Unit 4 - Lecture 21
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
1
New cards
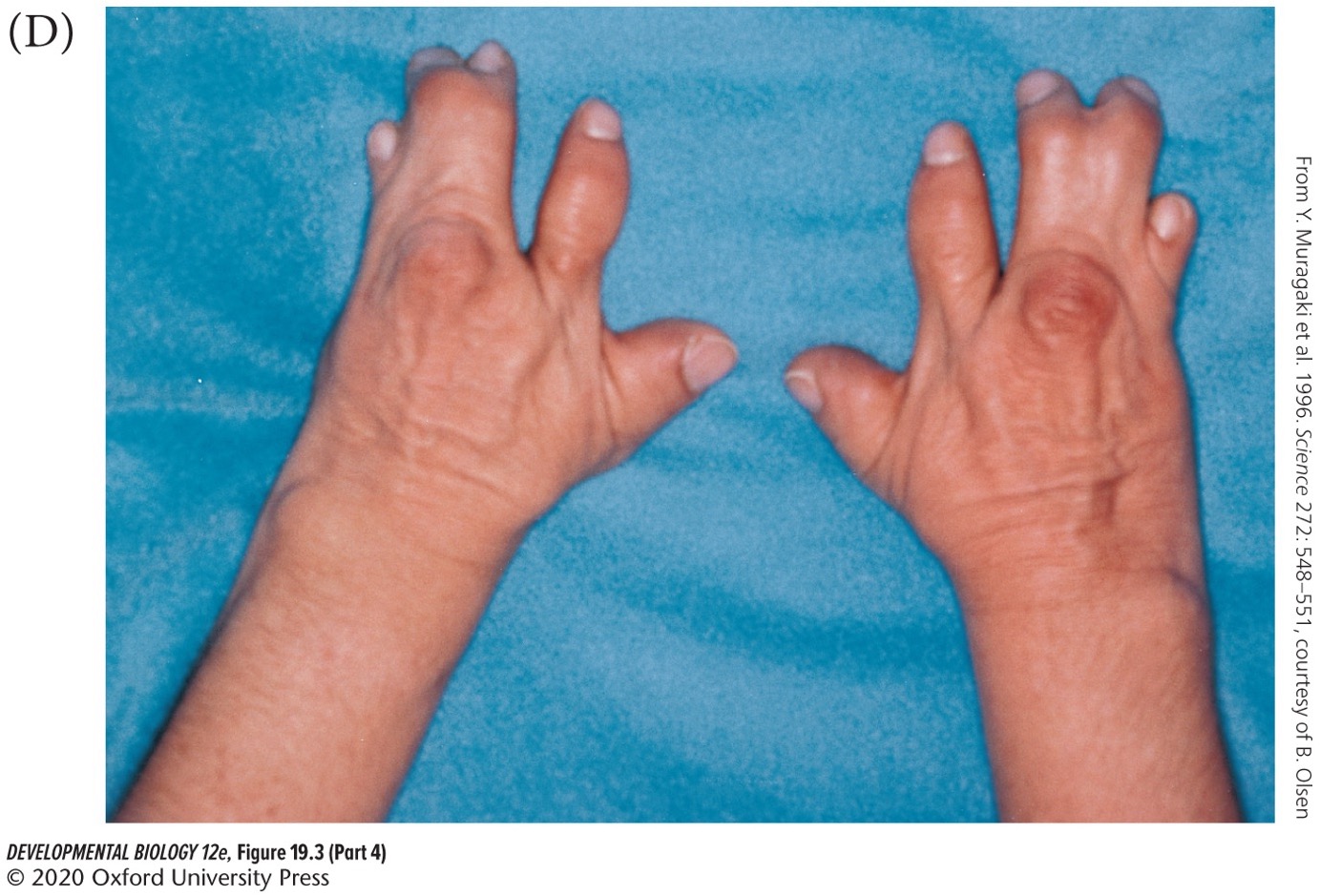
**Intermediate mesoderm**
Forms the urogenital system (kidneys, gonads, and associated duct systems).
2
New cards
The intermediate mesoderm is specified by which gradient?
BMP gradient.
3
New cards
Higher levels of BMP4 *farther/closer* to the midline.
farther.
4
New cards
For kidney production, besides intermediate mesoderm, another form of mesoderm is necessary. Which one?
A) Chorda mesoderm
B) Paraxial mesoderm
C) Lateral plate mesoderm
A) Chorda mesoderm
B) Paraxial mesoderm
C) Lateral plate mesoderm
B) Paraxial mesoderm
5
New cards
Does cutting paraxial mesoderm away from intermediate mesoderm prevents kidney formation?
Yes. Paraxial mesoderm can even induce lateral plate mesoderm to form some kidney tissues in culture.
6
New cards
Paraxial mesoderm induces the expression of which three transcription factors?
A) Lim1
B) Fgf2
C) Pax2
D)Nodal
E) Pitx2
F) Pax8
A) Lim1
B) Fgf2
C) Pax2
D)Nodal
E) Pitx2
F) Pax8
A + C + F) **Lim1**, **Pax2** and **Pax8**.
7
New cards
Kidneys formwhere Lim1 and Pax8 are both expressed. Would expression of Lim1 and Pax8 together in another tissue lead to kidney formation?
Yes.
8
New cards
Mouse Pax2 Pax8 double mutants can still form kidneys (T/F).
False. Can not for kidneys.
9
New cards
Expression of Pax2 in presomiticmesoderm converts it into intermediate mesoderm and causes kidney formation (T/F).
True.
10
New cards
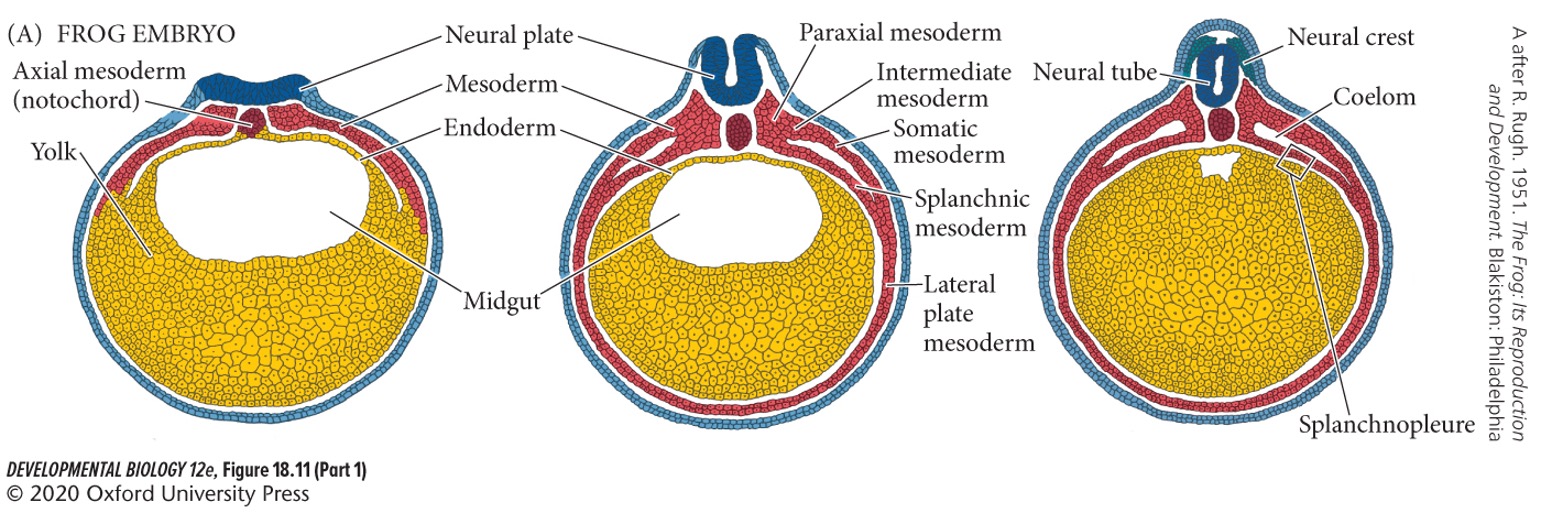
•During embryogenesis, the lateral plate mesoderm splits horizontally into which two layers?
