⚙️ | Chapter 11: Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
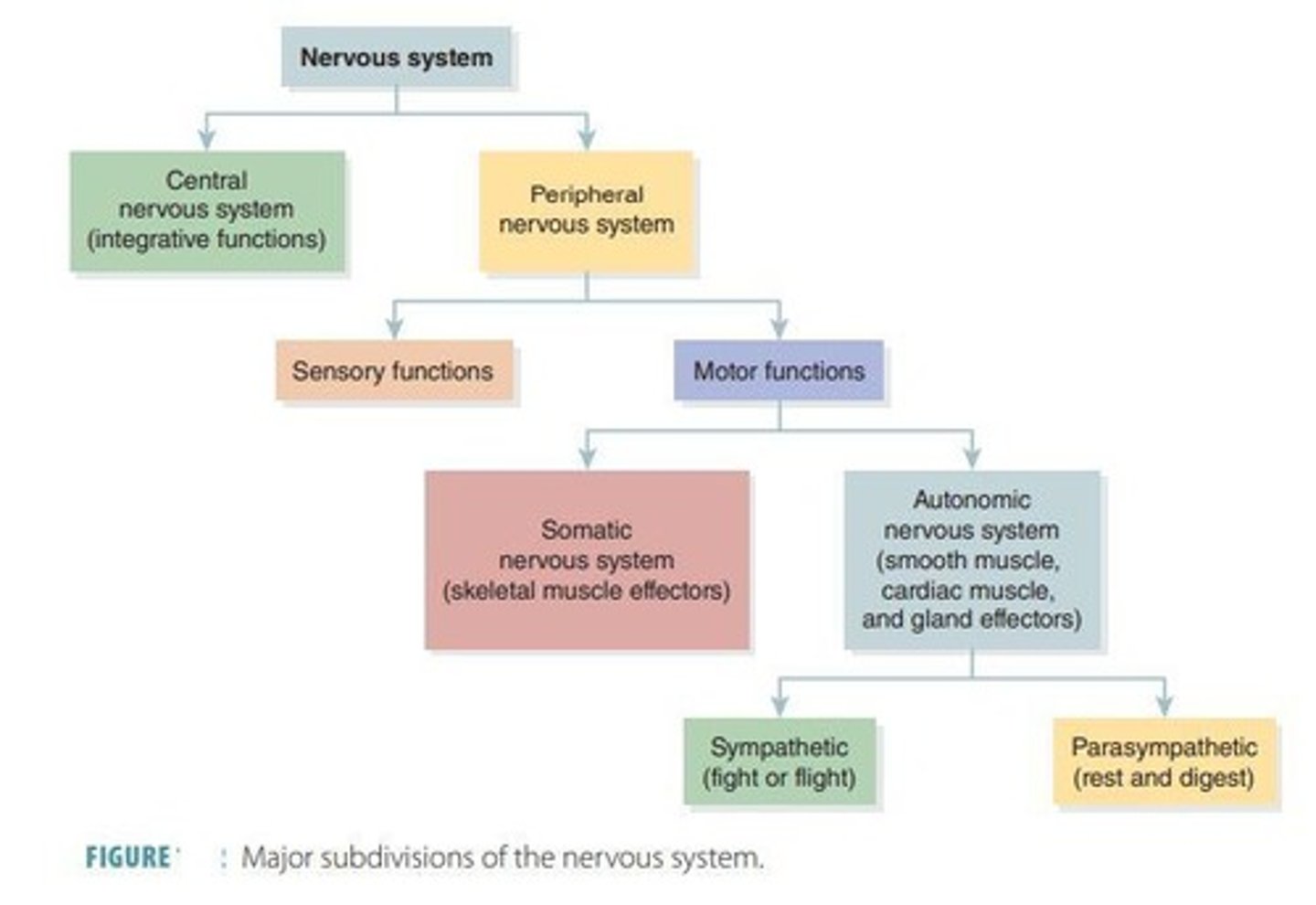
Central nervous system (C N S)
Brain and spinal cord; Integration and command center.
