anatomy midterm study guide
1/180
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
181 Terms
Anatomical Position
Hands at the sides with palms facing forward and feet together
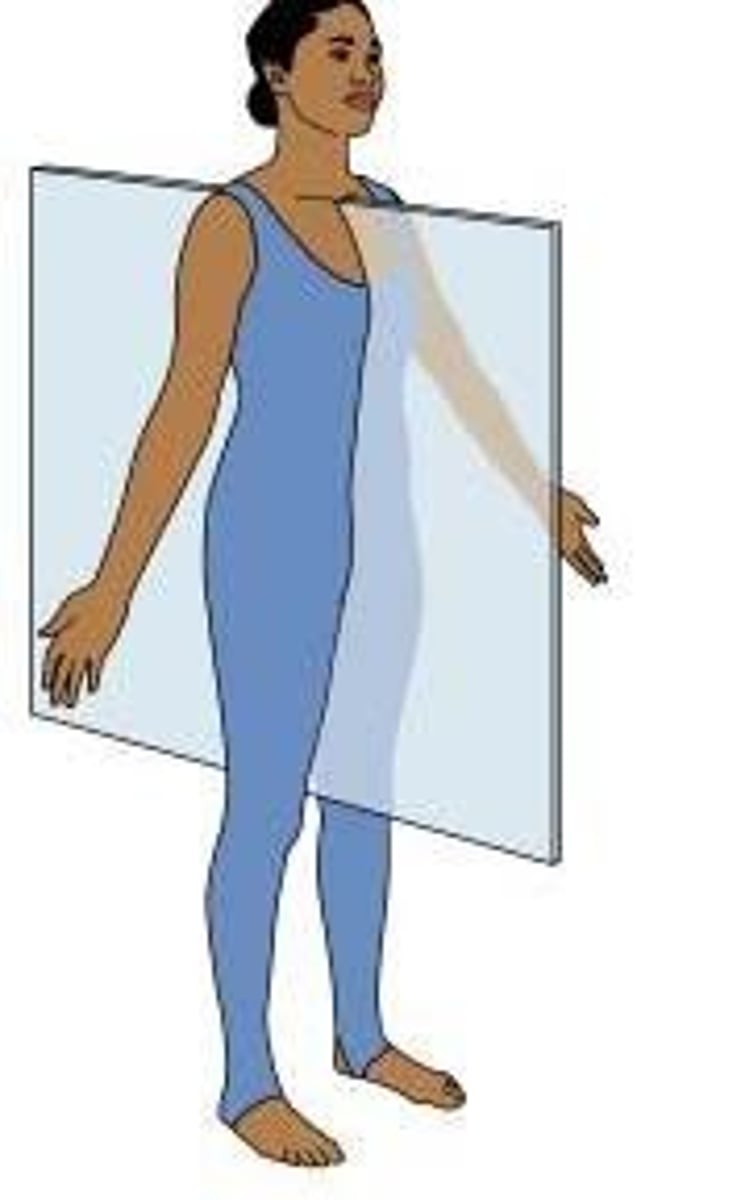
Sagittal Plane
divides body into left and right
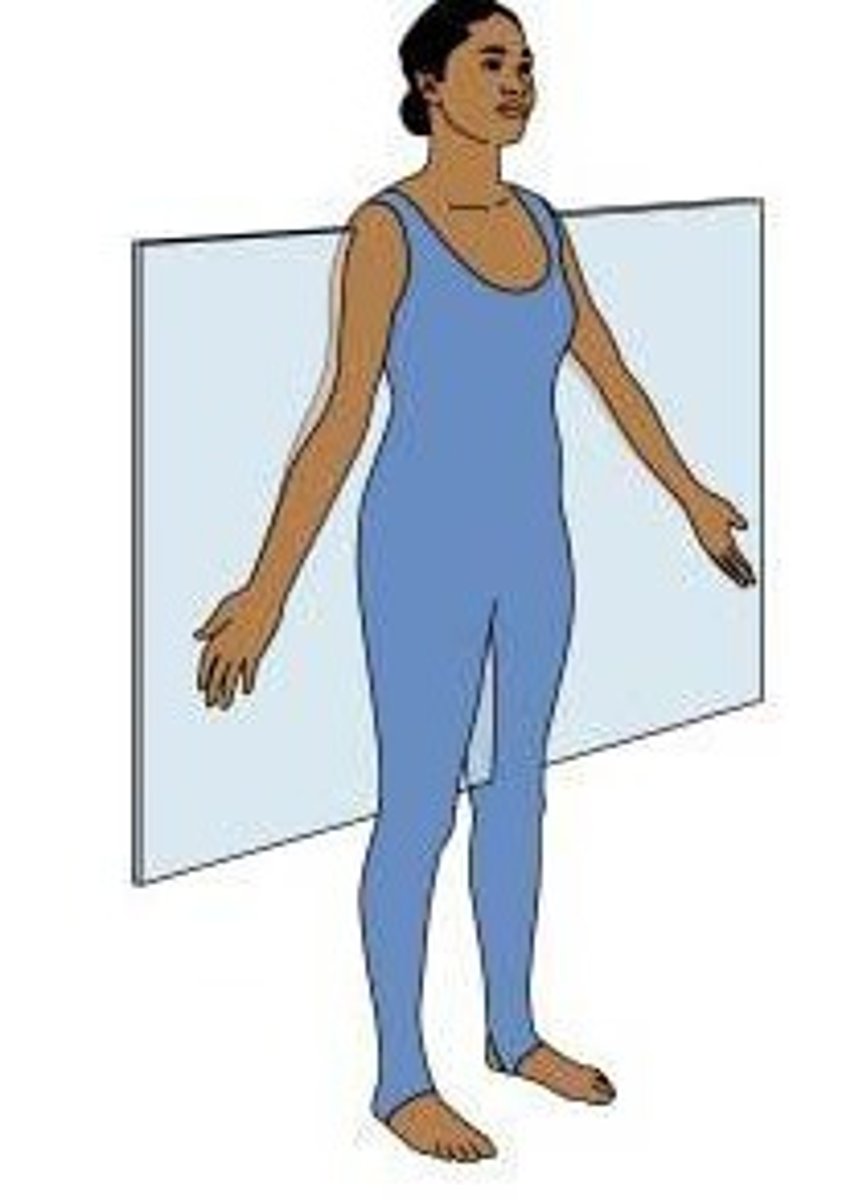
Frontal/Coronal Plane
divides the body into anterior and posterior parts
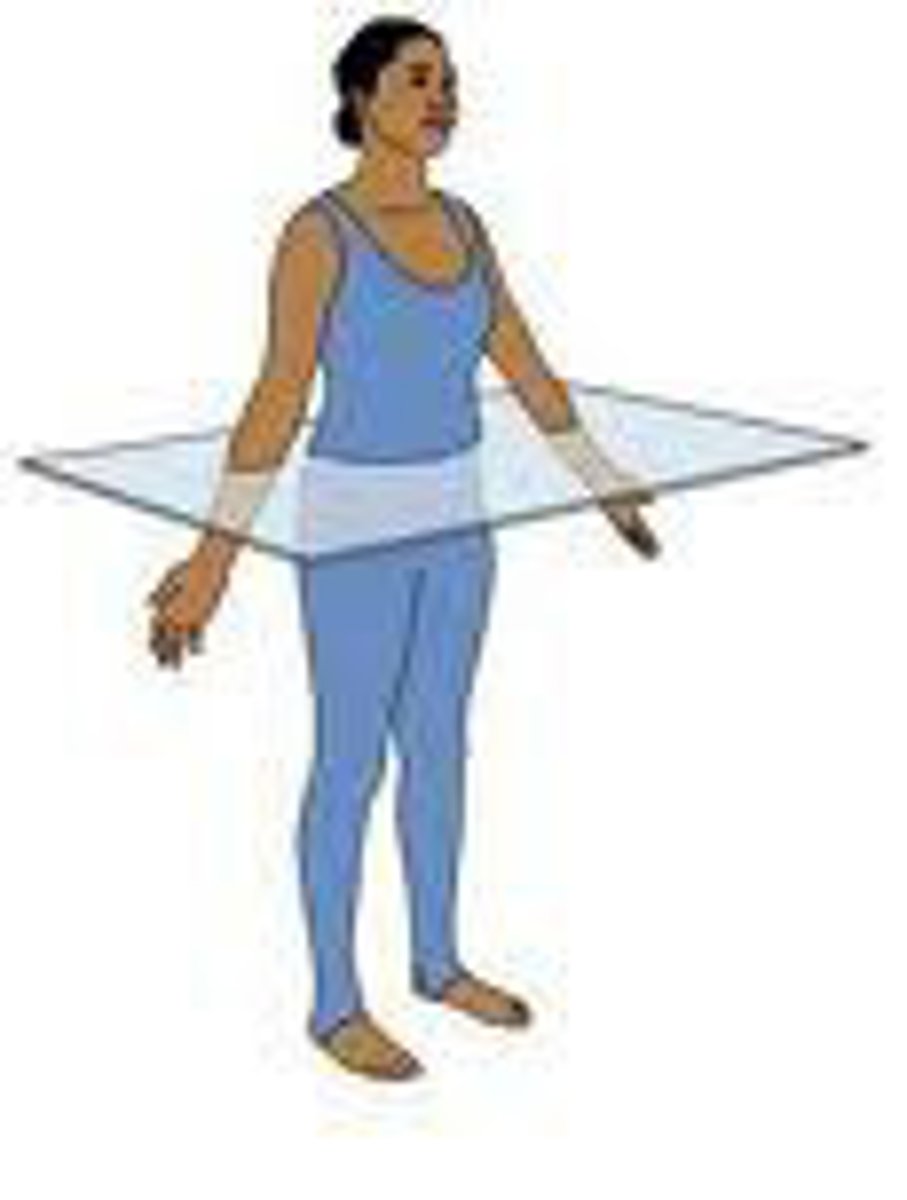
Transverse Plane
divides the body into superior and inferior parts
Anterior/Ventral
front of the body
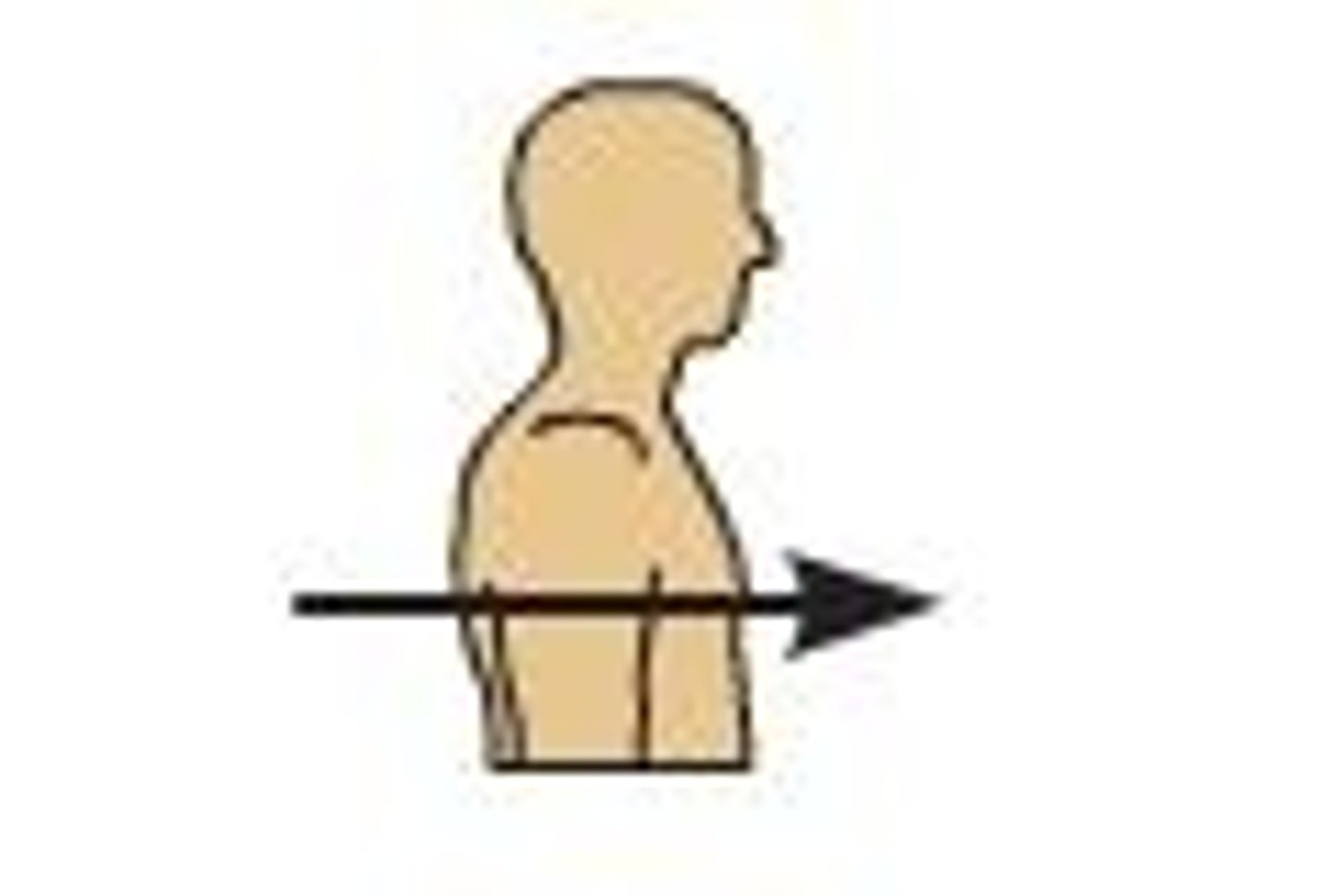
Posterior/Dorsal
back of body
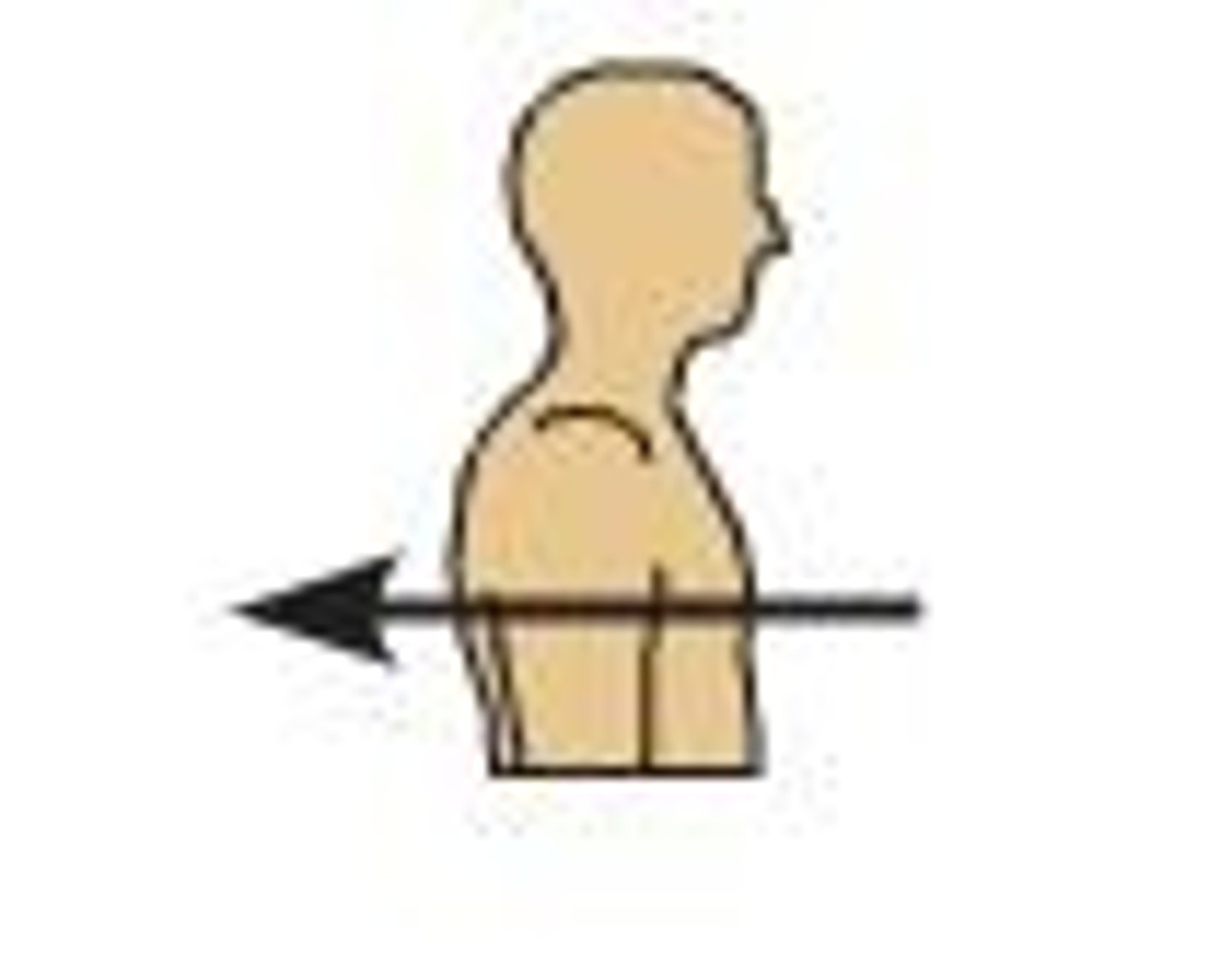
Medial
Toward the midline of the body
