6.4c&d Naming Skeletal Muscles and Arrangement of Fascicles
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
DIRECTION OF THE MUSCLE FIBERS
Some muscles are named in reference to some imaginary line, usually the midline of the body or the long axis of a limb bone.
Rectus (straight): it’s fibers or whole structure run parallel to that imaginary line
Oblique: a muscle’s name tells you that the muscle fibers run obliquely (at a slant) to the imaginary line.
RELATIVE SIZE OF THE MUSCLE
Maximus: largest
Minimus: smallest
Longus: long
LOCATION OF THE MUSCLE
Some muscles are named for the bone with which they are associated.
For example, the temporalis and frontalis muscles overlie the temporal and frontal bones of the skull, respectively.
NUMBER OF ORIGINS
When the term biceps, triceps, or quadriceps forms part of a muscle name, you can assume that the muscle has two, three, or four origins, respectively.
LOCATION OF THE MUSCLE’S ORIGIN AND INSERTION
Occasionally, muscles are named for their attachment sites.
Sterno: sternum
Cleido: clavicle
SHAPE OF THE MUSCLE
Some muscles have a distinctive shape that helps to identify them.
Deltoid: triangle
ACTION OF THE MUSCLE
When muscles are named for their actions, terms such as flexor, extensor, and adductor appear in their names.
Arrangement of fascicles
Skeletal muscles consist of fascicles, but fascicle arrangements vary, producing muscles with different structures and functional properties.
A muscle’s fascicle arrangement determines its range of motion and power.
The longer and the more nearly parallel the fascicles are to
a muscle’s long axis, the more the muscle can shorten.
Muscle power depends more on the total number of muscle fibers in the muscle.

CIRCULAR
The fascicles are arranged in concentric rings.
Circular muscles are typically found surrounding external body openings, which they close by contracting, creating a valve.
Sphincters “squeezers”
E.g. orbicular muscles surrounding the eyes and mouth

CONVERGENT
The fascicles converge toward a single insertion tendon
Triangular or fan-shaped
E.g., the pectoralis major muscle of the anterior thorax
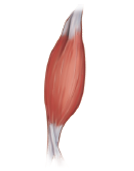
FUSIFORM
Modification of the parallel arrangement
A spindle-shaped muscle with an expanded belly (midsection) and tapered ends
An example is the biceps brachii muscle of the arm.

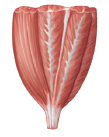
PARALLEL
The length of the fascicles runs parallel to the long axis of the muscle.
Sartorius of the anterior thigh.
Muscles are straplike
PENNATE
(pen′āt; “feather”) pattern
Short fascicles attach obliquely to a central tendon
Unipennate: fascicles insert into only one side of the tendon
Bipennate: fascicles insert into opposite sides of the tendon
What is the fascicle arrangement of the orbicularis oris muscle?
Circular