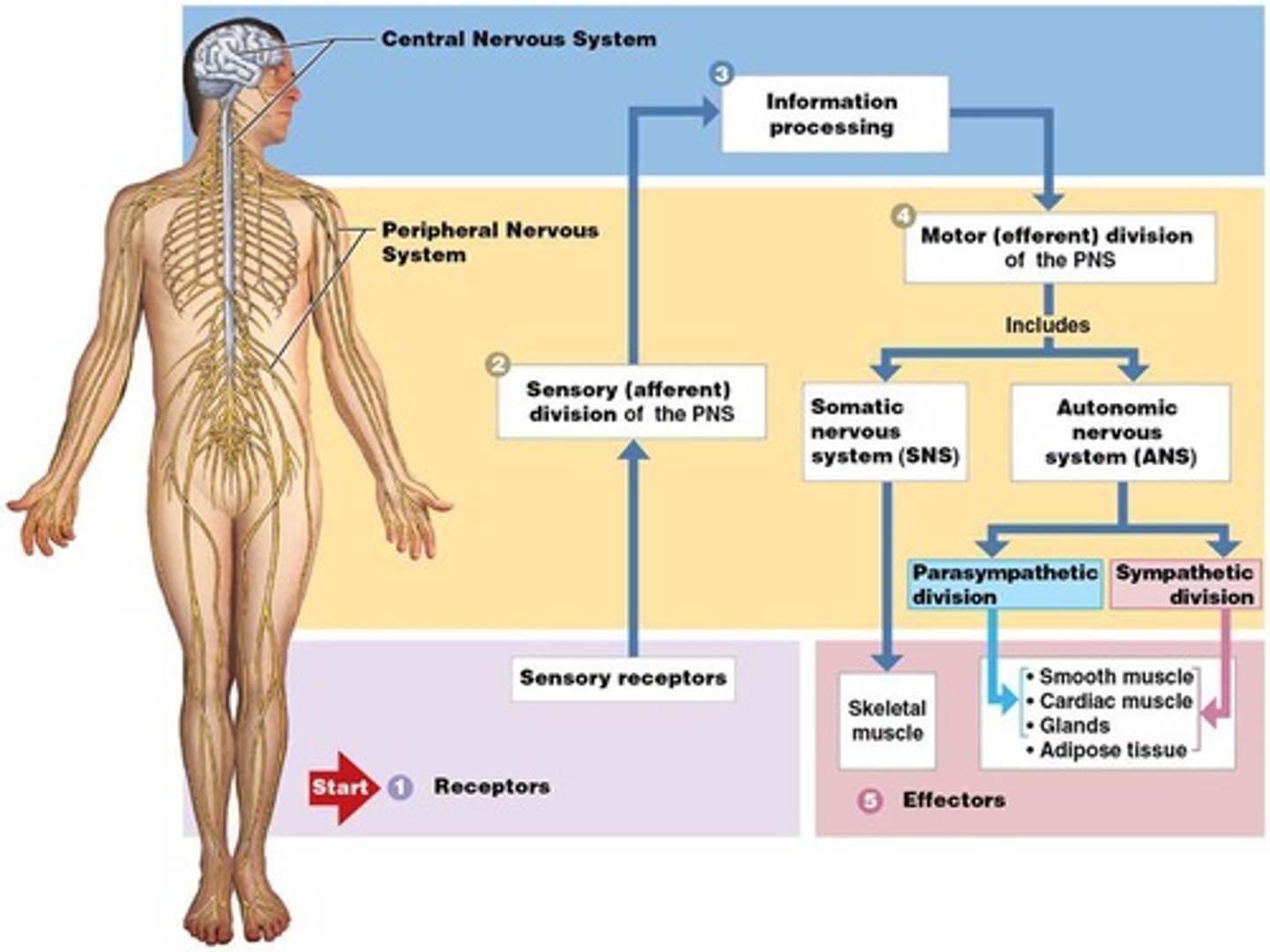
Peripheral nervous system (P N S)
Spinal and cranial nerves; Carries messages to and from the spinal cord and brain.
