BIO-NYA Notepack 1
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/300
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
301 Terms
1
New cards
What are the properties of life?
1) Unity in living world
2) Growth and development
3) Reproduction
4) Order
5) Natural selection
6) Regulation
7) Homeostasis
2) Growth and development
3) Reproduction
4) Order
5) Natural selection
6) Regulation
7) Homeostasis
2
New cards
How is order exhibited in organisms?
Parts/organs/organelles with specific functions
3
New cards
What is the 1st law of thermodynamics?
Law of conservation of energy
4
New cards
What is the 2nd law of thermodynamics?
The total amount of entropy/disorder tends to increase in the Universe => release of heat (unusable form of energy) + small molecules
Cells need to constantly counteract the tendency => require continual energy input from food (cellular respiration) or sunlight (photosynthesis)
Cells need to constantly counteract the tendency => require continual energy input from food (cellular respiration) or sunlight (photosynthesis)
5
New cards
What do the 2 energy laws explain?
Energy processing
Energy flows but does not cycle
Energy flows but does not cycle
6
New cards
What is homeostasis
Cells and organisms regulate chemical activities (metabolism) in order to maintain a balanced internal environment
7
New cards
What’s adaptation to environment?
Organisms can respond to specific conditions in the environment by changing their metabolism, patterns of behaviour
8
New cards
How are organisms adapted to their environment?
Through evolution by natural selection
9
New cards
What happens through reproduction?
Organisms pass on their characteristics/traits to offspring based on the heritable instructions encoded in the molecular structure of their DNA
10
New cards
What are the hierarchical levels of biological organization?
Cell
Tissue
Organ
Organ system
Organism
Population
Community
Ecosystem
Biosphere
Tissue
Organ
Organ system
Organism
Population
Community
Ecosystem
Biosphere
11
New cards
What are the macromolecules?
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic acids
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic acids
12
New cards
What are the 3 domains?
Bacteria
Archae
Eukarya
Archae
Eukarya
13
New cards
What are the divisions in eukarya?
Super group protists
Kingdom Planta
Kingdom Fungi
Kingdom Animalia
Kingdom Planta
Kingdom Fungi
Kingdom Animalia
14
New cards
Which cells are prokaryotes?
Bacteria + archaebacteria
15
New cards
What are the characteristics of prokaryotes?
Very small
1 micron
No nucleus
1 micron
No nucleus
16
New cards
Which cells are eukaryotes?
Protists
Fungi
Plants
Animals
Fungi
Plants
Animals
17
New cards
What are the characteristics of eukaryotic cells?
Large
100 micron
Nucleus
100 micron
Nucleus
18
New cards
What is Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection?
1) Individuals of a given population differ in their versions of the same heritable traits; variant forms of traits may affect the ability to survive and reproduce
2) Overproduction of off-spring
3) Competition in a given environment
4) Differential survival an reproductive success
2) Overproduction of off-spring
3) Competition in a given environment
4) Differential survival an reproductive success
19
New cards
What is natural selection?
The outcome of differences in survival and reproduction among individuals that show variation in one or more traits
20
New cards
What are metabolic activities?
Homeostasis
Synthesis of macromolecules
Synthesis of macromolecules
21
New cards
What are autotrophs?
Producers
22
New cards
How do autotrophs work?
Depend on light energy + inorganic CHNOPS for synthesizing their own macromolecules
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
23
New cards
What does inorganic mean?
Not from living matter but from minerals in soil and grass
24
New cards
What’s a heterotroph?
Consumer + decomposer
Rely on other
Rely on other
25
New cards
How does a heterotroph work?
Depend on other organisms for their energy and CHNOPS sources
Cellular respiration
Cellular respiration
26
New cards
What are types of consumers?
Protists
Animals
Animals
27
New cards
What are types of decomposers?
Bacteria
Fungi
Fungi
28
New cards
What do decomposers do?
Recycle important elements (CHNOPS) back into the environment for reuse by producers
29
New cards
What is the Pyramid of Energy/net productivity?
Chart showing the amount of energy transferred from one trophic level to the next
Bottom heavy (more in producers)
Bottom heavy (more in producers)
30
New cards
What is the pyramid of biomass?
Chart showing the total amount of biomass for each trophic level
Each tropic level retains \~10% biomass + energy of a lower trophic level
\
Each tropic level retains \~10% biomass + energy of a lower trophic level
\
31
New cards
What is biomass?