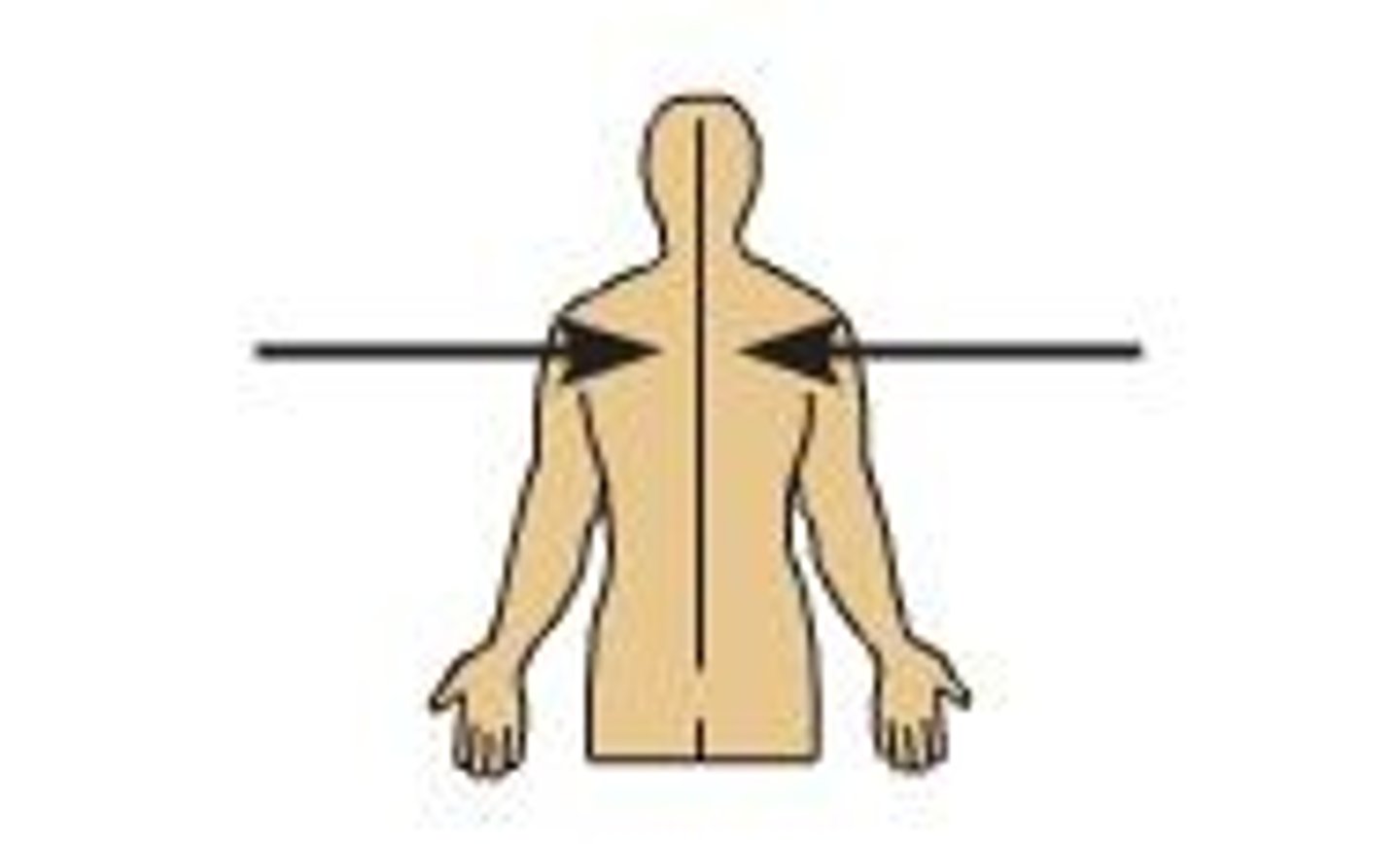
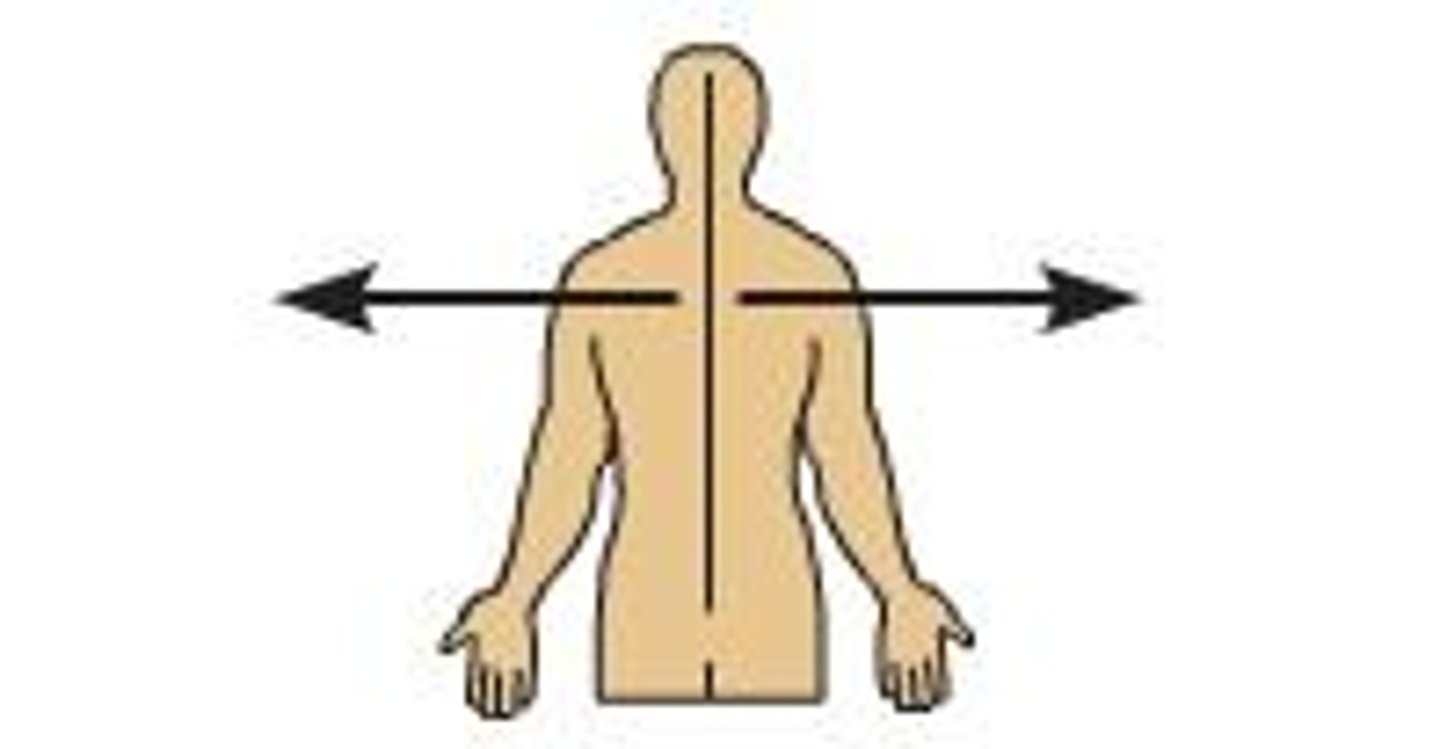
Lateral
Away from the midline of the body
Superior
above
Inferior
below
Proximal
Nearer to the trunk of the body
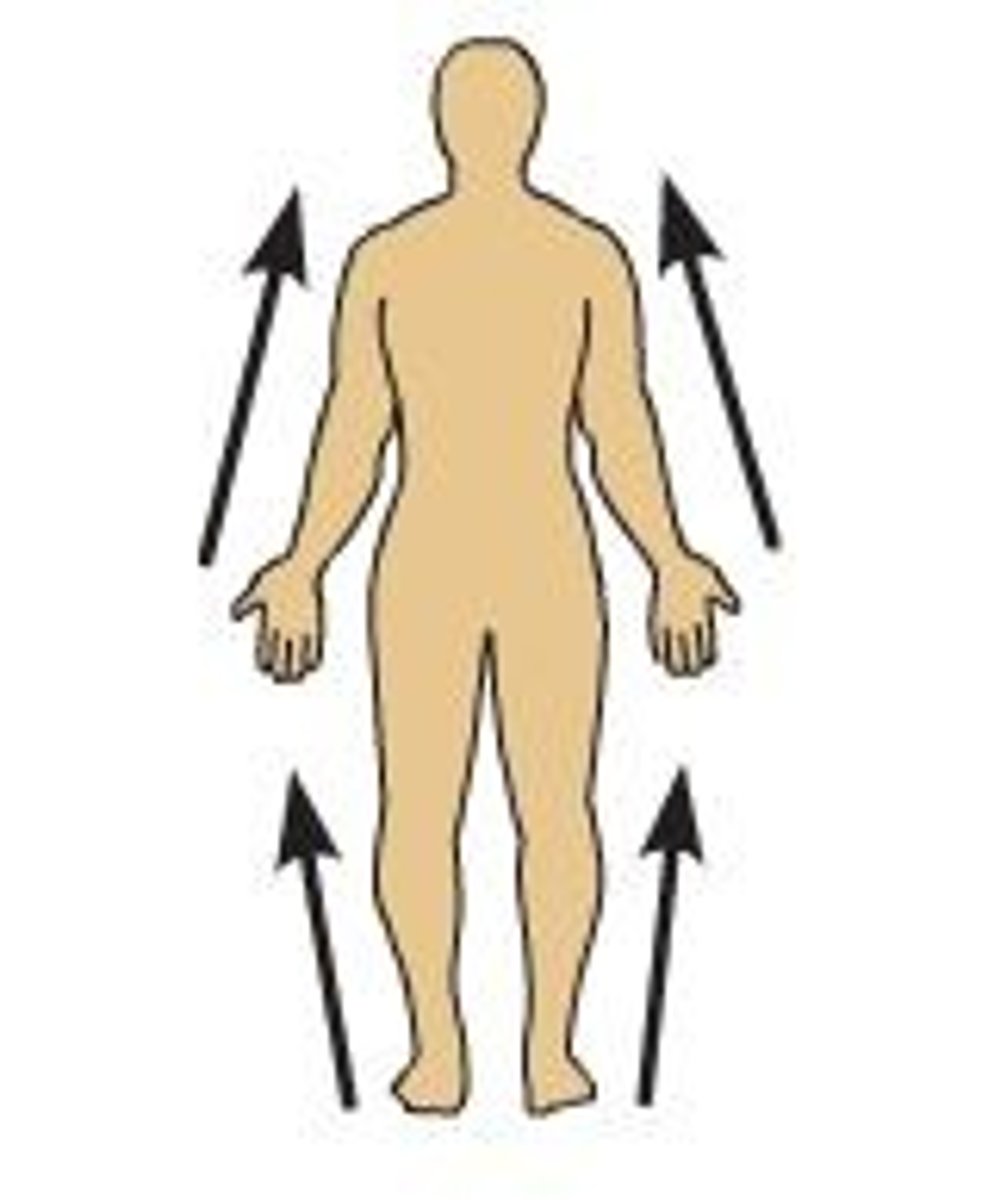
Distal
Farther from the trunk of the body
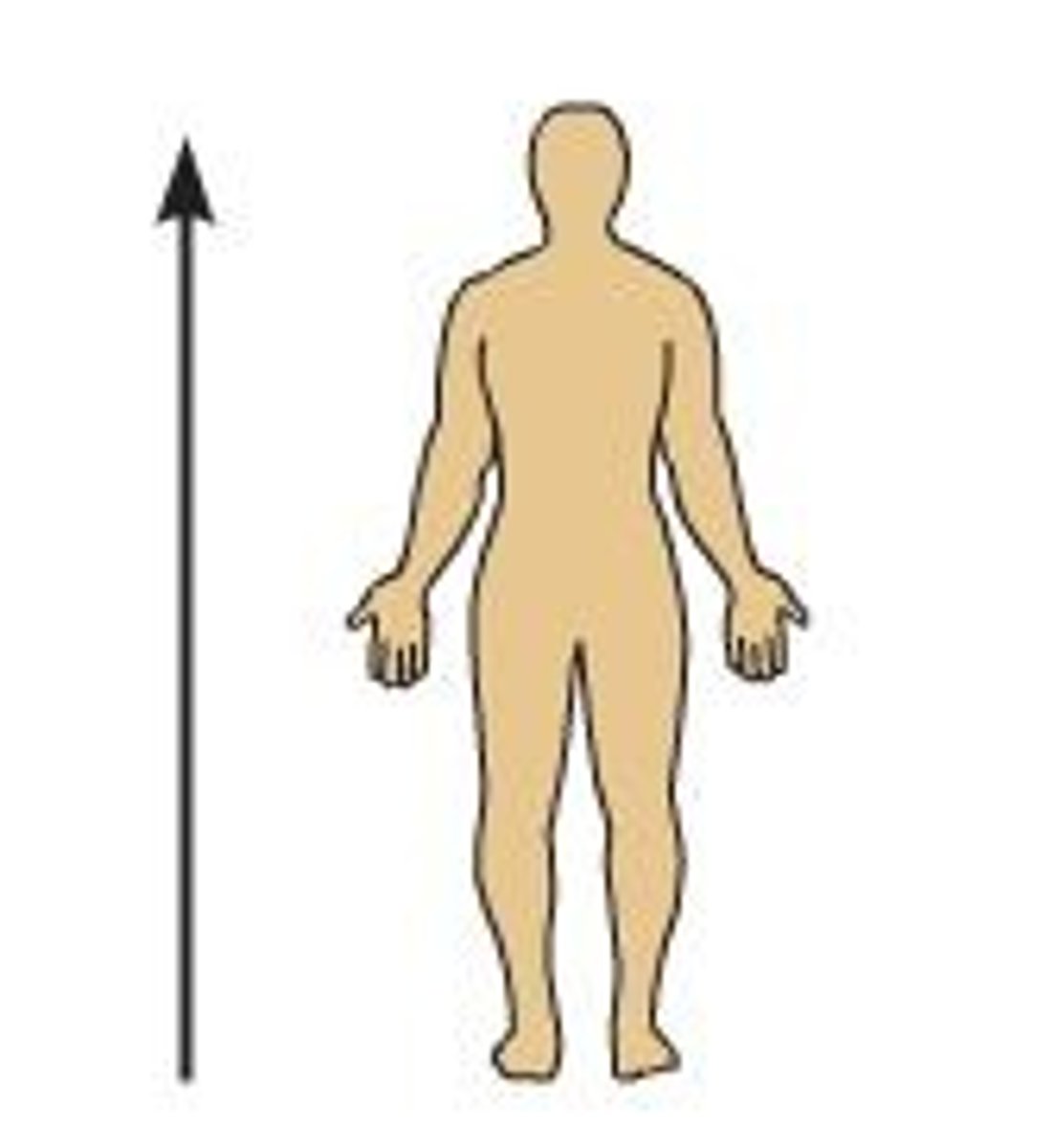
Cranial
toward the head
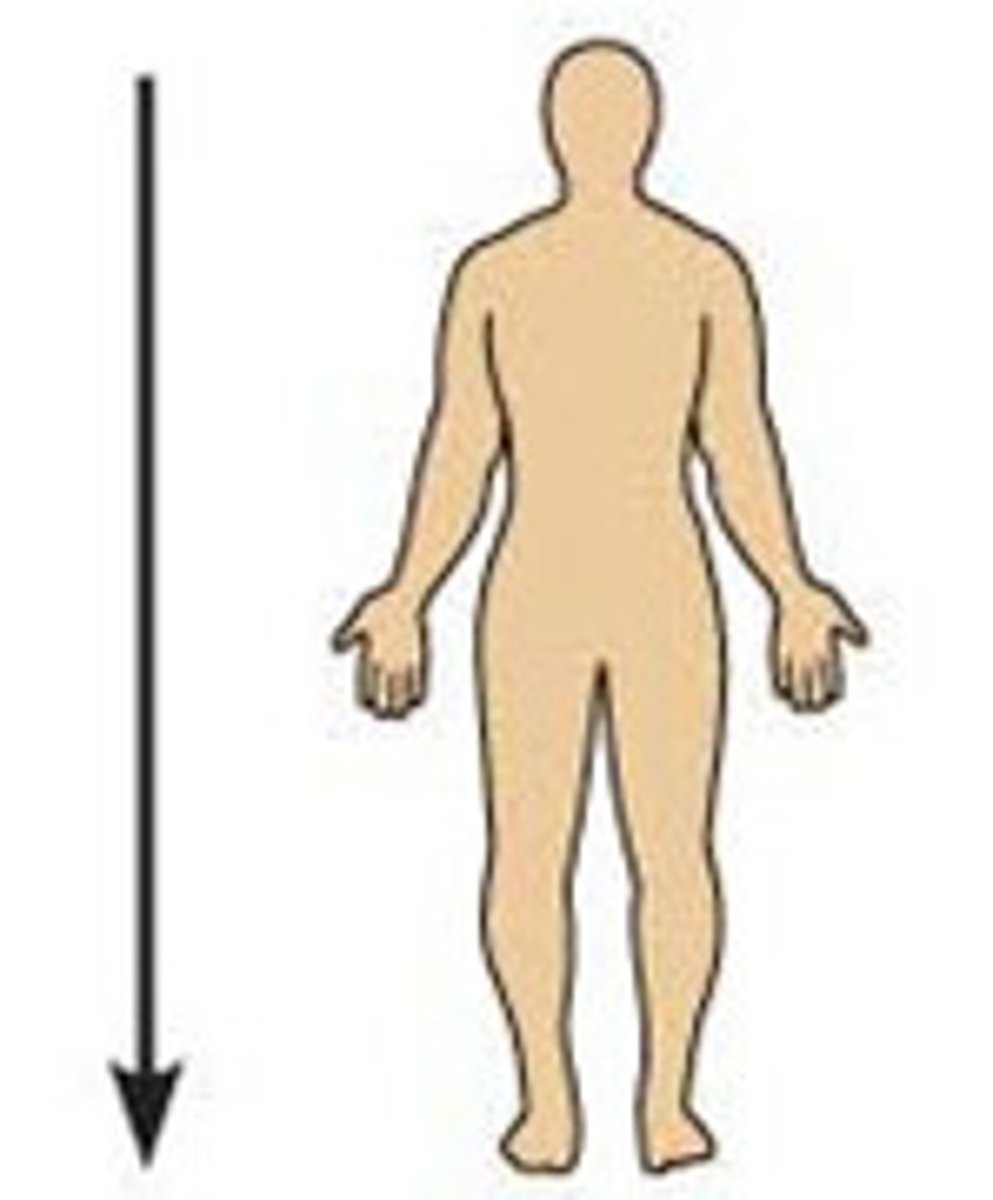
Caudal
toward the tail
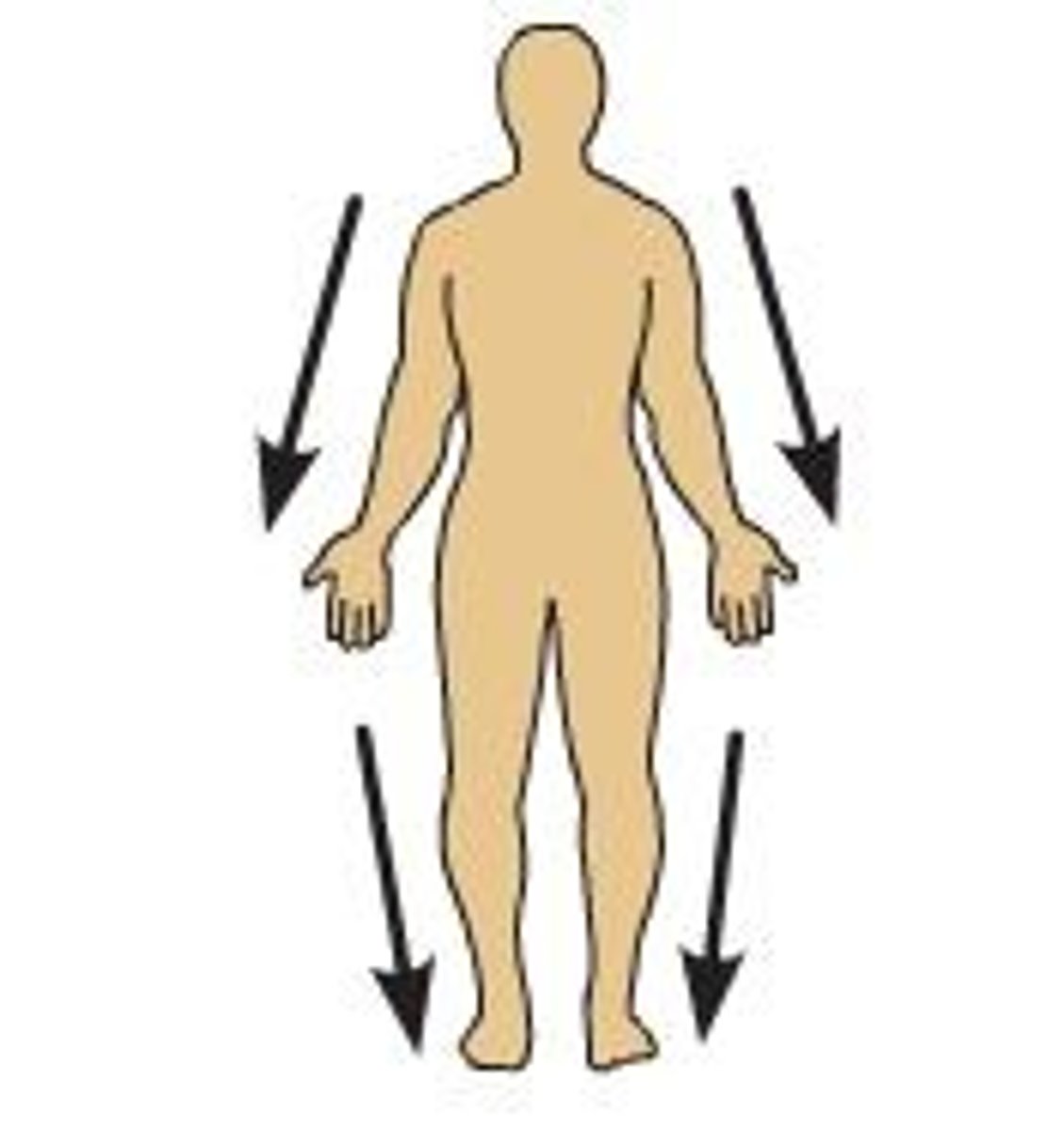
Superficial
near the surface
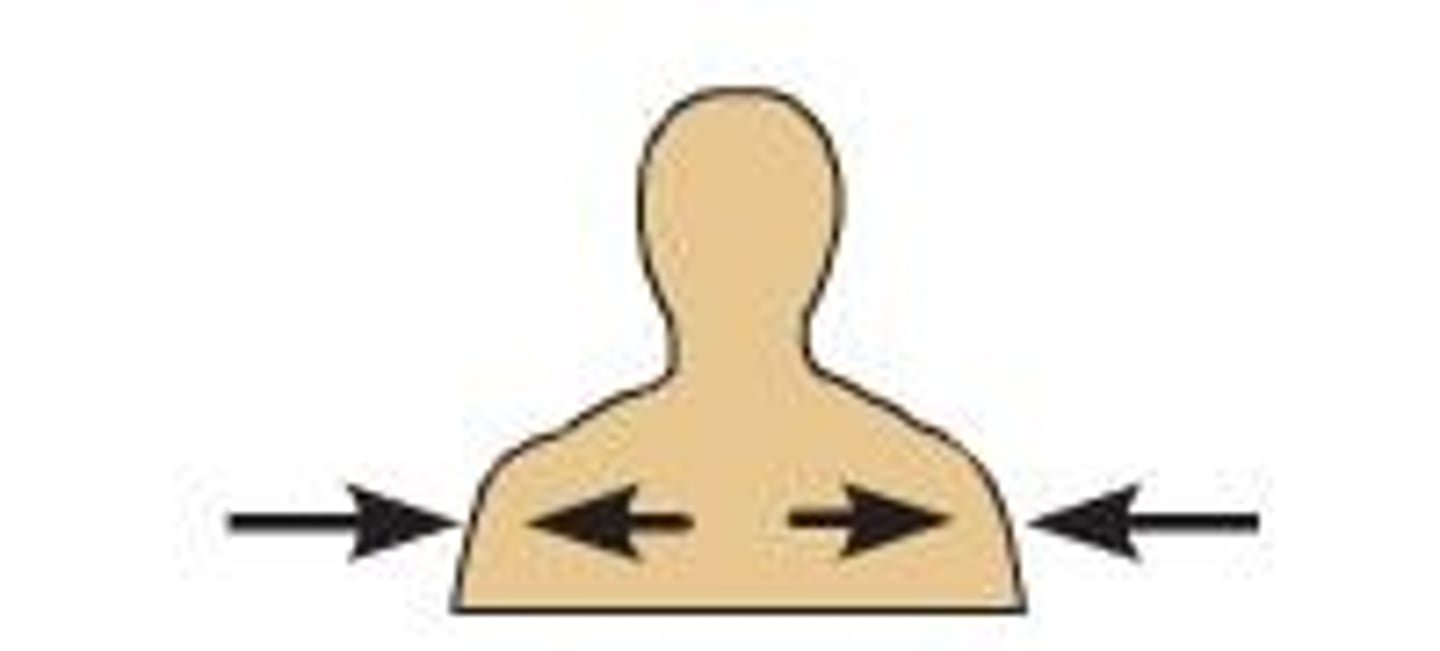
Deep
away from the surface
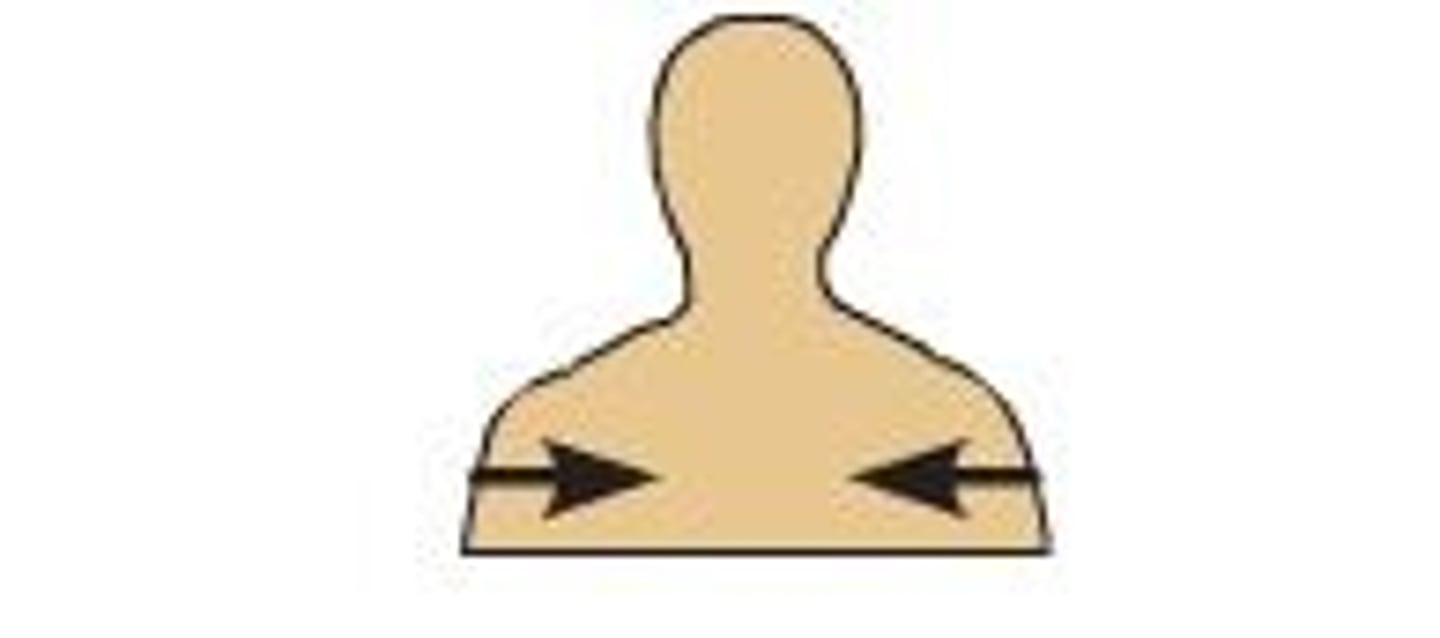
axillary
pertaining to the armpit
carpal
pertaining to the wrist
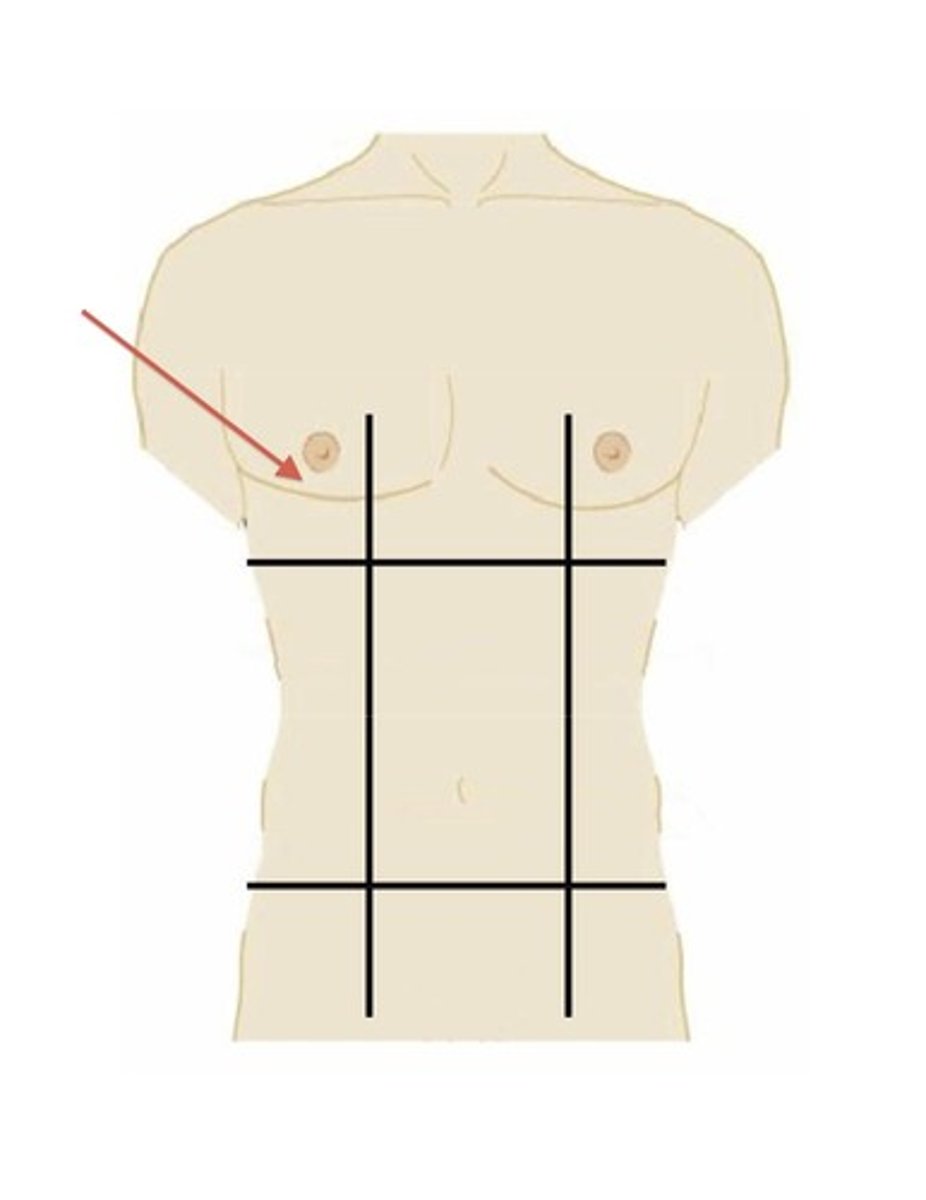
