Cell Transport
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Cell Membrane Structure, Cell Size & Diffusion, Passive Transport, Active Transport
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
isotonic (concentration of solutes and water in the cell compared to outside; water movement; what is the “balance” called)
equal amounts of solutes and water in the cell and the outside; water will move equally in and out; the cell is in an osmotic balance
hypotonic (concentration of solutes outside; concentration of water outside; water movement)
less solutes outside the cell; more water outside the cell; water will move into the cell
hypertonic (concentration of solutes outside; concentration of water outside; water movement)
more solutes outside; less water outside; water will move out of the cell
cytosis (for what cell; for what solution; effects of it)
animal cells; hypotonic; cell expands, bursts, and dies
turgor pressure (for what cell; for what solution; effects of it)
in plant cells; in hypotonic solution; ideal environment, cytoplasm and vacuole are full
why is turgor pressure ideal? Why does the cell that this occurs in not burst compared to the other cell type?
The plant cell will have enough water to do photosynthesis. Plant cells have a large vacuole and a cell wall that stops the cell from bursting
Plasmolysis (for what cell; for what solution; effects of it)
animal cells; hypertonic; the cell will shrink and die
Wilting (for what cell; for what solution; effects of it)
in plant cells; hypertonic; cytoplasm and vacuole shrinks and COULD die if not watered later
What is the fluid mosaic model?
Model that visualizes the cell membrane’s components
What is selective permeability?
A property in the membrane that allows only certain molecules to pass through it.
What is the name of the double layer of lipids in a cell membrane?
Phospholipid bilayer
What acts as channels for molecules to enter in a cell membrane?
proteins
carbohydrates (where are they; purpose)
attached to proteins on surface; cell recognition and adhesion
What attaches the membrane to the rest of the cell?
cytoskeleton filaments
Where is cholesterol found? Its use?
Found only in animal cells and keeps membrane fluid
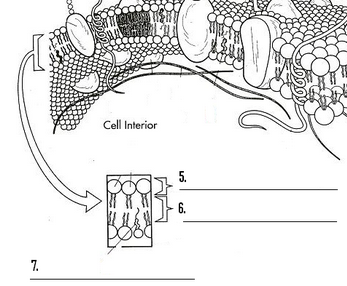
What are 5, 6, and 7?
Phosphate head, fatty acid tails, and cholesterol
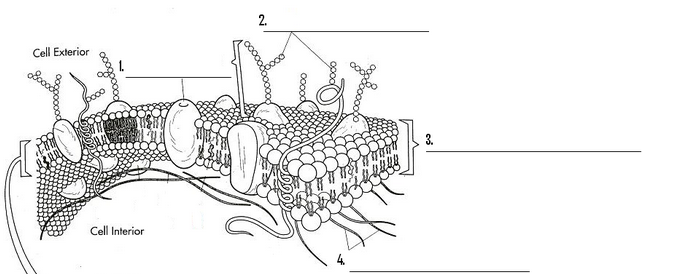
What are 1, 2, 3, and 4?
Protein, carbohydrates, phospholipid bilayer, and cytoskeleton filament
Are larger or smaller cells more efficient for diffusion? Why?
Smaller, they have a larger surface area to volume ratio
What are the functions of the cell membrane?
To control entry and exit of materials (maintain homeostasis) and to protect and support the cell
The phosphate heads within the lipid bilayer are hydrophobic/hydrophilic, while the fatty acid tails are hydrophilic/hydrophobic. (choose which one)
hydrophilic, hydrophobic
The cell membrane is permeable/impermeable to small, nonpolar/polar molecules and permeable/impermeable to larger, polar/nonpolar molecules and ions.(choose which one)
permeable, nonpolar, impermeable, polar
The movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration is called:
simple diffusion
The movement of materials through membrane proteins from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration is called:
facilitated diffusion
The diffusion of water from an area of higher water concentration to an area of lower concentration is called:
osmosis
The substance that dissolves to make a solution is called the:
solvent
Glucose enters cells most rapidly by:
facilitated diffusion
Gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide move across cell membranes using:
simple diffusion
What is active transport?
