cell stucture and functions
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
representative cell
an example of the most common organelles and structures of around 200 types of cells
3 major parts of a cell
nucleus, cytoplasm, plasma membrane
the cytoplasm has three parts
organelles, cytoskeleton, and cytosol
plasma membrane
outer cell barrier that separates the 'INSIDE' of the cell from the 'OUTSIDE' of the cell; has a phospholipid bilayer
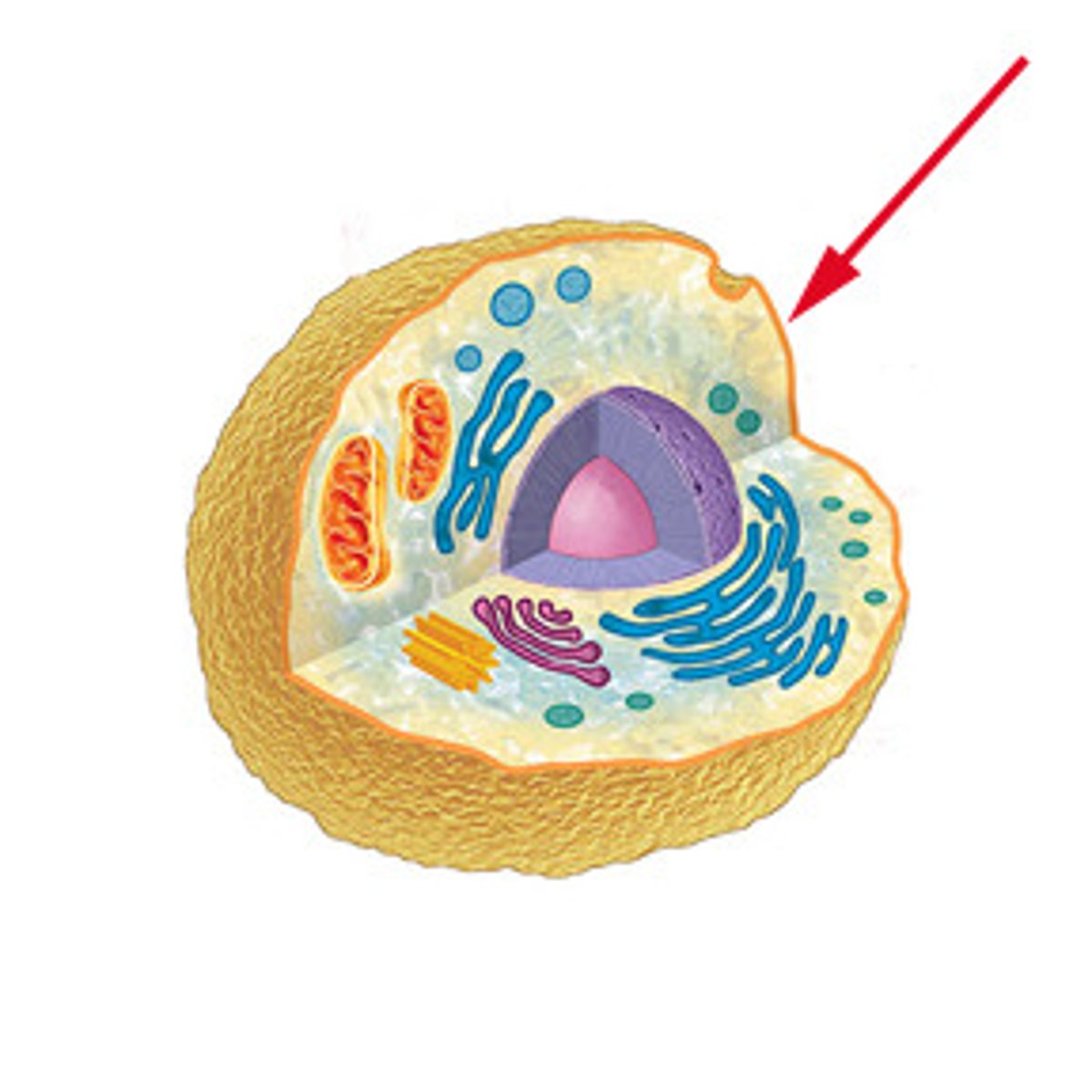
extensions of the plasma membrane
cilia, flagella, microvilli, pseudopods
microvilli
fingerlike projections that increase the cell's surface area for increased absorption of water and nutrients