right hypochondriac region
upper right region
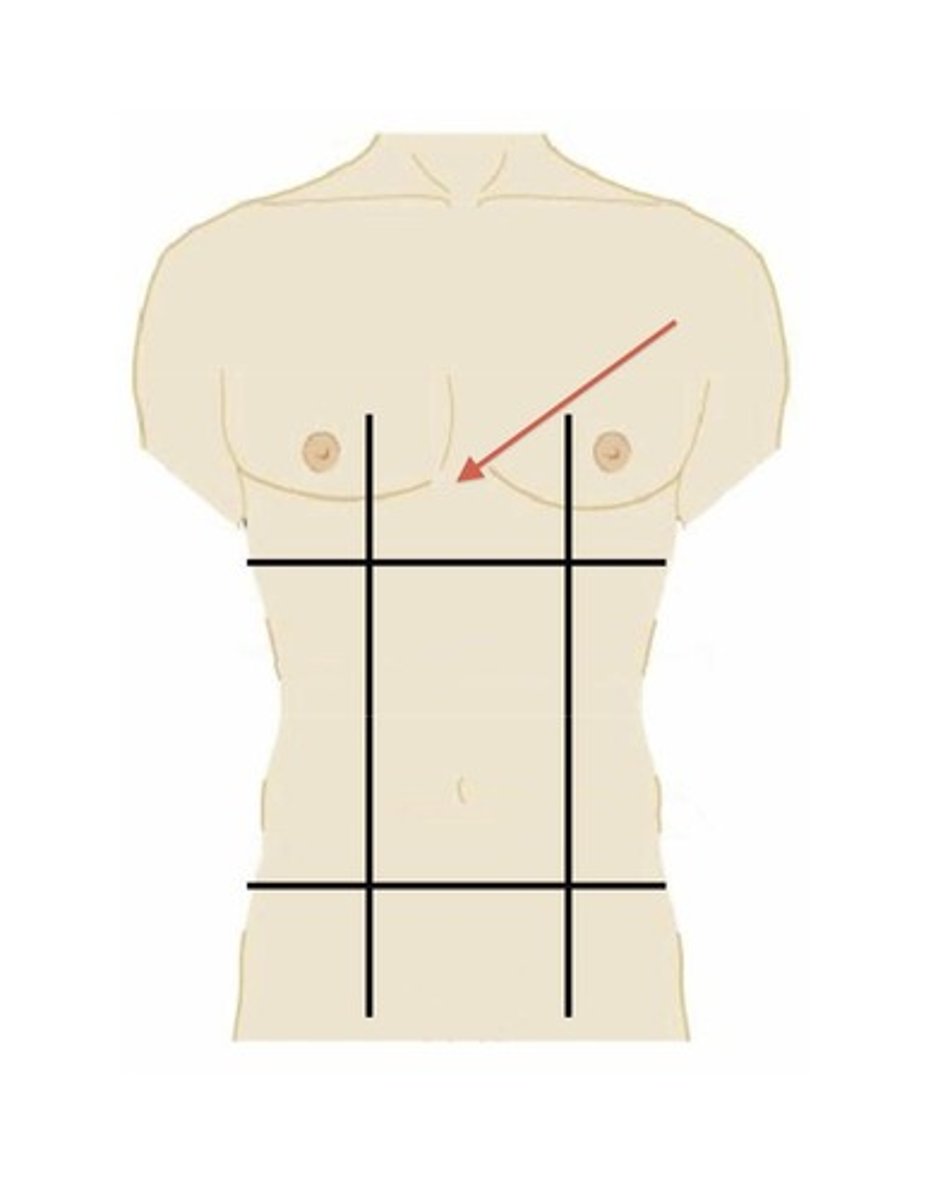
epigastric region
upper middle region
left hypochondriac region
top left region
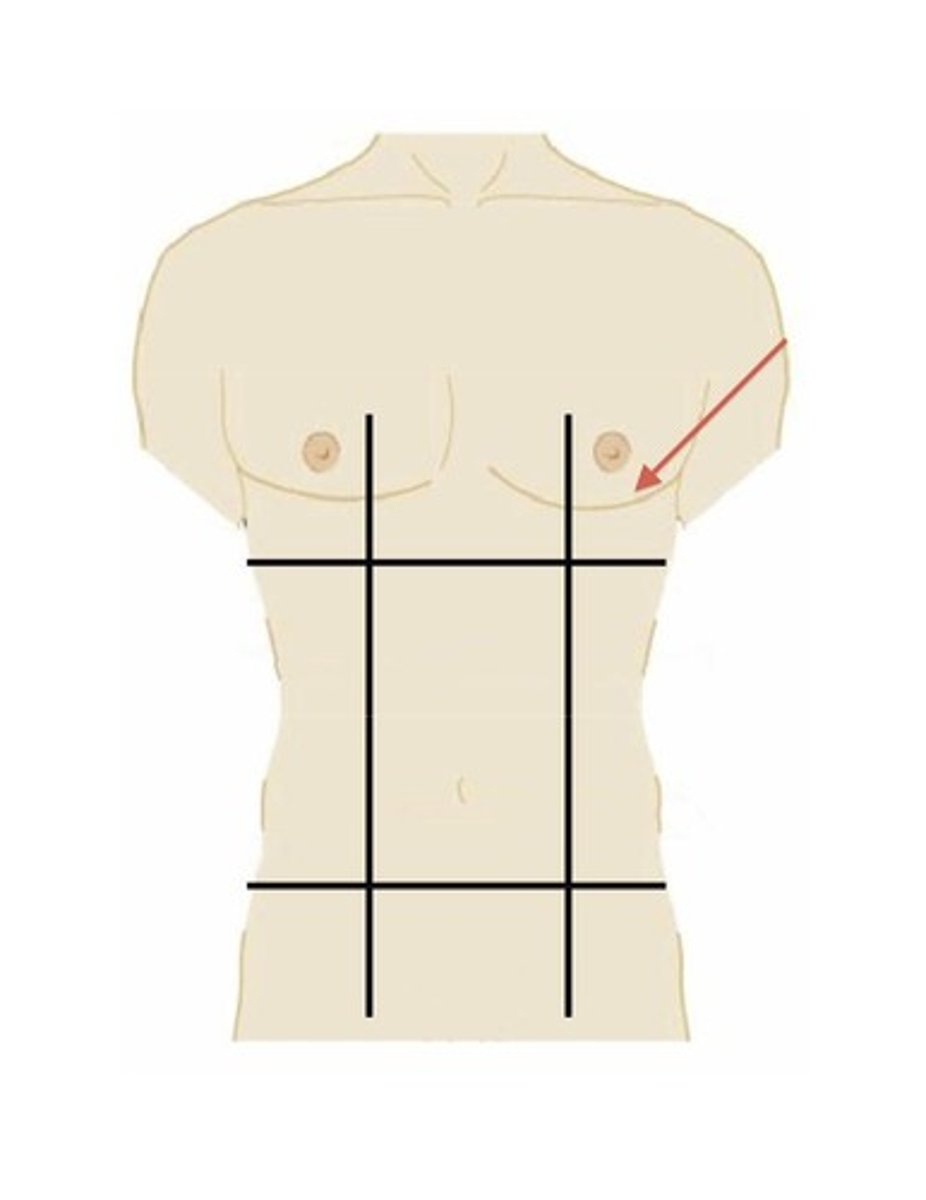
right lumbar region
middle right region
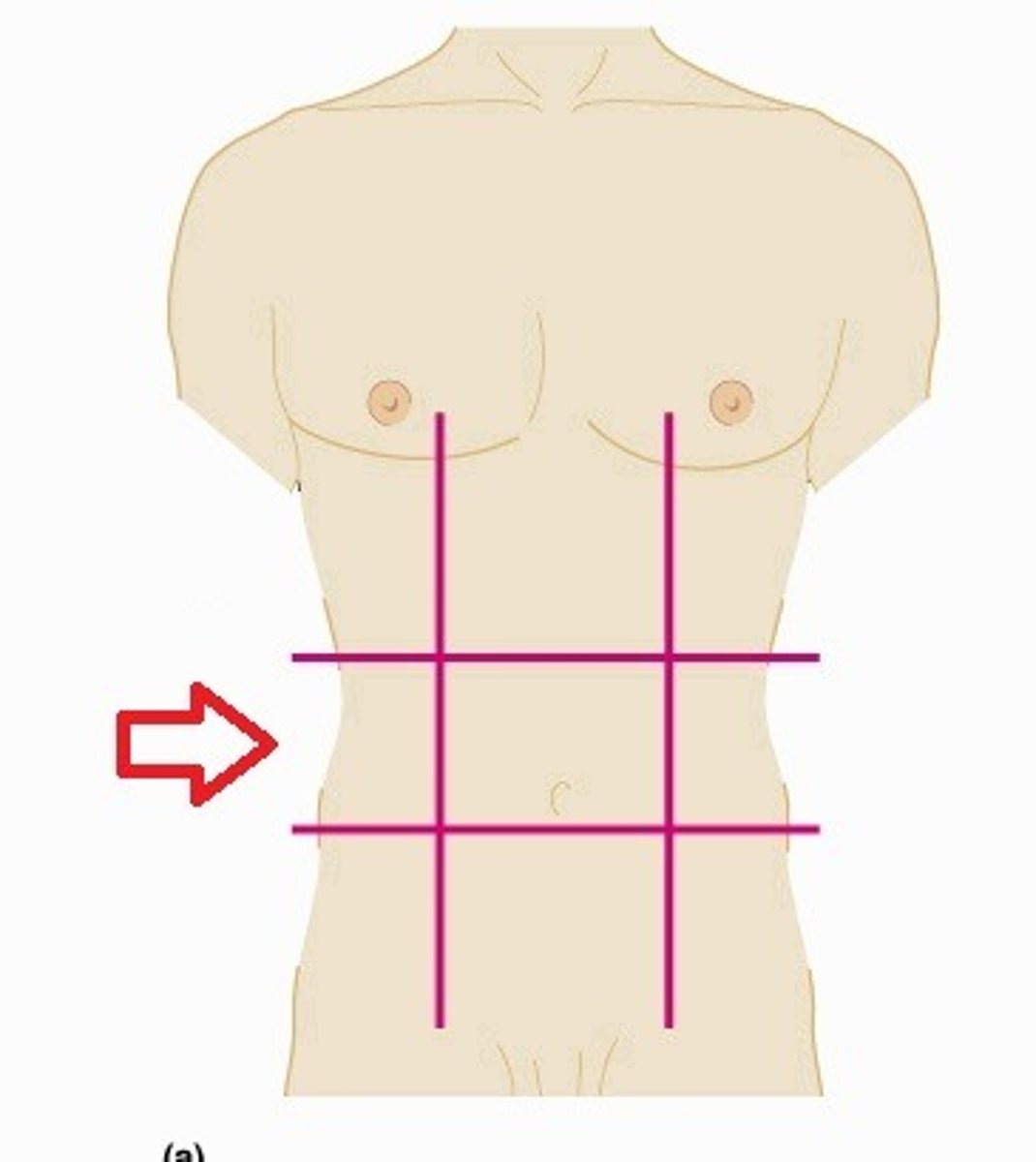
Umbilical region
The centermost region, includes the umbilicus
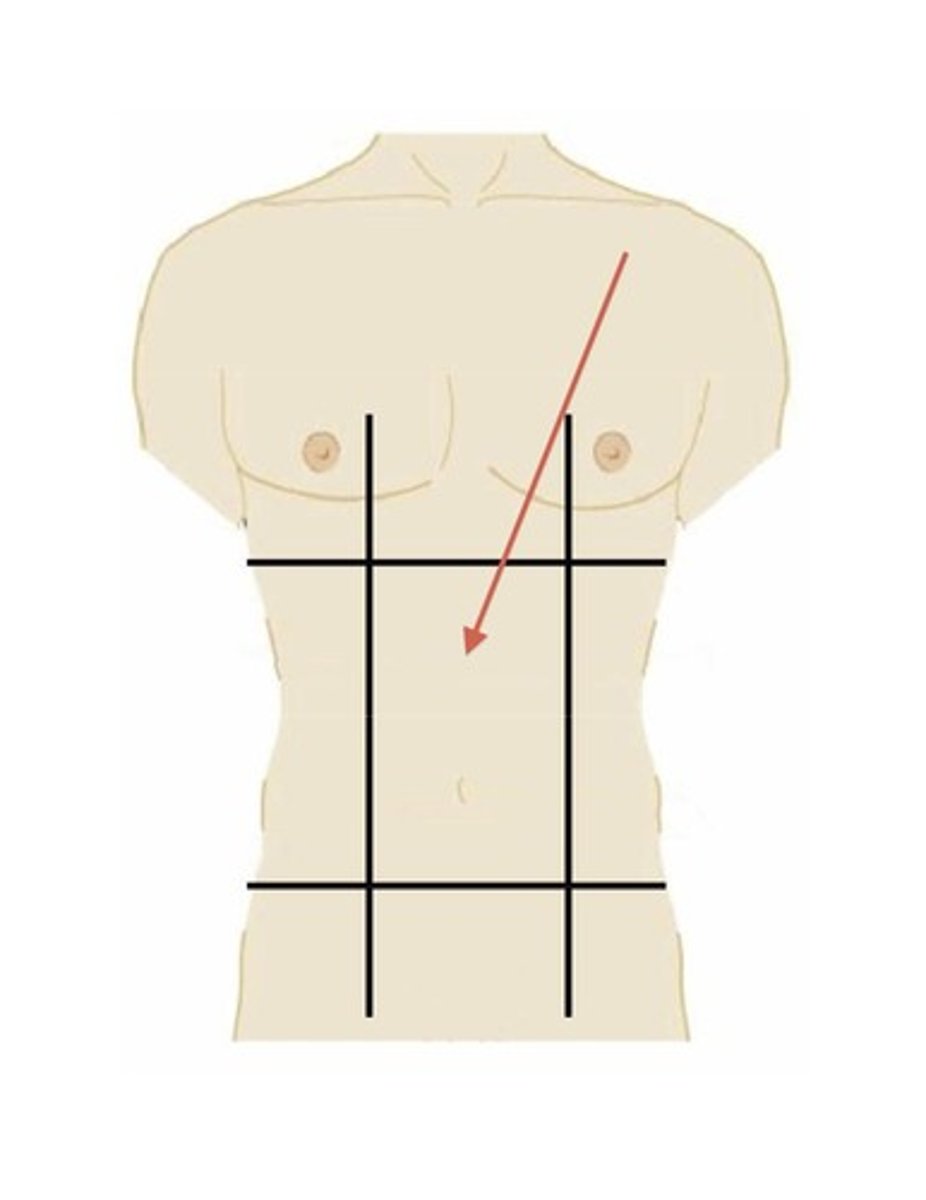
left lumbar region
left middle region
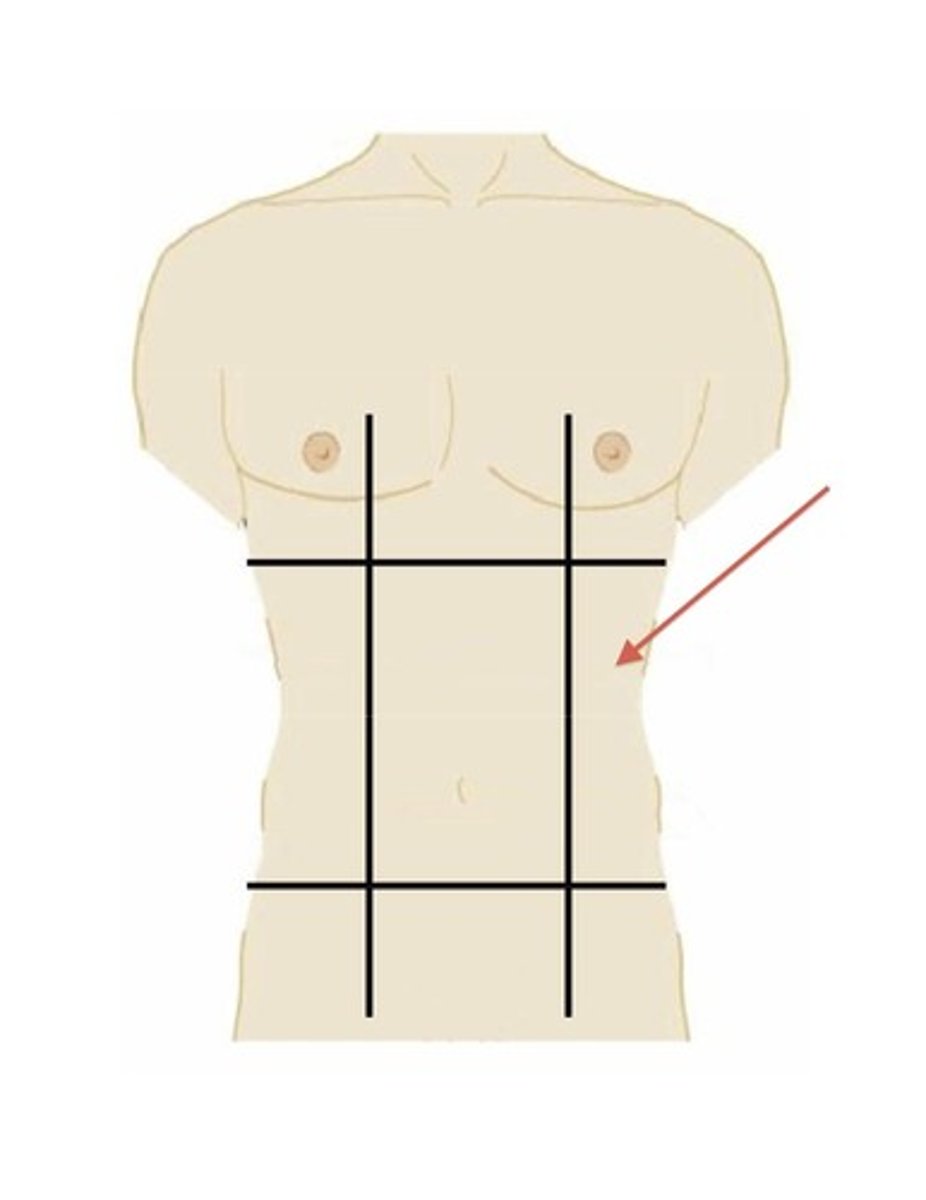
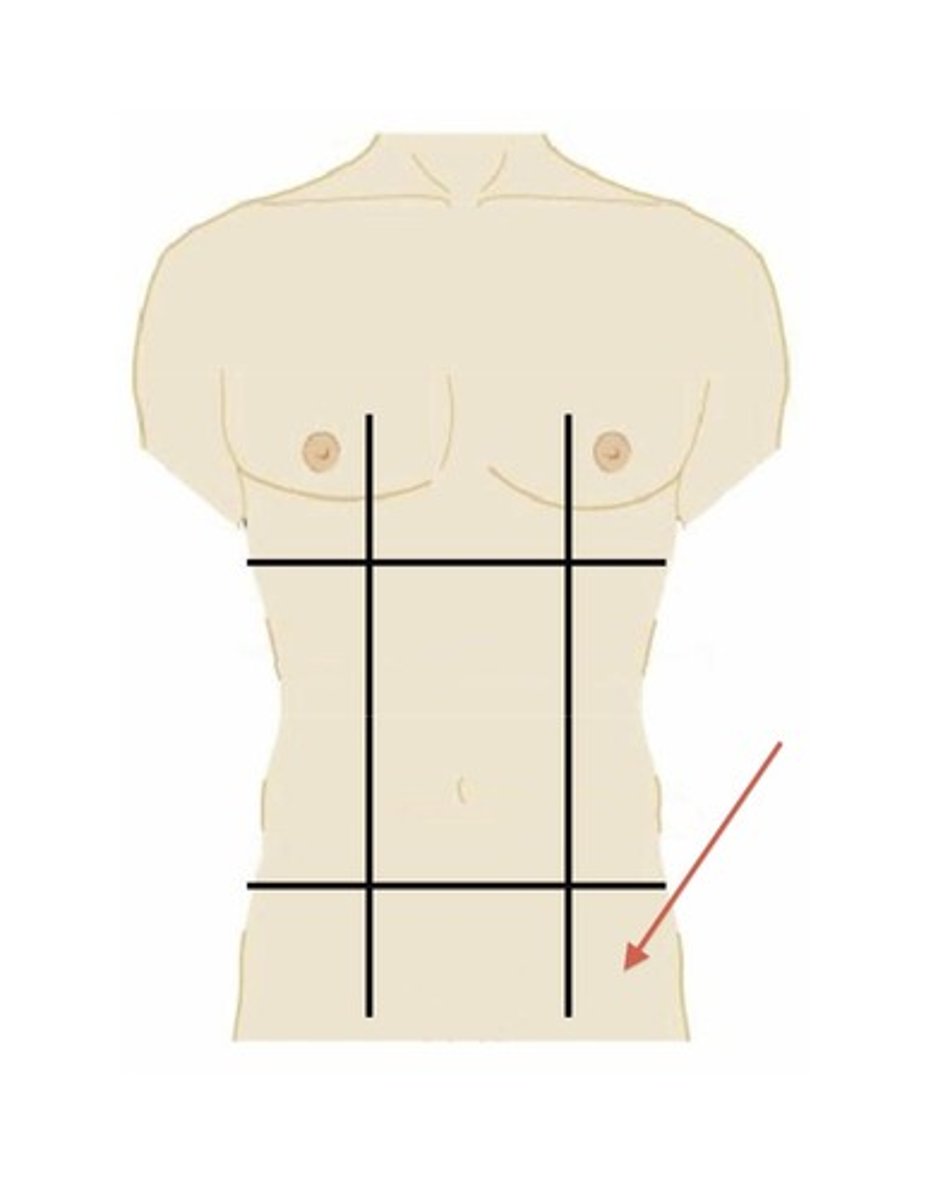
right iliac region
lower right region
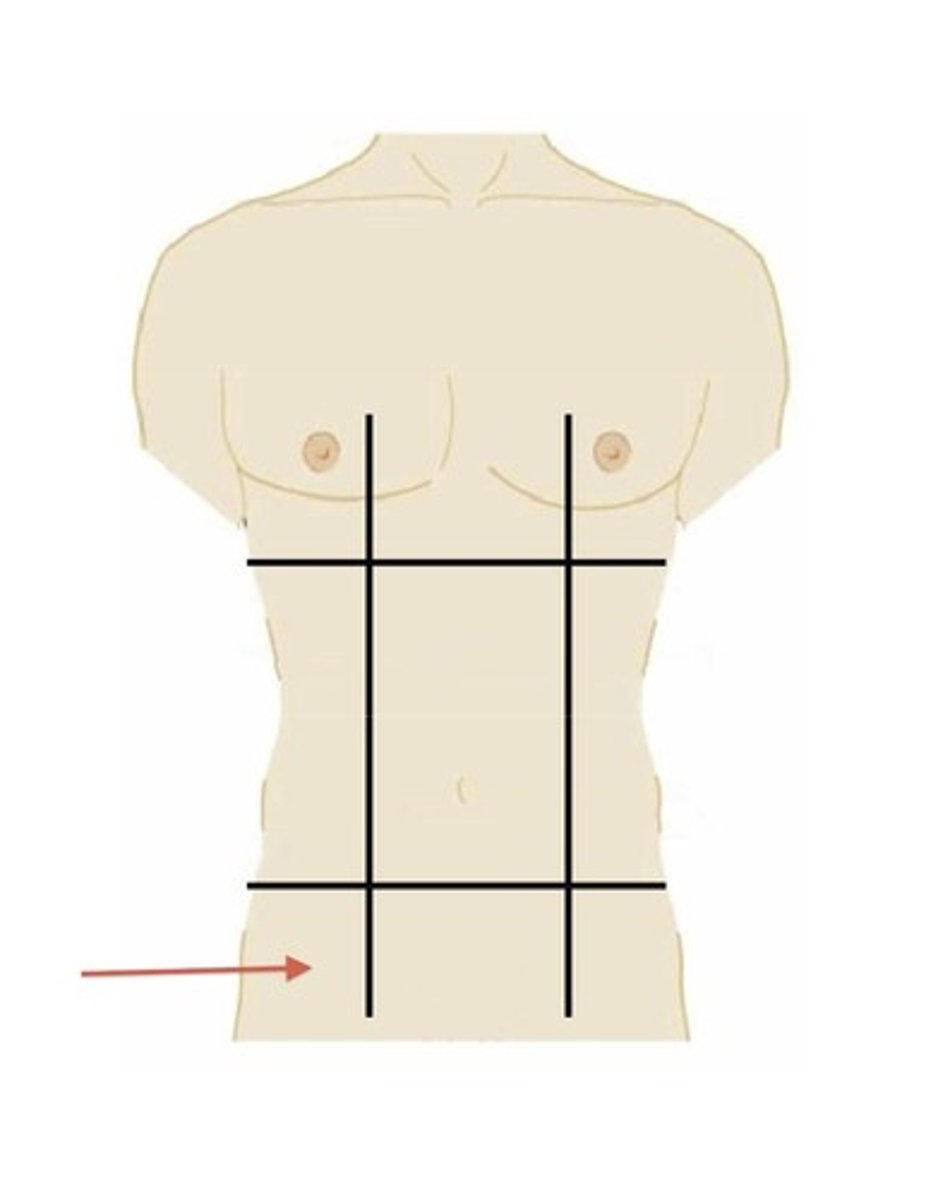
hypogastric region
lower middle region
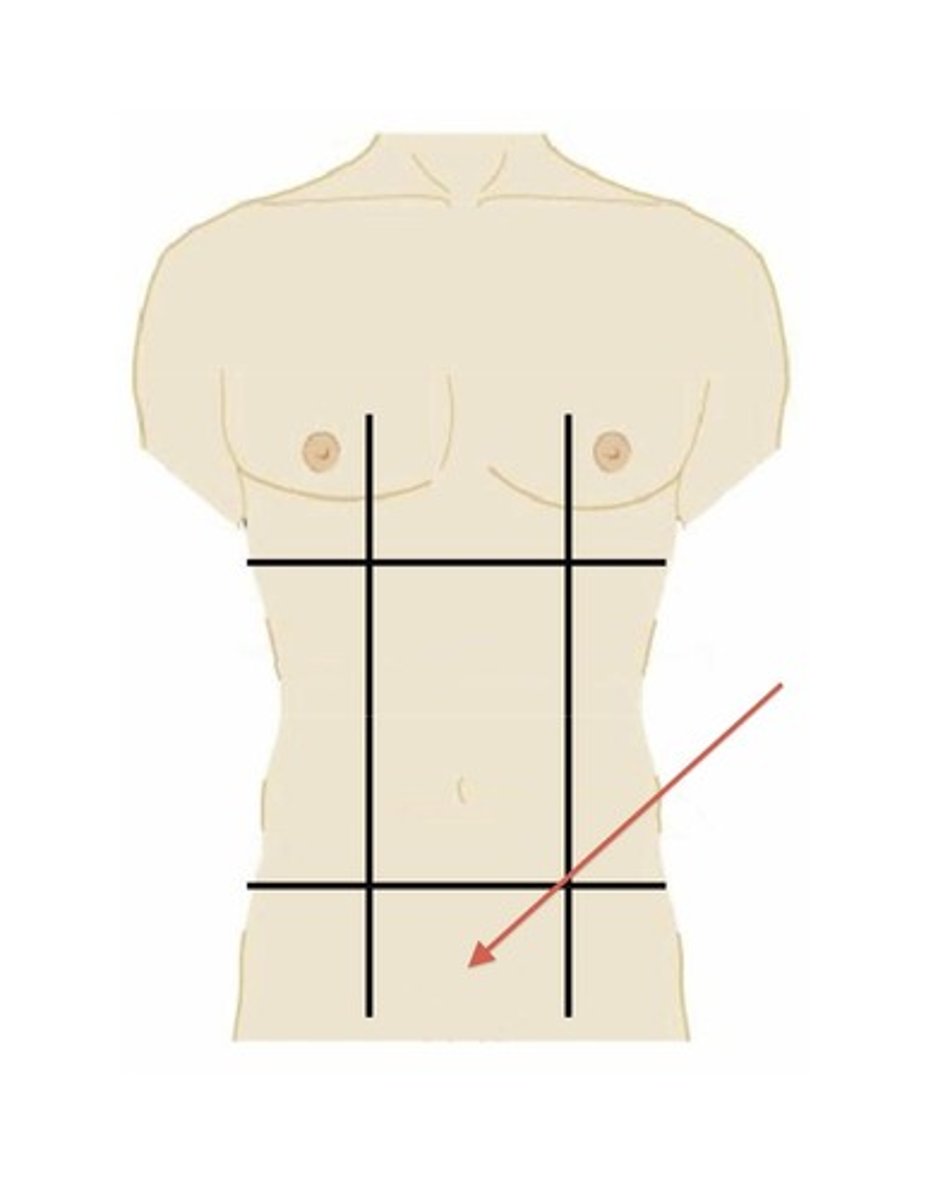
left iliac region