* **Somatic** (**parietal**) **mesoderm**
* **Splanchnic** (**visceral**) **mesoderm**
* **Splanchnic** (**visceral**) **mesoderm**
11
New cards
The somatic mesoderm is formed at the *ventral/dorsal* layer, the splanchnic mesoderm is formed at the *ventral/dorsal* layer.
Ventral, Dorsal.
Somatic mesoderm → ventral
Splanchnic mesoderm → dorsal
Somatic mesoderm → ventral
Splanchnic mesoderm → dorsal
12
New cards
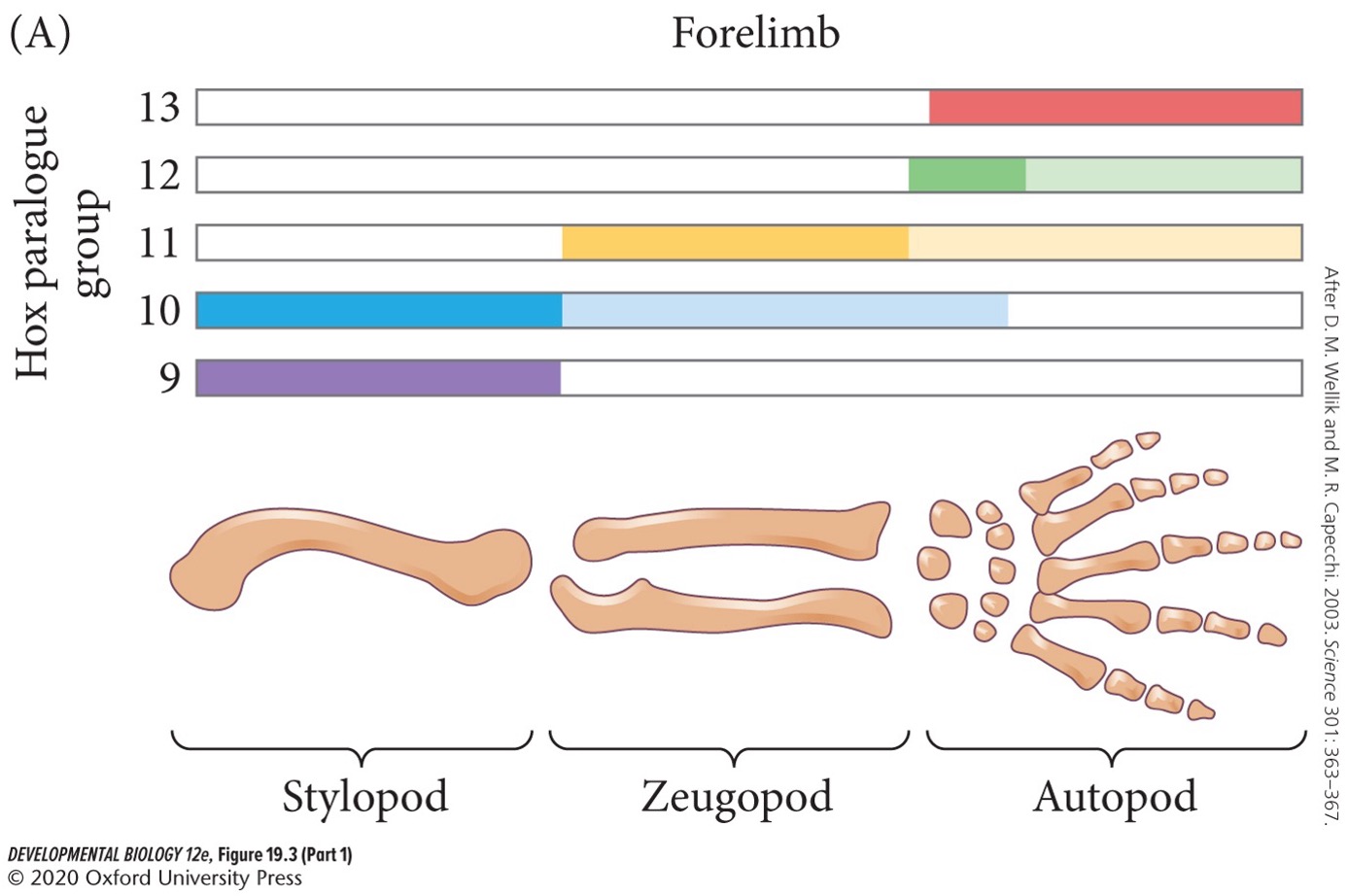
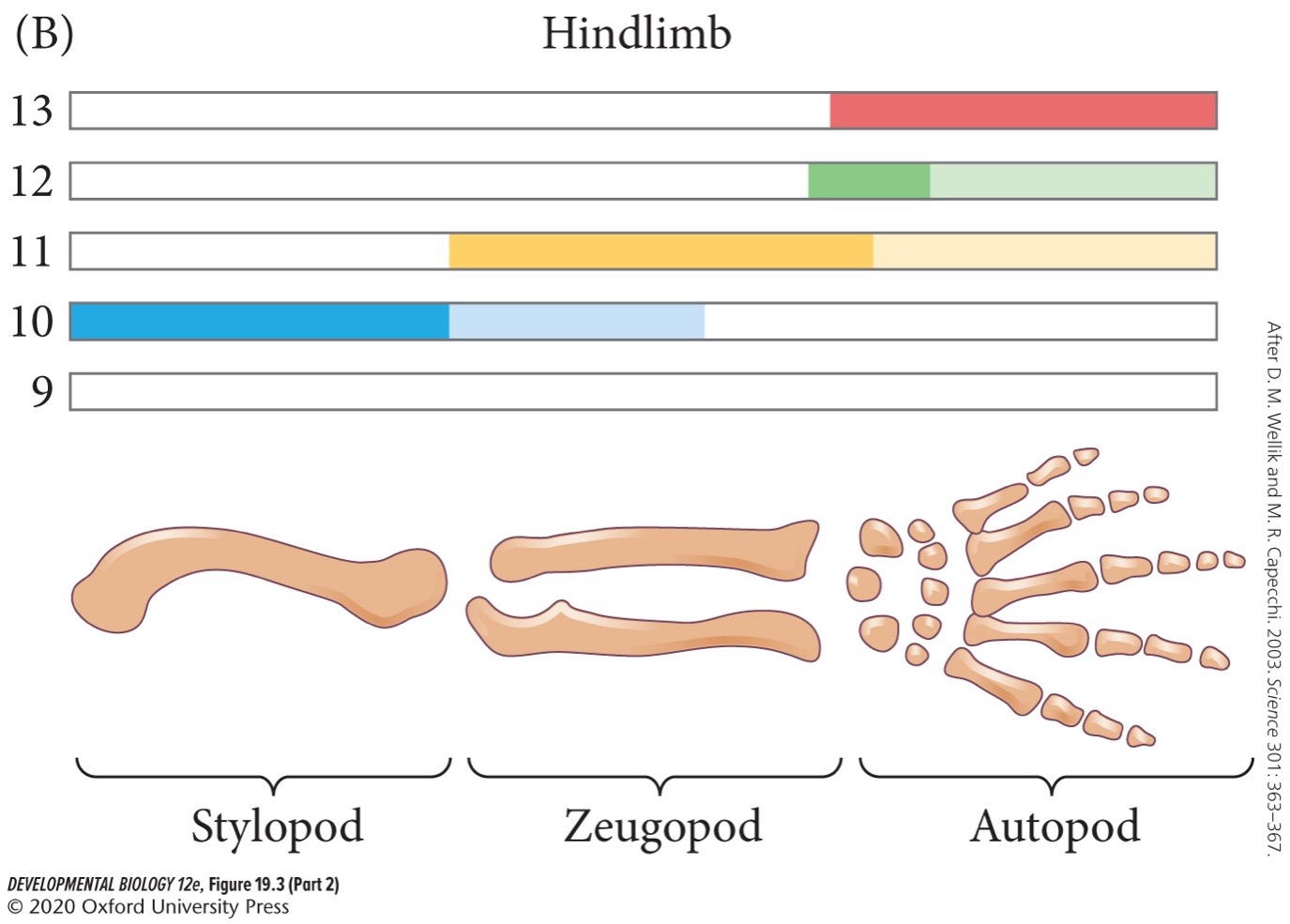
**Somatic** (**parietal**) **mesoderm**
Underlies the ectoderm. Together with the ectoderm it forms the **somatopleure**.
13
New cards
**Splanchnic** (**visceral**) **mesoderm**
overlies the endoderm and together with the endoderm forms the **splanchnopleure**.
14
New cards
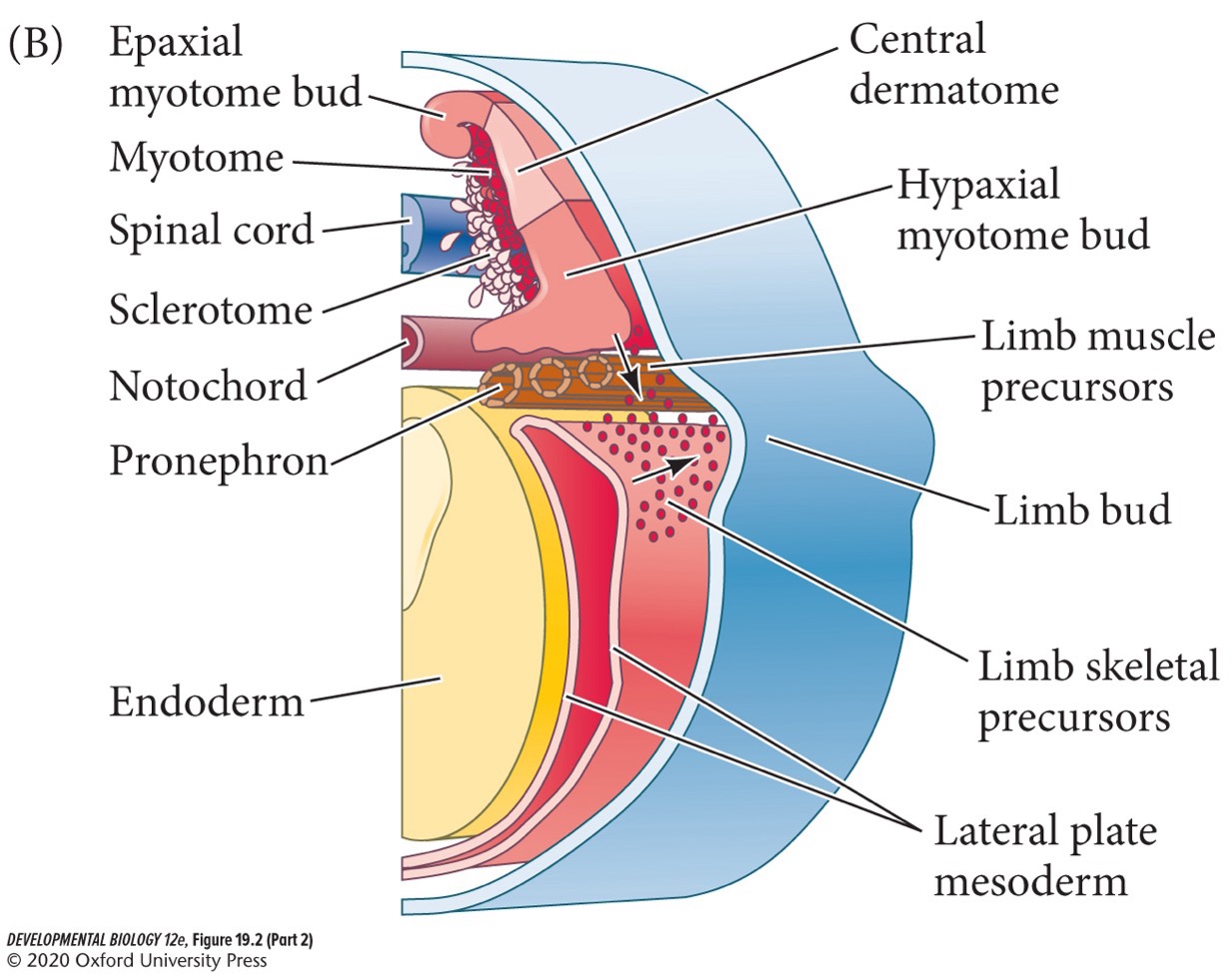
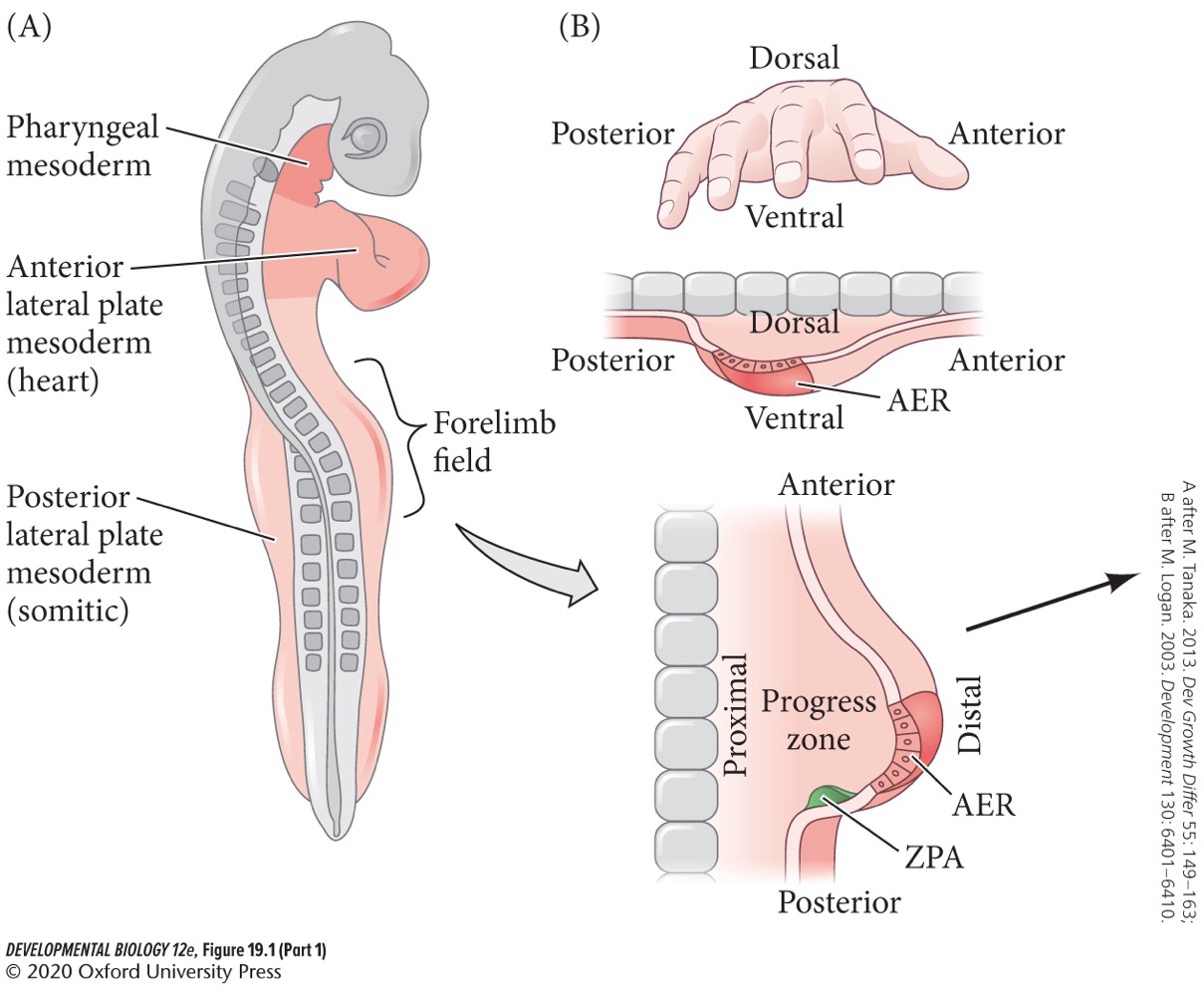
**Coelom**
Body cavity, created from the space between the somatopleure and the splanchnopleure. It stretches from the future neck region to the posterior of the body.
15
New cards
Later in development the left and right sides of the coelom fuse, and folds from the somatic mesoderm divide the coelom into which three separate cavities?
* **Pleural** (envelopment the thorax).
* **Pericardial** (heart).
* **Peritoneal** (abdomen).
* **Pericardial** (heart).
* **Peritoneal** (abdomen).
16
New cards
The creation of the body cavity has changed a lot over vertebrate evolution (T/F).
False. It has changed very little, despite difference in gastrulation.
17
New cards
The heart is the first functional organ formed in the embryo (T/F).
True, and the circulatory system is the first functional unit.
