Medical Physcis CH 5 Waves& Sound
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Mechanical waves are waves that require a …………..
medium
A medium is a form of ……………through which the wave travels such as
matter (water, air, glass)
Waves such as light, X-rays and other forms of radiation do not require a ………….
medium
Transverse wave is a type of …………. waves that moves…….
Mechanical wave that moves up and down a right angle to the direction of the wave
Types of Mechanical waves are
Transverse, Longitudinal (compression waves)
In longitudinal waves the matter in the wave moves……….
back and forth parallel to the direction of the wave
The tuning fork ………. and you hear a sound
vibrates
sounds are made when an object
vibrates
Sound is a ………that ………………………… in a medium
longitudinal wave, that propagates via pressure variations
pressure waves vibration produces areas of …………. and changes are recorded by the ear ……….
higher pressure , drum
Place a ringing clock inside bell jar and what happens?
There is air inside the jar so sound can travel and be heard
Remove air from bell jar and what happens?
The sound cannot be heard because there is no air inside (vacuum)
Required elements of sound
1- Source of vibration 2- energy 3- path or medium 4- receiver
Speed of sound is dependent on……………..and………, and doesn’t depend on the frequency of the wave
the medium and the temperature
Speed of sound can roughly be considered as a constant=…………
1540m/s in the human body
Speed of sound equation

Speed of sound is constant for …… and is determined by ……and……..
any medium, by density and compressibility of the medium(measured with bulk modulus of elasticity k)
Incompressible medium has …………velocity
high
Bone is very ………….., has ……… k and higher………….than…..
incompressiblem high k, higher speed of sound than muscle
sound needs substance to travels by
particles vibrating
Sound waves travel fastest through ………..
solids.
in a solid particles are closer together This means vibrations are more easily ………..from particle to particle and so sound travels ………….
passed, faster
The ………..the medium, the faster sound will travel.
denser
type of substance …………the speed of sound
affects
A healthy human ear can hear frequencies in the range of ………………….(sonic).
20 Hz to 20,000 Hz
Humans cannot hear below Hz. Sounds below this frequency are termed infrasonic
20
The higher the temperature, the faster the particles of the medium will move and the ………. sound will travel
faster
Sounds above 20,000 Hz are termed………. dogs can hear them but not humans
ultrasonic
The larger the amplitude of the wave on the trace, the
……….. the sound
louder
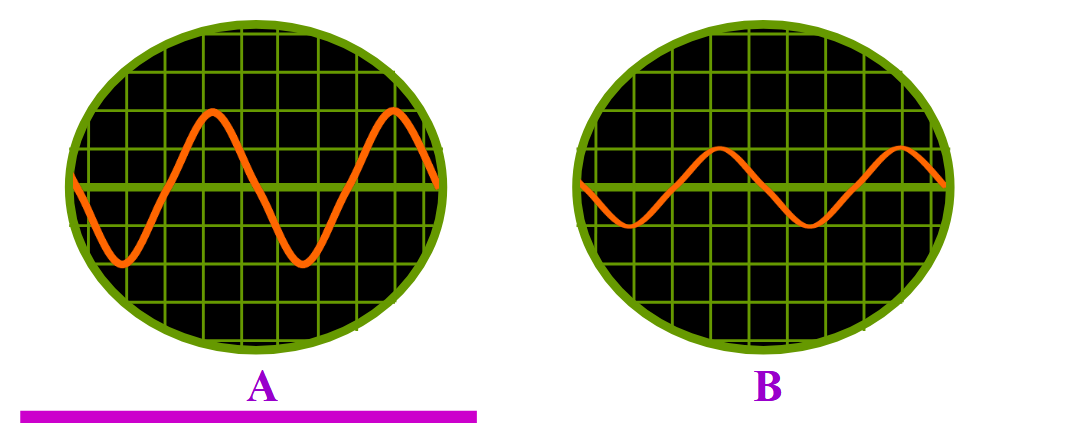
which is louder
A
the pitch of a sound is shown by…………
frequency
The greater the number of waves across the oscilloscope trace, the……………the frequency and pitc
higher
Frequency is perceived as pitch; Low freq. =………… High freq.=………………..
Low→bass pitch
High→ treble
Sound intensity is the …………..that the sound
wave possesses
energy
The greater the intensity of sound the ………. the sound will travel and the ………….the sound will appear.
farther, louder
Loudness is a ………..Relative to surrounding and intensity
sensation
Humans can detect intensities
as low as……..
The threshold of pain
is
10-12 W/m2, 1
intensity formula
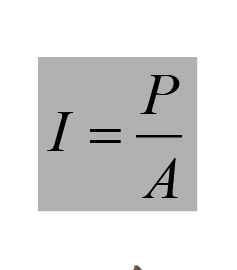
Acoustic Impedance (Z ) It is a measure of the ………..of the particles of the medium to mechanical vibrations
resistance
For a plane wave Z is also given by: …..with unit
Kg/m2 . s
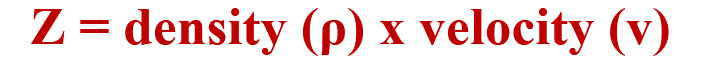
Bone has a ……….acoustic impedance than fat, since the density of the bone is very high
higher
The most important single interaction process for purposes
of generating an ultrasound image
Reflection
types of reflection
1- Specular reflection
2- Non-specular (diffuser or scattered) reflection
Types of reflection depend on
- Size of the boundary relative to wavelength of the
ultrasound beam.
- Irregularities of the shape on the surface of the reflector
What’s the difference between Wave Reflection Types
-specular
-Medium
-Scattered
specular → large impedance→ large reflection reducing wave amplitude
Medium→ dense tissue(muscle)
Scattered(diffuse)→ soft tissue(liver)
When a sound wave hits the body:
- part of the wave is reflected
- part is transmitted into the
body
in interference The alternating pattern produces a ……………..
beat
If an ultrasound wave meets, at an oblique angle, a boundary
between two media having different speeds of sound, the transmitted wave will be …………
deflected
(ultrasound waves) if the velocities are equal, There would be no …………..occurred
and the beam goes straight into the second medium
refraction
the velocities of the different tissues in the human body are
quite close, refraction's can be ………
ignored
A echoes is a ………..sound wave
reflected
Sonar systems use ………… to map out objects
underwater
sound waves
The amount of time it takes for echoes to return
depends on …………… the reflecting surface is
how far away
……………. – the ability to emit high pitched
squeaks and listen for echoes. Bats and dolphins use it
Echolocation
In ………………. sound is received by chest piece and sent to the earpieces by multiple reflecting through a long tube.
stethoscope,
In doppler, As you move closer to the source you encounter each sound wave a ……………,ex of using doppler effect are……
little earlier, radar for speeding cars
The closer you get the …………the pitch
higher
When you move away , each sound wave takes longer to reach
you, you hear fewer ……………., which results in a …………pitch
wavelength, lower
Clinical Ultrasound – uses……….. sound waves
high frequency