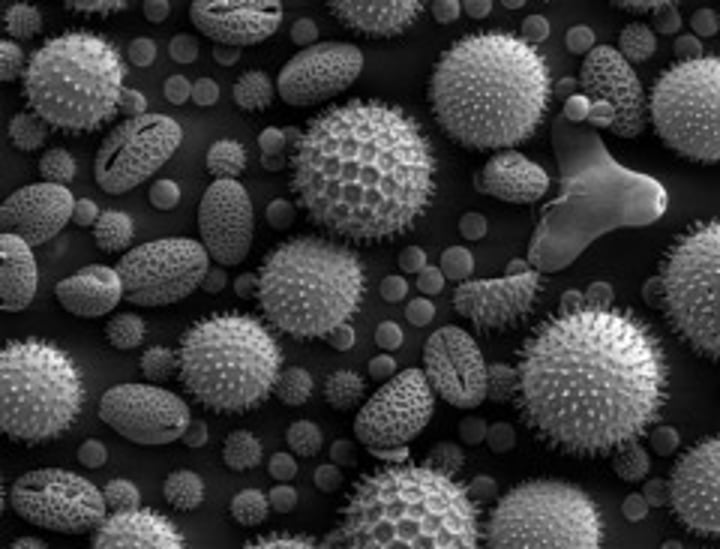
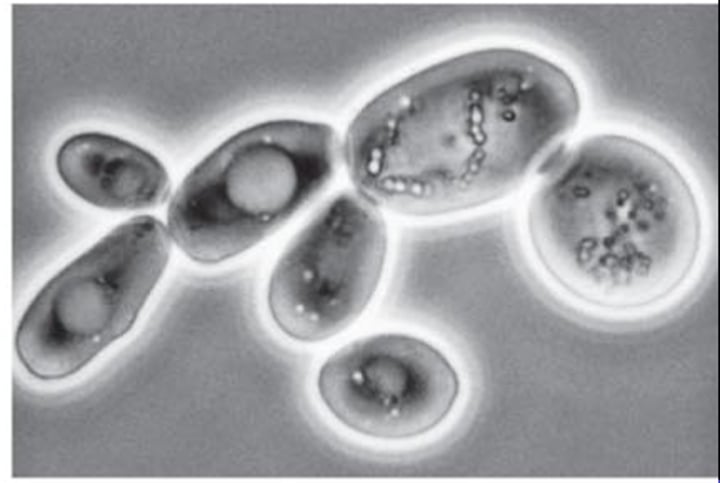
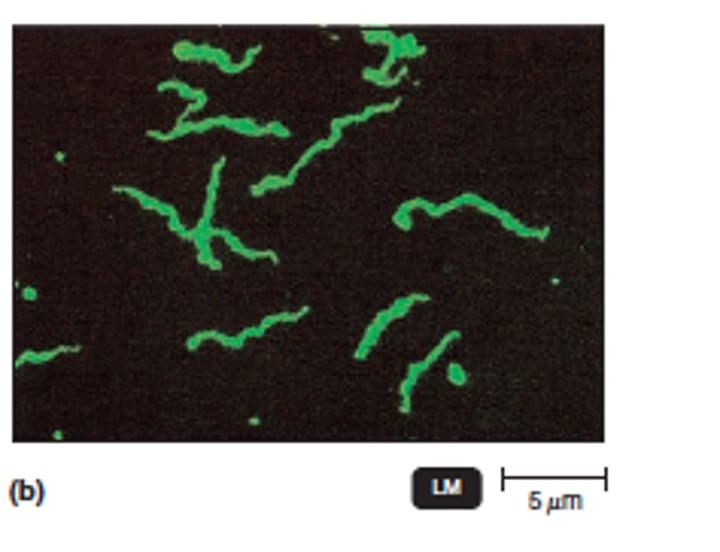
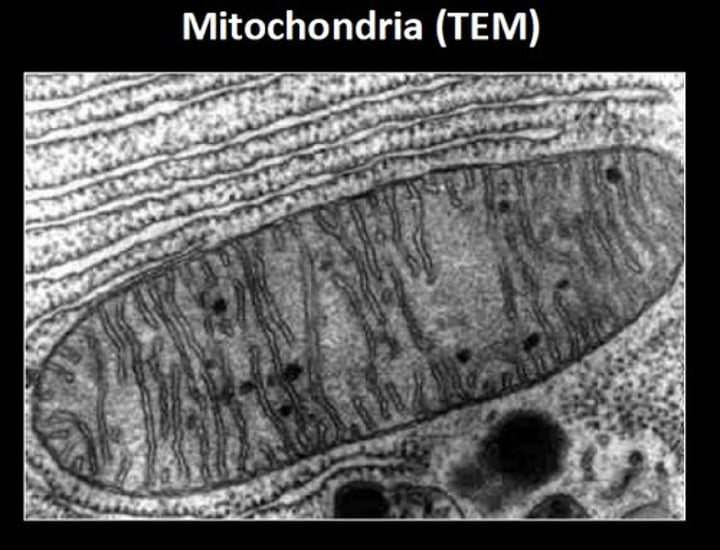
Identify which type of microscopy was used to obtain a given picture
1/15
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
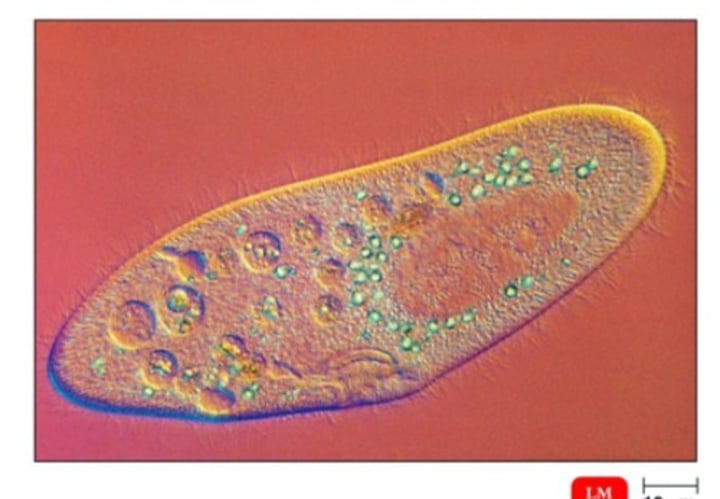
Phase contrast microscopy (light)
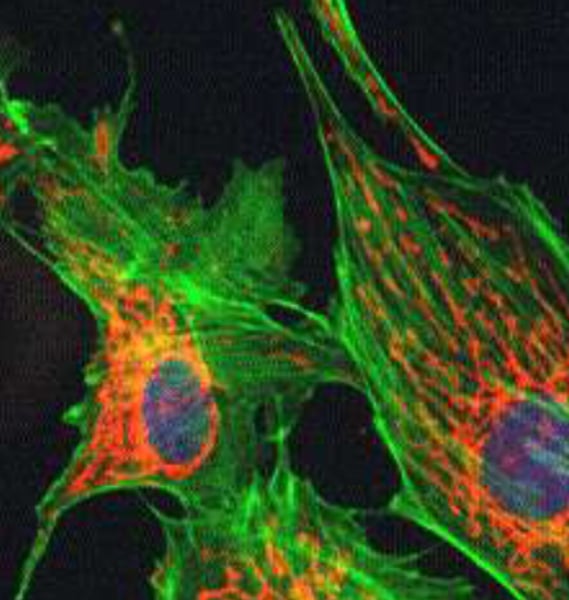
Fluorescence microscopy
