Lecture 4: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
What is anatomy?
study of body structure
What is physiology?
study of body function
The functional role of a part depends on what?
the way it was constructed
Why do we study anatomy/physiology?
general curiosity
dissatisfaction with supernatural explanations
treat illness and injuries
learn how the body works (normal vs abnormal)
prevention/stay healthy
What is the order of life?
atom → molecule → macromolecule → organelle → cell → tissue → organ → organ system → organism
What is the process of life?
movement
growth
reproduction
digestion
absorption
respiration
circulation
responsiveness
assimilation
excretion
the process of life traits constitute what?
metabolism
What is the sum of all chemical processes in the body?
metabolism
What are the environmental factors needed for life?
water, oxygen, pressure, food and heat
What is defined by maintaining a stable internal environment?
Homeostasis
How is homeostasis maintained? What are these ways?
through two self-regulating control systems
negative feedback and positive feedback loops
What is a negative feedback loop?
correcting an imbalance; moving back towards “normal”
What is the most common feedback loop?
negative feedback loop
Maintaining “normal” blood pressure, body temp, blood sugar levels is an example of what kind of feedback loop?
negative feedback loop
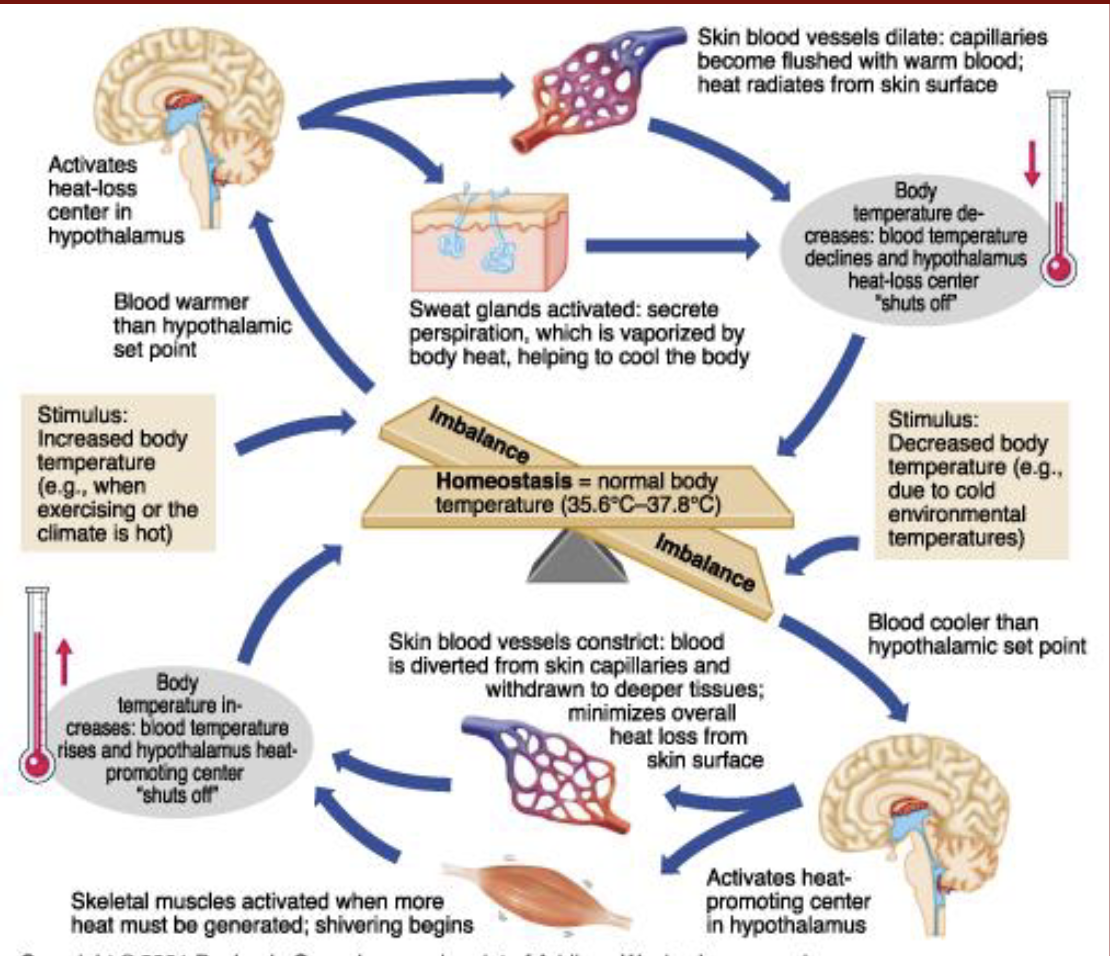
The following image is what kind of feedback loop?