Receptors
Detect changes in internal or external environment.
Sensory division of the P N S
Sends information to the C N S from receptors in peripheral tissues and organs.
Information processing
Integration and distribution of information occurs in the C N S.
Motor division of the P N S
Carries motor commands from the C N S.
Effectors
Respond to motor commands and change their activities.
Sensory receptors
Detect position, touch, pressure, pain, temperature.
Special sensory organs
Involved in smell, taste, sight, balance, hearing.
Somatic nervous system (SNS)
Voluntary nervous system; conscious control of movement to skeletal muscles.
Autonomic nervous system (AN)
Involuntary nervous system; automatically regulates activities to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands, adipose tissue.
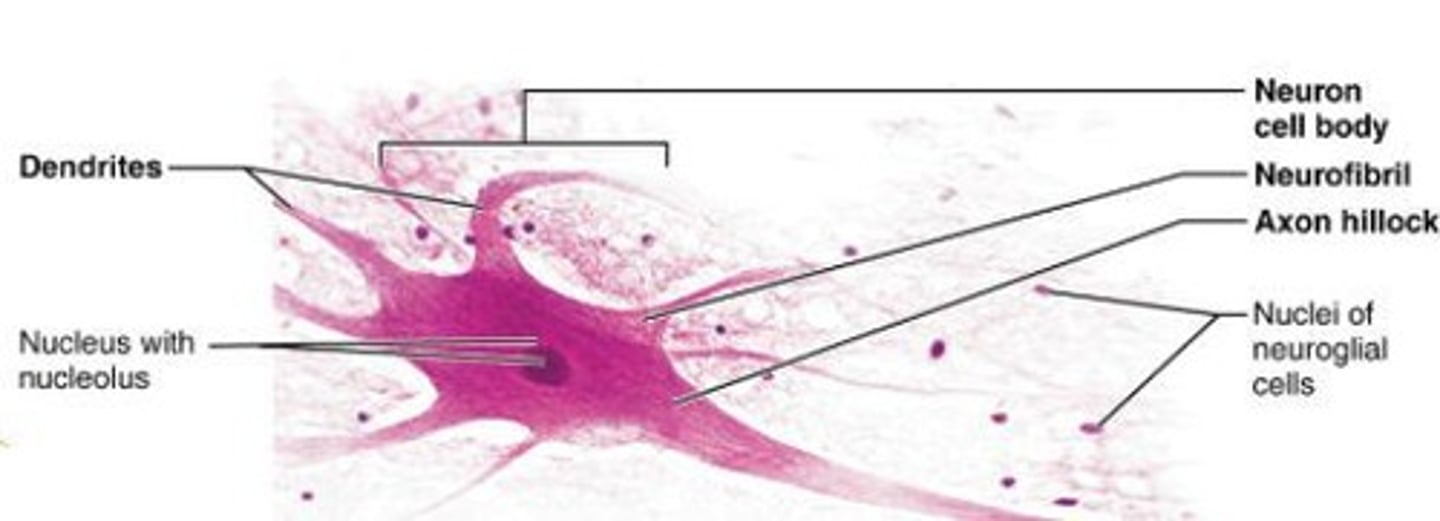
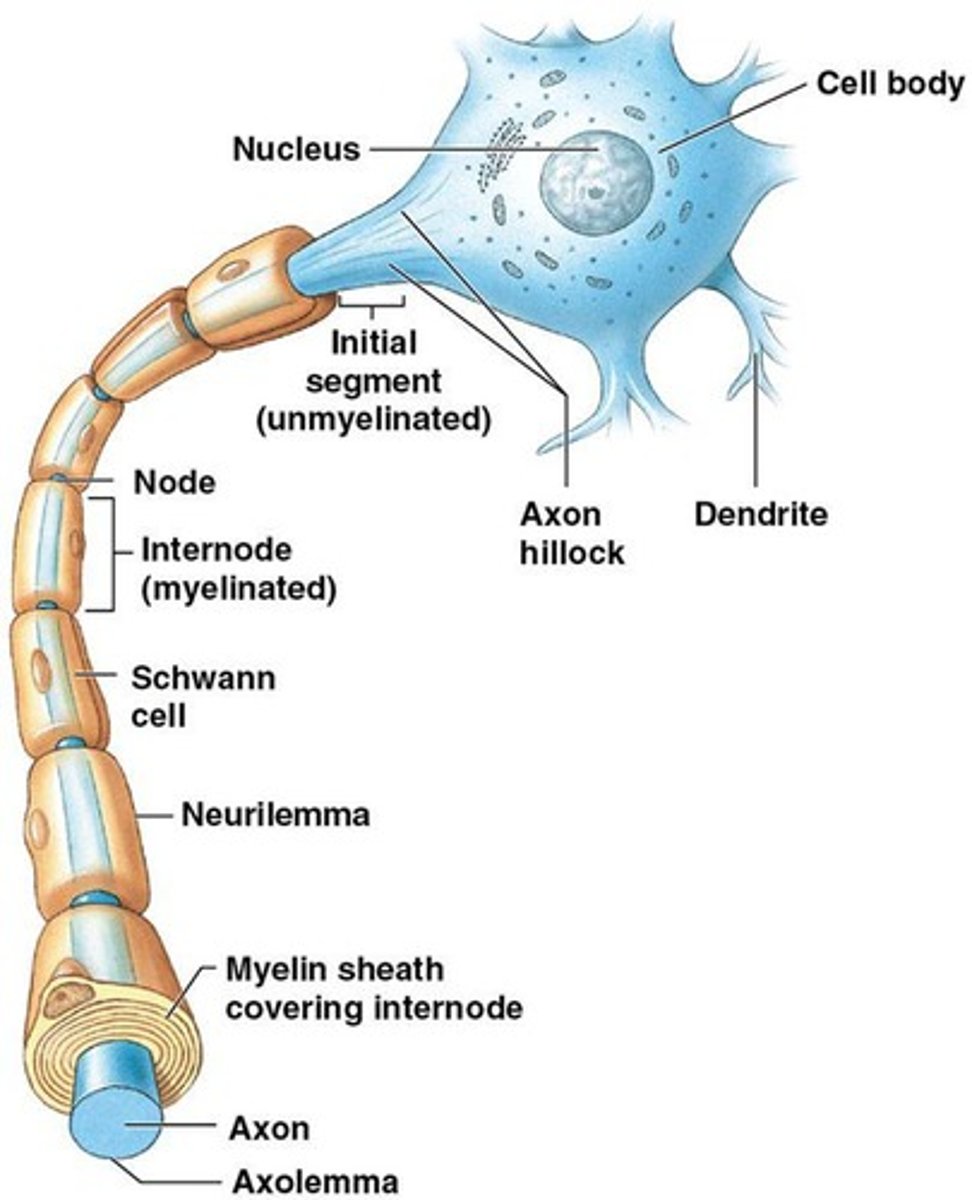
Neurons
Nerve cells specialized for intercellular communication.
Neuroglial cells
Support cells that are non-excitable and surround and wrap neurons.
Dendrites
Receive stimuli from the environment or other neurons; highly branched.
