Solar Energy and PV Systems
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is solar energy?
The electromagnetic energy emitted by the sun due to nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium.
What are the three main solar energy conversion processes?
Heliochemical, Heliothermal, and Helioelectric.
What is the heliothermal process?
Conversion of sunlight into heat energy, typically using solar collectors.
What is the helioelectric process?
Direct conversion of sunlight into electrical energy using photovoltaic cells.
What are flat-plate solar collectors used for?
Heating water or air for residential or industrial applications.
What are concentrated solar power (CSP) systems used for?
Generating high-temperature heat or steam for electricity generation.
Name two common CSP configurations.
Parabolic trough and Linear Fresnel reflector systems.
What is the purpose of an inverter in a solar PV system?
To convert DC output of solar panels into AC power.
What is the function of MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking)?
IT continuously adjusts the operating voltage and current of a solar PV system so that it operates at the maximum power point on the panel’s I-V curve.
It ensures the system extracts the highest possible power output from the solar panels under changing sunlight and temperature conditions.
What is the Panel Generation Factor (PGF)?
PGF is a location-based value that represents how much daily energy (kWh) a solar panel can produce per watt of rated power under typical sunlight conditions.
It accounts for solar radiation, weather, and system losses and is used to estimate total panel power requirements.
W_{P}=\frac{DailyEnergyRequirement(Wh)}{PGF} Wp (watt peak) total rated power needed by panels
How is required PV panel power calculated using PGF?
Wp = Daily energy consumption (kWh) / PGF.
Wp (watt peak) = The total rated power of the solar panels required. It tells you how many watts of panels you need to meet your daily energy demand.
What is Depth of Discharge (DoD)?
Both a measurement and a rating characteristic that varies by battery type — it tells you how much of a battery’s capacity can safely be used without damaging it.
DoD = Energy Used/Total Battery Capacity * 100%
DoD = Energy Used/Total Battery Capacity * 100%
Which battery type typically allows higher DoD?
Lithium-Ion batteries (approximately 80-90%) compared to Lead-Acid (approximately 50%).
What is the average lifespan of inverters and MPPTs in a PV system?
Around 5 years.
Describe the layout of a basic PV system.
Photovoltaic Panels get hit with sunlight
DC energy goes to a MPPT
Then goes to an Inverter where it is turned into AC
Powers home or gets sold to the grid.
Describe a parabolic trough CSP setup.
Long curved mirrors focus sunlight onto a receiver tube containing fluid heated up to about 400 degrees C, used to drive a steam turbine.

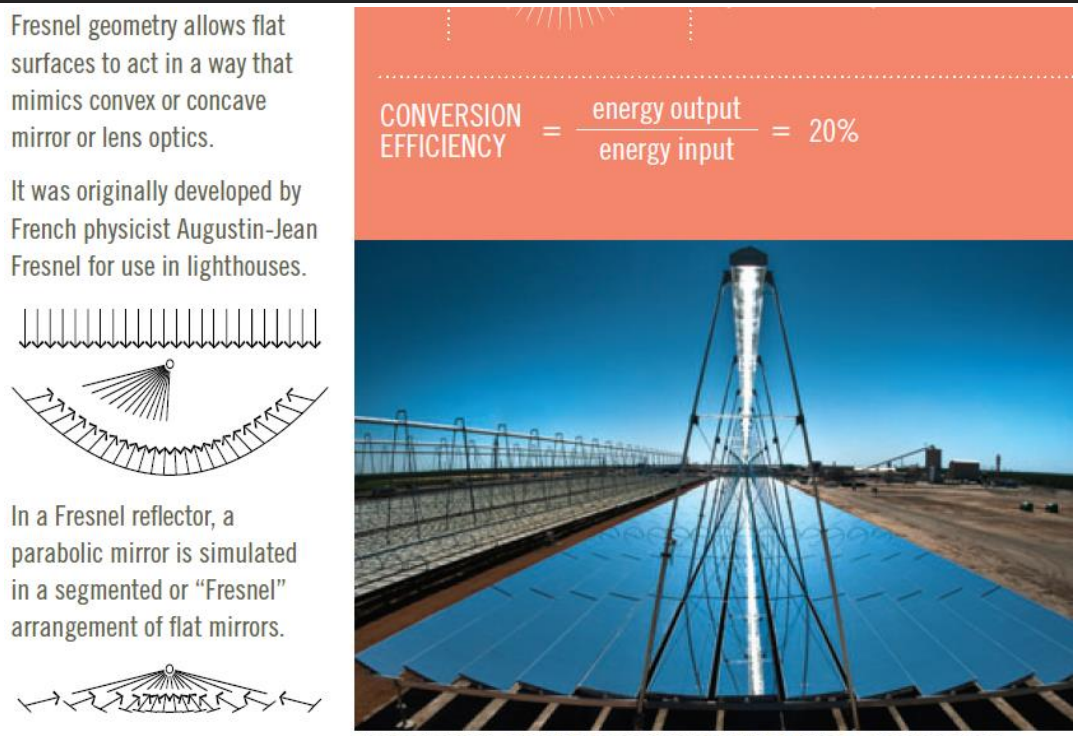
Describe a Linear Fresnel reflector CSP system.
Multiple flat or slightly curved mirrors reflect sunlight onto a fixed linear receiver; it is simpler, cheaper, and easier to maintain than parabolic systems.
Describe the characteristics of a monocrystalline photovoltaic panel.
Made from a single continuous crystal structure (pure silicon).
Highest efficiency (≈15–22%) and best performance in low light.
Most space-efficient, with a uniform dark color and rounded cell edges.
More expensive due to complex manufacturing.
Long lifespan and stable performance in hot conditions.
Describe the characteristics of a polycrystalline photovoltaic panel.
Made from multiple silicon crystals melted together.
Moderate efficiency (≈13–17%), slightly lower than monocrystalline.
Less expensive and easier to produce.
Blue-speckled appearance due to multiple crystal orientations.
Slightly reduced performance in high temperatures.
Describe the characteristics of a thin-film photovoltaic panel.
Made by depositing thin semiconductor layers (like amorphous silicon, CdTe, or CIGS) onto a substrate.
Lowest efficiency (≈10–12%) but performs better in diffuse light and high heat.
Lightweight, flexible, and suitable for large-area or portable installations.
Lower cost per panel but requires more surface area for the same output.
Degrades faster and has a shorter lifespan than crystalline types.
Which photovoltaic panel type is most efficient and performs best in limited space?
Monocrystalline panels — they offer the highest efficiency and power output per area.
Which photovoltaic panel type is least expensive to produce?
Thin-film panels are cheaper to produce than poly and monocrystalline panels, though they’re generally less efficient and require more space for the same power output.
Which photovoltaic panel type is best for flexible or portable applications?
Thin-film panels — lightweight and flexible, suitable for building integration or mobile uses.