negative feedback
What is a positive feedback loop?
moving away from a “normal” state; amplifies changes
Childbirth and stopping bleeding is an example of what kind of feedback loop?
positive feedback loop
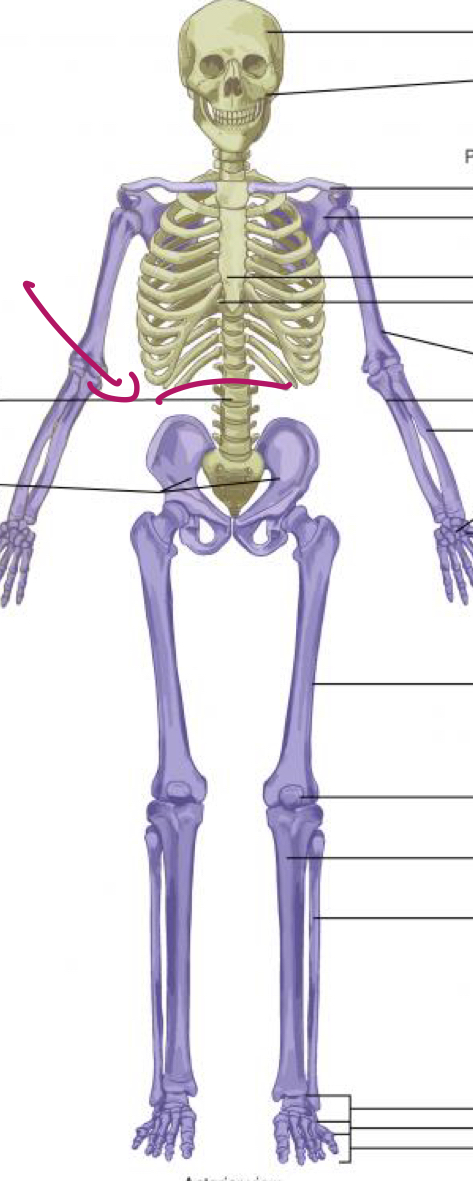
The body is organized into two main segments, what are they (skeletal)?
Appendiular skeleton
Axial skeleton
What does the appendicular skeleton include?
upper and lower limbs
What does the axial skeleton include?
head, neck, trunk/chest
What are the two cavities within the axial skeleton?
dorsal cavities
ventral cavities
What is within the dorsal cavities?
cranial cavity (brain)
vertebral canal (spinal cord)
What is within the ventral cavities?
thoracic cavity (lungs + heart)
abdominopelvic cavity
What does the mediastinum do?
divides cavity into left and right
What does the diaphragm do?
muscle that separates thoracic and abdominopelvic
What is within the thoracic cavity?
mediastinum
diaphragm
Dorsal meaning?
to the back of the body
Ventral meaning?
front of body
What does this line represent?
