Unit 1 Biological Bases MBHS
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
148 Terms
Nature vs. nurture
name for a controversy in which it is debated whether genetics or environment is responsible for driving behavior

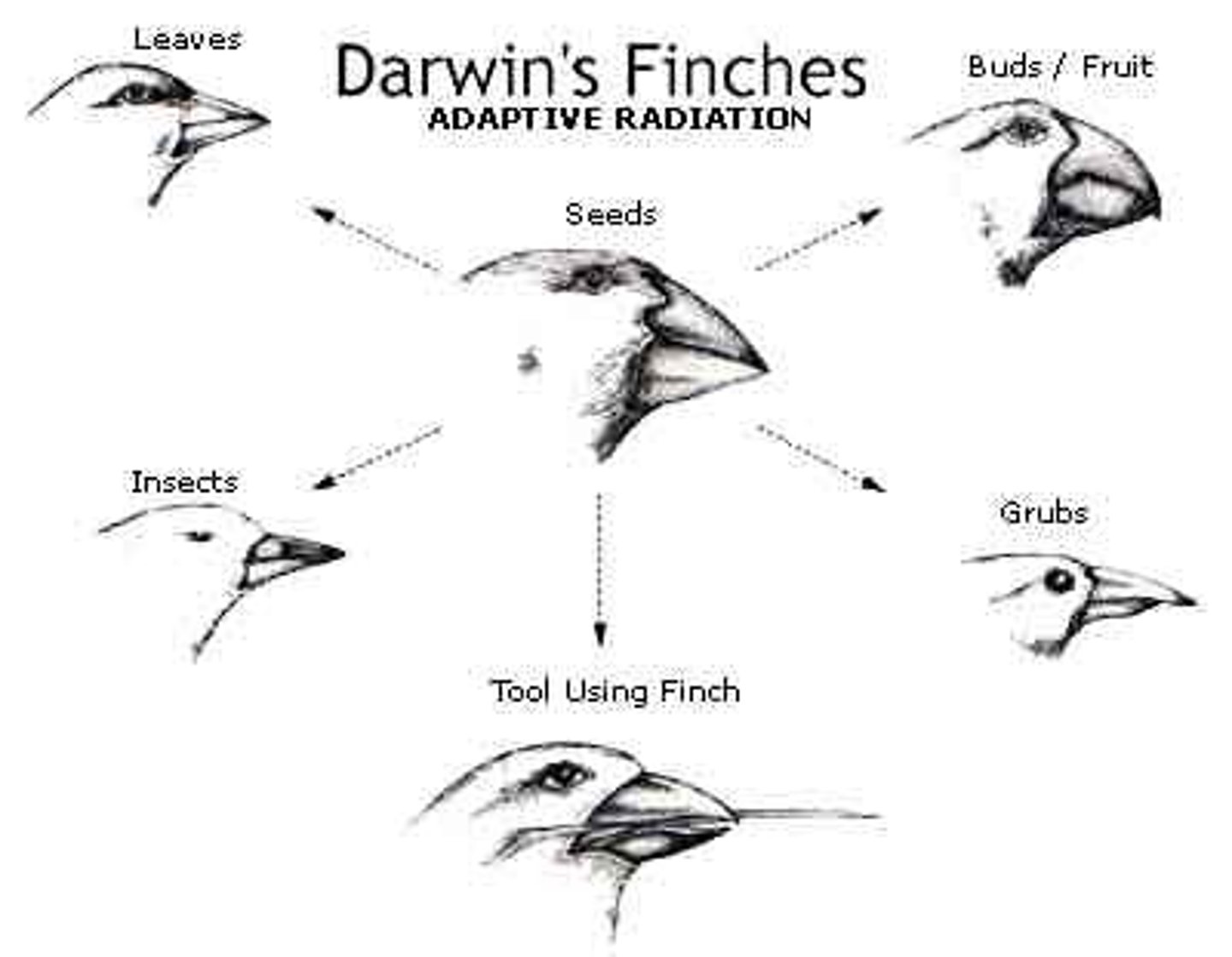
Natural Selection
A process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits.
behavior genetics
the study of the relative power and limits of genetic and environmental influences on behavior

heredity
Passing of traits from parents to offspring
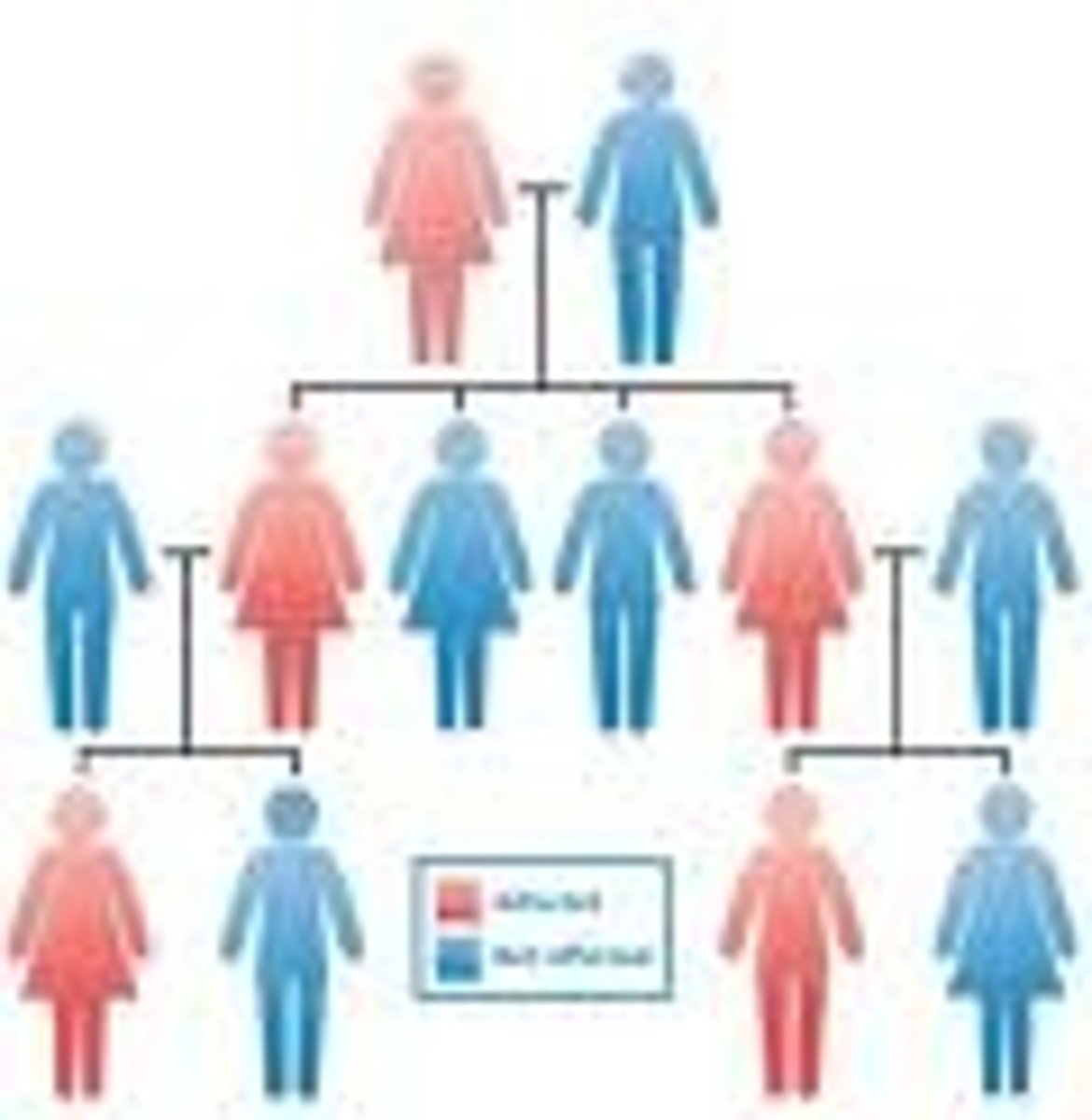
eugenics
is a social and scientific movement that aims to improve the genetic quality of a population. This often involves selective breeding, where certain traits are encouraged while others are discouraged or eliminated.
brainstem
responsible for automatic survival functions
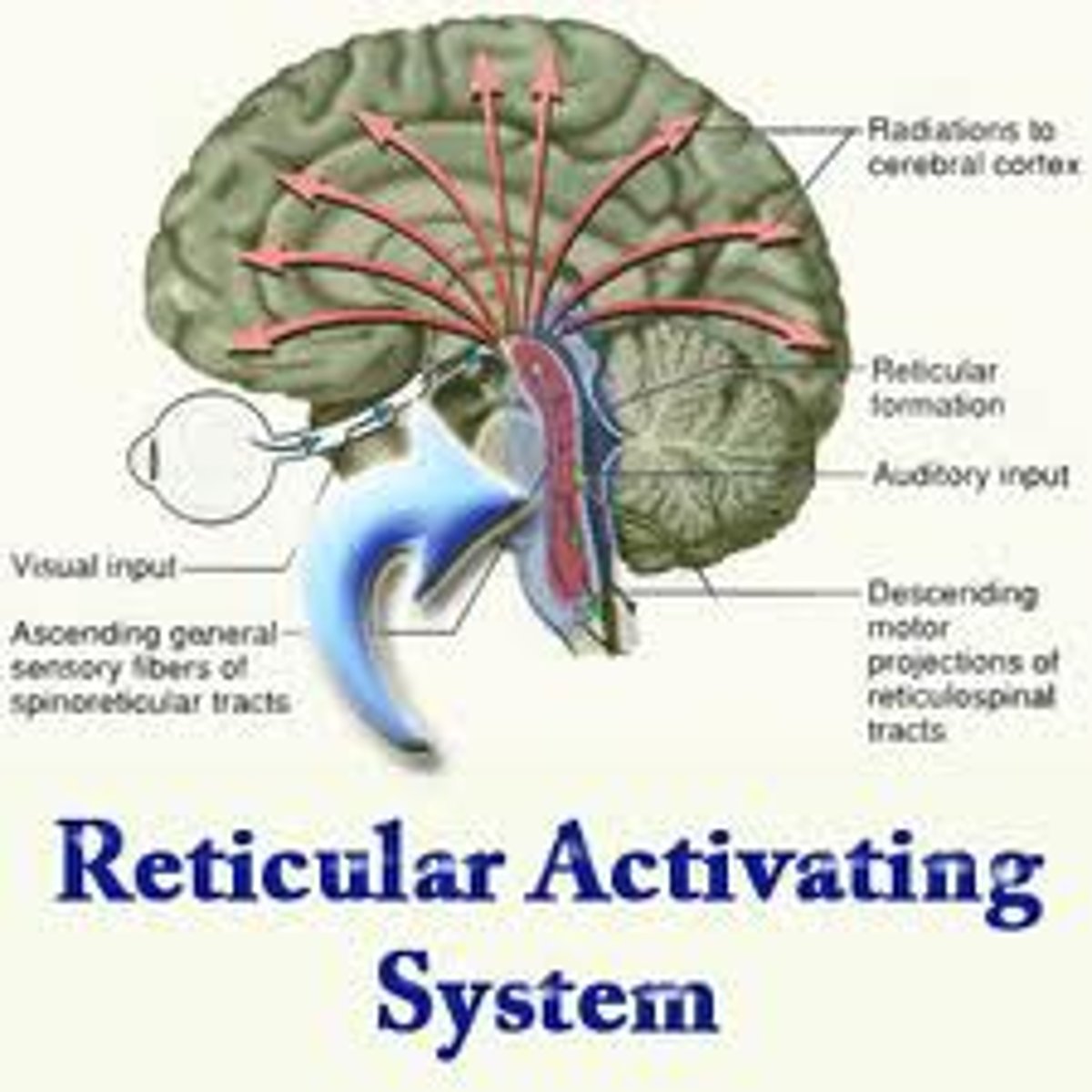
reticular activating system
the part of the brain that is involved in attention, sleep, and arousal
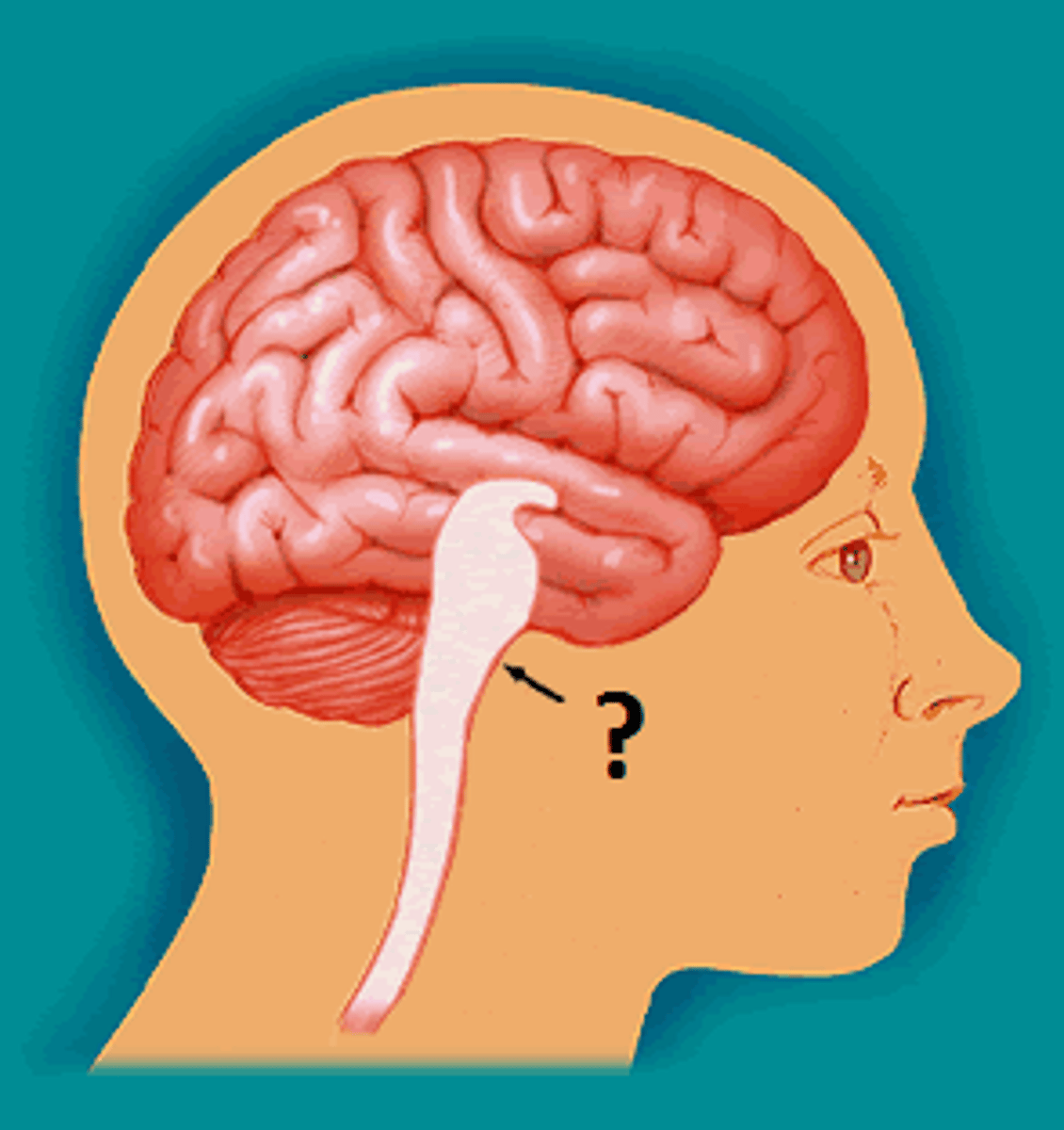
cerebellum
the "little brain" at the rear of the brainstem; functions include processing sensory input and coordinating movement output and balance
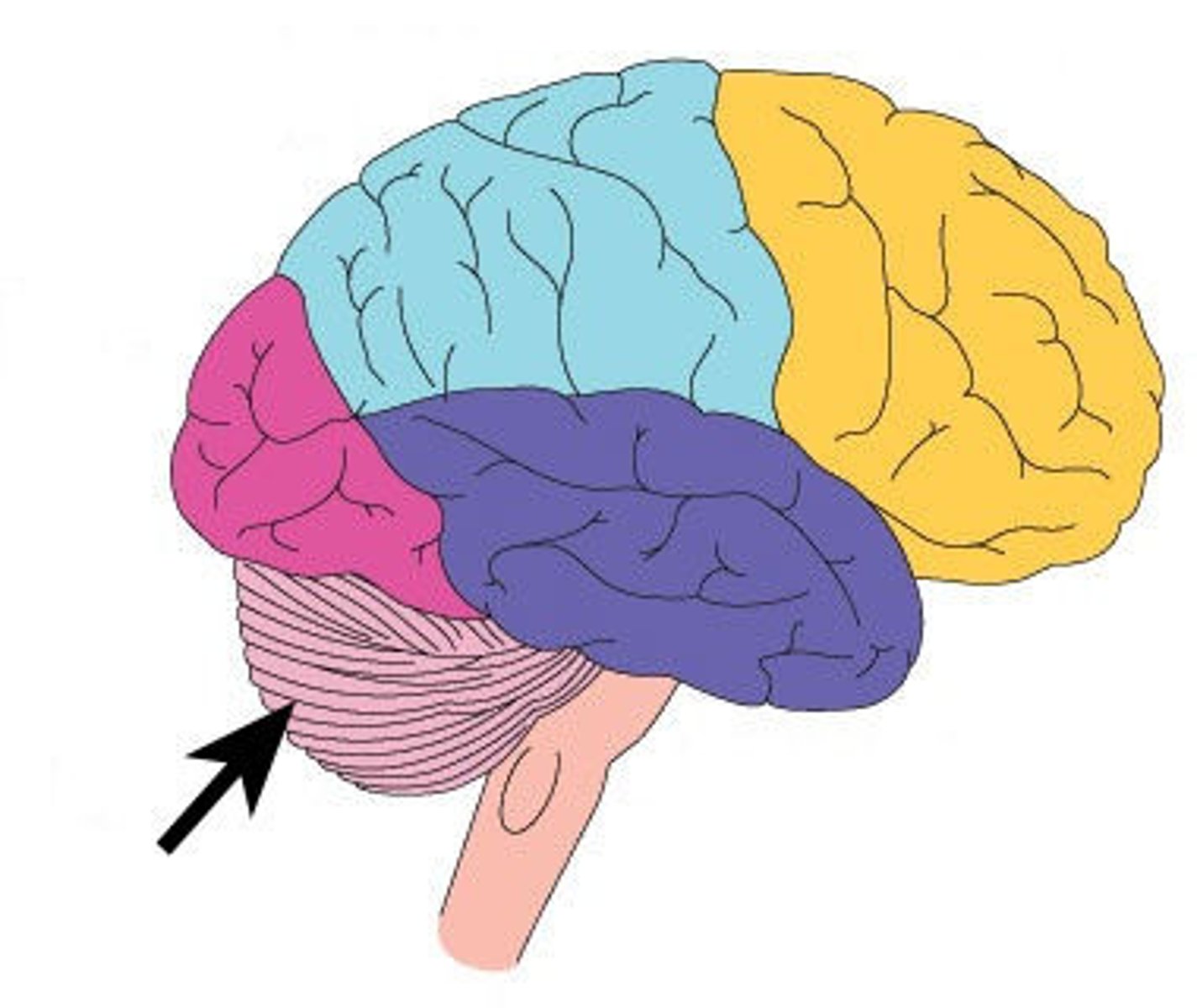
medulla
the base of the brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing
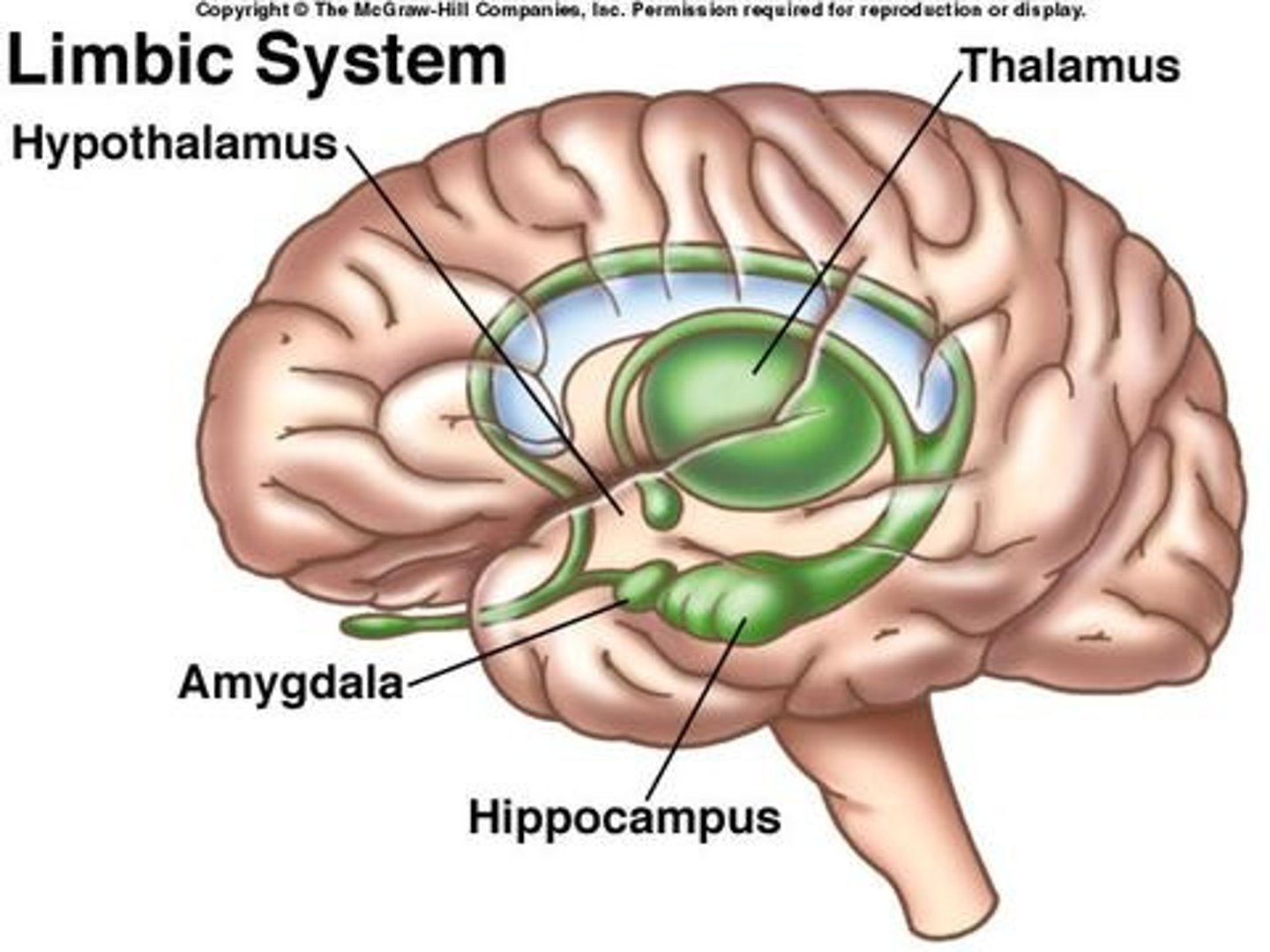
limbic system
neural system located below the cerebral hemispheres; associated with emotions and drives
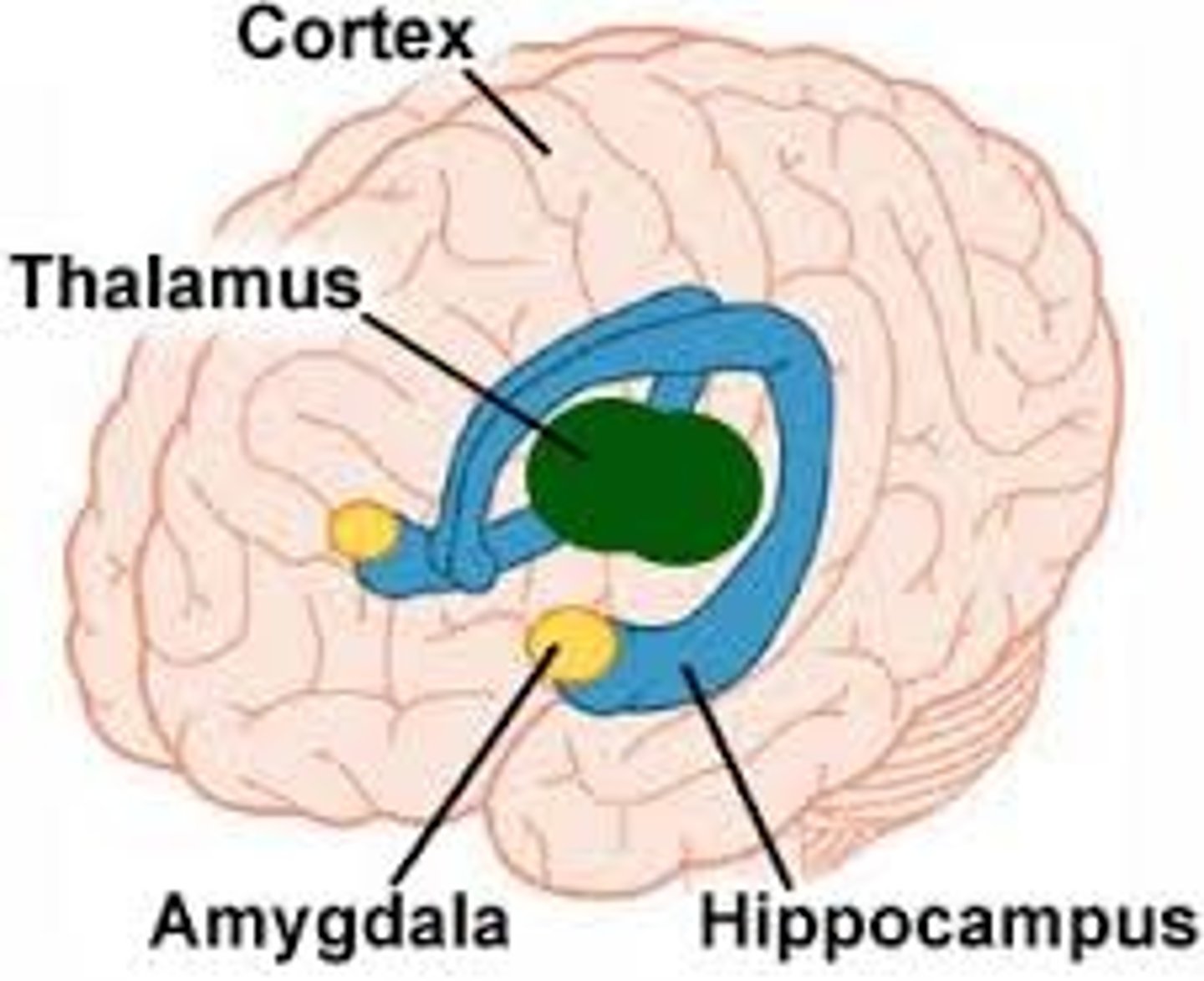
thalamus
the brain's sensory switchboard, located on top of the brainstem