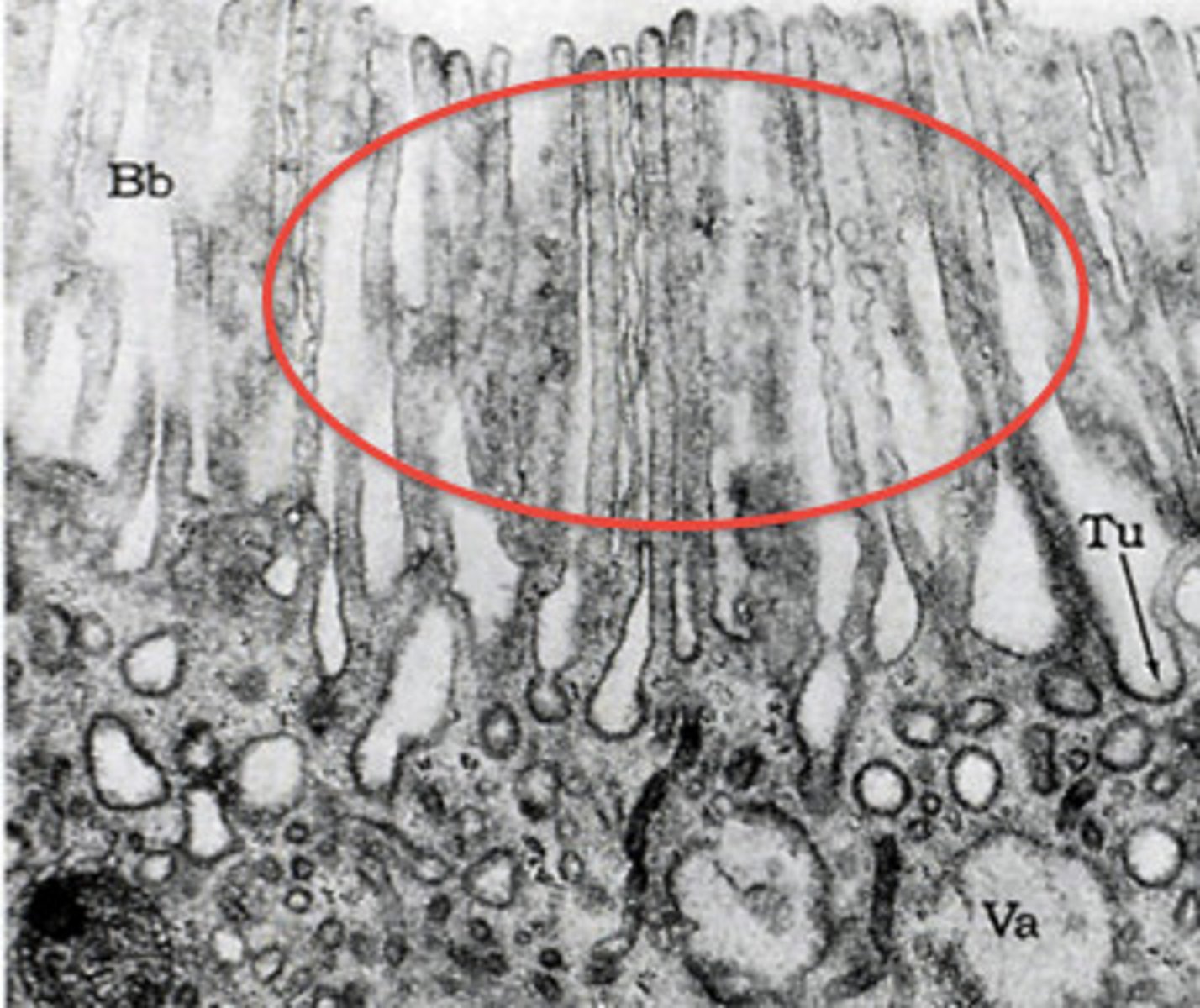
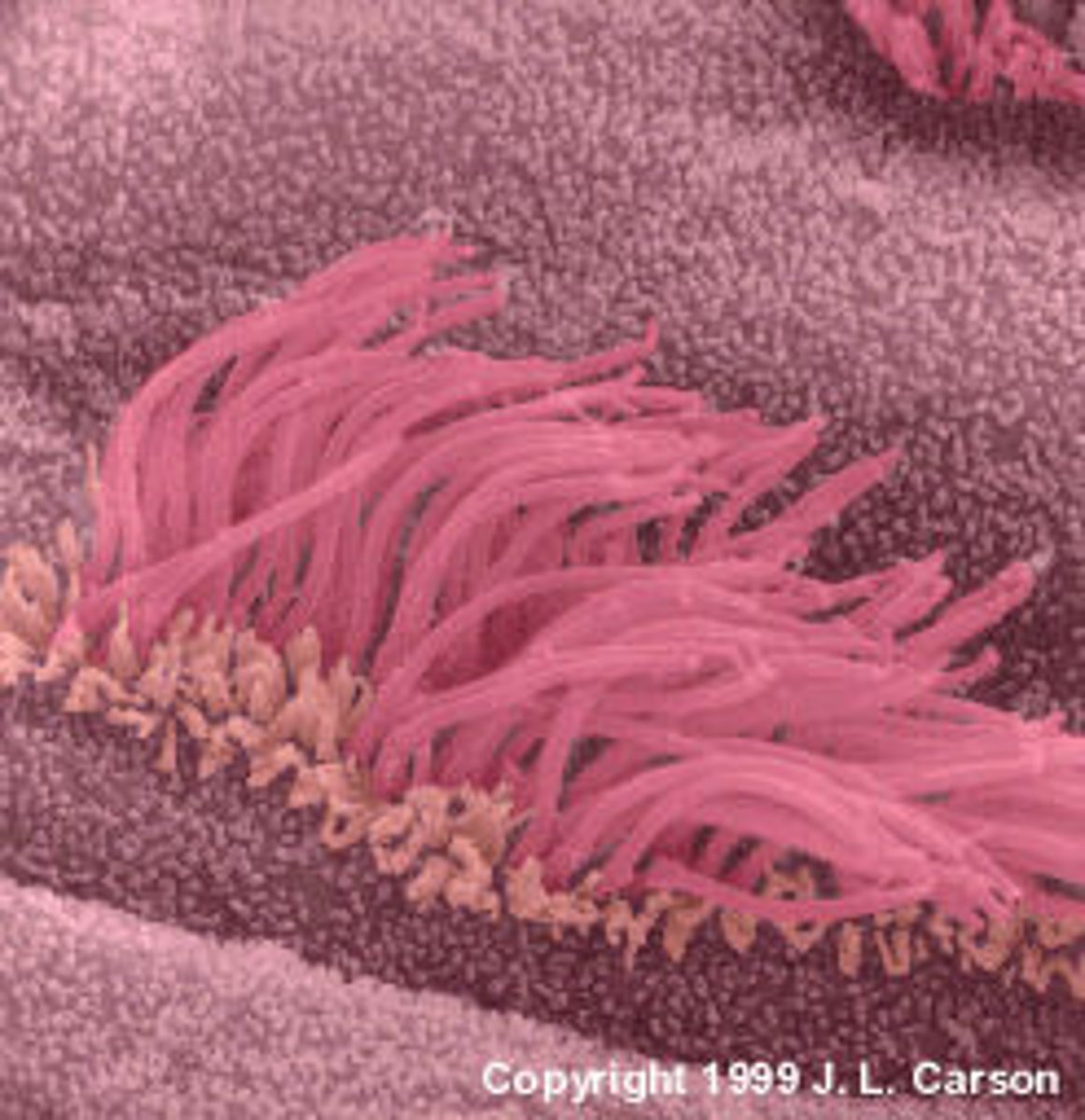
cilia
larger 'fingerlike' projections on the apical surface of some cells. some don't move while most are motile and beat back and forth to move substances across their surface
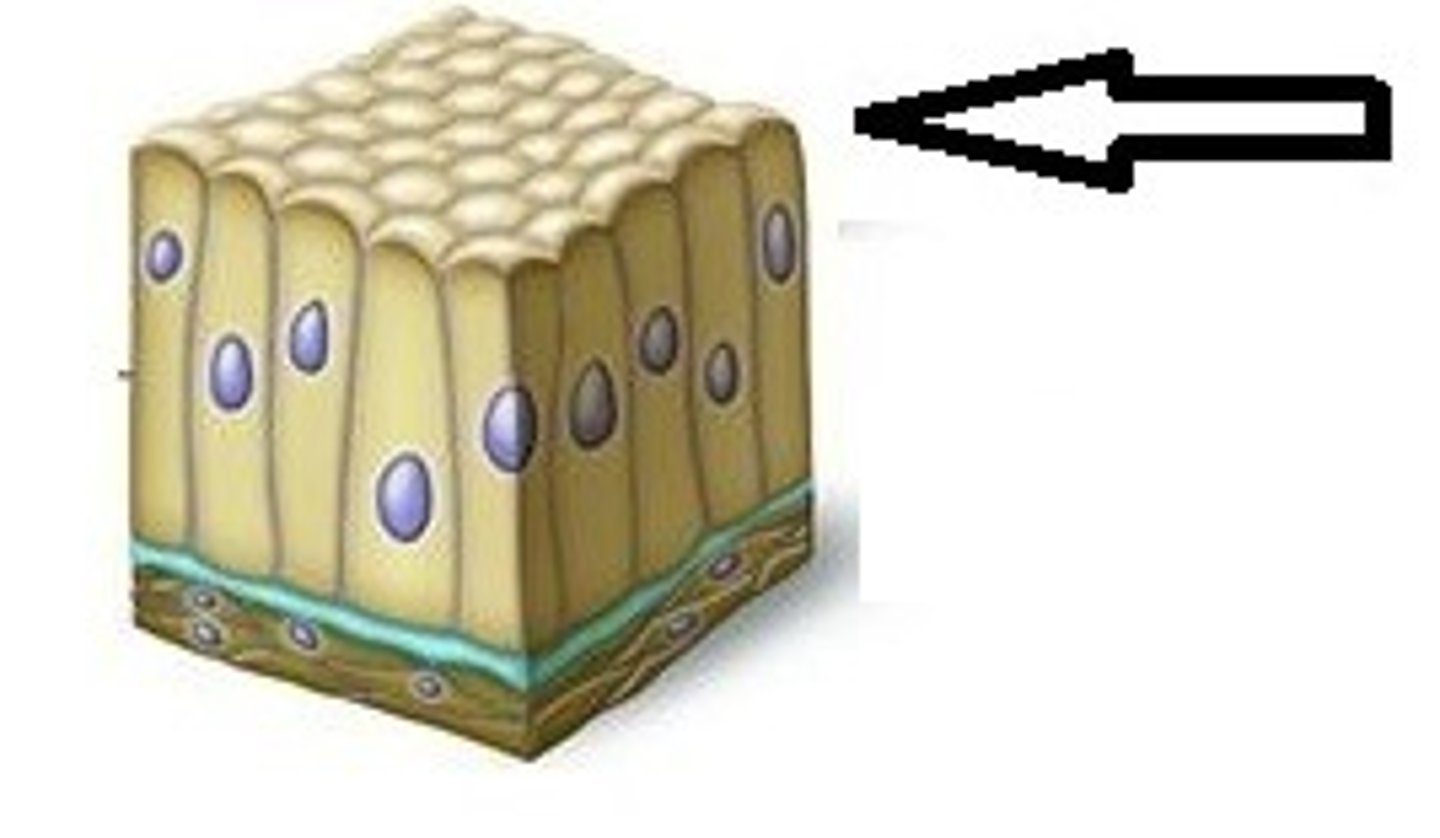
apical surface
an upper free surface exposed to the body exterior or the cavity of an internal organ
flagellum
A long, whiplike structure that helps a cell to move
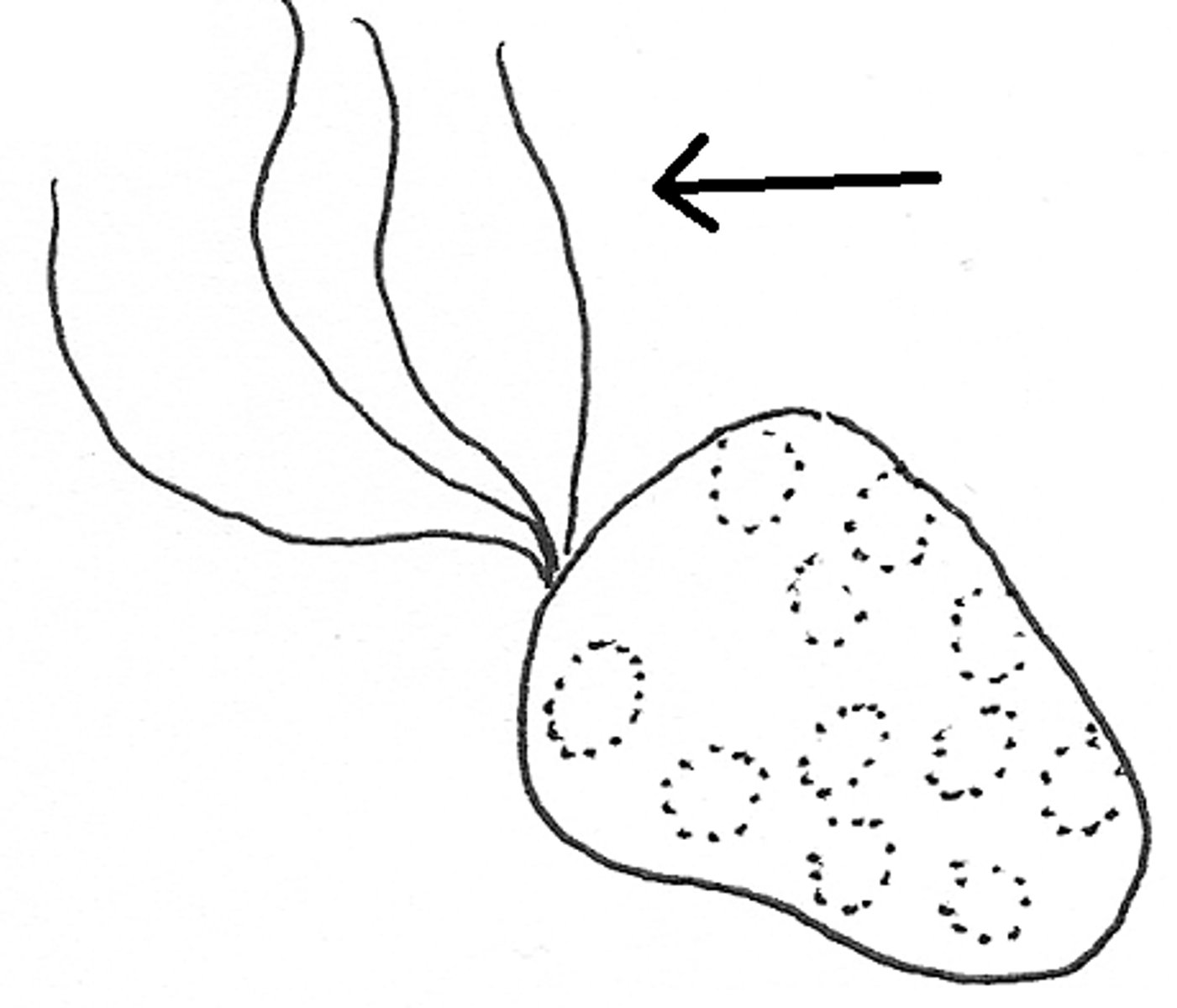
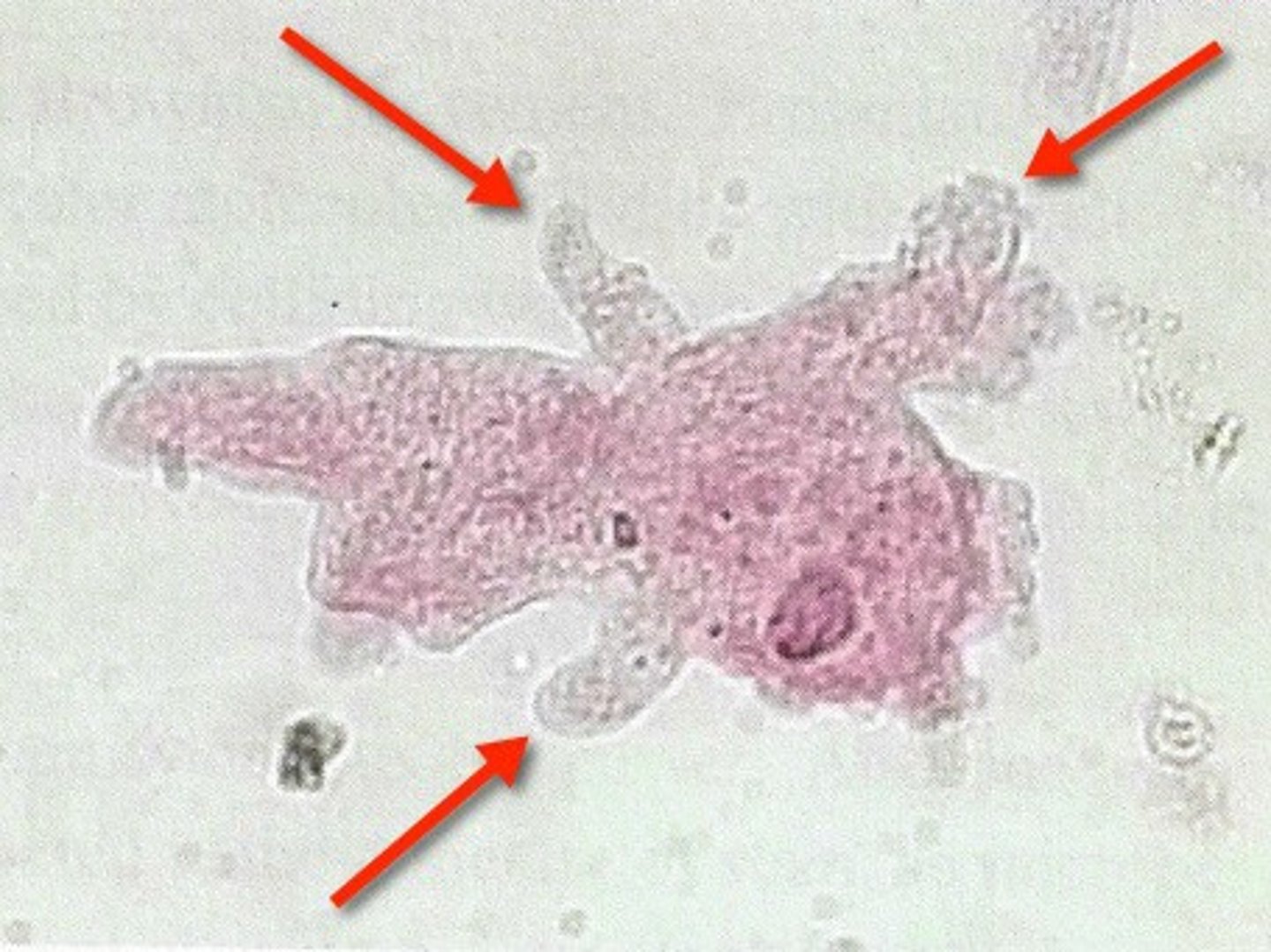
pseudopods
temporary extensions of the plasma membrane; they change constantly
