h, Understanding Electron Configuration and Valence Electrons, Atomic Models and Electron Behavior in Atoms, Modern Atomic Theory and the Electromagnetic Spectrum
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
What is radioactivity?
Radioactivity is the process by which nuclei of unstable isotopes emit radiation.
What is a radioisotope?
A radioisotope is an unstable isotope that is subject to radioactive decay.
What is radioactive decay?
Radioactive decay is the spontaneous breaking down of an unstable atomic nucleus to produce radiation and a more stable nucleus of a different element.
Does radioactive decay require an input of energy?
No, radioactive decay does not require an input of energy.
What factors do not affect radioactive decay?
Radioactive decay is not affected by pressure, temperature, catalysts, or the compound the isotope is in.
What does the discovery of radioactivity disprove?
The discovery of radioactivity disproved Dalton's theory that atoms are indivisible.
What is transmutation?
Transmutation is the changing of one element into another element by radioactive decay.
What determines the stability of a nucleus?
The stability of a nucleus depends on the ratio of neutrons to protons.
What is the neutron-to-proton ratio for stable nuclei of low atomic number?
For elements with atomic numbers below ~20, the neutron-to-proton ratio is around 1.
What is the neutron-to-proton ratio for stable nuclei of higher atomic number?
For elements above atomic number 20, stable nuclei have more neutrons than protons.
What is the band of stability?
The band of stability is a pattern formed by a neutron-vs-proton plot of all stable nuclei.
What is the atomic number (Z)?
The atomic number (Z) is the number of protons in a nucleus.
What is the mass number (A)?
The mass number (A) is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons.
What are isotopes?
Isotopes are atoms with identical atomic numbers but different mass numbers.
What is a nuclide?
A nuclide is each unique atom.
What is a radioactive nucleus?
A nucleus that spontaneously decomposes, forming a different nucleus and producing one or more particles.
What does a nuclear equation show?
The radioactive decomposition of an element.
What are the types of radiation?
Alpha, beta, and gamma radiation.
alpha decay
Alpha (α)
What is it?: Helium nucleus (+2 charge)
Mass # Change: -4
Atomic # Change: -2
When does it happen?: With heavier elements; if the nucleus has too many protons and neutrons
Example: See above
beta decay
Beta (β)
What is it?: Electron ejected from nucleus (-1 charge)
Mass # Change: Stays same
Atomic # Change: +1
When does it happen?: If the nucleus has too many neutrons; neutron (n0) decays into a proton (p+) and an electron (e-), which is ejected from the nucleus
gamma decay
Gamma (γ)
What is it?: A high-energy photon (electromagnetic radiation, so no charge or mass)
Mass # Change: Stays same
Atomic # Change: Stays same
When does it happen?: Allows the nucleus to get rid of excess energy to stabilize; often accompanies other radiation
Example: See above
Positron Emission
Positron Emission (β⁺)
What is it?: Particle with mass of an electron but a + charge
Mass # Change: Stays same
Atomic # Change: -1
When does it happen?: If the nucleus has too many protons, it emits a positron to decrease protons and increase neutrons; proton (p+) converts to a neutron (n0) and emits a positron (β⁺)
What holds all atomic nuclei together?
The strong nuclear force
What type of force acts between nuclear particles that are extremely close together?
An attractive force
What does the strong nuclear force overcome at small distances?
Electrostatic repulsion
What are elements with atomic numbers above 92 called?
Transuranium elements
How can transmutation occur?
By decay or bombardment
What were the first artificial elements produced in the 1940s?
Neptunium (Np) and Plutonium (Pu)
How many artificial elements have been produced since the 1940s?
26 artificial elements
What is nuclear transformation?
The change of one element into another
What is required for bombarding particles to penetrate a target in nuclear transformations?
They must move at a very high speed
How are high speeds for bombarding particles achieved?
Using various types of particle accelerators
What is a decay series?
A decay series is a series of radioisotopes produced by successive radioactive decay until a stable isotope is reached.