lower left region
Anatomy
The study of body structures and their relationship to other body parts
Physiology
The study of how those body parts function
Principle of complementarity
Certain structures perform specific functions and vice versa (“form follows function”)
Homeostasis
Maintaining a stable internal environment
Made possible by feedback mechanisms (negative and positive)
Molecular
1st level of organization
Cellular
2nd level of organization
Tissue
3rd level of organization
Organ
4th level of organization
Organ System
5th level of organization
Organism
6th level of organization
Negative Feedback
Counteracts a change
Ex. thermoregulation
Positive Feedback
Exaggerates or enhances the original change
Ex. Childbirth, Blood Clotting
Sliding filament theory
A theory that explains how muscles contract by the sliding of actin and myosin filaments past each other.
Signal & Calcium Release: A nerve impulse triggers the release of calcium into the muscle fiber.
Binding Site Exposure: Calcium binds to troponin, shifting tropomyosin and exposing the myosin-binding sites on the actin
Cross-Bridge Formation: Myosin heads attach to the exposed sites on actin
Power Stroke: ADP and phosphate are released, causing the myosin head to pivot and pull the actin filament towards the sarcomere's center
Detachment & Reattachment: A new ATP molecule binds to the myosin head, causing it to detach; the ATP breaks down, re-energizing the head to repeat the cycle
Neuromuscular junction
Contains:
Axon
Synaptic cleft
Possynaptic membrane
ACh
The site where skeletal muscles must be stimulated to contract, receiving an electrical signal from the nervous system through a motor neuron.
Motor unit
One motor neuron and all the skeletal muscle cells stimulated by that neuron.
Twitch
A single cycle of stimulus-contraction-relaxation in a muscle fiber.
Rigor Mortis
Begins 2-7 hours after death, and lasts until decomposition begins (1-6 days after death)
calcium leaks out of storage and into sarcoplasm of muscle fibers, stimulating myosin to form cross-bridges with actin.