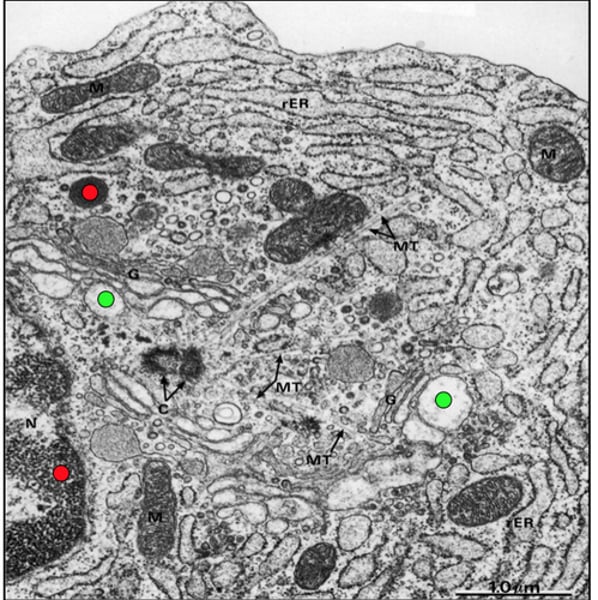
transmission electron microscope (TEM)
Scanning electron microscope (SEM)
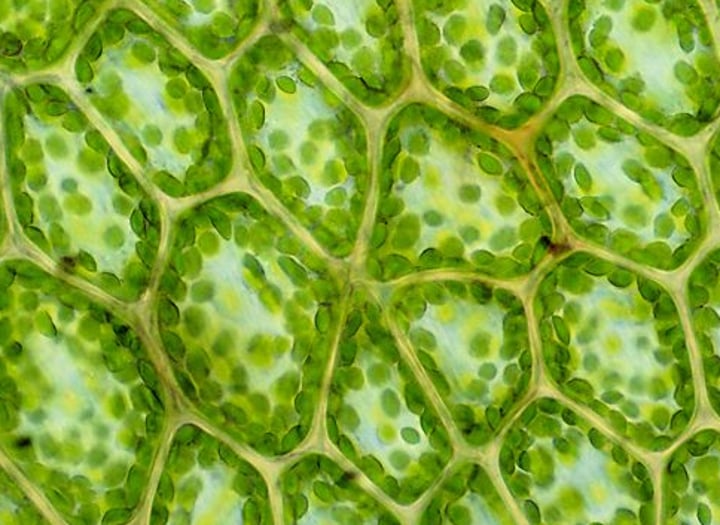
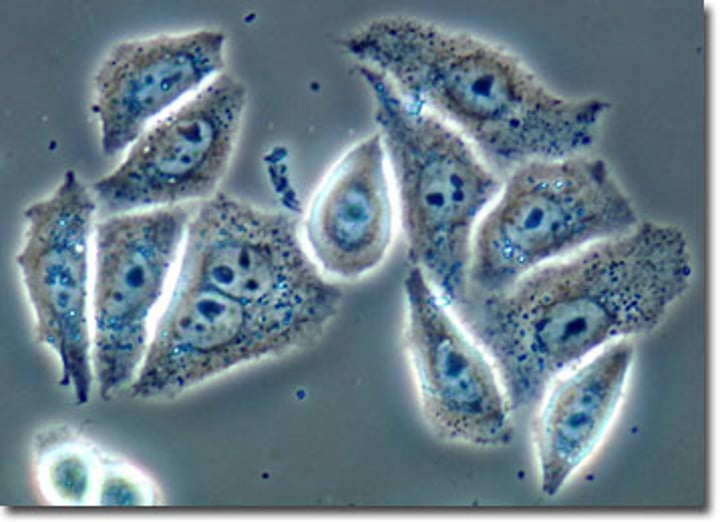
Brightfield/Light/Compound Microscope
Type: Optical microscope
Pros: Inexpensive, can view living organisms
Cons: Low resolution, medium magnification, samples must be stained

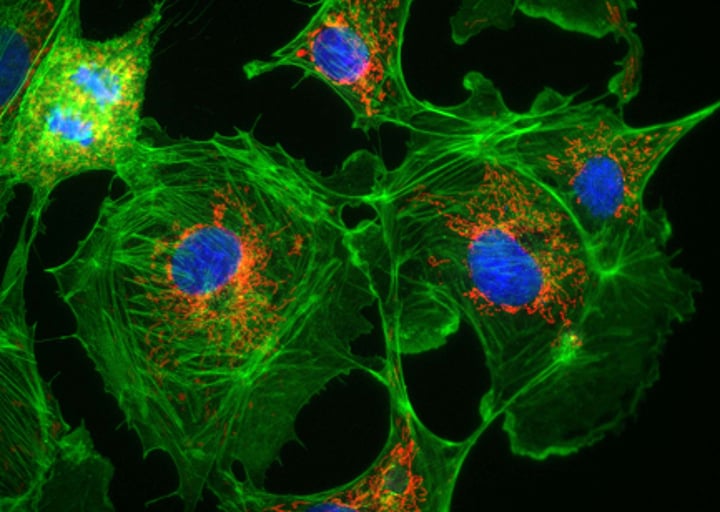
Fluorescence Microscope