What is the heaviest radioisotope in a decay series called?
The heaviest radioisotope of each decay series is called the parent nuclide.
What are the radioisotopes produced by the decay of the parent nuclide called?
They are called the daughter nuclides.
What is the half-life?
The half-life is the time required for half of the original sample of radioactive nuclei to decay.
How are radioactive decay rates measured?
Radioactive decay rates are measured in half-lives.
What is the half-life of Thorium-219?
1.05 x 10^-6 seconds.
What is the half-life of Radon-222?
3.8 days.
What is the half-life of Carbon-14?
5730 years.
What is the half-life of Potassium-40?
1.28 x 10^9 years.
What is the half-life of Uranium-238?
4.47 x 10^9 years.
What is the formula to find the remaining amount of a radioactive element?
N = N0 (1/2)^n, where n is the number of half-lives that have passed, N0 is the initial amount, and N is the remaining amount.
How do you calculate the number of half-lives that have passed?
n = t/T, where t is the elapsed time and T is the duration of the half-life.
What are some medical uses of radioactive substances?
They are used for diagnosing, treating, and detecting diseases, including cancer.
How are radioactive substances used in food preservation?
They are used for sterilization of medical supplies and food preservation using gamma radiation.
What radioactive substance is commonly used in smoke detectors?
Americium-241
Which isotopes are used by geologists and archaeologists to date rocks and organic materials?
Potassium-40 and Carbon-14
What are radioactive tracers used for in medicine?
To observe organ functions and detect diseases.
How are radioactive tracers used in agriculture?
To measure fertilizer absorption.
What is the use of radioactive tracers in industry?
To locate leaks in underground pipes.
What is nuclear fission?
The process of splitting a heavy nucleus into smaller, more stable nuclei, releasing significant energy.
What is critical mass in nuclear fission?
The minimum amount of fissionable material needed to sustain a chain reaction.
What is nuclear fusion?
The process of joining smaller nuclei to form a larger nucleus, releasing more energy than fission.
Where does nuclear fusion naturally occur?
In stars like the sun.
What are the current applications of artificial nuclear fusion?
Limited applications, such as in hydrogen bombs.
Who wrote the first extensive list of all known elements in 1789?
Antoine Lavoisier
What did Jöns Jakob Berzelius develop in 1828?
A table of atomic weights and introduced letters to symbolize elements.
What did Johann Dobereiner attempt to do in 1829?
Group elements into triads with similar properties.
What was the state of element identification by 1860?
There were more than 60 identified elements, and chemists struggled to classify them and determine their atomic masses.
Who developed a workable method to accurately measure atomic masses in 1860?
Stanislao Cannizzaro
What did Alexandre-Émile Beguiler de Chancourtois do in 1862?
Arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic weights.
What is the 'Law of Octaves' proposed by John Newland in 1864?
A method to order elements where certain chemical properties repeat roughly every 8 elements.
What did Lothar Meyer compile in 1869?
A table of 56 elements based on periodic properties arranged by increasing atomic weight.
Electron configuration
The way that electrons are systematically arranged around the nucleus of an atom and accounted for.
Aufbau Principle
An electron will occupy the lowest energy configuration available to it.
Hund's Rule
Orbitals of equal energy are each occupied by one electron before any orbital can be occupied by a second electron.
Pauli Exclusion Principle
No two electrons in the same atom can have the same set of 4 quantum numbers.
Orbital notation
A method to represent electron configurations showing a line with the orbital's name written below.
Electron Configuration Notation
A method that eliminates lines and arrows, showing the number of electrons by adding a superscript to sublevel designation.
Noble-Gas Configuration
Simplifies the electron-configuration notation by including the noble gas of the previous period in brackets.
Valence Electrons
Electrons in the outermost orbitals in the highest principal energy level of an atom that determine chemical properties.
Core electrons
The inner shell electrons that are not involved in bonding atoms to each other.
