Brain and Cranial Nerve Anatomy
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Nervous system
Subdivided into 2 divisions: central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
Central nervous system
Consists of brain and spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system
Consists of cranial and spinal nerves
Brain regions
Cerebrum, diencephalon, cerebellum, and brainstem (midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata).
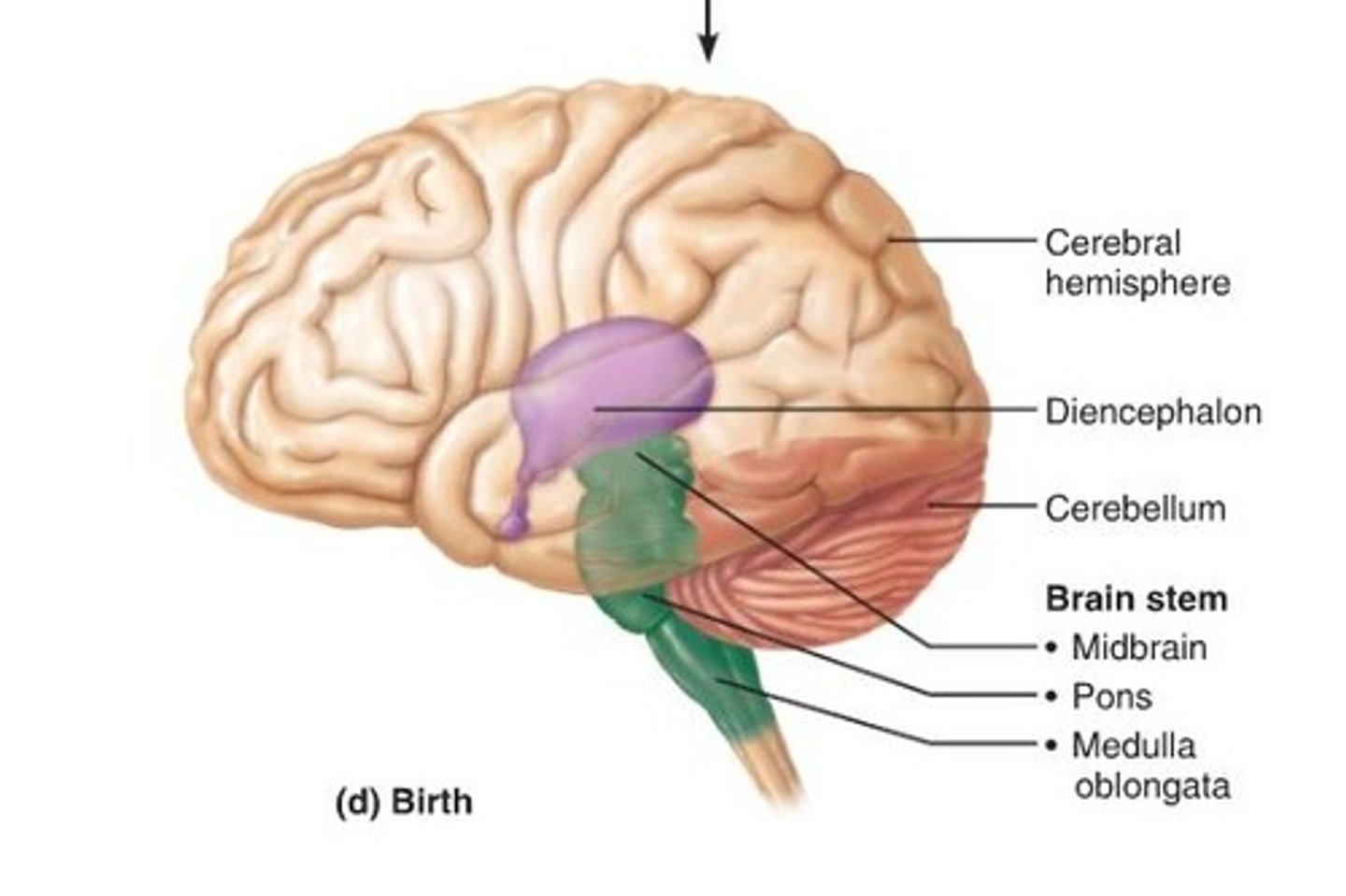
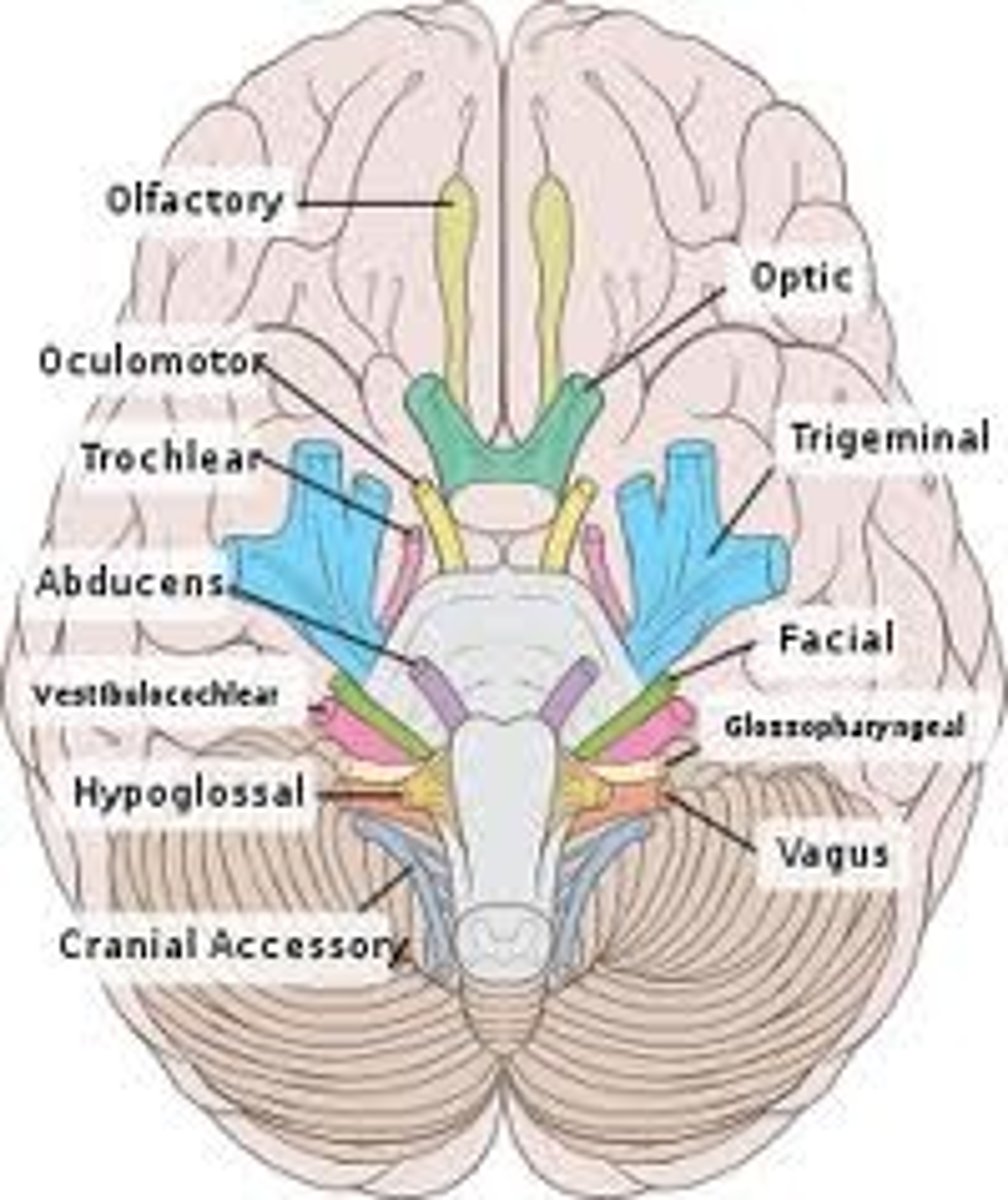
Cranial nerves
12 pairs
Cerebrum
Largest region of the brain comprising 80% of its total mass
Divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres by very deep longitidinal fissure
Corpus callosum
Two hemispheres are connected to each other by it
Formed by axons passing between the two hemispheres
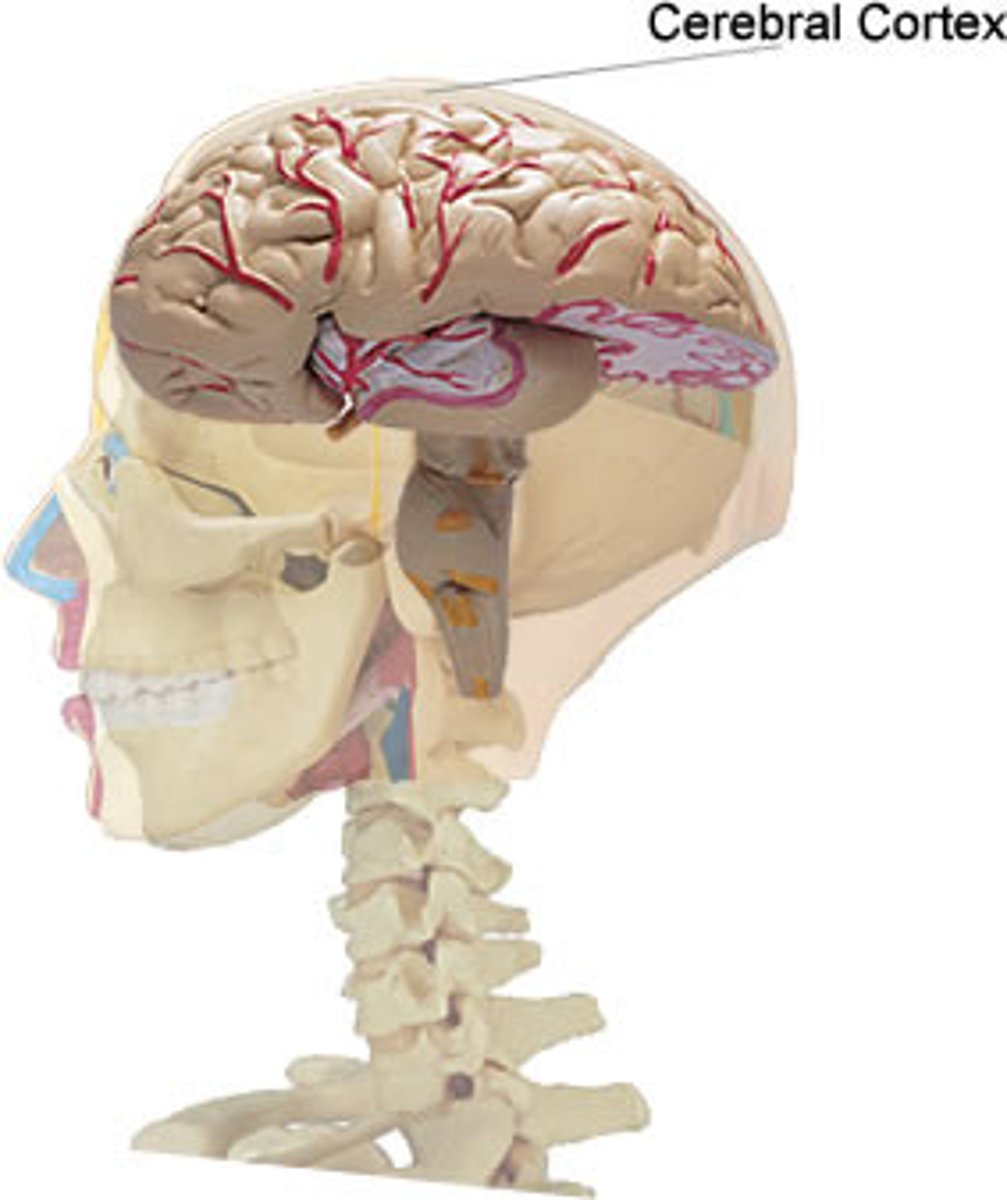
Cerebral cortex
Outer surface of each hemisphere that is gray matter
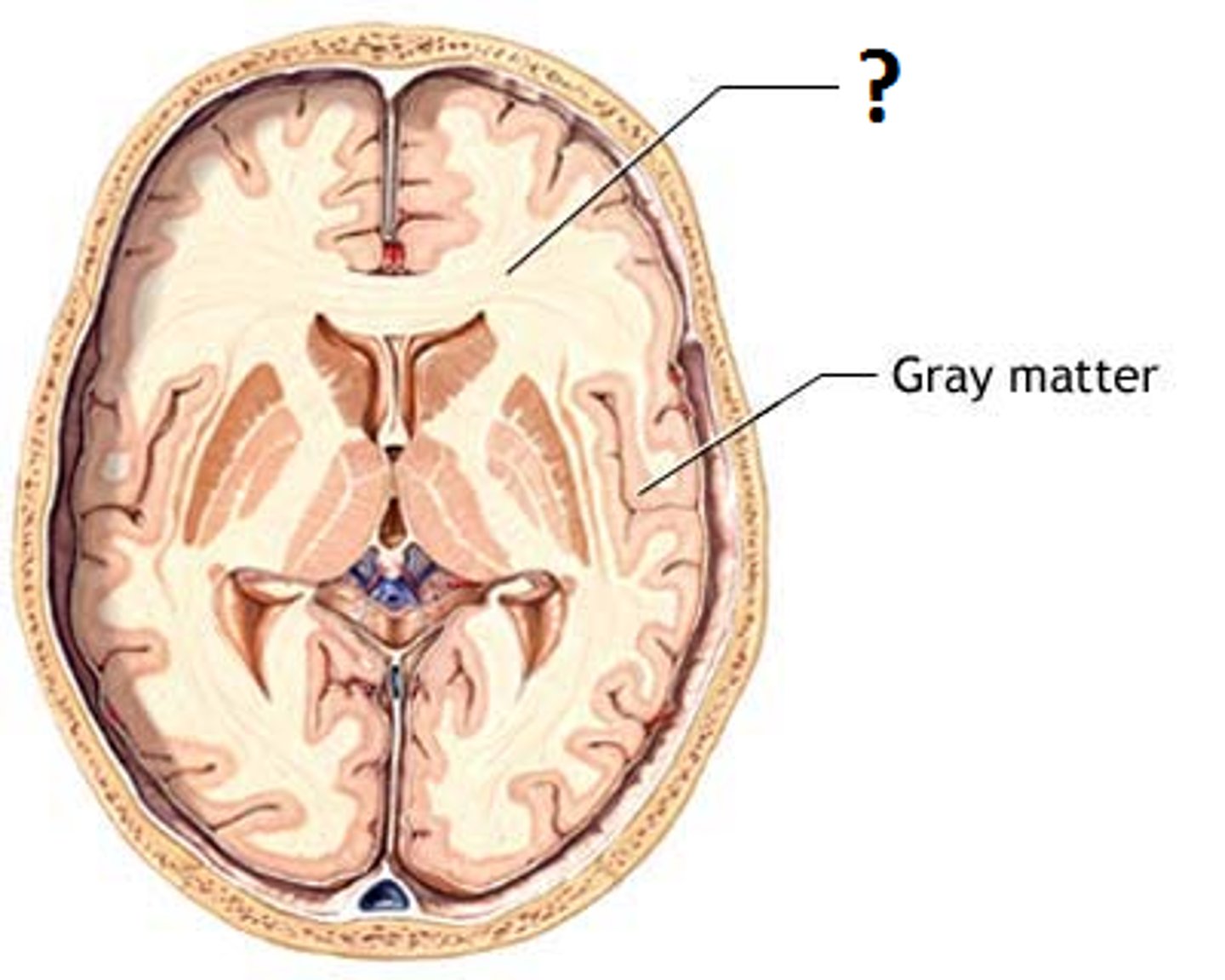
White matter