ATP is used up so myosin cannot detach
Skeletal muscles become locked in contracted position
Perimysium
Label B on the muscle tissue
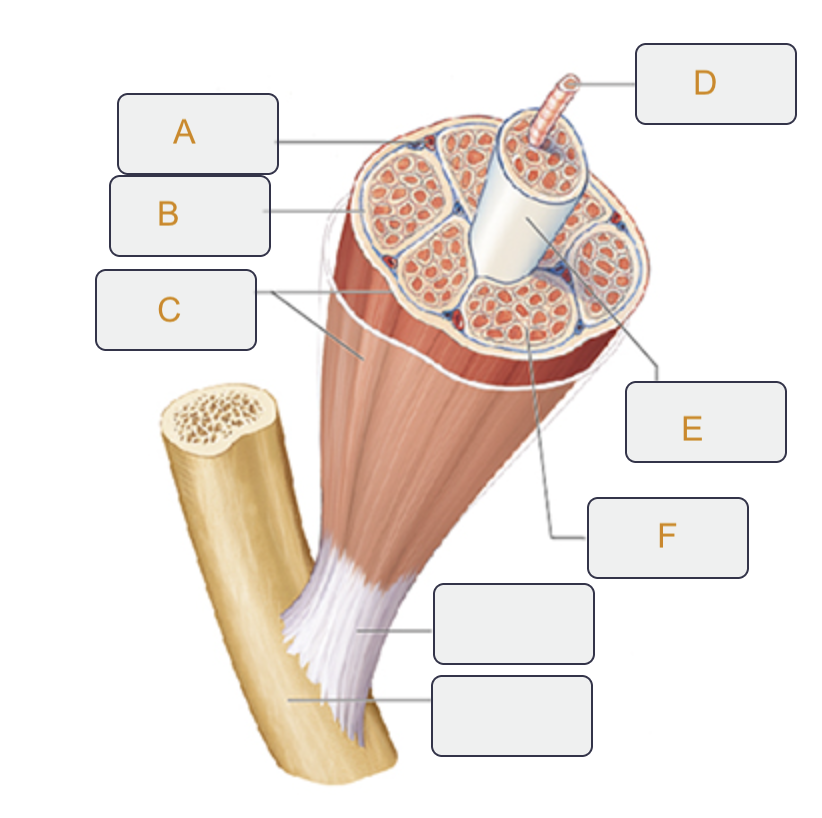
Epimysium
Label C on the muscle tissue
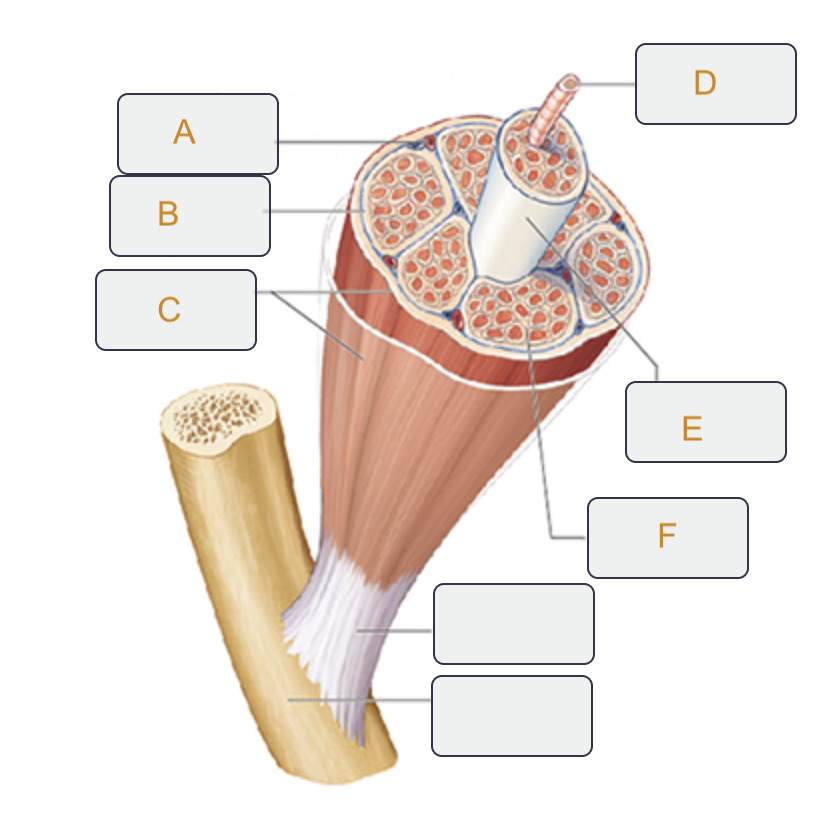
Muscle fiber (cell)
Label D on the muscle tissue
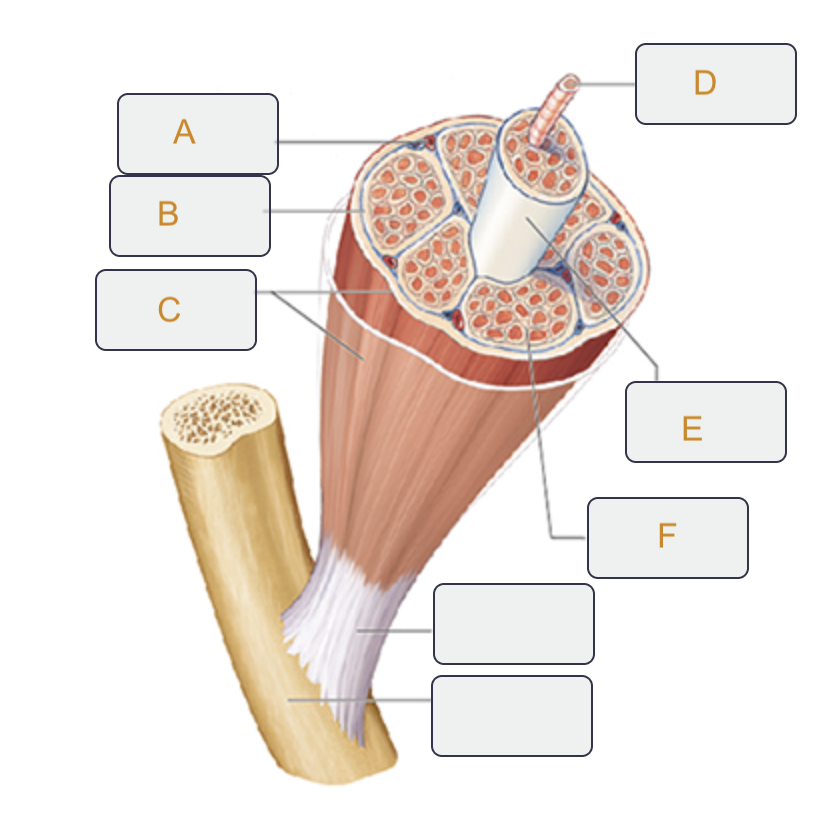
Fascicle
Label E on the muscle tissue
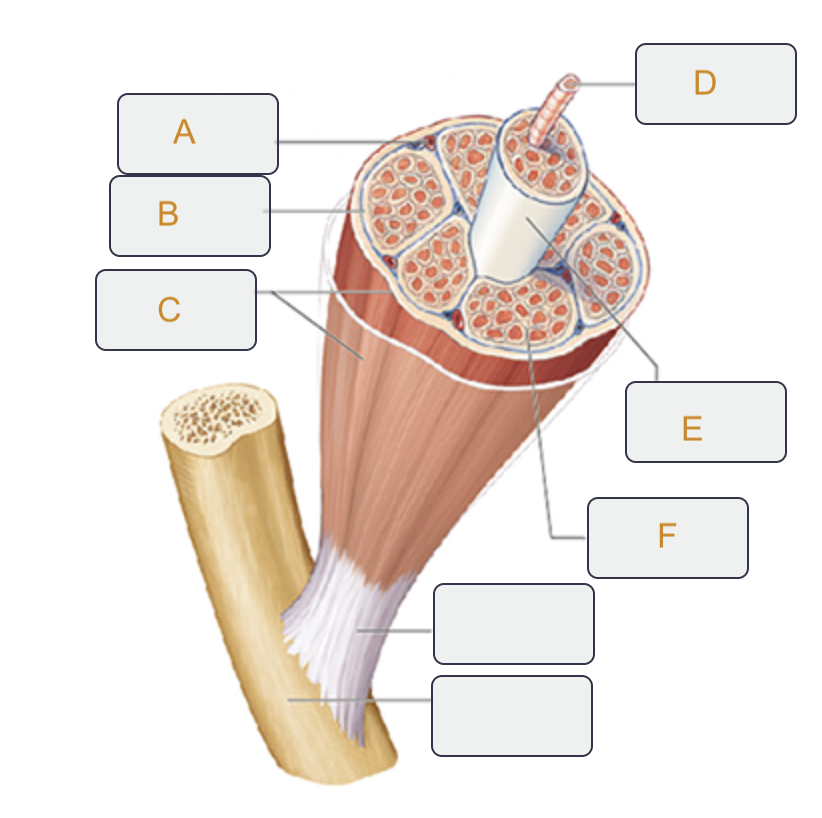
Endomysium
Label F on the muscle tissue
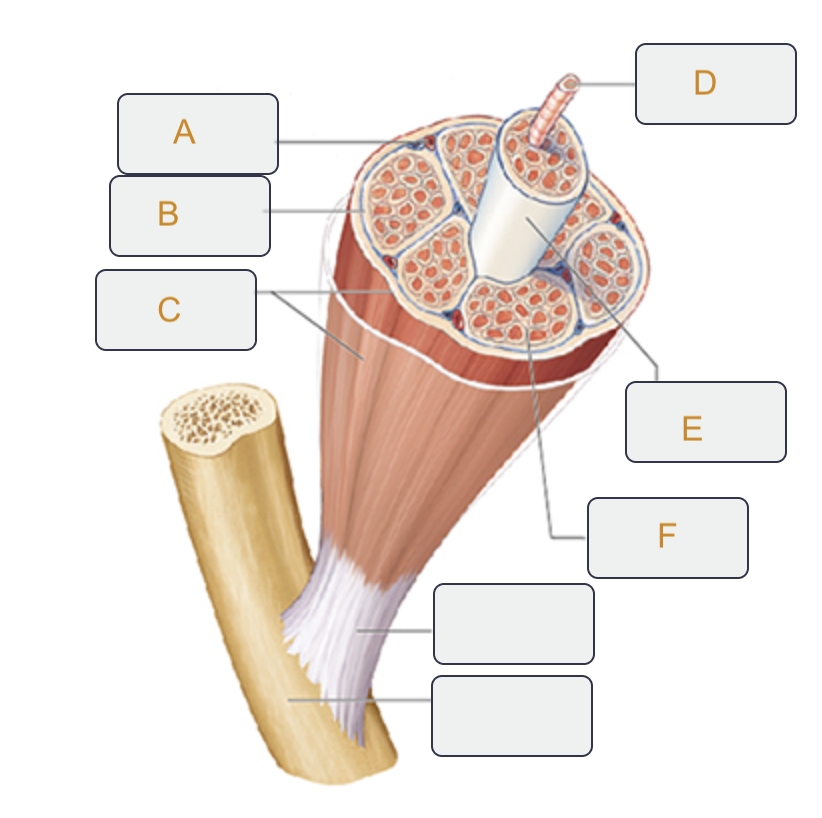
Action potential
Label A on the neuromuscular junction
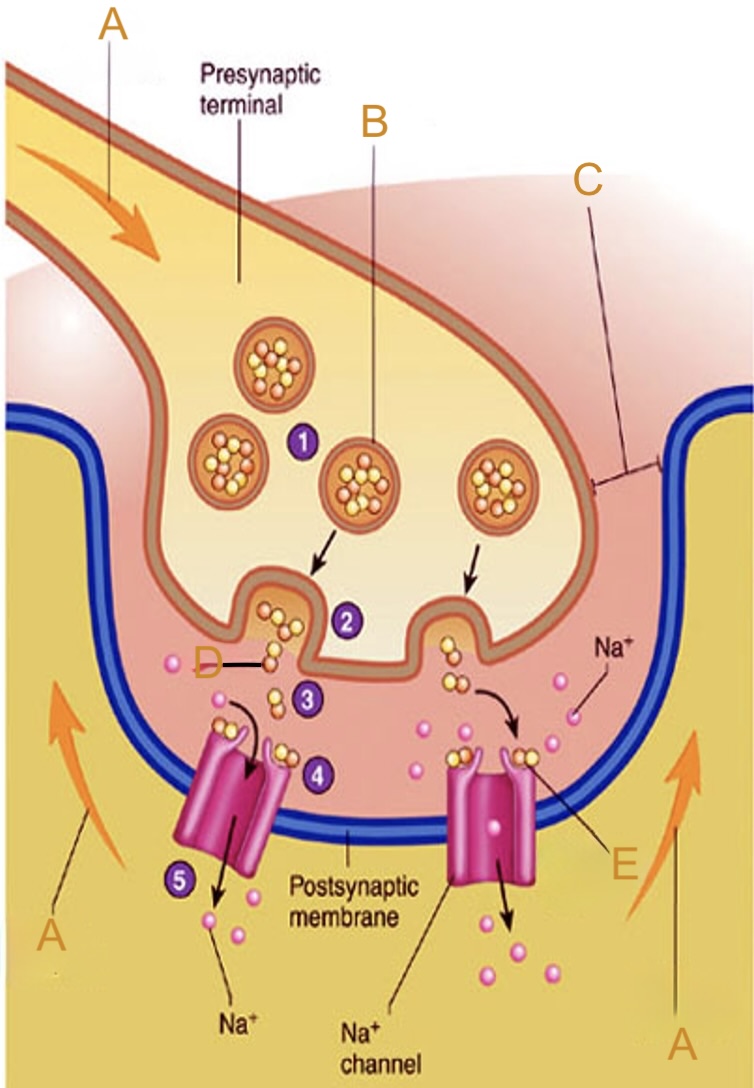
Synaptic vesicle
Label B on the neuromuscular junction
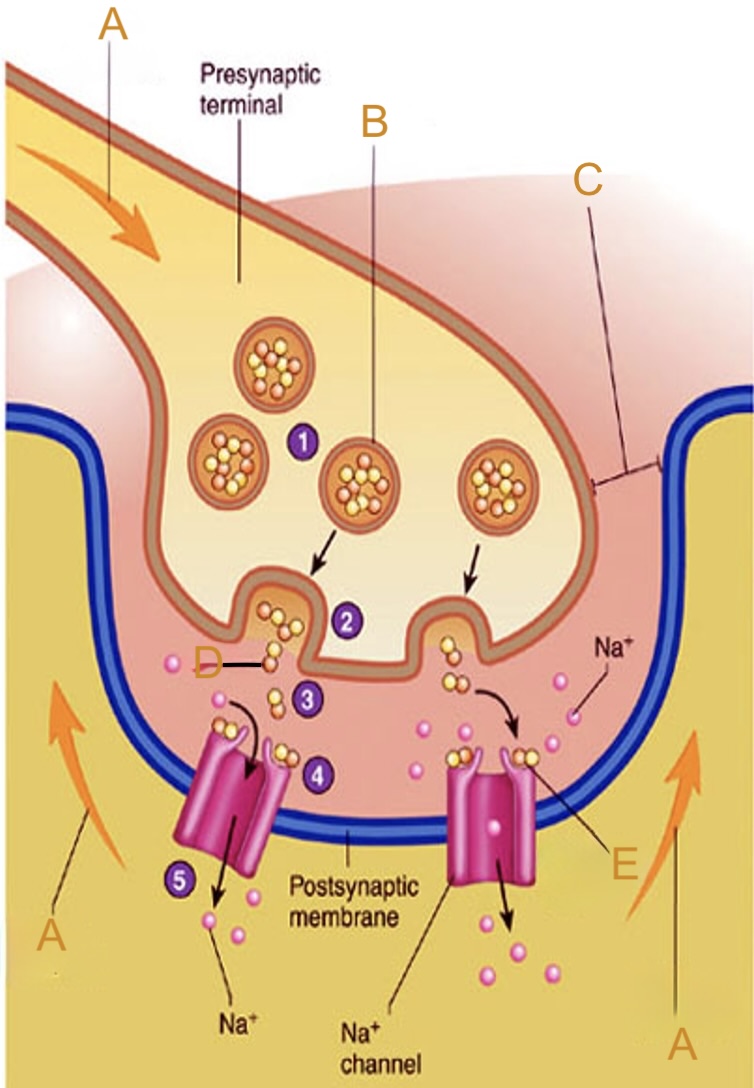
Synaptic cleft
Label C on the neuromuscular junction
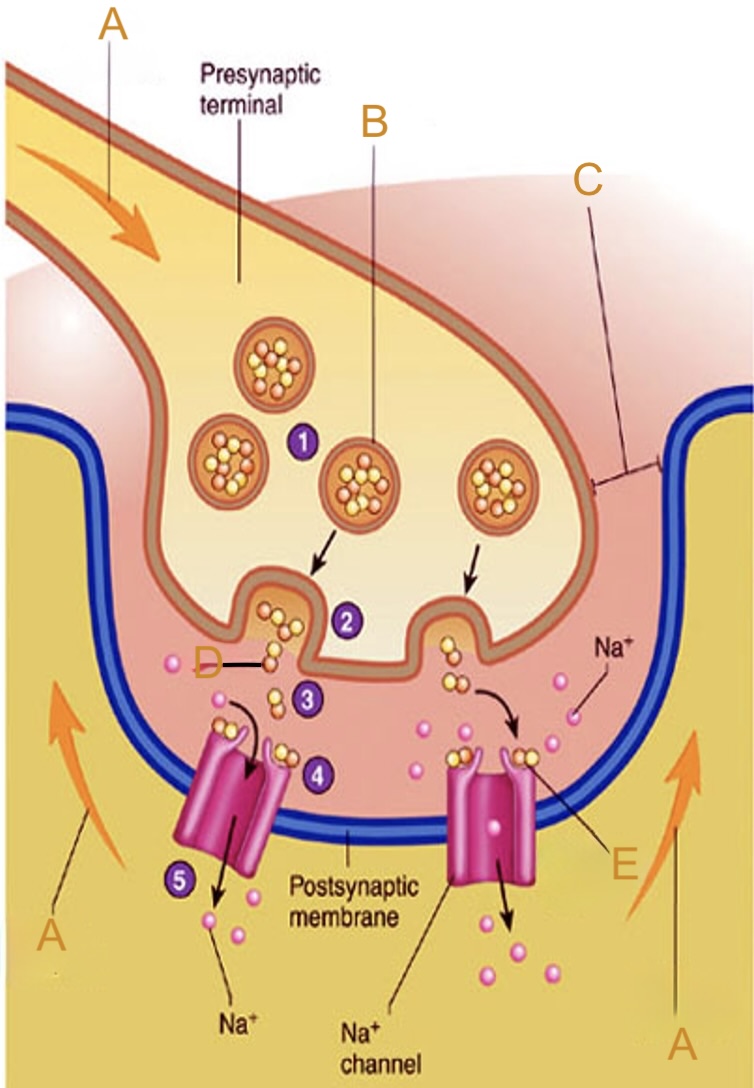
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Label D on the neuromuscular junction
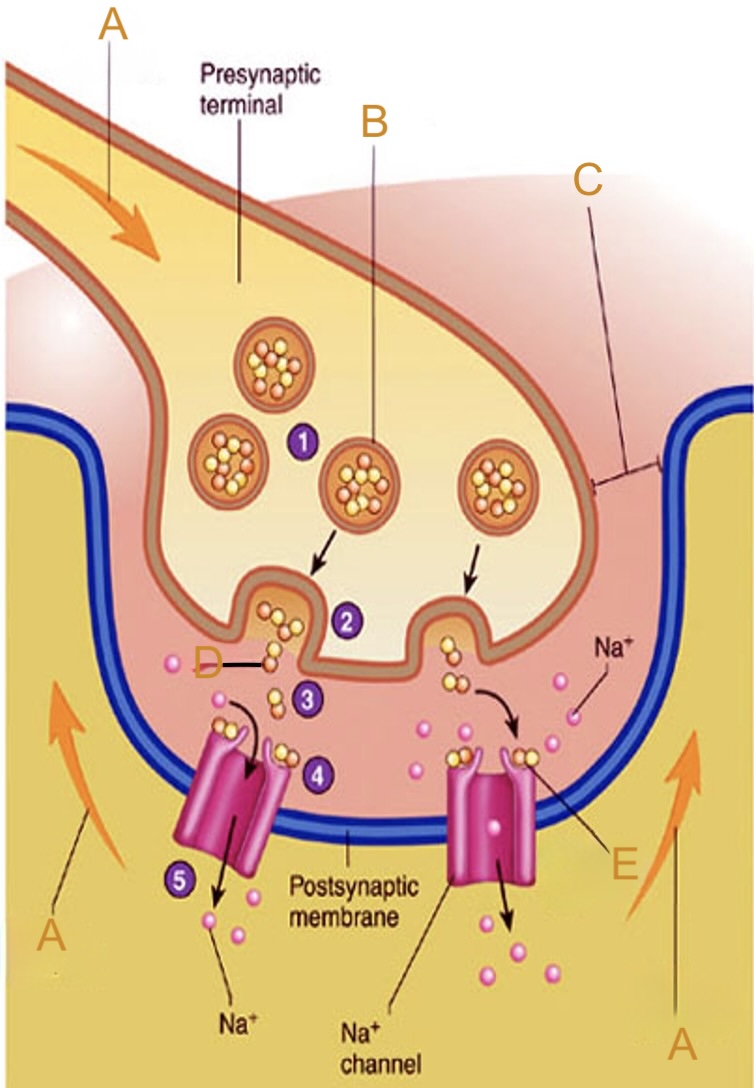
Acetylcholine (ACh) receptor
Label E on the neuromuscular junction
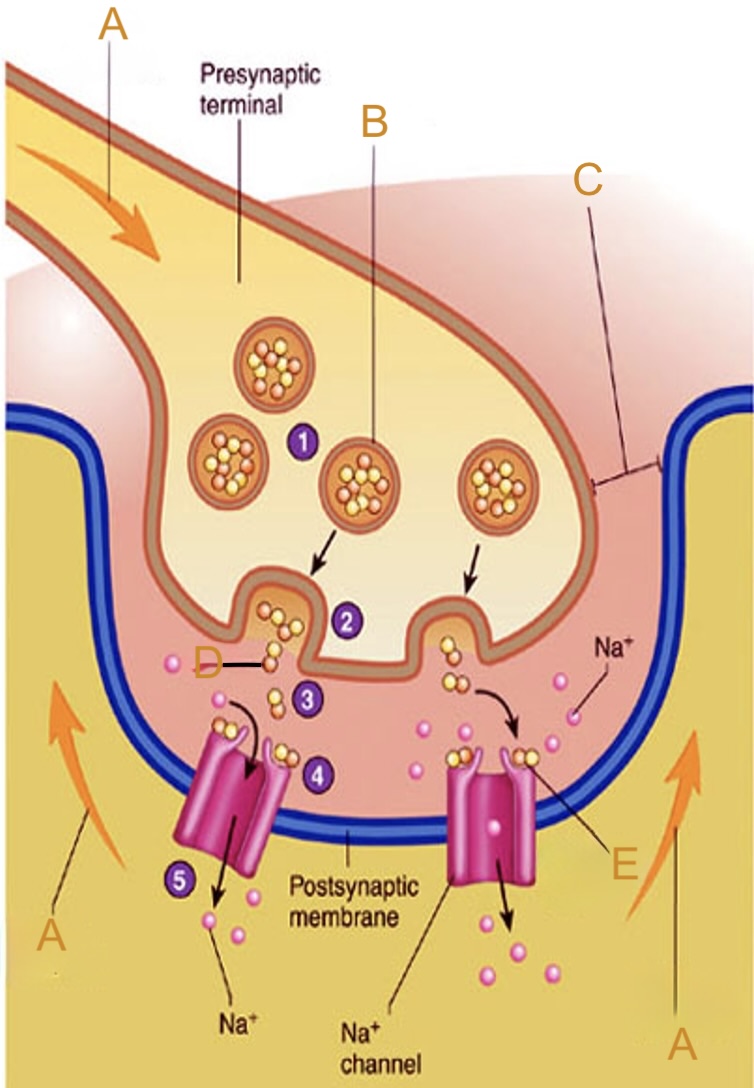
Actin
The protein strands that get pulled (Thin Filaments)
Mysoin
Have "heads" that bind to actin (Thick Filaments)
Characteristics of Muscle Tissue
Contractility: The ability to shorten and thicken.
Irritability/Excitability: The ability to receive and respond to stimuli.
Extensibility: The ability to stretch.
Elasticity: The ability to return to its original shape.
synarthroses
immovable joints
Ex. Skull sutures, tooth joints
amphiarthroses
slightly movable joints
Ex. Pubis symphysis, intervertebral discs
hinge joints
Ex. elbow, knee
intervertebral discs
contain gel-like nucleus pulposus and cartilaginous annulus fibrosus
diarthroses
freely movable joints
Ex. Shoulder, hip, knee, elbow, wrist
plantar flexion
pointing the toes down produces this motion
abduction
moving laterally
inversion
turning the bottom of the foot medially
flexion
decreasing the angle of a joint
eversion
turning the bottom of the foot laterally
supination
turning the palm facing upward
dorsiflexion
pointing toes up produces this motion
ball-and-socket joints
Ball-shaped end of one bone fits into rounded socket of the other
Allow movement in all axes (including rotation); mostly freely
moving synovial joints
Ex. Shoulder, hip
pronation
turning the palm facing downward
Bursa
fluid-filled sac that acts as a cushion between bones, muscles, tendons, and skin to reduce friction and allow smooth movement in joints