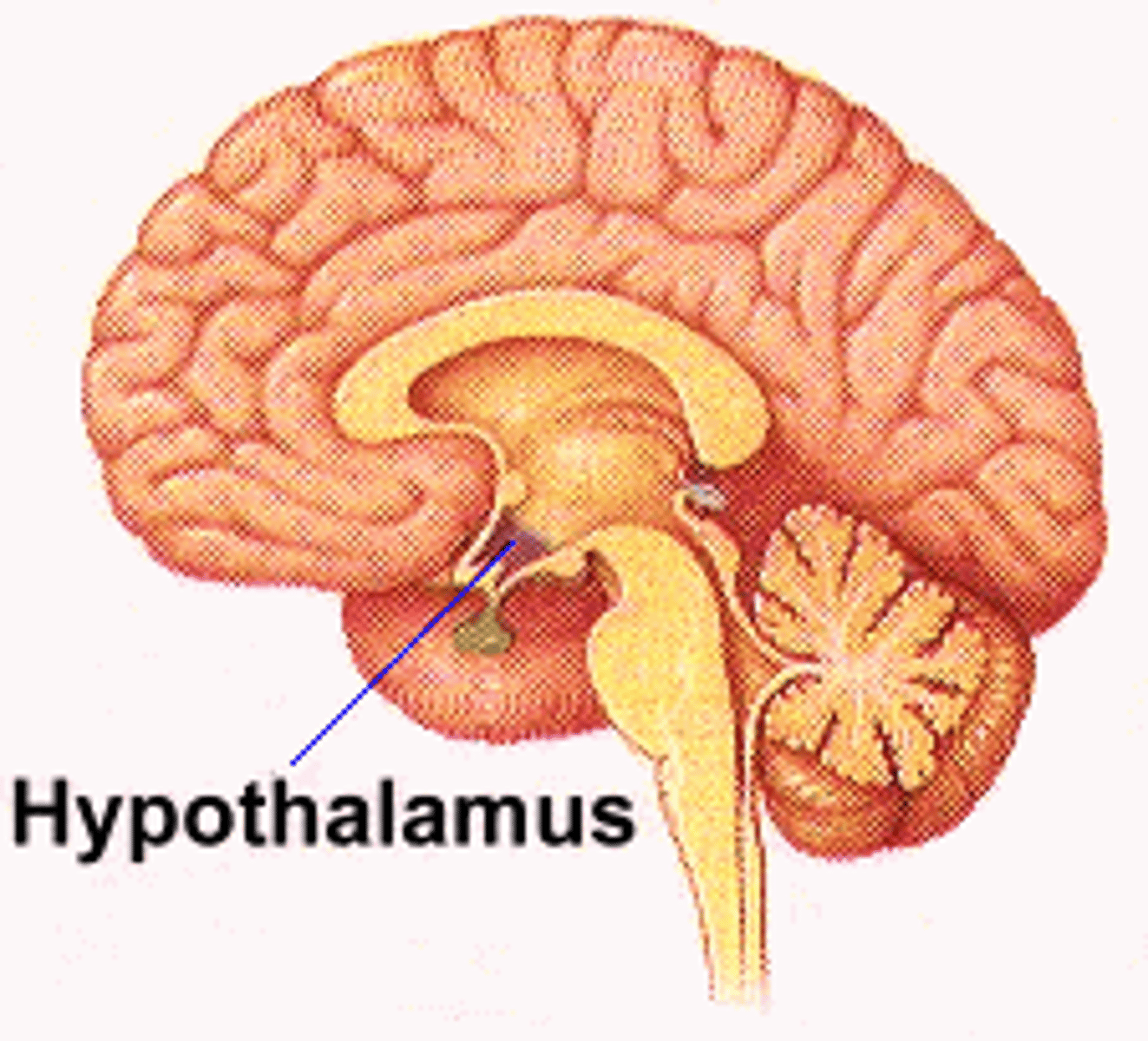
hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature)
amygdala
two lima bean-sized neural clusters in the limbic system; linked to emotion.
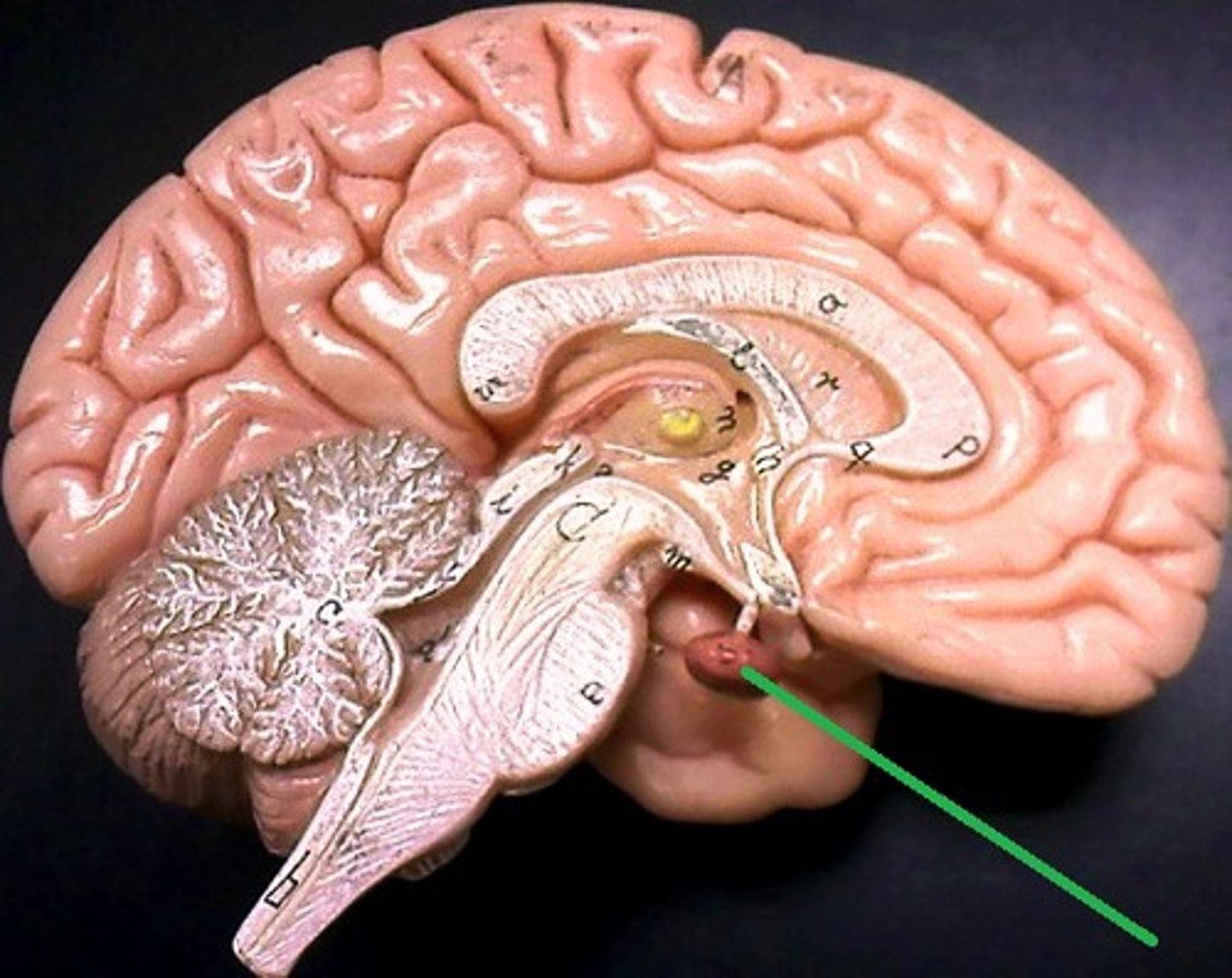
pituitary gland
The endocrine system's most influential gland. Under the influence of the hypothalamus, regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands.
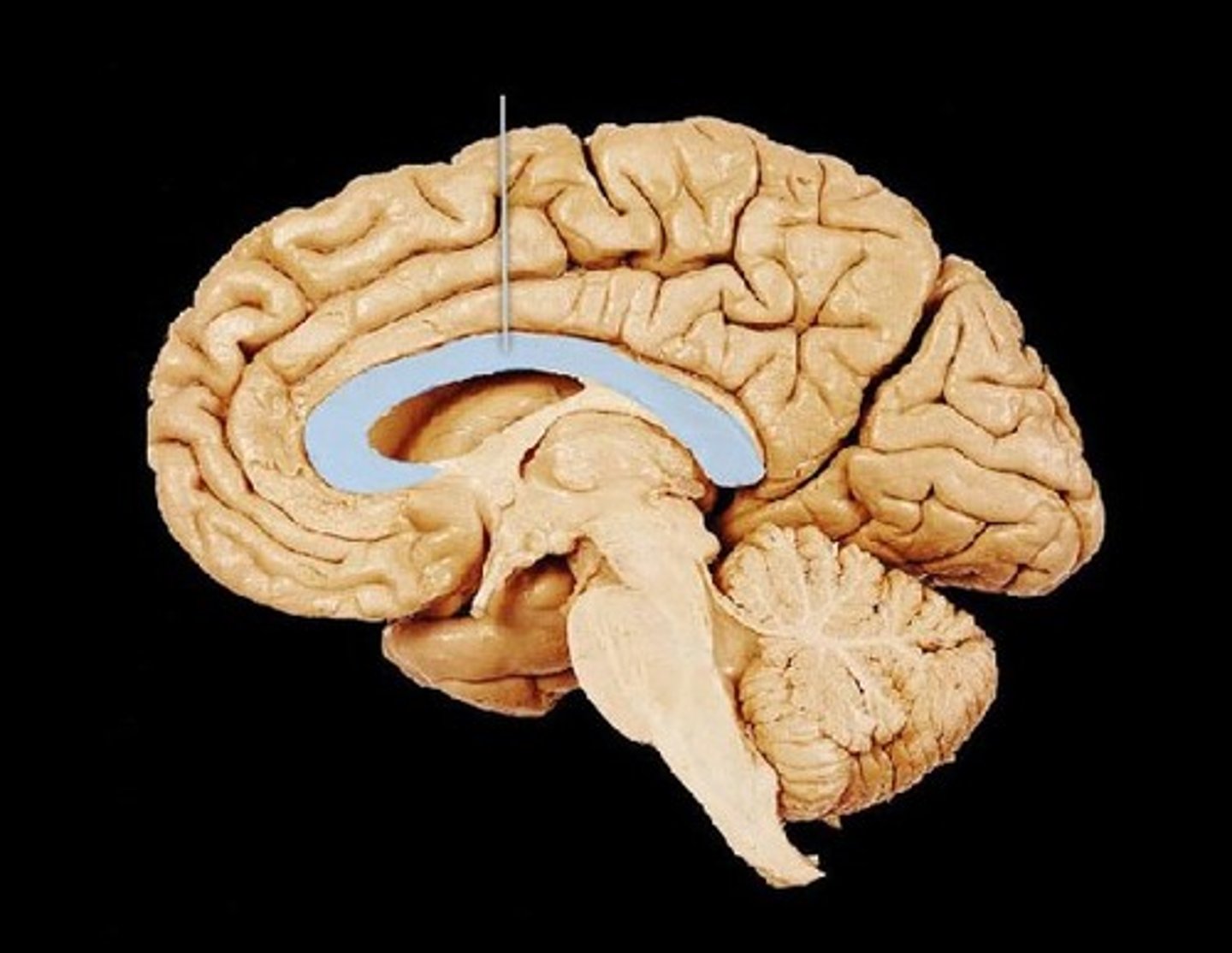
corpus callosum
the large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them
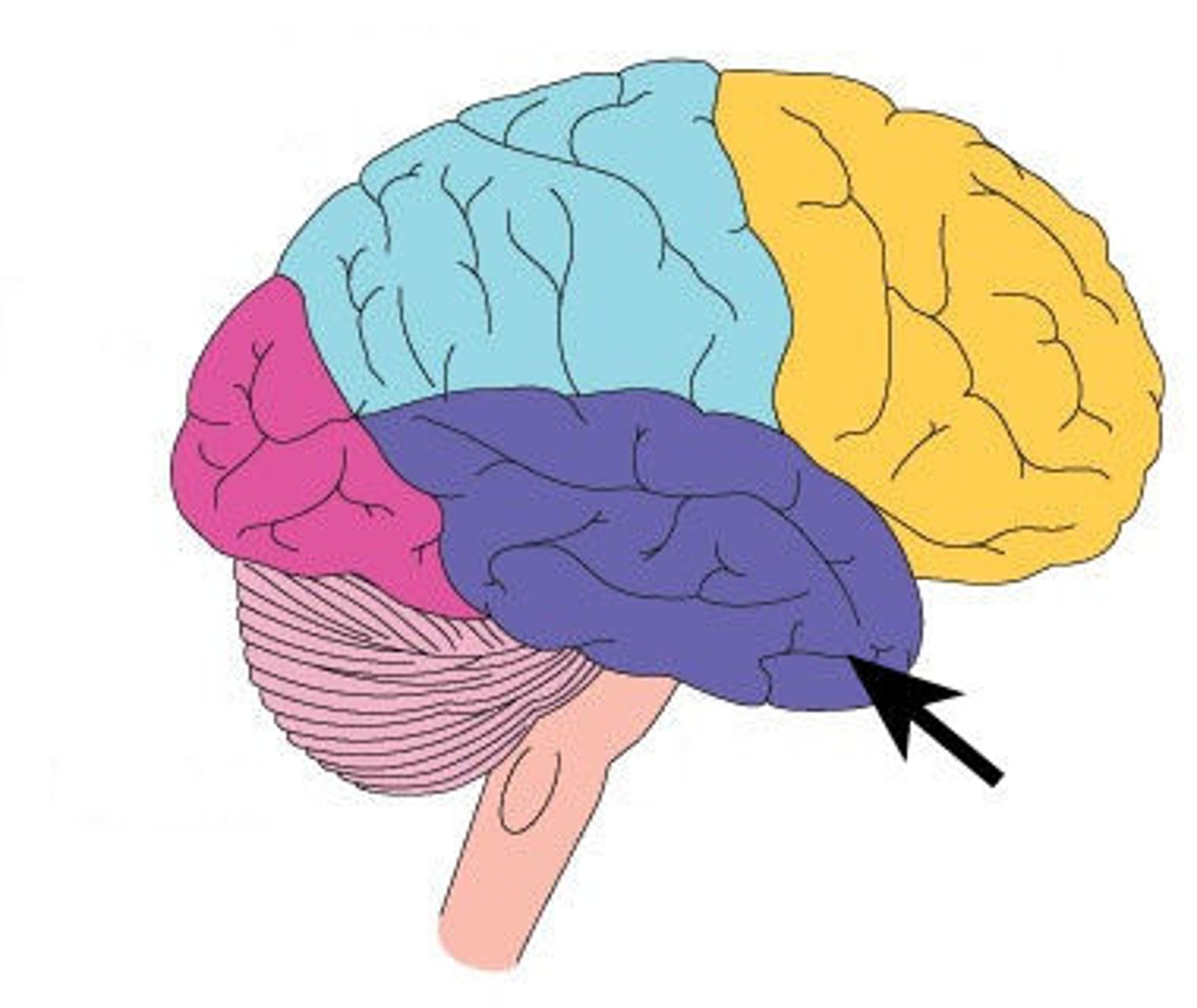
temporal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language.
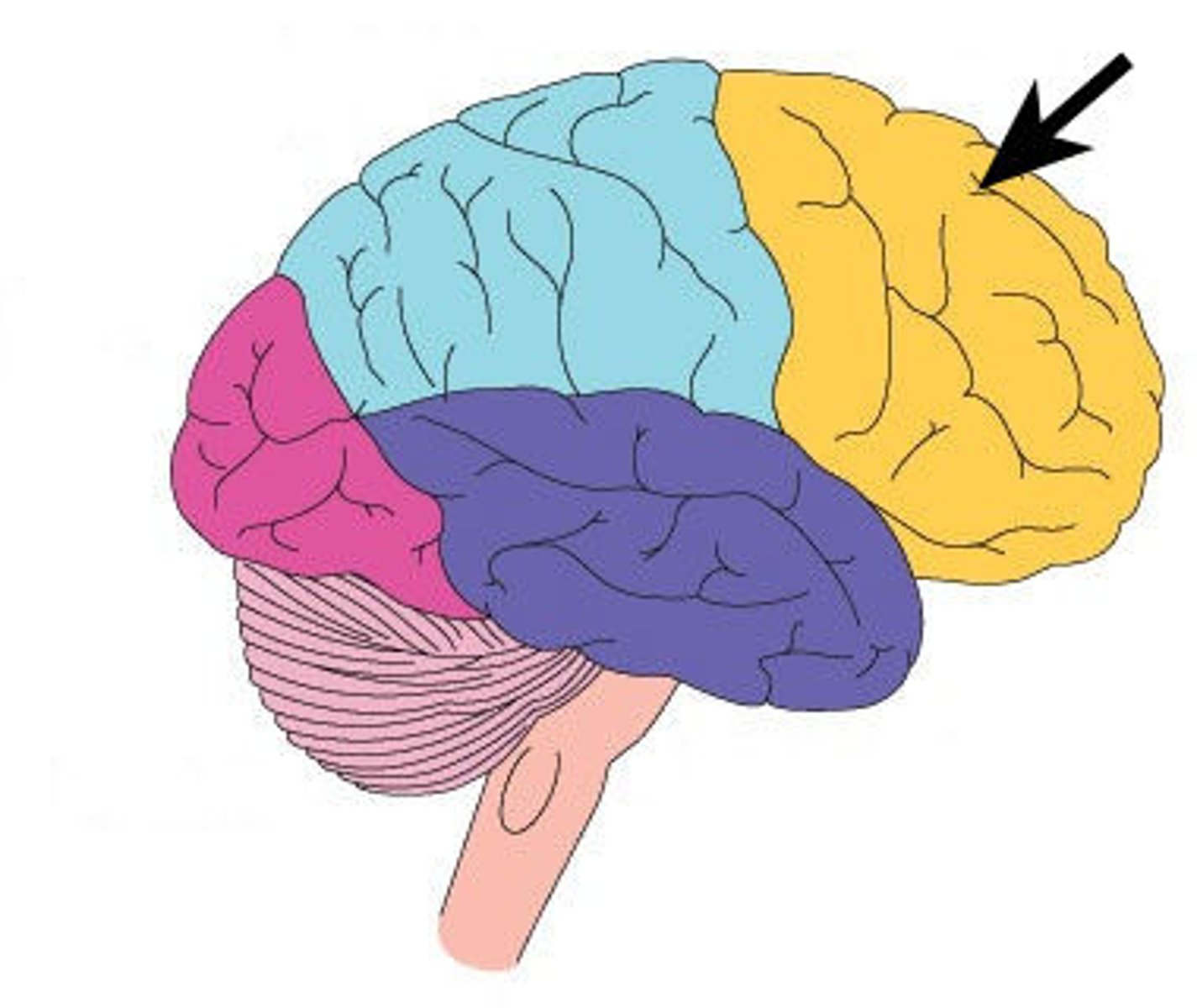
occipital lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information
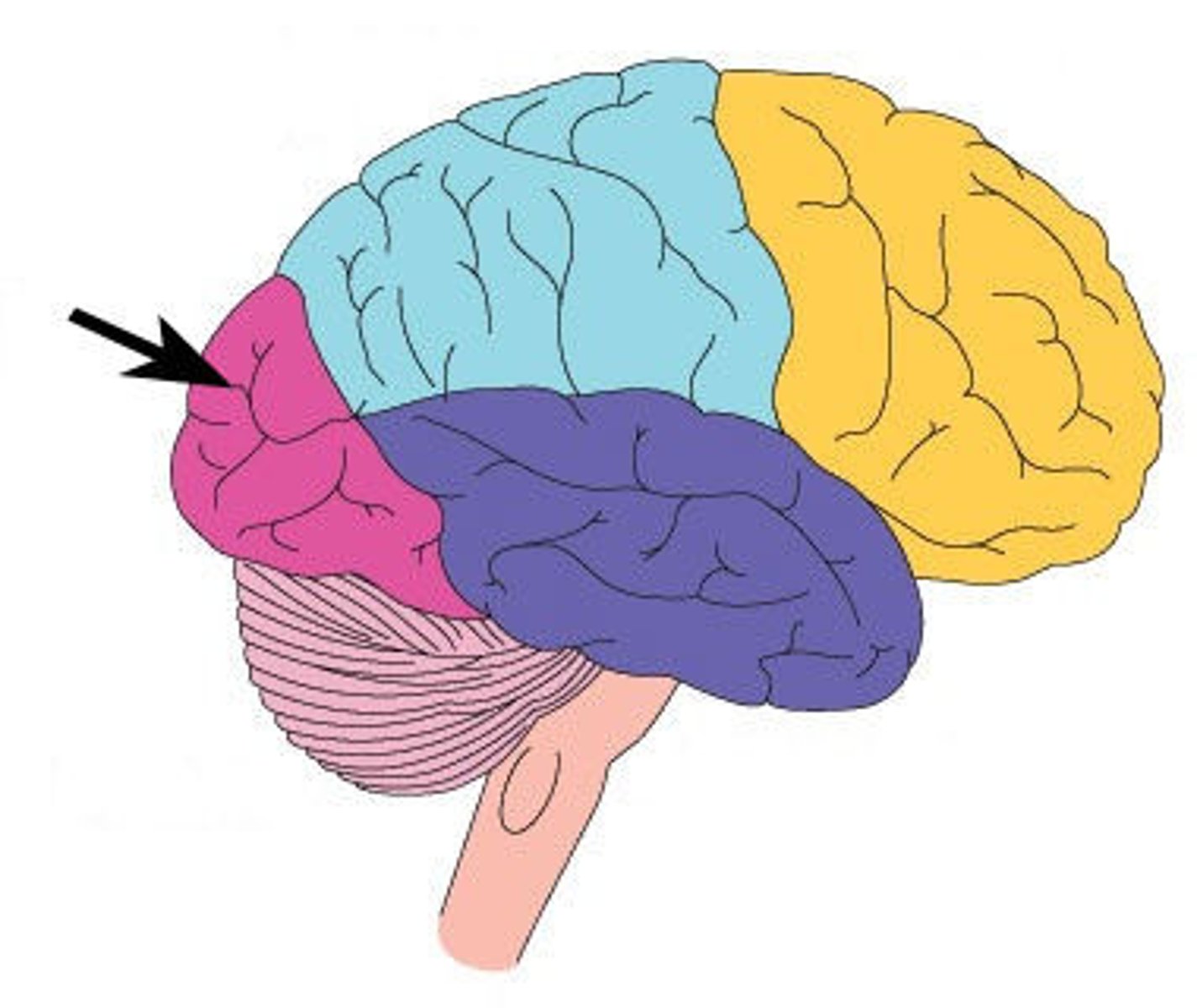
parietal lobe
portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body position
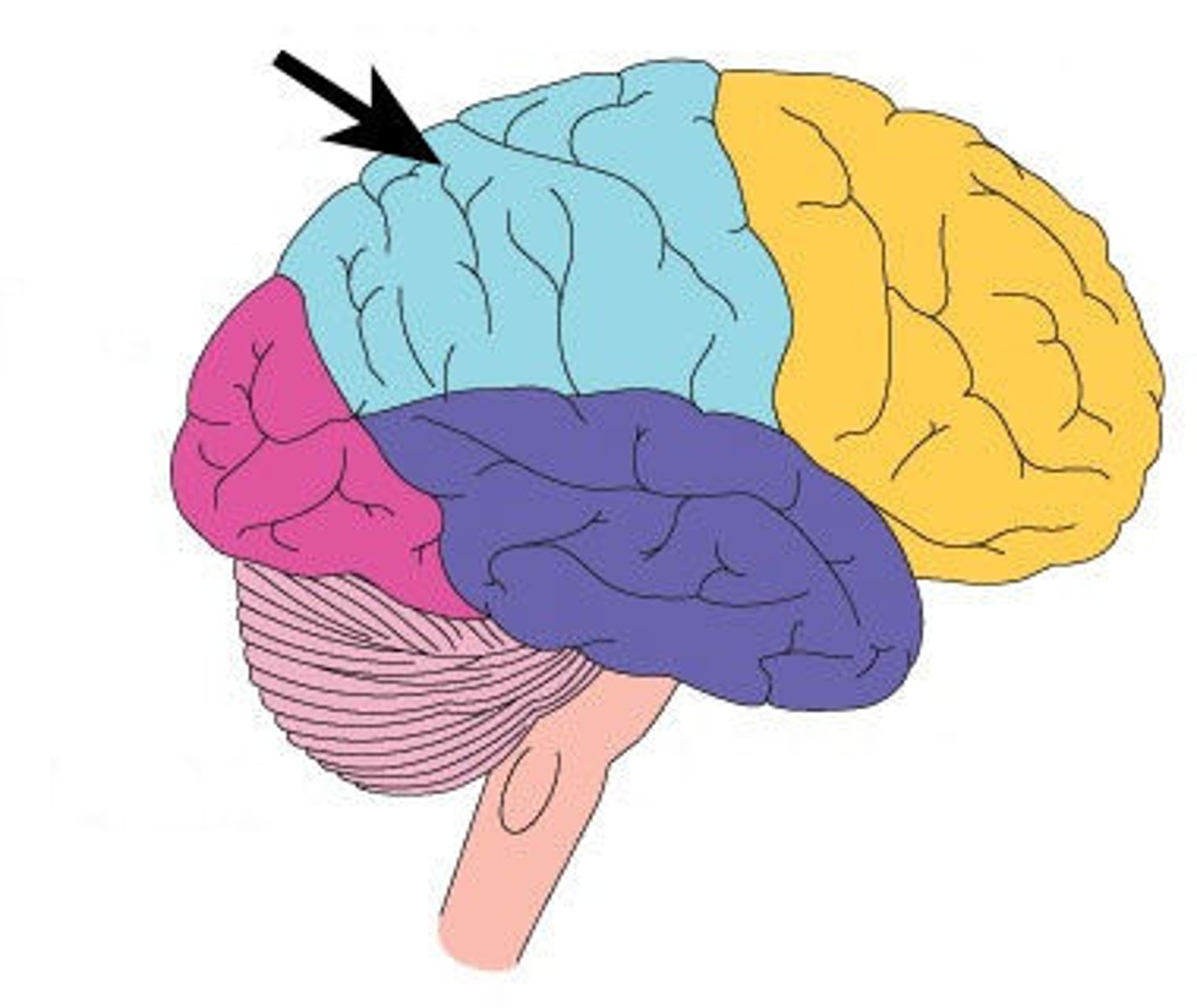