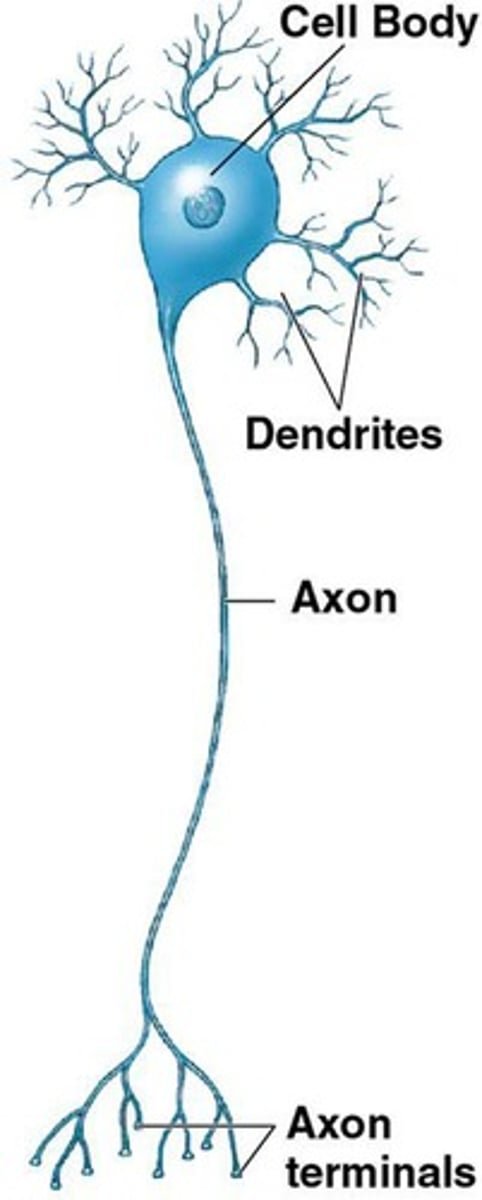
Cell body
Contains nucleus and organelles that provide energy and synthesize neurotransmitters.
Axon
Carries information toward other cells.
Anaxonic neurons
Small neurons lacking features distinguishing axons from dendrites; located in brain and special sense organs.
Unipolar neurons
Dendrites and axons continuous (fused); cell body off to one side; includes most sensory neurons in peripheral nervous system.
Bipolar neurons
Have two distinct processes; occur in special sense organs.
Multipolar neurons
Have two or more dendrites and a single axon; most common neurons in CNS.
Sensory neurons
Deliver information from exteroceptors, interoceptors, or proprioceptors.
Motor neurons
Form the efferent division of the PNS.
Interneurons
Located entirely within the CNS; usually between sensory and motor neurons.
Synapse
Where neuron communicates with another cell.
presynaptic cell
The cell that sends the signal in a synapse.
postsynaptic cell
The cell that receives the signal in a synapse.
Chemical Synapses
Most common, use chemical messengers to transmit signals.
synaptic cleft
Narrow space between the cells in a chemical synapse.
Neurotransmitter
Released from presynaptic membrane into synaptic cleft; binds receptors on postsynaptic membrane.
Electrical Synapses
Occur in certain CNS areas, use gap junctions for direct electrical communication.
Interoceptors
Monitor internal organs/systems; detect distension (stretch), deep pressure, pain.
Proprioceptors
Monitor position/movement of skeletal muscles/joints.
Exteroceptors
Monitor external environment (touch, temperature, pressure, input for special senses).
Neuroglia (or glial cells) of CNS
Cells that support/protect neurons; comprise ~ half the total volume of the nervous system.
Ependymal cells
Simple cuboidal to columnar epithelium that lines central canal (spinal cord) and ventricles (brain).
Microglia
Smallest and least abundant neuroglia in the CNS; act as phagocytes (macrophages of the CNS).
Astrocytes
Star-shaped glial cells; the most abundant in the CNS; maintain the blood-brain barrier.
Oligodendrocytes
Produce myelin sheaths around CNS axons.