Dry weight of organic material
32
New cards
What is the Pyramid of Numbers?
Chart showing the total number of individuals per trophic level for a given ecosystem
33
New cards
What is biomagnification?
Increased concentration of toxic chemicals in higher trophic levels
34
New cards
How does biomagnification happen?
1) Inefficient biomass/energy transfer
2) Hydrophobic (fatty/oily) nature of chemicals
2) Hydrophobic (fatty/oily) nature of chemicals
35
New cards
What is a food web?
Bunch of food chains interconnected
=> arrows for direction of energy
=> arrows for direction of energy
36
New cards
How do nutrients (CHO) cycle?
Through photosynthesis and cellular respiration
(explain in more detail with autotrophs + heterotrophs)
(explain in more detail with autotrophs + heterotrophs)
37
New cards
Where do energy transformations occur?
Chloroplasts
Mitochondria
Mitochondria
38
New cards
What is photosynthesis?
Transformation of light energy into chemical energy (organic molecules)
6 CO2 + 12 H2O => C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6 H2O
6 CO2 + 12 H2O => C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6 H2O
39
New cards
What is cellular respiration?
Extraction of chemical energy in food to produce ATP
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 => 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + chemical energy
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 => 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + chemical energy
40
New cards
What is ATP?
Adenosine **tri**phosphate
Sugar, Nitrogenous base (adenine) + 3 phosphate groups
Energy currency used by cells
Temporarily stores chemical energy into phosphodiester bonds
Sugar, Nitrogenous base (adenine) + 3 phosphate groups
Energy currency used by cells
Temporarily stores chemical energy into phosphodiester bonds
41
New cards
How is the energy stored in ATP release?
Through ATP hydrolysis
42
New cards
What does ATP hydrolysis serve to power?
Cellular work (movement, transport, anabolism)
43
New cards
What is hydrolysis?
Breaking down with water
44
New cards
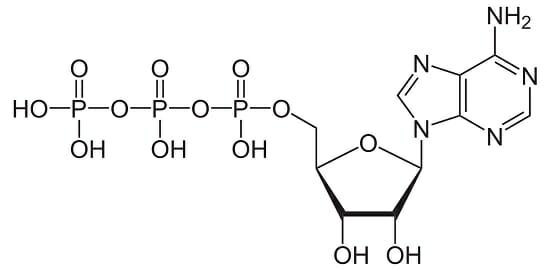
Identify this molecule
**ATP**
‘High energy’ P bonds
Sugar (ribose)
NB (nitrogenous base = adenine)
‘High energy’ P bonds
Sugar (ribose)
NB (nitrogenous base = adenine)
45
New cards
What does ATP hydrolysis produce?
A**D**P + P
46
New cards
How is ATP produced?
(ADP + P) + energy from catabolism (digestion of food by cellular respiration)