18
New cards
From which mesoderm does the heart arise on both sides of the body?
A) Sclerotome mesoderm
B) Somatic mesoderm
C) Dermatome mesoderm
D) Splanchnic mesoderm
A) Sclerotome mesoderm
B) Somatic mesoderm
C) Dermatome mesoderm
D) Splanchnic mesoderm
D) **Splanchnic** **mesoderm**
19
New cards
What is the heart precursor cells?
**Carfiogenic mesoderm** (**Heart field**)
20
New cards
Specification of cardiogenic mesoderm begins as these cells migrate inward through the primitive streak during gastrulation. What do they form first?
**Heart tube**
21
New cards
Heart tube
Linear, primitive heart.
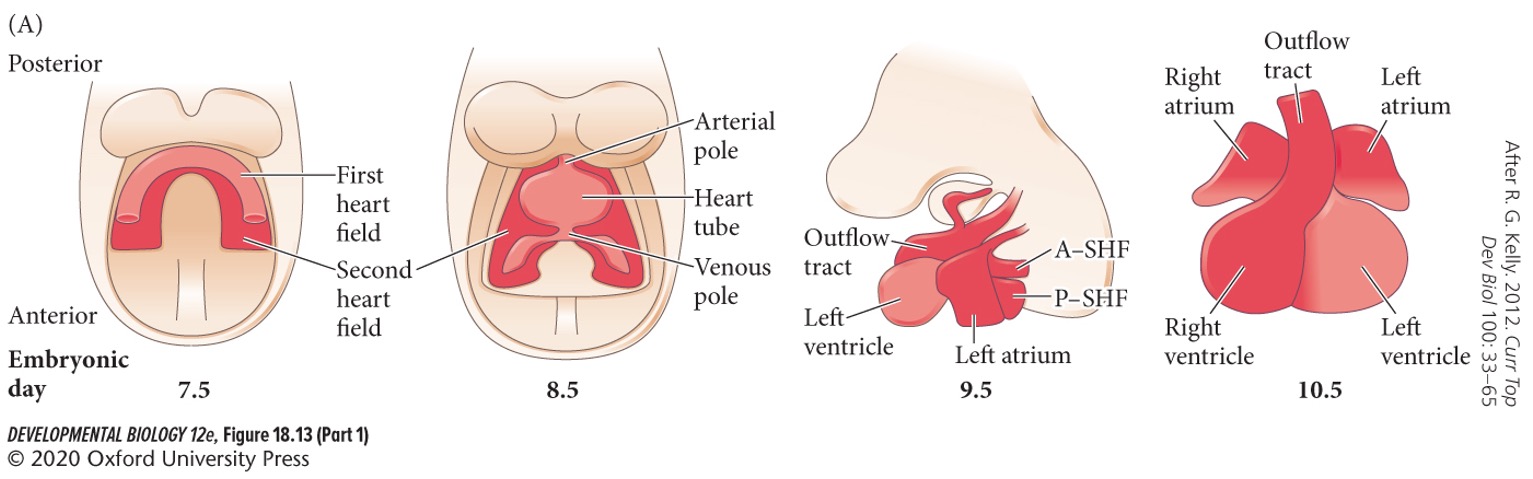
22
New cards
What does the **first heart field** form?
The scaffold of the developing heart. It is limited in its proliferative ability and generates only the major portion of the left ventricle of the adult heart (the chamber that pumps blood into the aorta).
23
New cards
What does the **second heart field** form?
The atria, the base of the aorta, pulmonary arteries, right ventricle, and inflow region (pulmonary veins and vena cava). It also helps form facial muscles and lung mesenchyme.
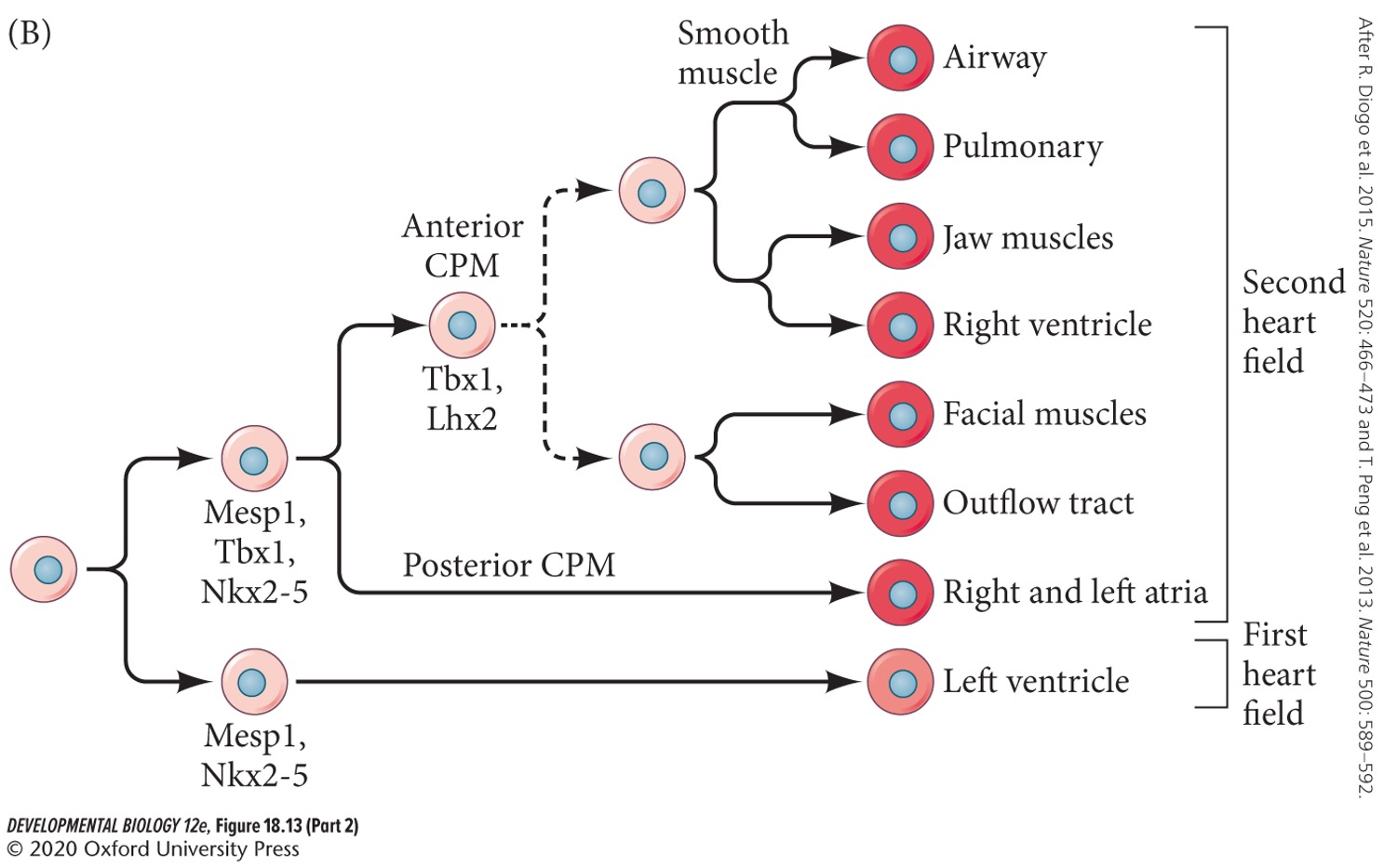
24
New cards
Nearly all the cells and tissues of the heart derive from the heart fields, including which five?
* **Cardiomyocytes**
* **Endocardium**
* **Endocardial cushions**
* **Epicardium**
* **Purkinje fibers**
* **Endocardium**
* **Endocardial cushions**
* **Epicardium**
* **Purkinje fibers**
25
New cards
**Cardiomyocytes**
Form the muscular layers of the heart.
26
New cards
**Endocardium**
Internal layer of the heart, similar to endothelial cells of blood vessels.
27
New cards
**Epicardium**
Forms the coronary blood vessels that feed the heart.
28
New cards
**Purkinje fibers**
Modified myocytes that control the heartbeat.
29
New cards
Neural crest contribute to the septum. What is the role of the septum?
Separating the aorta from the pulmonary artery, and portions of the outflow tract.
30
New cards
Heart formation is induced by:
A) Anterior ectoderm
B) Posterior ectoderm
C) Posterior endoderm
D) Anterior endoderm
A) Anterior ectoderm
B) Posterior ectoderm
C) Posterior endoderm
D) Anterior endoderm
D) Anterior endoderm
31
New cards
What happens to heart formation if anterior endoderm is removed?
No heart
32
New cards
When combining anterior endoderm with mesoderm, does it still form a heart?
Yes.
33
New cards
Which two signals from anterior endoderm induce the heart?
A) BMP2
B) Fgf8
C) Wnts
D) Nodal
E) Pitx2
A) BMP2
B) Fgf8
C) Wnts
D) Nodal
E) Pitx2
A + B) **BMP2** and **Fgf8**
34
New cards
Heart tissue is prevented from forming in regions where it shouldn’t by which three factors?
A) Noggin
B) Chordin
C) Wnts
D) Nodal
E) Pitx2
A) Noggin
B) Chordin
C) Wnts
D) Nodal
E) Pitx2
A + B + C) **Noggin**, **Chordin** and **Wnts**
35
New cards
Name two BMP inhibitors.
Noggin and Chordin
36
New cards
What does Wnt alone promote?
Blood and vessel formation.
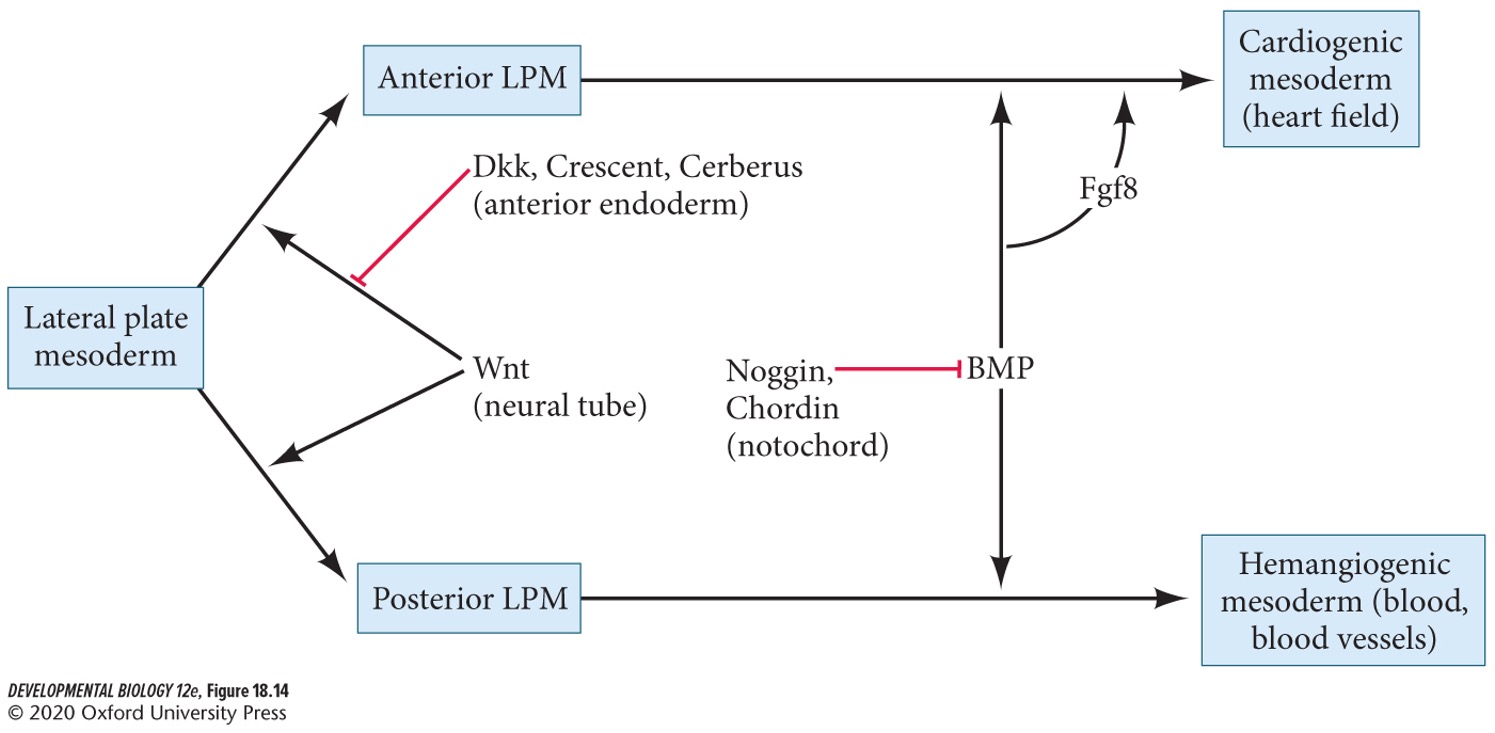
37
New cards
BMP and other signals activate two key transcription factors for specifying heart field cells.