Composed of myelinated axons interconnecting different regions of the cerebrum and other regions of the brain
Underneath the cerebral cortex and extending through the corpus callosum
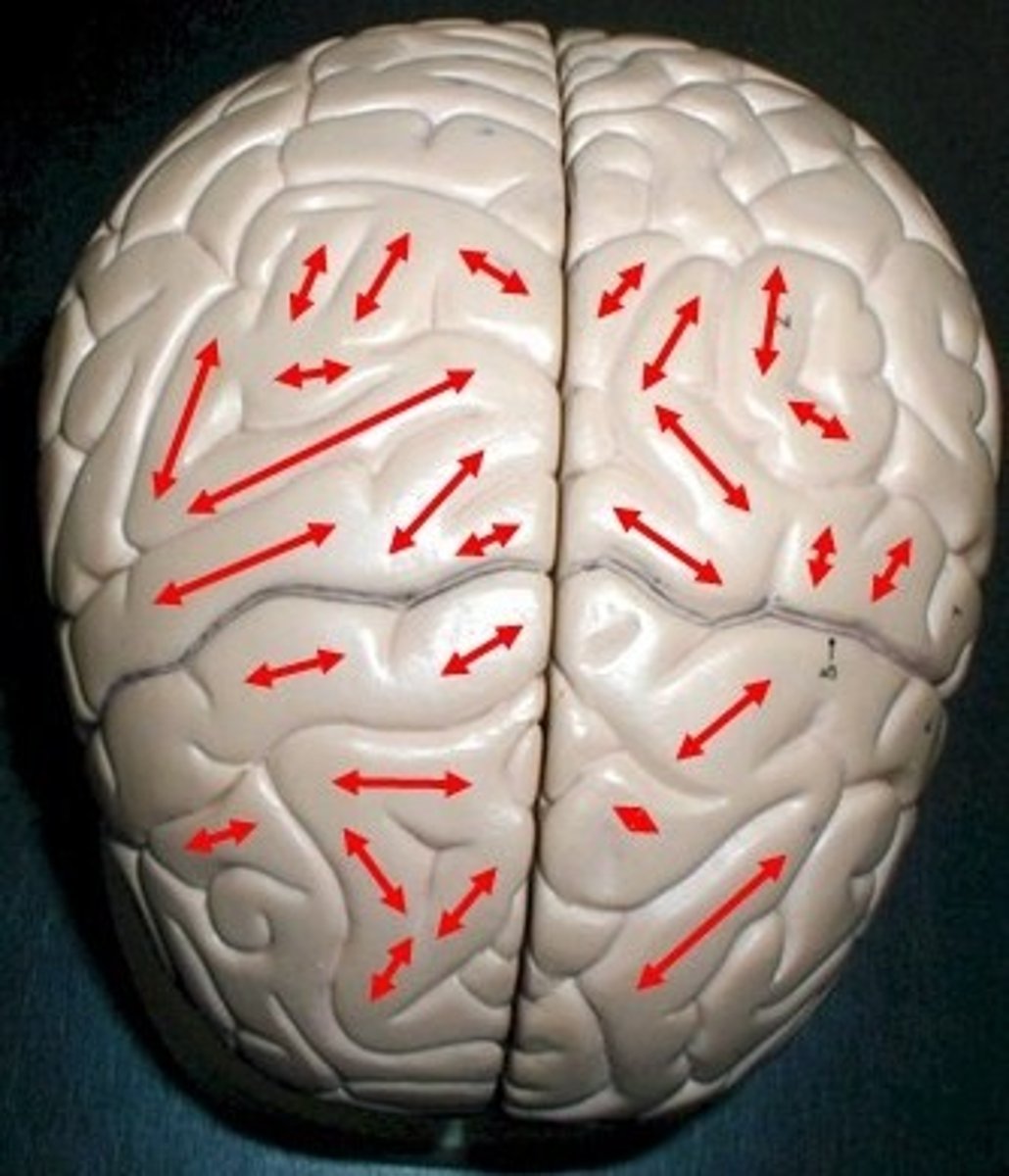
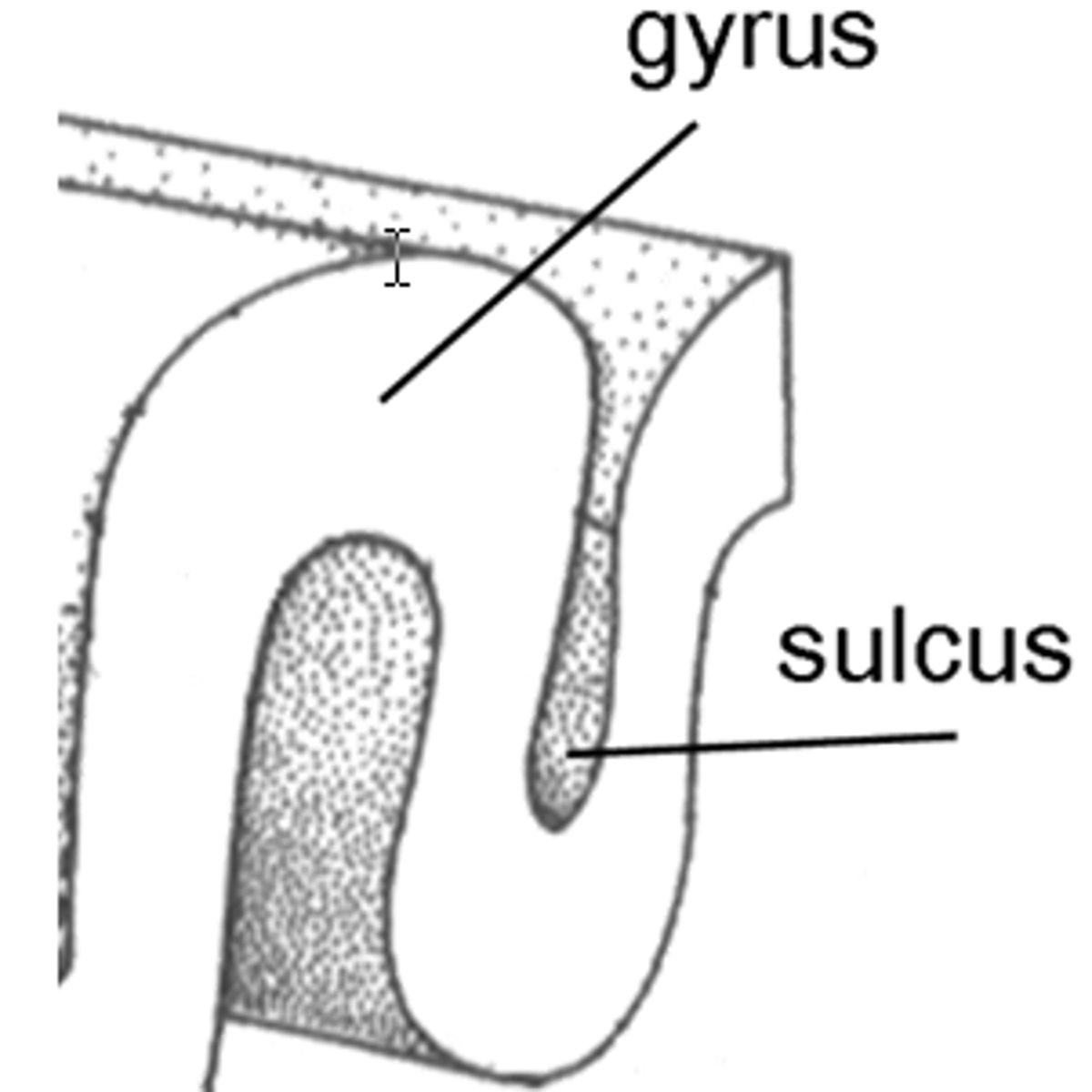
Gyri
Singular is gyrus
Peaks of the brain
Sulci
Singular is sulcus
Valleys of the brain
Exceptionally deep sulci are called fissures
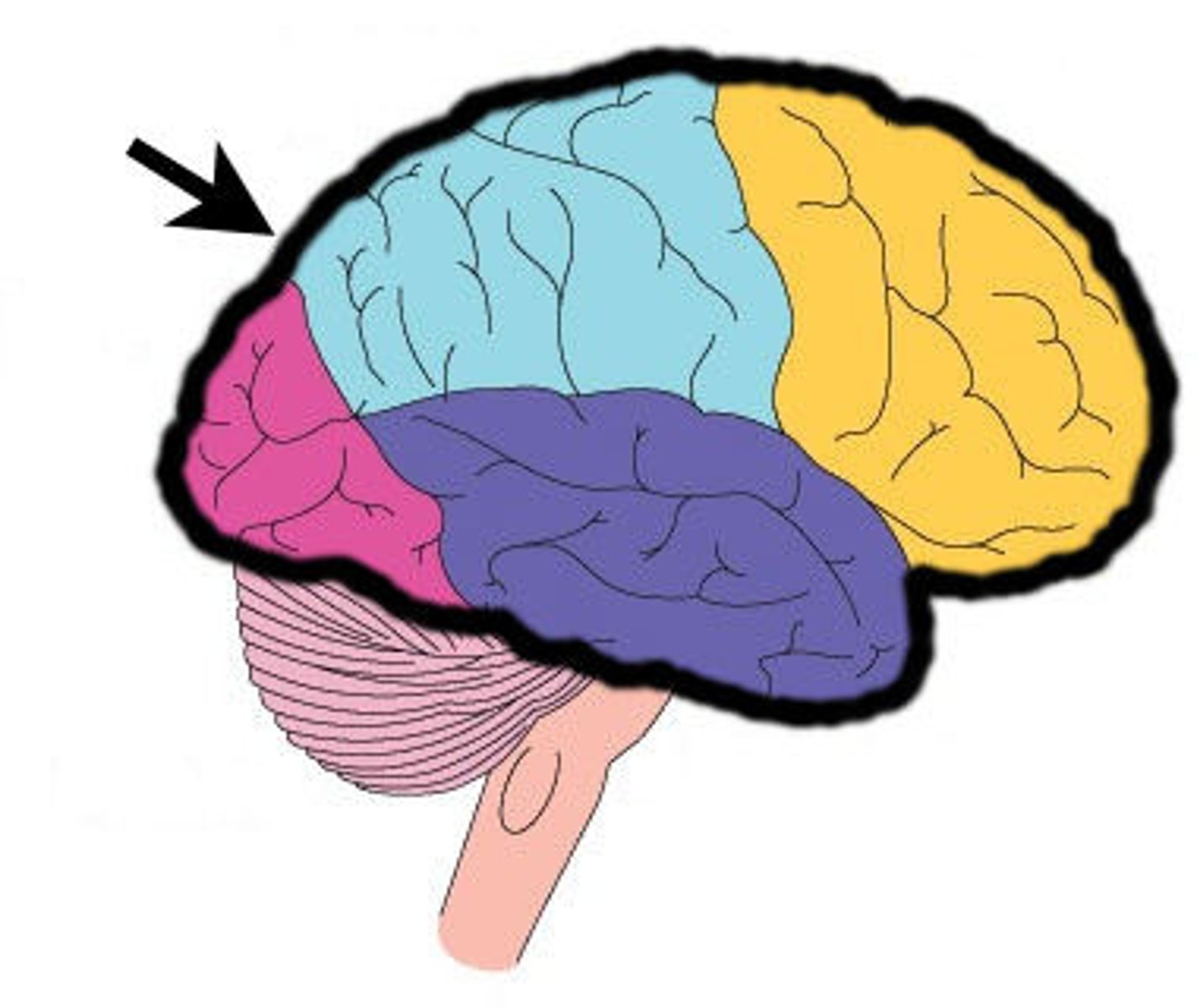
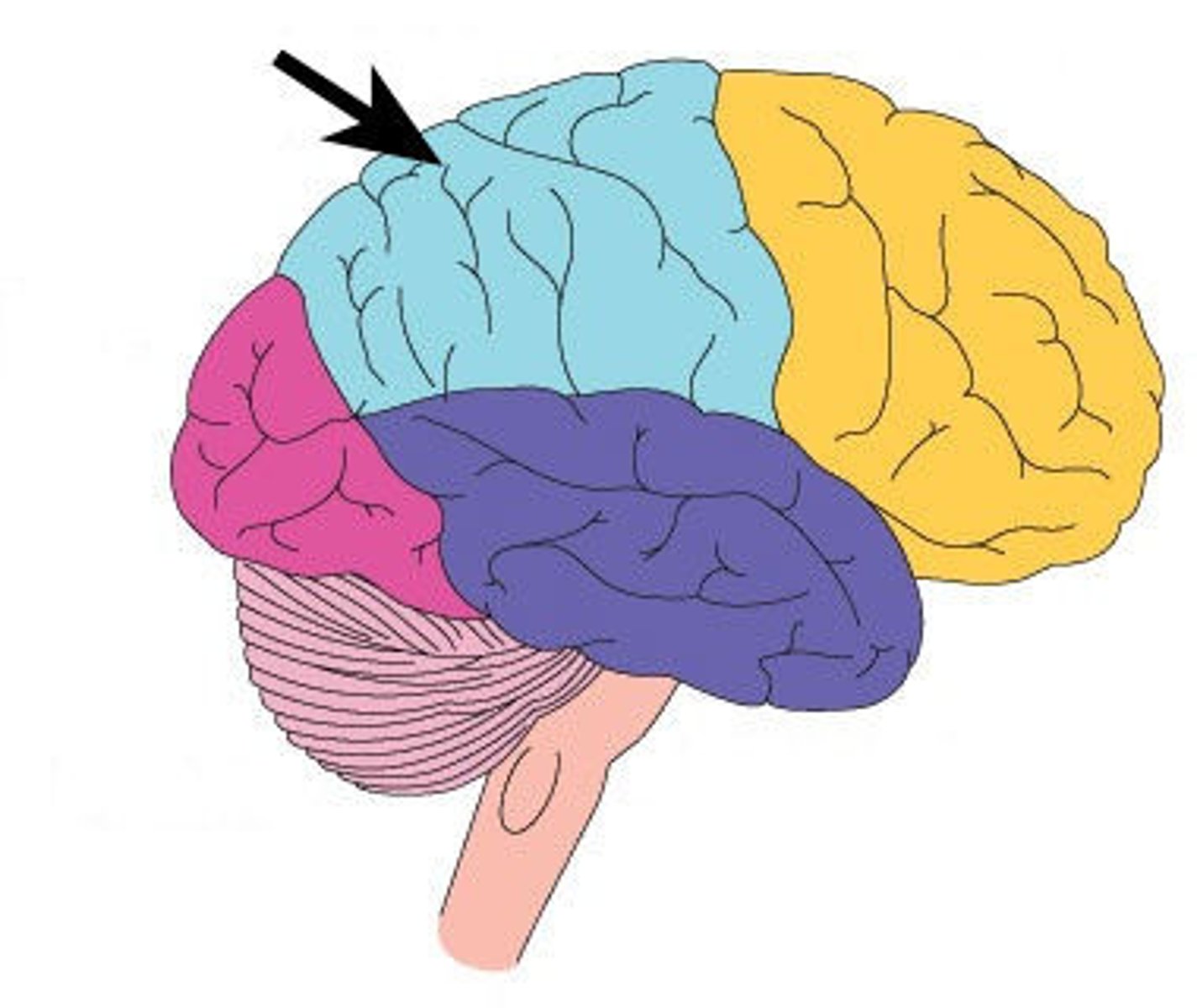
5 Lobes
Frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal, and insula
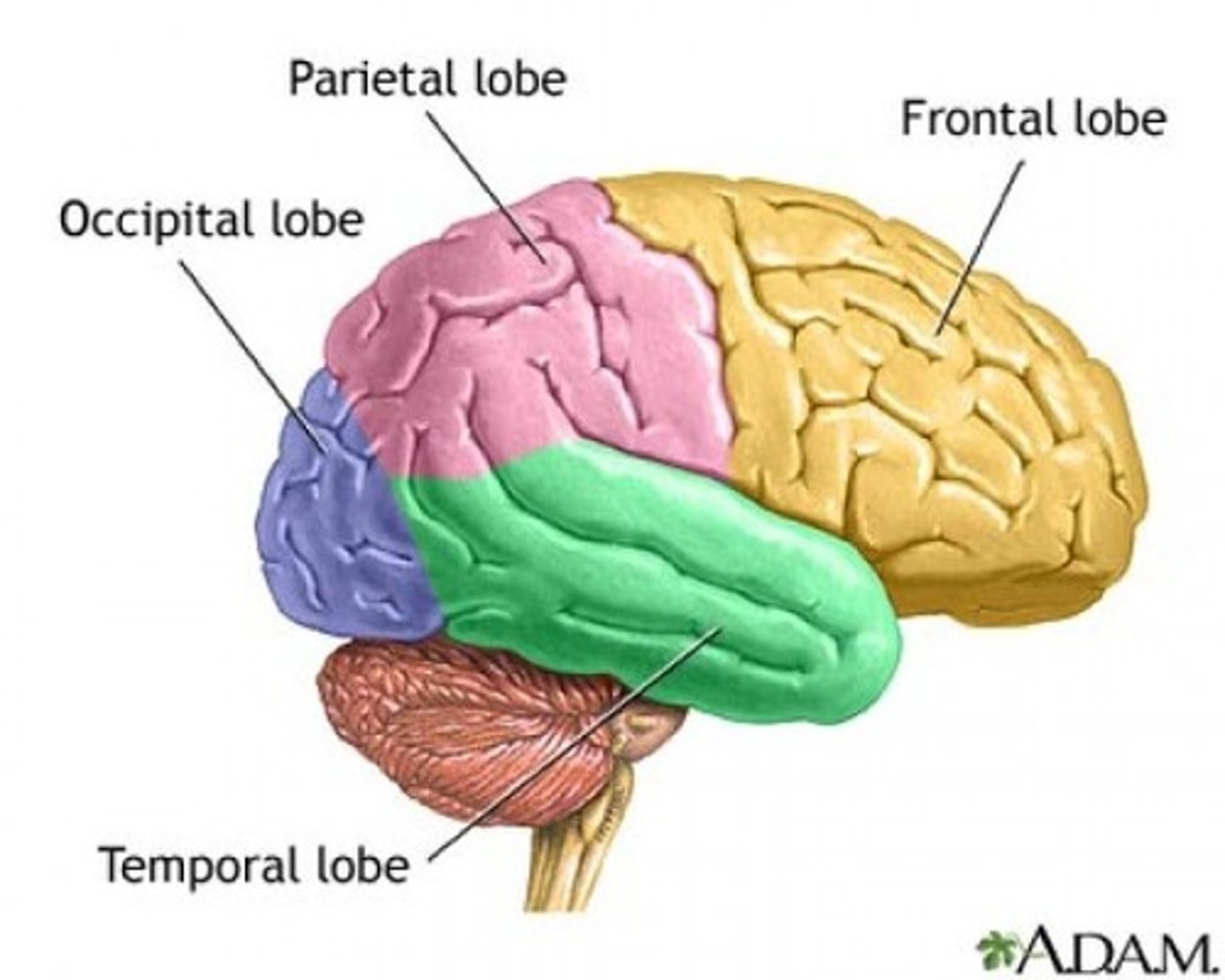
Frontal lobe
Functions include:
conscious thought
memory storage
motor control
judgement
problem solving
emotion
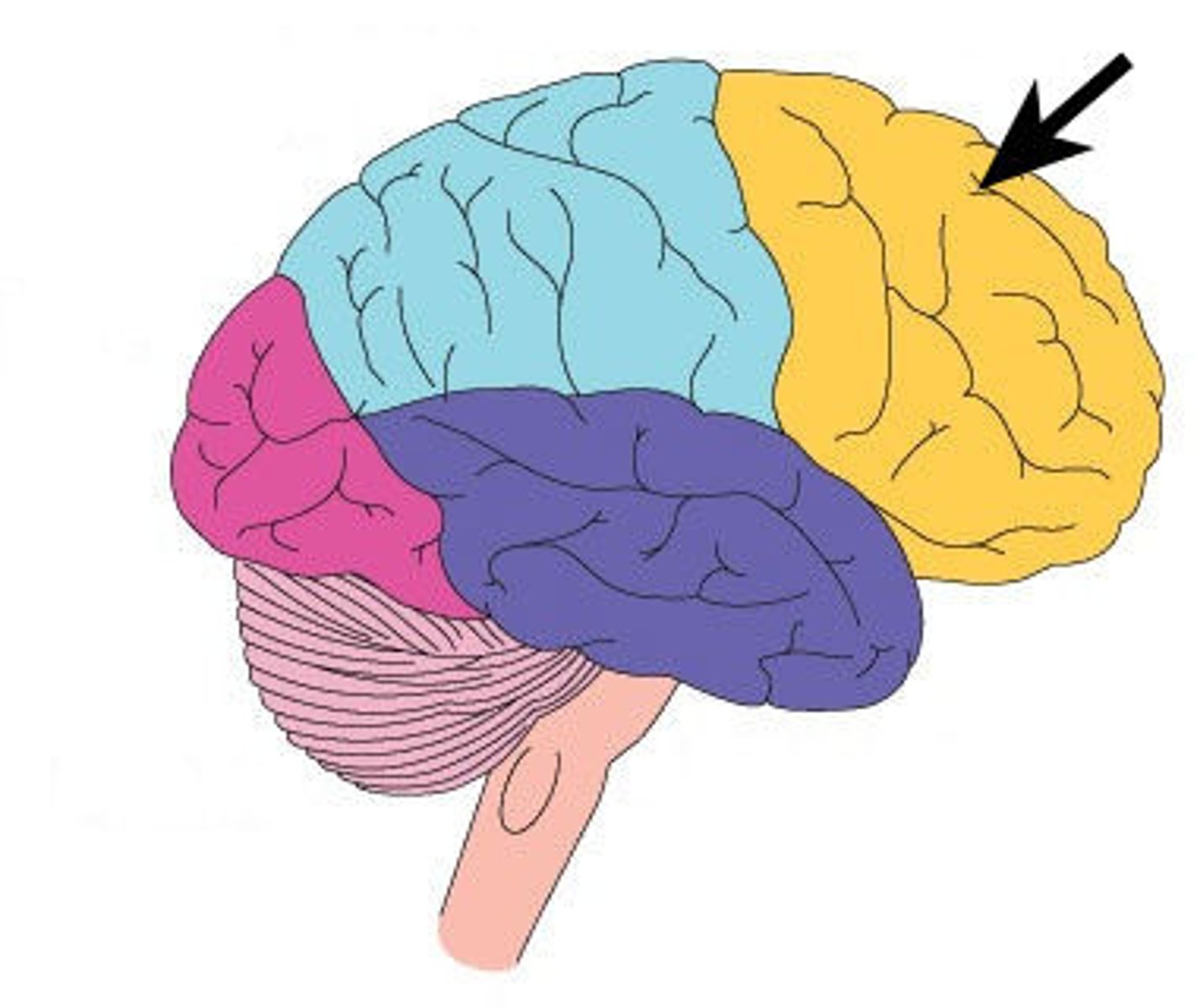
Broca's area
Motor control of the muscles involved in producing speech
In frontal lobe
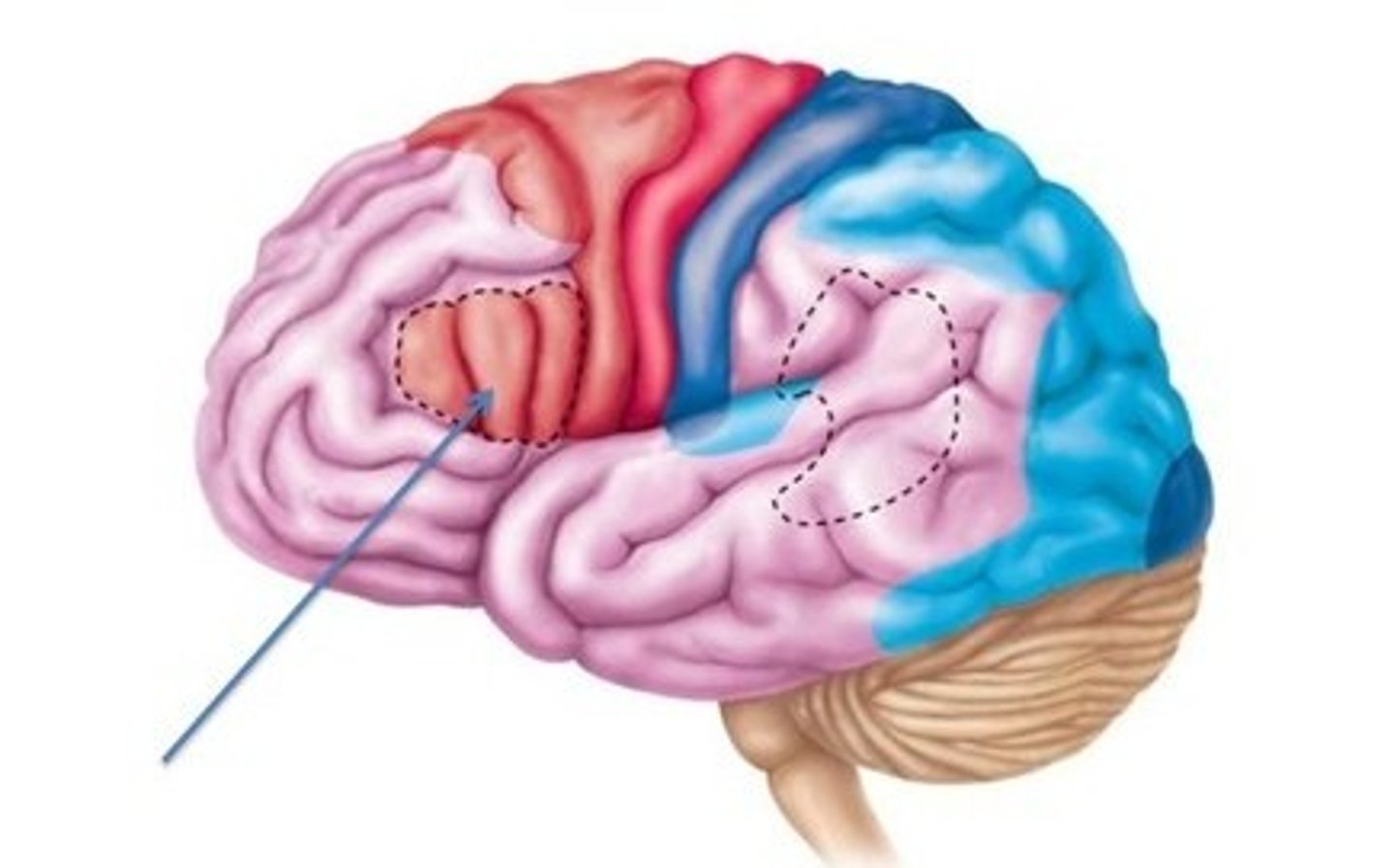
Temporal lobe
Recieves auditory stimuli from cochlea of the ear
Pons
Name means "bridge"
Links cerebellum with rest of brain