47
New cards
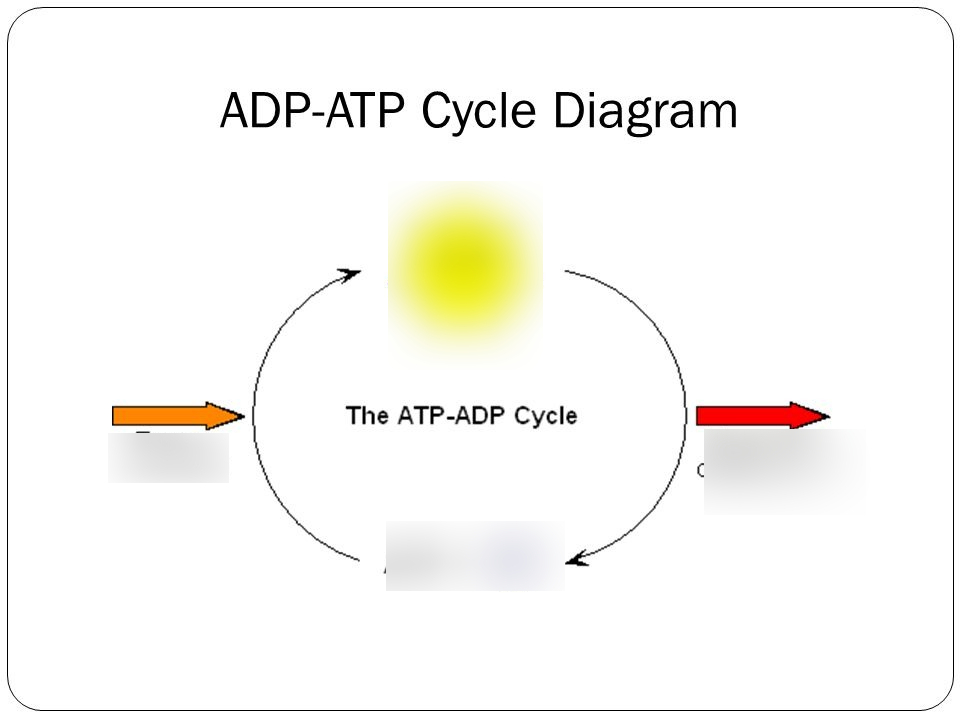
Identify the parts of the ATP cycle
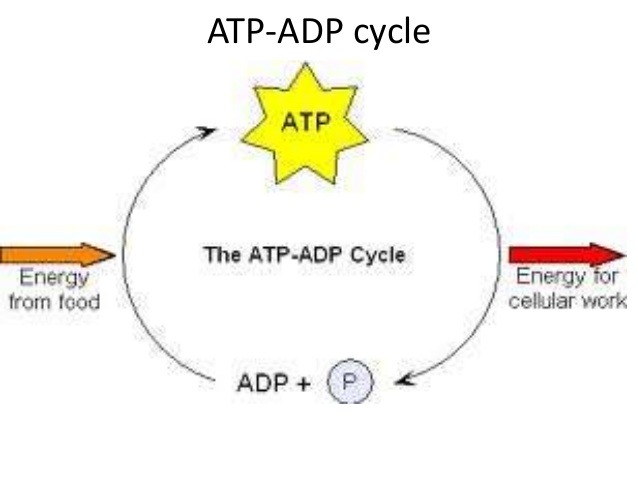
48
New cards
What is ecology?
Study of the interaction of organisms with one another and with their environment
49
New cards
What is a biosphere?
Portion of earth inhabited by life (all of the ecosystems of the planet)
Upper part of crust + lower part of atmosphere
Upper part of crust + lower part of atmosphere
50
New cards
What are biomes?
Major ecosystems defined by geographic area + dominant vegetation that inhabits it
51
New cards
What is an ecosystem?
Self-contained/stable and distinct community of organisms (BIOTIC factors) together with their physical environments (ABIOTIC factors)
52
New cards
What are biotic factors?
Living organism that shapes its environment
53
New cards
What are abiotic factors?
Physical environments
Wind, water, climate, soil, nutrients, fire
Wind, water, climate, soil, nutrients, fire
54
New cards
What is a community?
Many populations of different species
55
New cards
What is a population?
Members of one species living in the same area
56
New cards
What is an ecological niche?
Represents the lifestyle of a species in a particular habitat + roles of species in the ecosystem
57
New cards
What are factors of the ecological niche?
A) Physical factors (climate, elevation, topography)
B) Resource availability (seasonal, quality, type)
C) Interactions between species (Competition, predation, herbivory, symbiosis)
D) History (Immigration/emigration, disasters, human interference)
B) Resource availability (seasonal, quality, type)
C) Interactions between species (Competition, predation, herbivory, symbiosis)
D) History (Immigration/emigration, disasters, human interference)
58
New cards
What is mullerian mimicry?
Noxious potential preys exhibit the same warning colorations as other species
Ex. bees + wasps
Ex. bees + wasps
59
New cards
What is batesian mimicry?
Preys mimic harmful species to frighten predators away
60
New cards
What is camouflage?
Preys and predators show cryptic colorations to blend in with their surroundings
61
New cards
What are decomposers also called?
Saprobes
Saprotrophs
Saprotrophs
62
New cards
What are detrivores?
Organisms (usually animals) which feed on dead/decaying organic matter
63
New cards
What are trophic levels?
Hierarchy based on who eats who
64
New cards
Why isn’t all of the energy in one trophic level stored in the next?