frontal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that has specialized areas for movement, abstract thinking, planning, memory, and judgement
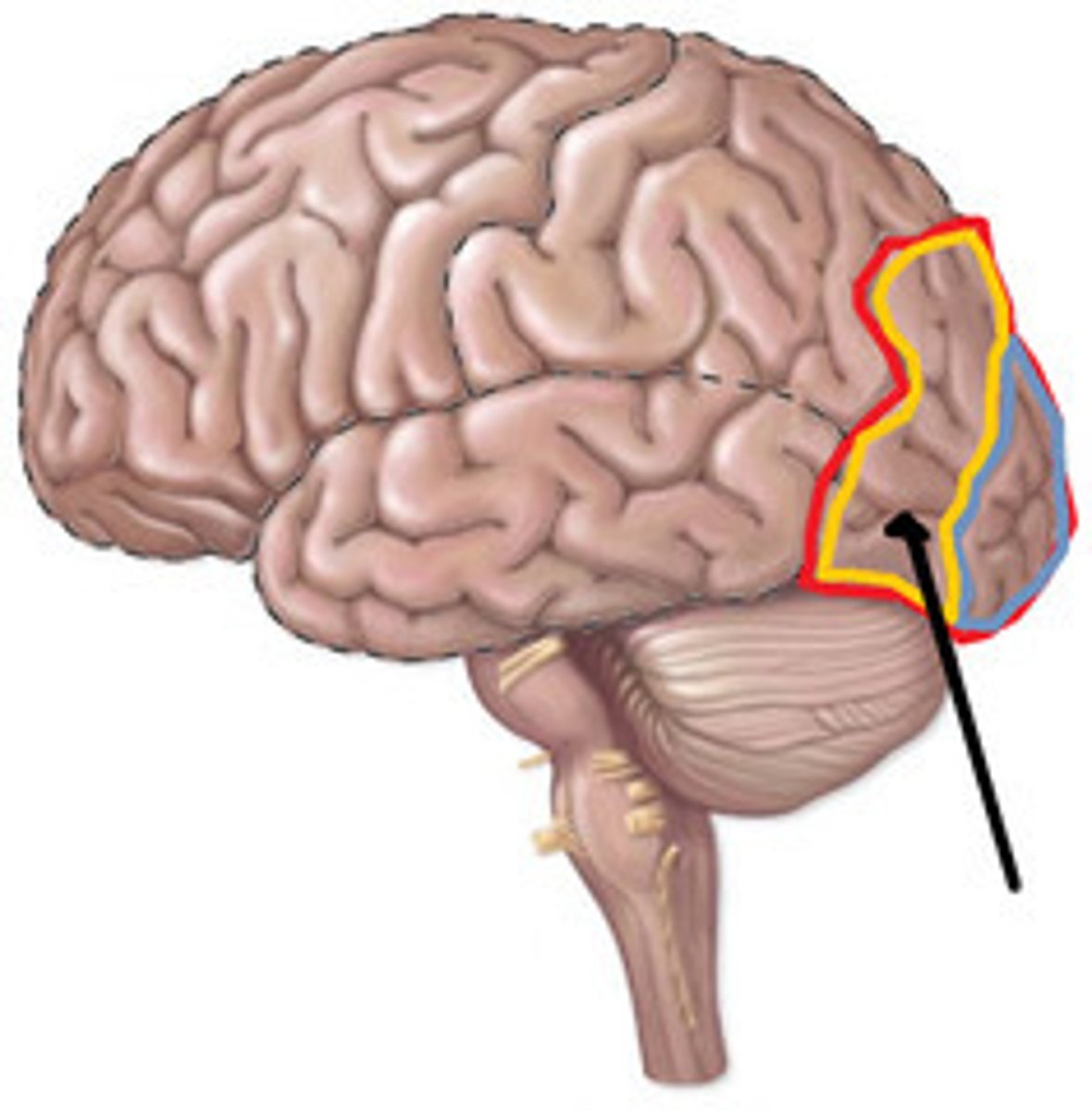
association areas
areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking
prefrontal cortex
part of frontal lobe responsible for thinking, planning, and language
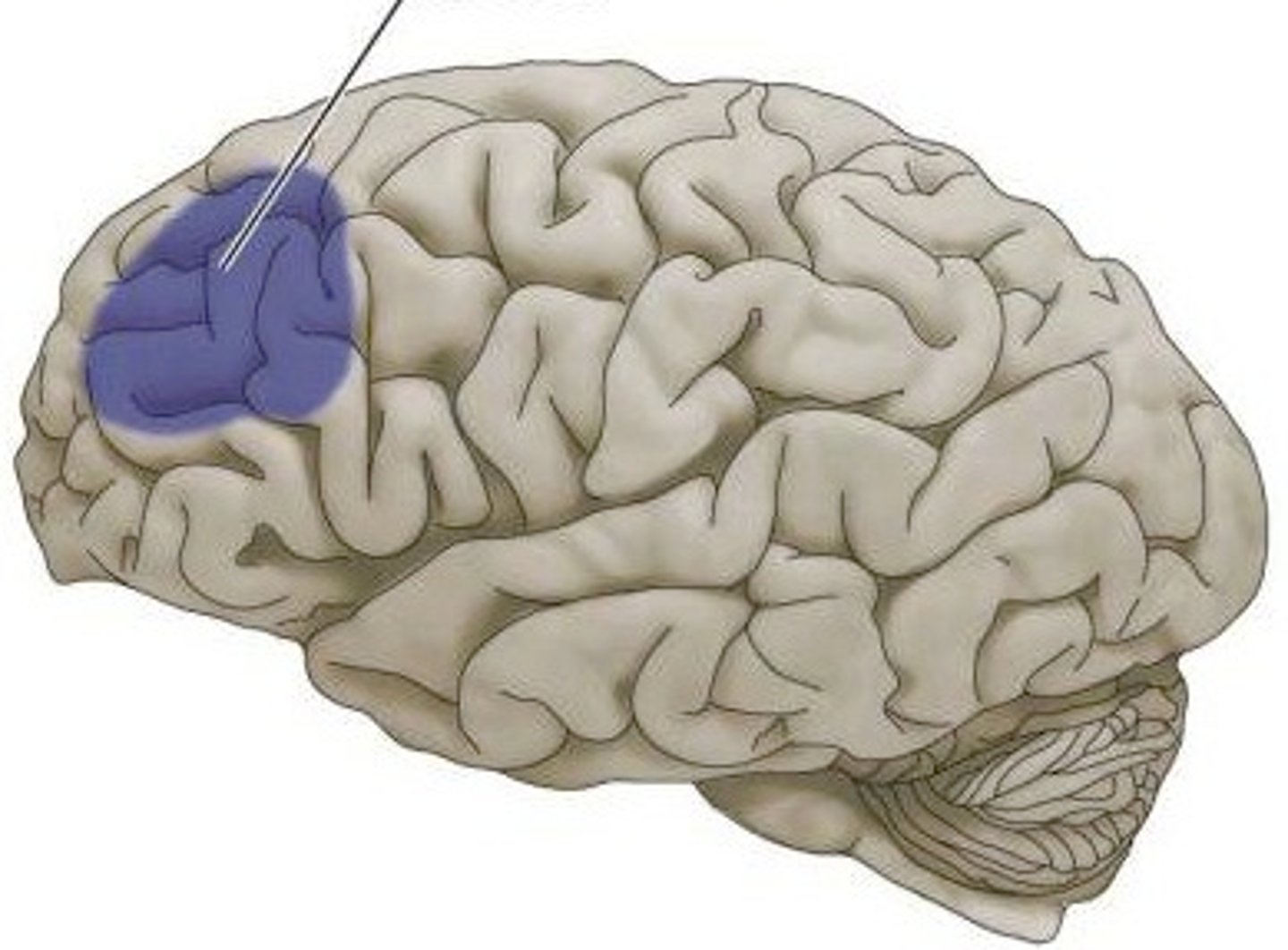
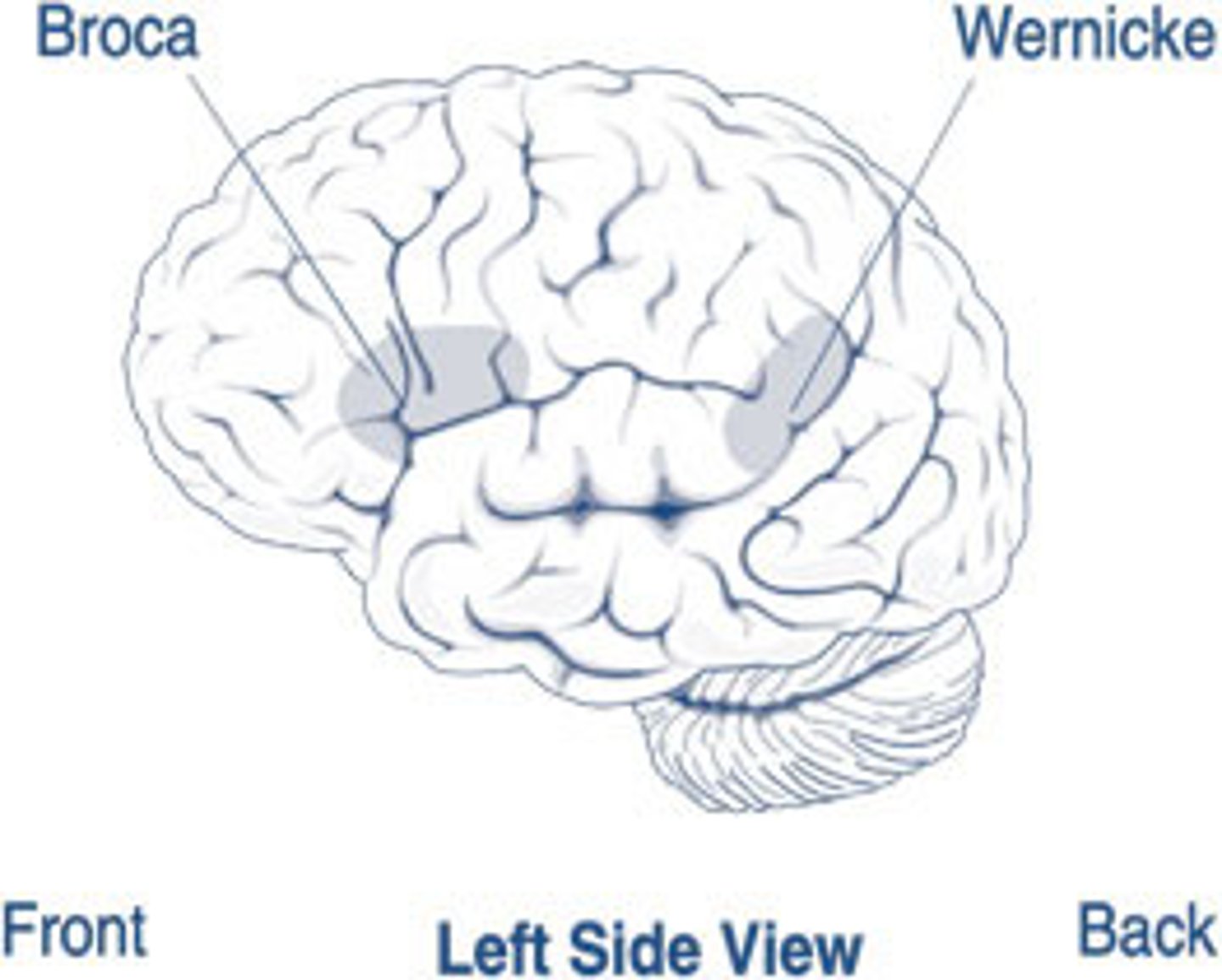
broca's area
Controls language expression - an area of the frontal lobe, usually in the left hemisphere, that directs the muscle movements involved in speech.
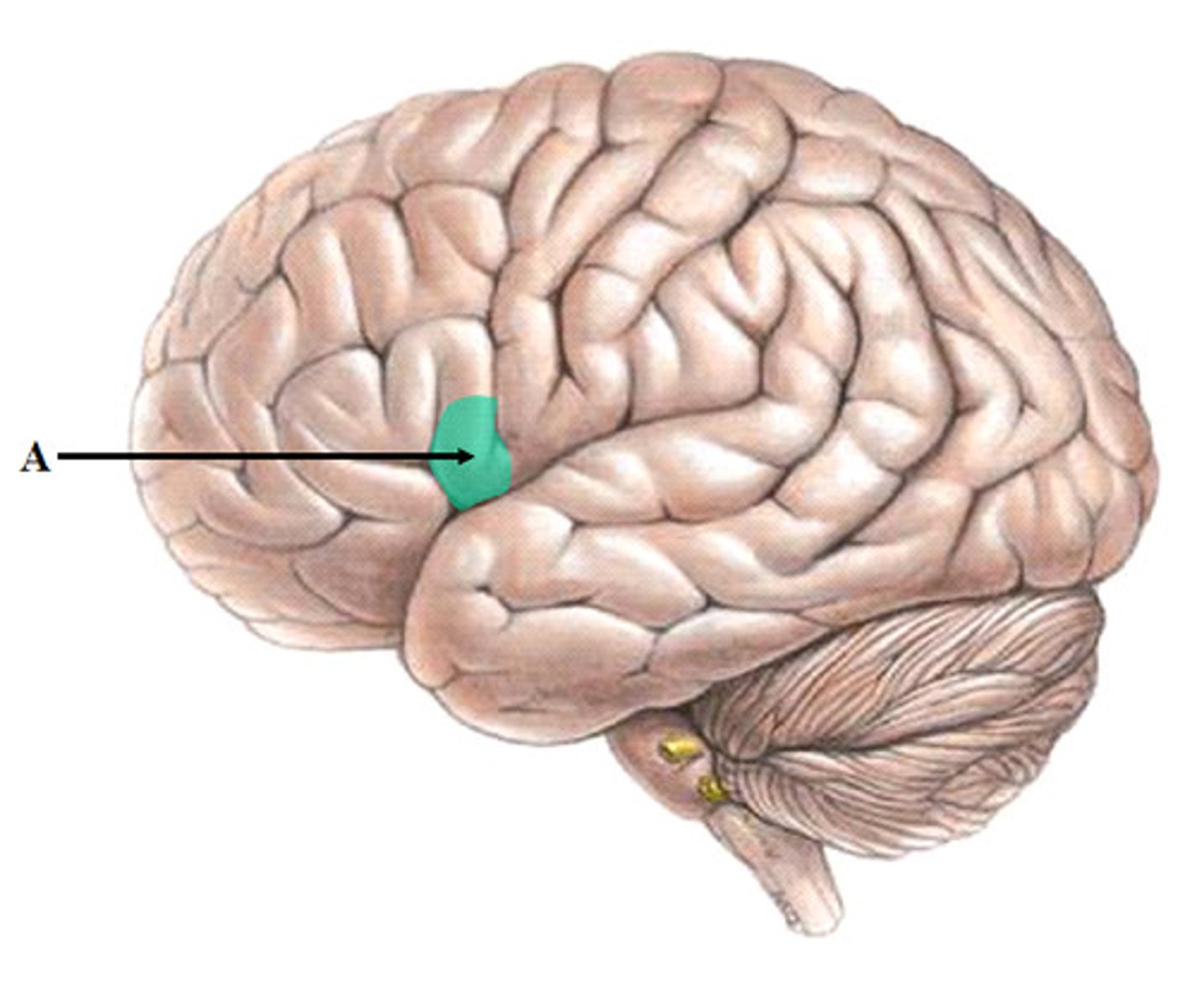
wernicke's area
controls language reception - a brain area involved in language comprehension and expression; usually in the left temporal lobe
lesion
tissue destruction
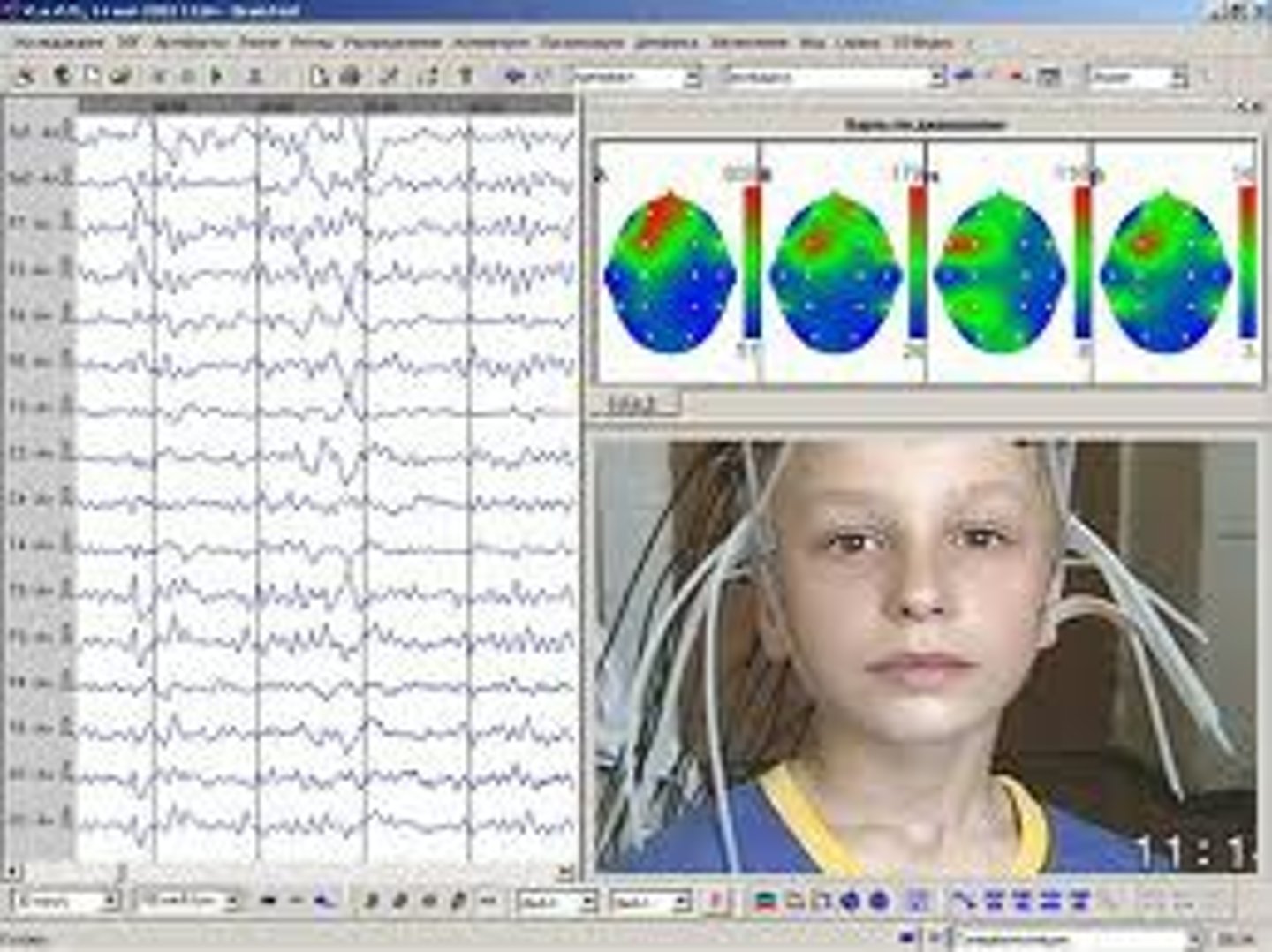
EEG (electroencephalogram)
An amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity that sweep across the brain's surface. These waves are measured by electrodes placed on the scalp.
fMRI