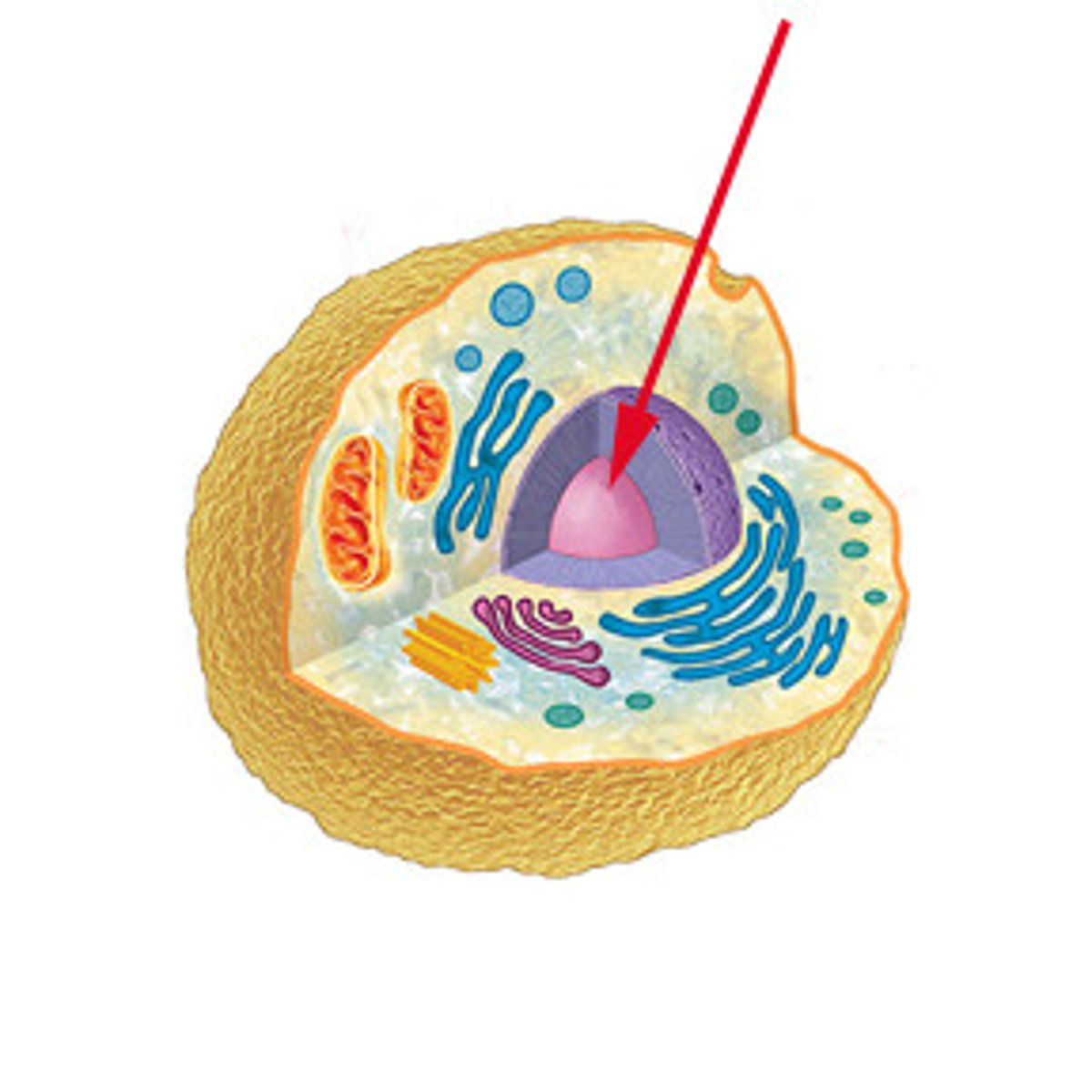
nucleus
houses DNA and produces ribosomal subunits
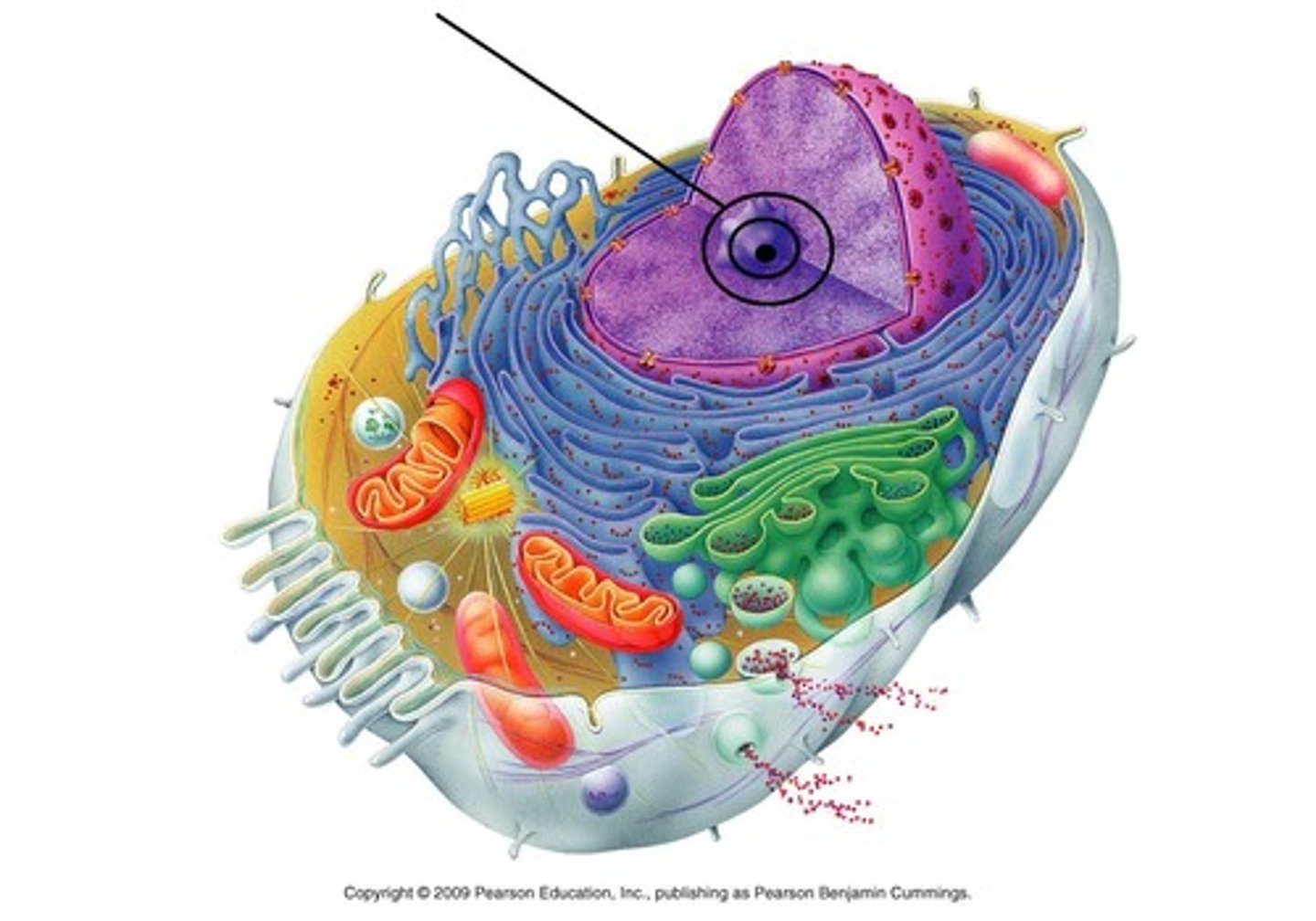
nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes
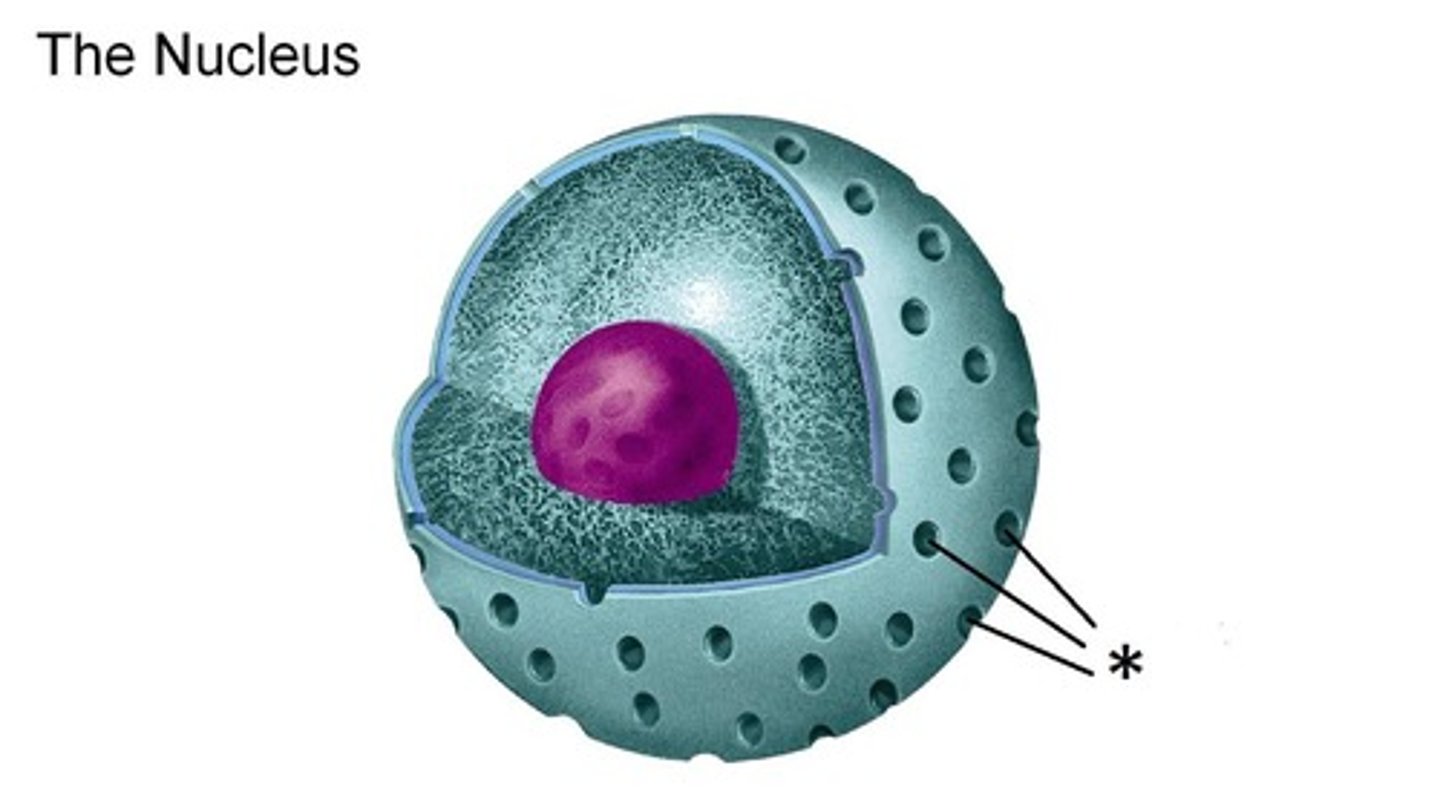
nuclear pores
structures in the nuclear envelope that allow passage of certain materials between the cell nucleus and the cytoplasm
nuclear envelope
A double membrane that surrounds the nucleus in the cell
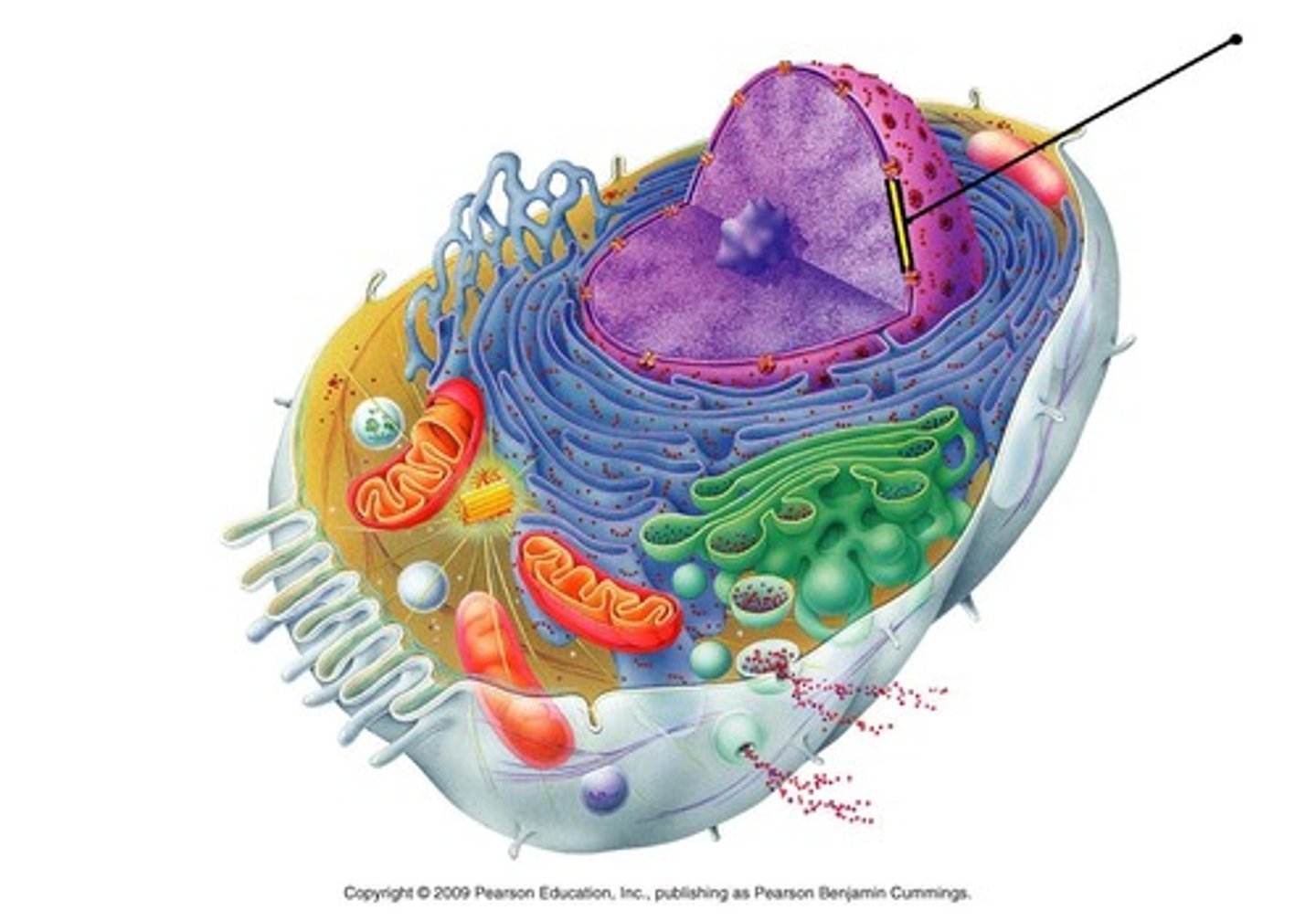
Chromatin
Clusters of DNA, RNA, and proteins in the nucleus of a cell
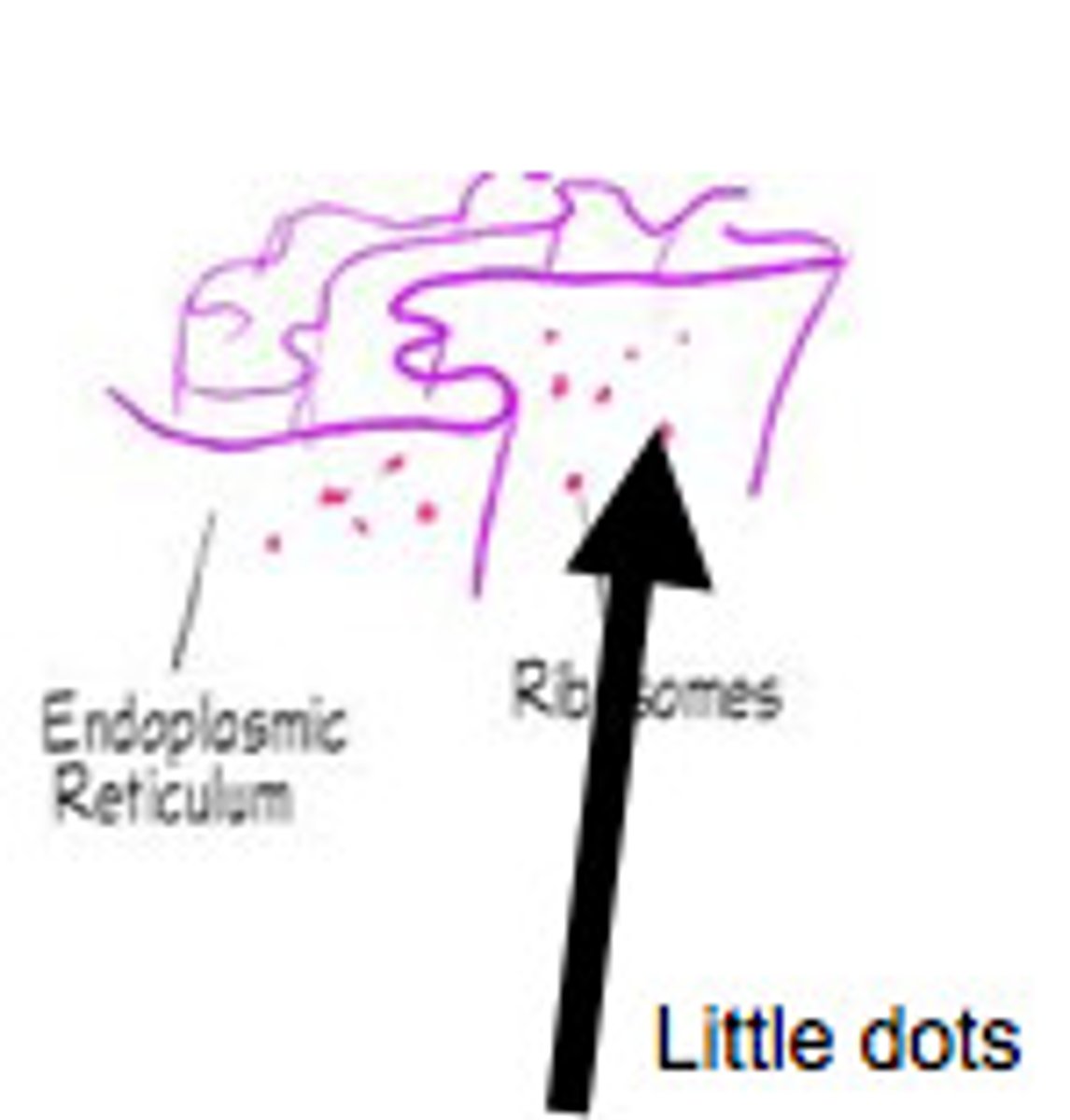
Ribosome
Cytoplasmic organelles at which proteins are synthesized.