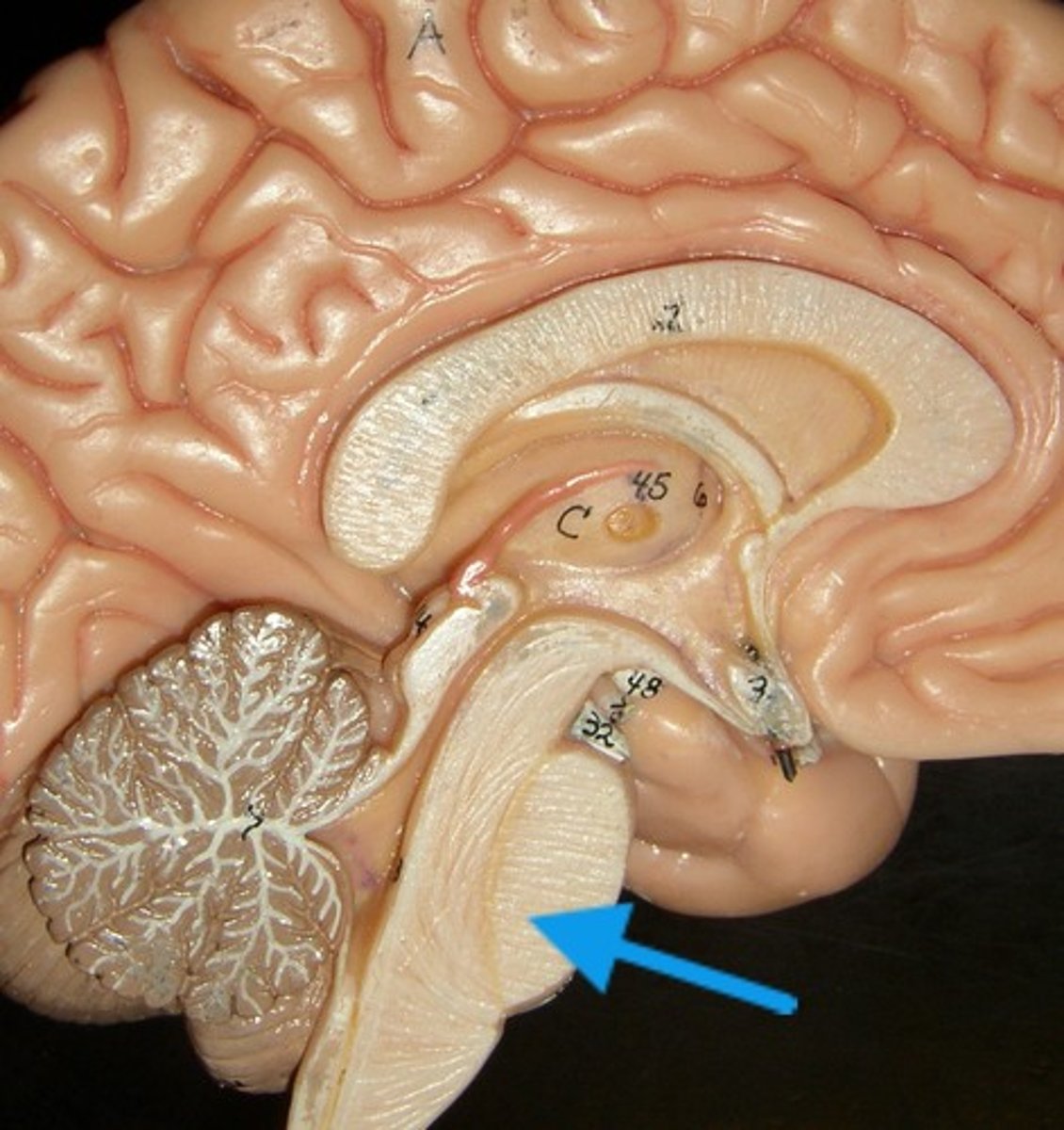
Medulla oblongata
Regulates blood pressure, heart rate, and force of contraction, and respiratory rate
All ascending sensory and descending motor impulses pass through medulla
Site where many fibers cross to the other side
Continuous with spinal cord
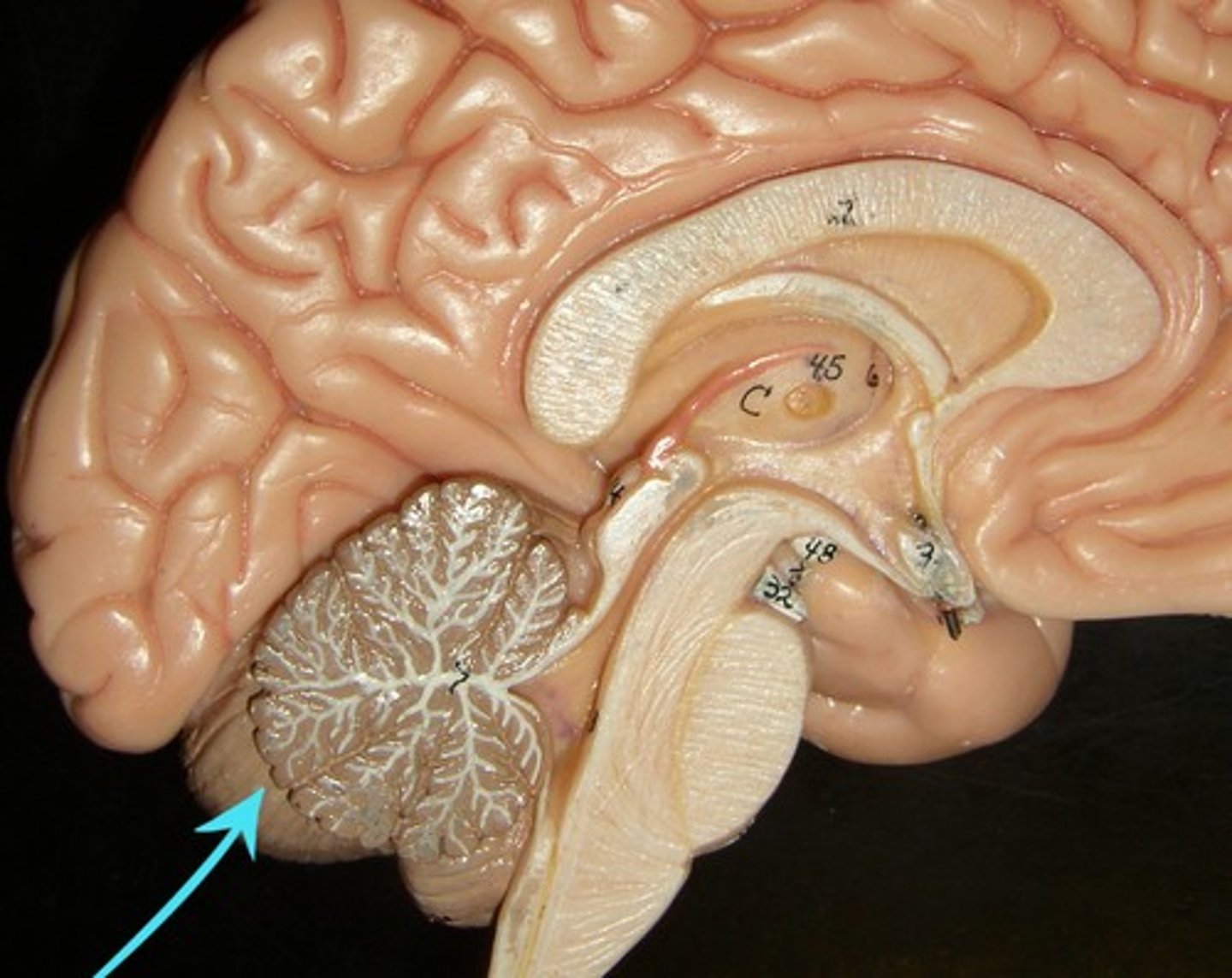
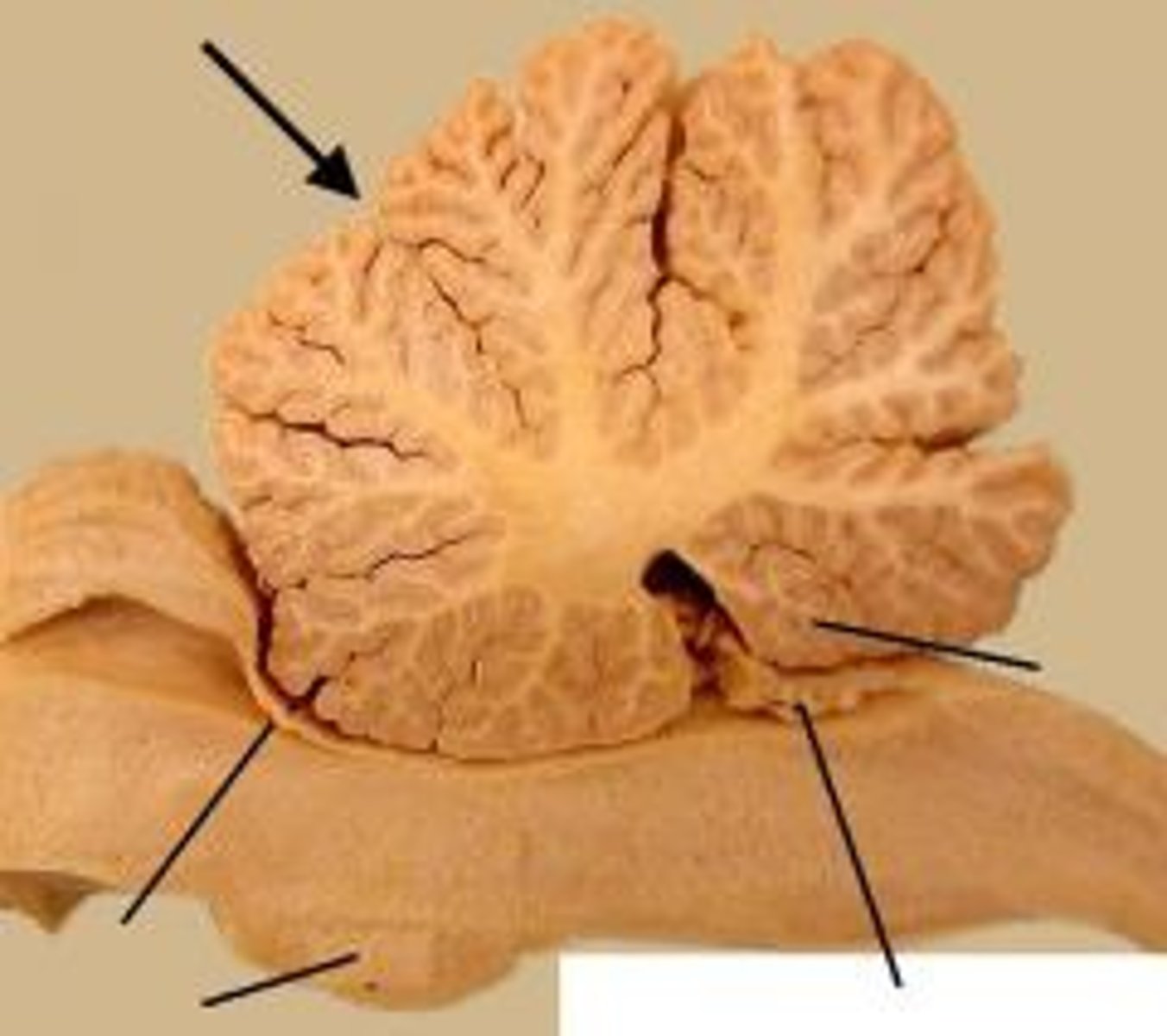
Cerebellum
Second largest region of the brain
Located inferior to the occipital lobe
Works with cerebrum to coordinate skeletal muscles
2 parts are arbor vitae and folia
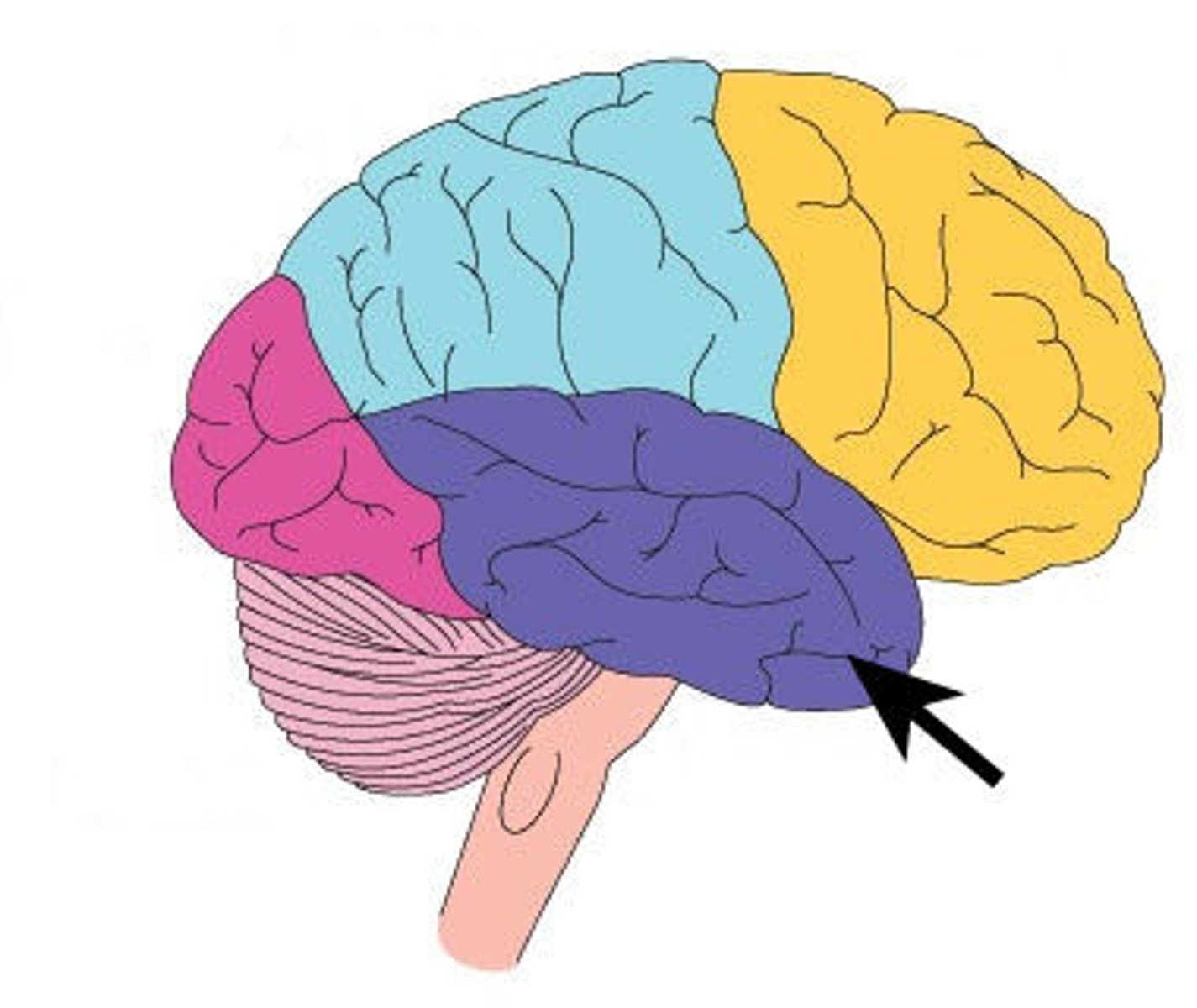
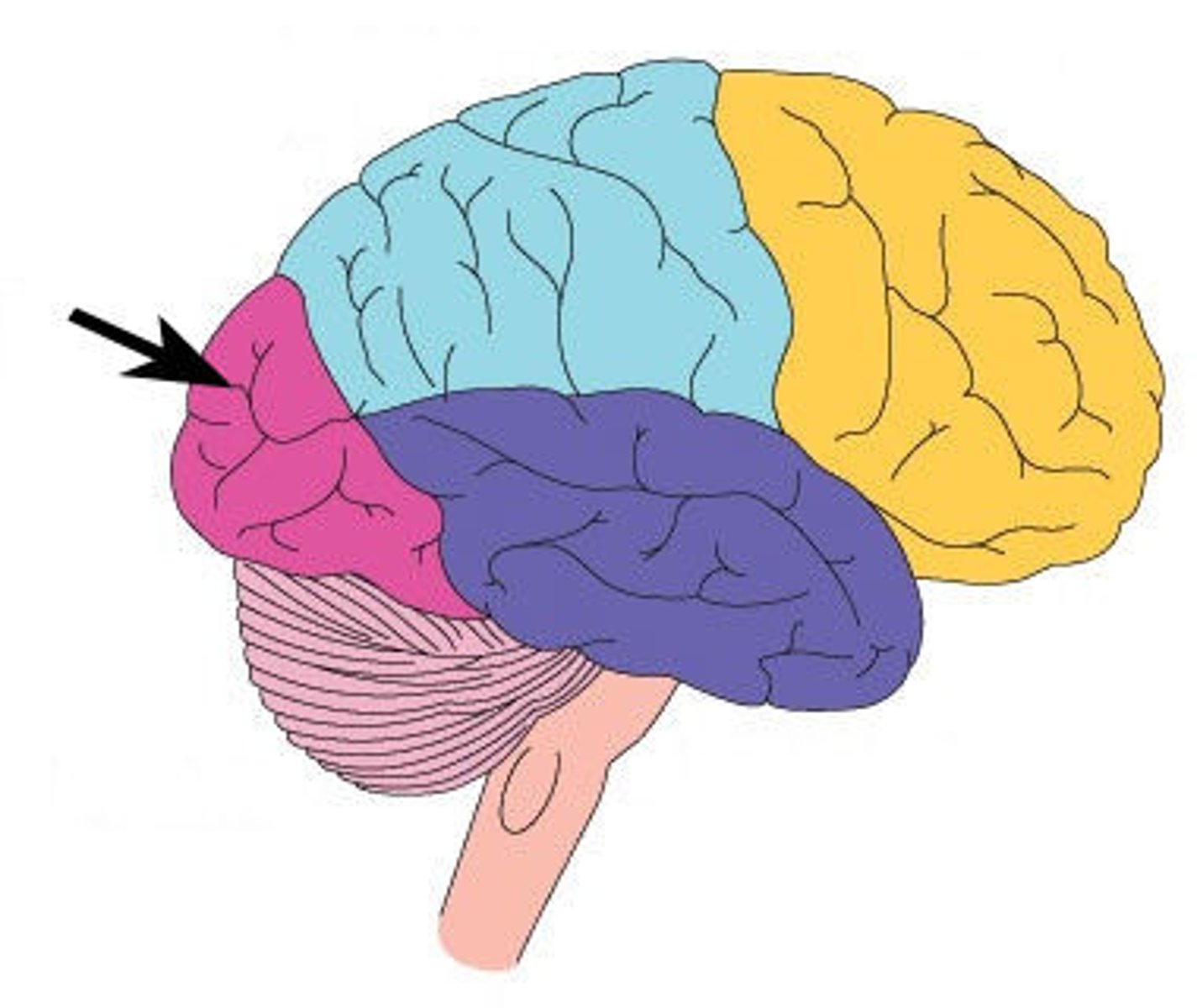
Occipital lobe
Receives visual stimuli from photoceptors in the eye
Parietal lobe
Functions include analyzing sensory stimuli
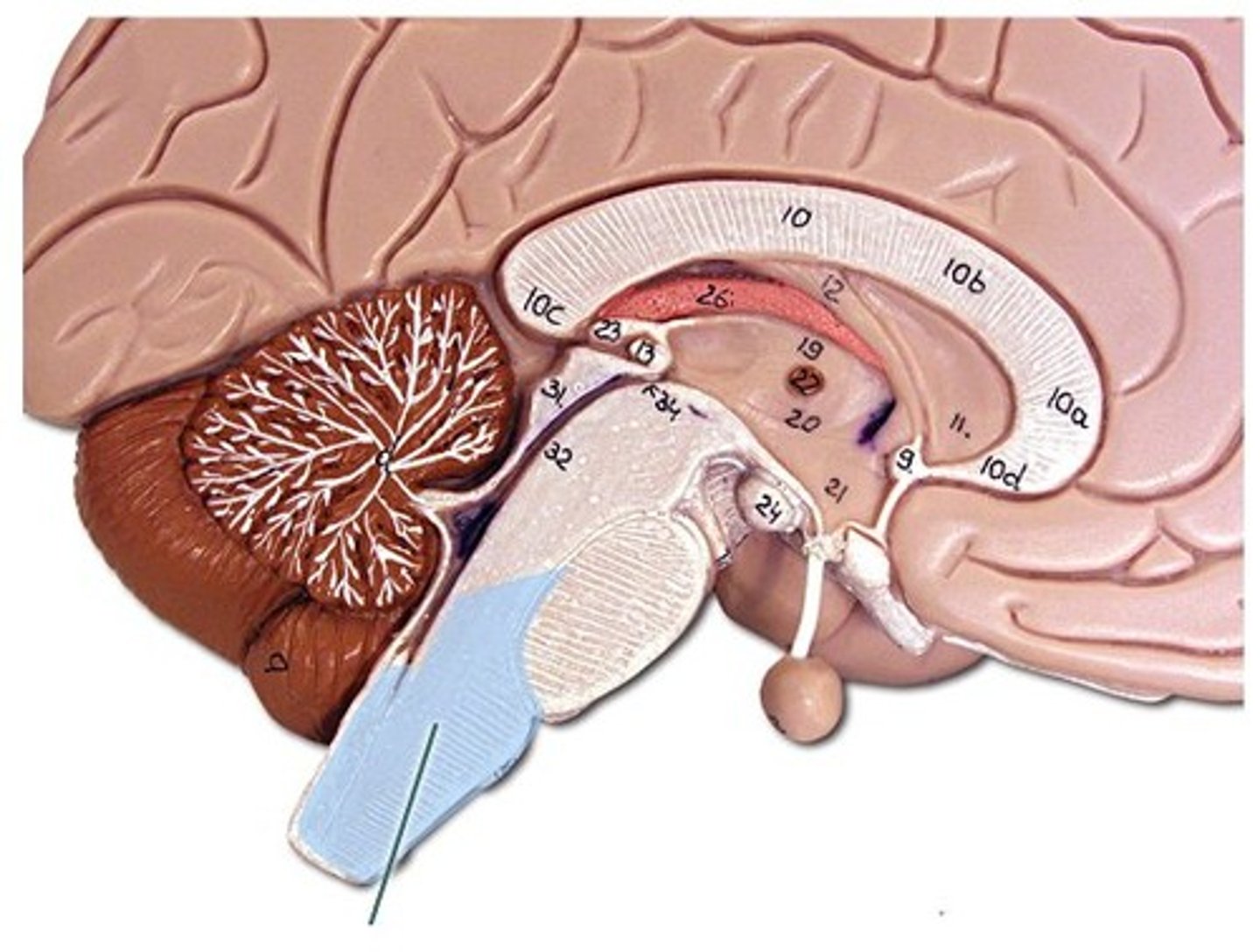
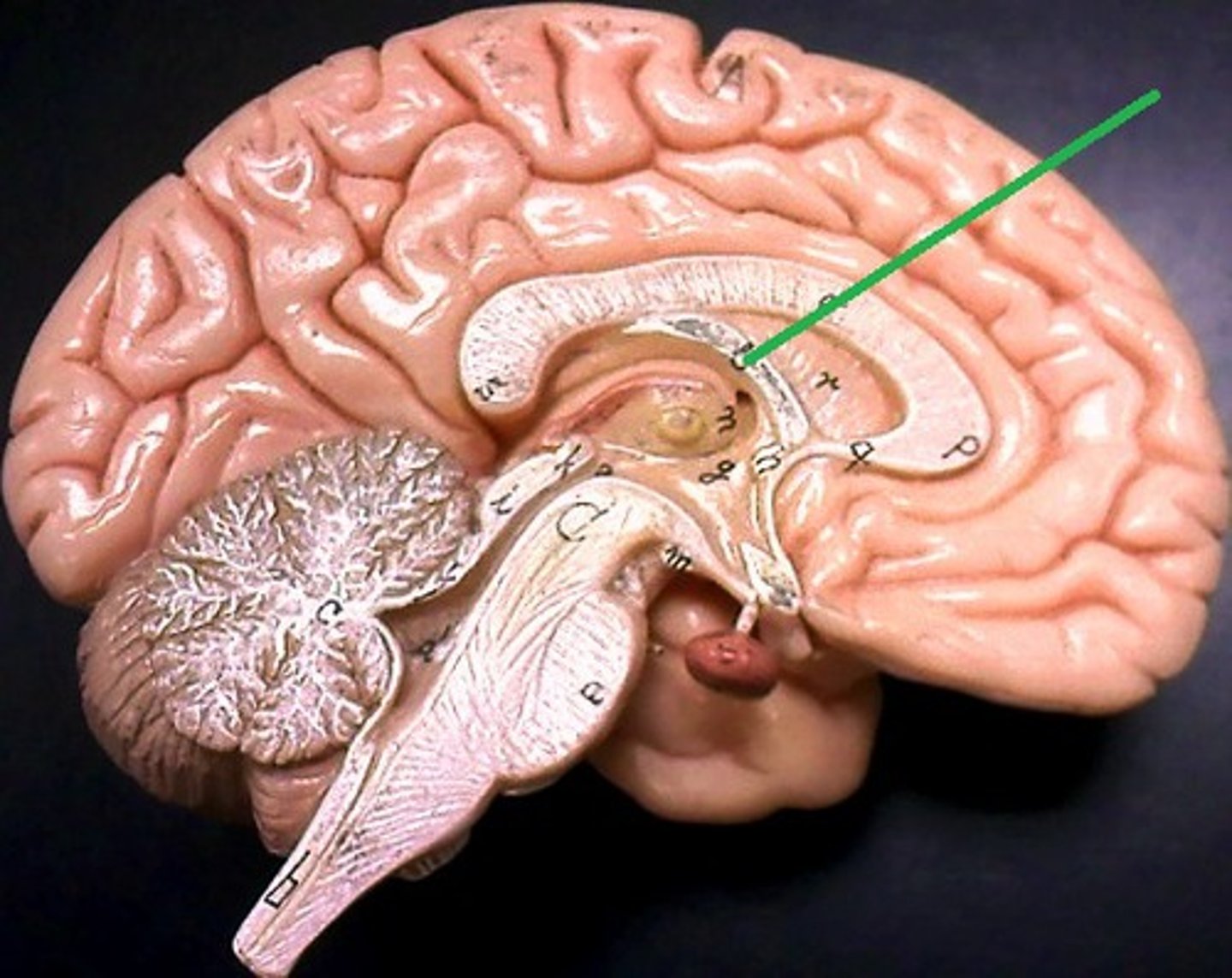
Fornix
Tract of white matter along inferior border of sptum pellucidum
Interconnects regions of cerebrum with the mammillary bodies
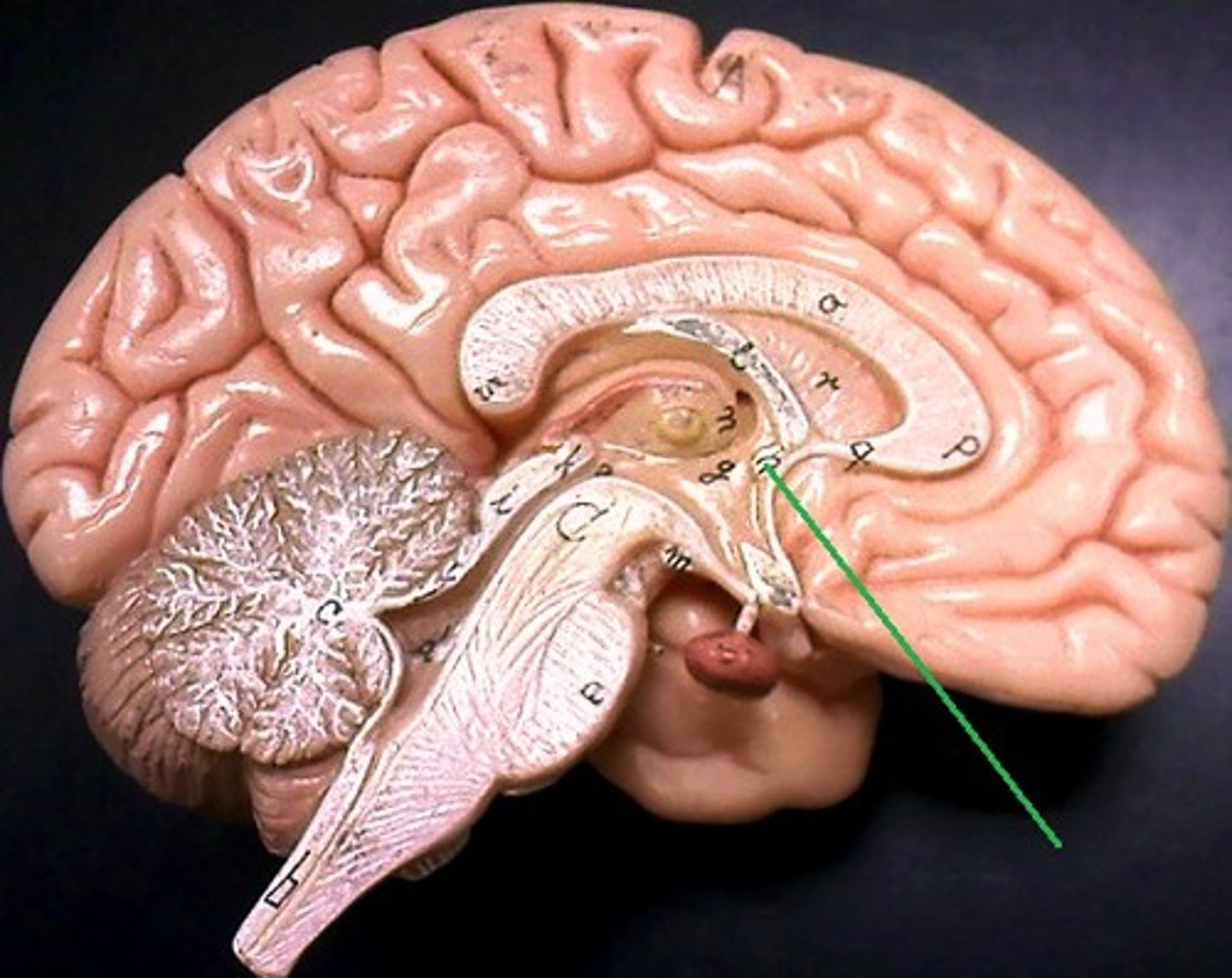