Some of the organic material (stores the energy) is consumed in respiration, released as heat or eliminated as unused material in feces
65
New cards
Describe the Arctic food web
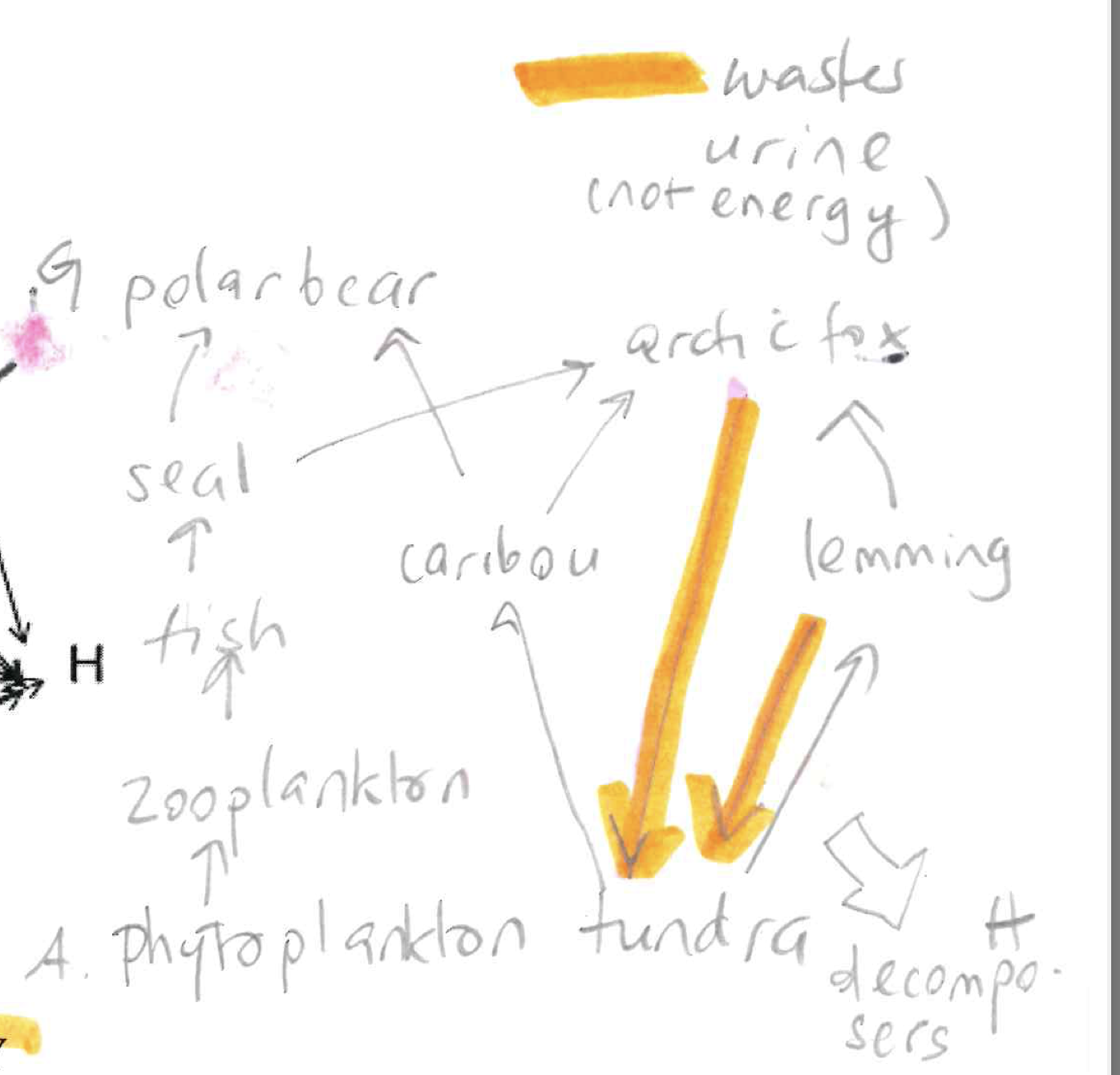
66
New cards
How are H bonds formed?
Interaction between partial - (O) and partial + (H) particles
67
New cards
What is cohesion?
Water molecules bind to each other
68
New cards
What explains surface tension?
Cohesion
69
New cards
What is adhesion?
Water molecules exhibit adhesion to polar surfaces
Polar = hydrophilic
Non-polar = hydrophobic
Polar = hydrophilic
Non-polar = hydrophobic
70
New cards
What is surface tension?