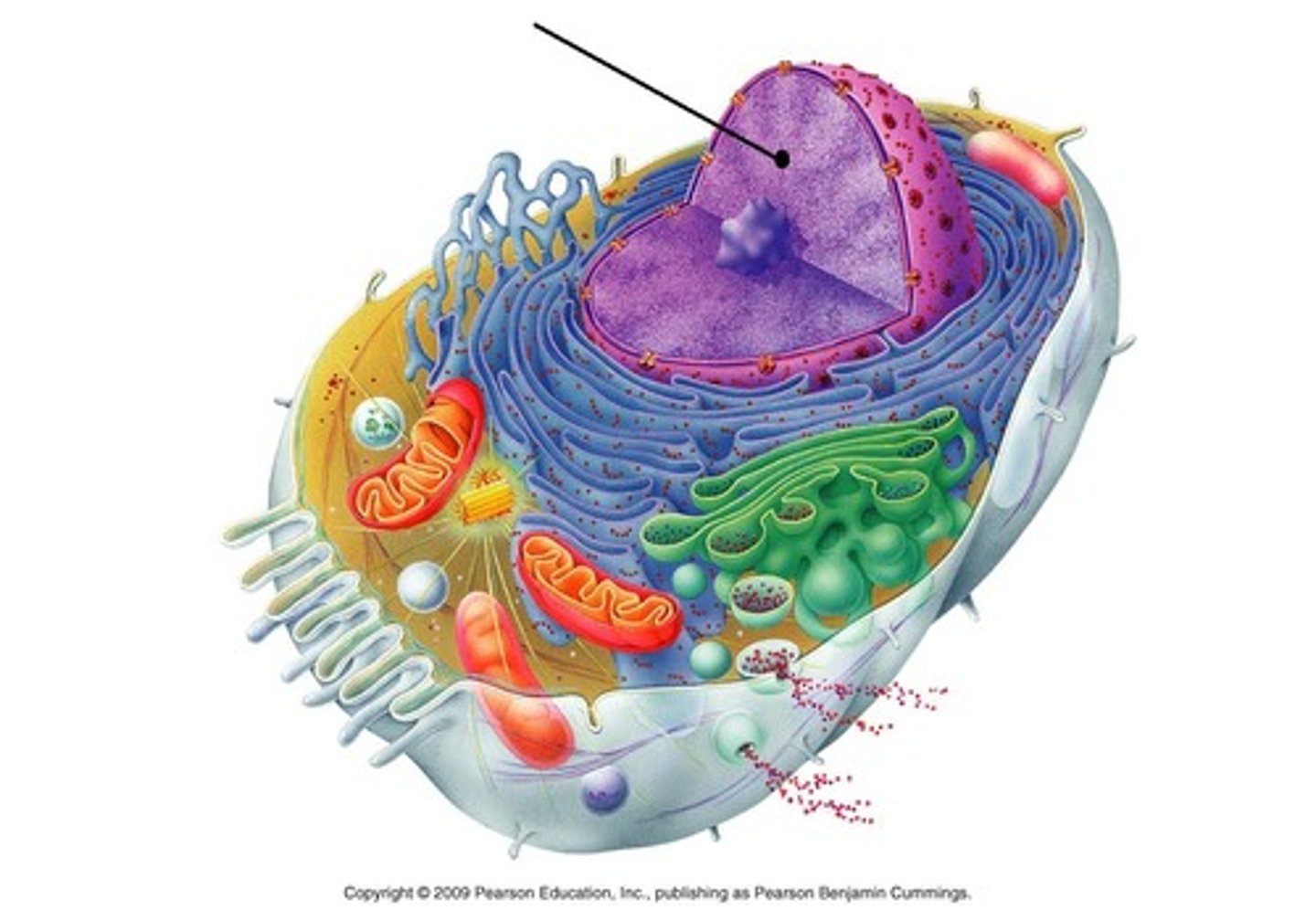
gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait
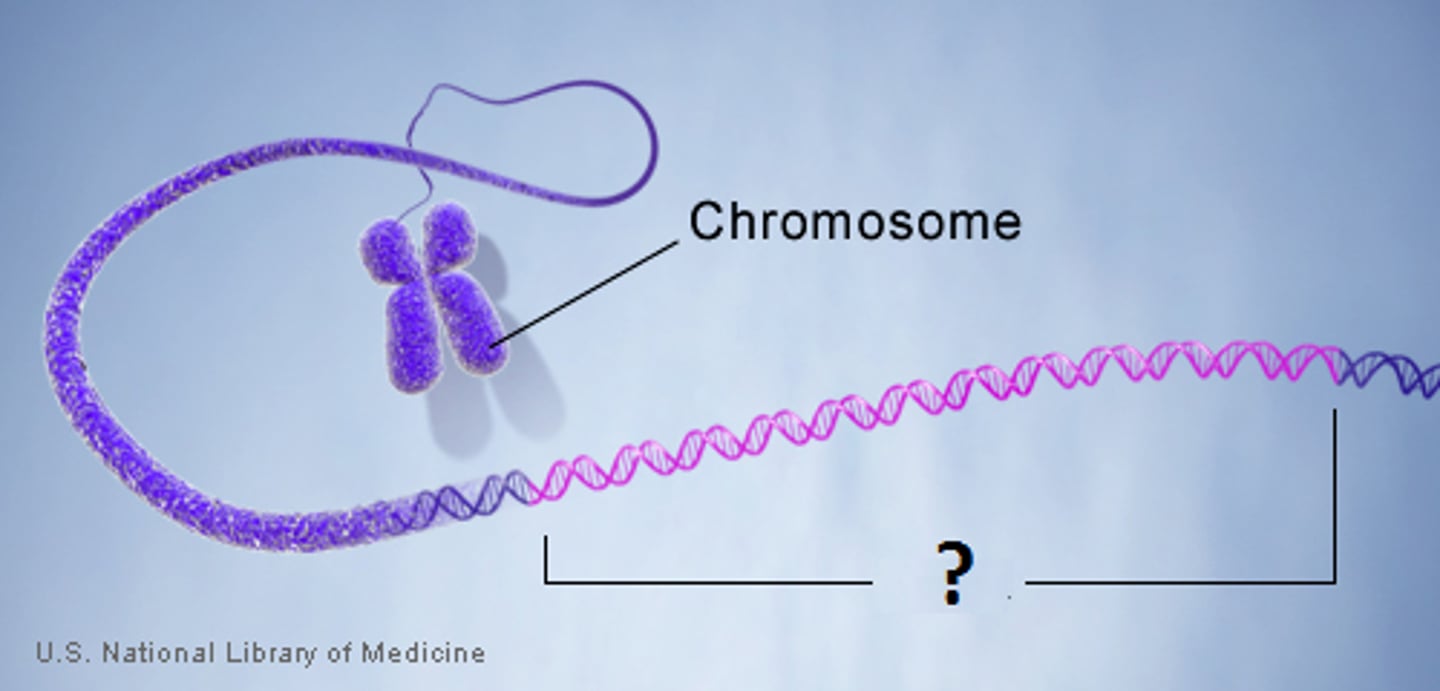
DNA
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the (46) chromosomes (in the human body)
organelles (ex: nucleus, cytosol)
'tiny organs' of the cell
Cytoplasm
the portion of the cell outside the nucleus
Cytosol
Fluid portion of cytoplasm
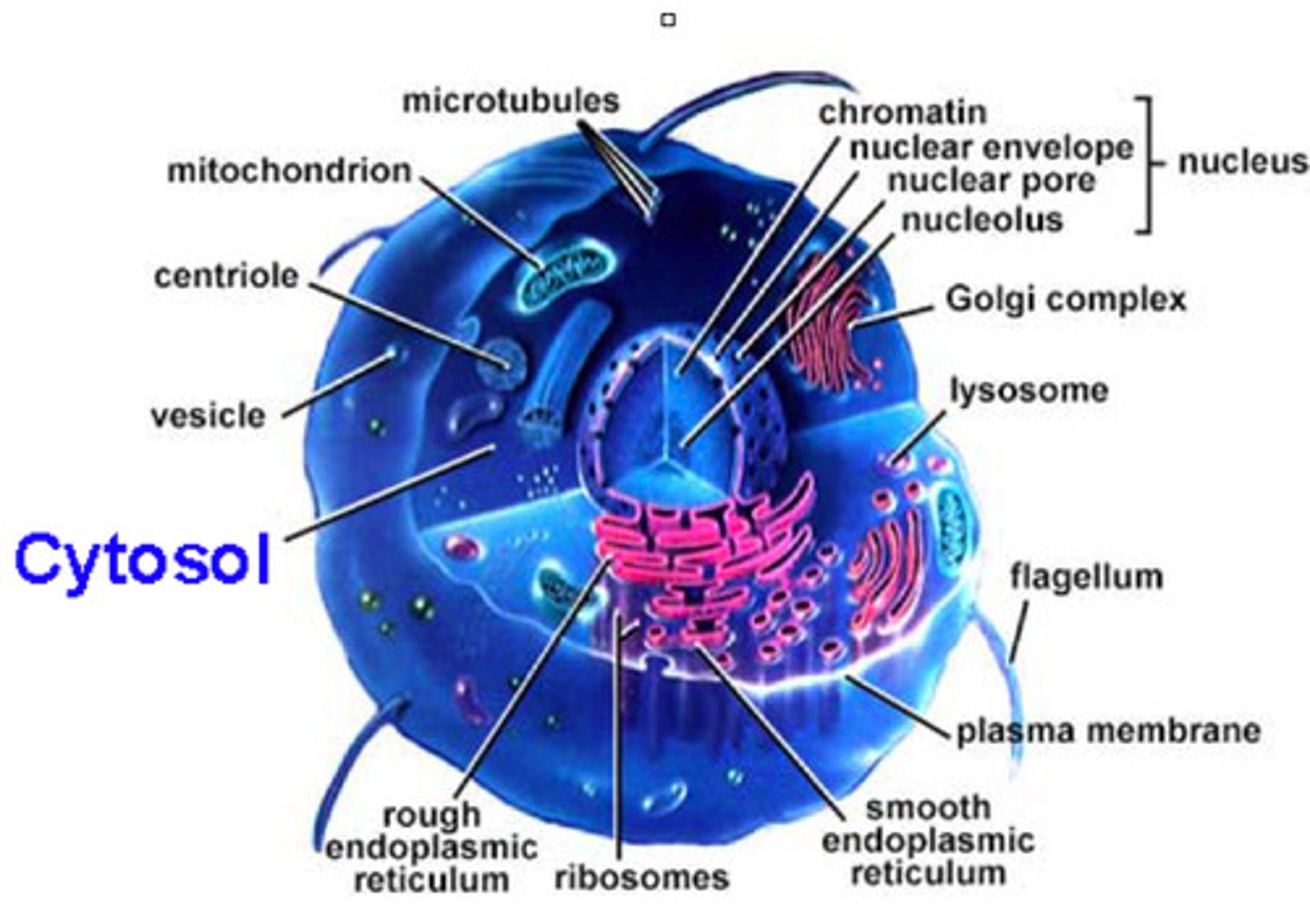
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
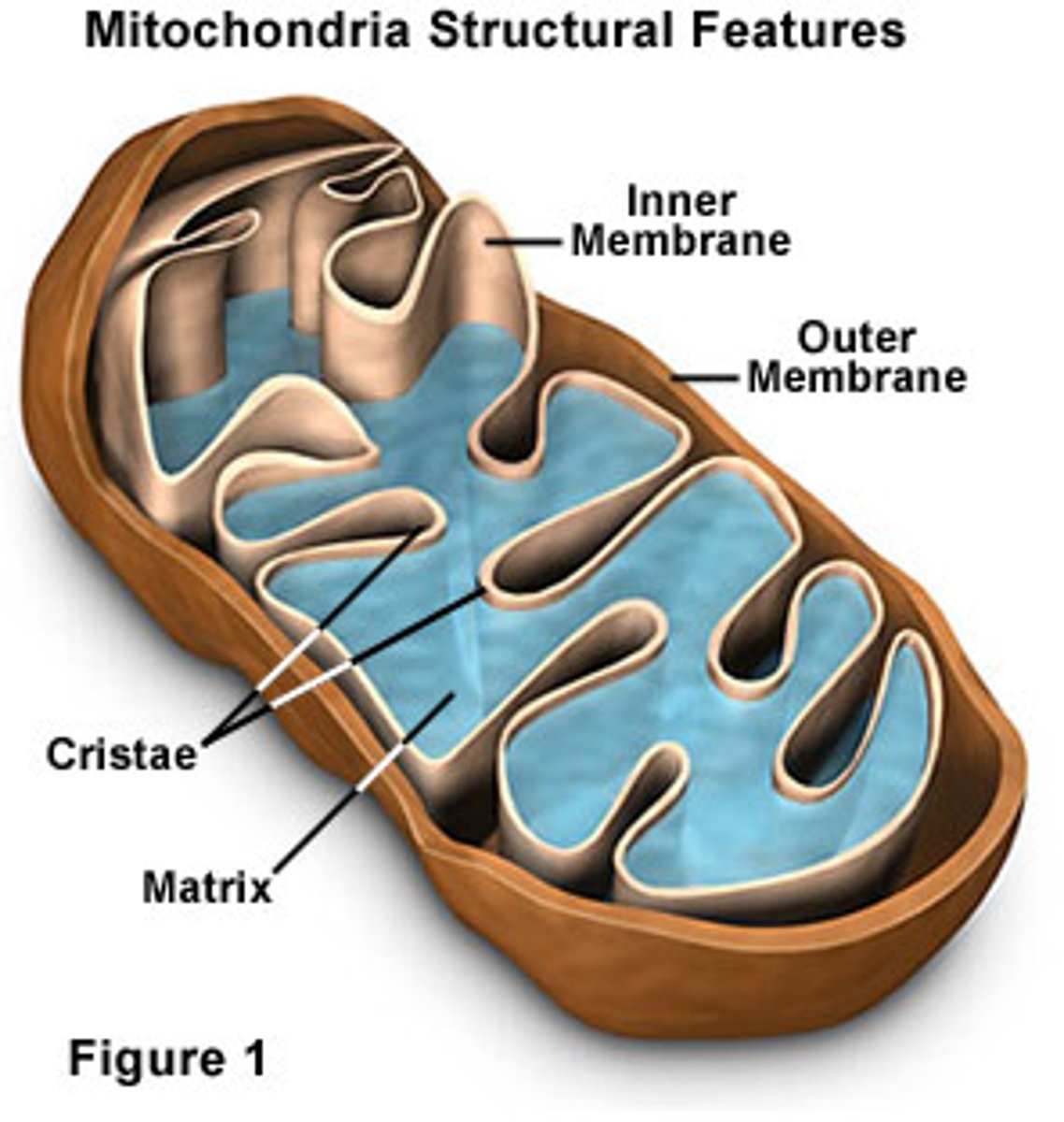
Mitochondria (mitochondrion is the plural form)
Powerhouse of the cell, organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production
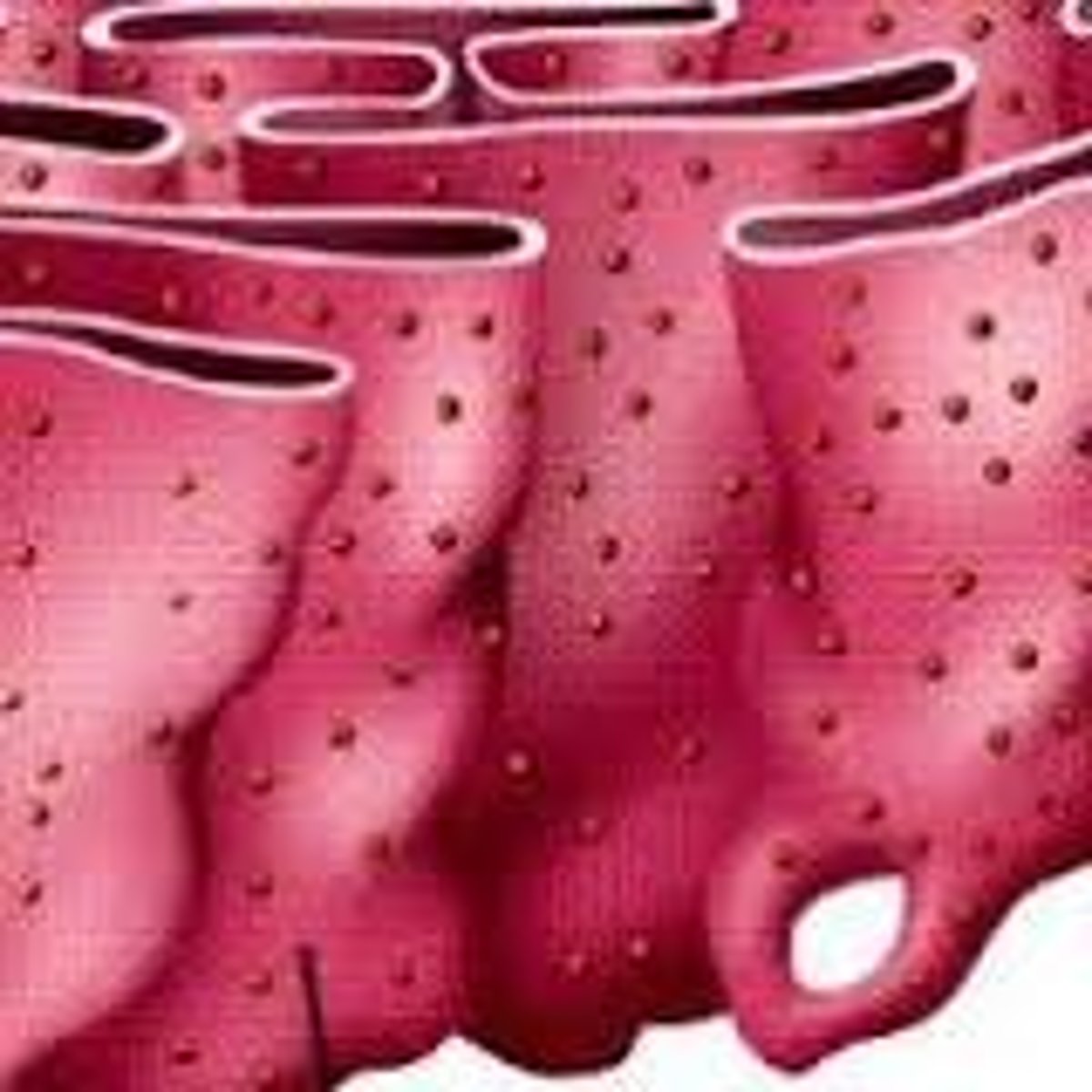
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Membranes are rough due to the presence of ribosomes; synthesizes protein