Example of Electron Configuration for Phosphorus
1s22s22p63s23p3
Example of Electron Configuration for Iron
1s22s22p63s23p64s23d6
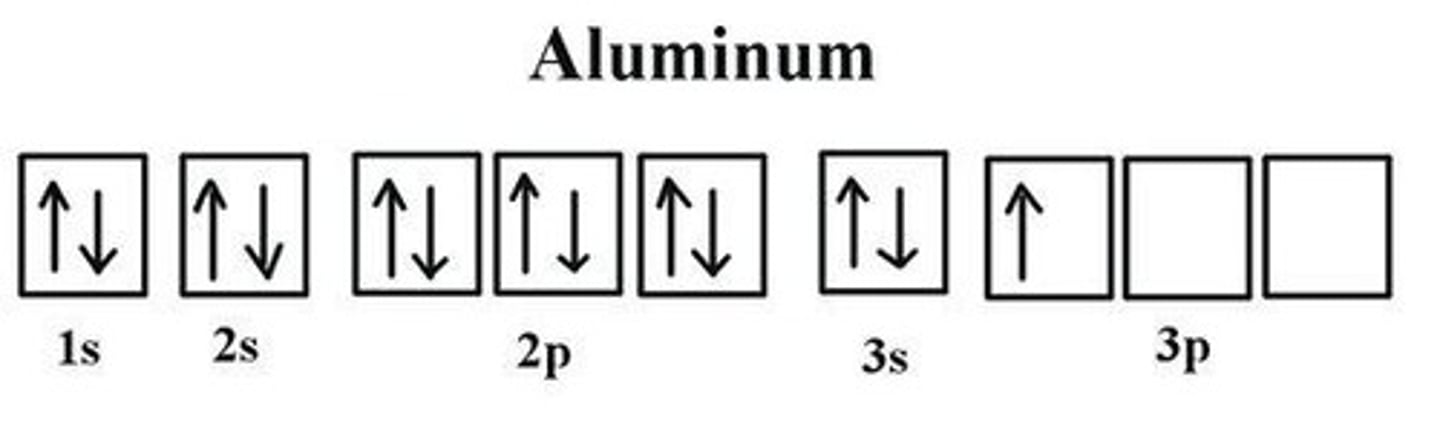
Example of Electron Configuration for Aluminum
1s22s22p63s23p1
Example of Noble-Gas Configuration for Phosphorus
[Ne] 3s23p3
Example of Noble-Gas Configuration for Iron
[Ar] 4s23d6
Example of Noble-Gas Configuration for Aluminum
[Ne] 3s23p1
Exceptions to Normal Order of Filling
Some half-filled orbital sublevels are not as chemically stable as alternate configurations.
Normal Configuration for Chromium
[Ar] 4s23d4
Exception Configuration for Chromium
[Ar] 4s13d5
Normal Configuration for Copper
[Ar] 4s23d9
Exception Configuration for Copper
[Ar] 4s13d10
Example of Valence Electrons for Sulfur
S [Ne] 3s2 3p4 has 6 valence electrons.
Example of Valence Electrons for Cesium
Cs [Xe] 6s1 has 1 valence electron.