Crowding of water molecules to form the smallest surface possible
71
New cards
What is capillary action?
Ability of water to rise in a water column defying gravity (cohesion + adhesion)
* Hydrophilic cell wall vessel
* Water moving up the stem of a plant
* Hydrophilic cell wall vessel
* Water moving up the stem of a plant
72
New cards
How is a spider able to walk on water?
Cohesion + surface tension
73
New cards
What is moderation of temperature in water?
Large bodies of water can maintain lower temperatures than the atmosphere because of the **high specific heat** of liquid water.
Takes a lot of E to bring the temperature of water up
Takes a lot of E to bring the temperature of water up
74
New cards
How is ice formed from liquid?
Water makes 4 H bonds
75
New cards
What is evaporative cooling/sweating?
Evaporation of water molecules cools the surface of the liquid.
As you sweat the heat disappears too
As you sweat the heat disappears too
76
New cards
What are examples of moderation of temperature?
* Winters and summers are mild next to the coast
* A well hydrated organism doesn’t readily overheat
* A well hydrated organism doesn’t readily overheat
77
New cards
What happens to water as it freezes?
It expands
Lakes freeze from top down => aquatic organisms can survive in the winter
Lakes freeze from top down => aquatic organisms can survive in the winter
78
New cards
Why is water a versatile solvent?
Polar solvent => most organic molecules + ions soluble in water
Forms a hydration shell around the particles
Forms a hydration shell around the particles
79
New cards
What reactions does water participate in?
Hydrolysis: water as a reactant breaks bonds
Condensation/dehydration synthesis: water as a product is released when a bond forms
Condensation/dehydration synthesis: water as a product is released when a bond forms
80
New cards
What are organic compounds?
One or more NOPS covalently bonded to C
81
New cards
Is CO2 a organic carbon compound?
No, it’s inorganic
82
New cards
What are large organic compounds called?
Macromolecules/polymers
83
New cards
What are monomers?
Building blocks/small pools of organic compounds
84
New cards
What is metabolism?
The sum total of the chemical reactions that occur in the cell + organism
Describes the transformation of substances into energy/materials that the cell can use or store
Describes the transformation of substances into energy/materials that the cell can use or store
85
New cards
What is anabolism?
Synthesis reactions
Ex.: dehydration synthesis/condensation (water as a product is released)
Ex.: dehydration synthesis/condensation (water as a product is released)
86
New cards
What is catabolism?
Breakdown reactions
Ex.: Macromolecules are broken down (digested) to their component monomers by hydrolysis (water is used as reactant)
Ex.: Macromolecules are broken down (digested) to their component monomers by hydrolysis (water is used as reactant)
87
New cards
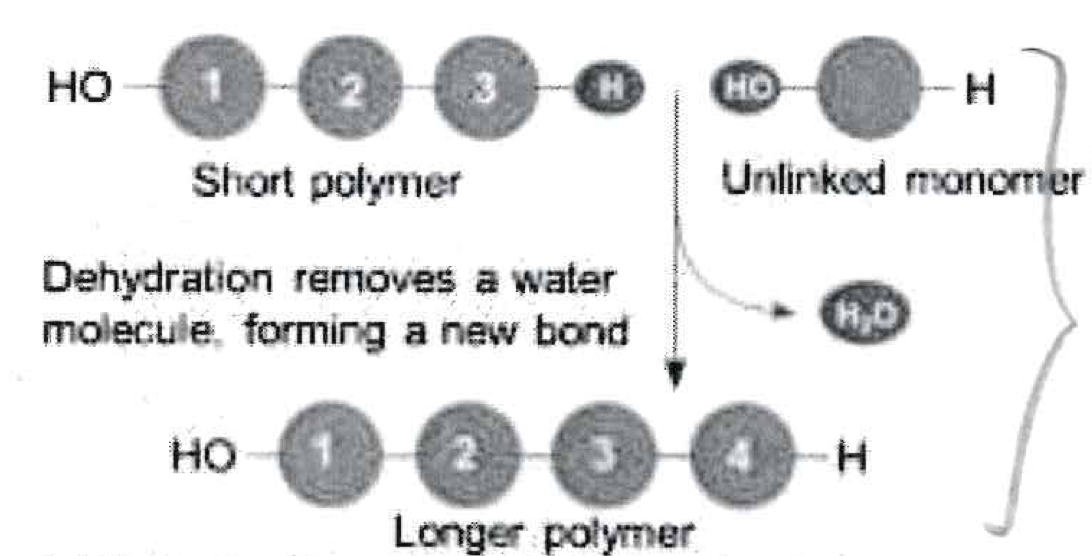
What type of reaction is this?
