Module 6 Carboxylic Acids
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
what does it mean when the carboxylic acid is soluble in water
it is able to form hydrogen bonds
what does the larger the acid mean in solubility
less soluble as proportion of soluble and insoluble parts becomes less of the soluble parts
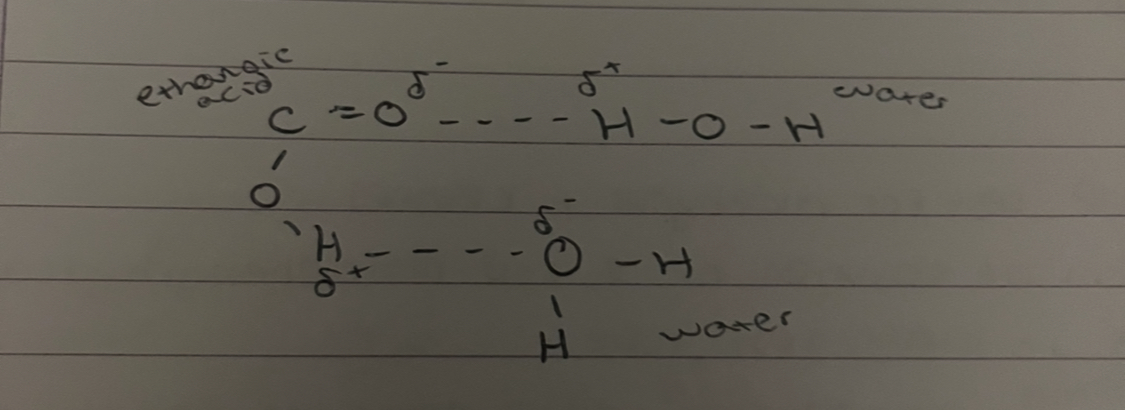
what is this
acid dissolving in water
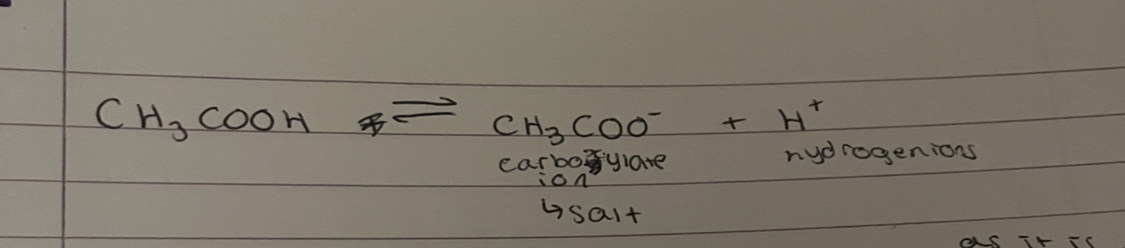
why is the H removed from here
dont removed H from anywhere else as it is stable otherwise it would form a carbocation (CH2) which is unstable
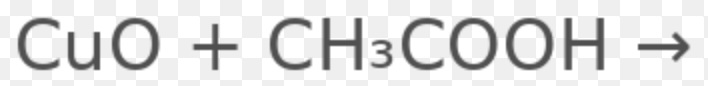
what is the rest of the equation
Cu(CH3COO)2 + H2O
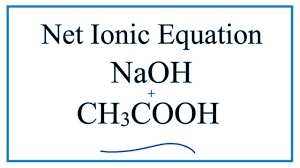
what is the rest of this equation
CH3COONa + H2O
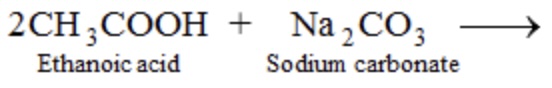
what is the rest of the equation
2CH3COONa + CO2 + H2O
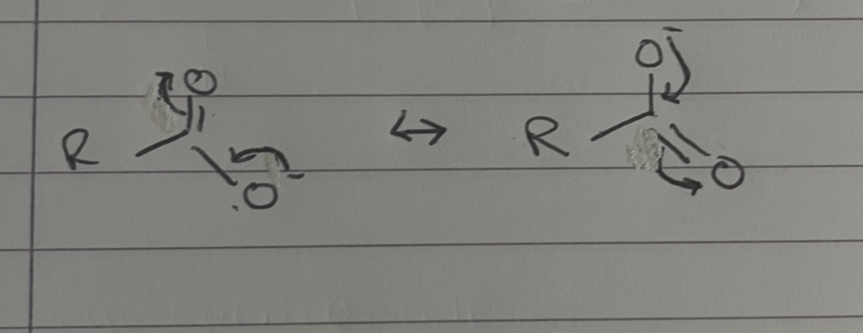
what happens to the negative charge
negative charge can be shared over 2 electronegative oxygen atoms, more spread of negative charge = more willing molecule will be to dissociate to produce H+