diaphragm
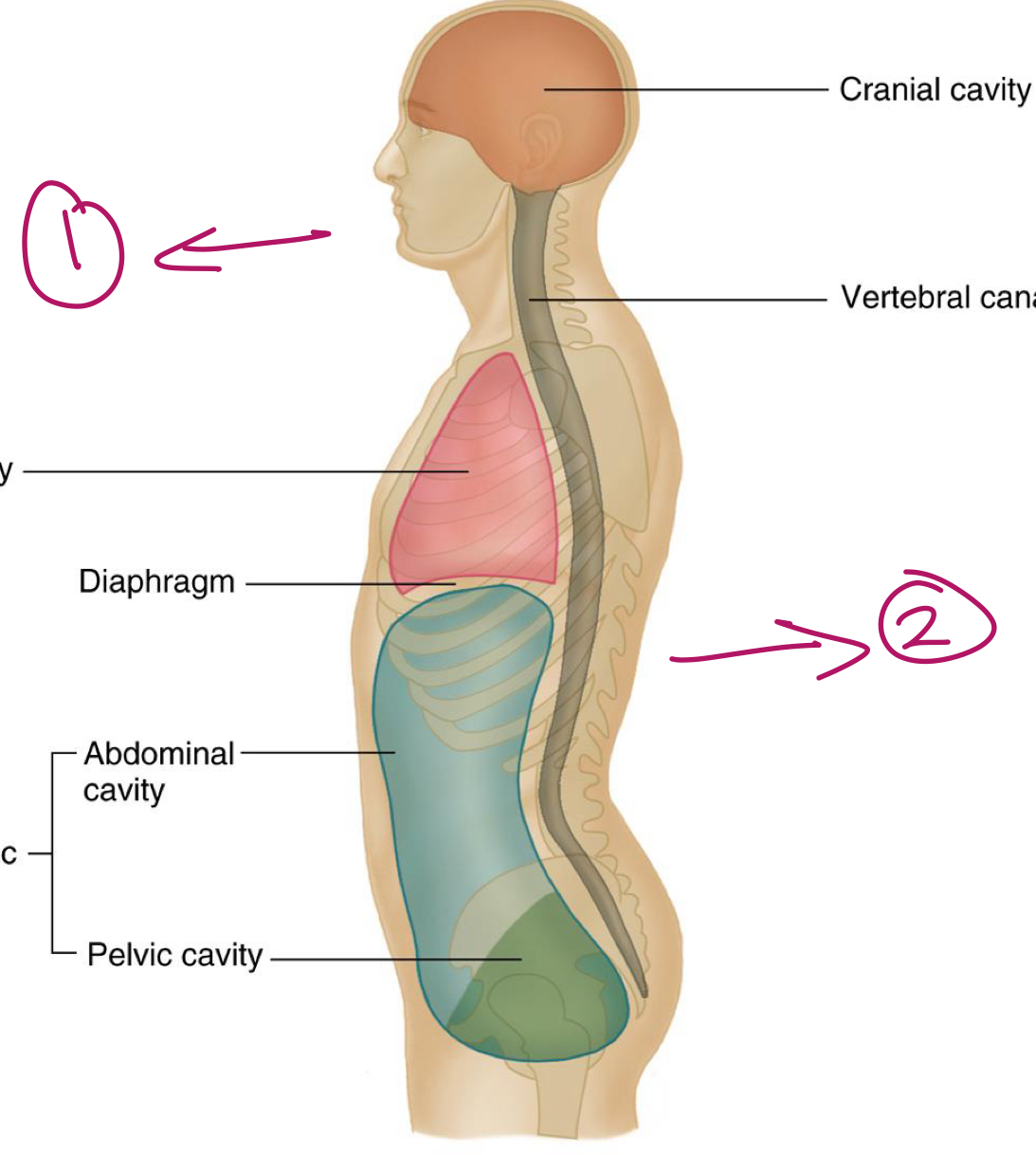
Label 1 and 2.
ventral side
dorsal side
What are the 4 body cavities in the cephalic region (head)?
oral cavity (mouth)
nasal cavity (nose)
orbital cavity (eye)
middle ear cavity
What are the two main types of membranes?
visceral/serous membrane
parietal/mucous membrane
What is the function of the visceral/serous membrane? Where is it located?
covers internal organs
lays directly on top of organ
Where is the parietal/mucous membrane located?
attached to the wall of a cavity
What are examples of the two membranes in the lungs (pleura)?