Anabolic
Dehydration synthesis of polymer
Dehydration synthesis of polymer
88
New cards
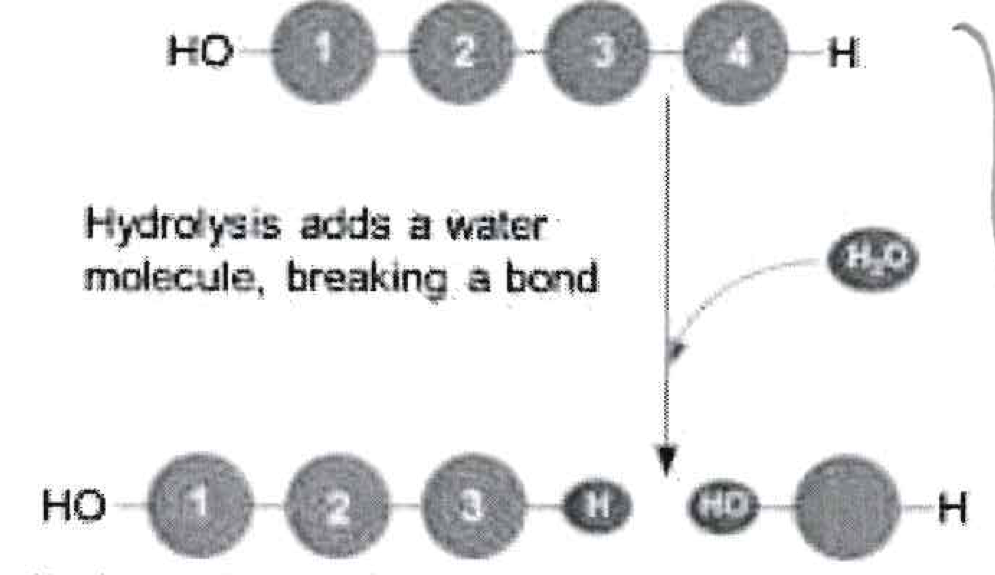
What type of reaction is this?
Catabolic
Hydrolysis of polymer
Hydrolysis of polymer
89
New cards
What are the most abundant macromolecules?
Carbohydrates
90
New cards
What is the composition of carbohydrates?
CHO + N in chitin
91
New cards
What are the monomers in carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides
Alpha glucose => starch
Beta glucose => cellulose
Alpha glucose => starch
Beta glucose => cellulose
92
New cards
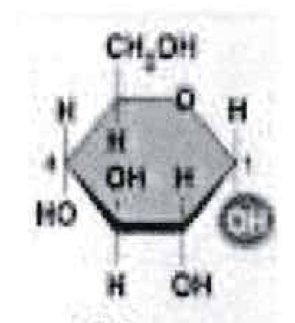
What is this?
Alpha glucose
Monomer
Monomer
93
New cards
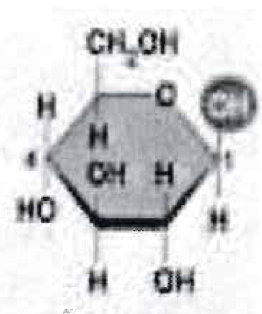
What is this?
Beta glucose
Monomer
Monomer
94
New cards
What are types of monosaccharides?
Glucose
Fructose
Galactose
Glucosamine
Fructose
Galactose
Glucosamine
95
New cards
What are types of disaccharides?
Maltose (beer)
Sucrose (table sugar)
Lactose (milk)
Sucrose (table sugar)
Lactose (milk)
96
New cards
What do disaccharides do?
Store energy
97
New cards
What are complex carbohydrates called?
Polysaccharides (polymers)
98
New cards
What is alpha glucose’s usage?
Energy and chemical storage
99
New cards
What are examples of alpha glucose?
Glycogen (animals; liver)
Starch (plants)
Starch (plants)
100
New cards
What is beta glucose’s usage?
Structural