Type: Optical microscope
Pros: Separate parts of a cell can be individually labeled
Cons: Fluorescence is temporary
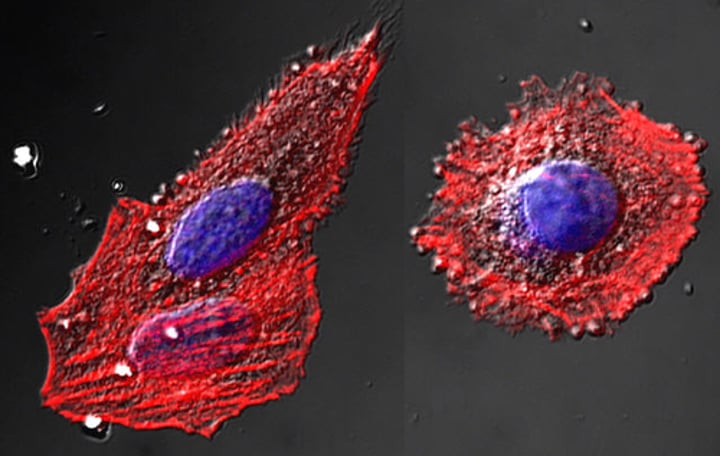
Phase Contrast Microscope
Type: Optical microscope
Pros: Can view living organisms, does not require staining, high contrast and resolution
Cons: Not good for thick samples, distorted "halo" around images
Laser Scanning Confocal Microscope
Type: Optical microscope