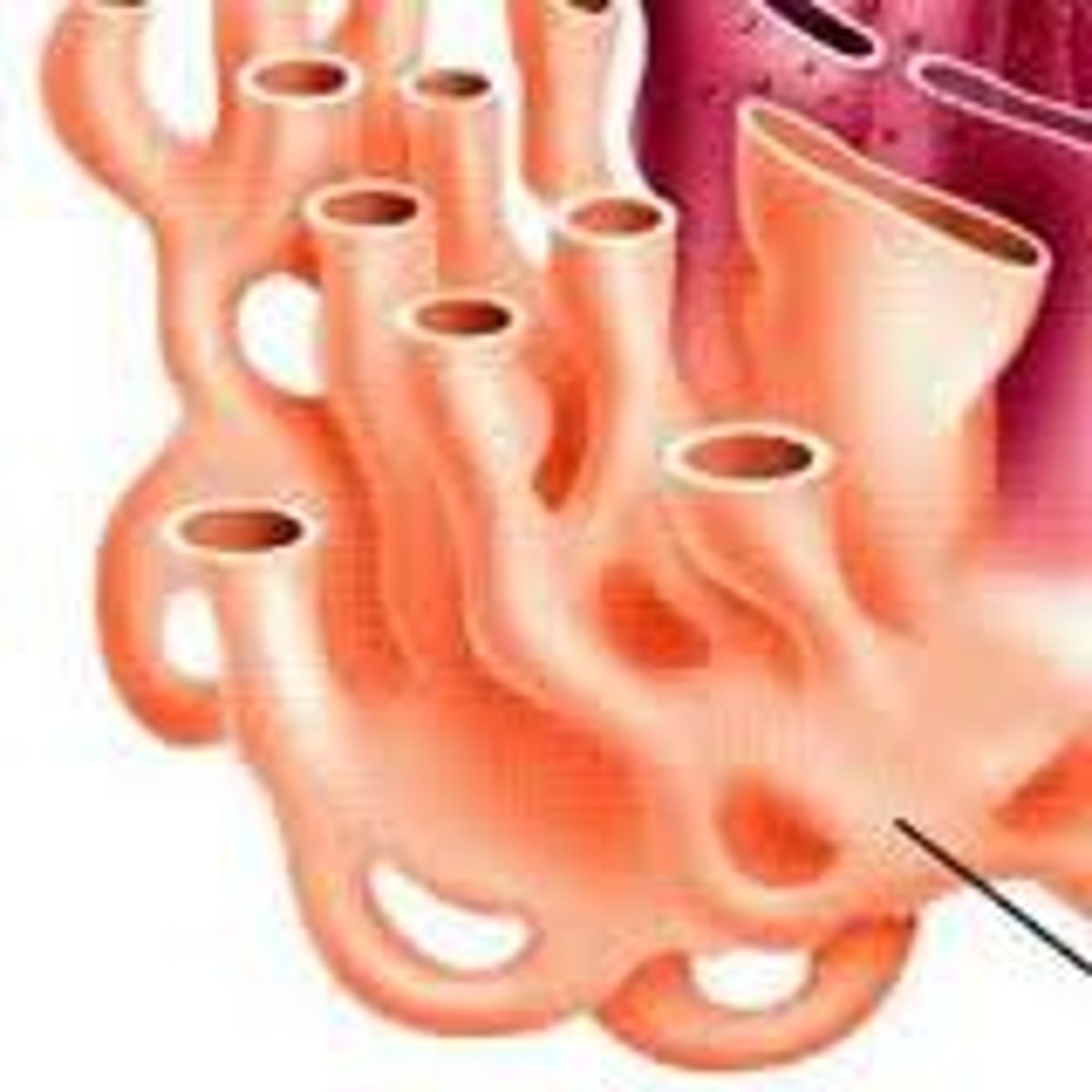
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
synthesis of carbohydrates, lipids, and steroid hormones, as well as the detoxification and storage of drugs and toxins
bound (fixed) ribosomes)
attached to the outside of the endoplasmic reticulum or nuclear envelope; make proteins for plasma membrane or destined to be exported out of cell
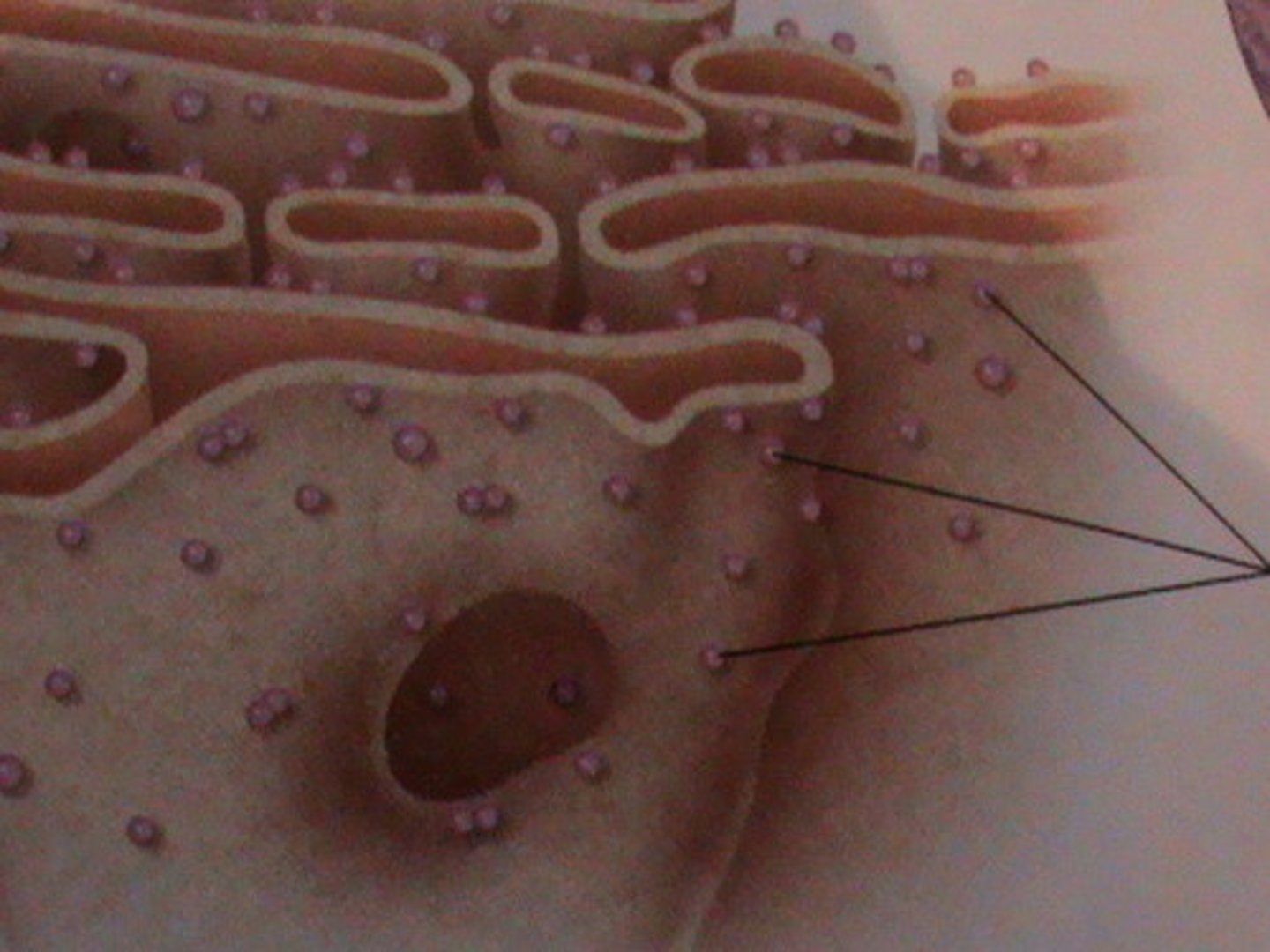
free ribosomes
ribosomes suspended in the cytosol; make proteins for use within the cell
golgi apparatus (complex)
a cell organelle that helps make and package materials to be transported out of the cell

Lysosomes
Uses chemicals to break down food and worn out cell parts
peroxisomes
Contain oxidase enzymes that detoxify alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, and other harmful chemicals
