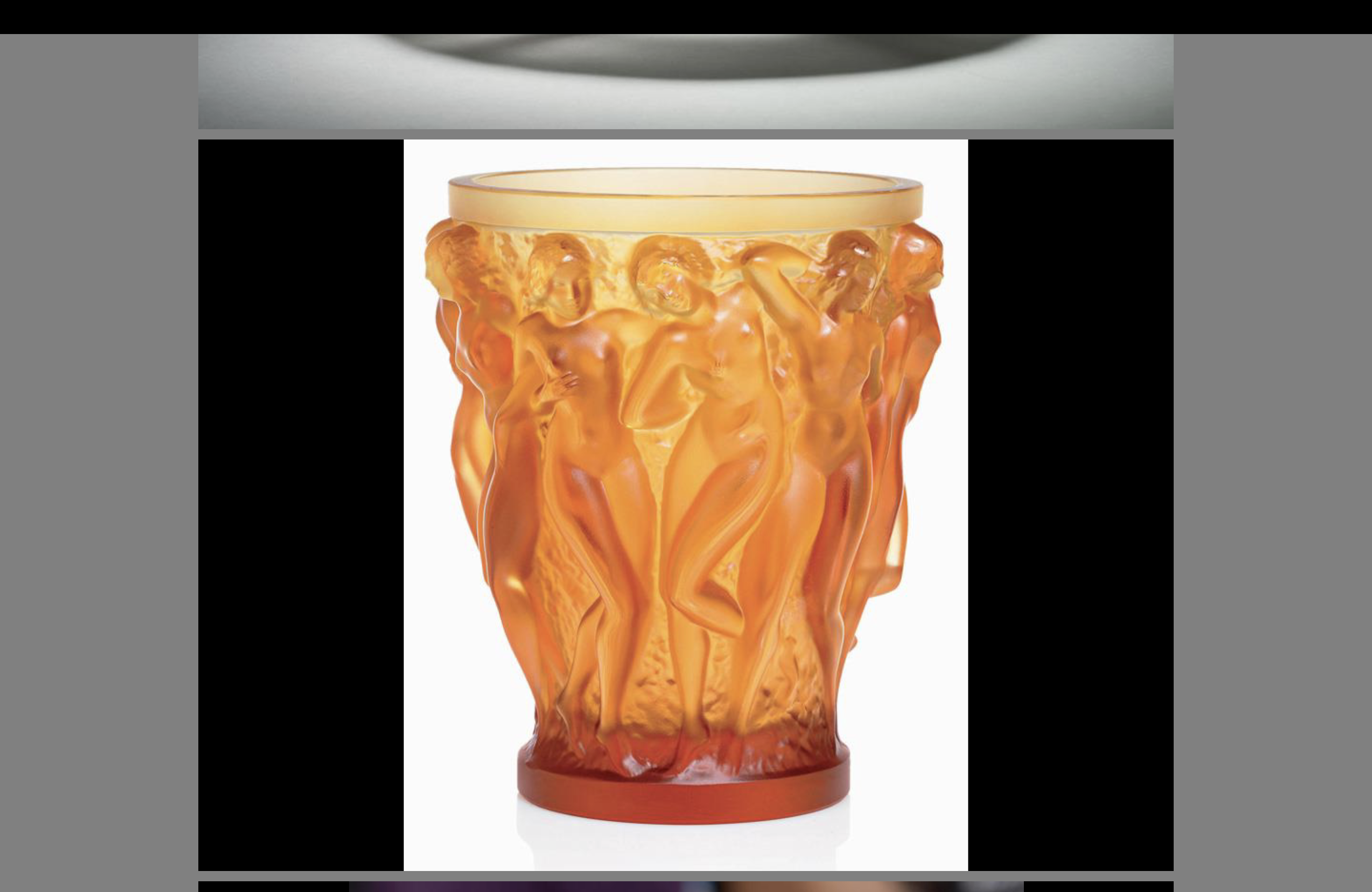
René Lalique
Jewelry/metal-working and glass-work
Art nouveau artist

Henri van de velde
Type
Celtic
Art nouveau artist

American Nouveau
More simple with flat colors
Will Bradley
Patterning/flat
American Nouveau artist

Maxfield Parish
Mythical themes
Sensualization
Neo-classical themes
American Nouveau artist

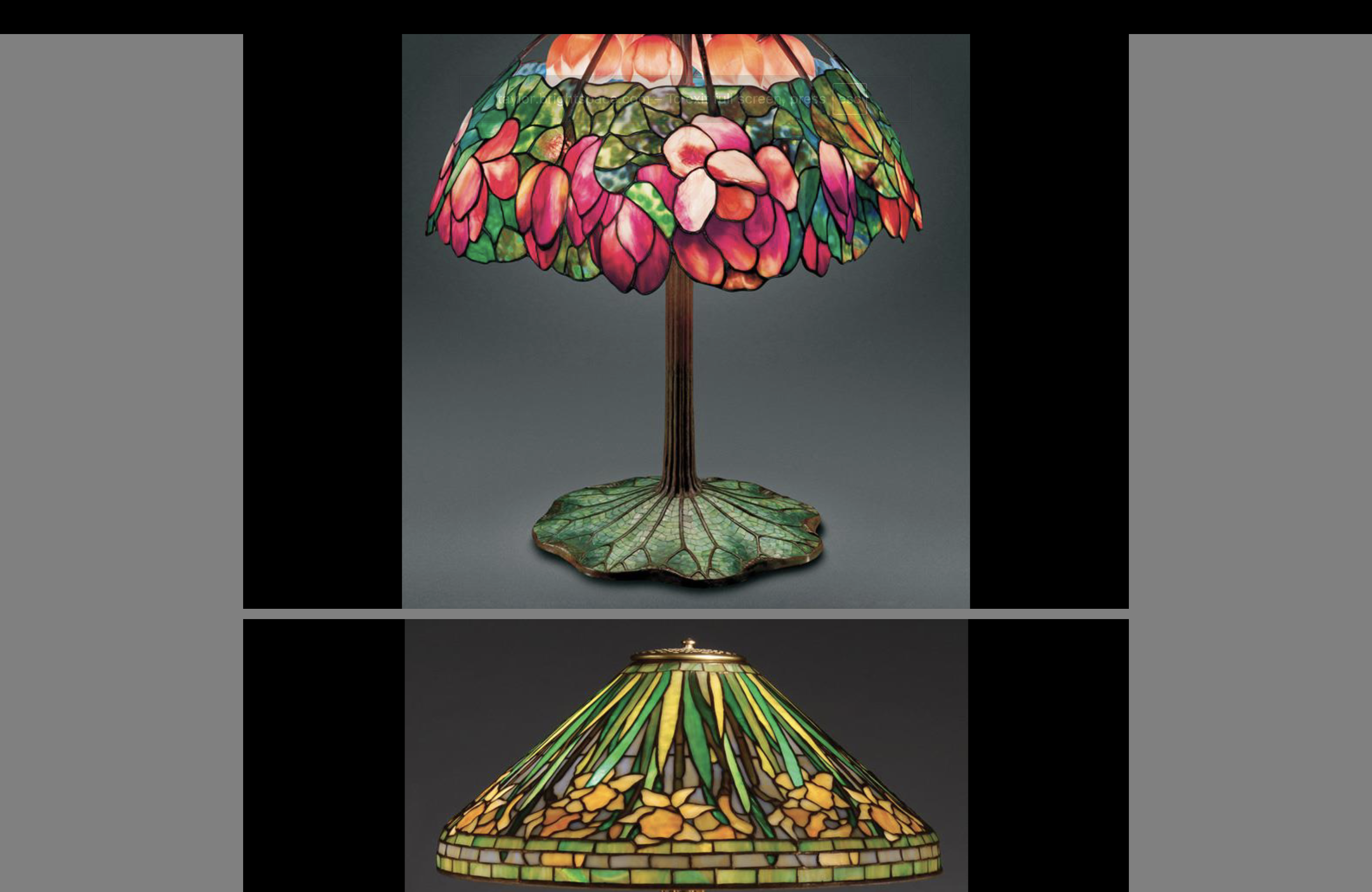
Louis Comfort Tiffany
Stained glass
American Nouveau artist

Early Modern Art movement — dates, cultural backdrop, art movements within
1900-1935
End of the Victorian Era
Plakatstil, expressionism, futurism, constructivism, suprematism, de stijl, anti-art
Plakatstil — Founder and Key
Lucian Bernhard — anti-ornamentation…the core of the design is what matters
Extreme simplicity
Bold, high-contrast, flat color palettes
Lack of ornamentation
Simplified type
Railed against Victorian opulence
The Gaiety Girl
Part of the Plakatstil movement
You can see the shift here from the previous movements

The Beggarstaff Brothers
William Nicholson and James Pryde
Part of the Plakatstil movement

Lucian Bernhard
Major player in the Plakatstil movement
Commercial work
Most evocative

Ludwig Hohlwein
Patterns
Some Nouveau
Key Plakatstil artist

Contemporary Plakatstil
iPhone 13 ads
Watches
Calvin Klein
Cartier
Expressionism
Industrialism = bad
Intense color palettes (also high contrast and B&W)
Energetic brush patterns and textures
Distorted, exaggerated forms
Not focused on representative depictions
Rejection of prominent academic technical skill
Revolt and protest!! — Influenced by WWI
Hermann Bahr
Expressionism artist
“Expressionism is a scream for the spirit”
Max Beckmann
Loud stuff!