Extension
increases the angle between body parts at a joint
Adduction
moving toward the midline of the body
Arthiritis
“joint inflammation”
Herniated disc
The nucleus pulposus (soft, jelly-like center of a spinal disc) has broken through the surrounding annulus fibrosus and can compress spinal nerves, irritating nearby nerves and causing pain, numbness, or weakness
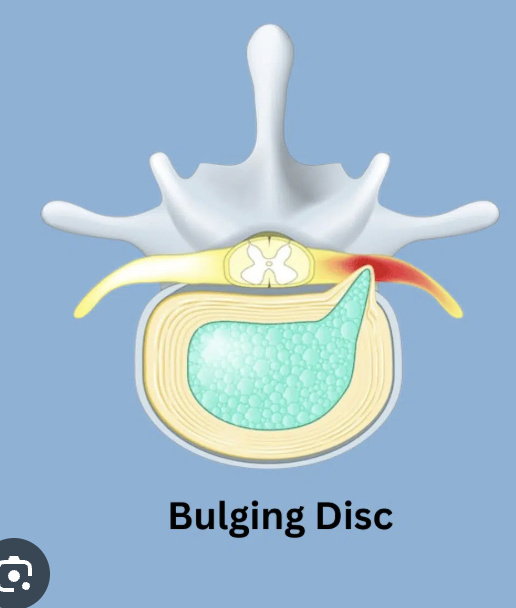
Bulging disc
Nucleus pulposus flattens and bulges outward, possibly entering the vertebral canal, with its outer layer remaining intact, often due to aging or wear and tear
diaphysis
long shaft of a bone
epiphysis
end of a bone
periosteum
fibrous membrane covering a bone
contains blood vessels and nerves that supply the bone with nutrients and sensation
short
bones that have similar length and width
Ex. Carpals
canaliculi
connections between lacunae so fluid can travel between them
parathyroid hormone (PTH)
hormone that raises calcium in the blood
hematoma formation
step one of fracture repair
soft callus formation
step two of fracture repair
bony callus formation
step three of fracture repair
remodeling
step four of fracture repair
osteoblasts
bone building cells
long
bones that have a greater length than width
Ex. Humerus, Femur
epiphyseal plate
In children, it separates the epiphysis from the diaphysis => bone growth
At puberty, this cartilage gradually narrows until it disappears completely and closes, forming an epiphyseal line
central canal
location of blood vessels and nerves in an osteon
osteoclasts
cells that break down bone
open/compound
type of fracture that breaks the skin
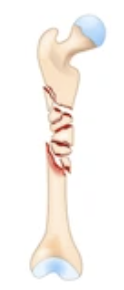
comminuted
type of fracture that shatters the bone
lamellae
rings of bone that encircle the central canal of an osteon
made of mineralized matrix and collagen fibers
provide strength and rigidity
osteocytes
cells found in lacunae
originally, osteoblasts that become embedded in the bone matrix
mechanosensors
lacunae
small areas of fluid between lamellae
housing/protection for osteocytes
exercise, diet, hormones
factors that affect bone remodeling
flat
thin, broad bones (wider than they are long)
protect internal organs
provide surfaces for muscle attachment
Ex. Cranial bones (frontal, parietal, occipital, etc), and ribs
irregular
bones with an odd shape
Ex. Vertebra