Proteasomes
degrades unwanted protein by tagging, unfolding, and degrading into small peptides or individual amino acids
centrosome
a cellular structure involved in the process of cell division
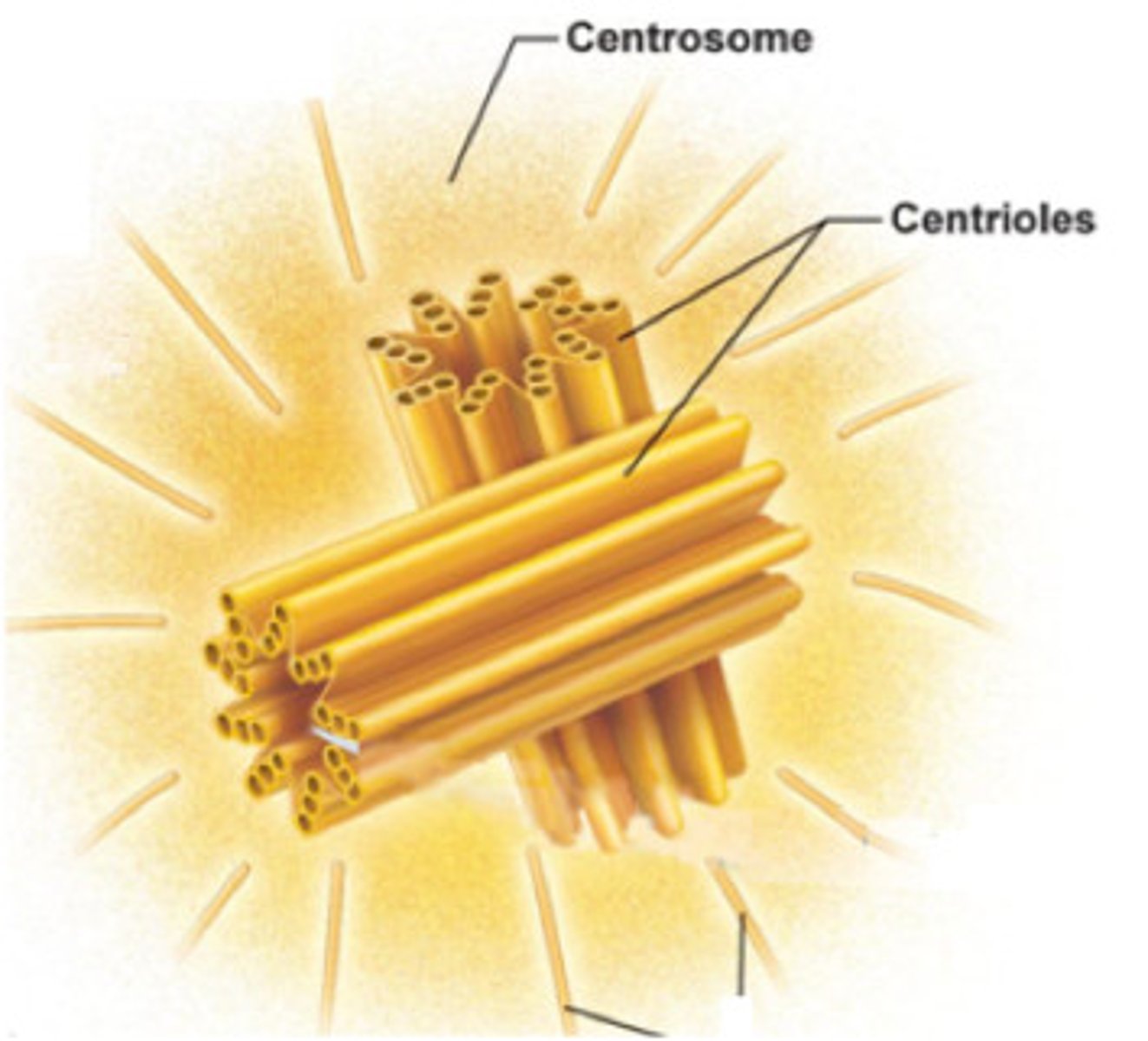
centrioles (singular version of centrosome)
paired barrel-shaped organelles located in the cytoplasm of animal cells near the nuclear envelope
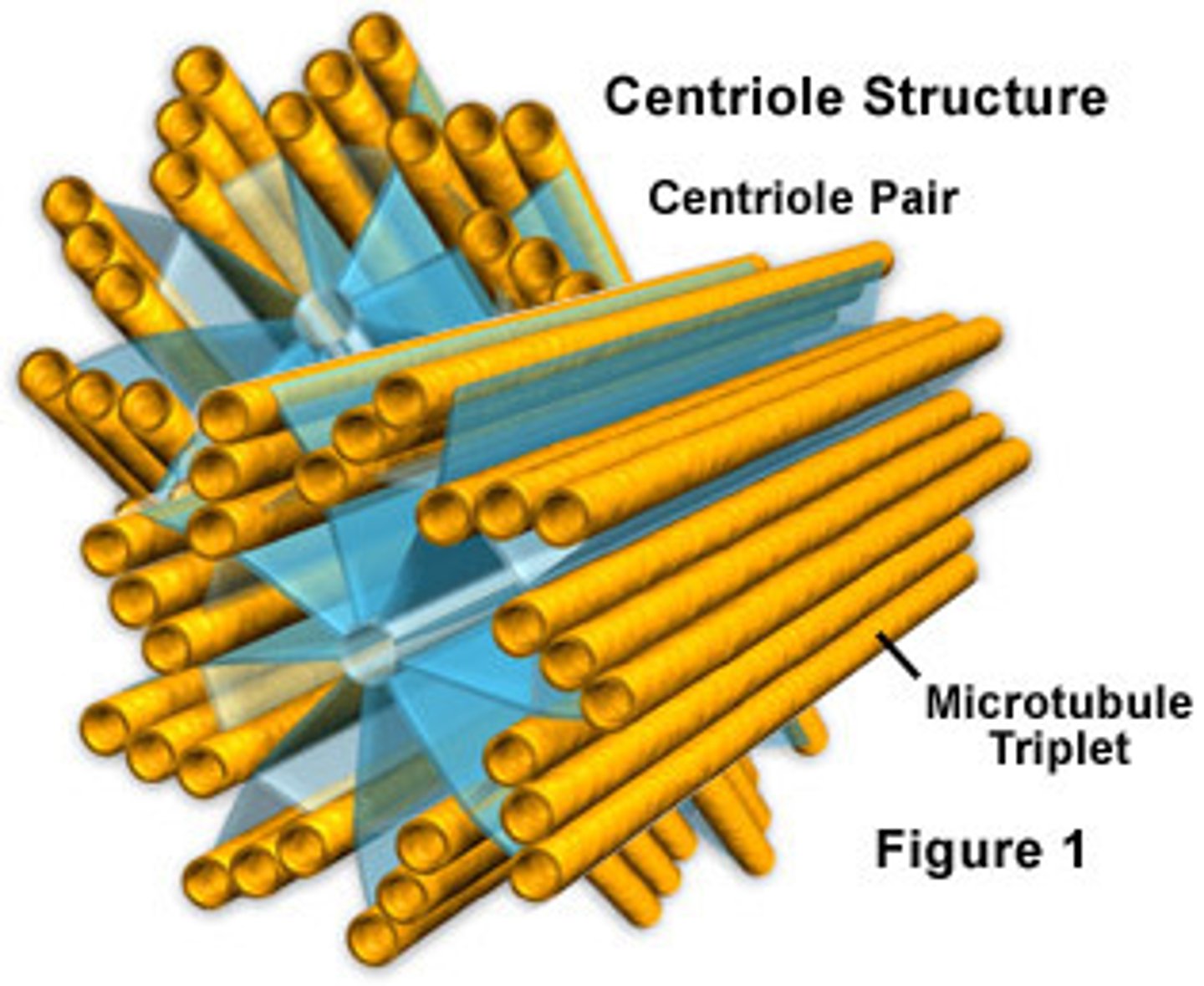
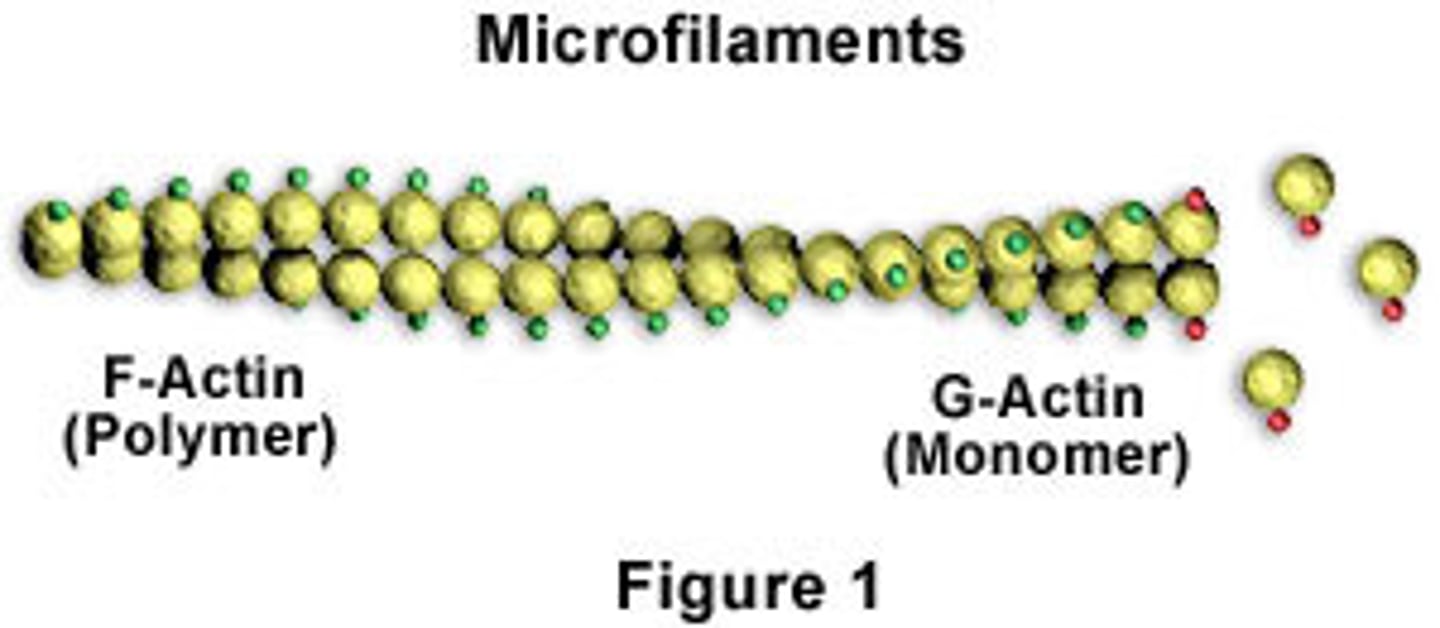
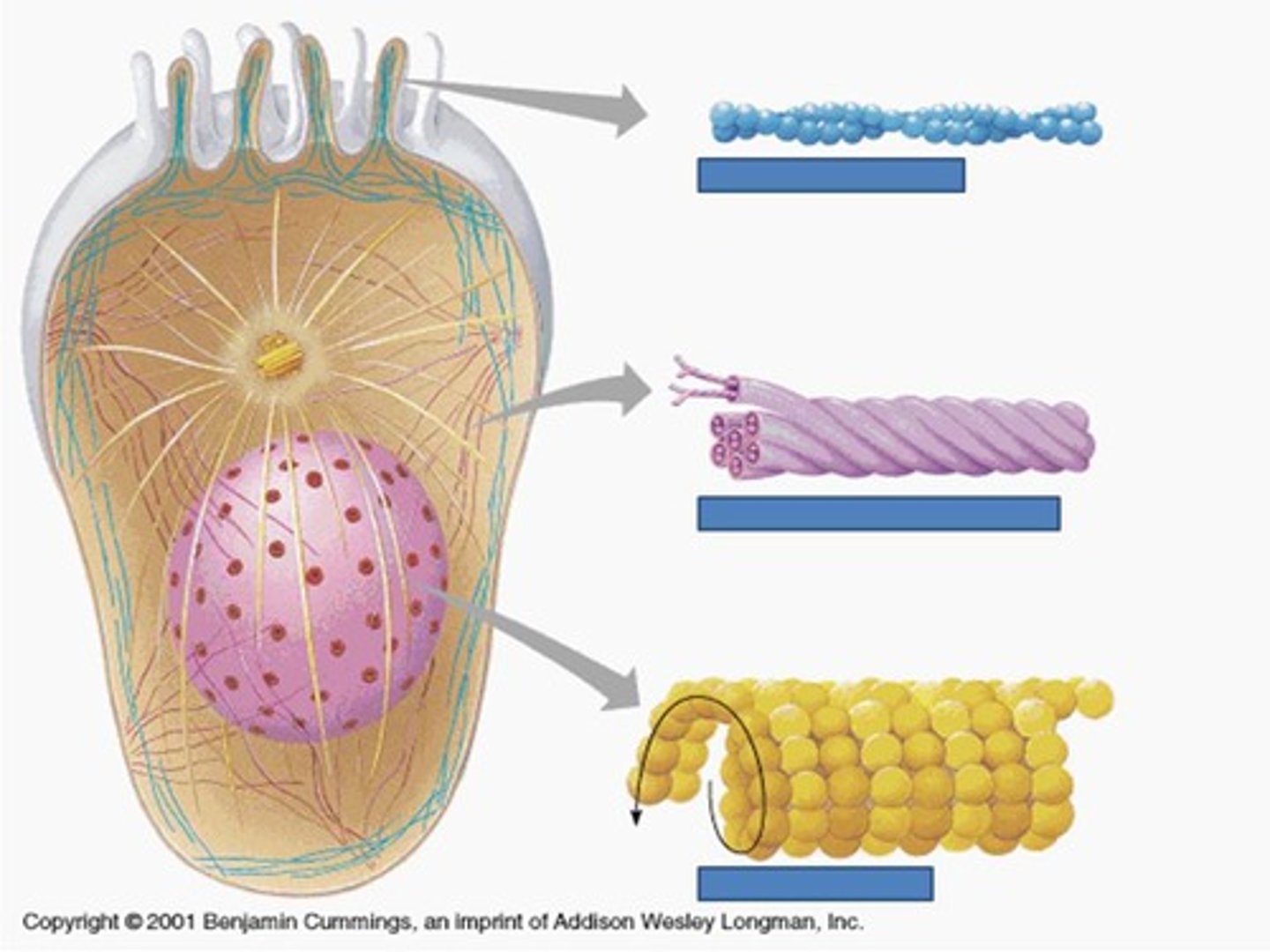
Microfilaments
Long, thin fibers that function in the movement and support of the cell
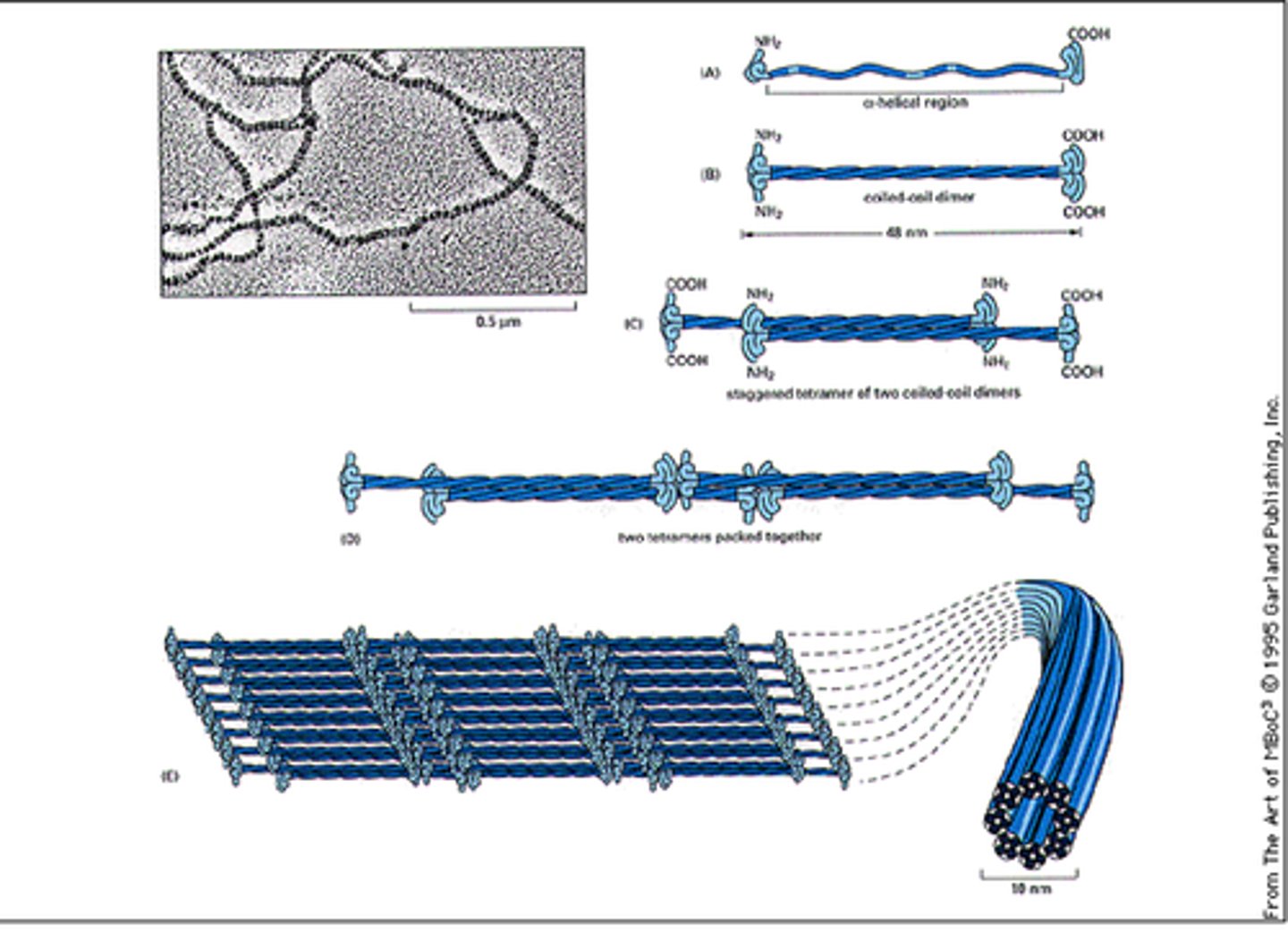
intermediate filaments
Threadlike proteins in the cell's cytoskeleton that are roughly twice as thick as microfilaments