A) NKx2-5
B) Pitx2
C) Mesp1
D) Fibronectin
E) Fgf2
A) NKx2-5
B) Pitx2
C) Mesp1
D) Fibronectin
E) Fgf2
A + C) **NKx2-5** and **Mesp1**
38
New cards
When are Mesp1 and NKx2-5 first turned on?
When cells migrate through the primitive streak.
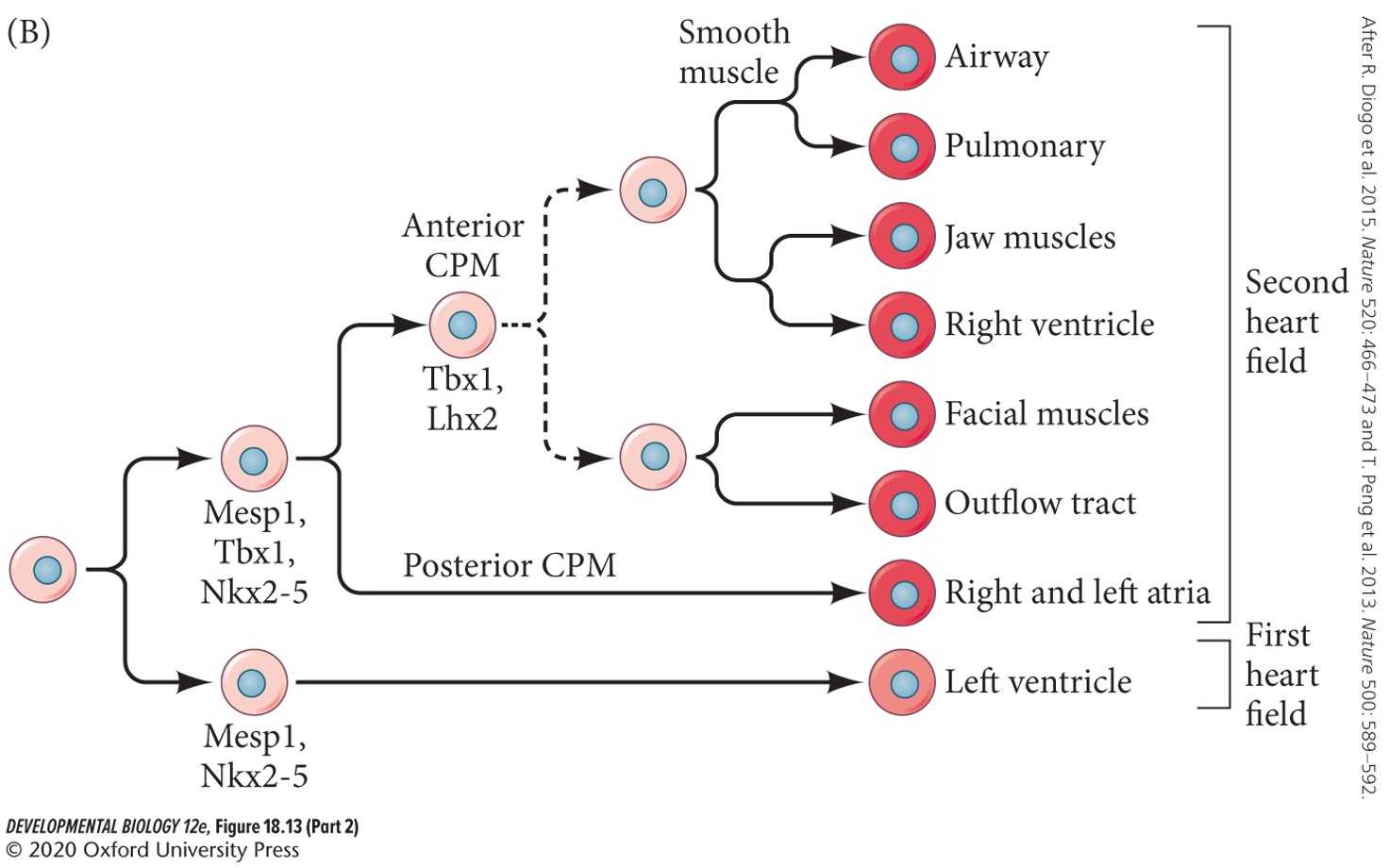
39
New cards
**Tinman**
Drosophila NKx2-5 homolog. Acts in heart development.
40
New cards
**Fibronectin**
Responsible for migration of heart field cells.
41
New cards
Higher concentration of fibronectin in the *anterior/posterior* promote migration.
Anterior
42
New cards
Each side of the lateral plate has heart fields. How are they brought together?
By inward folding of the splanchnopleure to form the foregut.
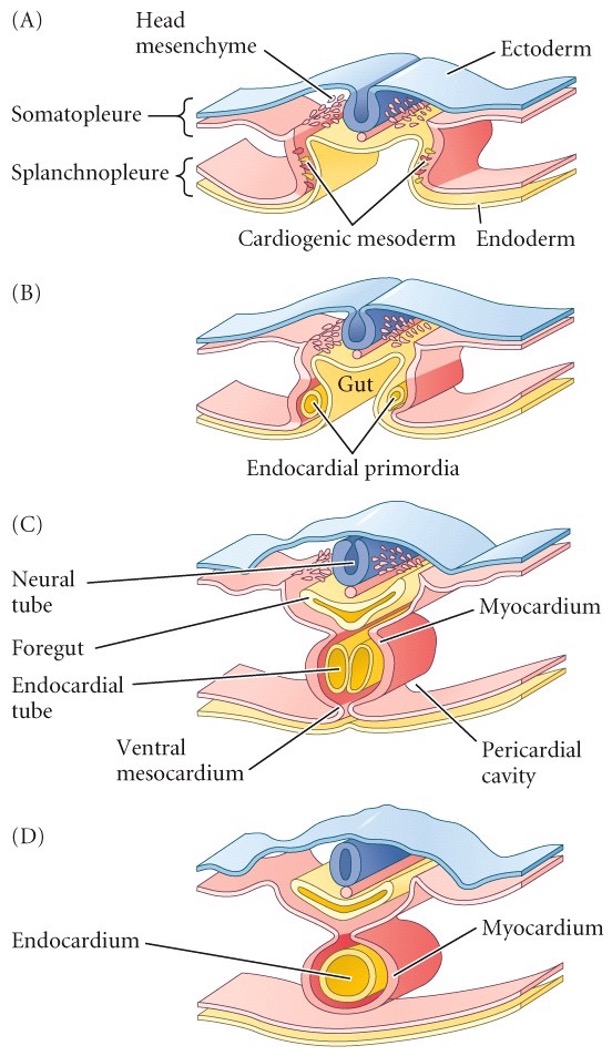
43
New cards
**Cardia bifida**
Two separate heart formations. Results from prevention of the merger of the two sides of lateral plate mesoderm.
44
New cards
**Miles apart**
Mutation in zebrafish that results in cardia bifida.
45
New cards
Foregut formation is tied to heart formation (T/F).
True.
46
New cards
1\. Early heart induction is mostly via _____________ and ____________from anterior endoderm.
A) BMP2; Fgf8
B) Hairy1; Mesp
C) Tbx6; Fgf8
D) Notch; BMP4
E) Tbx6; Eph
A) BMP2; Fgf8
B) Hairy1; Mesp
C) Tbx6; Fgf8
D) Notch; BMP4
E) Tbx6; Eph
A) BMP2; Fgf8
47
New cards
The anterior-posterior specification of different heart regions depends on what?
Retinoic acid-induced Hox gene expression.
48
New cards
RA levels are *highest/lowest* in the posterior in this region at this time, specifying the inflow tracks and atria, which will later loop to the anterior.
highest
49
New cards
RA originated from outside the body can cause heart birth defects (T/F).
True.
50
New cards
Cardiac field cells
A subset of an earlier progenitor population that also gives rise to the circulatory system.
51
New cards
Early progenitor cells give rise to which two structures?
* **Hemangioblasts**
* **Multipotent cardiac precursor cells**
* **Multipotent cardiac precursor cells**
52
New cards
Hemangioblasts give rise to which two structures?
* Hematopoietic (blood) cells.
* Angioblasts (blood vessel cells).
* Angioblasts (blood vessel cells).
53
New cards
The cardiac fields contain multipotentprogenitor cells that give rise to all the all the different cells of the heart (T/F).
True.
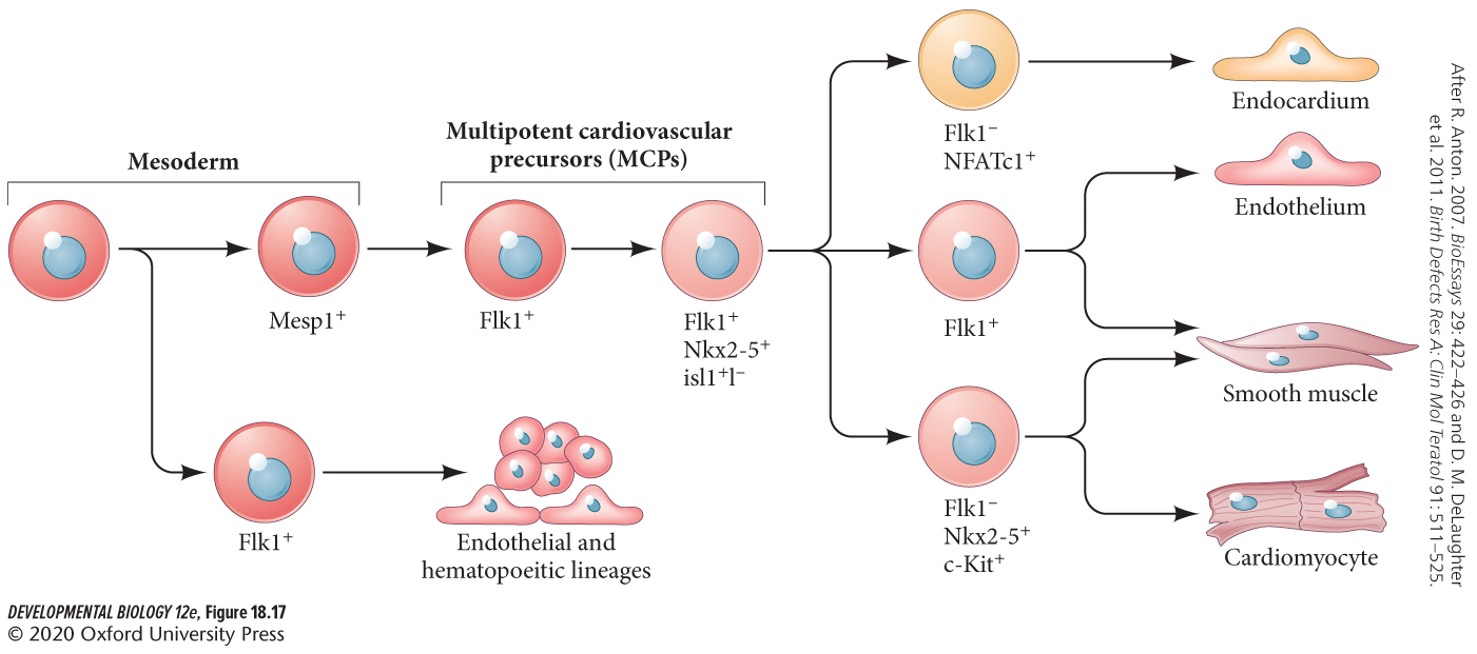
54
New cards
The early mammalian heart is a two- chambered tube, with the inflow (venous) portions in the *anterior/posterior*.
posterior.
55
New cards
Looping of the heart brings the atrial (inflow) regions to the anterior to make the four chambered heart. Direction of looping depends on which two factors?