Anterior commissure
Tract of white matter
Interconnects optic chiasma and cerebral hemispheres
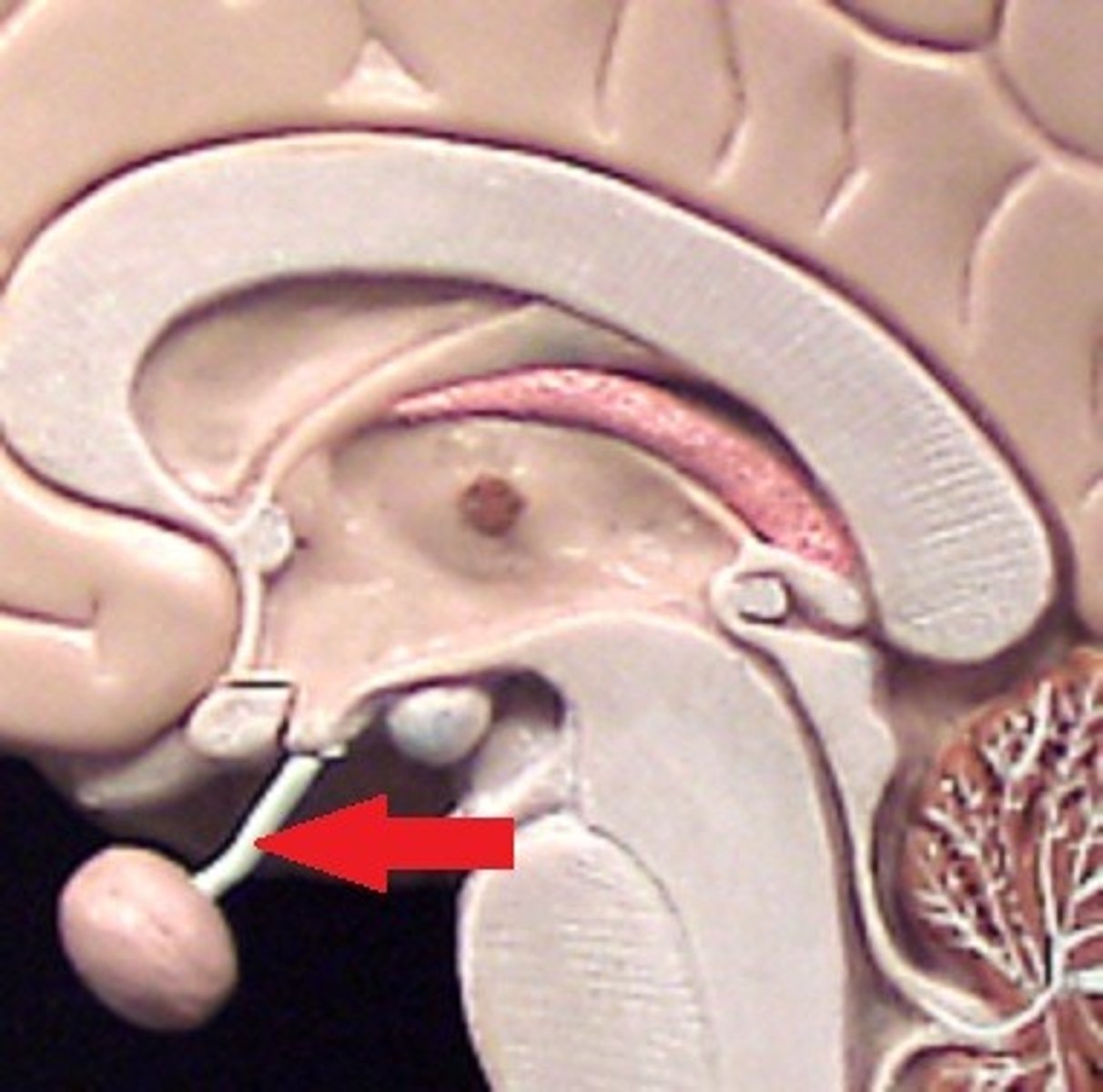
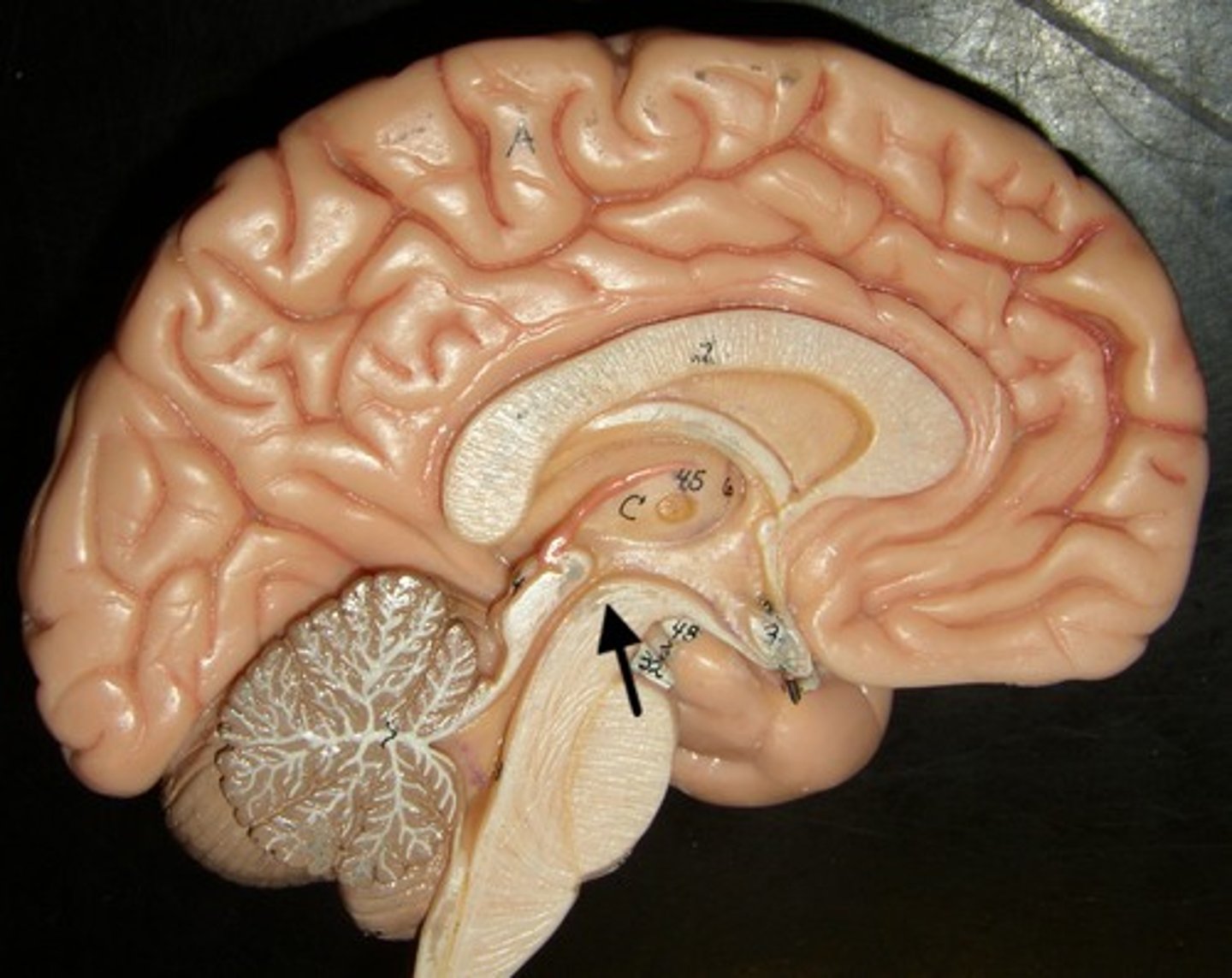
Infundibulum
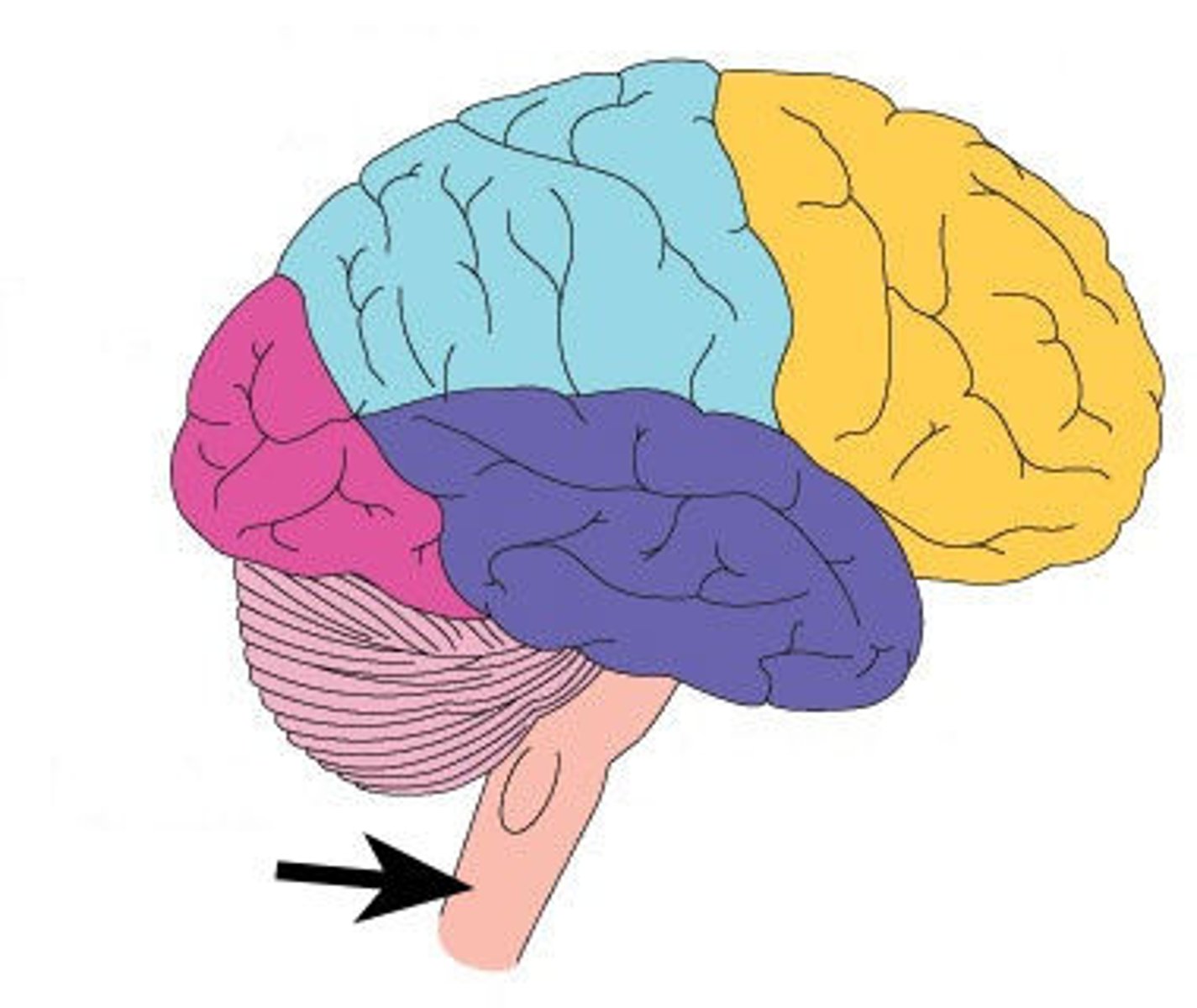
Brain stem
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla oblongata
Diencephalon
Lies inferior to the cerebrum
Epithalamus and choroid plexus form the roof and the hypothalamus forms the floor and the thalamus forms the lateral walls
Third ventricle
Center of the diencephalon, with regions of the diencephalon arranged around it
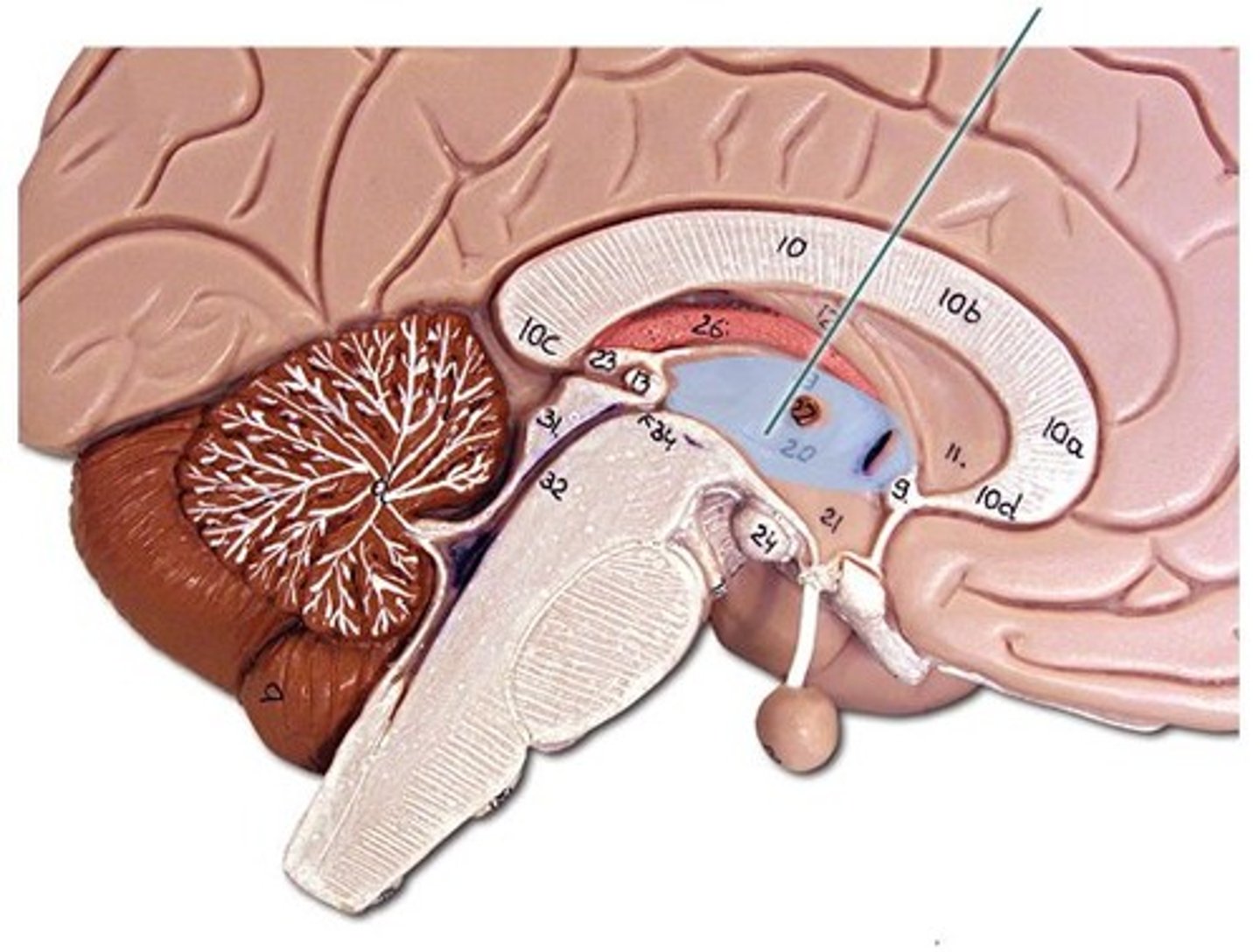
Thalamus
Gray matter
form walls of third ventricle
Relays sensory information to correct region of cerebrum
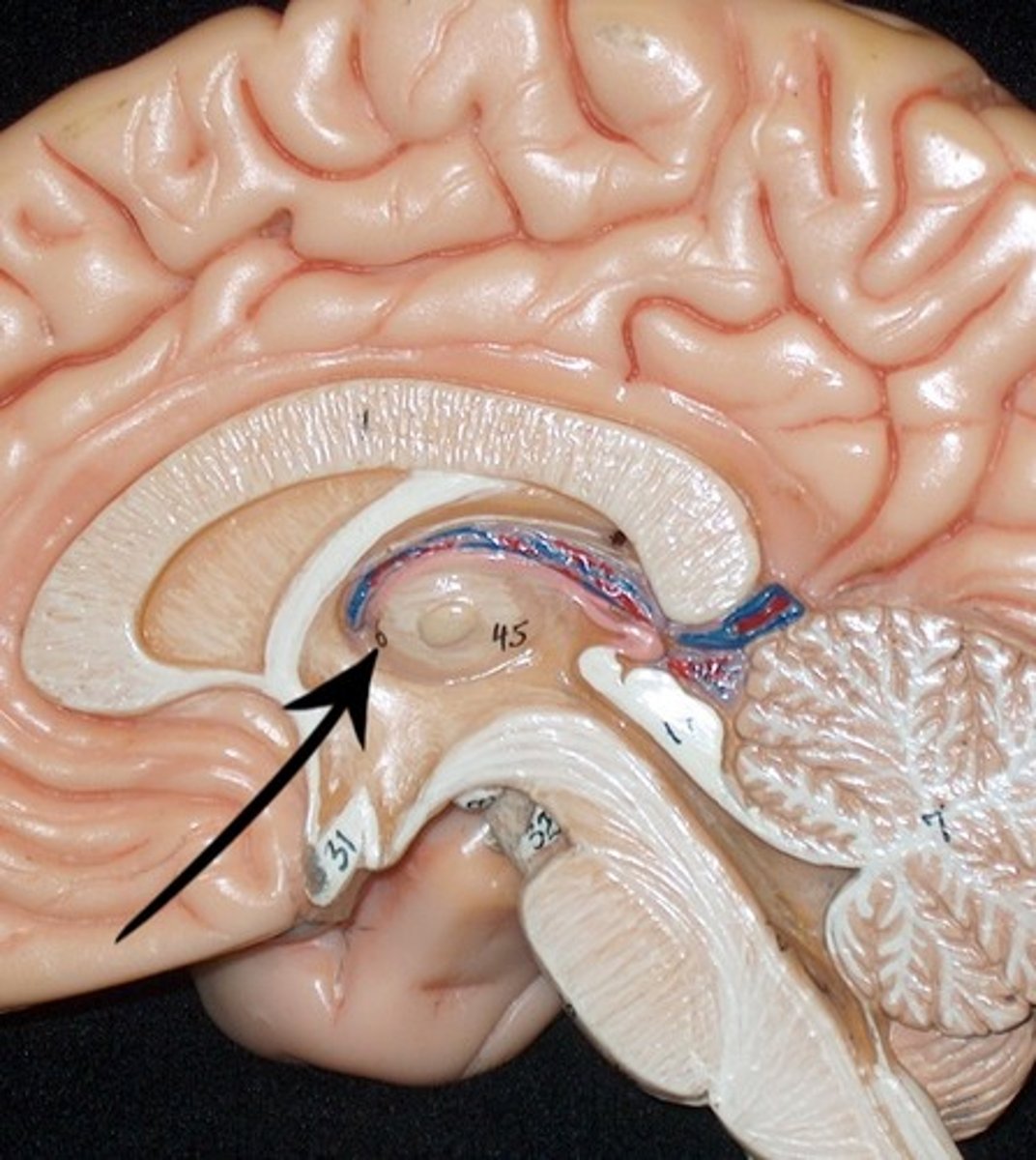
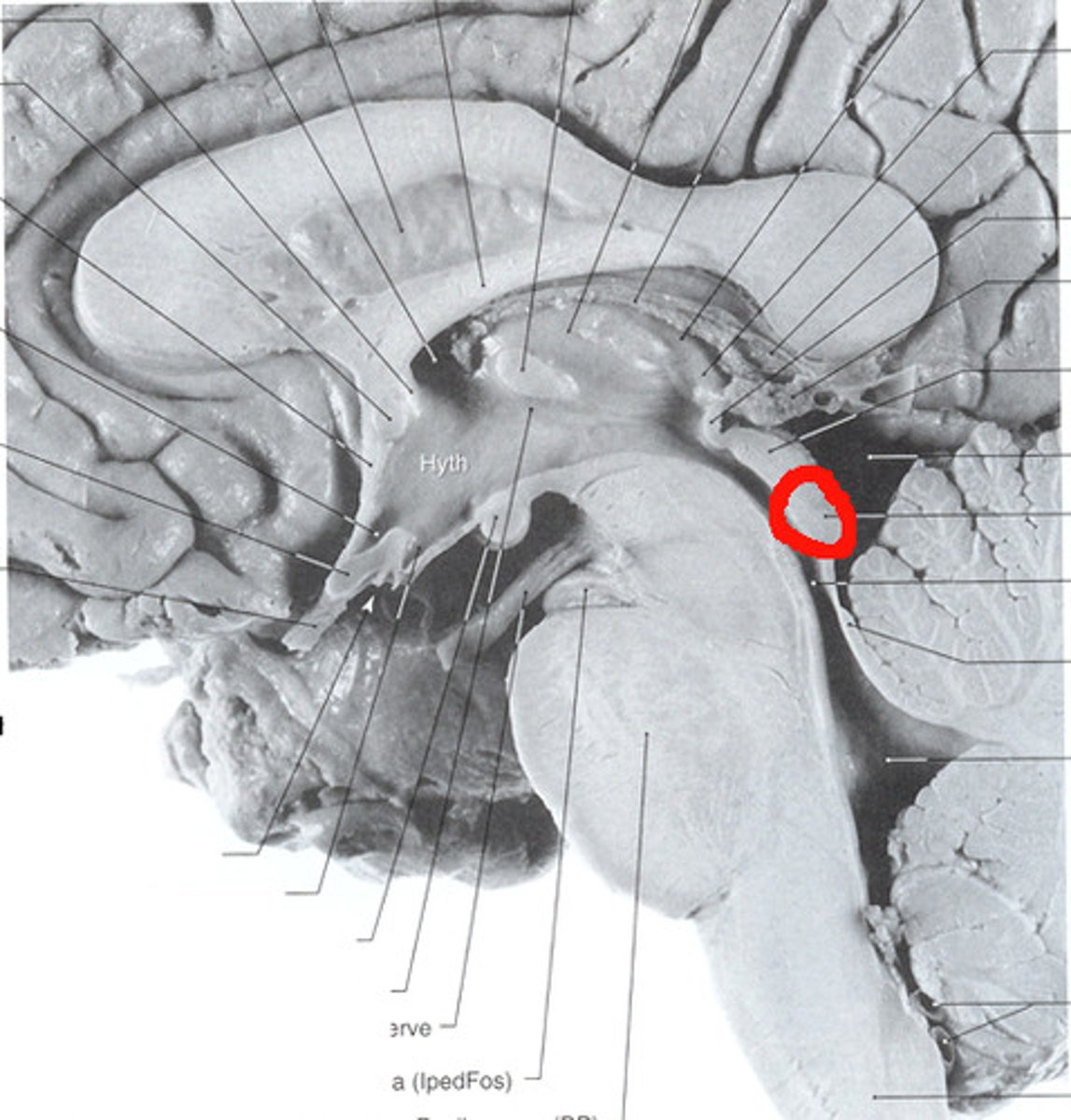
Pineal gland
Part of epithalamus
an endocrine gland
Secretes melatonin
Regulates circadian rhythm
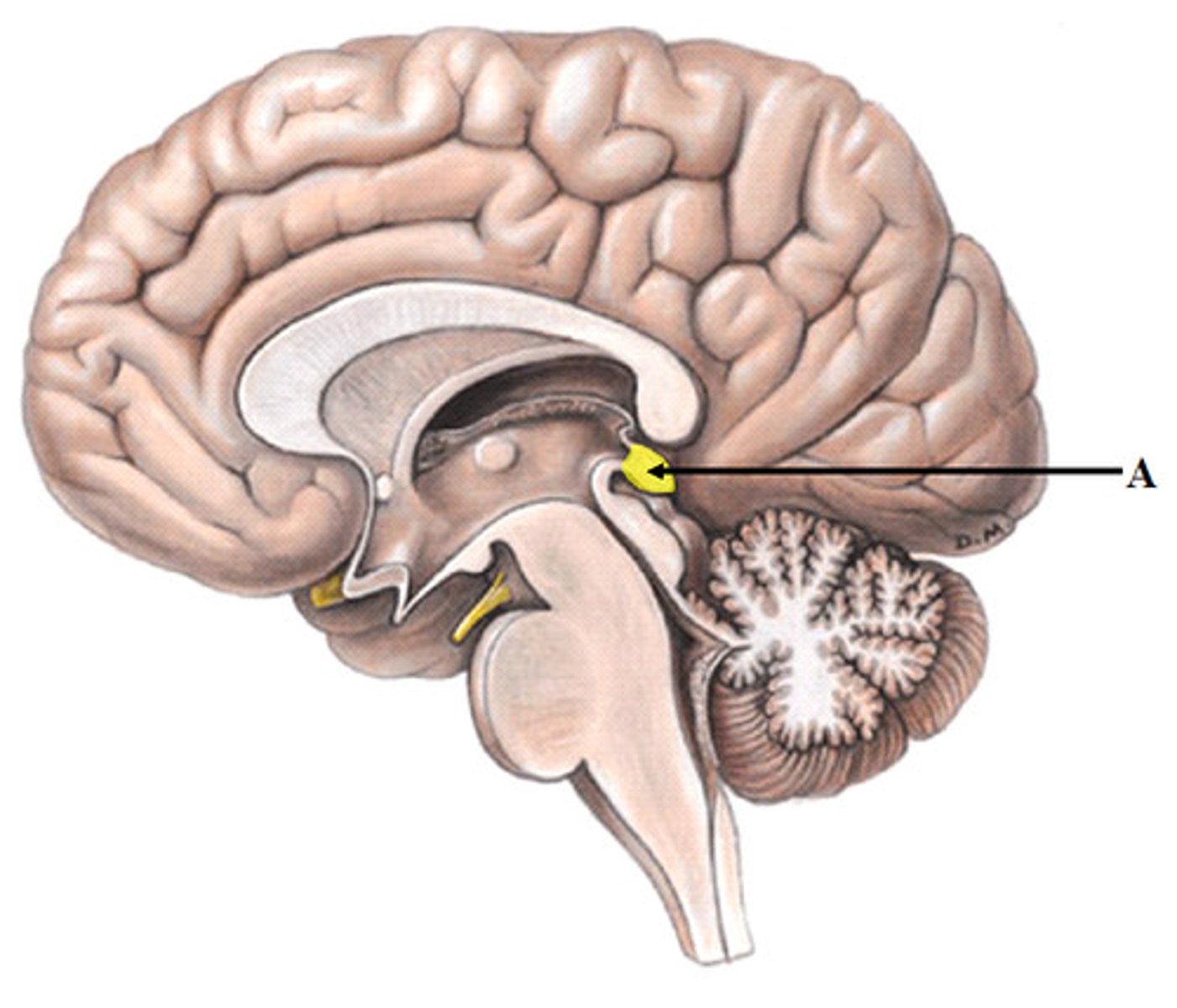
Mammillary body
Gray matter of the hypothalamus