visceral pleura (directly on lungs)
parietal pleura (lines thoracic cavity)
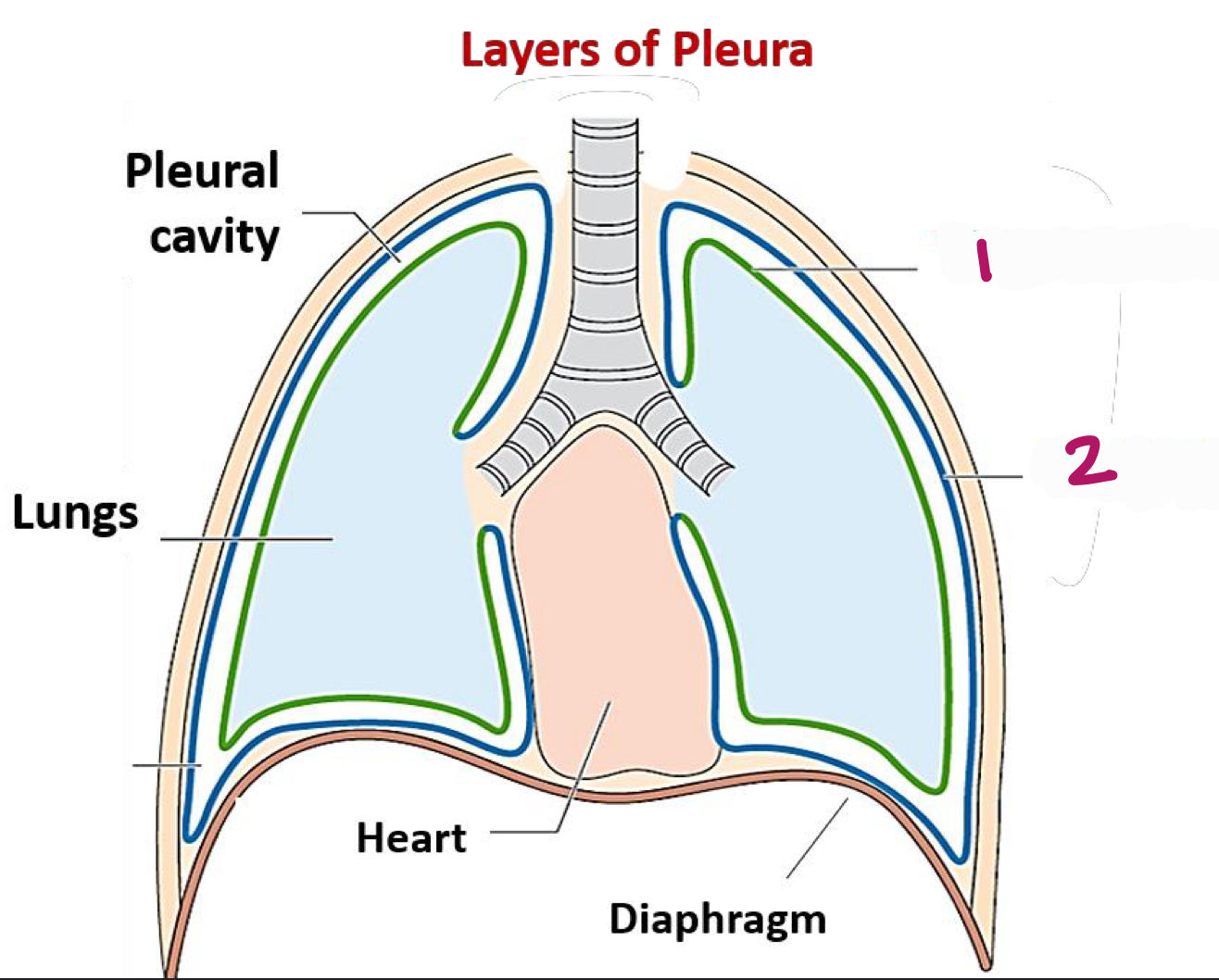
Label figure 1.