Pros: controlled depth of field - good for thick samples, reduction of background noise
Cons: Medium magnification
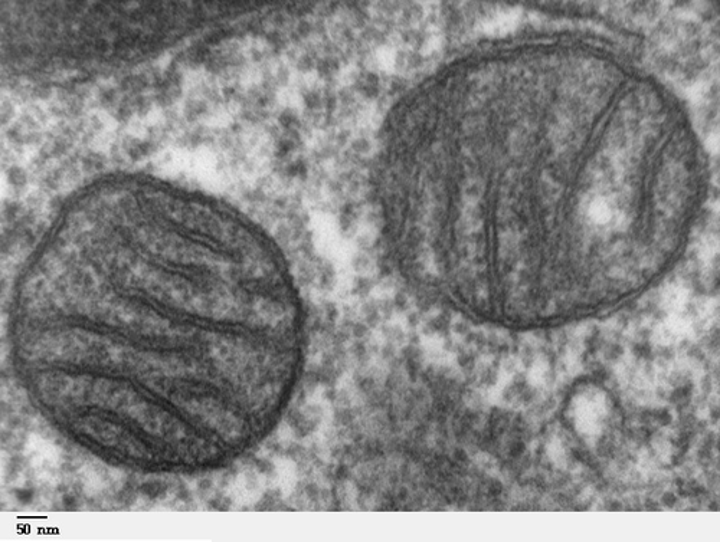
Transmission electron microscope (TEM)
Type: Electron microscope
Pros: Very high magnification, can view organelles and intercellular details
Cons: Preparation of samples requires fixation, expensive
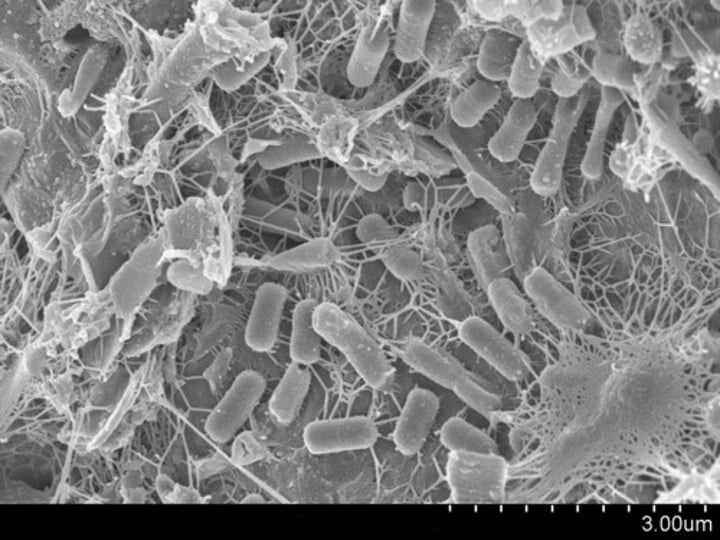
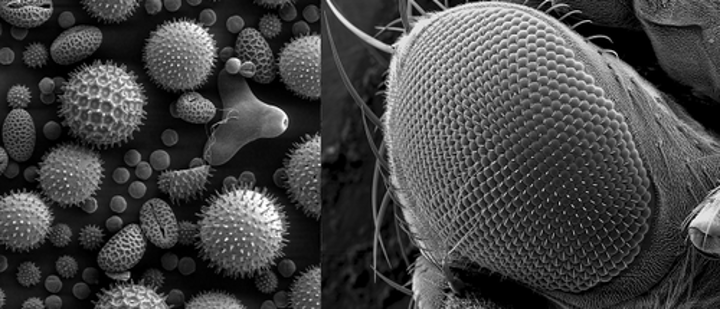