“Weird”
Feeling and emotion…the abstract
Käthe Kollwitz (love her work)
Darker work
Black and white printmaking
Expressionism artist
Otto Dix
Dark
Death and war
Expressionism artist
Contemporary Expressionism artists
Marshall Arisman — TIME Magazine
Sue Coe — political themes; vegan propaganda
Futurism — Dates, founder, key
1909-1916
Beauty of industry!
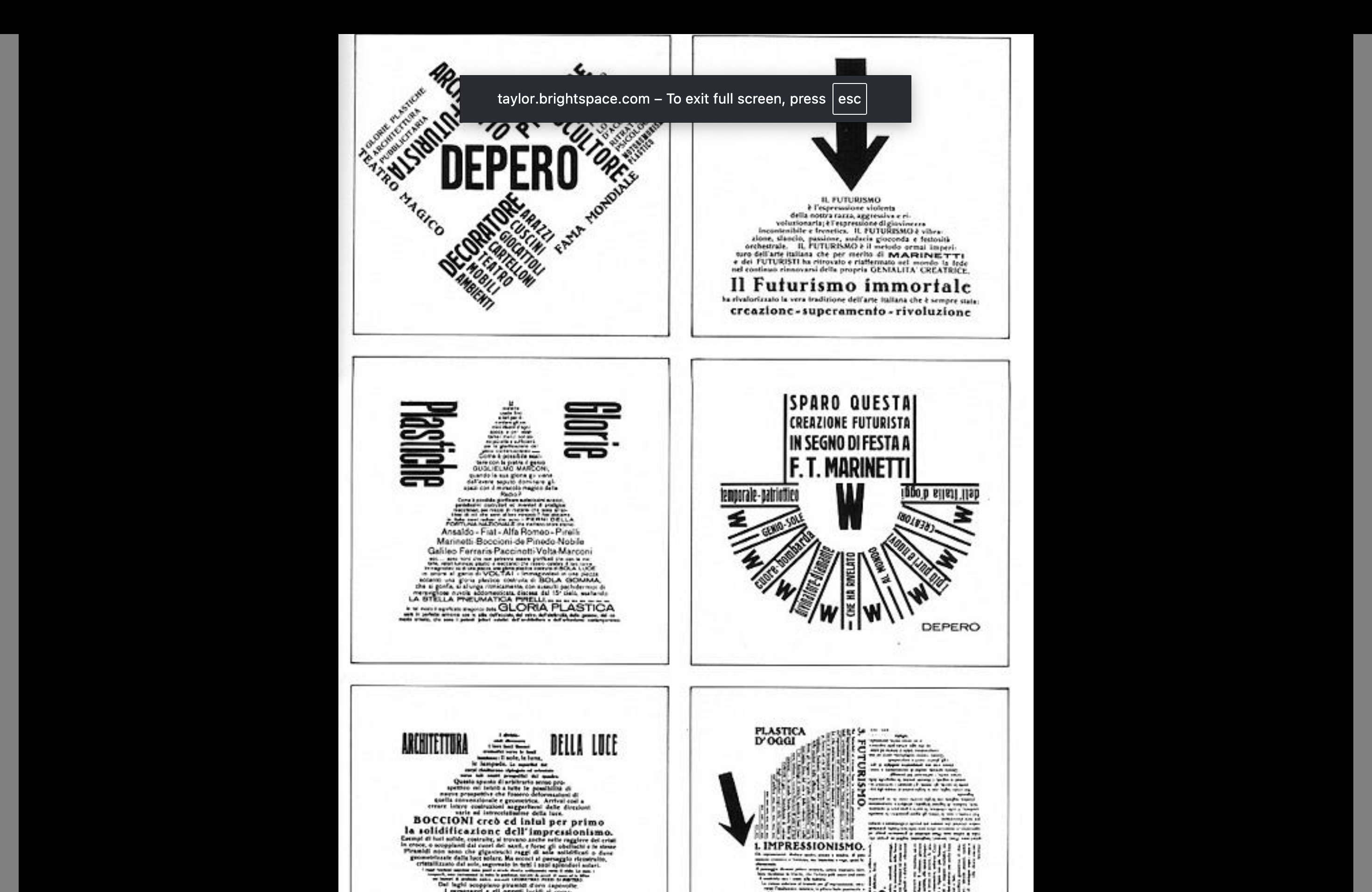
F.T. Marinetti
Speed and technology
Dynamic type — focused less on readability
Bold linework
Fractured shapes
Picasso influence — Cubiform
Italian Politics — Fascism
Machinery
Constructivism — Founder and key
Vladamir Mayakovsky, 1918
Integration and enriching life
Abstract/geometric
Bold colors
Strong type
Functionality
Rejects traditional beauty
Picasso influence — black squares by Kasimir Malevich and architecture
Embracing progress!