microtubules (yellow figure in the picture)
Spiral strands of protein molecules that form a tubelike structure
double helix
Shape of DNA
adenine and thymine
always pair
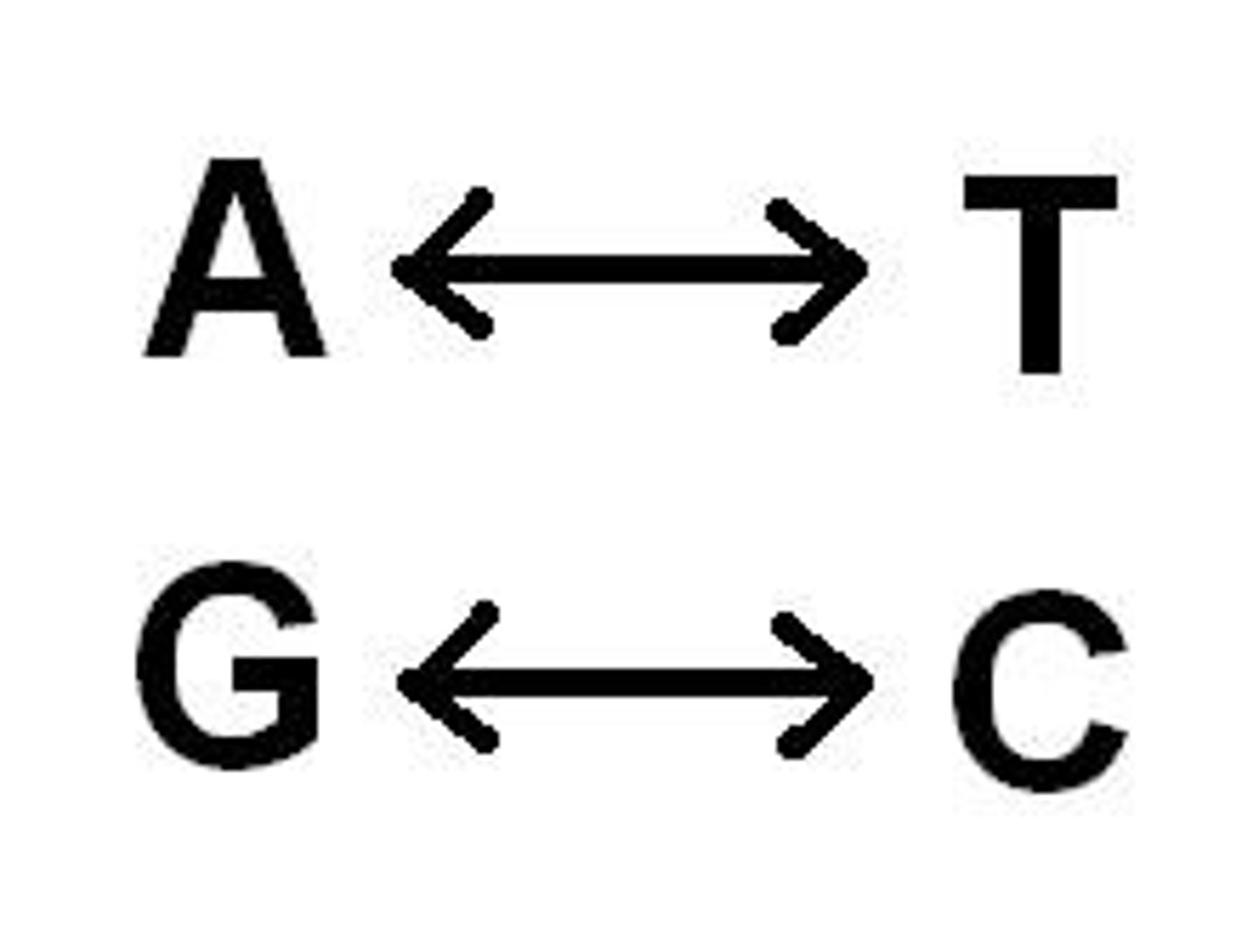
guanine and cytosine
always pair
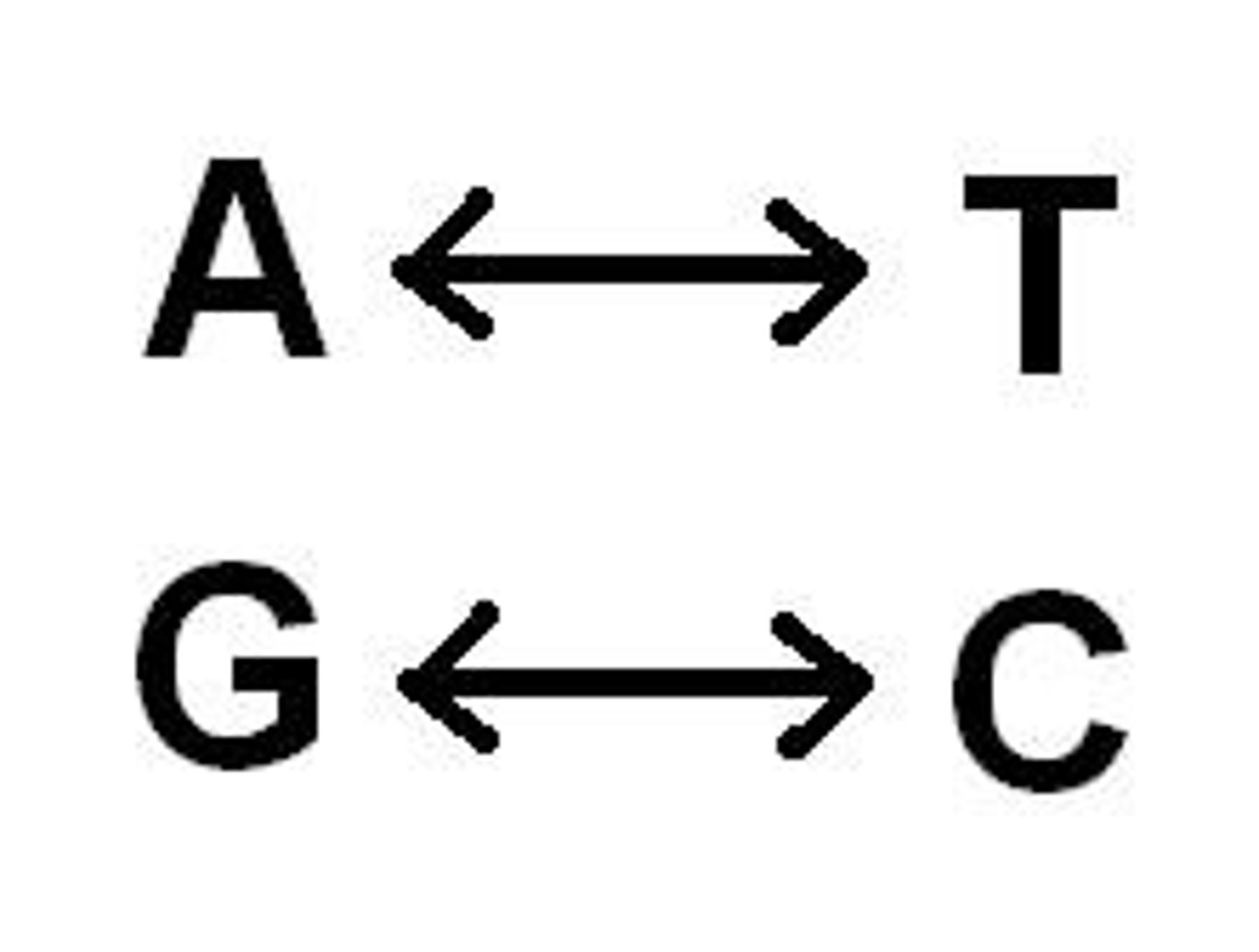
nucleotides of dna
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine
RNA nucleotides
adenine, cytosine, guanine, uracil
Deoxyribose sugar
sugar used in DNA to make up the "backbone"
phosphate group
a phosphorus atom bound to four oxygen atoms (makes up nucleic acids, it provides energy for moving our muscles)
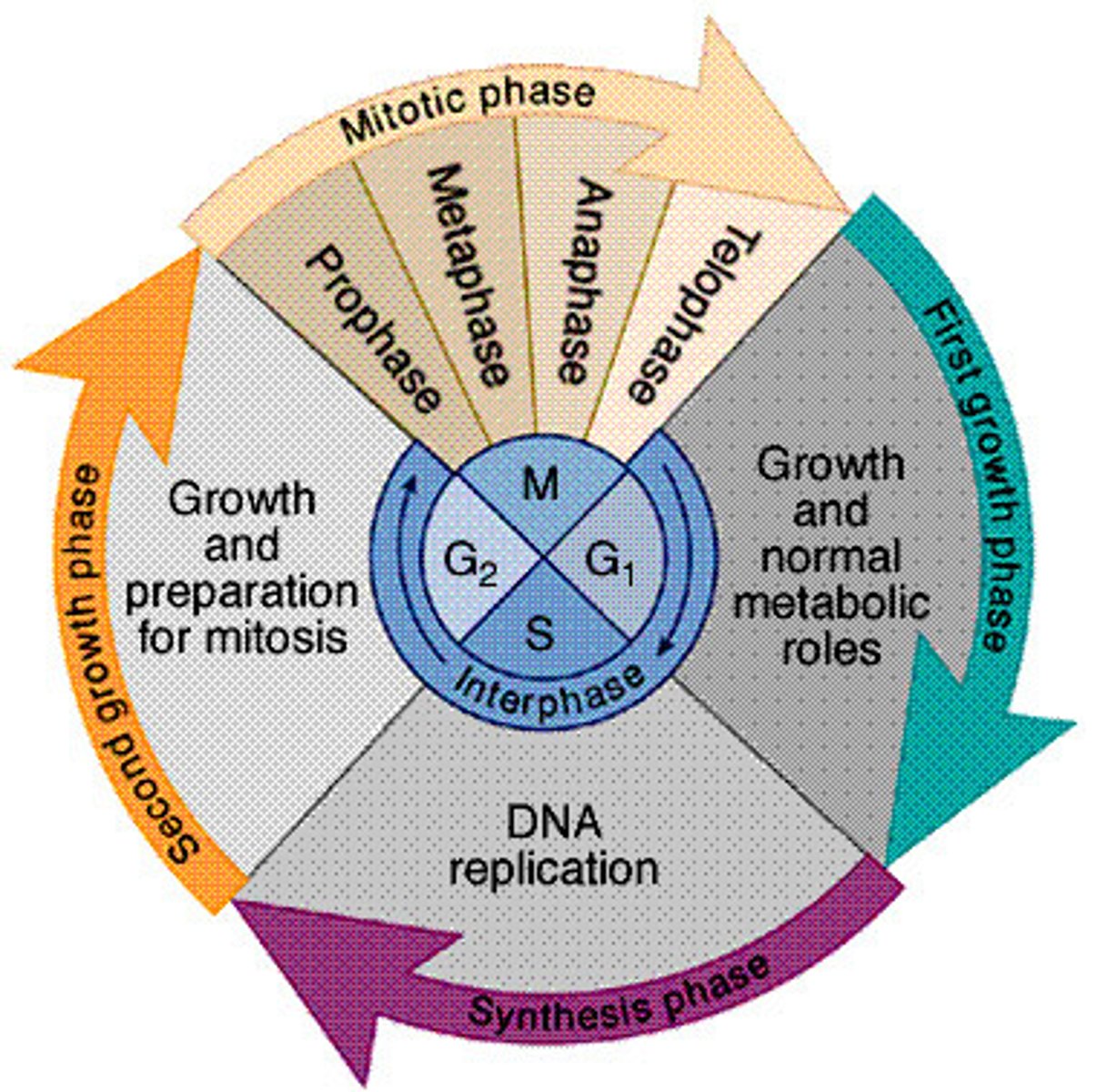
cell cycle
series of events that cells go through until it divides
Mitosis
division of the nuclear material
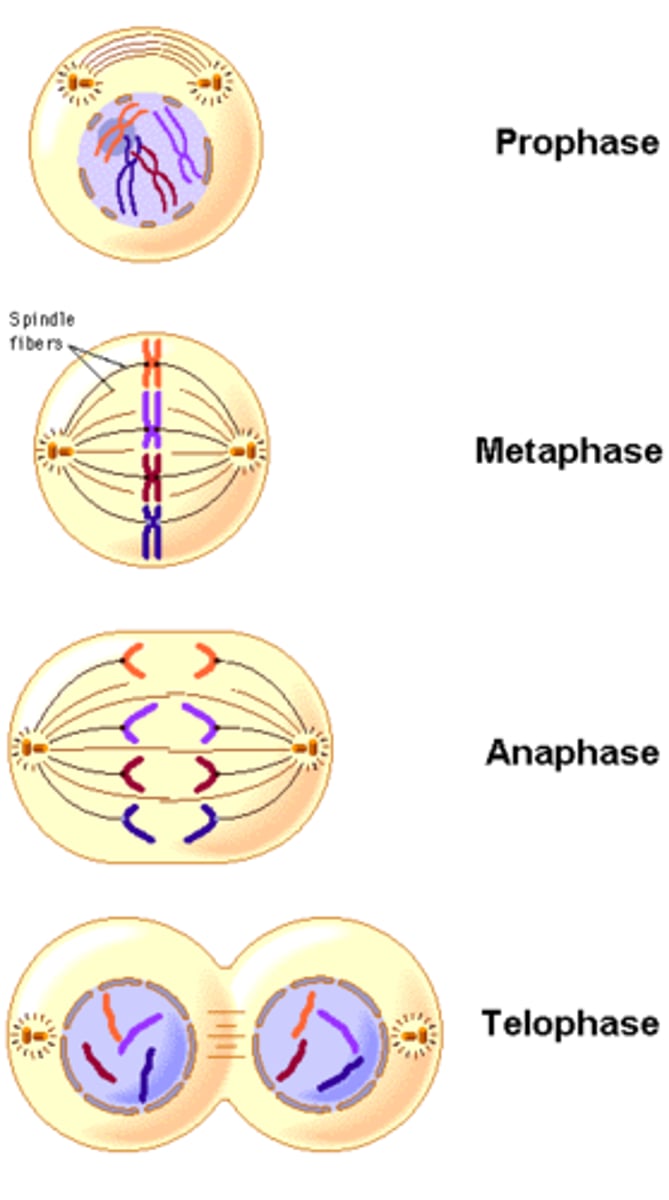
4 phases of mitosis