A technique for revealing blood flow and, therefore, brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans.
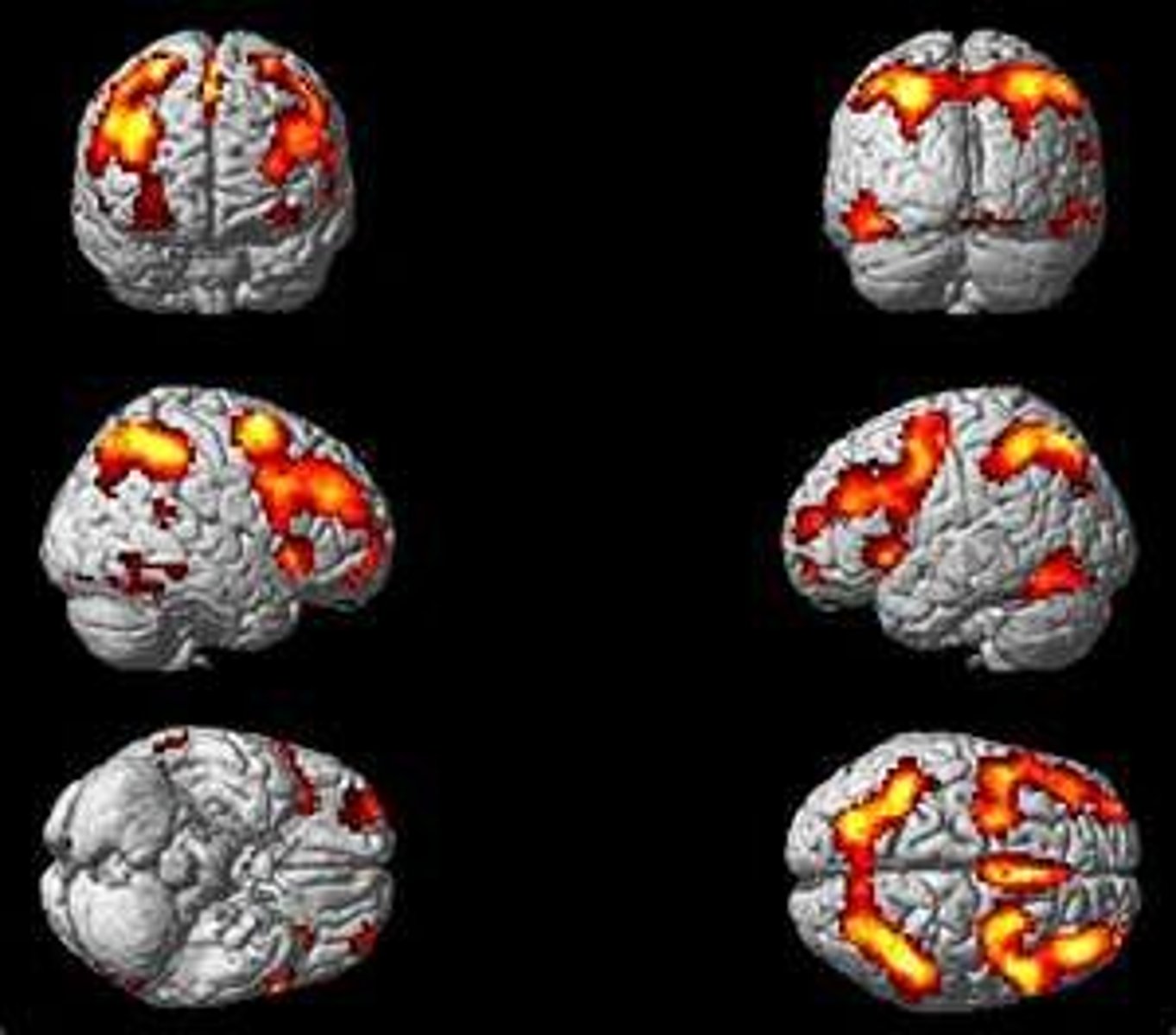
brain plasticity
The capacity for the brain to alter its structure and function.
neurogenesis
the formation of new neurons
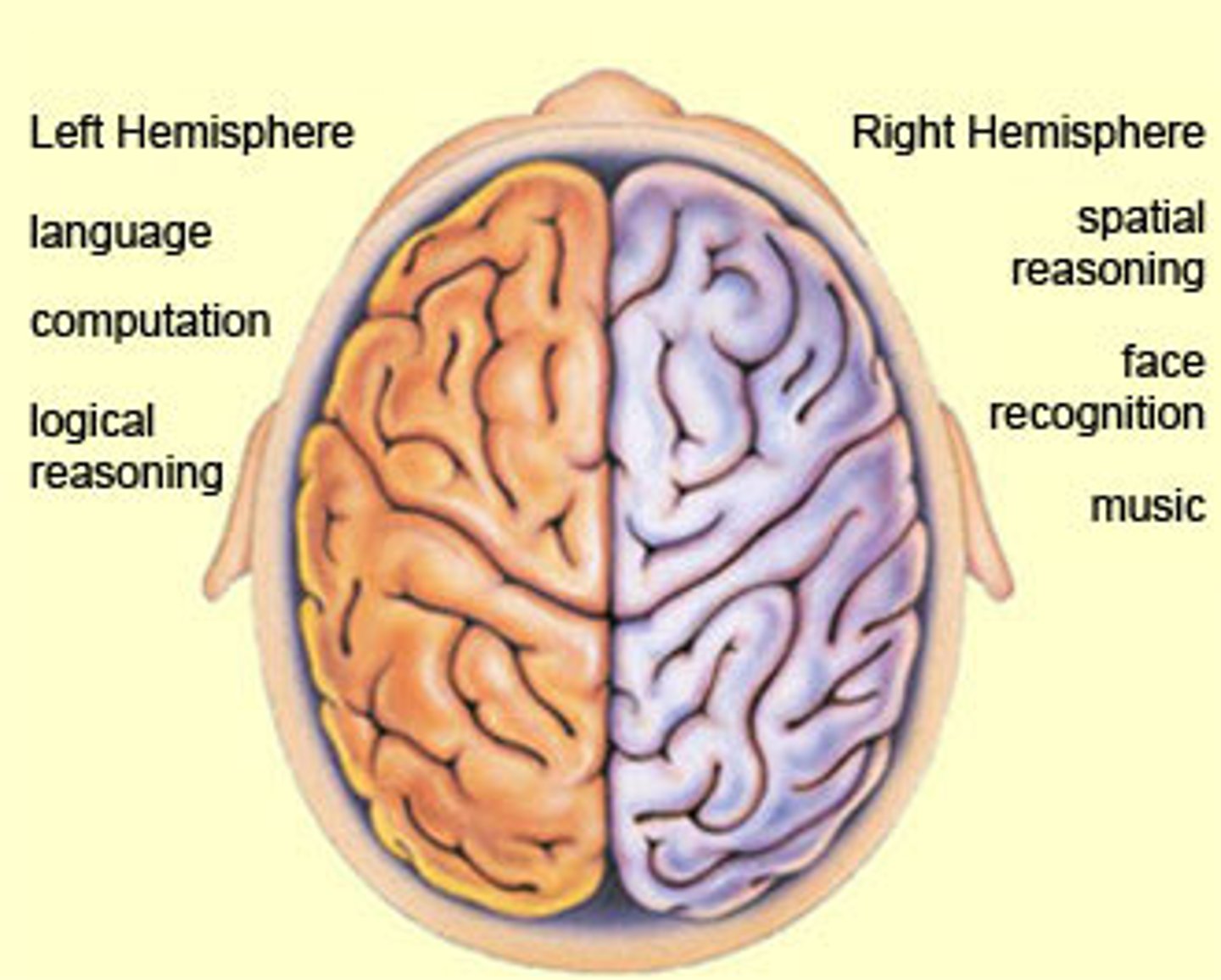
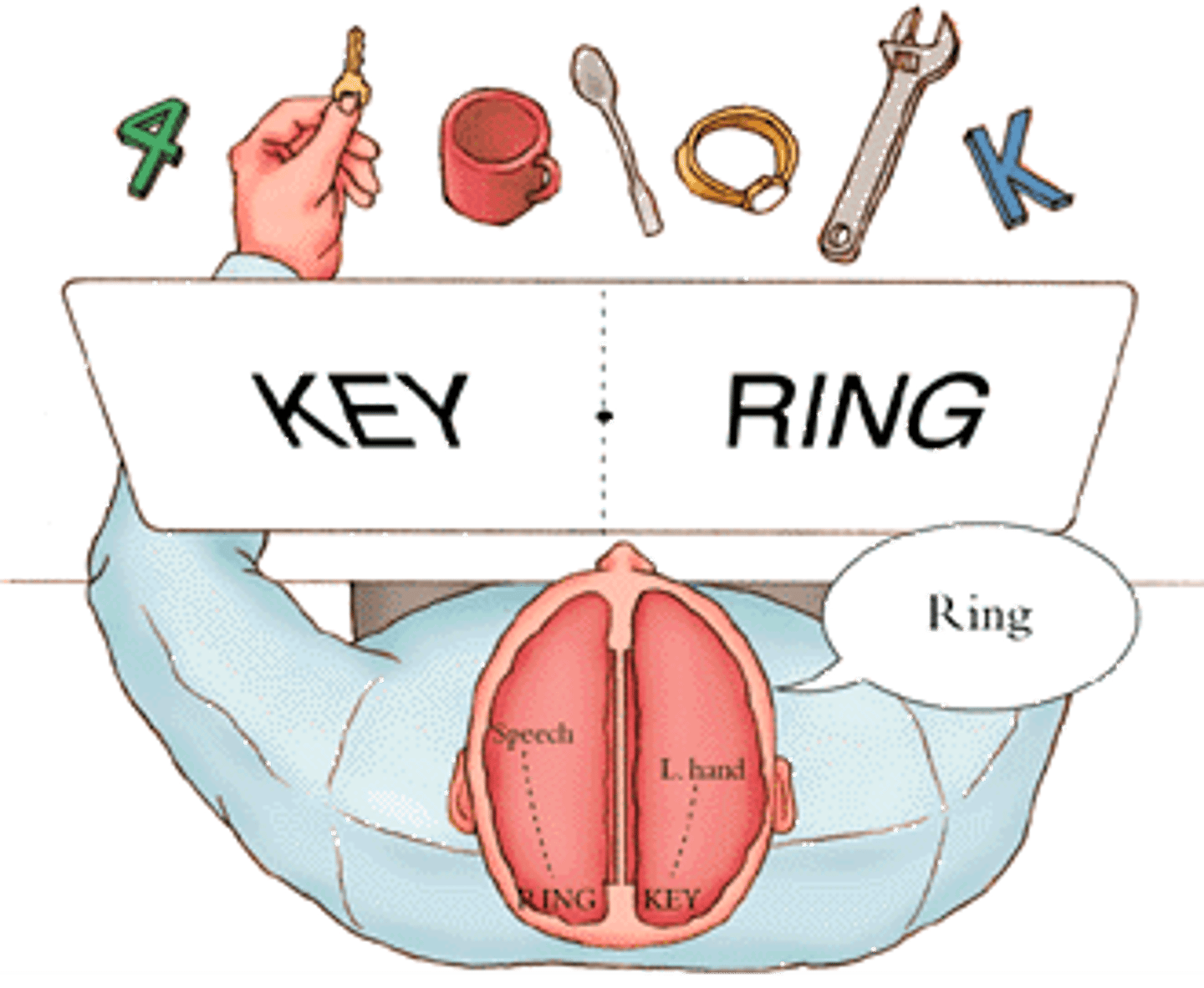
lateralization
cognitive function that relies more on one side of the brain than the other
contralateral organization
opposite-side organization, in which stimulation of neurons on one side of the body or sensory organ is represented by the activity of neurons in the opposite side of the brain
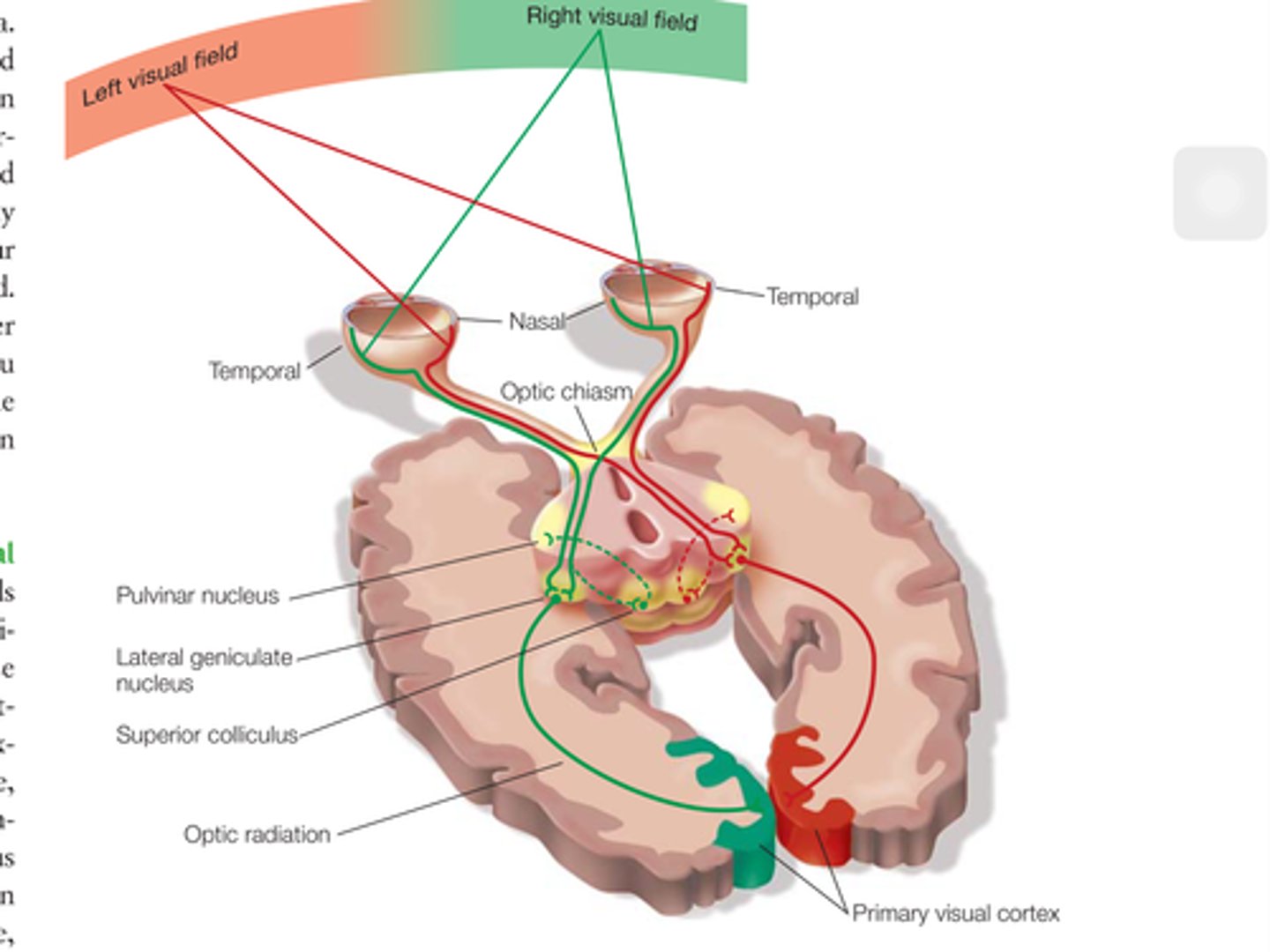
split brain patients
people whose corpus callosum has been surgically severed
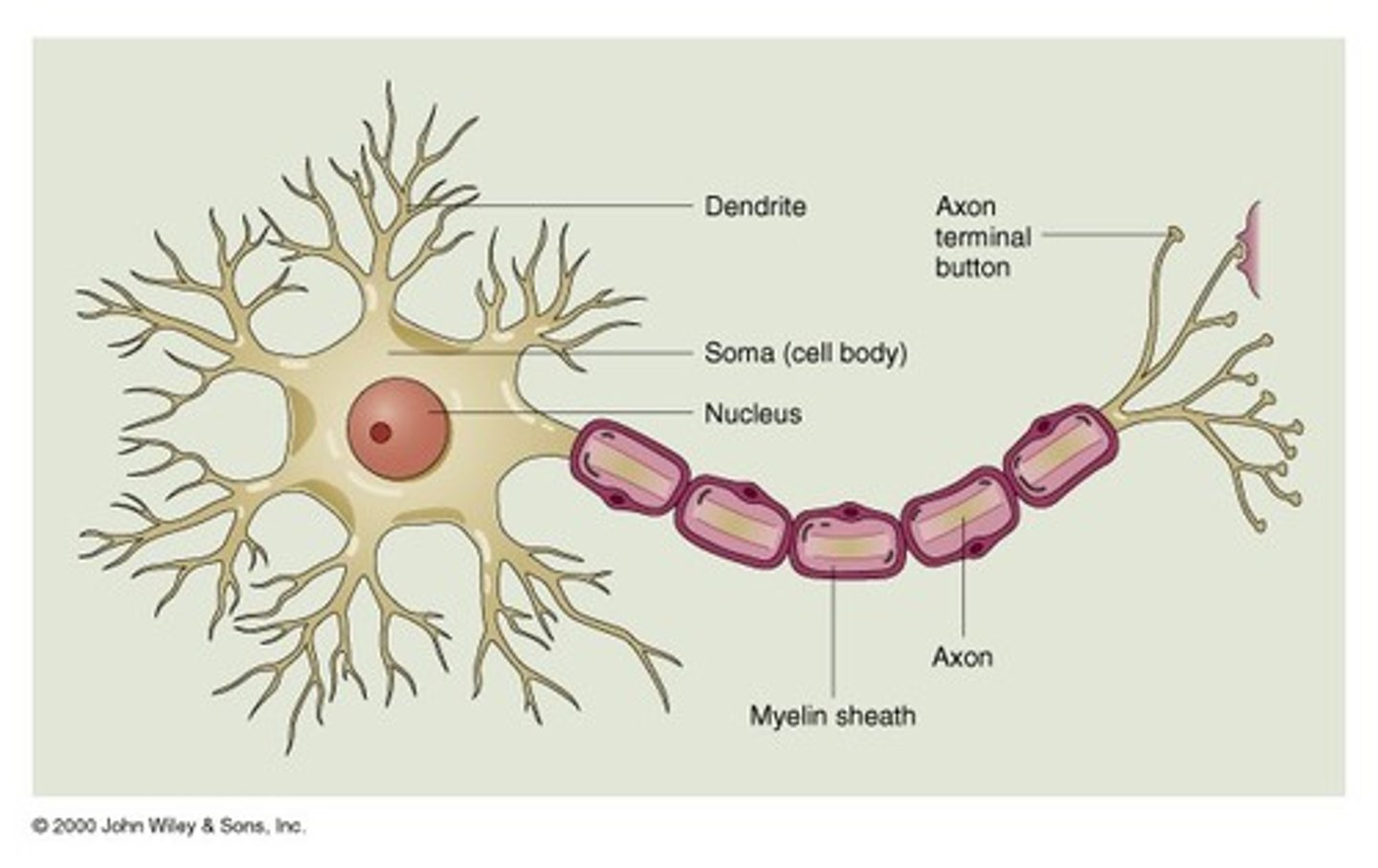
neurons
nerve cells
glial cells
cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons
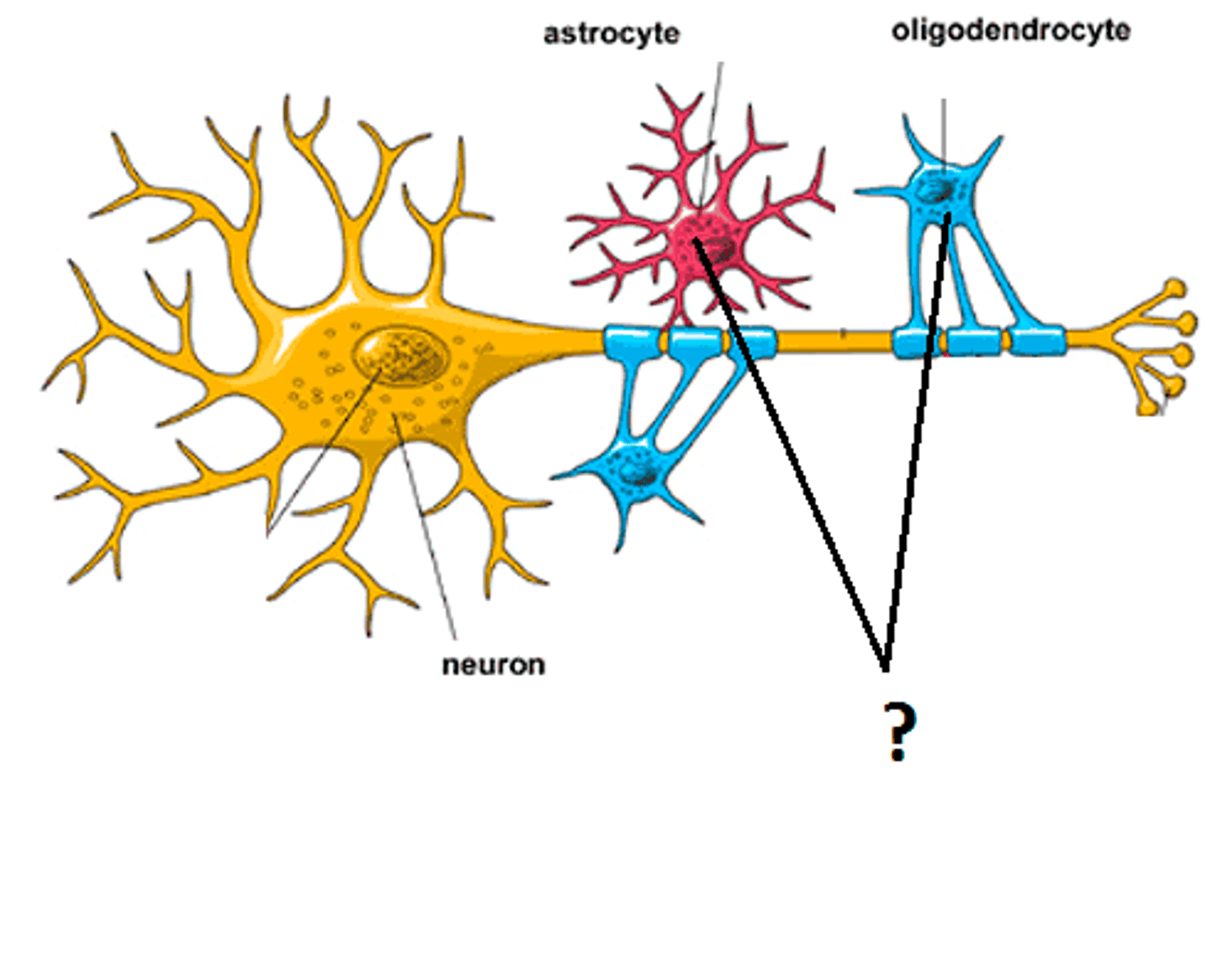
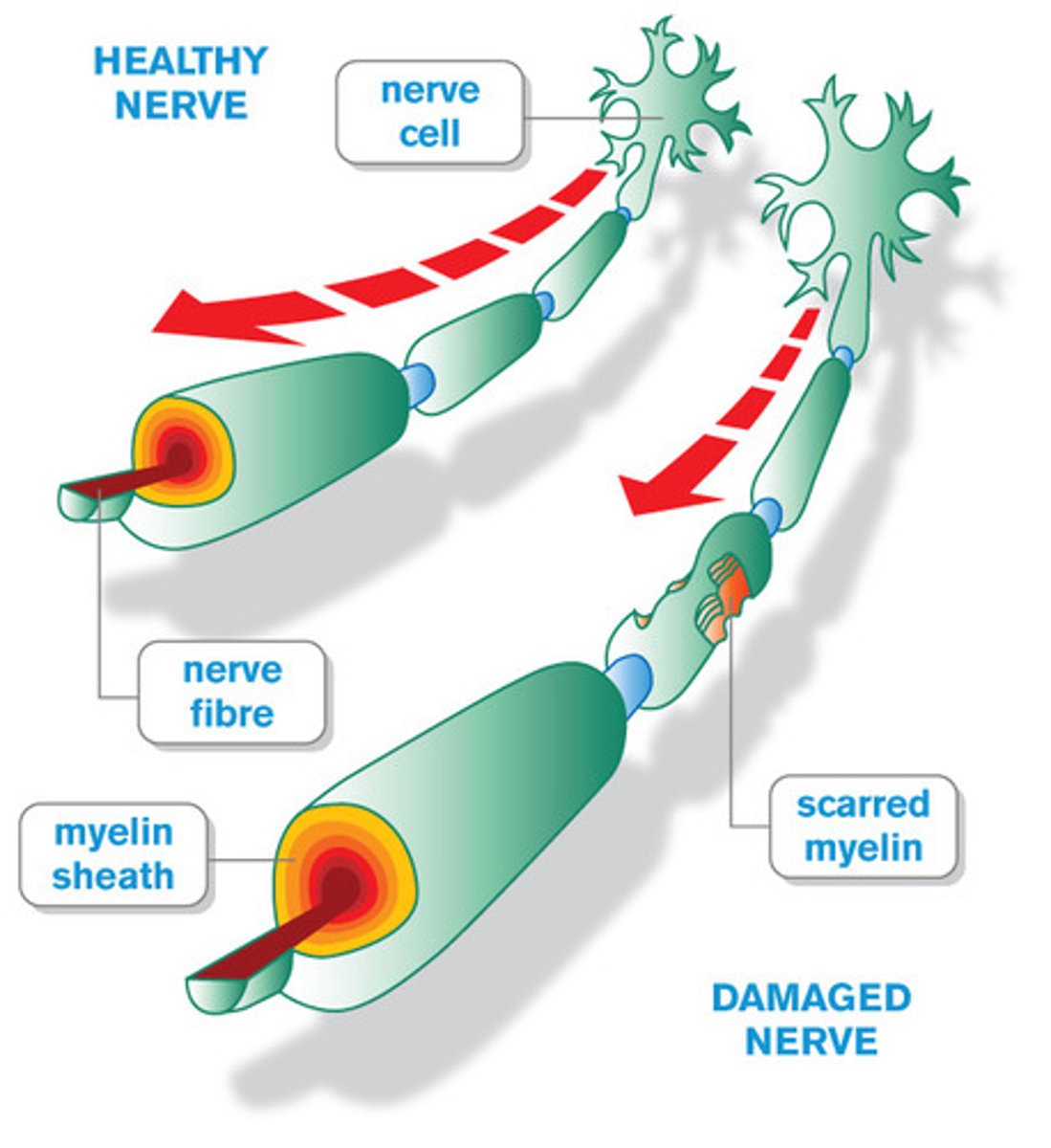
multiple sclerosis