A) Pitx2
B) NKx2-5
C) Nodal
D) Fibronectin
E) Wnt
A) Pitx2
B) NKx2-5
C) Nodal
D) Fibronectin
E) Wnt
A + C) **Pitx2** and **Nodal**
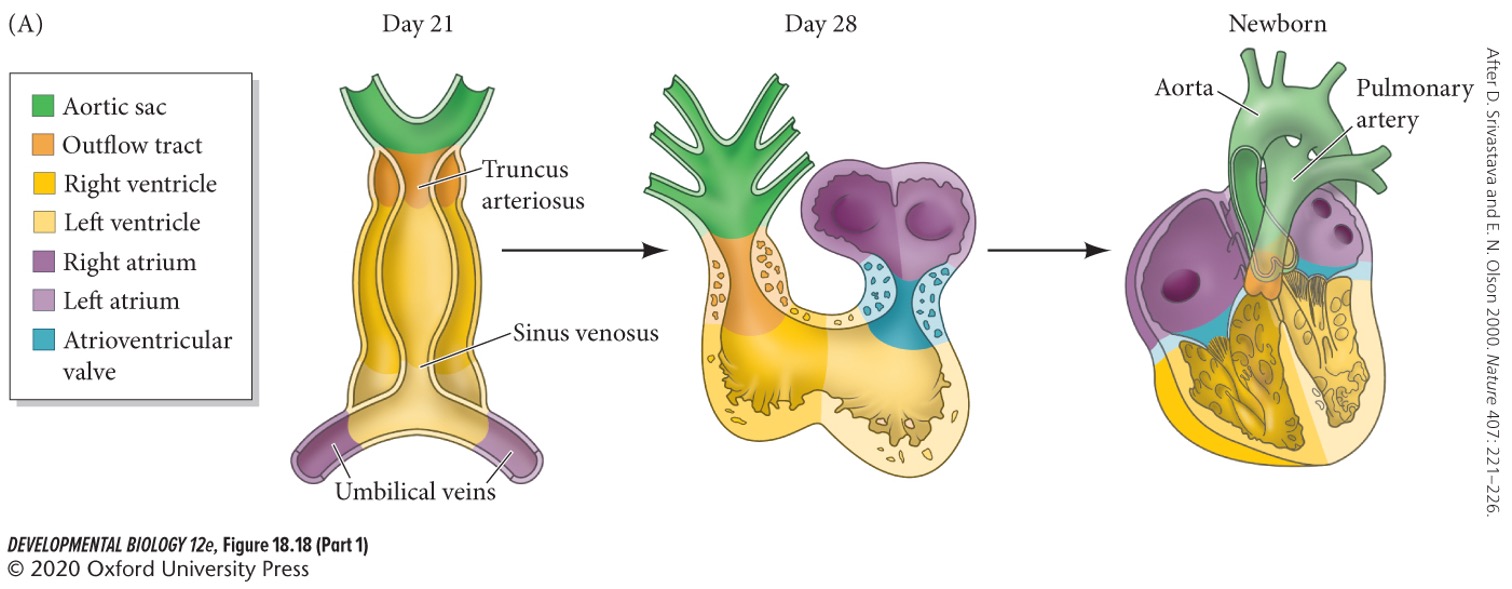
56
New cards
Mammalian embryos get nutrients from the placenta or the yolk?
Yolk.
57
New cards
Do mammalian embryos utilize the same or different embryonic circulatory system compared to birds and reptiles?
Different.
58
New cards
The right **vitelline vein** of chicks is modified to become what in mammals?
Umbilical vein.
59
New cards
The **allantoic artery**, which carries waste to the allantois in chicks, is modified to become what in mammals?
Umbilical artery.
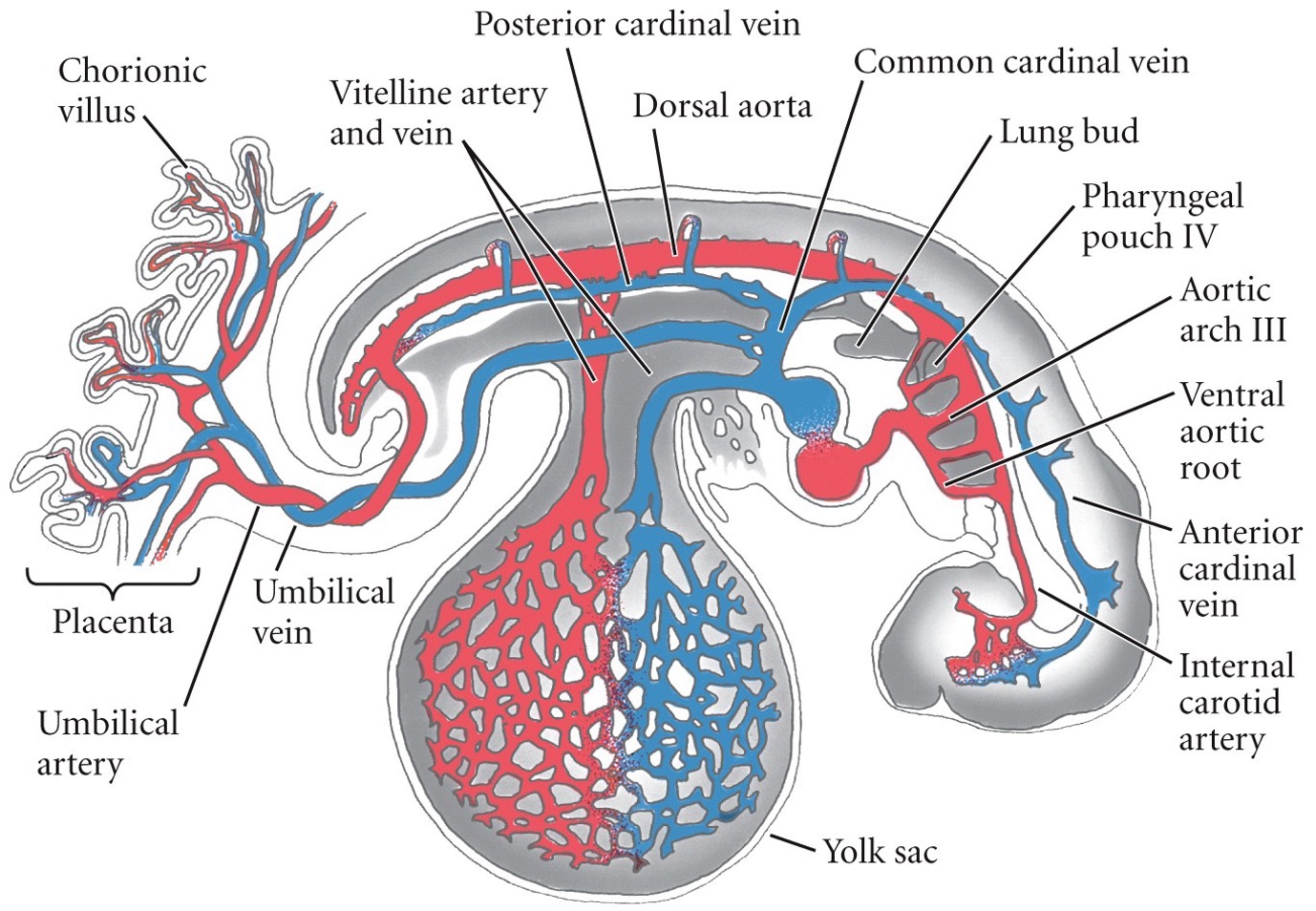
60
New cards
Mammalian fetal hemoglobin is different than that of adults, and have a slightly *lower/higher* affinity to oxygen, attracting oxygen from the blood of the mother.
higher
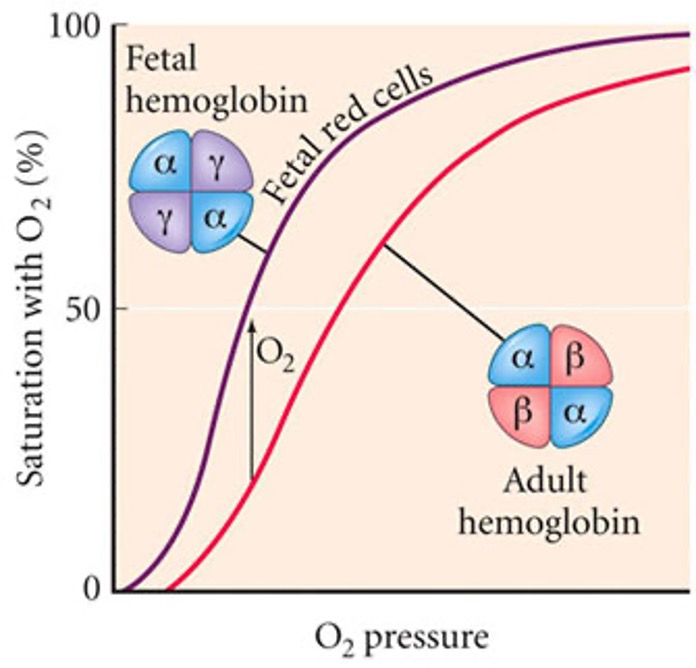
61
New cards
Blood vessels form *dependently/independently* of the heart.
Independently, and link up to the heart soon afterward.
62
New cards
**Vasculogenesis**
A network of blood vessels is created new from the lateral plate mesoderm.
63
New cards
**Angiogenesis**
The vasculogenesis network is remodeled into a distinct capillary bed, arteries, and veins.
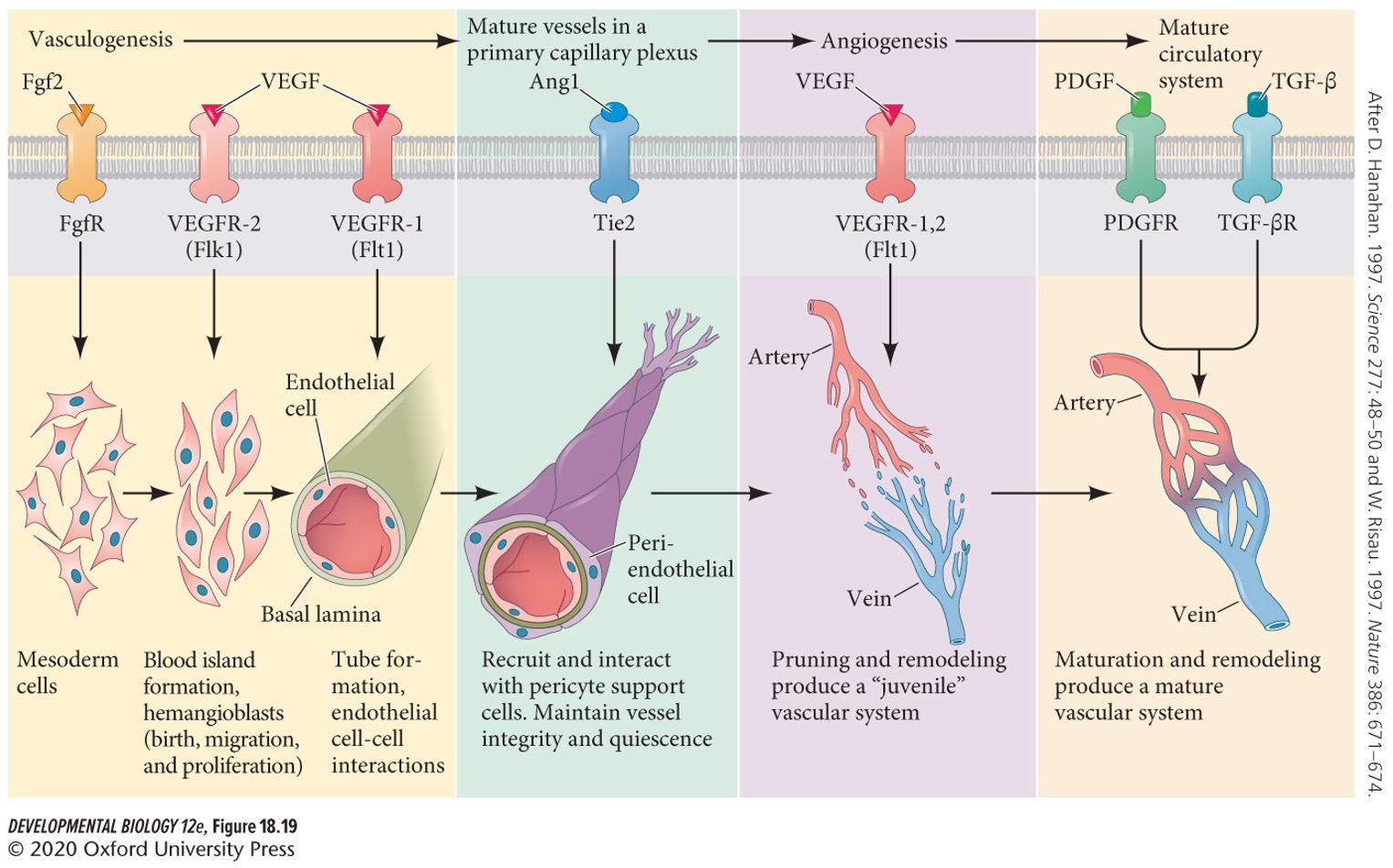
64
New cards
**Extraembryonic vasculogenesis** (first step)
**Blood islands** form in the yolk sac mesodermal mesenchyme.
65
New cards
**Blood islands**
Made up of **hemangioblasts**, the precursors to both blood cells and blood vessels.