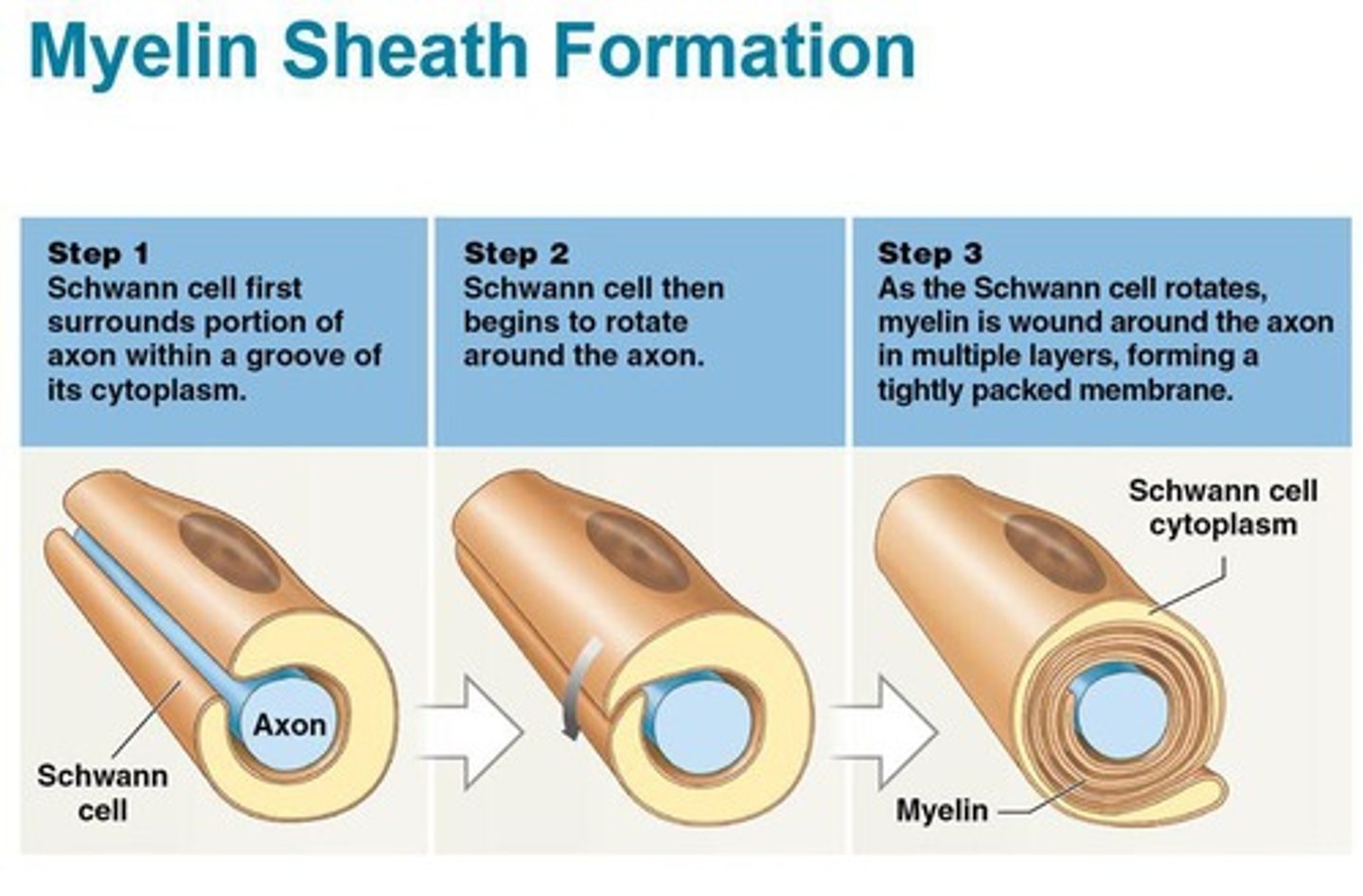
Myelinated axons
Axons with myelin sheaths; appear white because of lipid content of myelin.
Unmyelinated axons
Axons without myelin sheath.
CNS white matter
Areas with many myelinated (whitish) axons.