Controls eating and swallowing reflexes
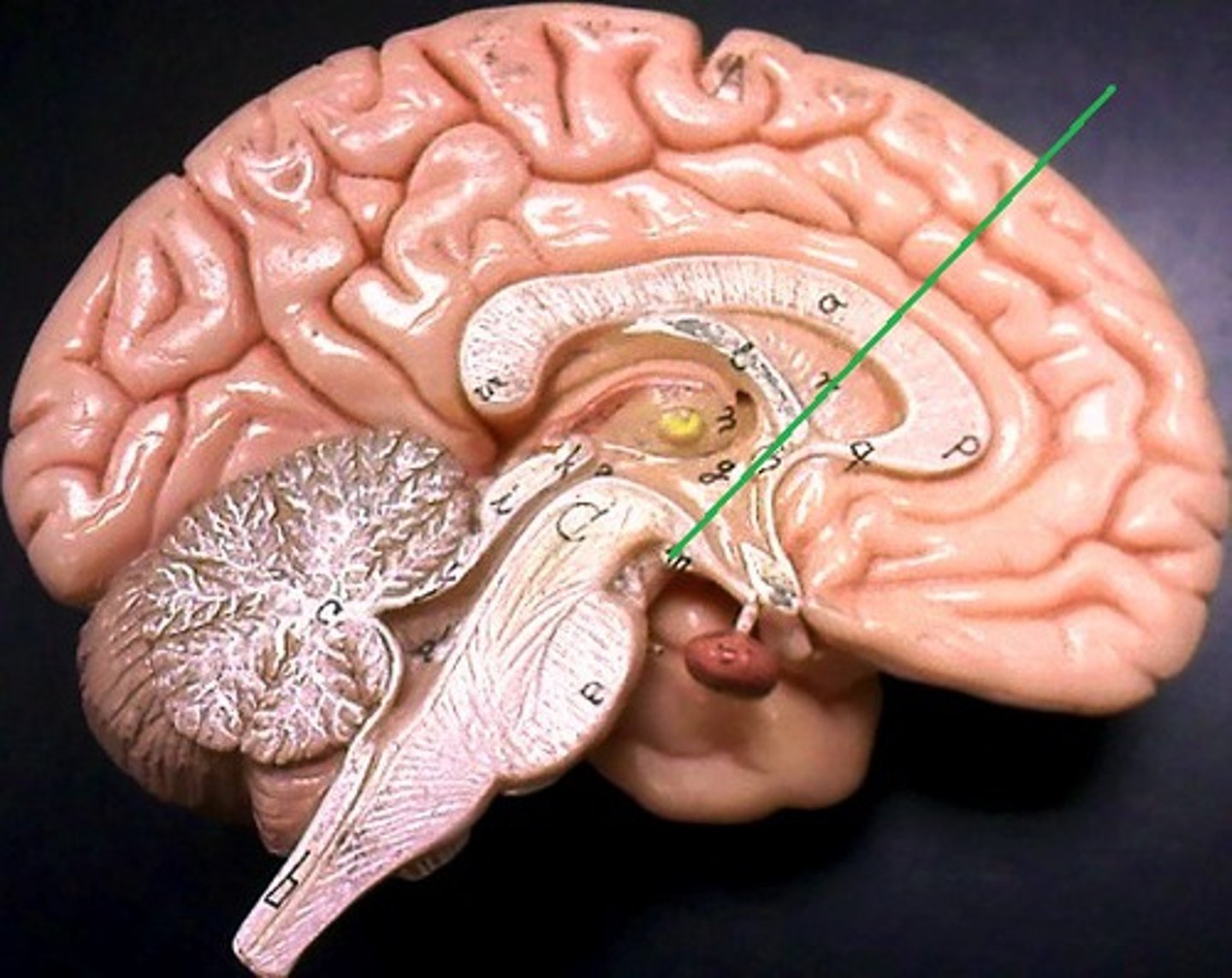
Pituitary gland
An endocrine gland
Connected to the hypothalamus by stalk of tissue called infundibulum
Secretion is regulated by hypothalamus
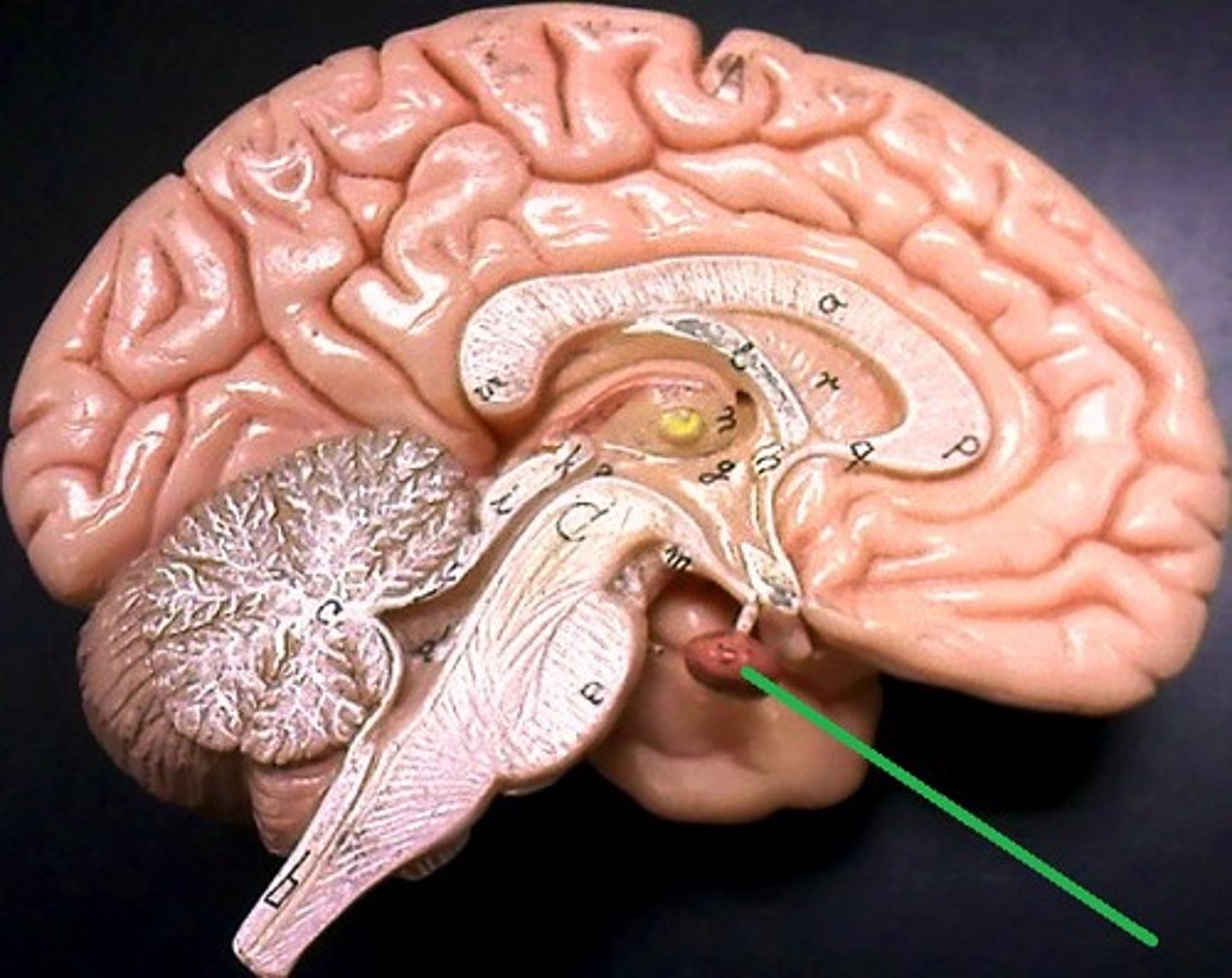
Optic chiasma
Point at which optic nerves cross
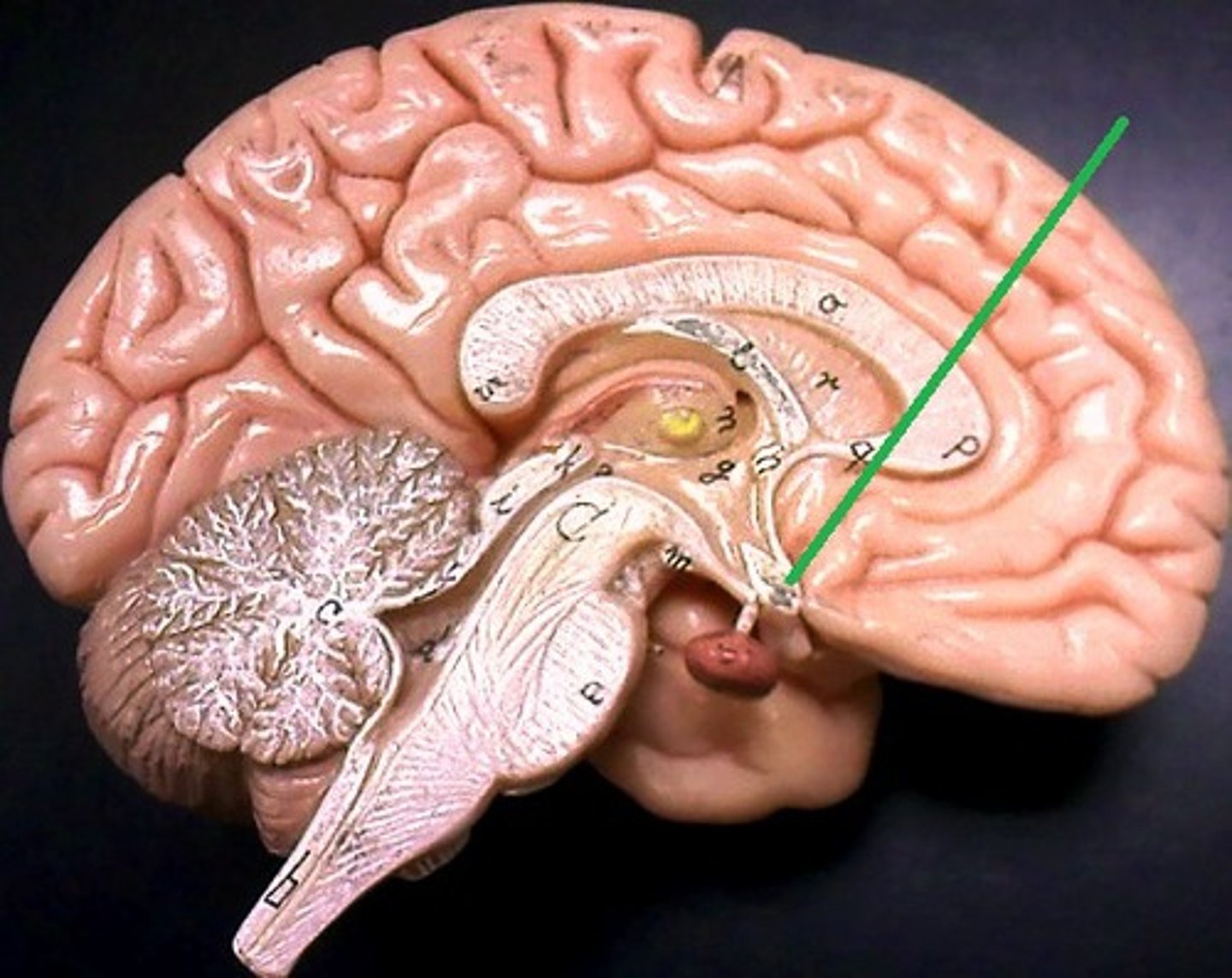
Hypothalamus
Lies below thalamus
Regulates appetite, thirst, body temperature
Controls pituitary gland
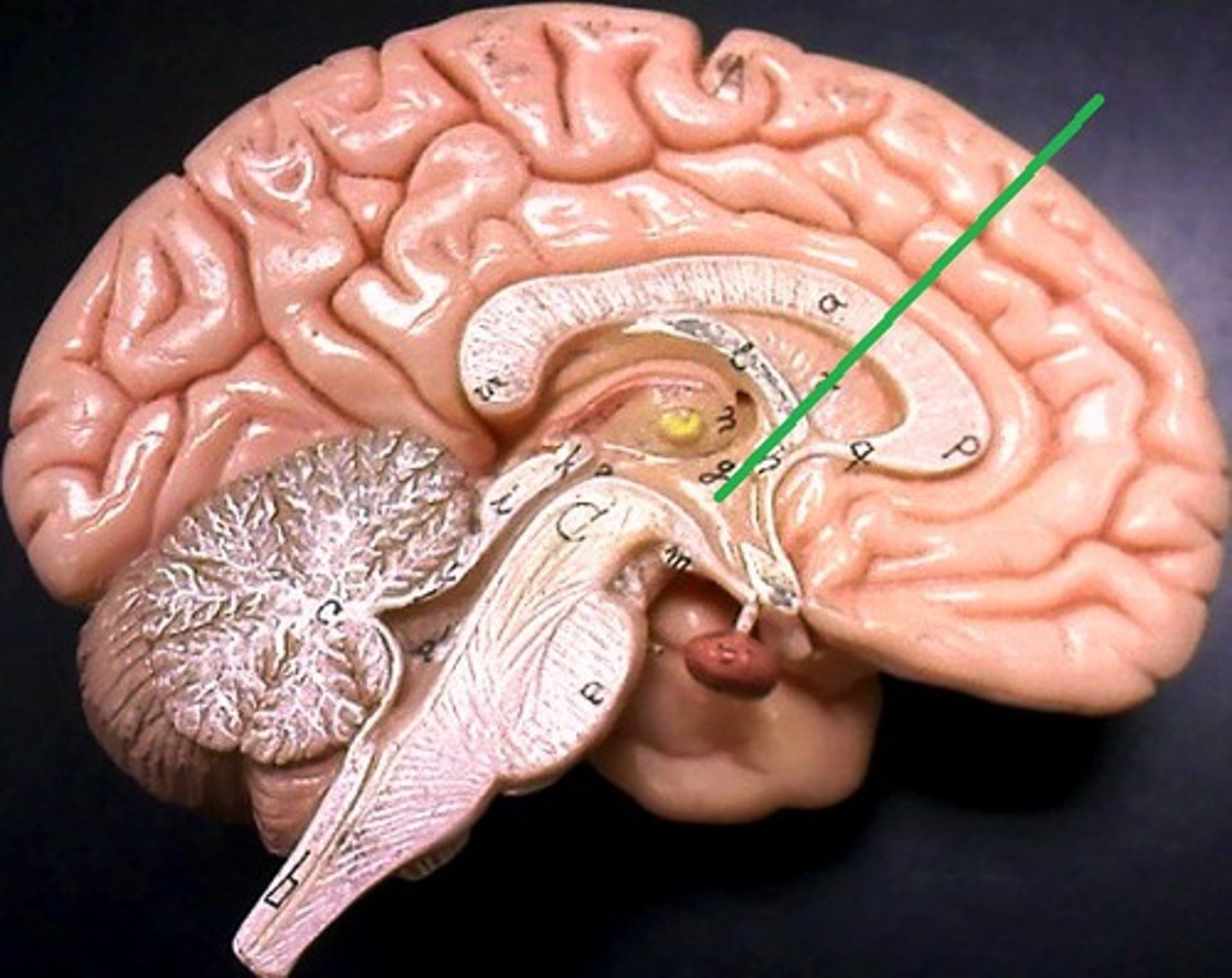
Choroid plexus
Vascular tissue in roof of third ventricle
Secretes cerebrospial fluid
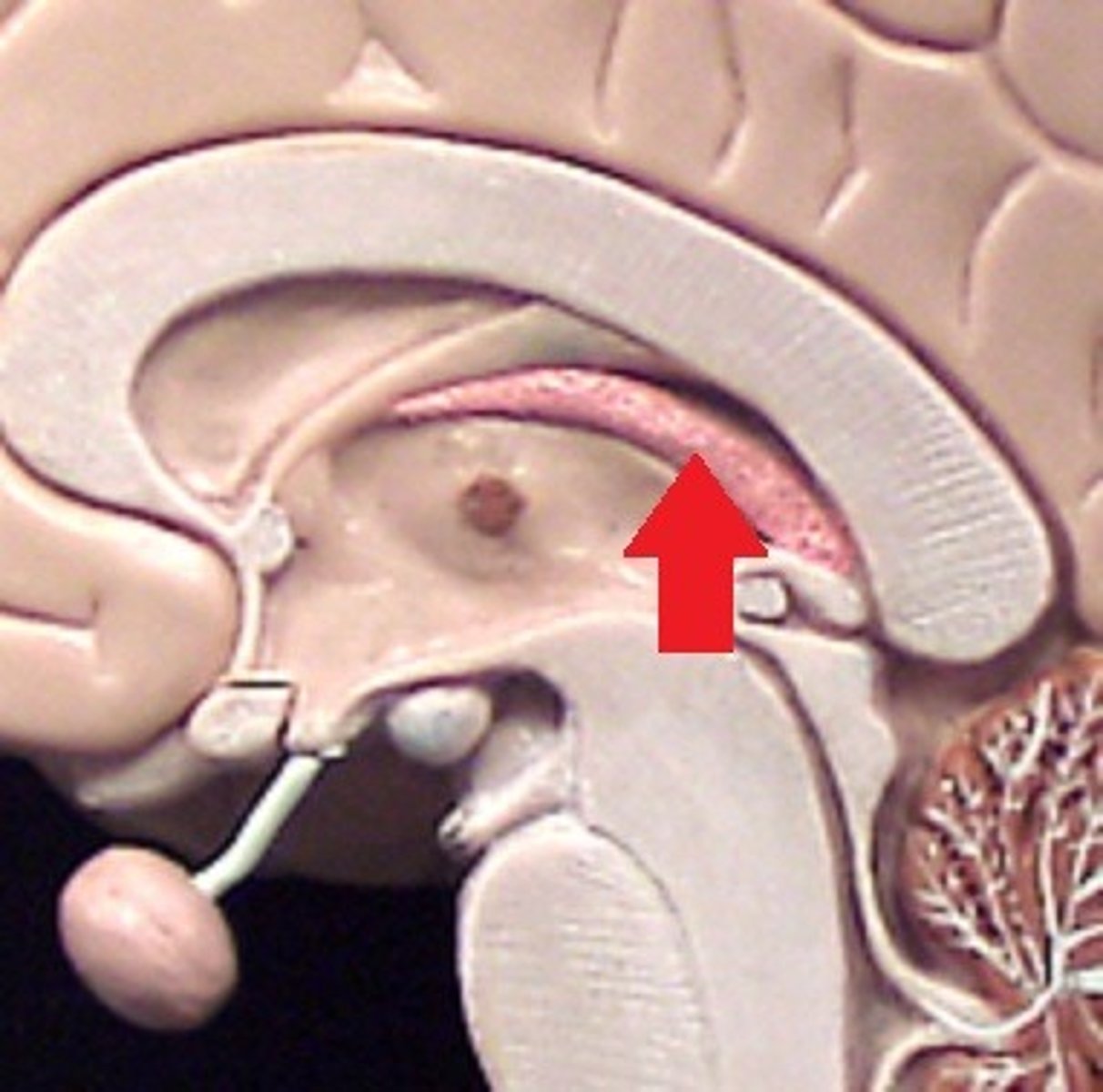
Intermediate adhesion
Projection of gray matter from thalamus into the third ventricle
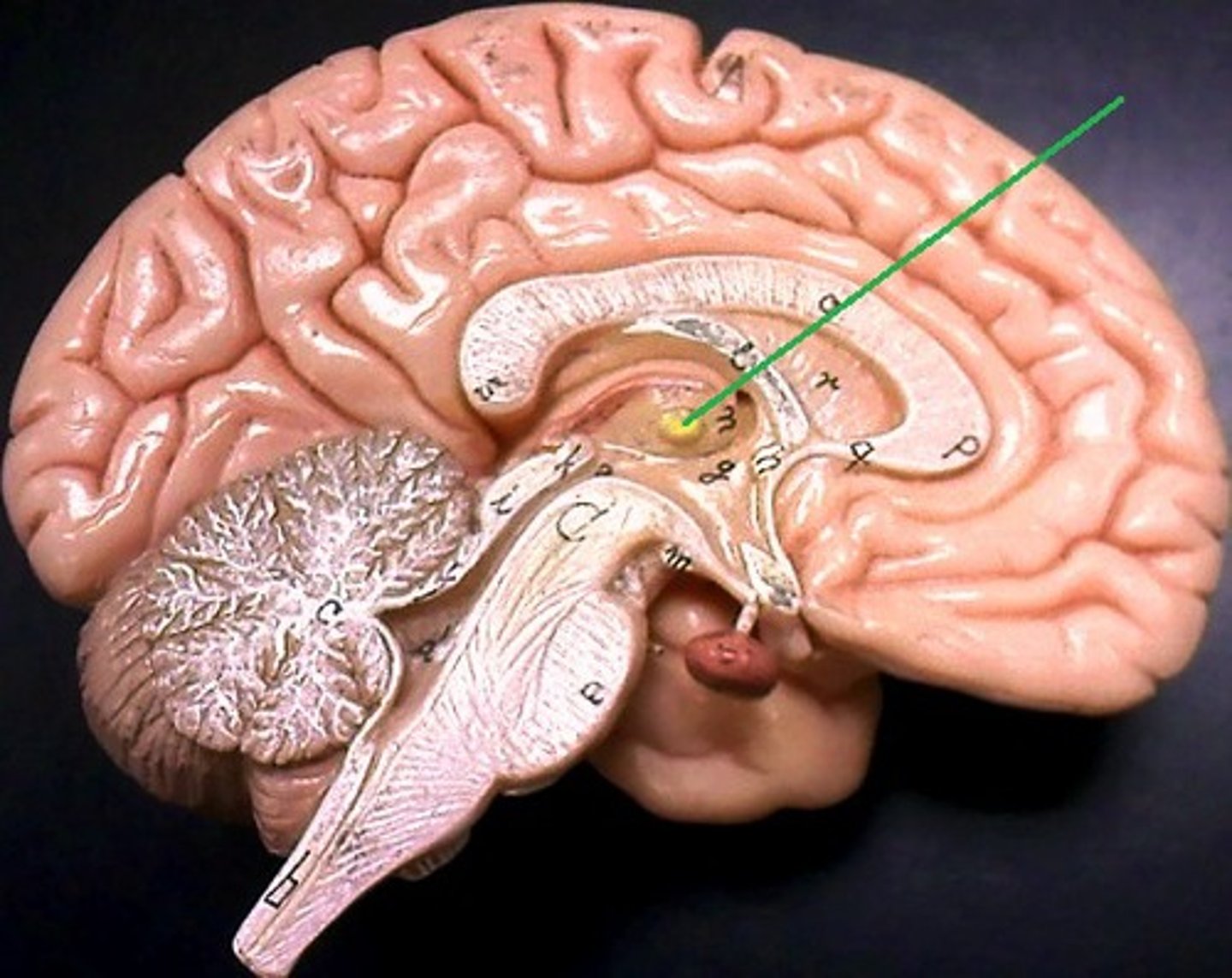
Fourth ventricle
Anterior to the cerebellum
Brainstem is anterior to the fourth ventricle
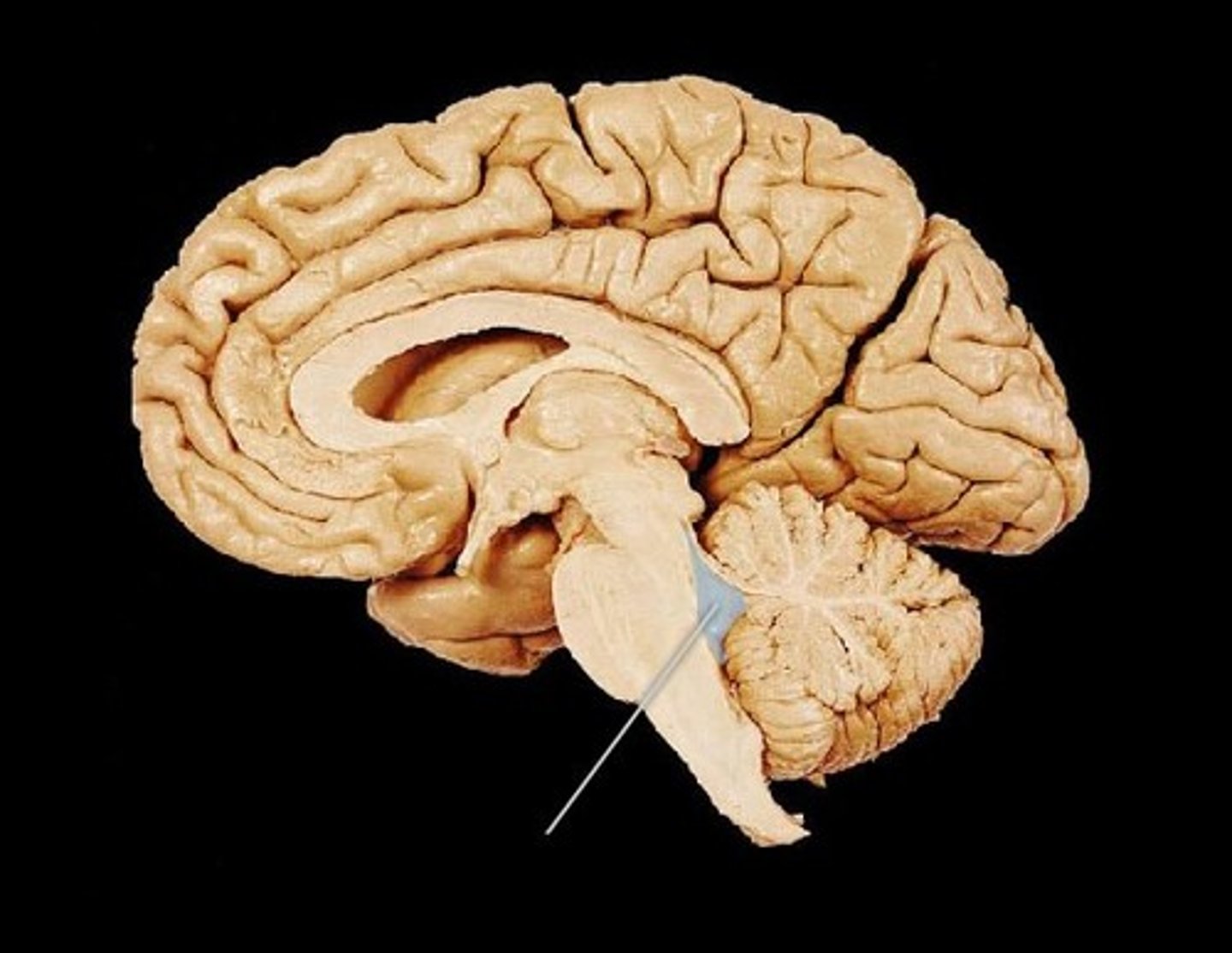
Arbor vitae
Network of white matter inside cerebellum
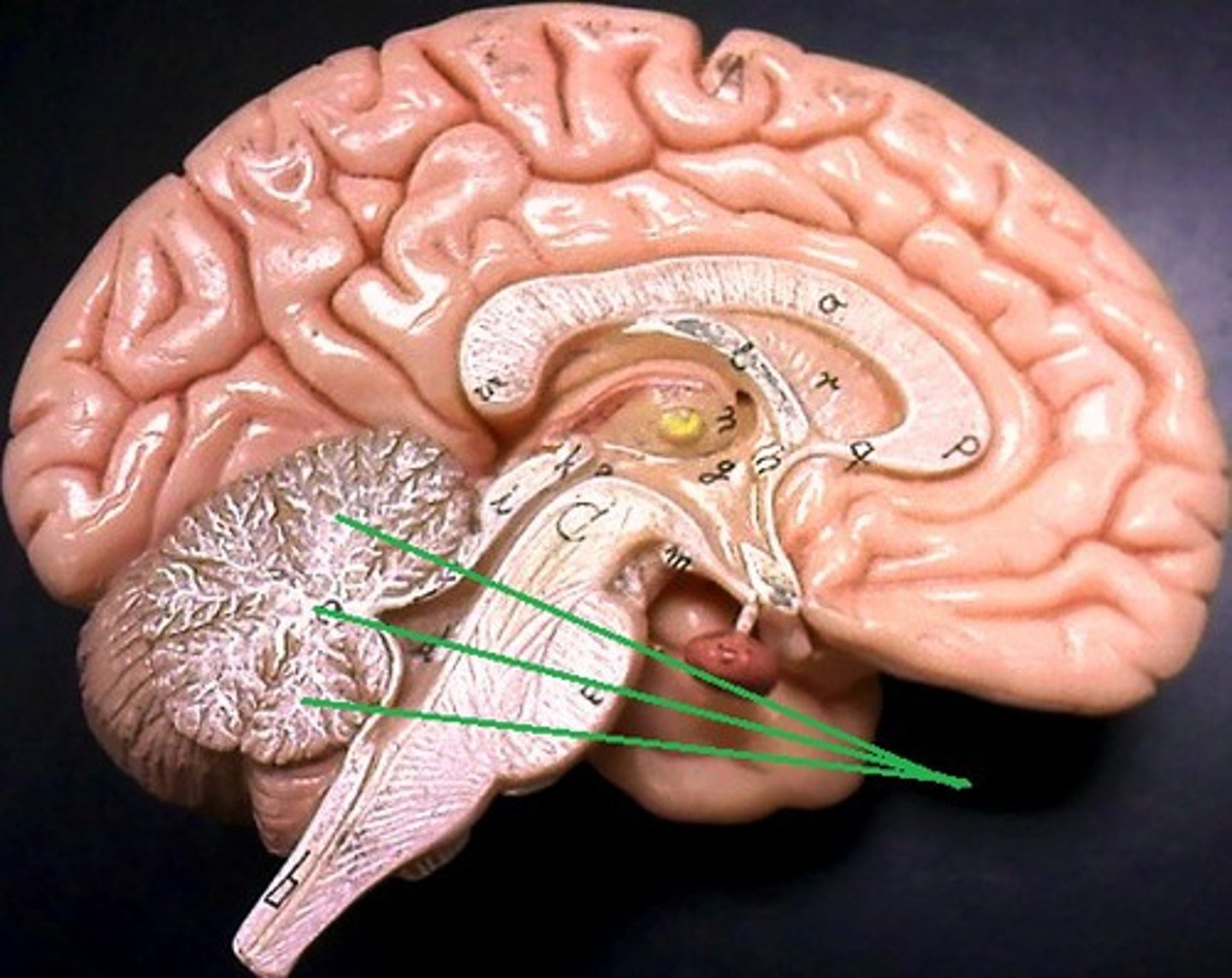
Folia
Folds in the surface of the cerebellum