66
New cards
**Angioblasts**
The cells that form blood vessels.
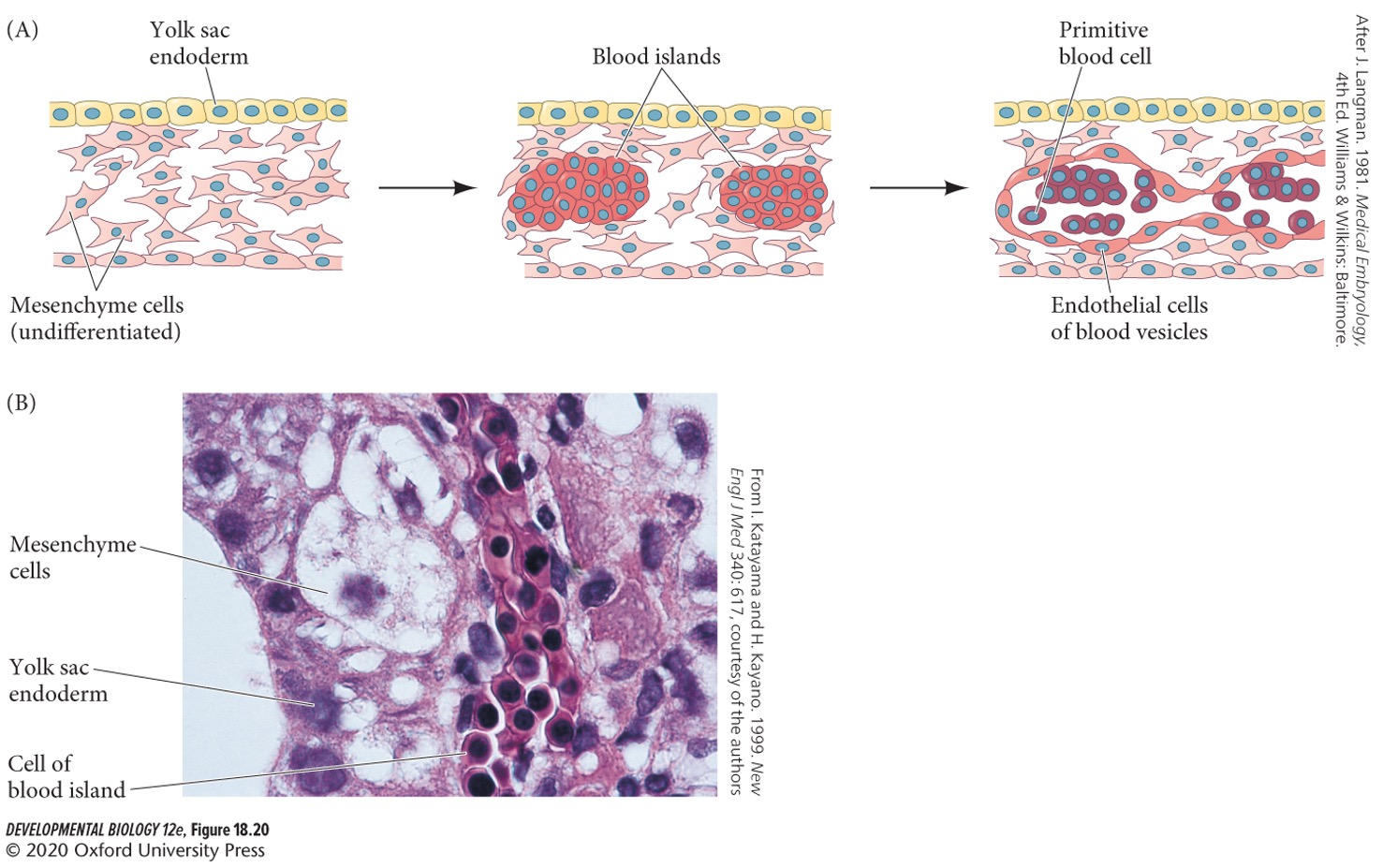
67
New cards
**Intraembryonic vasculogenesis** (second step)
Forms the dorsal aorta, and this connects with capillary networks that form from mesodermal cells within each organ.
68
New cards
Angioblasts multiply and differentiate into which cells?
**Endothelial** cells.
69
New cards
**Endothelial cells**
From the lining of the blood vessels. These cells form tubes and connect to form a network of capillaries.
70
New cards
Which two factors are required for vasculogenesis?
A) VEGFs
B) Fgf2
C) Prox1
D) Nodal
E) Pitx2
A) VEGFs
B) Fgf2
C) Prox1
D) Nodal
E) Pitx2
A) **Vascular endothelial growth factors** (**VEGFs**)
B) **Basic fibroblast growth factor** (**Fgf2**)
B) **Basic fibroblast growth factor** (**Fgf2**)
71
New cards
Angiogenesis requires which type of VEGF?
VEGF-A
72
New cards
Green tea contains a compound that inhibits VEGF, inhibiting angiogenesis, which may lead to tumor growth suppression and lower incidence of cancer (T/F).
True.
73
New cards
**Lymphatic vasculature**
Forms a separate circulatory system, important for draining fluid and transporting lymphocytes.
74
New cards
During lymphatic vasculature, sprouting from jugular vein in the neck forms what?
Lymphatic sacs.
75
New cards
During lymphatic vasculature, sprouting from the lymphatic sacks forms what?
Peripheral lymphatic.
76
New cards
Which factor specifies lymphatic lineage (and represses blood vessel lineage)?
A) VEGF-C
B) Fgf2
C) Prox1
D) Nodal
E) Pitx2
A) VEGF-C
B) Fgf2
C) Prox1
D) Nodal
E) Pitx2
C) **Prox1**
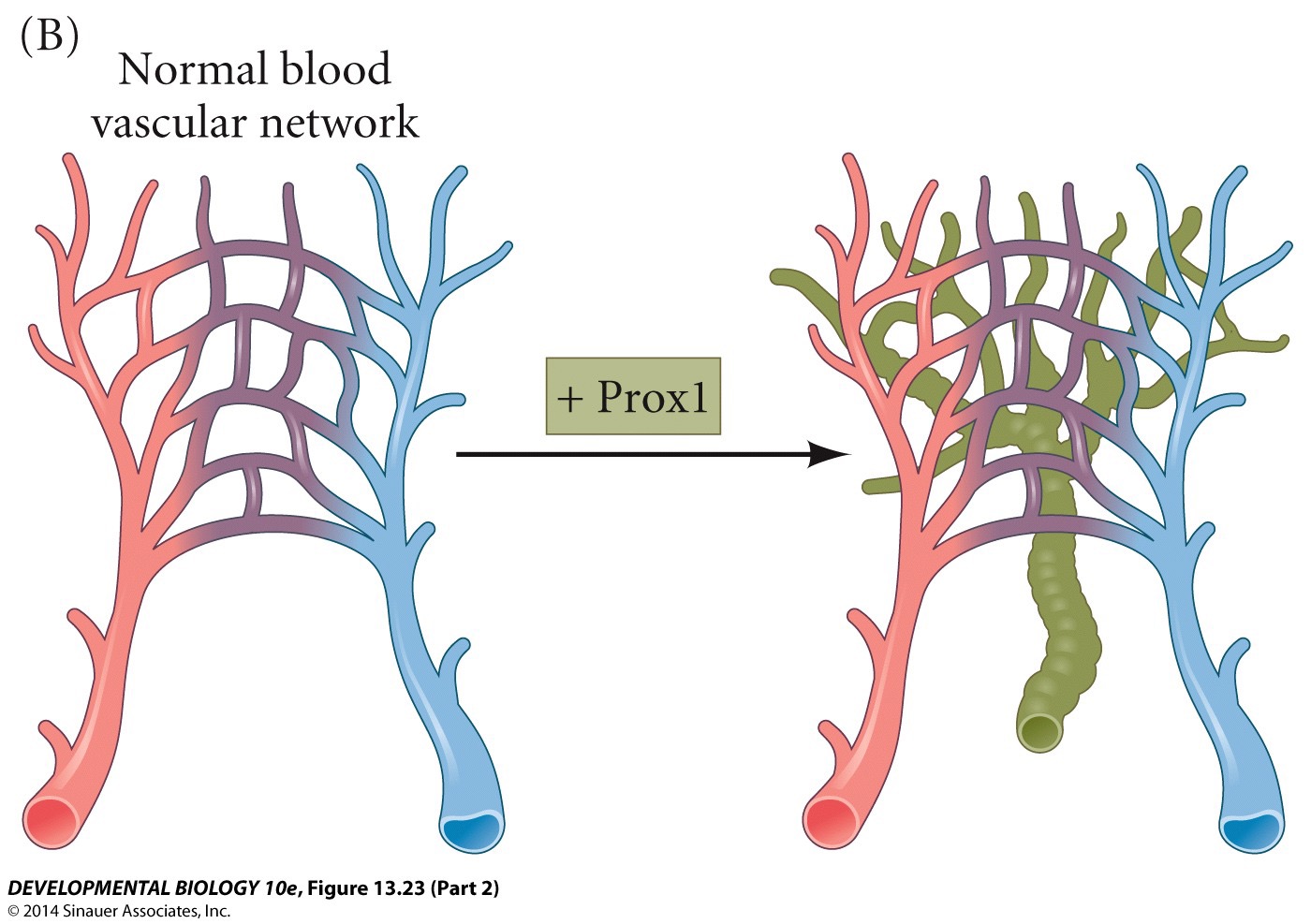
77
New cards
Which factors promotes lymphatic vessel growth?
A) VEGF-C
B) Fgf2
C) Prox1
D) Nodal
E) Pitx2
A) VEGF-C
B) Fgf2
C) Prox1
D) Nodal
E) Pitx2
A) **VEGF-C**
78
New cards
2\. In the early heart field, Retinoic Acid (RA) levels are highest in the _____________, which specifies the sinus venosus (inflow tracks) and atria.
A) Anterior
B) Posterior
C) Dorsal
D) Ventral
E) Ventral midline
A) Anterior
B) Posterior
C) Dorsal
D) Ventral
E) Ventral midline
B) Posterior
79
New cards
Limb development
→
80
New cards
Tetrapod limbs share a common pattern (T/F).
True. Similarities in bone numbers and positions of arms, legs, wings, flippers, etc.
81
New cards
**Stylopod** (**humerus/femur** in arm/leg)
Proximal structure of the tetrapod limb (closest to the body wall).