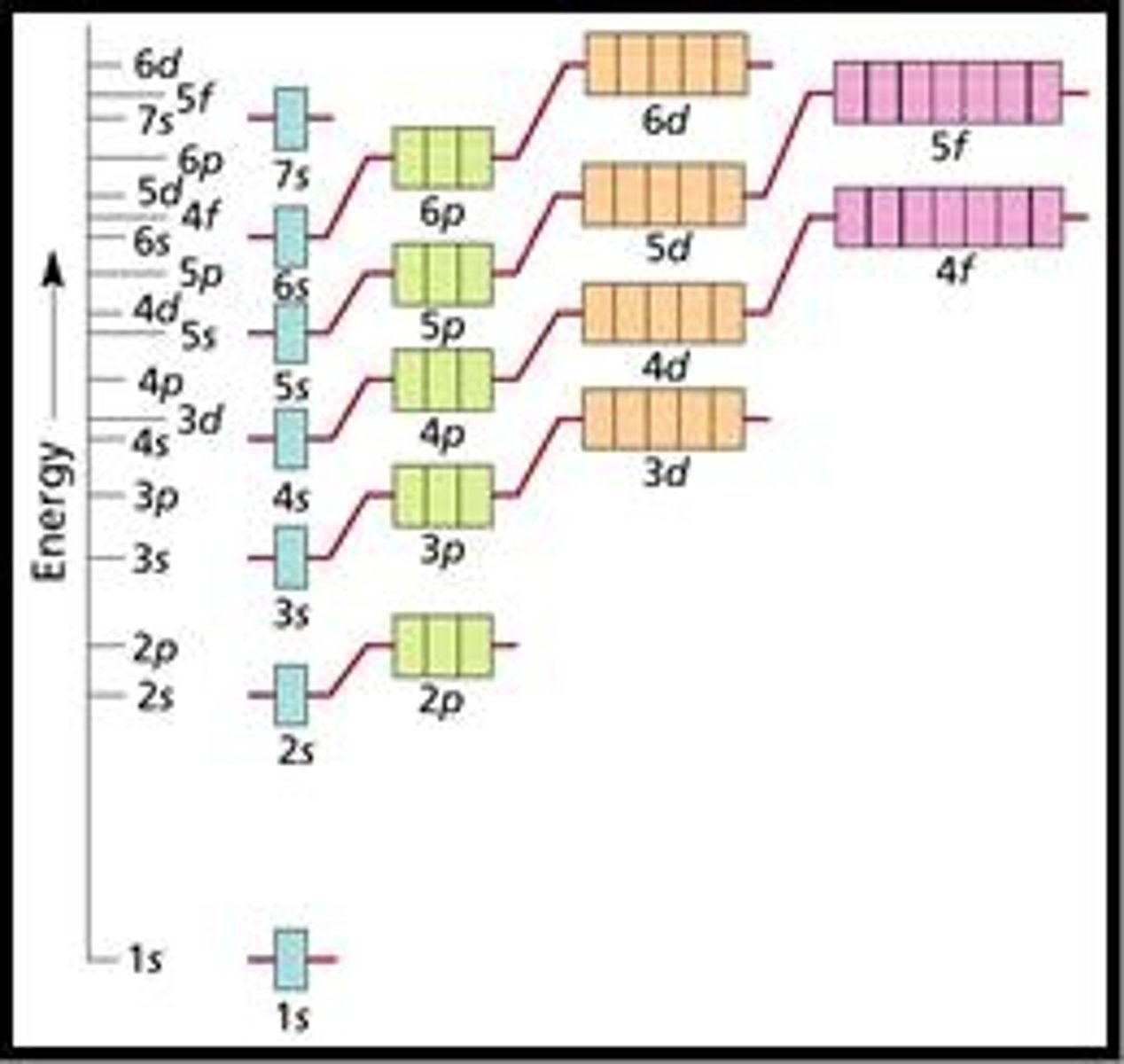
Order of Orbital Filling
1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d, 7p.
Question about Electron Configuration
Which one is correct? The 3rd one!
Photoelectric Effect
Emission of electrons from materials upon light exposure.
Wave-Particle Duality
Concept that particles exhibit both wave and particle properties.
Rutherford's Model
Atom structure: empty space, dense nucleus, orbiting electrons.
Line Emission Spectra
Distinct light bands emitted by excited gas atoms.