Midbrain
Pons and diencephalon
Path for descending fibers to cerebellum and medulla
Cerebral aqueduct
Connects third and fourth ventricles
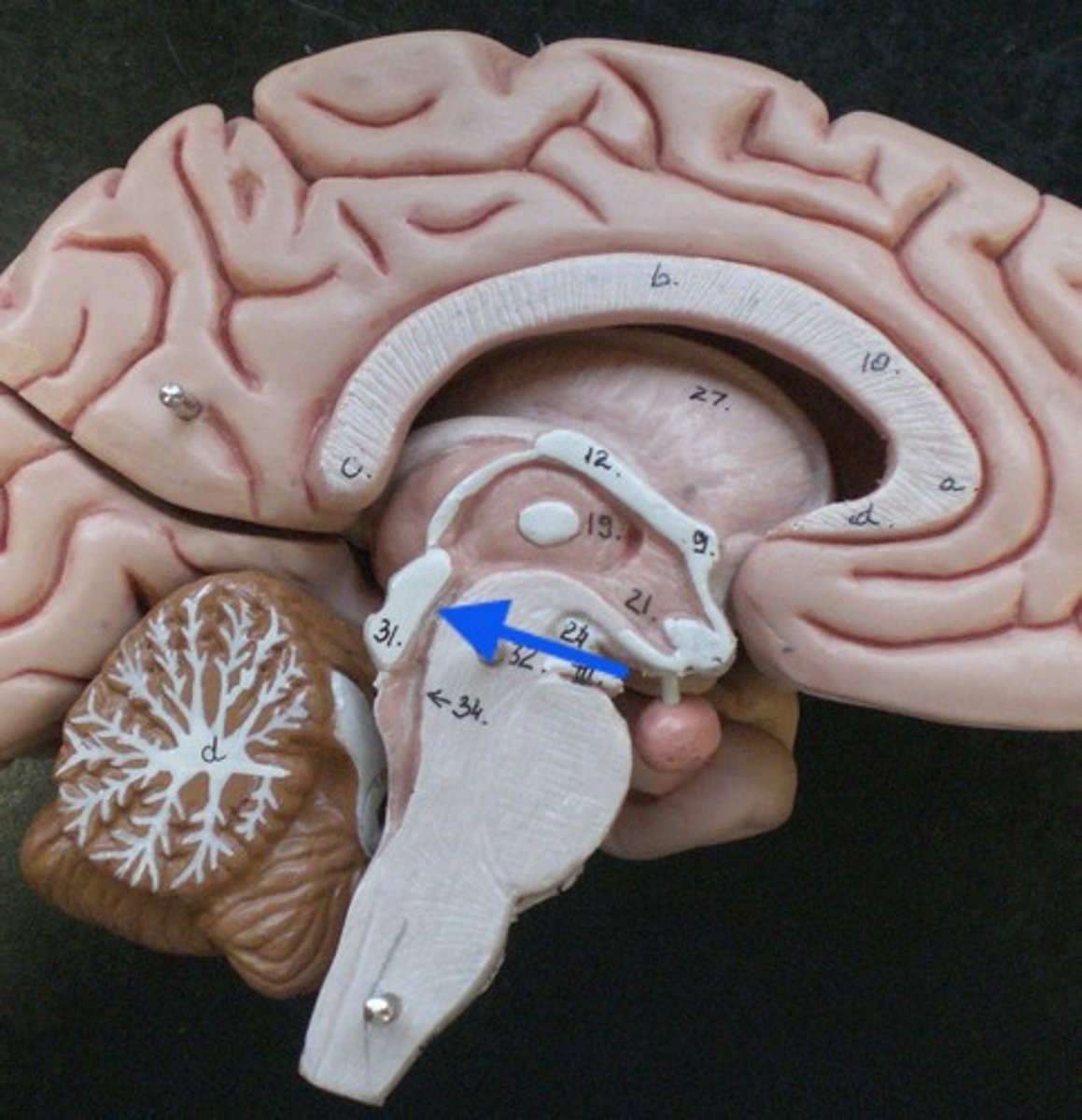
Superior colliculus
Part of midbrain
Form the corpora quadrigemina with inferior colliculi
Controls visual reflexes
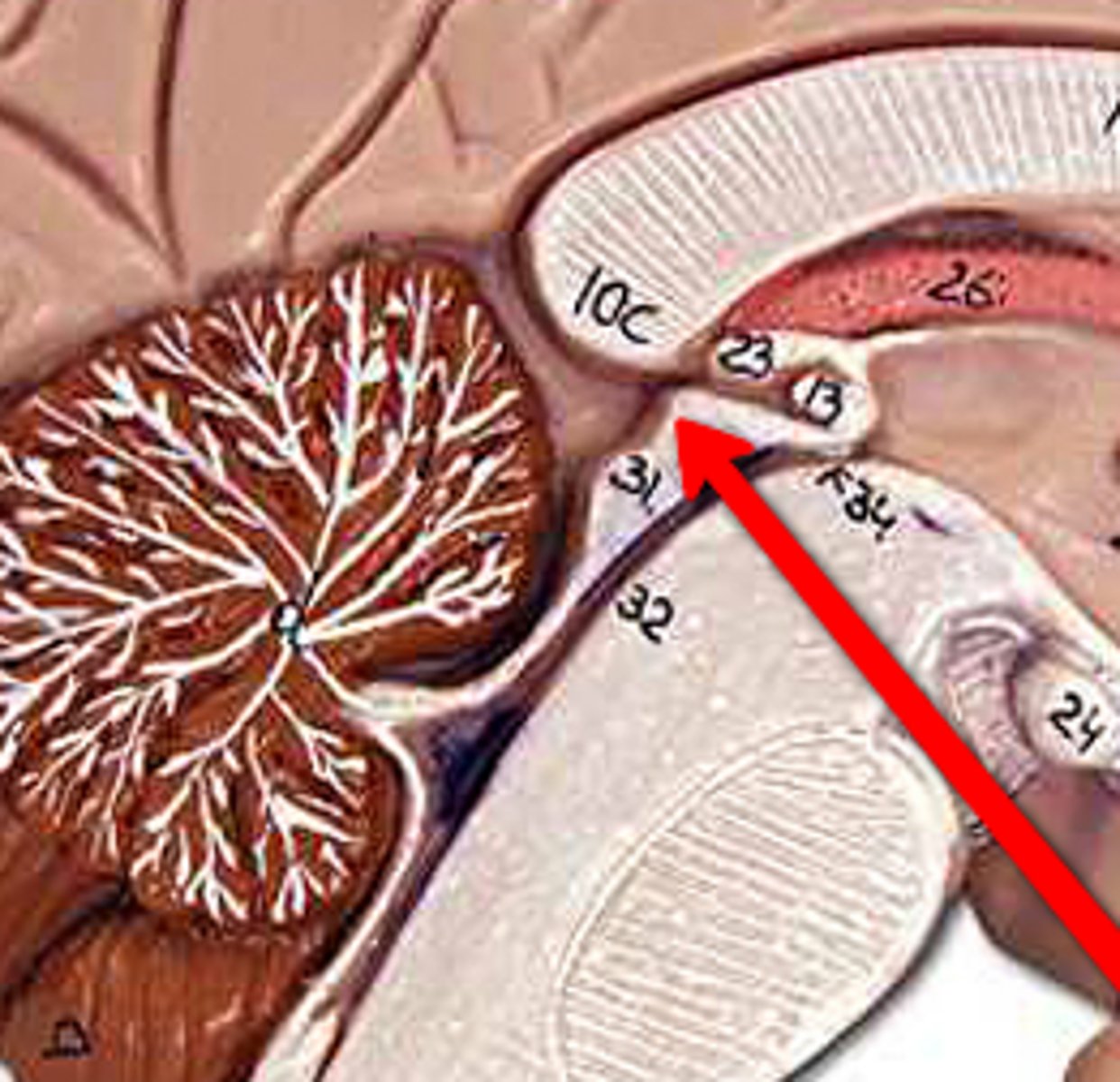
Inferior colliculus
Part of the midbrain
Form the corpora quadrigemina with superior colliculi
Controls auditory reflexes
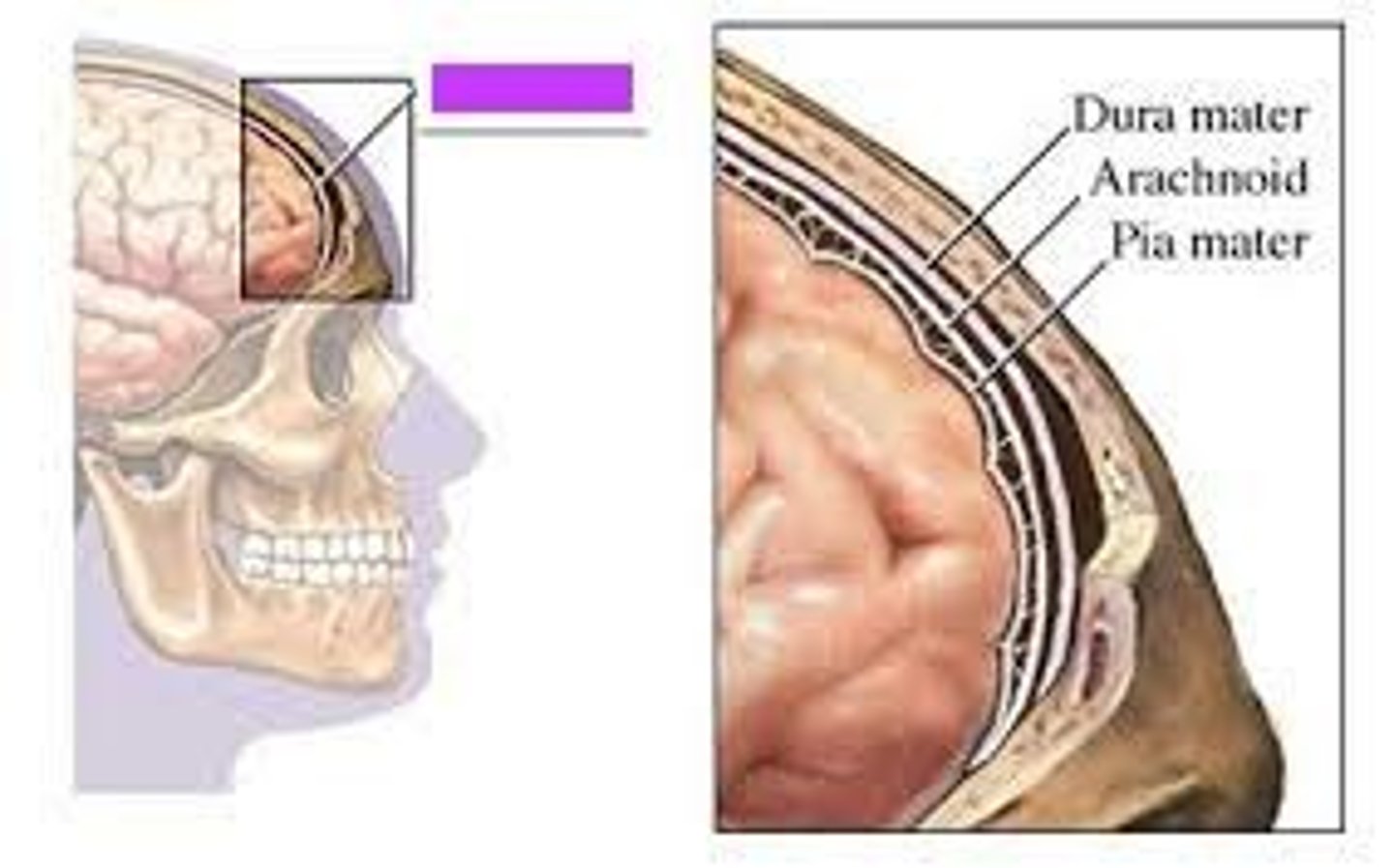
Meninges
Connective tissue layers that form a protective sac around the brain and spinal cord
Cerebral spinal fluid
acts as a cushion by absorbing jarring motions of the brain within the cranium
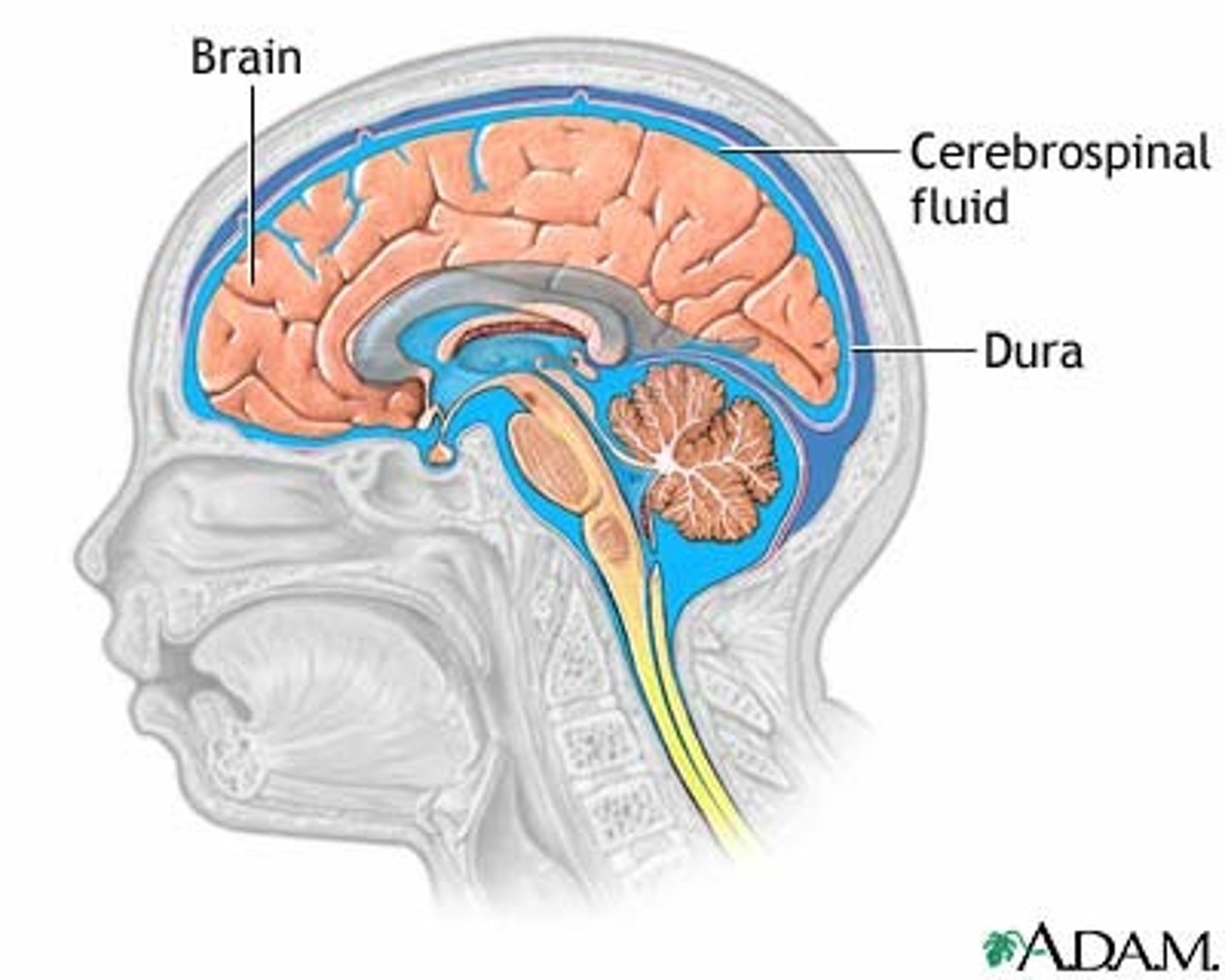
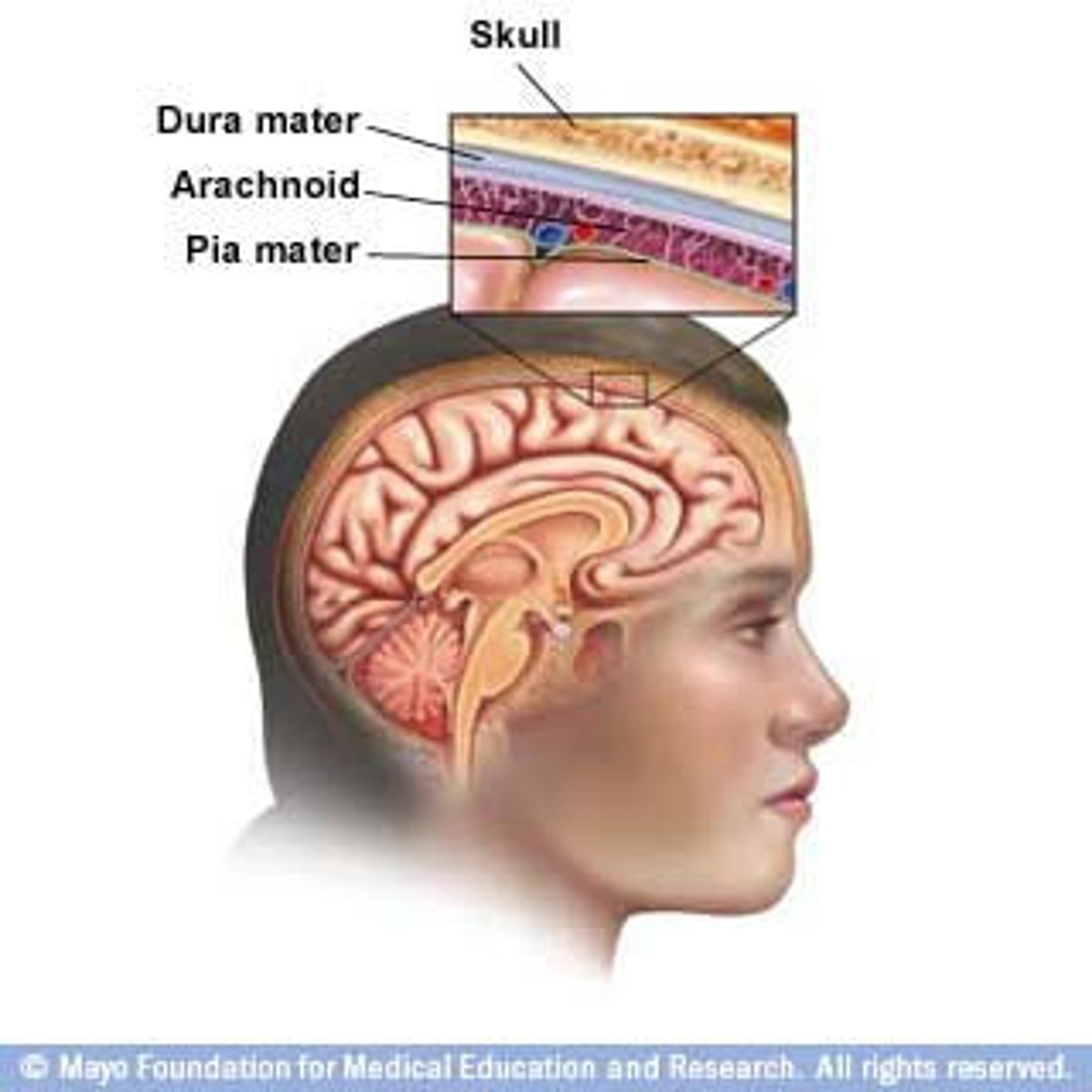
Dura mater
Superficial layer of meninges
Composed of dense irregular connective tissue
Forms a tough, protective sac
Consists of the outer periosteal layer and inner meningeal layer
Periosteal layer
Fused to periosteum of sull