Scanning electron microscope (SEM)
Type: Electron microscope
Pros: 3D picture of samples, high magnification
Cons: Samples must be dried and covered in metal - difficult preparation, expensive
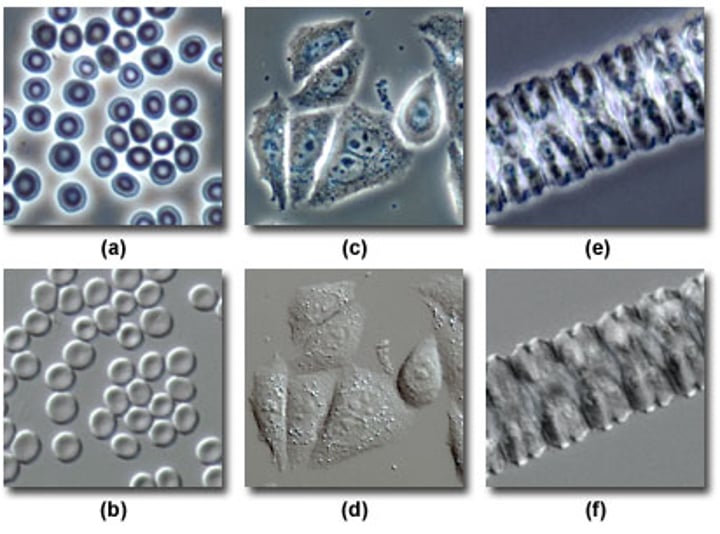
Brightfield Microscopy
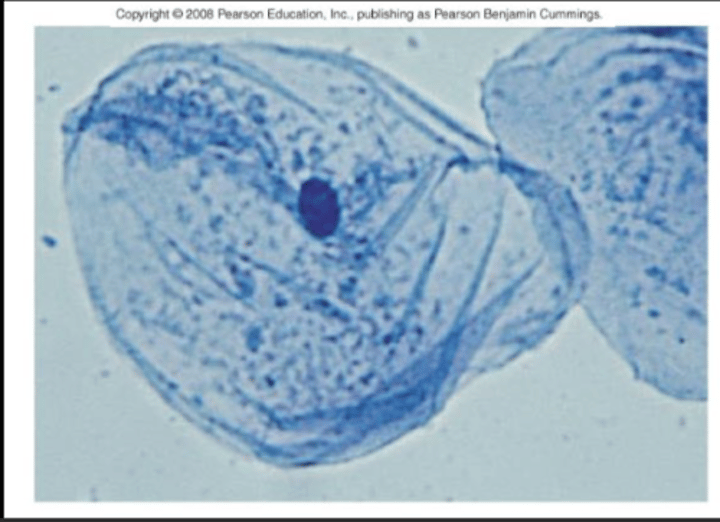
Phase Contrast Microscopy
Differential Interference Contrast Microscopy
Confocal Microscopy
Transmission Electron Microscopy
Scanning Electron Microscopy