Introduction to Business Law
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:36 PM on 2/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
1
New cards
What is a civil law (Roman) system?
Where the legal rules and principles are derived from written codes
It’s clear and there is no ambiguity
It’s clear and there is no ambiguity
2
New cards
What is a common law (Anglo-American) system?
Where the legal rules and principles are derived from court, it is not written down
More flexible and open to interpretation
More flexible and open to interpretation
3
New cards
Which legal system does Scotland follow?
A hybrid system - mixture of civil and common
4
New cards
What makes up a tripartite legal system?
Executive - proposes new laws
government/Scottish parliament/Westminister
\
Legislature - law making body (passes the laws)
Scottish parliament/house of commons and lords
\
Judiciary - interprets the law
court system
government/Scottish parliament/Westminister
\
Legislature - law making body (passes the laws)
Scottish parliament/house of commons and lords
\
Judiciary - interprets the law
court system
5
New cards
What is the nature of the law?
set a minimum standard of behaviour for all
6
New cards
What is the aim of criminal law?
to punish the offender
7
New cards
What is the aim of civil law?
compensation - rectification of a wrong
8
New cards
What are the sources of law in order of highest to lowest power?
Legislation (civil law)
Case Law - precedent (common law)
Institutional writings
Custom
Equity
Case Law - precedent (common law)
Institutional writings
Custom
Equity
9
New cards
What is the hierarchy for legislation starting at highest?
UK (Westminister) legislation
Scottish legislation
Delegated legislation
Scottish legislation
Delegated legislation
10
New cards
What is judicial precendent?
Where a judge must follow the judgement and decisions of a higher court in previous cases
\
Court decision follow existing legal principles, extend those principles or lay down/amend rules
\
Judges must provide ratio decidendi - reason for their decision
\
Court decision follow existing legal principles, extend those principles or lay down/amend rules
\
Judges must provide ratio decidendi - reason for their decision
11
New cards
What are institutional writers?
e.g. Stair
\
codifications/statements of law
if not contradicted by legislation or precedent taken by court as ascertaining the law
their authority depends on their recognition by the courts
\
codifications/statements of law
if not contradicted by legislation or precedent taken by court as ascertaining the law
their authority depends on their recognition by the courts
12
New cards
What are customs?
Course of conduct over time gaining the weight of law
\
Must-
\-not contradict general law
\-definite, certain and regularly practised
\-fair and reasonable
\-accepted and followed for long period
\
If it falls to be enforced it will lose it’s authority
\
Must-
\-not contradict general law
\-definite, certain and regularly practised
\-fair and reasonable
\-accepted and followed for long period
\
If it falls to be enforced it will lose it’s authority
13
New cards
What is equity?