visceral pleura
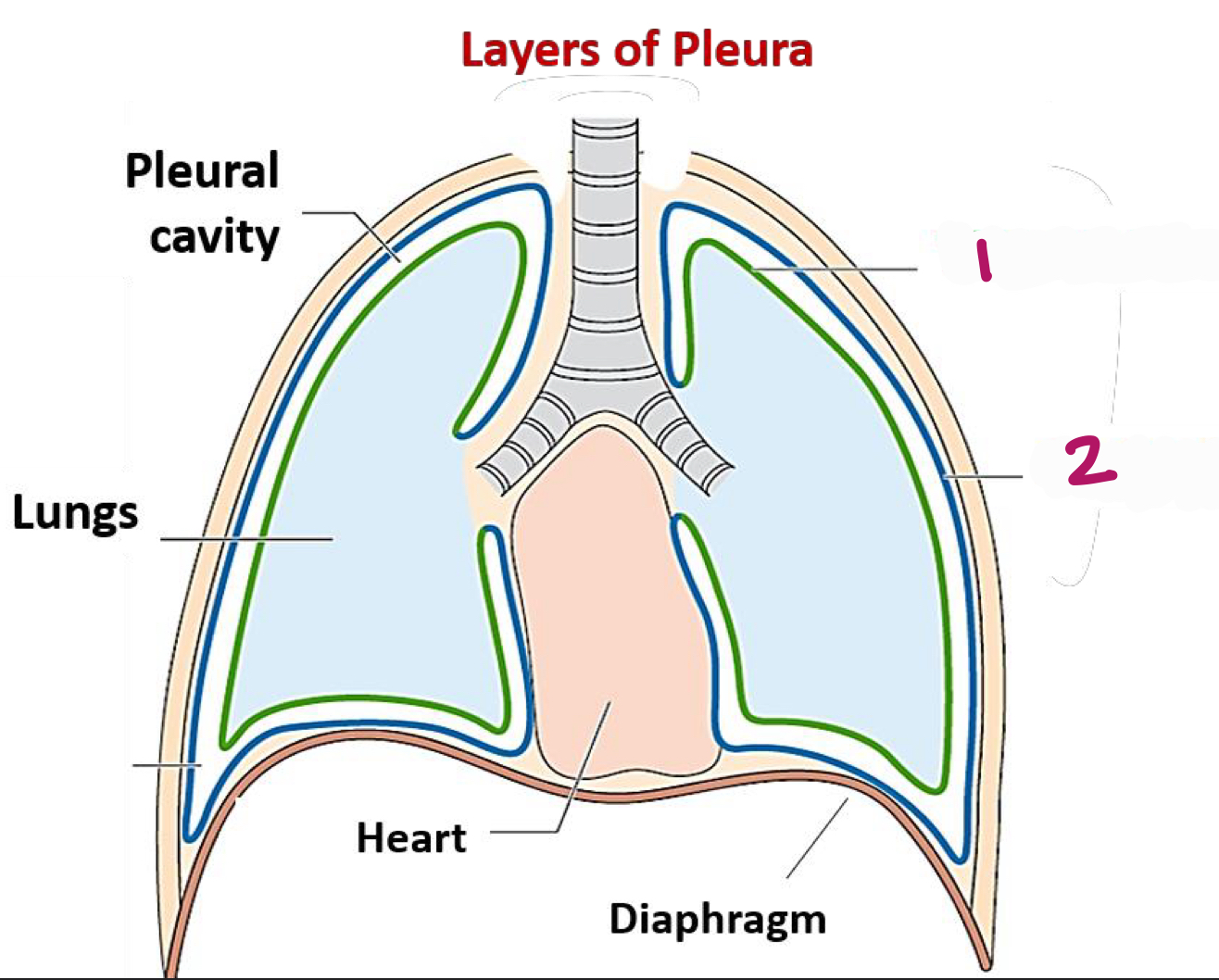
Label figure 2.
parietal pleura
What are all the body systems?
integumentary system
skeletal system
muscular system
nervous system
endocrine system
cardiovascular system
lymphatic and immune system
digestive system
respiratory system
urinary system
female and male reproduction system
Which system is responsible for body covering; protects, senses changes and regulates body temperature?
integumentary system
What is part of the integumentary system?
skin, hair, nails, sweat and sebaceous glands
Which system is responsible for movement, support, protection, storage, blood cell production?
skeletal system
What is part of the skeletal system?
bones. ligaments and tendons
Which system is responsible for movement, support, heat?
muscular system
What is part of the muscular system?
skeletal, smooth, and cardiac
Tendons connect what?
muscle to bone
ligaments connect what?
bone to bone
Which system is responsible for sensory input, interprets & motor response; fast communication?
nervous system
What is part of the nervous sytem?
brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory organs
Which system is responsible for “slower” response to body activities with long term effects?
endocrine system
What is part of the endocrine system?
glands, hormones
Which system is responsible for transportation of O2, nutrients, water, heat, and waste (CO2)?
cardiovascular system
What is part of the cardiovascular system?
heart, blood vessels, blood
Which system is responsible for immunity; removal of excess fluid?
lymphatic and immune system
What is part of the lymphatic and immune system?