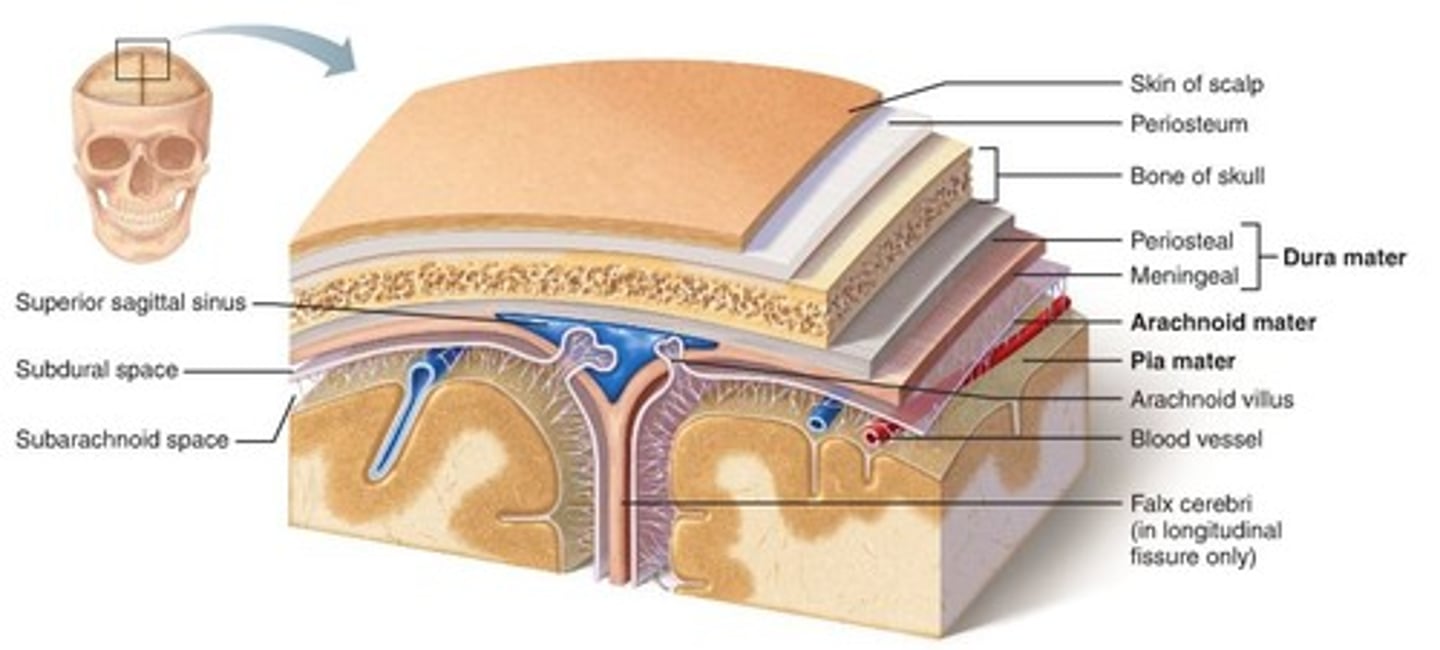
Meningeal layer
Becomes outer covering for the brain
Arachnoid mater
Middle layer of meninges lying deep to dura mater
Thin layer of interstitial fluid separates two layers
Network of primarily collagen fibers
Connected to pia mater by web-like filaments
Pia mater
Deepest layer of meninges
Thin, delicate meshwork of elastic and collagen fibers
Fused to surface of brain
Subarachnoid space
Between arachnoid mater and pia mater
Contains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Falx cerebri
Fold of dura mater
In longitudinal fissure between cerebral hemispheres
Superior sagittal sinus
Meningeal layer of dura mater splits to form sinus
Collects blood draining from brain
Subdural space
Between dura mater and arachnoid mater
Arachnoid villi
Extension of arachnoid mater through dura mater and into superior sagittal sinus
Allows CSF to be reabsorbed by venous system
Efferent
Motor
Afferent
Sensory
On Old Olympus' Towering Top A Friendly Viking Grew Vines And Hops
Cranial nerves mnemonic device
Olfactory (I)
"On"
Sensory: smell
Optic (II)
"Old"
Sensory: vision
Oculomotor (III)
"Olympus"
Motor: eyelid and eyeball movement, accommodation, and pupil constriction
Trochlear (IV)
"Towering"
Motor: movement of the eyeball
Trigeminal (V)
"Top"
Sensory: cutaneous sensations from face and mouth;
Motor: chewing from maxillary and mandibular
Abducens (VI)
"A"
Motor: movement of the eyeball
Facial (VII)
"Friendly"
Sensory: taste;
Motor: facial expression, saliva production, tear production
Vestibulo-cochlear (VIII)
"Viking"
Sensory: hearing and equilibrium
Glosso-pharyngeal (IX)
"Grew"
Sensory: taste; motor: swallowing and speech, saliva production
Vagus (X)
"Vines"
Sensory: general sense from the pharynx and epiglottis;
Motor: swallowing, coughing, speech, GI peristalsis, secretion of GI glands
Accessory (XI)
"And"
Motor: swallowing, movement of the head
Hypoglossal (XII)
"Hops"
Motor: swallowing and speech
medulla oblangata
controls heartbeat and breathing