Lots of black, white and red
3 Principles of Constructivism
Tectonics (communist ideology w/ vizual form), texture and construction
Poster > Paintings
El Lissitzky and Rodchenko
2 Constructivism artists
El Lissitzky was also a Suprematism artist
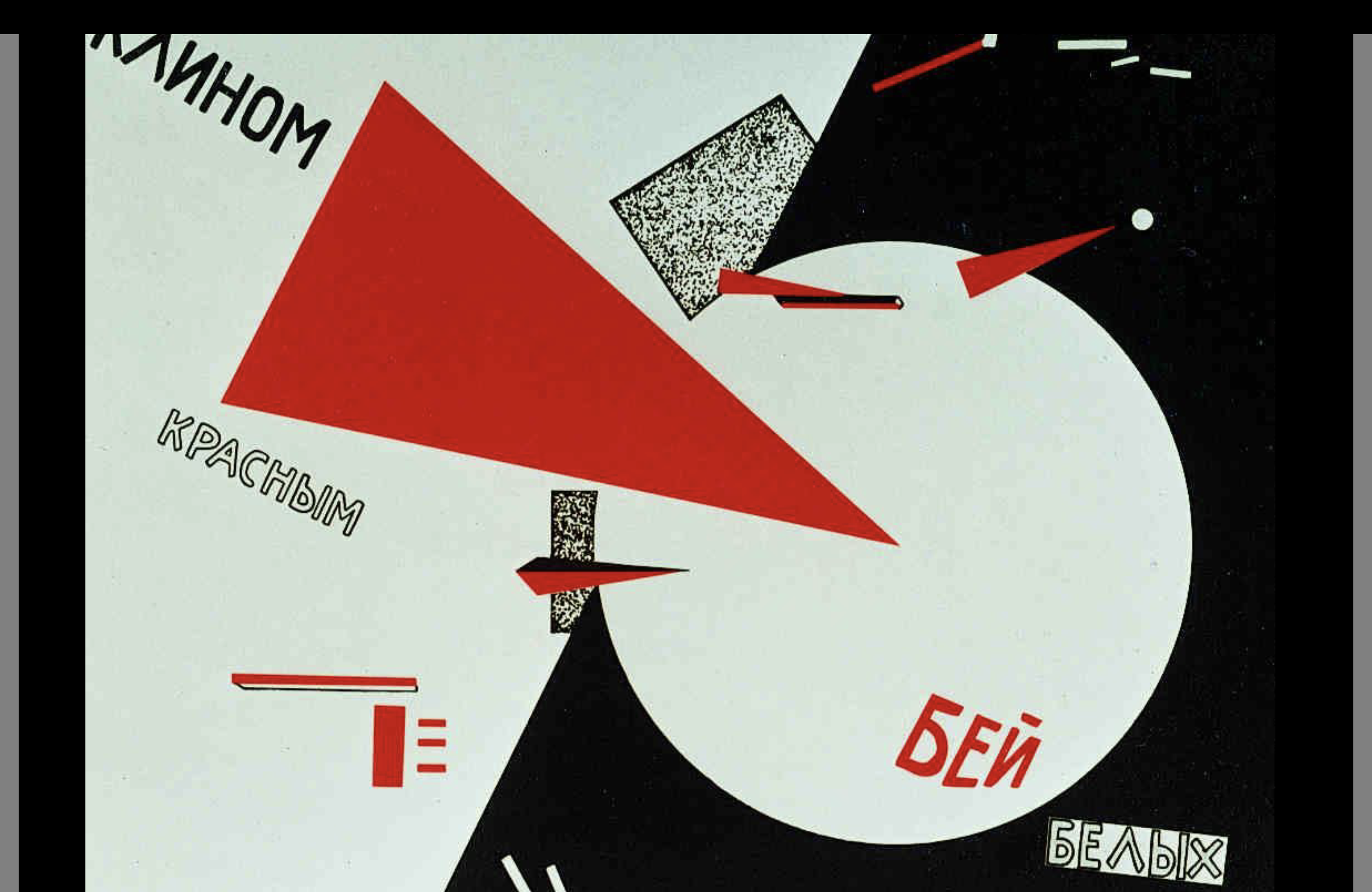
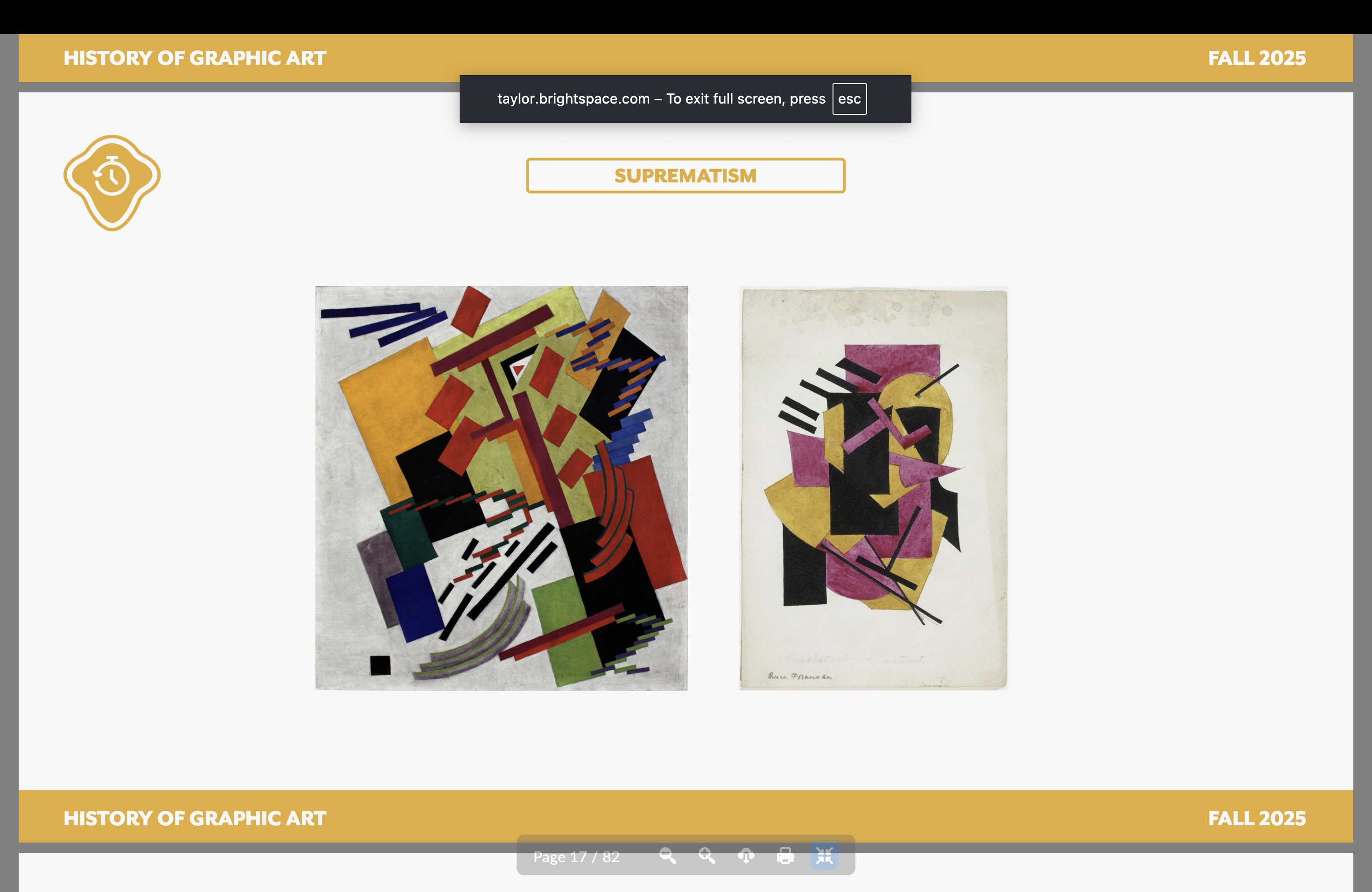
Suprematism (Russian) — Dates, key, founder
Black, white, red
All about Russian revolution (Bolsheviks led it)
Part of the Avant-Garde movement (like Constructivism)
Kazimir Malevich
Geometric abstraction
Dynamic, yet balanced
Limited color
“Pure” creation
Objective rep. was no longer relevant
Rejection of the political and religious utility of art
Kazmir Malevich
Black squares!