nobile officium - both the inner court of session and the high court of justiciary have the extraordinary equitable jurisdiction to fill in the gaps in the law or provide a remedy if one is not otherwise available
\
always a bit controversial so not used often
\
Khaliq v HM Advocate
Glue sniffing
\
always a bit controversial so not used often
\
Khaliq v HM Advocate
Glue sniffing
14
New cards
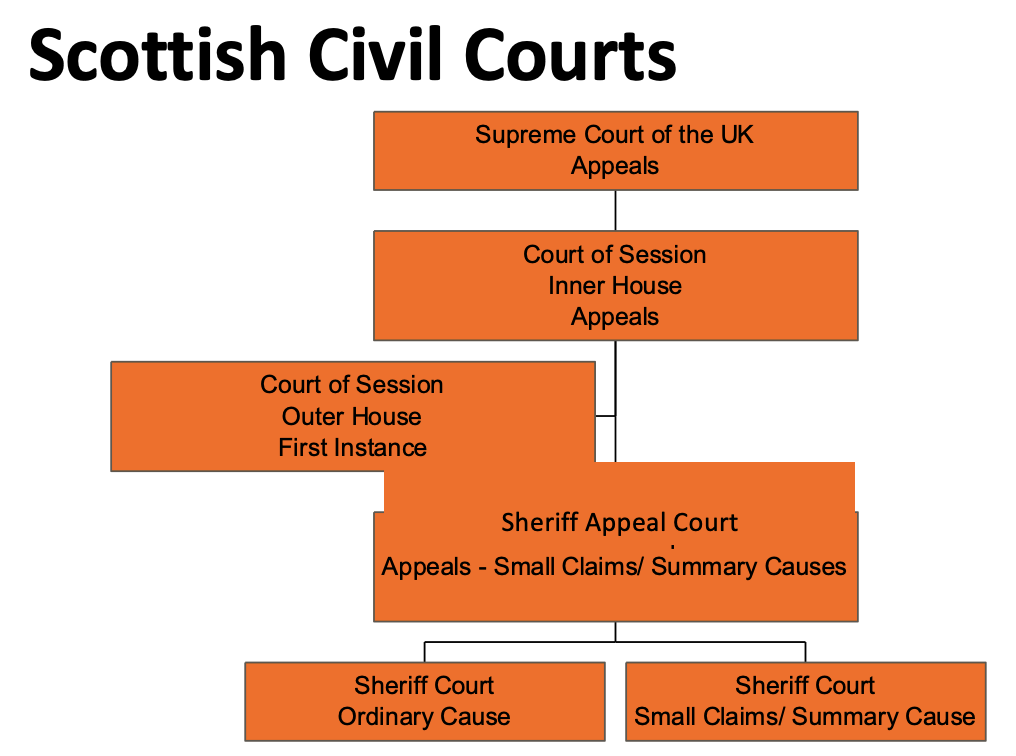
How is the Scottish Civil Court structured?
The supreme court will never hear a case for the first time
Can potentially raise an issue for the first time in the outer house court of sessions
Can potentially raise an issue for the first time in the outer house court of sessions
15
New cards
What is a small claims procedure?
action for payment less than £5000
simple
procedure - no record of evidence, appeal on point of law to Sheriff Appeal court
can represent yourself
simple
procedure - no record of evidence, appeal on point of law to Sheriff Appeal court
can represent yourself
16
New cards
What is a summary cause procedure?
action for payment between £3000 and £5000
more complicated e.g. personal injury
procedure - no record of evidence, appeal to sheriff appeal court and then to inner house court of session by permission of sheriff appeal court
more complicated e.g. personal injury
procedure - no record of evidence, appeal to sheriff appeal court and then to inner house court of session by permission of sheriff appeal court
17
New cards
What is ordinary cause procedure?
action for over £5000
full procedure - evidence recorded
divorce, bankruptcy, adoption, succession
appeal as summary cause
full procedure - evidence recorded
divorce, bankruptcy, adoption, succession
appeal as summary cause
18
New cards
What is the court of session?
Highest civil court in Scotland
Compromises of inner and outer house
Deals with complex cases
\-contract
\-delict
\-commercial law
\-judicial review
\-patent infringement
Compromises of inner and outer house
Deals with complex cases
\-contract
\-delict
\-commercial law
\-judicial review
\-patent infringement
19
New cards
What is the outer house court of session?
court of first instance
presided over by a lord ordinary (a judge of a court session other than one sitting in the inner house)
sits alone
in limited range of cases (e.g. industrial accidents) jury of 12 sit
presided over by a lord ordinary (a judge of a court session other than one sitting in the inner house)
sits alone
in limited range of cases (e.g. industrial accidents) jury of 12 sit
20
New cards
What is the inner court of session?
has two division of equal stature
\
first division - lord president and 3 senior lords of session
\
second division - lord justice-clerk and 3 lords of session
\
primarily an appeal court on points of law
can be a first instance in special cases where facts agreed and only law is in dispute
\
first division - lord president and 3 senior lords of session
\
second division - lord justice-clerk and 3 lords of session
\
primarily an appeal court on points of law
can be a first instance in special cases where facts agreed and only law is in dispute
21
New cards
What is the supreme court?