myelin sheath destruction. disruptions in nerve impulse conduction
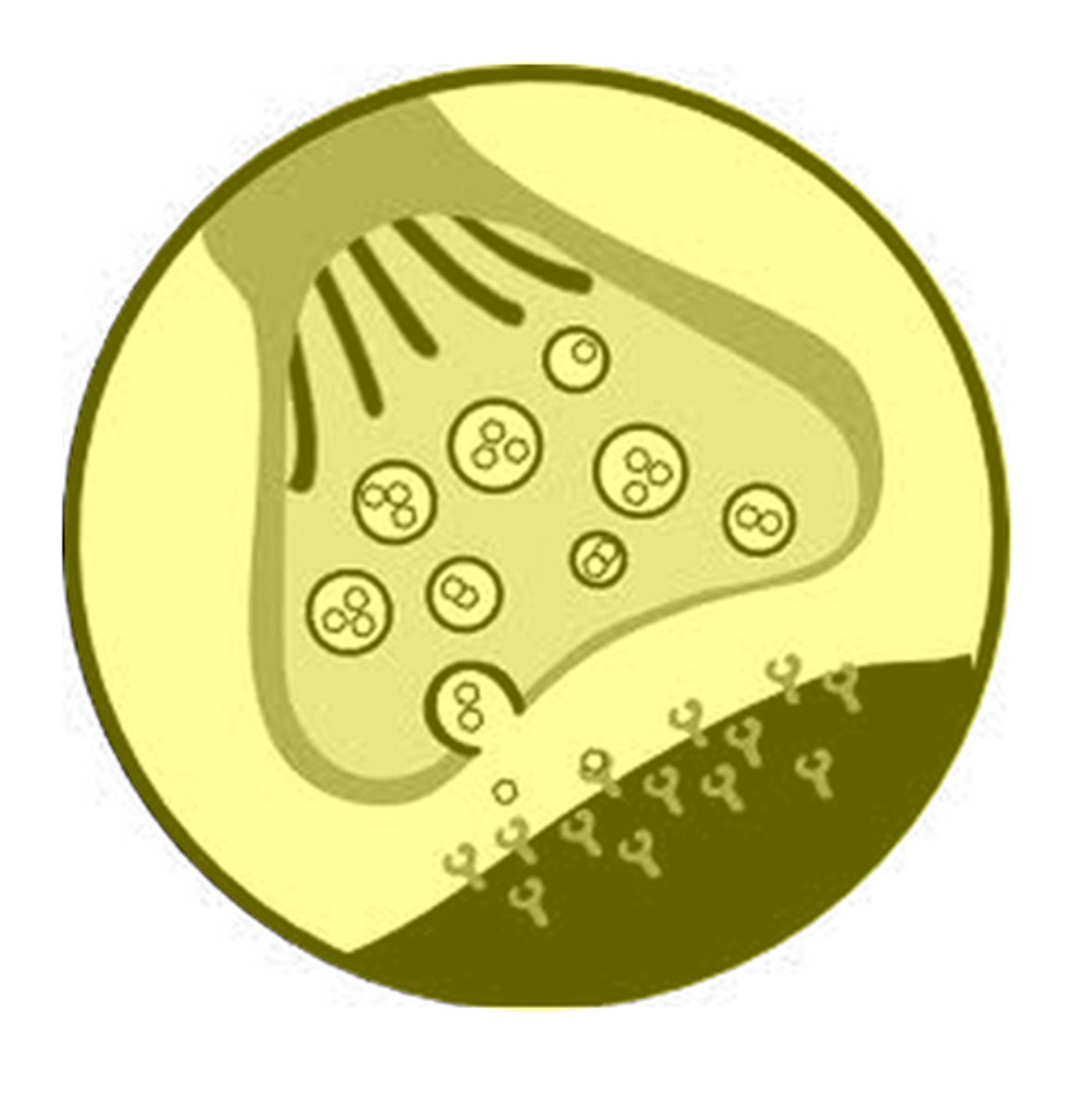
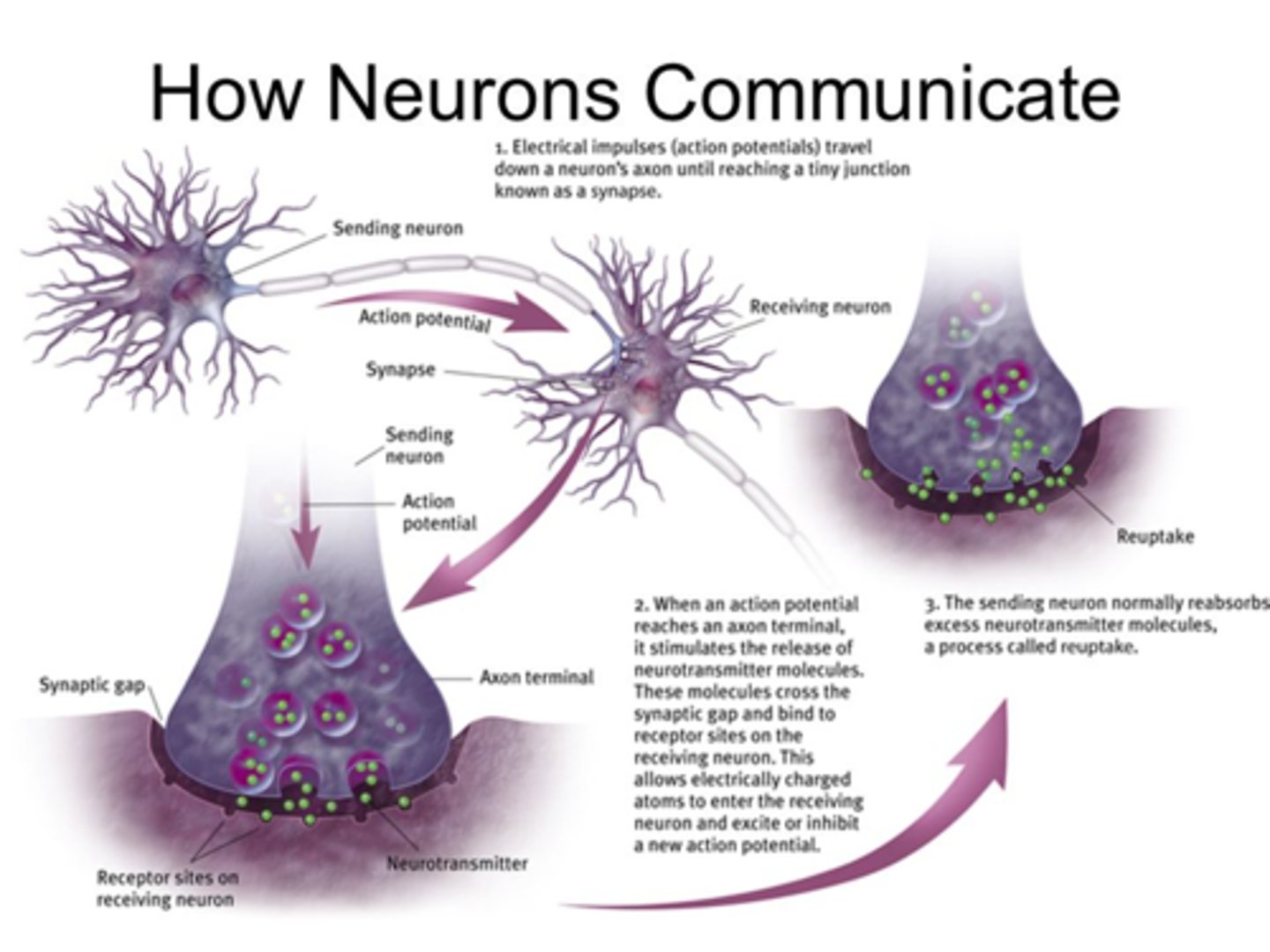
Synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
sensory neuron
neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord
motor neurons
neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands
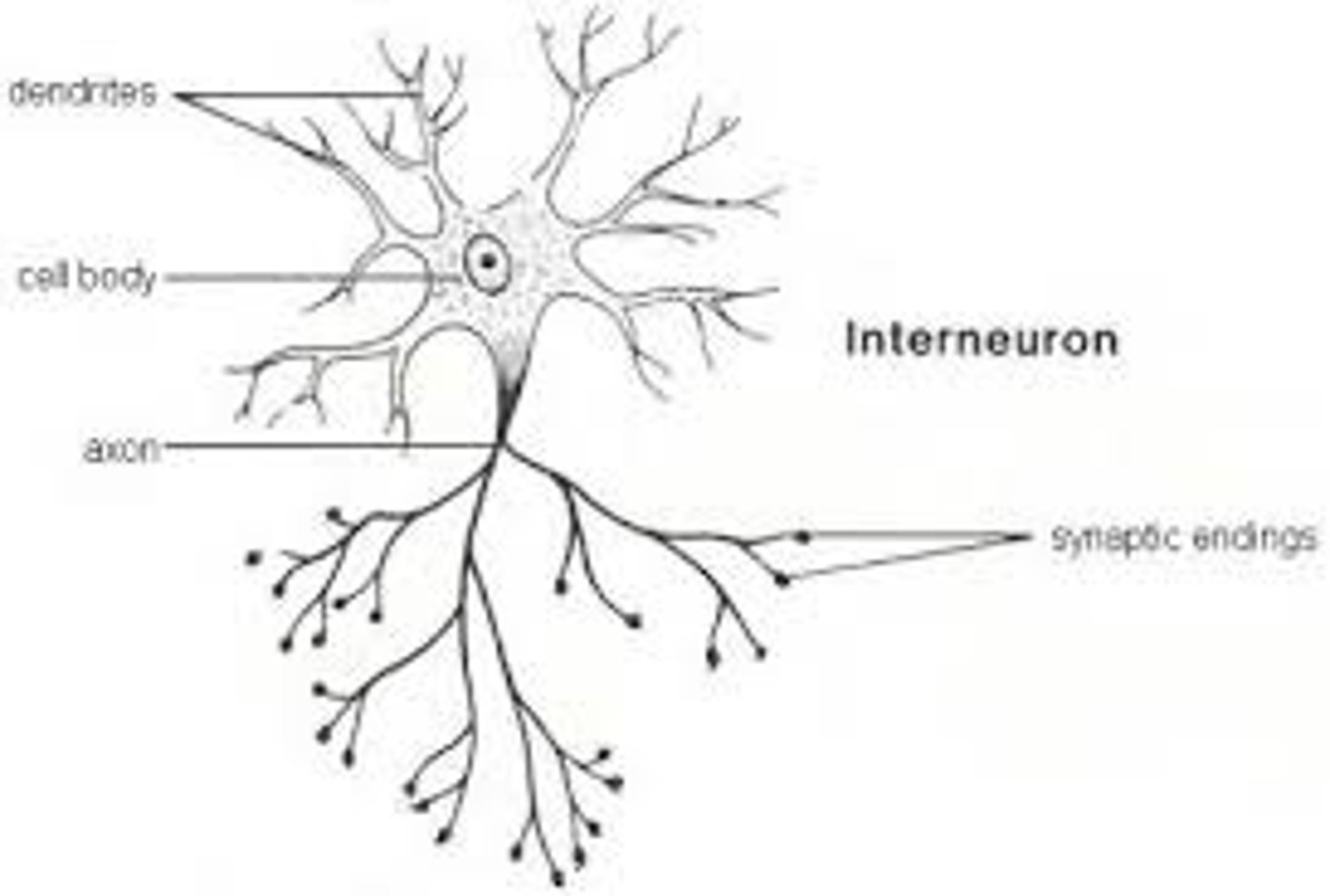
interneuron
a neuron that carries nerve impulses from one neuron to another
acetylcholine
A neurotransmitter that enables learning and memory and also triggers muscle contraction
myasthenia gravis
autoimmune neuromuscular disorder characterized by weakness of voluntary muscles (caused by deficit of acetylcholine)
alzheimer's disease
a progressive and irreversible brain disorder characterized by gradual deterioration of memory, reasoning, language, and, finally, physical functioning (caused by deficit of acetylcholine)
Dopamine
influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion

schizophrenia
a group of severe disorders characterized by disorganized and delusional thinking, disturbed perceptions, and inappropriate emotions and actions (caused by excess of dopamine)
parkinson's disease
A disorder of the central nervous system that affects movement, often including tremors. (caused by deficit of dopamine)
serotonin
Affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal
norepinephrine
A neurotransmitter involved in arousal, as well as in learning and mood regulation
GABA
An inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain that
helps to reduce neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system. This means it can help calm things down when your brain is firing on all cylinders.
glutamate
A major excitatory neurotransmitter; involved in memory
endorphins
"morphine within"--natural, opiatelike neurotransmitters linked to pain control and to pleasure.
substance P
A neurotransmitter that is involved in the transmission of pain messages to the brain.

adrenaline
A hormone released into the bloodstream in response to physical or mental stress
leptin
hormone that signals the hypothalamus and brain stem to reduce appetite and increase the amount of energy used
ghrelin
A hunger-arousing hormone secreted by an empty stomach

melatonin
A hormone manufactured by the pineal gland that produces sleepiness.

oxytocin
a hormone released by the pituitary gland that causes increased contraction of the uterus during labor and stimulates the ejection of milk into the ducts of the breasts.
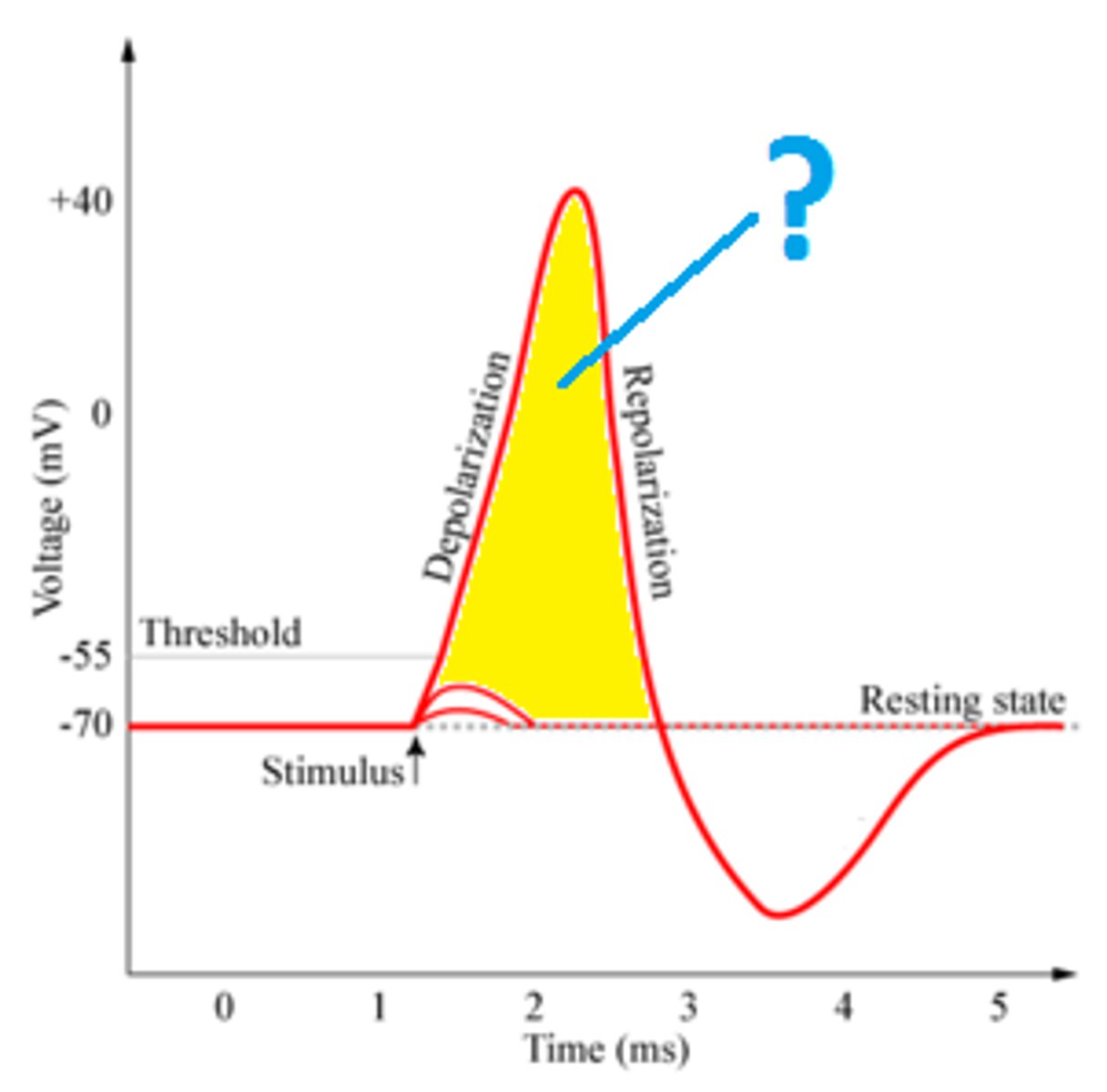
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
all or nothing response
a neuron's reaction of either firing or not firing

depolarization
The process during the action potential when sodium is rushing into the cell causing the interior to become more positive.
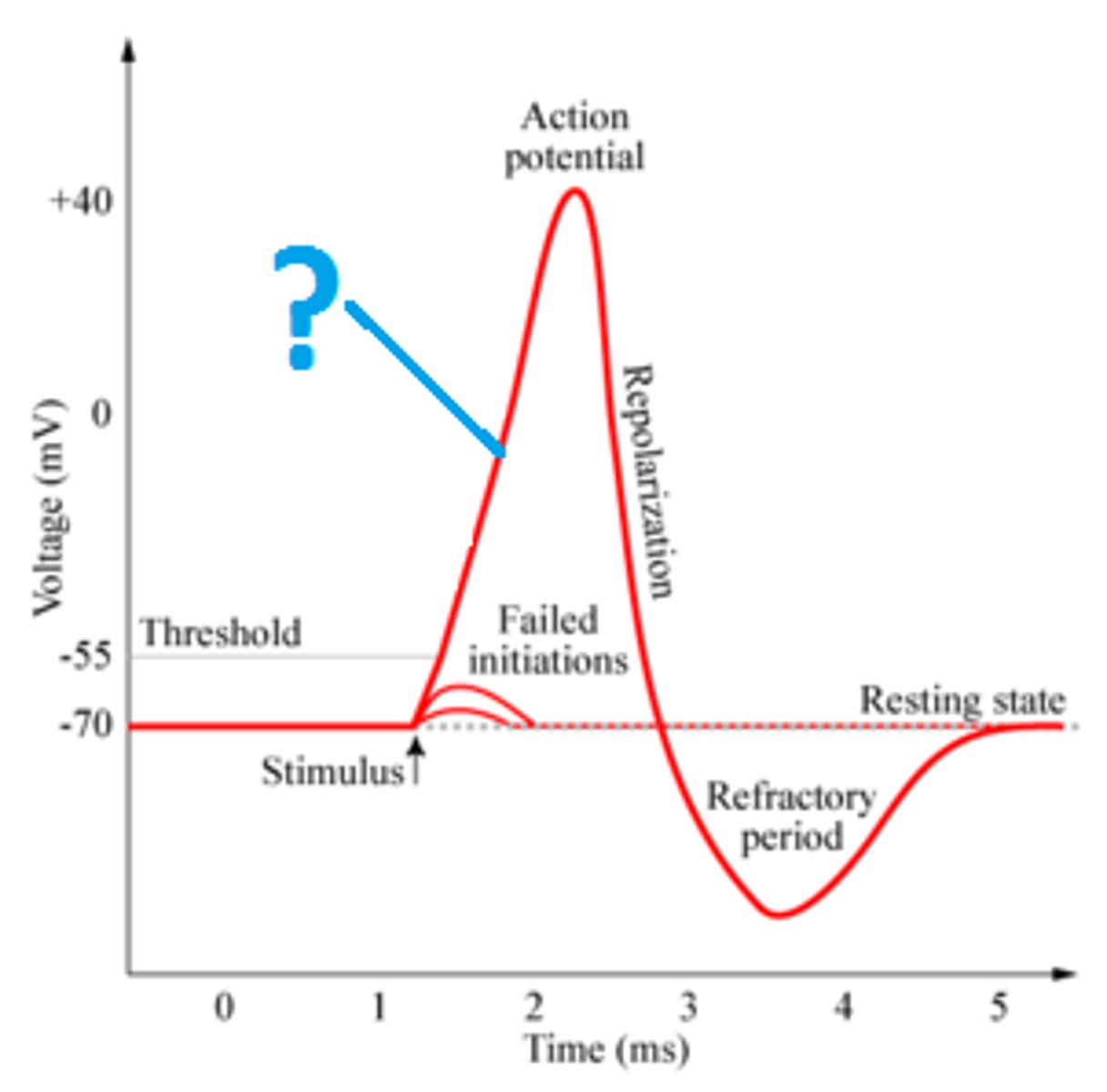
refractory period
a period of inactivity after a neuron has fired
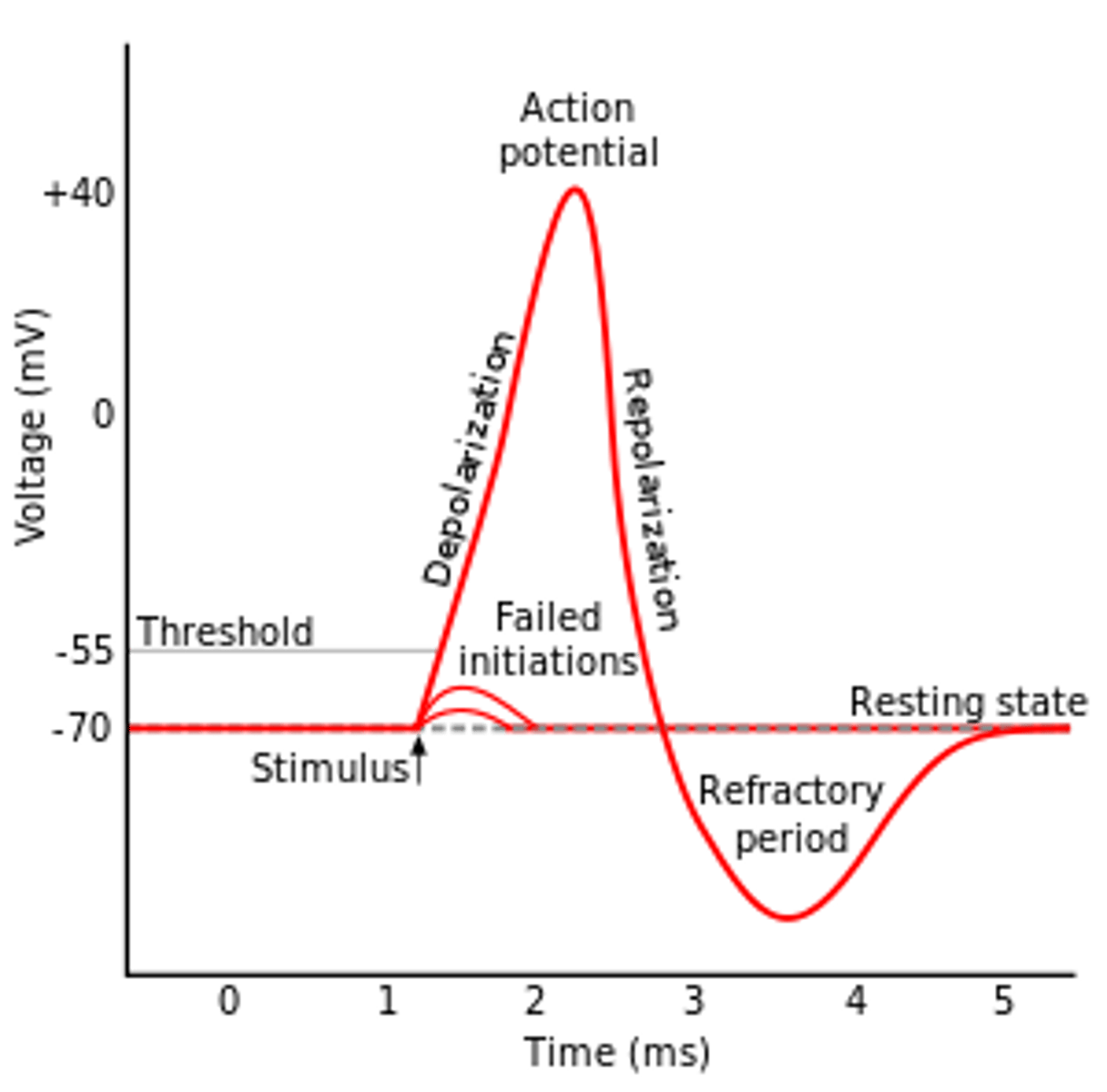
resting potential
The difference in electric charge between the inside and outside of a neuron's cell membrane
reuptake
a neurotransmitter's reabsorption by the sending neuron
threshold
the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
agonist
a molecule that, by binding to a receptor site, stimulates a response
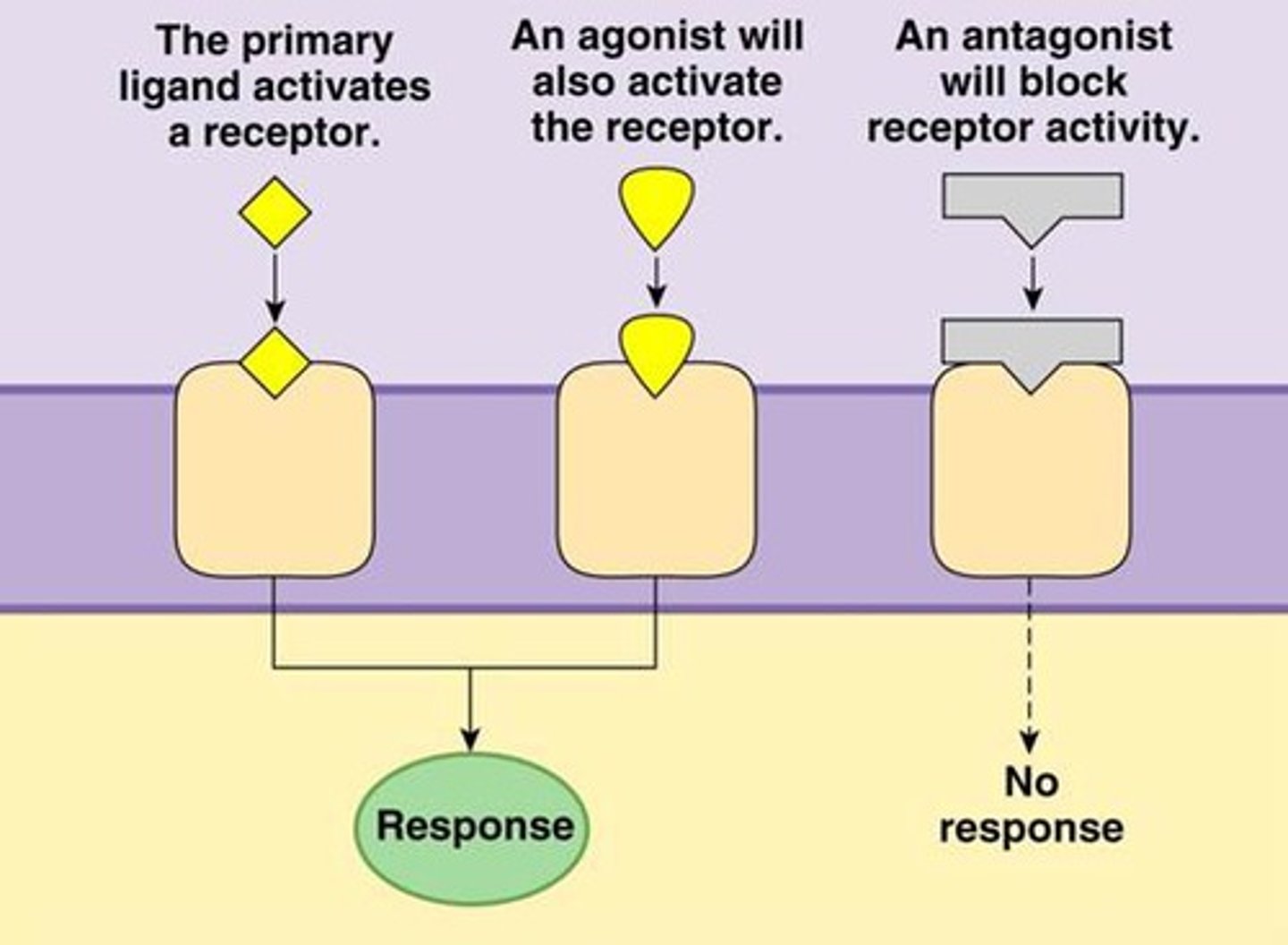
antagonist chemicals
chemical type that binds to and blocks receptor sites, minimizing the effects of neurotransmitters
psychoactive drug
a chemical substance that alters perceptions and moods
tolerance
the diminishing effect with regular use of the same dose of a drug, requiring the user to take larger and larger doses before experiencing the drug's effect
addiction
compulsive drug craving and use, despite adverse consequences
withdrawal
the discomfort and distress that follow discontinuing the use of an addictive drug
stimulants
Drugs (such as caffeine, nicotine, and the more powerful amphetamines, cocaine, and Ecstasy) that excite neural activity and speed up body functions.

depressants
drugs that reduce neural activity and slow body functions

hallucinogens
psychedelic ("mind-manifesting") drugs, such as LSD, that distort perceptions and evoke sensory images in the absence of sensory input