Suprematism & Constructivism artist
Olga Rozanova
Suprematism artist
Lyu bov Popova
Suprematism artist
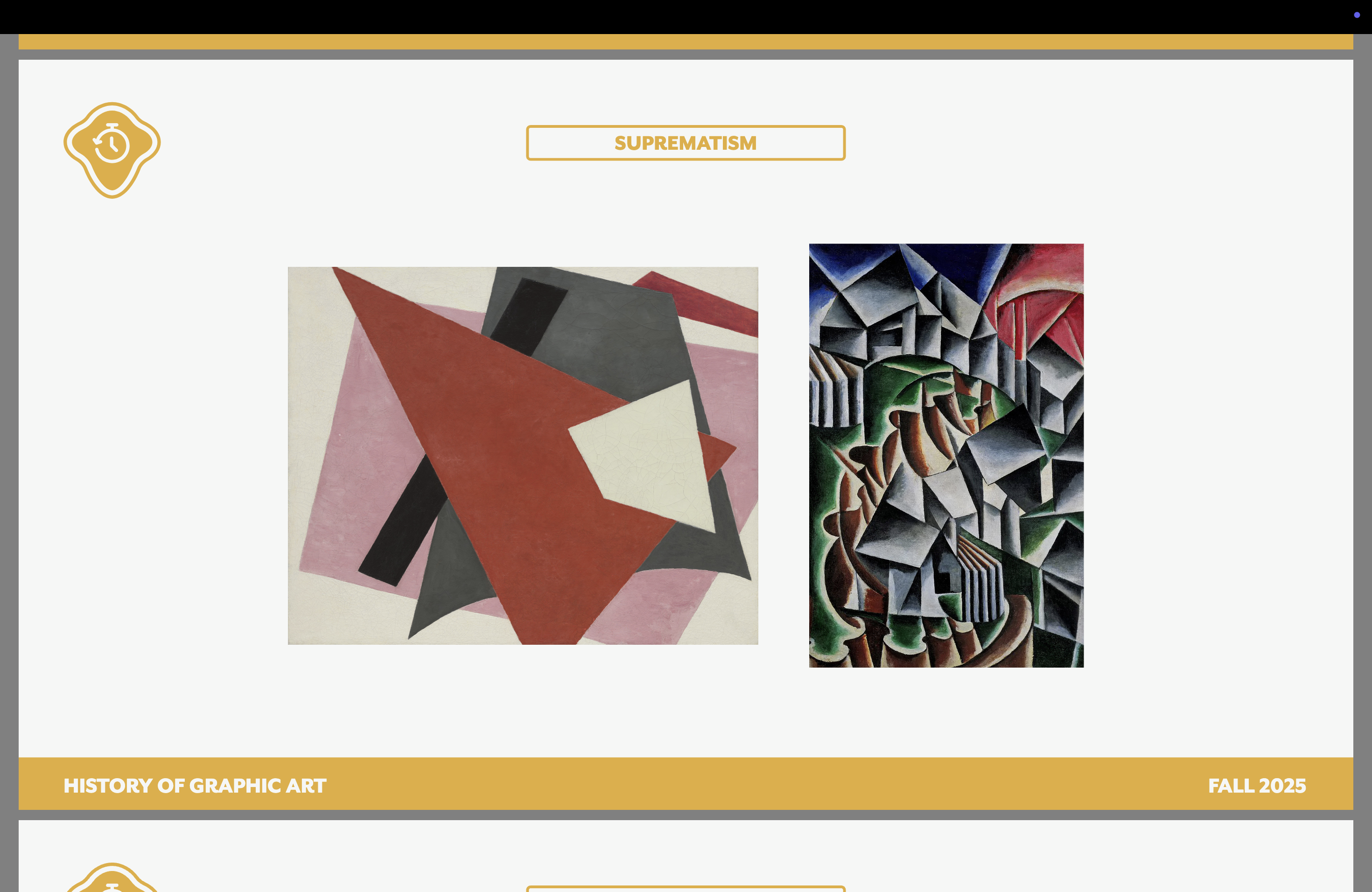
Alexander Rodchenko
Suprematism artist
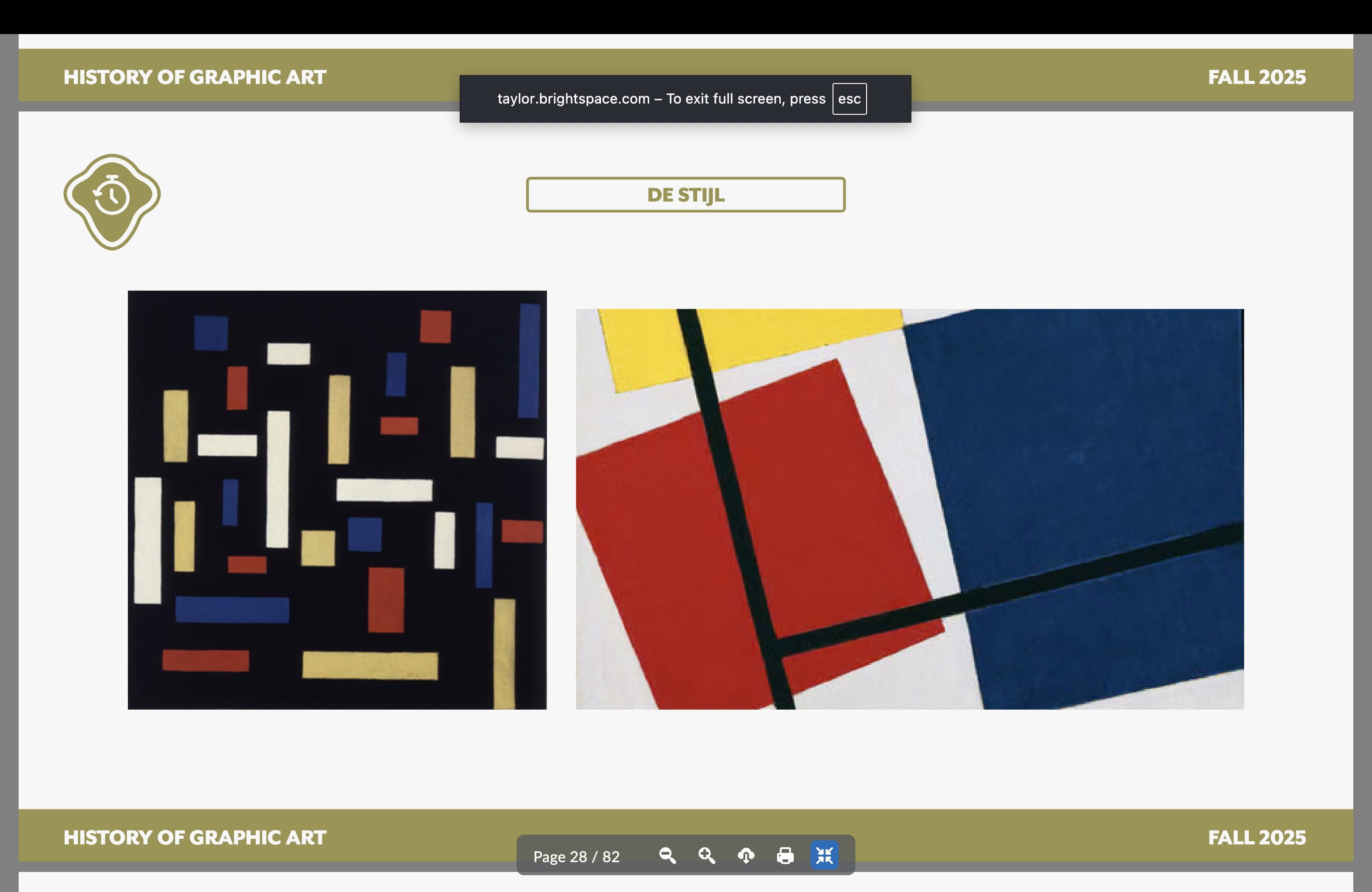
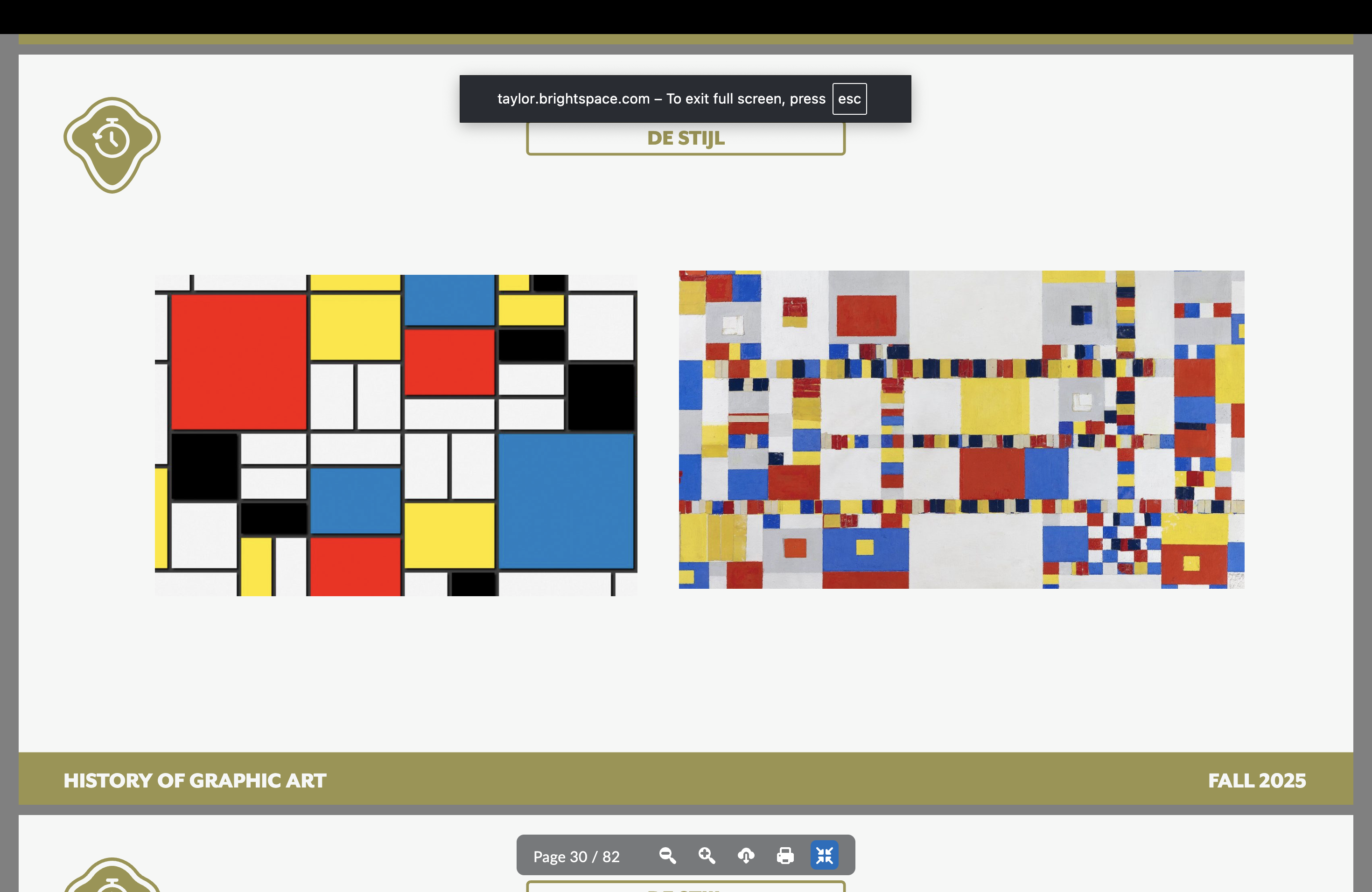
Dutch De Stijl — Dates, key, founder
1917-1931
Rejection of natural representation
Geometric
Red, yellow, blue — primaries
White and black
The new “Plastic Art”
Theo van Doesburg — founder
Theo Van Doesburg
De Stijl artist
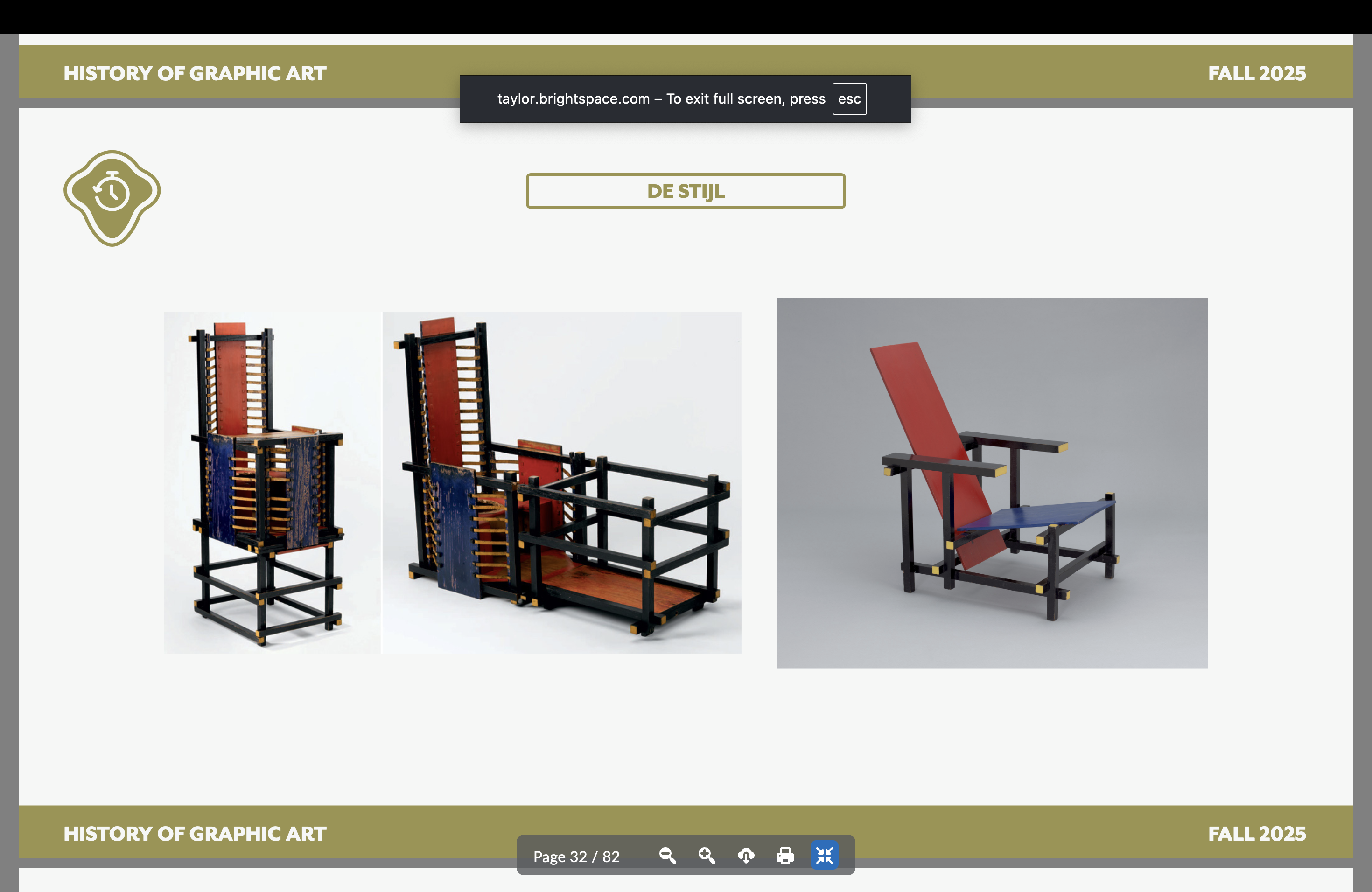
Gerrit Reitveld
De Stijl furniture designer
Piet Mondrian
De Stijl artist
Anti-Art Movement — Slogan and Creatives
“We must destroy art”
Theo van Doesburg
Piet Mondrian (had a falling out w/ Theo because Theo tilted the squares, lol)
Gerrit Rietveld — Furniture
German Bauhaus — Dates, key, cultural background, founder
1919-1933 (Early Modernism Movement)
After WWI but before WWII
Functional design and simplicity
No ornamentation
Clean lines and geometric shapes
Industrial materials
Focus on creating a unified arts and crafts approach
Bridge the gap between artists and the industrial
★ Highly influenced by constructivist movement
Germany was viewed as the villains after WWI loss
Political unrest
Economic instability
Housing shortage
Walter Gropius — Founder (1919)
“Art and the people must form an entity…[it] should be enjoyed and experienced by the broad masses.”