WBC, lymph nodes, lymph fluid and lymph vessels
Which system is responsible for break down and absorption of nutrients; elimination of waste?
digestive system
What is part of the digestive system?
mouth, stomach, small and large intestine
Which system is responsible for gas exchange (O2 and CO2 diffusion)?
respiratory system
What is part of the respiratory system?
pharynx, larynx, trachea, lungs
Which system is responsible for filtration of blood and removal of fluid waste; regulation of water and electrolytes?
urinary system
What is part of the urinary system?
kidney, bladder, ureters, urethra
Which system is responsible for production of gametes and offspring?
females and males reproductive system
What is the only system that does not function for homeostasis?
female and male reproductive system
Describe the anatomical position.
body presented facing forward, with toes facing forward, the feet shoulder width apart, and palms facing forward
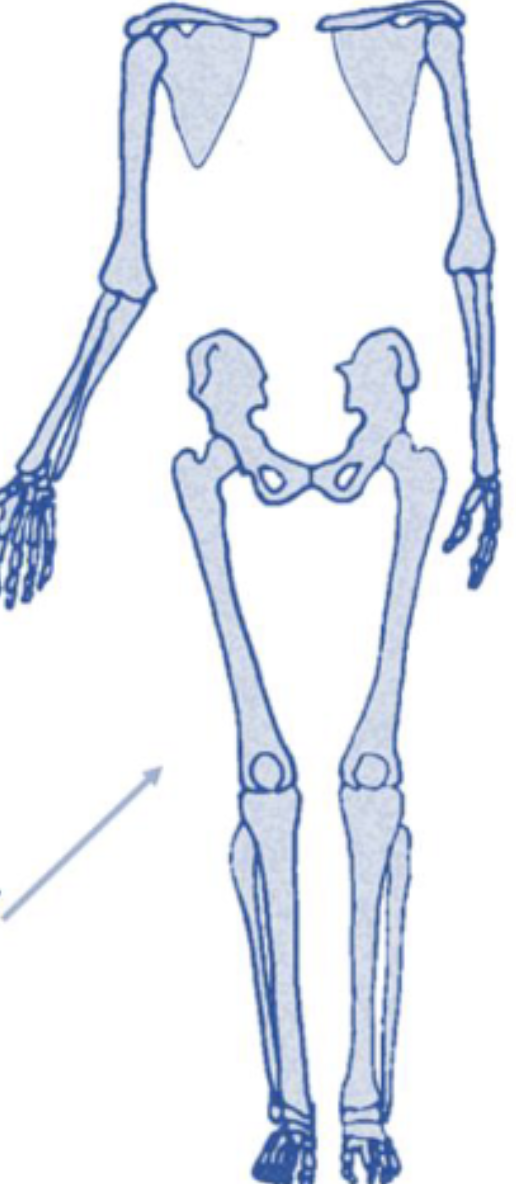
What part of the skeleton is shown in this image?
Appendicular skeleton
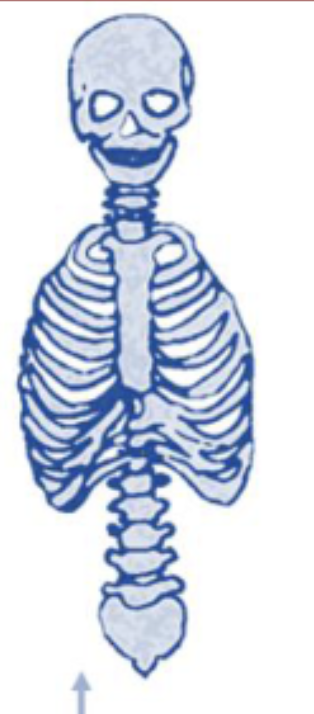
What part of the skeleton is shown in this image?
Axial skeleton