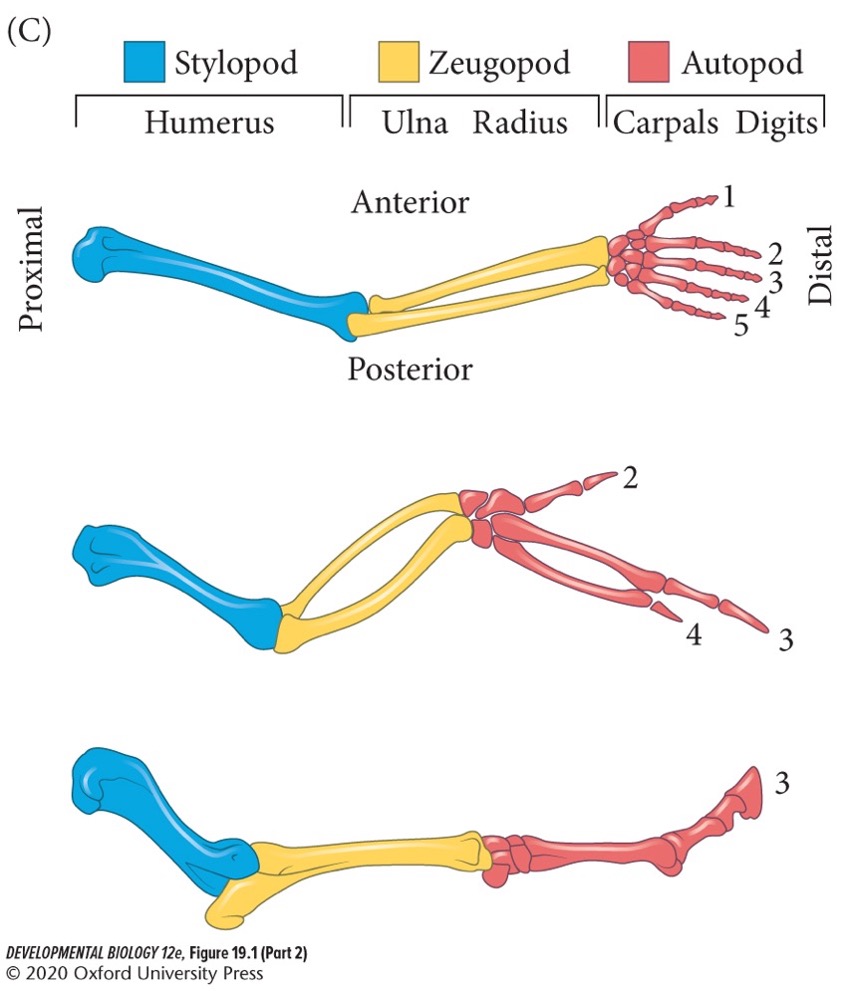
82
New cards
**Zeugopod** (**radius-ulna/tibia-fibula**)
Middle structure.
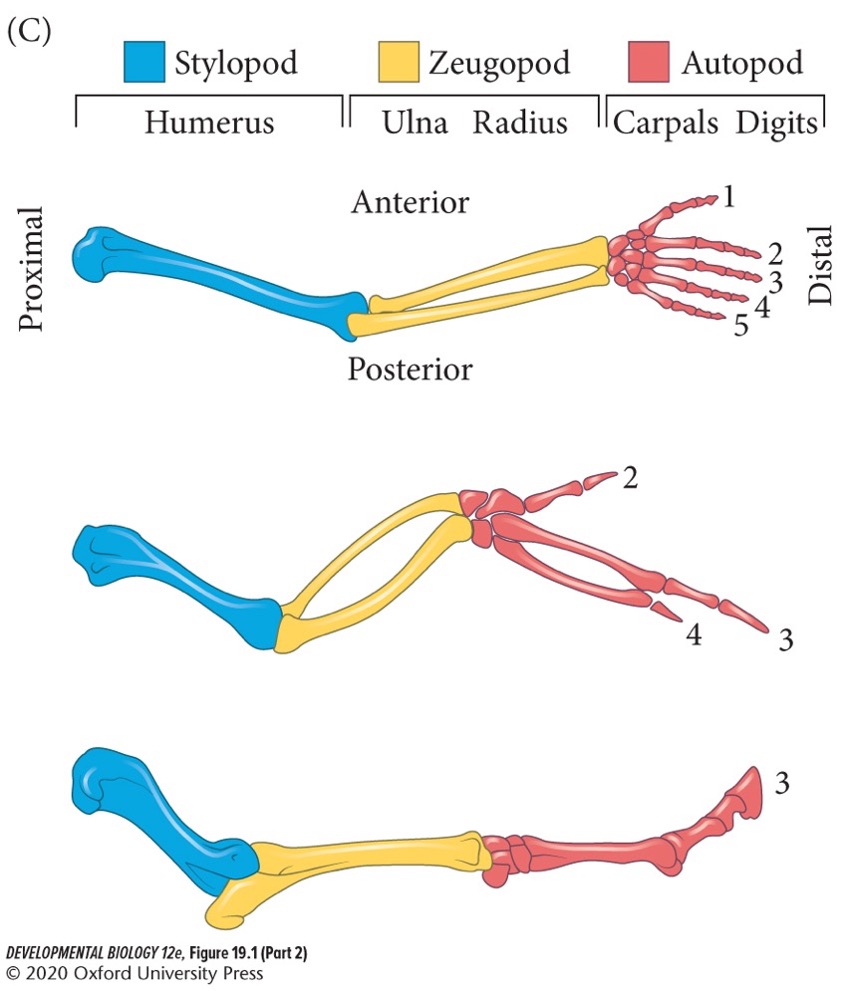
83
New cards
**Autopod** (**carpels-fingers/tarsals-toes**)
Distal structure farthest from the body.
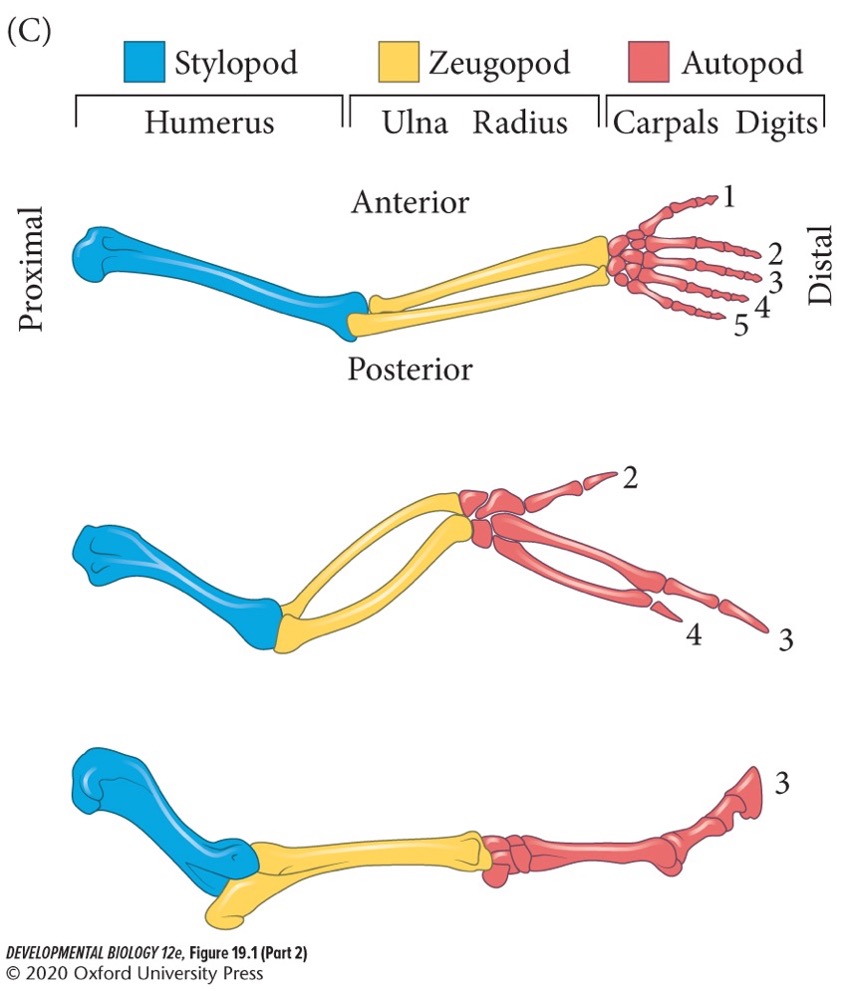
84
New cards
Positions of bones are conserved and show similar morphologies among species (T/F).
False. Positions of bones are conserved but show vastly different morphologies among species.
85
New cards
What are the three axes of the limbs?
* **Proximal-distal** axis
* **Anterior-posterior** axis
* **Dorsal-ventral** axis
* **Anterior-posterior** axis
* **Dorsal-ventral** axis
86
New cards
Proximal-distal axis of the limb
Proximal = closest to the body
Distal = farthest of the body (fingers)
Distal = farthest of the body (fingers)
87
New cards
**Anterior-posterior** axis of the of the llimbs
Anterior = thumb and big toe
Posterior = pinkie and little toe
Posterior = pinkie and little toe
88
New cards
**Dorsal-ventral** axis of the limb
Dorsal = knuckles
Ventral = palm
Ventral = palm
89
New cards
When does limb development begin?
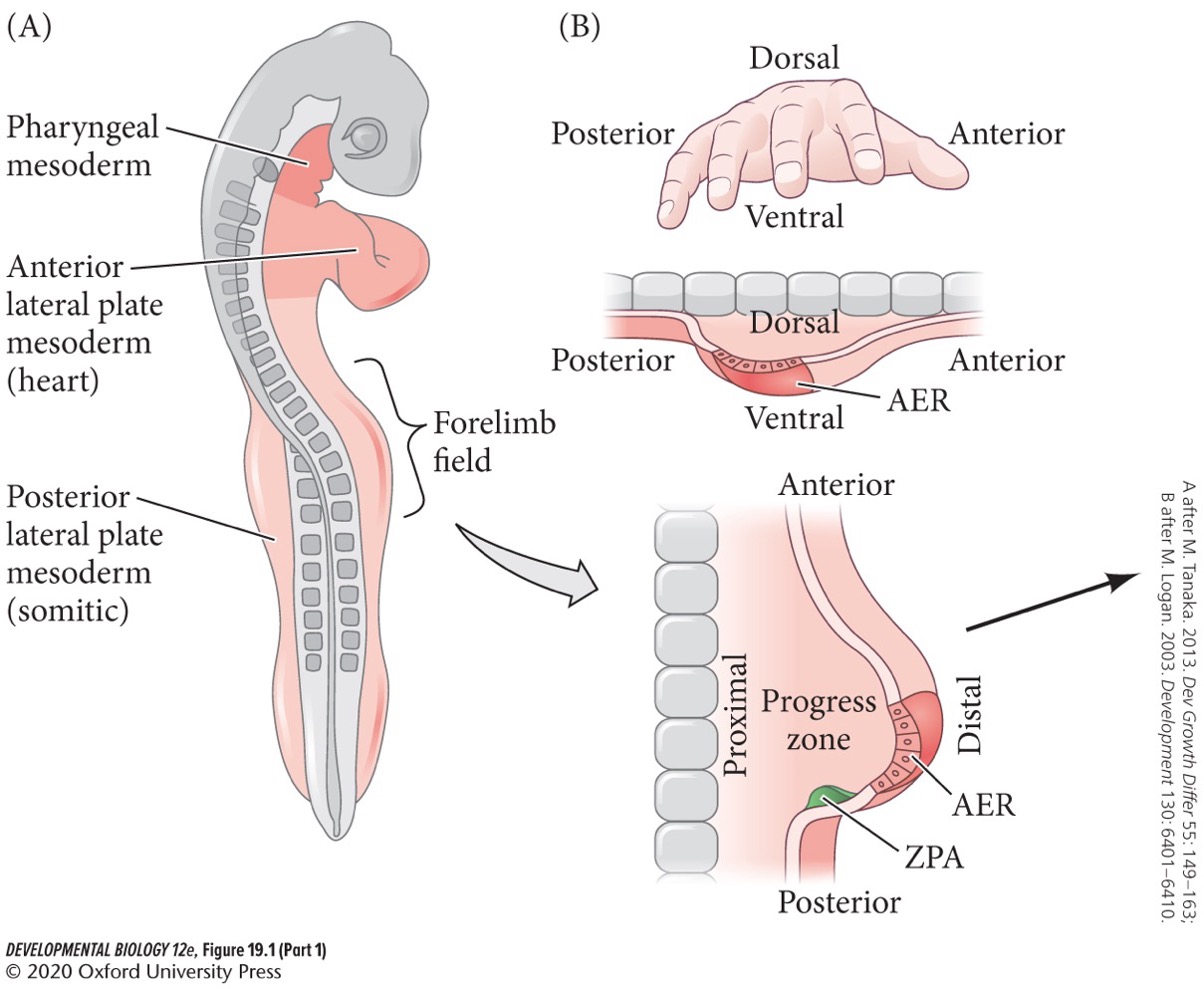
When mesenchyme cells migrate from the somatic layer of the limb field lateral plate mesoderm and from the somites at the same anterior-posterior level.