Weimar Kuntsgewerbeschule (school of arts & crafts) [Progressive]
Dusseldorf School of Arts and Crafts [Reform]
Progressive vs. Reform-Oriented
2 Schools Opposed to One Another in the German Bauhaus movement:
3 places/schools where German Bauhaus grew
Weimar — 1919-1925
Founded with anti-academic, progressive, and modernist mindsets. The far-right (Nazi) ideology pushed Bauhaus out of this initial location
Dessau — 1925-1932
The prominent location most think of when they think of Bauhaus, the school lasted here until forced out by Nazi ideology again
Berlin — 1932-1933
The final location for the school; was done in an attempt to have a more private setting, but teaching became impossible due to Nazi collaborators
Hitler’s view of Bauhaus
Hitler:
“It is not the missions of art to wallow in filth for filth’s sake”
Viewed modern art as deformed and hideous
He was a good landscape painter, but he didn’t get into art school because he wasn’t seen as being creative enough (due to the modern art surge).
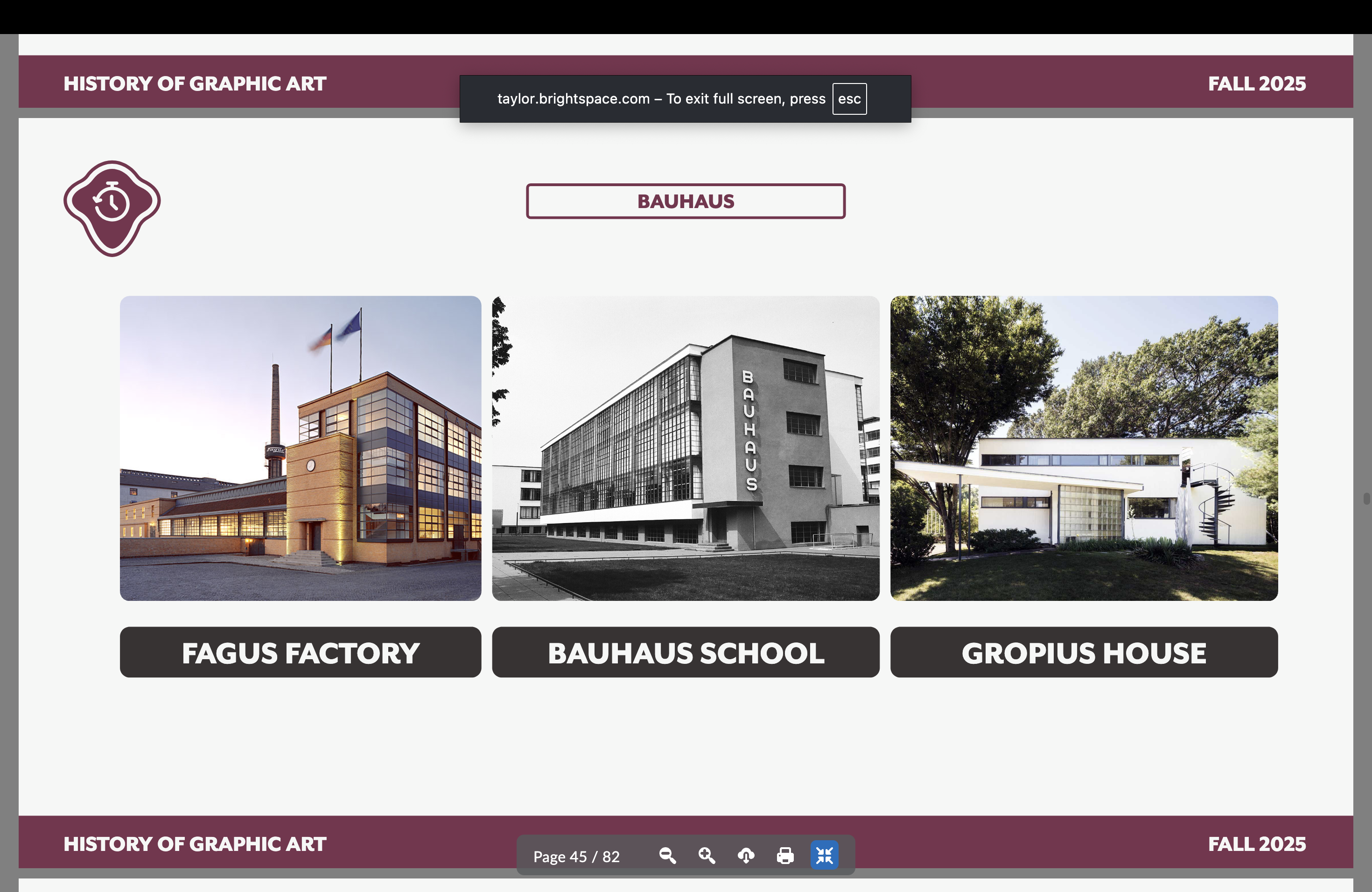
Walter Gropius —1883-1969
Founder of Bauhaus
Key buildings he designed — Fagus Factory, Bauhaus School, Gropius House
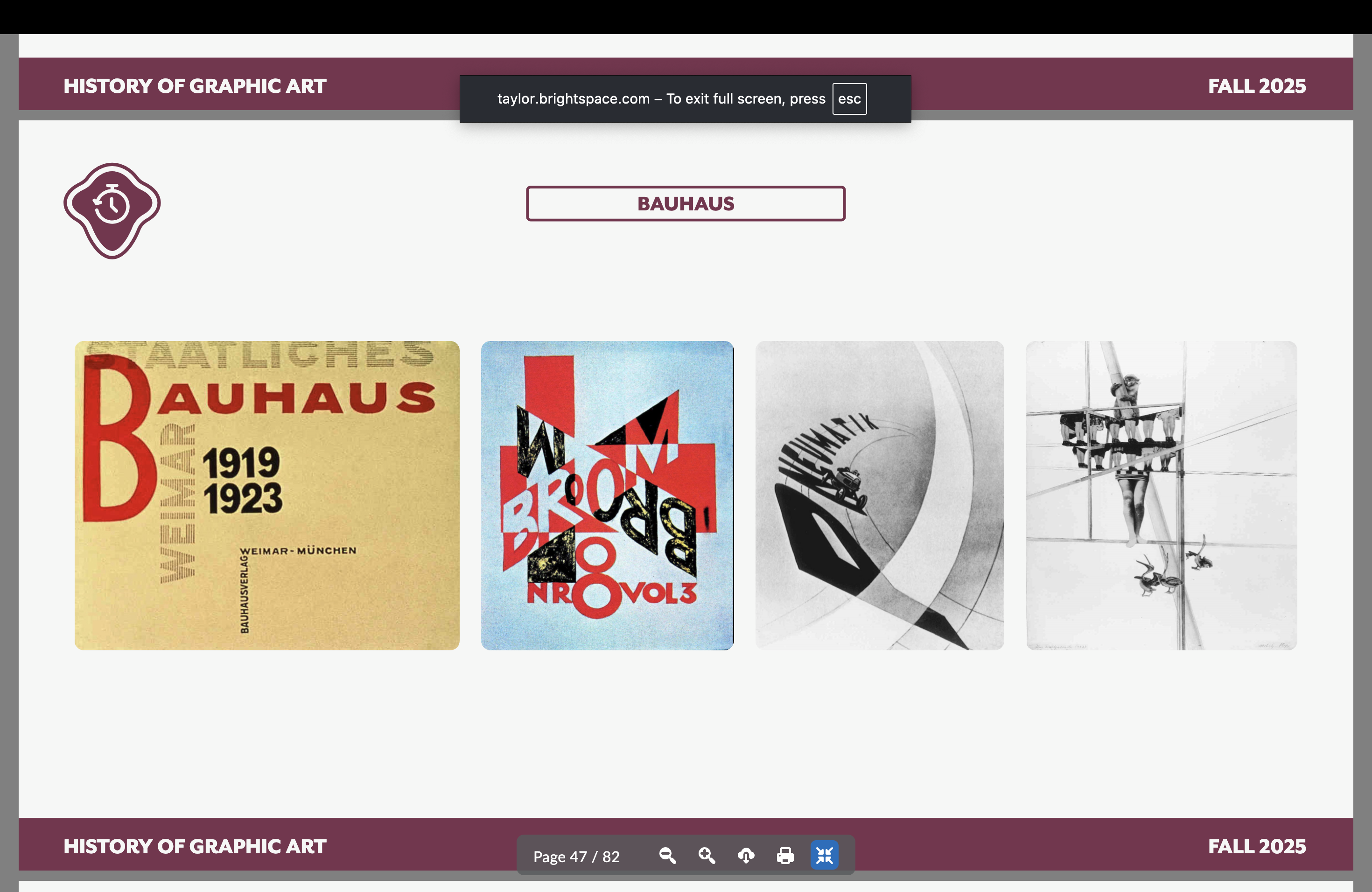
László Moholy-Nagy
Came out of a Constructivist background…heavy impact on Bauhaus typography, asymmetrical approach while also emphasizing photo and printing
Dynamic type!
Bauhaus and New Typeface artist/designer
Coins the term “typophoto” (the integration of type and photo). He pursued absolute clarity and intensity in his artistic communication.
Black, white, red mostly
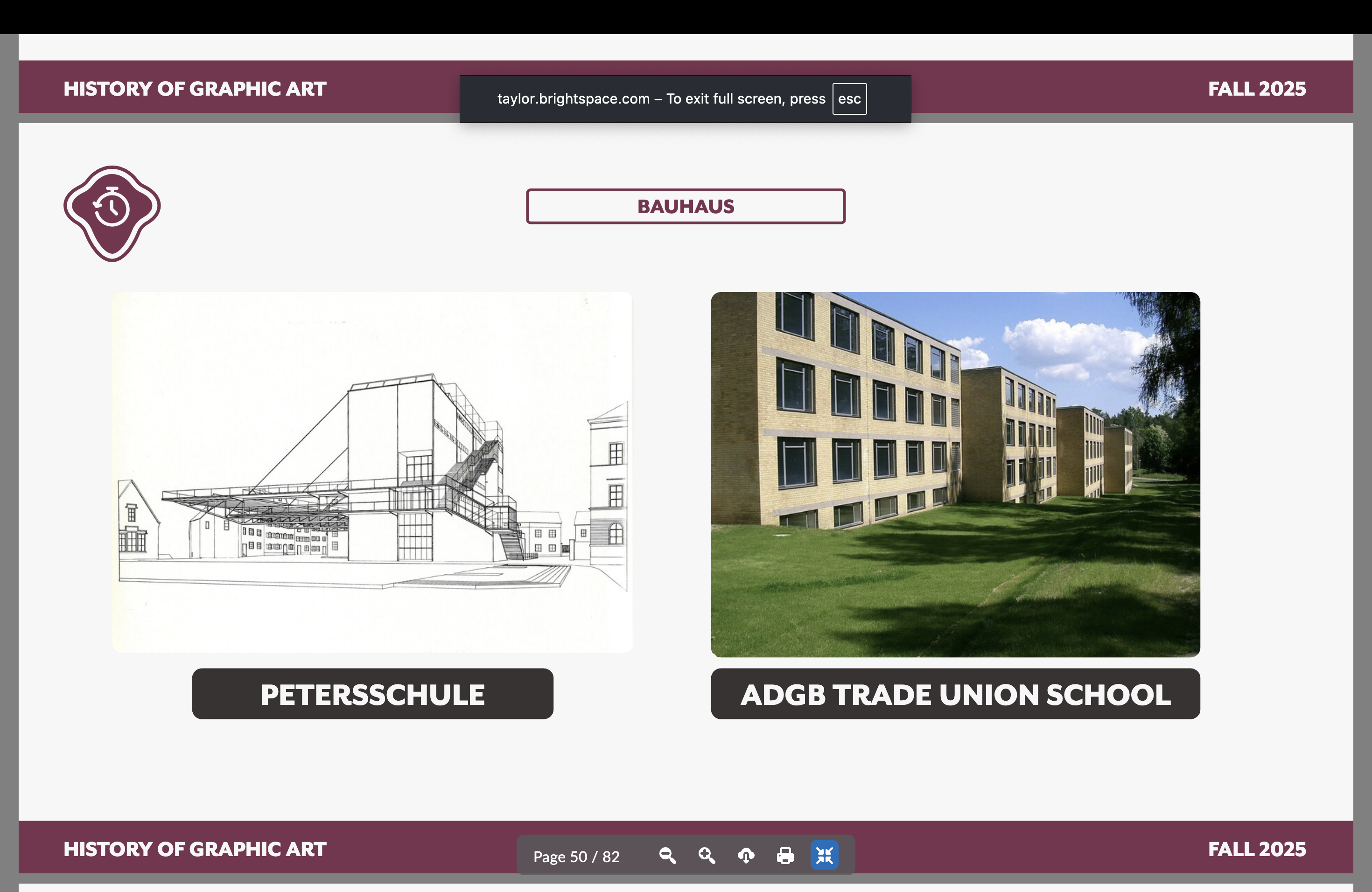
Hannes Mayer