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
interphase
the resting phase between successive mitotic divisions of a cell
prophase
Chromosomes become visable, nuclear envelop dissolves, spindle forms
metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
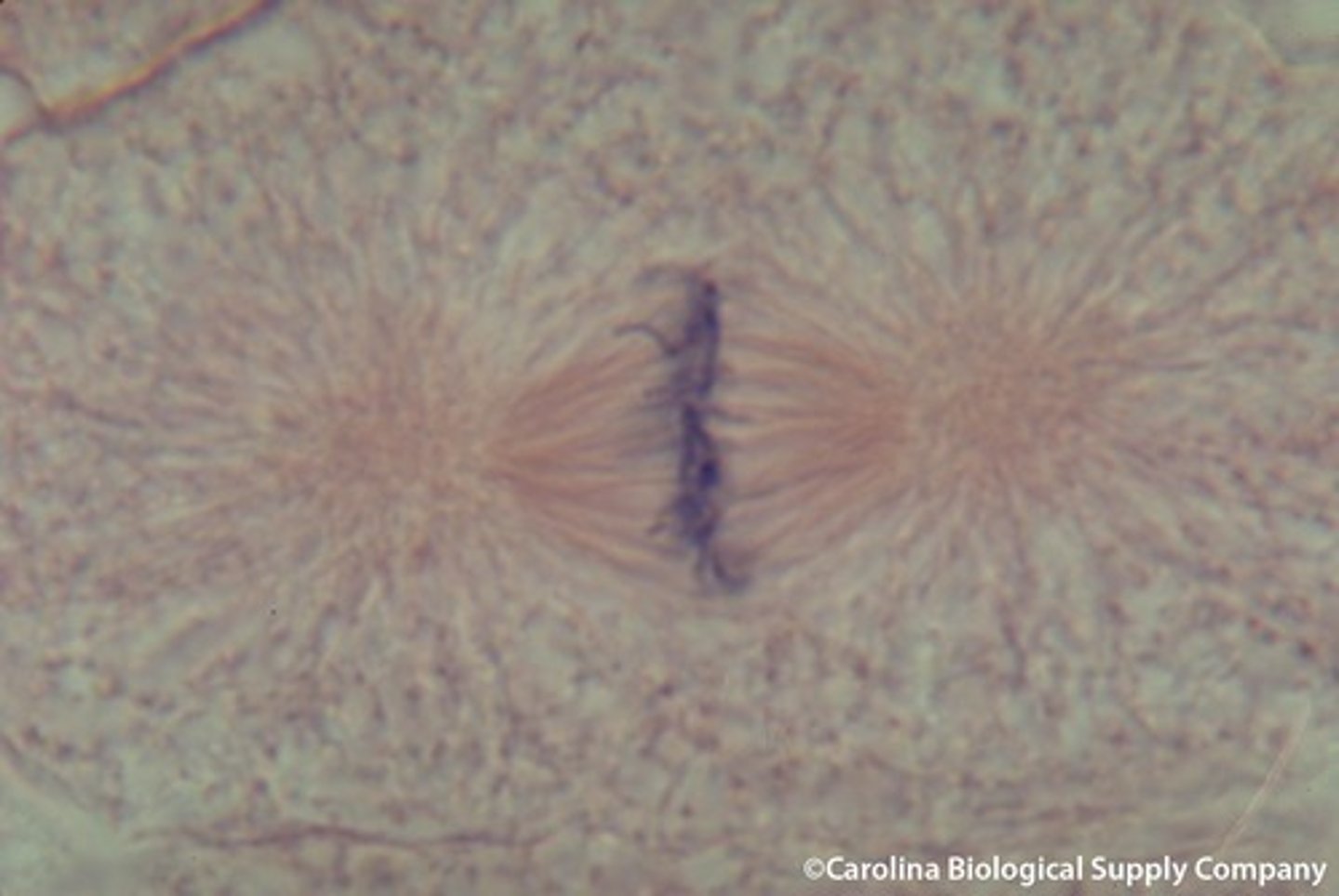
anaphase
Phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell
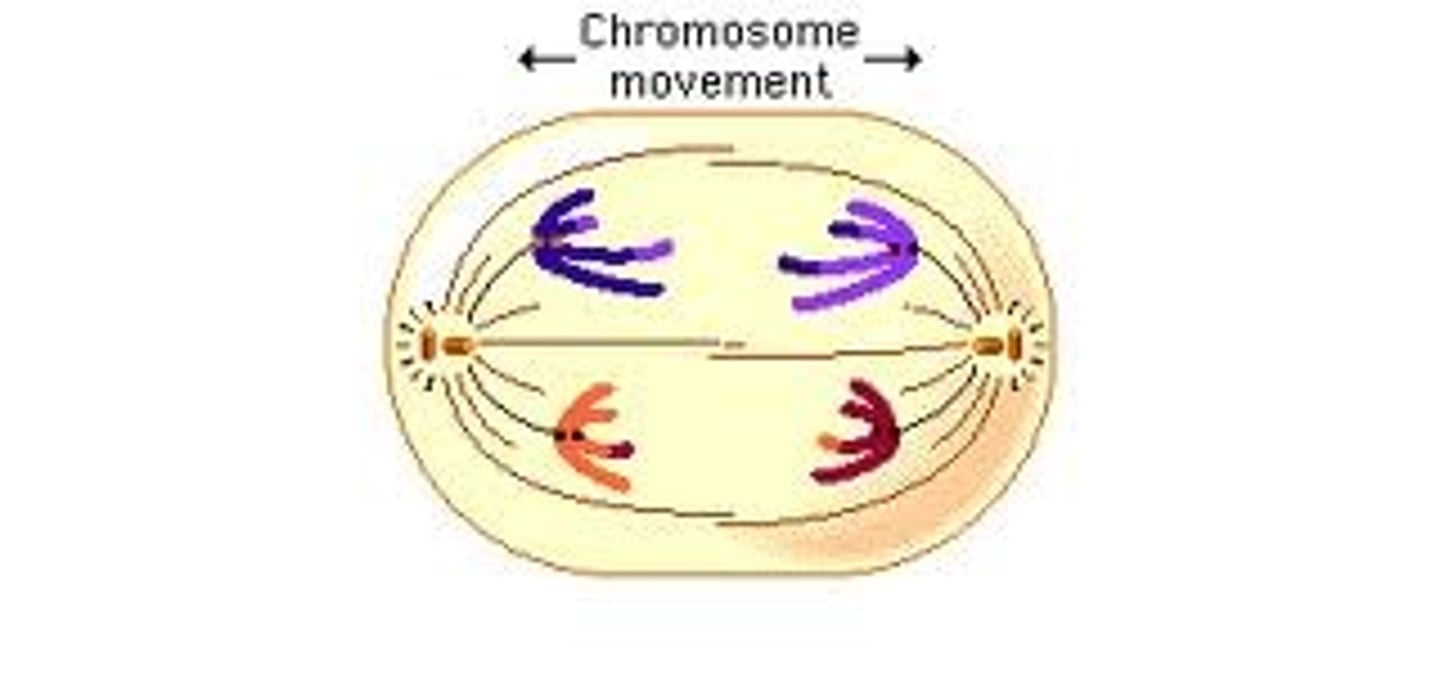
telophase
phase of mitosis in which the distinct individual chromosomes begin to spread out into a tangle of chromatin
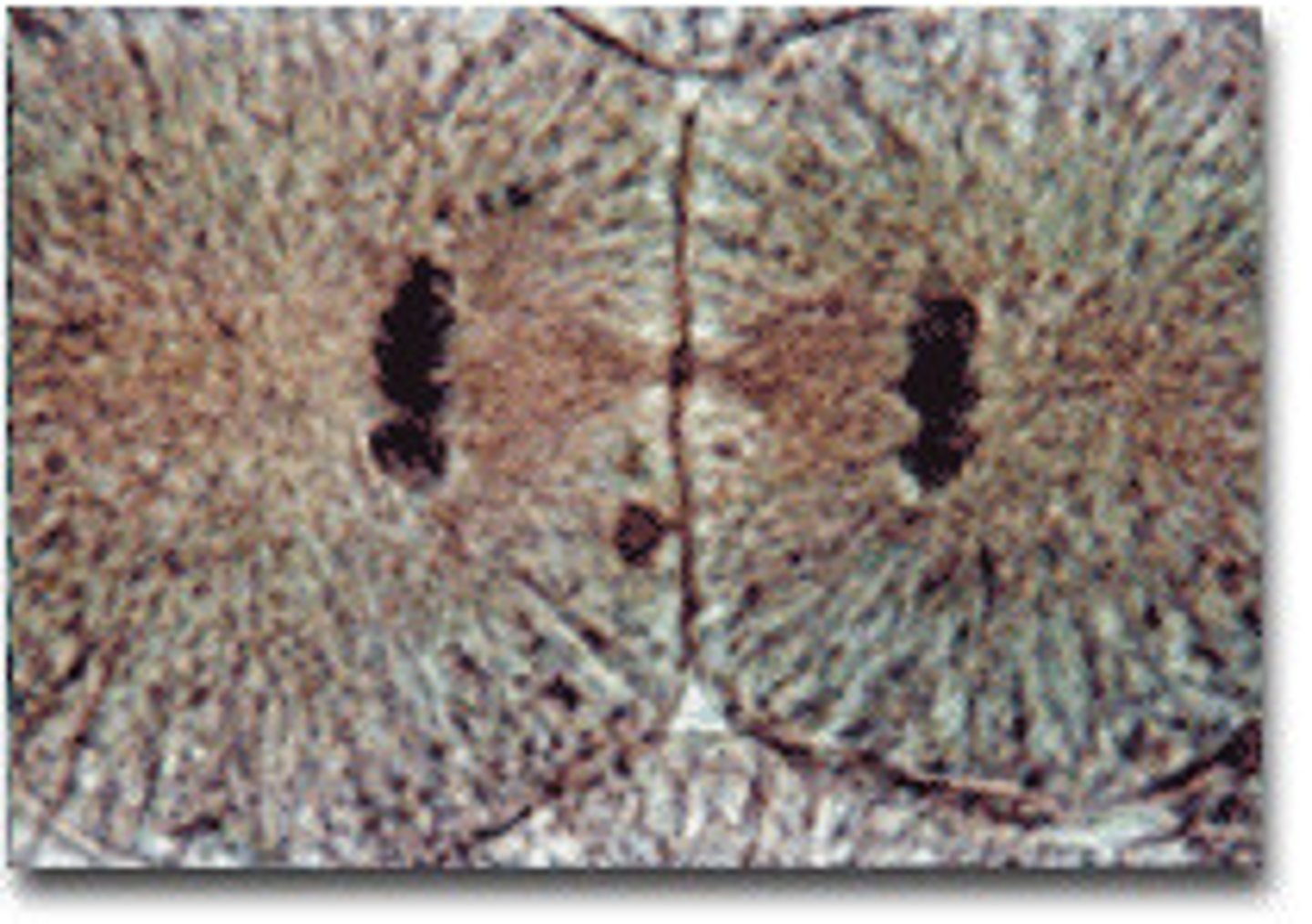
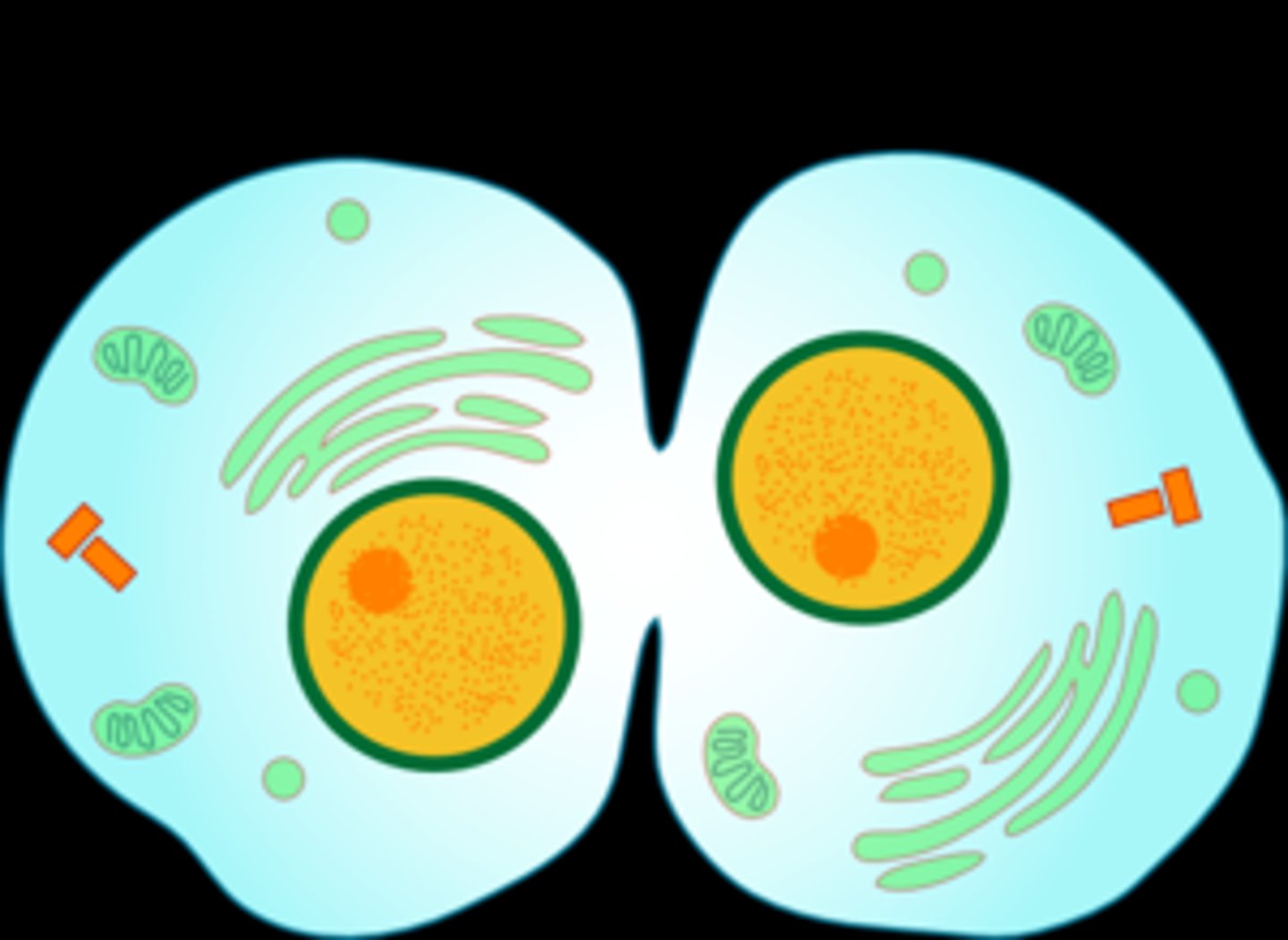
cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm
dna replication
the process of making a copy of DNA
Interphase cycle
g1 (growth), s phase (DNA replication and growth), g2 phase (growth)