opiates
A category of psychoactive drugs that are chemically similar to morphine and have strong pain-relieving properties.
nervous system
the body's speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems
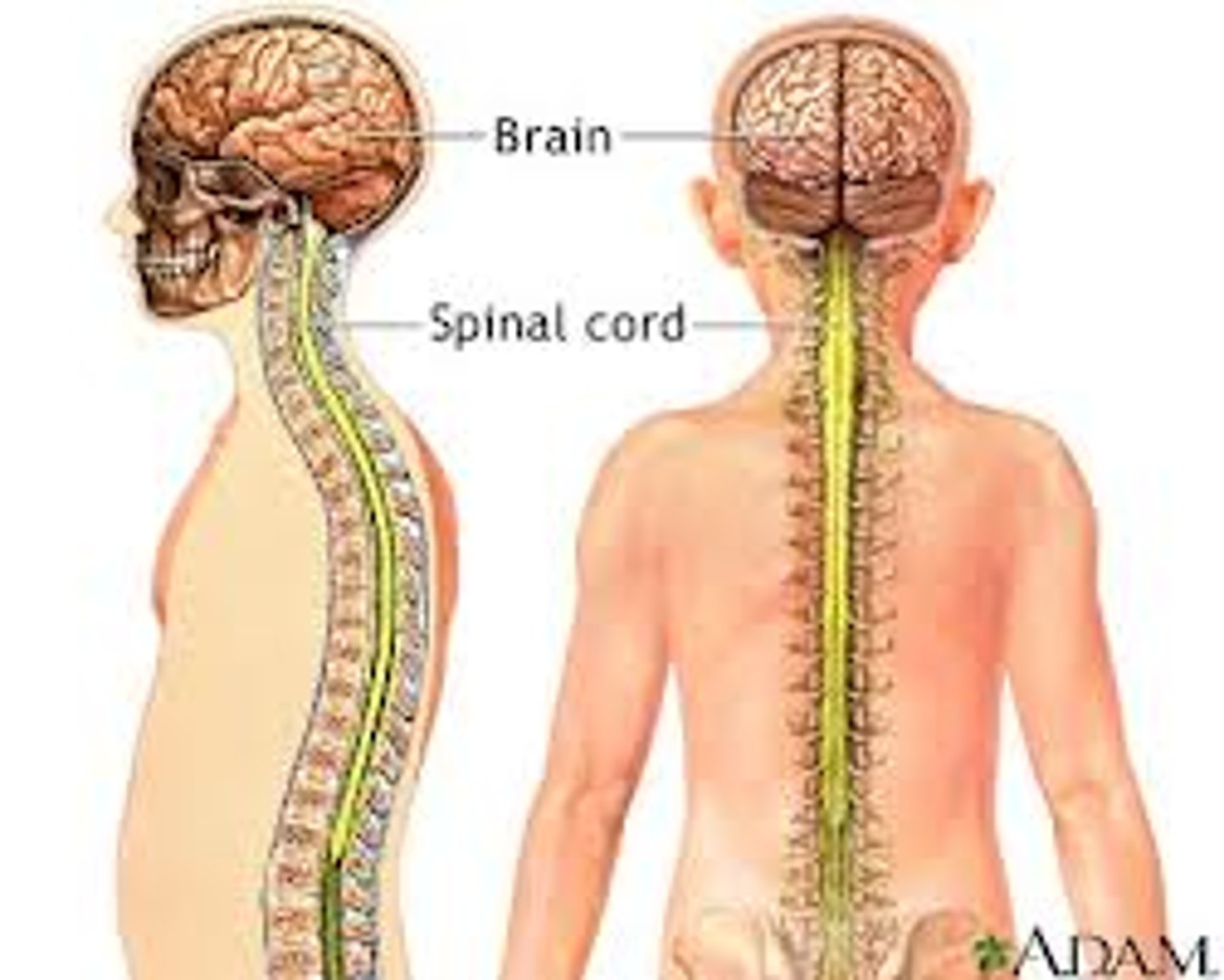
central nervous system
brain and spinal cord
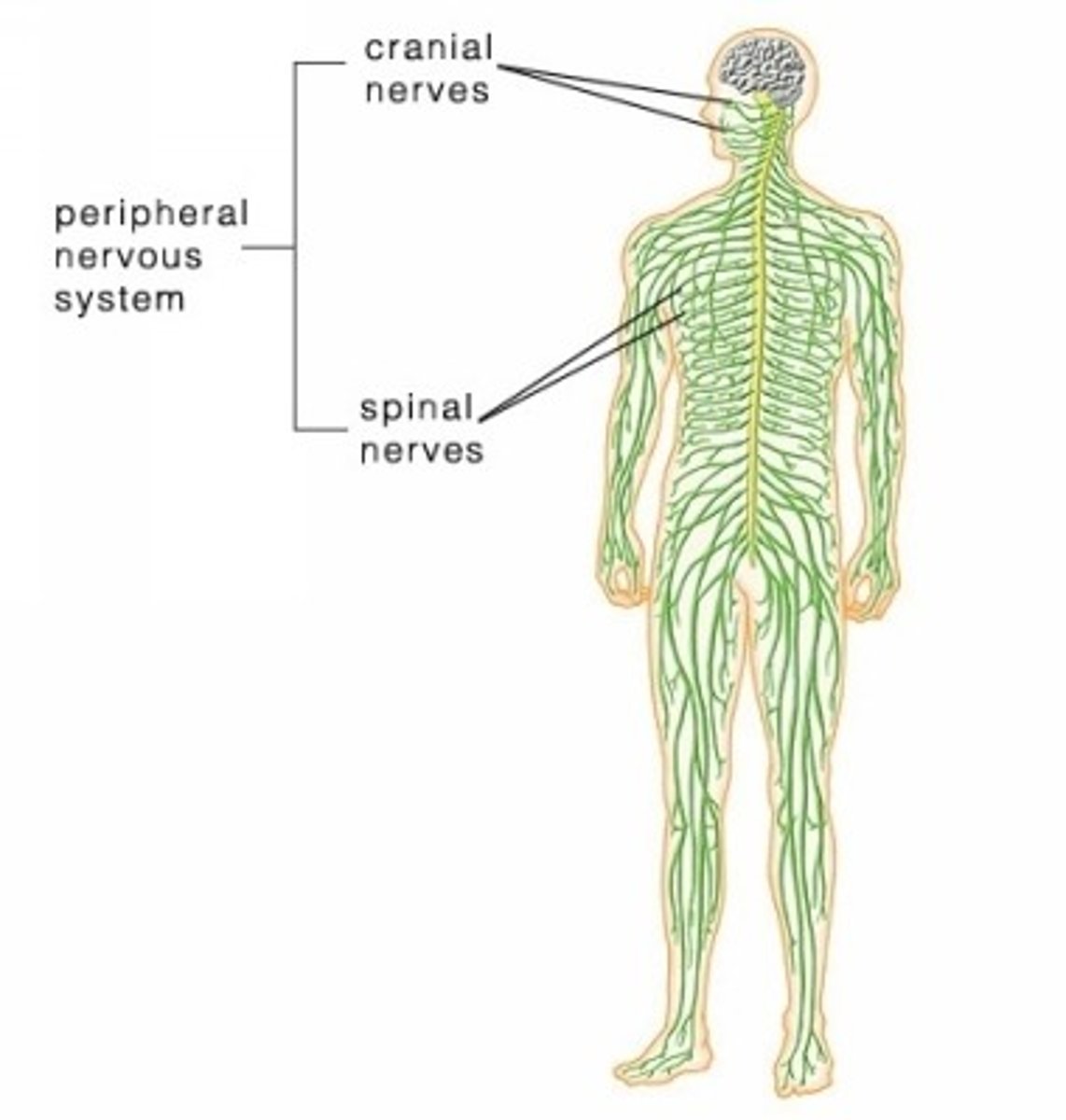
peripheral nervous system
A division of the nervous system consisting of all nerves that are not part of the brain or spinal cord.
autonomic nervous system
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart).
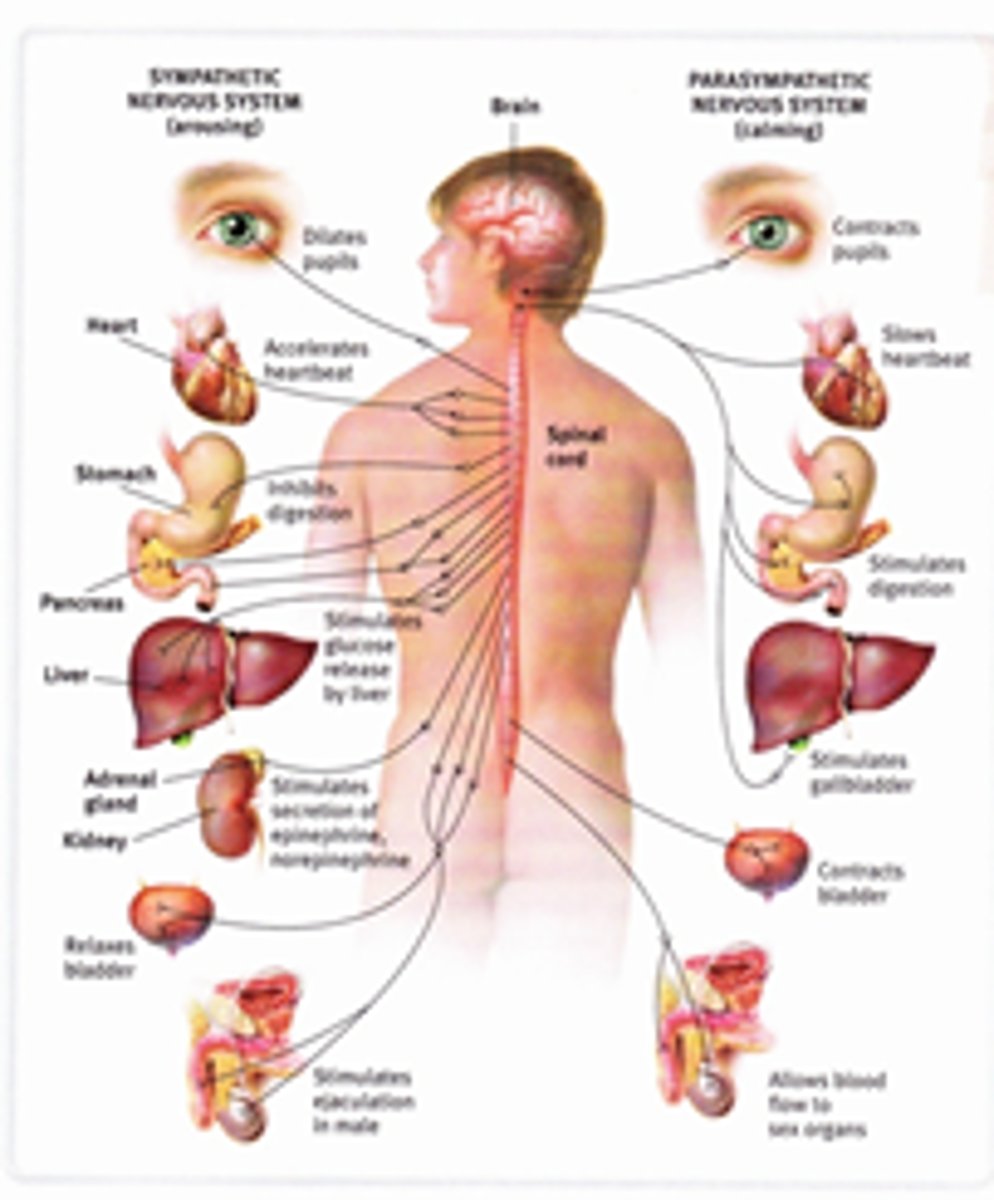
sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
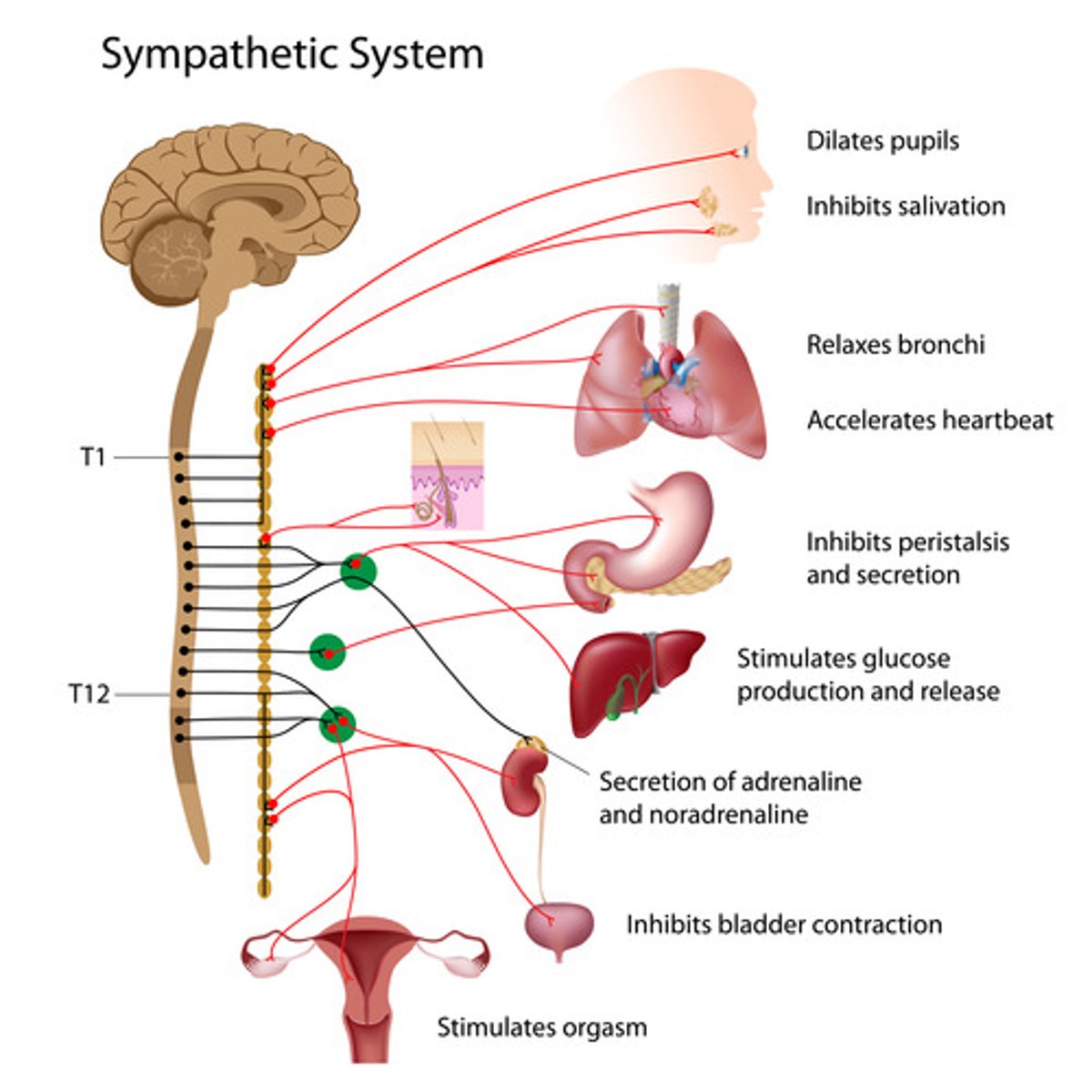
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy

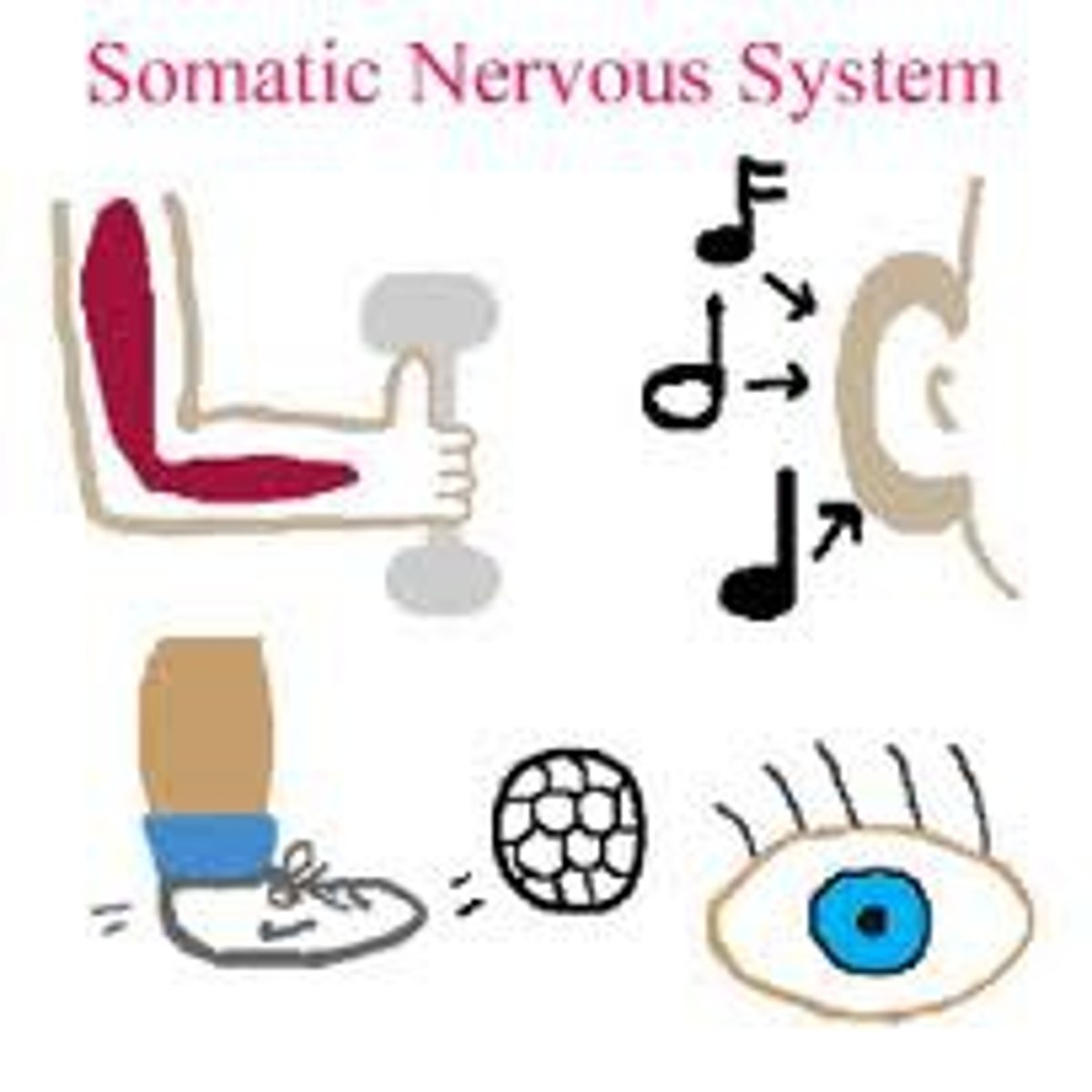
somatic nervous system
the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body's skeletal muscles
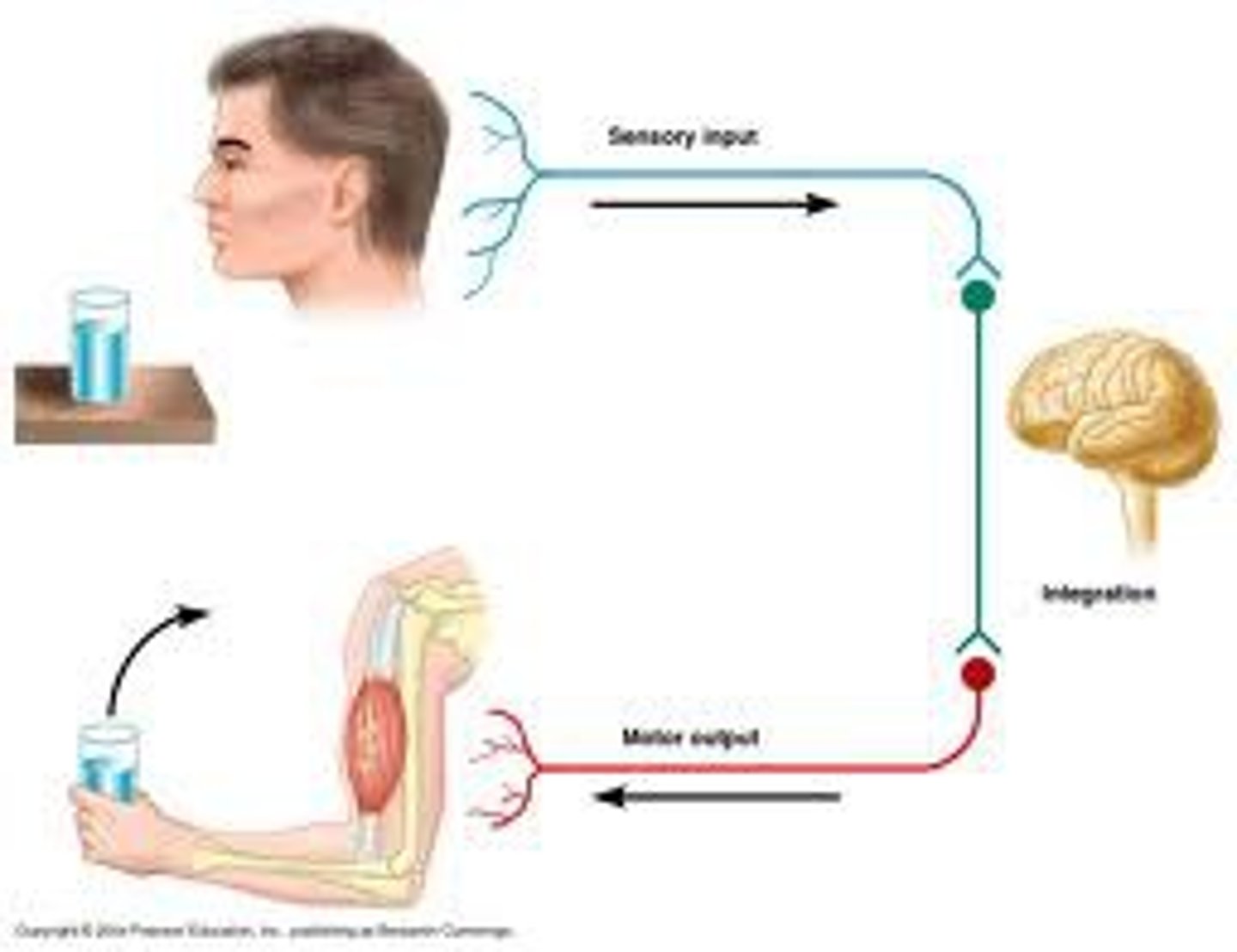
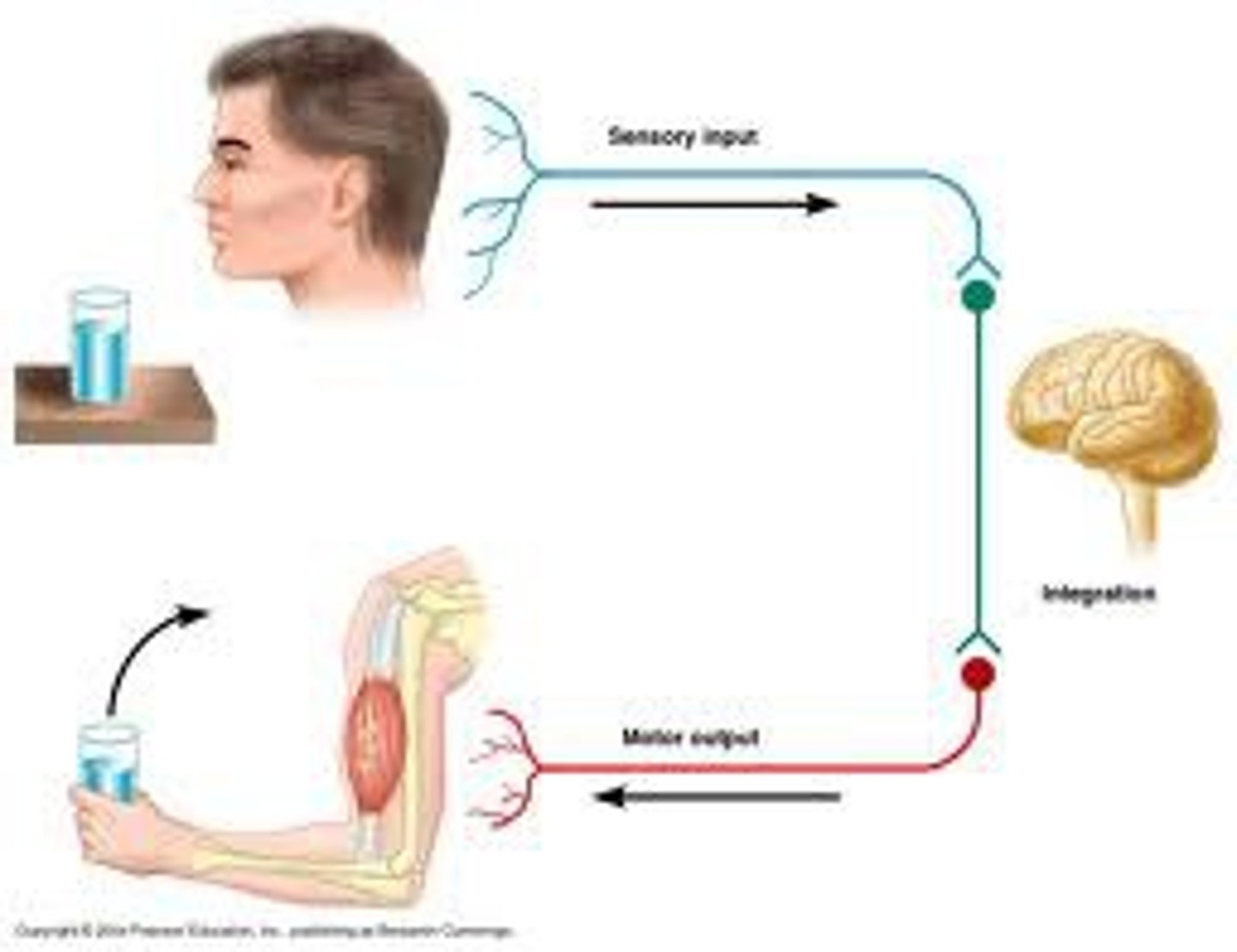
reflex arc
A relatively direct connection between a sensory neuron and a motor neuron that allows an extremely rapid response to a stimulus, often without conscious brain involvement.
consciousness
our awareness of ourselves and our environment

dual processing
the principle that information is often simultaneously processed on separate conscious and unconscious tracks
parallel processing
the processing of many aspects of a problem simultaneously; the brain's natural mode of information processing for many functions, including vision.
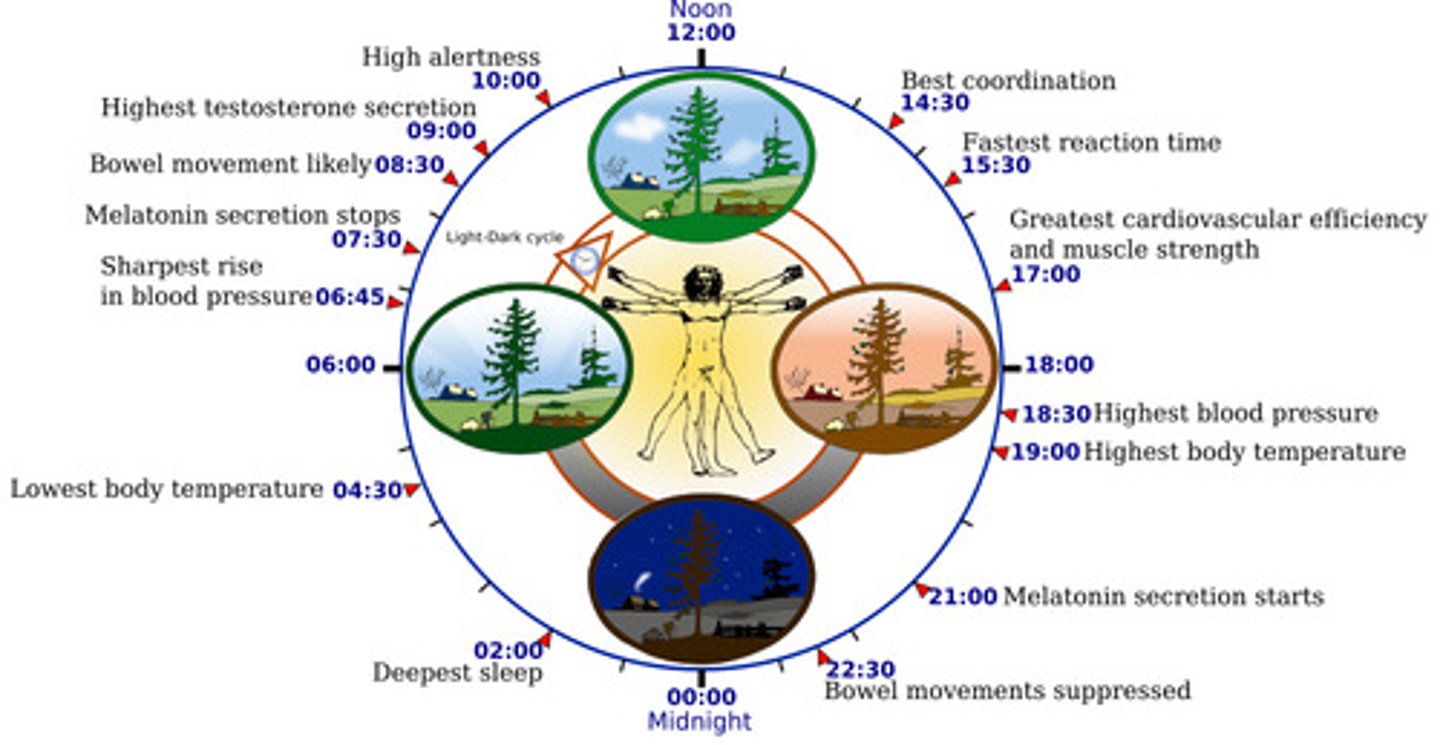
circadian rhythm
the biological clock; regular bodily rhythms that occur on a 24-hour cycle
REM rebound
the tendency for REM sleep to increase following REM sleep deprivation (created by repeated awakenings during REM sleep)