Uses energy (ATP) and moves molecules against the concentration gradient
endocytosis (what it is; what occurs; how it occurs)
form of active transport; movement of large particles into cell; membrane pinches in and forms a vesicle around the material
phagocytosis (what form of active transport; for what materials; how does it do it)
for endocytosis; “cell eating” for solid materials; cell engulfs large particles
pinocytosis (what form of active transport; for what materials; how does it do it)
for endocytosis; “cell drinking” for liquid materials; cell takes in dissolved molecules as a vesicle
Exocytosis (What is it; what occurs; how does it occur)
Form of active transport; moves large particles out of the cell; vesicle attaches to membrane and empties its contents
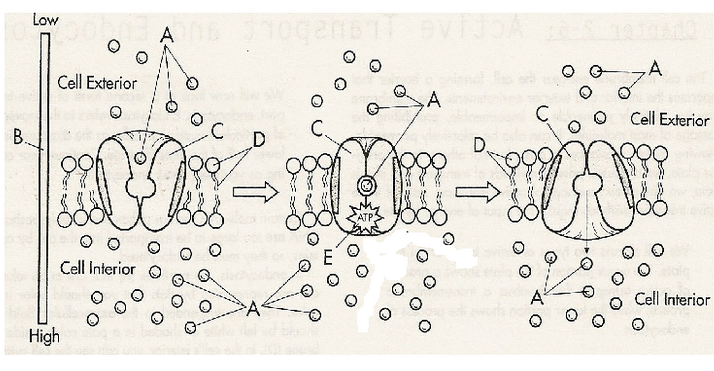
What is this diagram representing? What is A, B, C, D, and E?
Active transport through carrier proteins. Amino acids, concentration gradient, carrier protein, phospholipid bilayer, and ATP (energy)
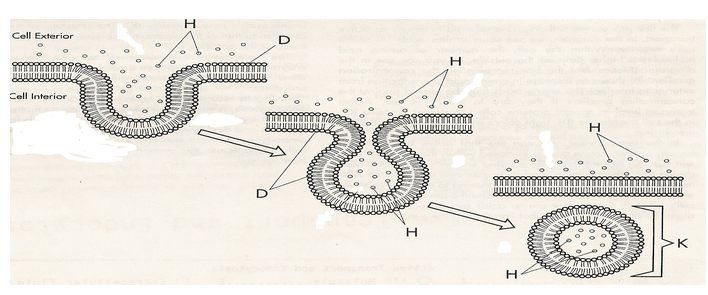
What is this diagram representing? What is H, D, K?
pinocytosis. Dissolved particles, phospholipid bilayer, and vesicle
What is the sodium-potassium pump?
A transport protein used in active transport
What is passive transport?
the movement of molecules into and out of cells, using no energy (ATP), goes with the concentration gradient (high-low), and molecules move to reach equilibrium
What is equilibrium?
A state where solutes are evenly distributed between a cell and the outside of it, but particles still move back and forth across a membrane, just equally
What is facilitated diffusion? (define; what molecules use it)
Diffusion (passive transport) using carrier/transport proteins; carbohydrates and amino acids are transported this way
What is (simple) diffusion?
the net movement of molecules from an area of a higher concentration to an area of a lower concentration
transport proteins
channels for nutrients to enter and wastes to leave
receptor proteins
bind to extracellular substances
recognition proteins
identify cells/substances
adhesion proteins
stick to other cells
Active transport through transport proteins involves the use of ATP energy made in the ____
mitochondria
Process by which a cell expels waste from a vacuole
exocytosis
Process by which a cell takes in liquids
pinocytosis
form of passive transport that uses proteins
facilitated diffusion
During ________ carrier proteins move glucose molecules across the membrane from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration
facilitated diffusion
______ moves oxygen and carbon dioxide molecules across a membrane from a high concentration to a low concentration
diffusion (simple)