CNS gray matter
Areas with mostly cell bodies, dendrites, unmyelinated axons; lack of myelin makes them appear gray.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the myelin sheath, causing inflammation and disrupting nerve communication.
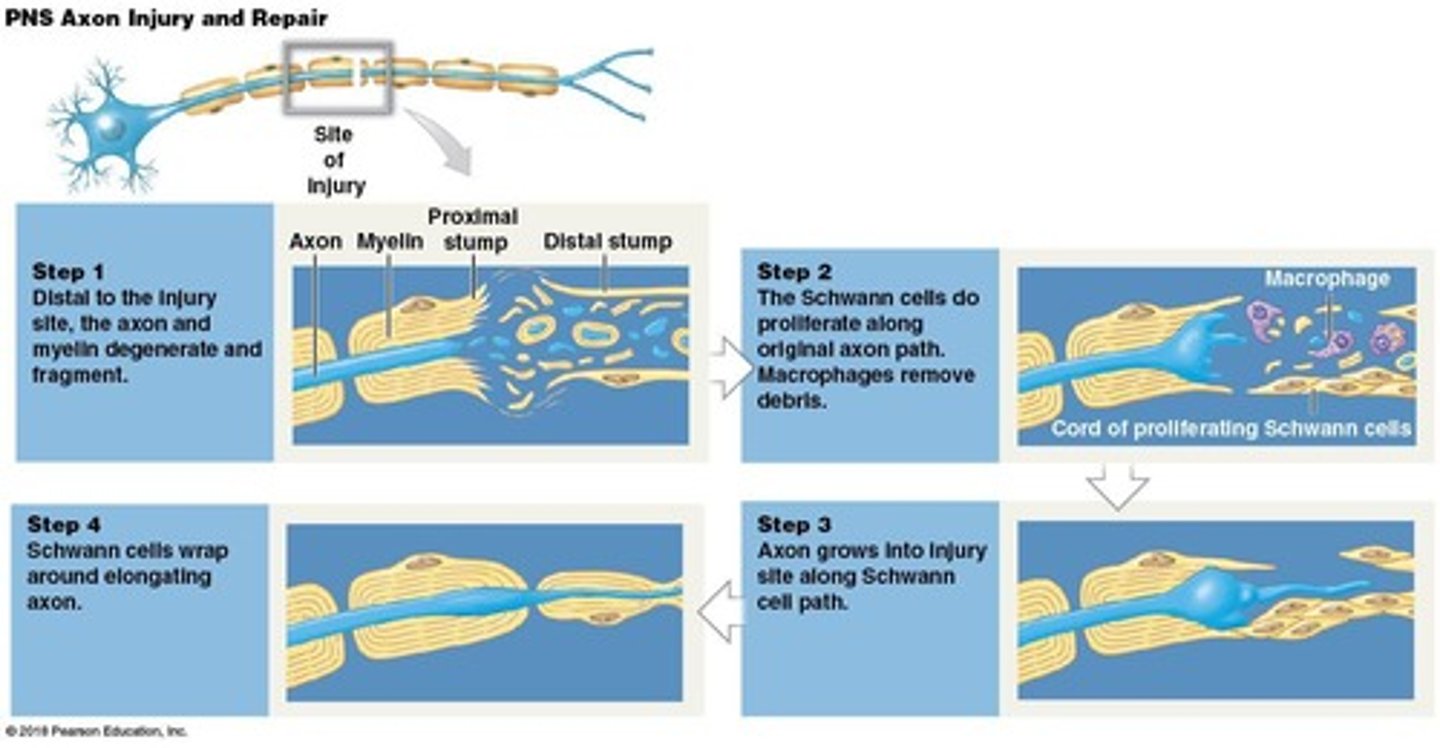
Wallerian degeneration
The repair process where Schwann cells assist in repairing damaged nerves.
Neurilemma
Outer surface of Schwann cells.