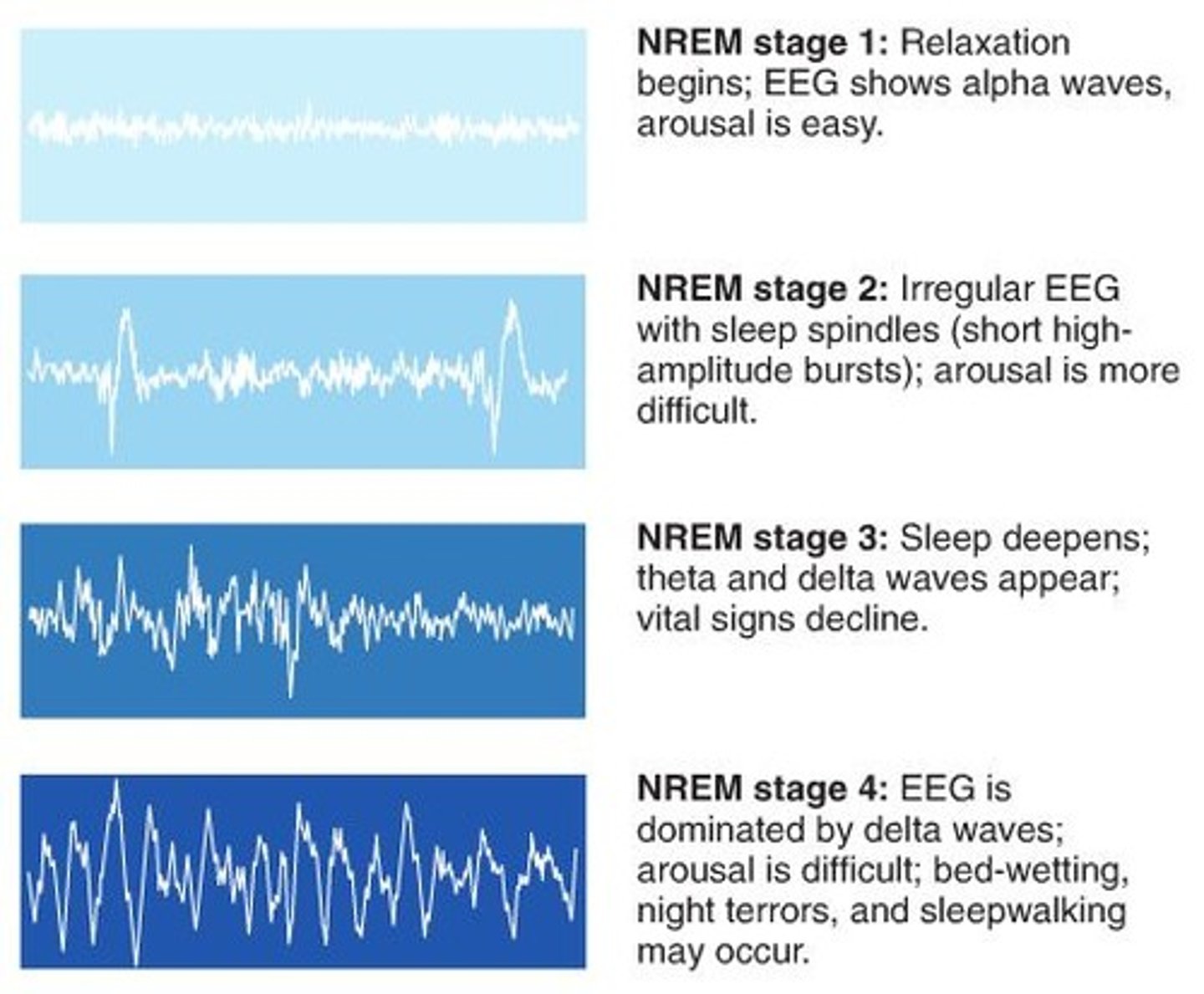
NREM 1
the transition into sleep, marked by slowed breathing and irregular brain waves; hypnagogic sensations/hallucinations, and myclonic jerks may occur
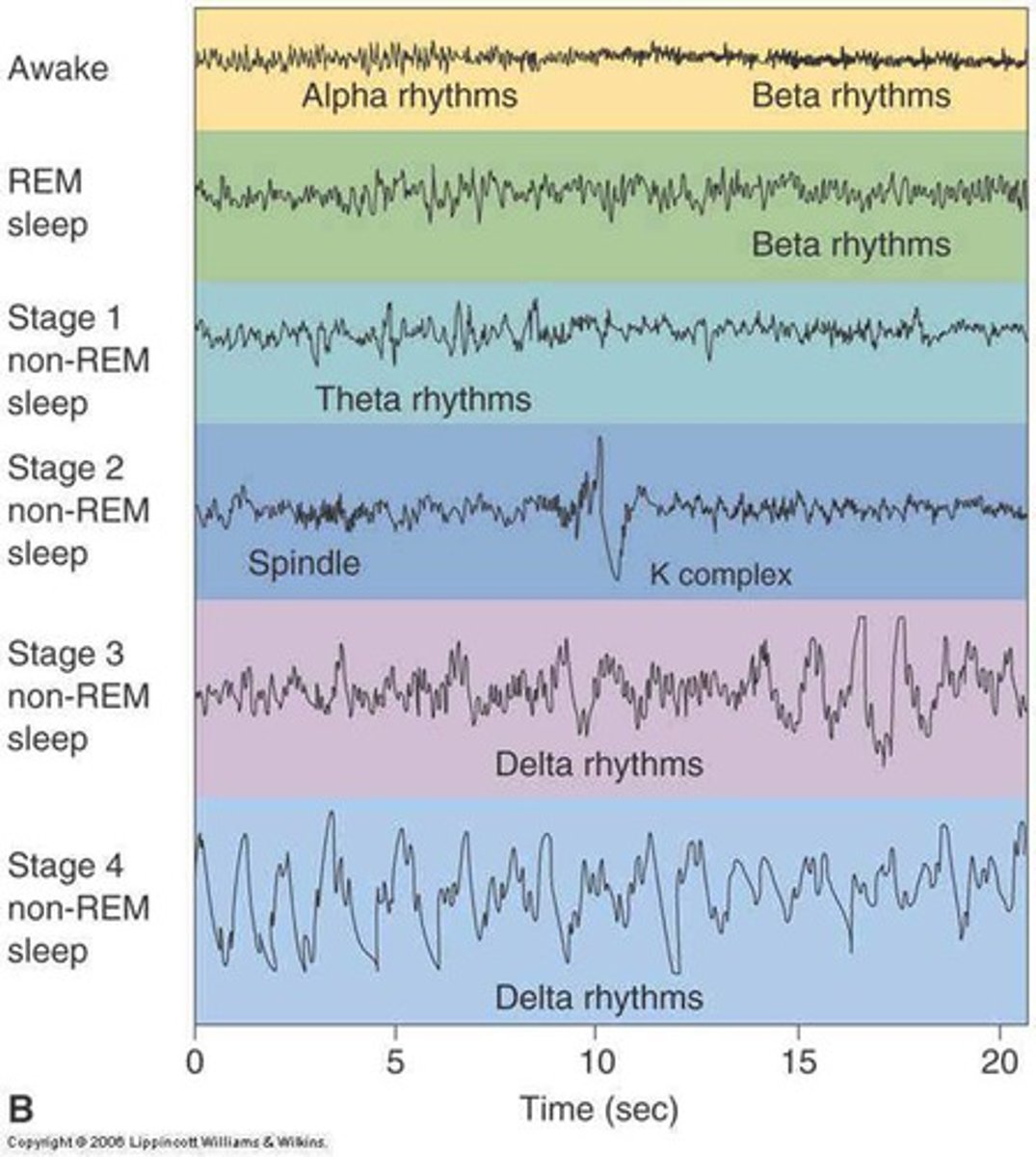
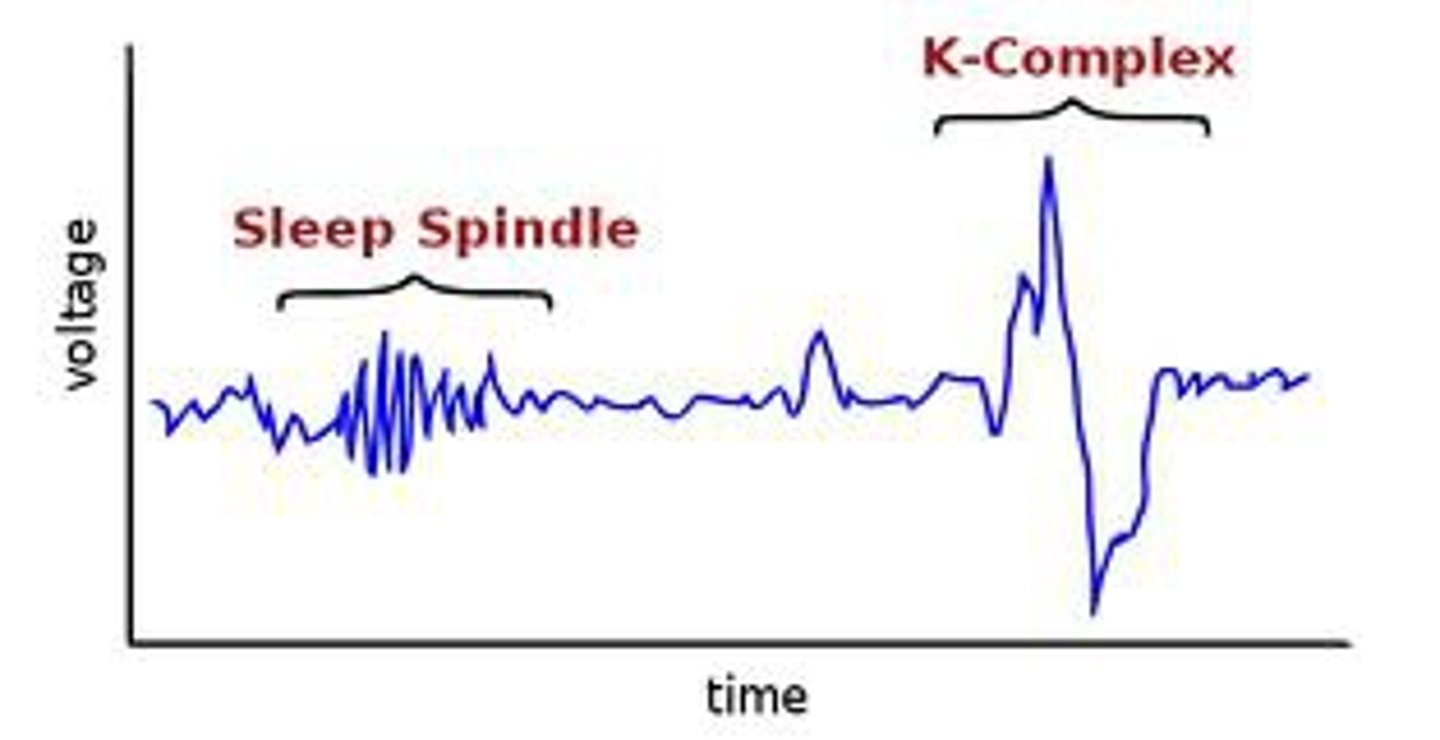
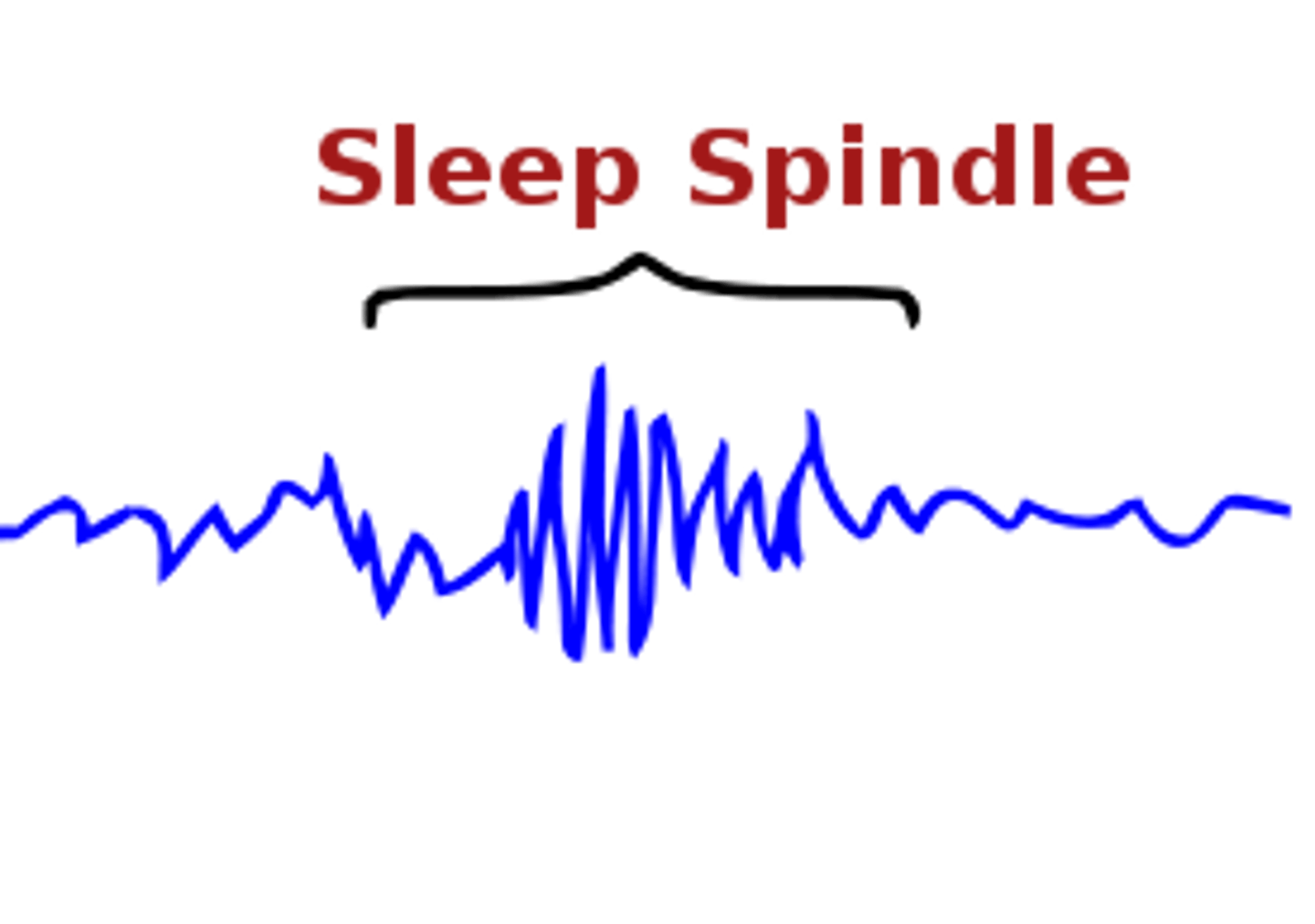
NREM 2
Sleep stage characterized by its periodic sleep spindles, or bursts of rapid, rhythmic brain-wave activity. About half the night is spent in this phase.
NREM 3
sleep stage that lasts about 30 minutes and your brain emits large, slow delta waves, and you are hard to awaken.
REM
describes sleep in which vivid dreams typically occur; this type of sleep increases as the night progresses while stage 4 sleep decreases
hypnagogic sensations
bizarre experiences, such as jerking or a feeling of falling or floating weightlessly, while transitioning to sleep
sleep spindles
short bursts of brain waves detected in stage 2 sleep
delta waves
the large, slow brain waves associated with deep sleep
insomnia
recurring problems in falling or staying asleep

narcolepsy
A sleep disorder characterized by uncontrollable sleep attacks. The sufferer may lapse directly into REM sleep, often at inopportune times.
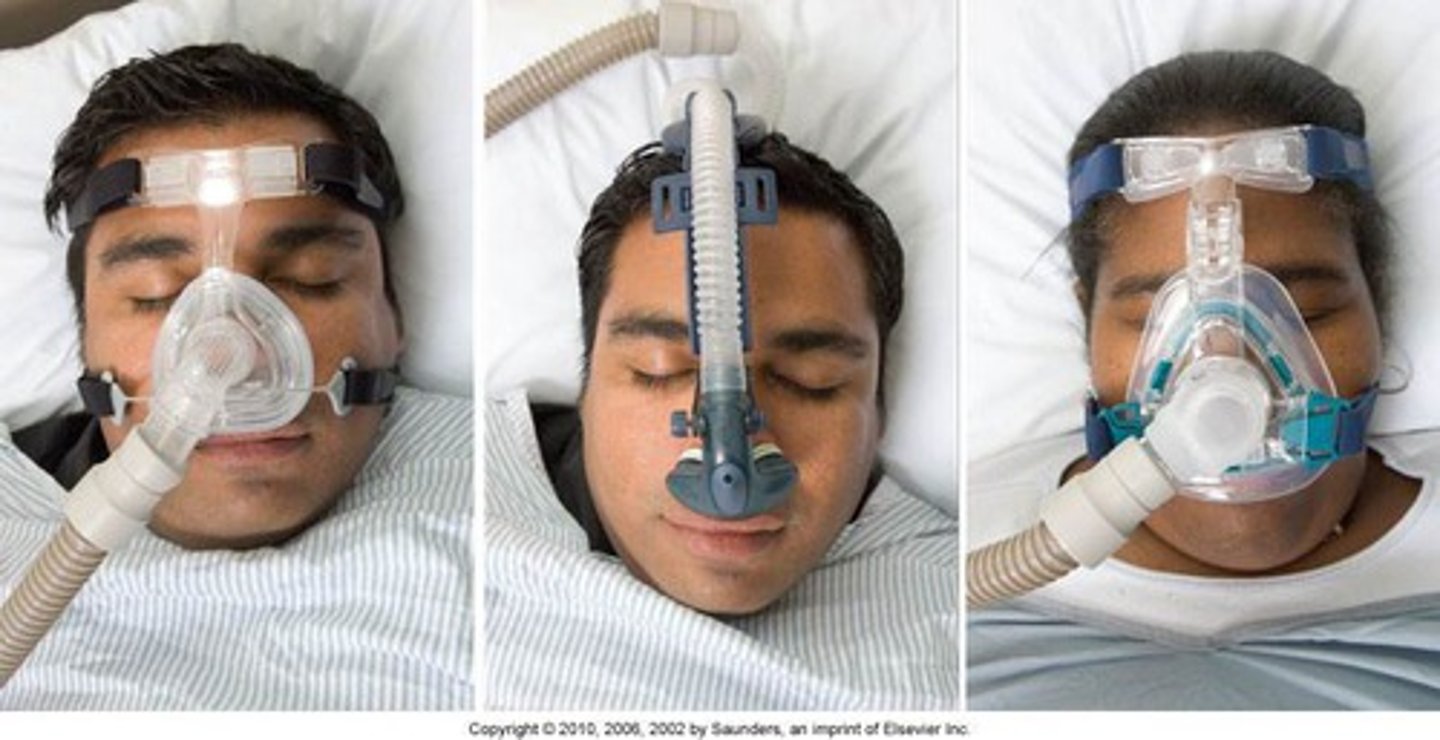
sleep apnea
a sleep disorder characterized by temporary cessations of breathing during sleep and repeated momentary awakenings
information processing dream theory
dreams help us sort out the day's events and consolidate our memories

activation synthesis theory
theory that dreams reflect inputs from brain activation originating in the pons, which the forebrain then attempts to weave into a story

sensation
the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment
perception
the process of organizing and interpreting sensory information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events

sensory adaptation
diminished sensitivity as a consequence of constant stimulation