court of appeal
12 justices (formerly law lords)
normally sits 5
decision by majority
appeals all civil law cases in the UK and most criminal (excluding Scotland)
appeals are rare
12 justices (formerly law lords)
normally sits 5
decision by majority
appeals all civil law cases in the UK and most criminal (excluding Scotland)
appeals are rare
22
New cards
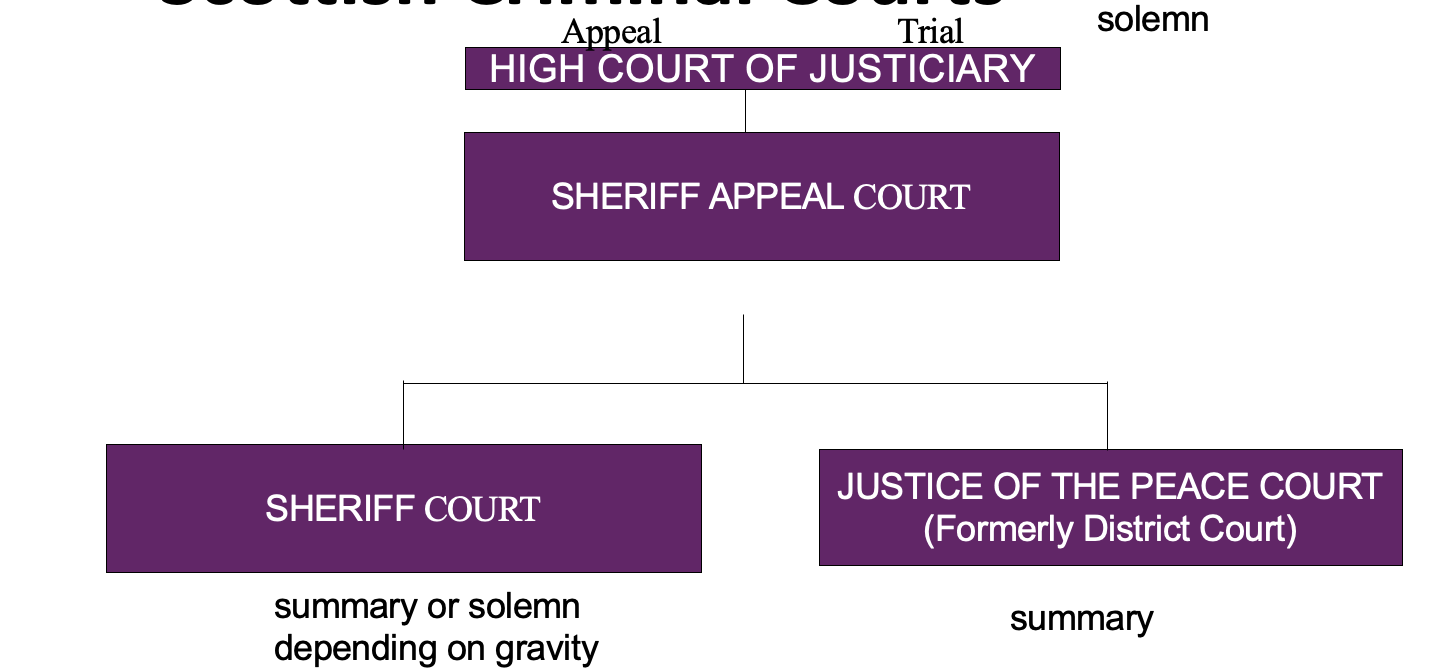
How is the Scottish Criminal Court structured?
23
New cards
What is solemn procedure?
There is a jury
Trail on indictment - an accusation of crime running in the name of Lord Advocate
Tried by a jury, in serious cases in high court, or in Sheriff court
A document setting out the charge against the accused in more serious crimes
\
High court - judge + jury of 15
Sheriff court - sheriff or sheriff principle + jury of 15
Trail on indictment - an accusation of crime running in the name of Lord Advocate
Tried by a jury, in serious cases in high court, or in Sheriff court
A document setting out the charge against the accused in more serious crimes
\
High court - judge + jury of 15
Sheriff court - sheriff or sheriff principle + jury of 15
24
New cards
What is summary procedure?
No jury
Trail on complaint - a document instituting summary (minor) criminal proceedings in a sheriff or JP court setting out the offence charged
\
Sheriff court - sheriff or sheriff principle
Justice of the Peace court - justice of the peace
Trail on complaint - a document instituting summary (minor) criminal proceedings in a sheriff or JP court setting out the offence charged
\
Sheriff court - sheriff or sheriff principle
Justice of the Peace court - justice of the peace
25
New cards
What is public prosecution?
the police’s job to investigate crimes and gather evidence
crown office and procurator fiscal service decide if it goes to court
crown office and procurator fiscal service decide if it goes to court