THROMBOSIS
1/6
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
| 1. Define Thrombosis
Thrombosis is the formation of a solid mass (thrombus) from blood constituents within the vascular system during life. It is distinct from postmortem clotting. |
| 2. Predisposing Factors (Virchow's Triad) | Virchow's Triad describes the three primary abnormalities leading to thrombosis:
Endothelial Injury: Dominant influence; leads to exposure of vWF/collagen and downregulation of anticoagulants
Abnormal Blood Flow: Turbulence (arterial) and Stasis (venous) disrupt laminar flow, bringing platelets into contact with endothelium.
Hypercoagulability: Genetic (e.g., Factor V Leiden) or Acquired (e.g., cancer, pregnancy) tendency to clot.
| 3. Arterial vs. Venous Thrombosis | Arterial Thrombi:
① blood flow ② sites ③ morphology ④ effect ⑤ thrombogeneis
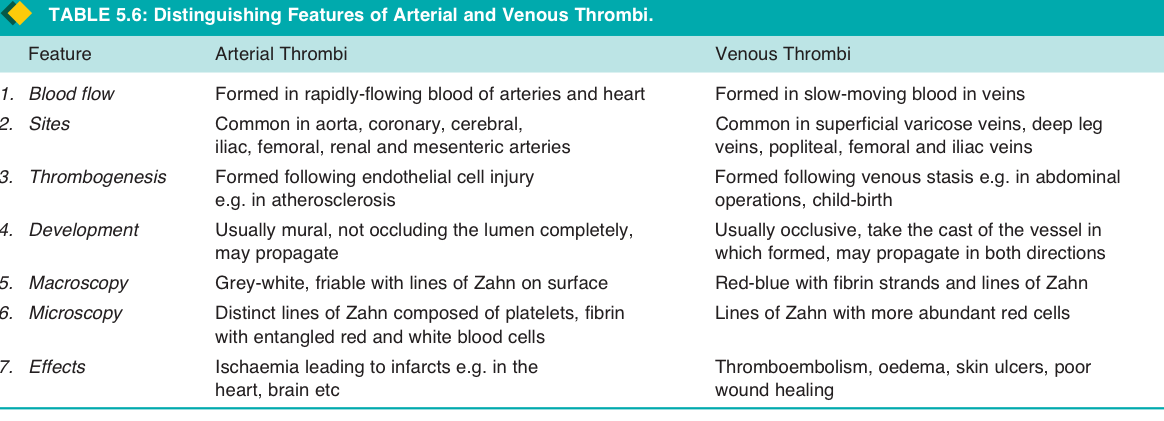
| 4. Morphology of Thrombus |
Venous thrombosis
at the site of stasis
Rarely occlusive
Common at lower limb
Arterial thrombosis
at the site of endothelial injury or cardiac thrombosis
Occlusive
Propagation
arterial thrombosis—> retrograde
Venous thrombosis —> in direction of blood flow
Line of Zahn
Lamination line of pale of fibrin and platelet deposition with dark red RBC layer
Post Mortem thrombosis
soft gelatinous and rubbery
No lamination line
Red RBC deposition dominate
| 5. Fate of Thrombus |
1. Dissolution: Recent thrombi may dissolve via fibrinolysis.
Organization & Recanalization: Ingrowth of endothelial cells and fibroblasts; capillaries form to restore blood flow.
Propagation: Thrombus accumulates more platelets/fibrin and enlarges
Embolism: Thrombus dislodges and travels to other sites (e.g., lungs).
| 6. Clinical Effects
• Superficial Venous Thrombosis: Causes local congestion, pain, and edema; rarely embolizes.
deep venous thrombosis: usually in popliteal, femoral and iliac artery, lead to pulmonary embolism
General effects: • Vascular Obstruction—>Leads to ischemia and infarction of the supplied tissue.
Type of thrombosis
Mural thrombosis
at heart chamber or aortic lumen
Abdominal aortic aneurysm
Vegatation
at heart valve
Rheumatic heart disease
Arterial thrombosis
At site of ndothelial or cardiac injury, turbulence
Cerebral, coronary and aorta
Venous thrombosis
at site of stasis
Popliteal, femoral and iliac vein