Swiss architect and the second director of the Bauhaus; injected the curriculum with sciences and social issues, creating a more rigid structure
Petersschule and the ADGB Trade Union School
Bauhaus artist
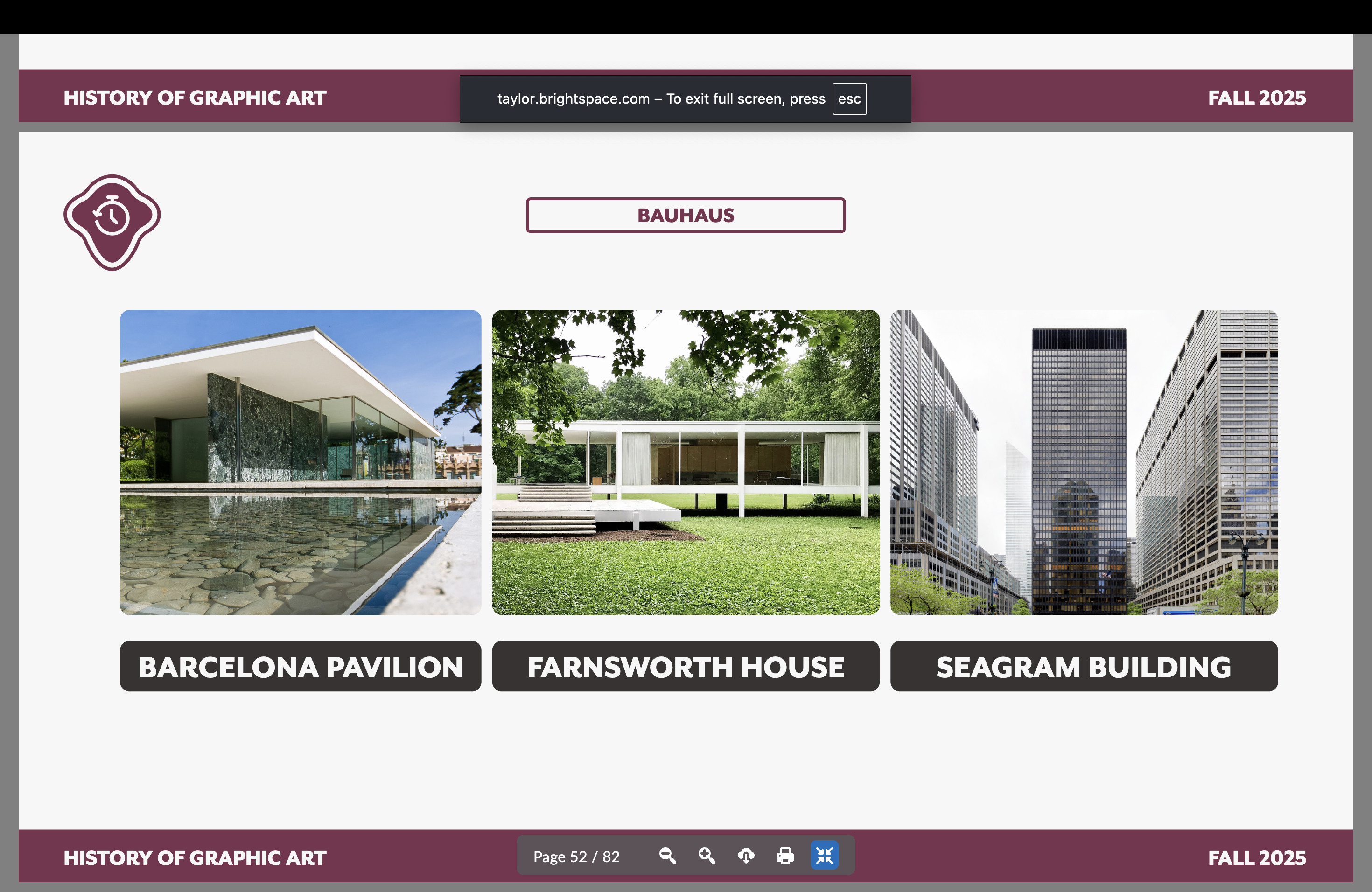
Ludwig Mies Van Der Rohe
Brought in after Mayer was forced out by Nazi ideology, he attempted to stabilize the Bauhaus by focusing on aesthetic perfection.
Architecture — Barcelona pavilion, Farnsworth House, the Seagram Building, the Neue Nationalgalerie, the Lakeshore Drive Apartments and the Barcelona chair.
Bauhaus artist
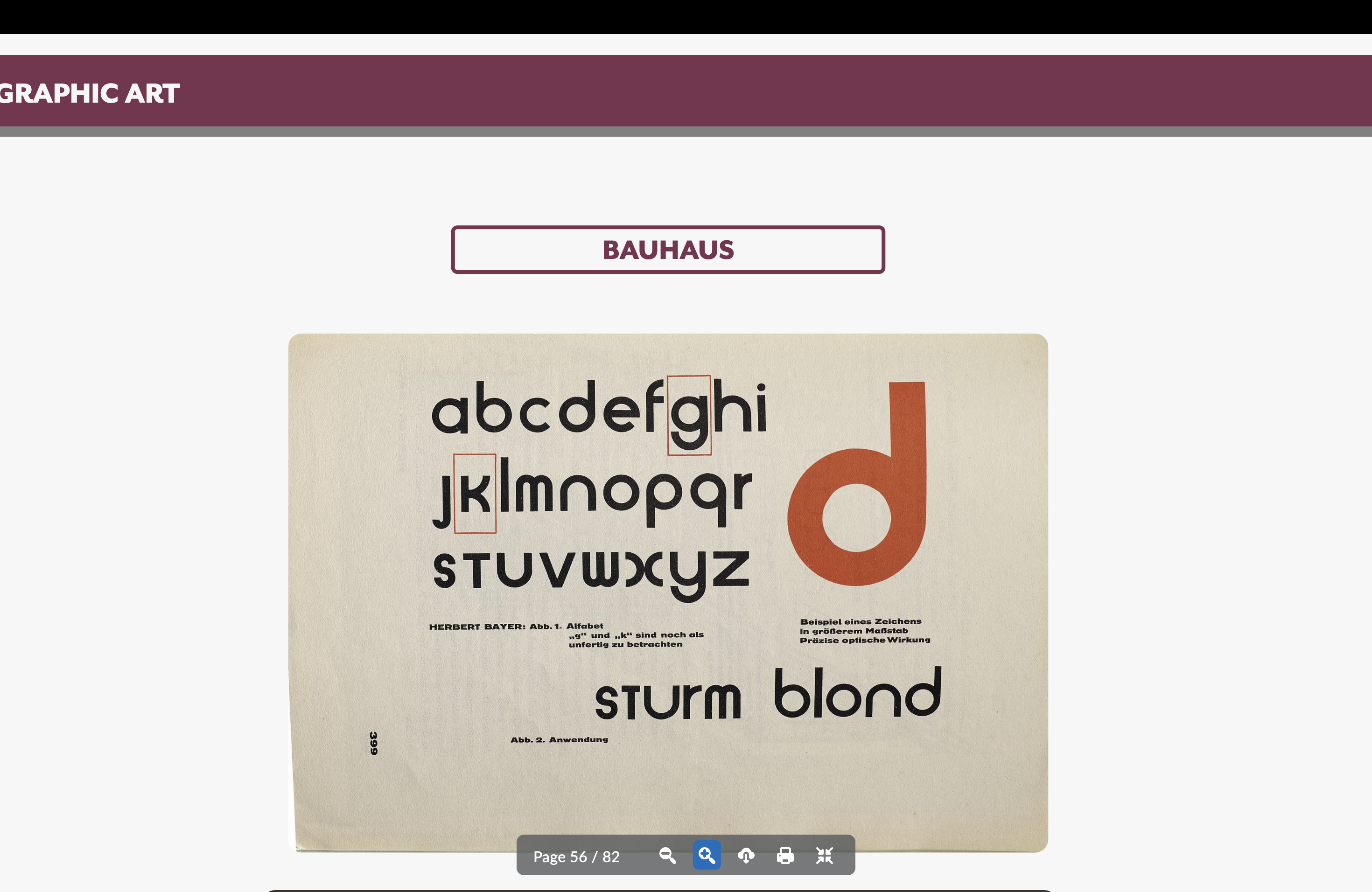
Herbert Bayer
Pioneer in graphic design and typography and a student + teacher at the Bauhaus. Created many influential print pieces.
“Menstral Cycle” Poster (not really Bauhaus, though)
Known for the Universal Typeface—kind of got rid of uppercase letters (except for T)
Bauhaus artist