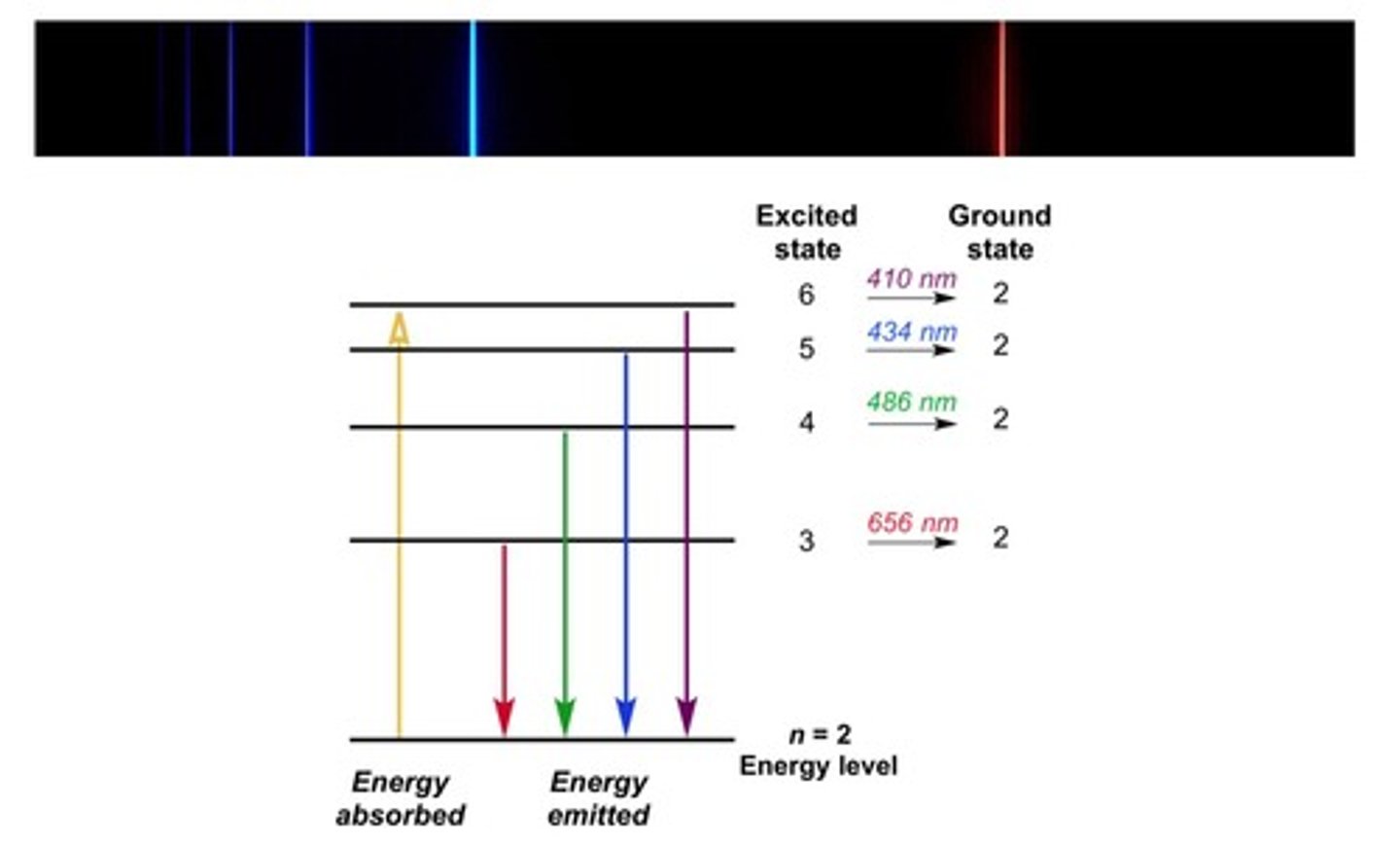
Excited State
Higher energy state of an electron after energy absorption.
Ground State
Lowest energy state of an electron in an atom.
Niels Bohr
Proposed circular orbits for electrons with fixed energy.
Energy Level
Fixed energy state of an electron, akin to ladder rungs.
Photon
Light particle emitted when an electron returns to ground state.
Atomic Fingerprint
Unique bright-line emission spectrum of each element.
De Broglie Hypothesis
Electrons exhibit wave characteristics, traveling as waves.
Standing Wave
Wave pattern sustaining itself around the nucleus.