90
New cards
During the starts of limb development, mesenchymal cells accumulate under the ectodermal tissue to form a circular bulge, called:
**Limb bud**
91
New cards
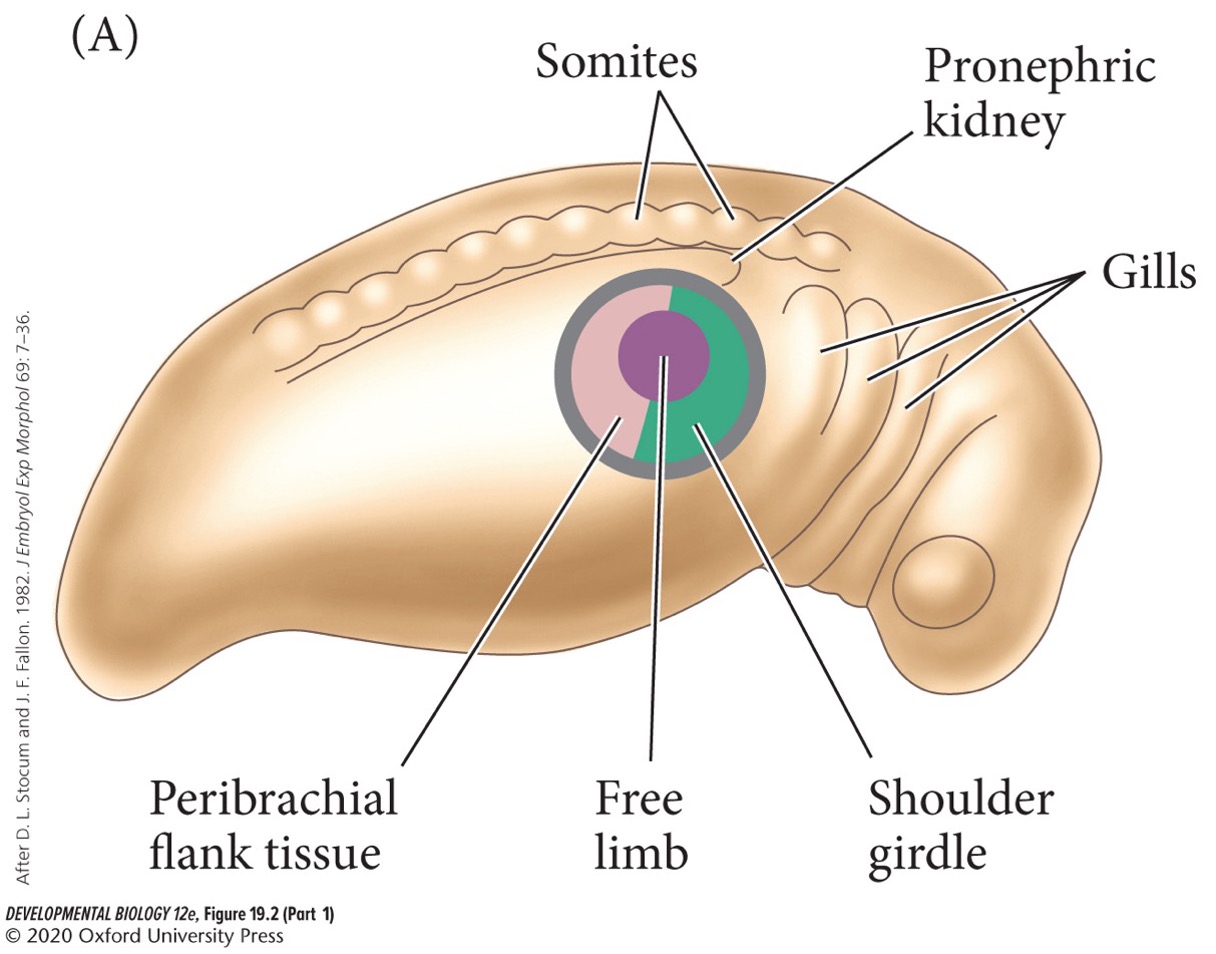
Many different cells are capable of forming limbs (T/F).
False. Only certain cells are capable of forming limbs. Removing these cells prevents limb formation, and transplanting these cells results in limb formation at the new location.
92
New cards
Limb field
Represents all the cells in the embryo capable of forming limbs. It is much larger than the area destined to form the limb, but if limb-specified cells are removed, surrounding limb field cells will form the limb.
93
New cards
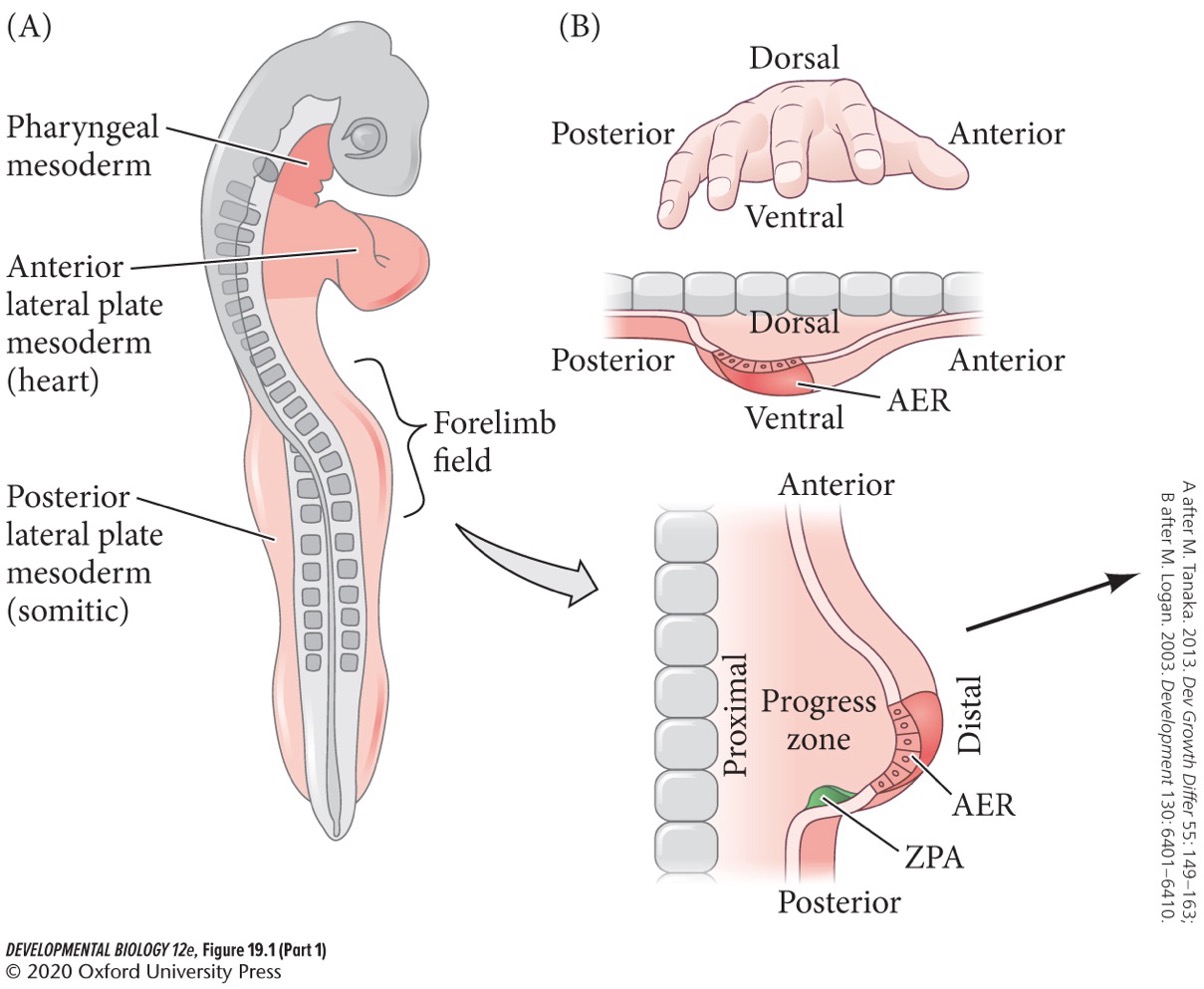
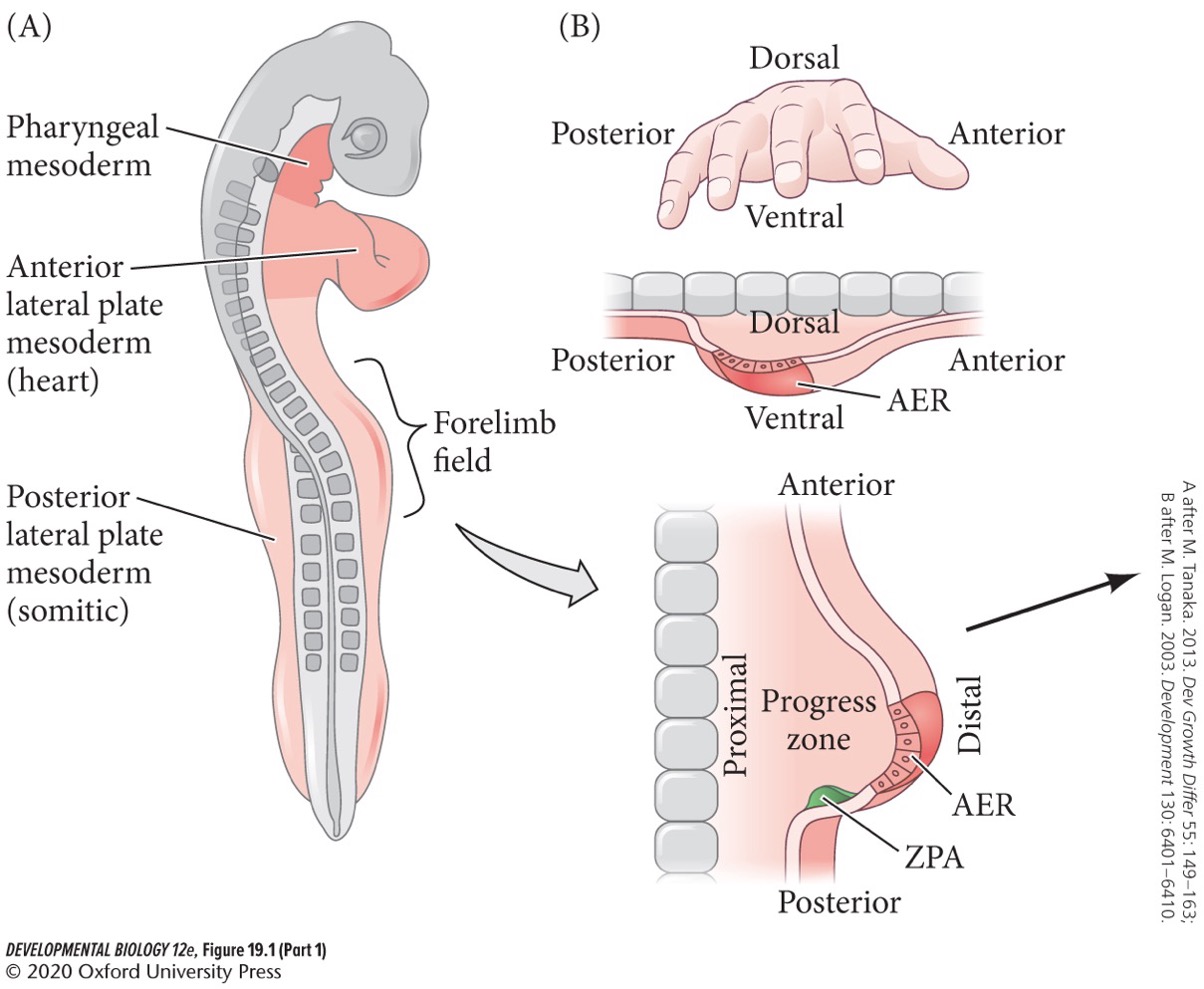
The early limb bud contains which three functionally distinct domains?
* **Progress zone** (**PZ**)
* **Zone of polarizing activity** (**ZPA**)
* **Apical ectodermal ridge** (**AER**)
* **Zone of polarizing activity** (**ZPA**)
* **Apical ectodermal ridge** (**AER**)
94
New cards
Progress zone (PZ)
The highly proliferative mesenchyme that fuels limb bud growth. It determines proximal-distal fate.
95
New cards
Zone of polarizing activity (ZPA)
The most posterior region of the progress zone. It pattens cell fates along the anterior-posterior axis.
96
New cards
Apical ectodermal ridge (AER)
Thickening of the ectoderm at the apex of the developing limb bud.
97
New cards
Hox genes specify the identity of a limb along the proximal-distal axis. Which two Hox genes specify stylopod?
* Hox9
* Hox10
* Hox10
98
New cards
Which Hox gene specify zeugopod?
* Hox11
99
New cards
Which two Hox genes specify autopod?
* Hox12
* Hox13
* Hox13
100
New cards
A mouse with Hox10 knockouts lack what?
Femur.