unit 9 chemical bonds honors chem
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
nice
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
electronegativity of 0-0.4
nonpolar covalent
electronegativity of 0.5 to 1.9
polar covalent
electronegativity of 2-4
ionic
what is an ionic bond?
compound with chemical bonds that are from electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions.
properties of ionic bonds
high boiling and melting points, stronger attraction, doesnt readily vaporize at room temp and is a good conductor
what is a covalent bond
sharing of electrons between 2 atoms
properties of covalent bonds
low boiling and melting, weaker attraction, easily vaporizable at room temp, poor conductors
what is npc and value of ionic character
covalent bond when electrons are shared equally on both sides, 0% ionic character.
what is a PC bond, and ionic value
covalent bond in which the atoms have a unique attraction for the shared electrons, 5% to 50%
what is polarity
uneven distribution of charge
how to determine polarity 2 ways
symmetry of molecule or lone pairs of electrons on central atom
proportionality with bond length, bond energy and bond amount
bond length does down, then bond energy goes UP and so does # of bonds.
energy and # of bonds are directly proportional
octet rule is what
chemical compounds form by making each atom gain or lose or share electrons, they have an octet of electrons in its highest energy level.
what is expanded valence
exception to octet, when central atom has no more than 8 electrons around it, bonding electrons in the d orbitals and the s and p orbitals.
3 types of intermolecular forces
Dipole Dipole, Hydrogen bond and London Dispersion Forces.
Dipole Dipole is what
forces of attraction between polar molecules, (positive attracted to neg)
Hydrogen bonding is what
When a hydrogen bonds on a very electronegative atom. Polar compounds containing hydrogen
What is london dispercement forces
attraction from the motion of electrons, when they move there is slight energy.
this is in everyting
bent
AB2E, 120 deg, Polar,
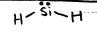
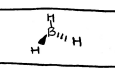
trigonal pyramidal
AB3E, 109.5 deg, polar

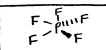
trigonal bipyramidal
AB5, 120 and 90, Nonpolar
linear
AB or AB2, 180, P if its AB and NP for AB2
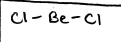
tetrahedral
AB4, 109.5, Nonpolar,
octahedral
AB6, 90 Nonpolar

trigonal planar
AB3, 120, NP