EE 8 - Three-Phase Transformer Connections
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Three Phase
Transformers used to step-up or step-down high voltages in power transmission systems are called _ transformers.
Iron Core
A three-phase transformer consists of three sets of primary and secondary windings wound around an _ assembly.
Amperage
The electric grid uses a three-phase system because it allows for higher transmission at lower _.
Reduces
Using higher gauge (thinner) copper wire in three-phase systems significantly ___ material and labor costs.
Core Type
The type of construction where the core has three limbs in the same plane and each leg carries both LV and HV windings
Core
In Core Type construction, the low voltage windings are insulated from the __ rather than the High Voltage windings.
Shell Type
The type of construction where each phase has its individual magnetic circuit, similar to three single-phase transformers stacked
Magnetic Fluxes
When the primary is excited with a three-phase source, currents flow through individual windings producing _.
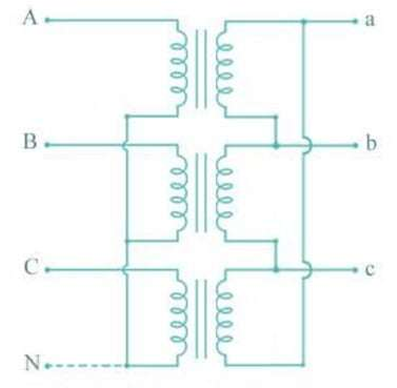
Star-Delta
The connection type commonly used to step-down voltages in transmission end substations
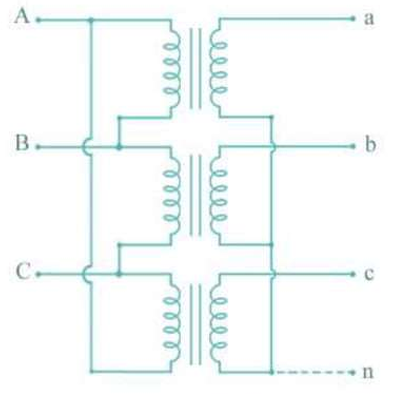
Delta-Star
The connection type used to step-up voltage, commonly employed at the sending end of high tension transmission systems
4 (or Four)
In a Delta-Star connection, the secondary is connected in star fashion so that a _ wire system is possible.
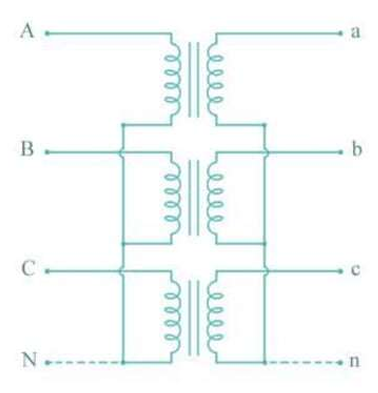
Delta-Delta
The connection type generally employed for three-phase power loads like motors where the load needs single voltage with high current
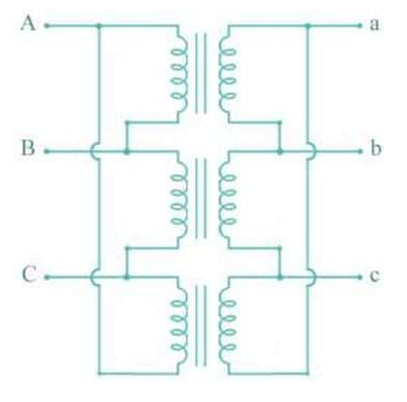
Star-Star
The connection type where both primary and secondary are connected in star and there is no phase difference between voltages
Operating Frequency
In the formula for Turns per Volt $1 / (4.44 \times f \times B \times A)$, 'f' stands for _.
Magnetic Flux Density
In the formula for Turns per Volt, 'B' represents the _.
Iron Losses
Losses caused by the alternating flux in the core, also known as Core loss
Copper Losses
Losses that occur due to the transformer winding resistance ($I^2R$ loss)
Hysteresis Losses
Losses occurring because of the variation of magnetization in the core of the transformer
Eddy Current Losses
Losses caused by EMF circulating currents within the body of the conducting core material
Space
Compared to three single-phase units, a three-phase transformer is cheaper and occupies less _.
Whole Unit
A major disadvantage of three-phase transformers is that if one phase is defective, the _ must be shut down.
Capacity
Because three-phase transformers are typically self-cooled, their _ is reduced simultaneously.
Step Up
In the generation side of applications, the transformer is used to _ the voltage level.
Steps Down
In the distribution side for commercial use, the transformer _ the level of voltage.
120 degrees
The phase difference between any two phases in a three-phase system.
1/sqrt(3)
In a star connection, the phase voltage is _ times the line voltage.
Star-Star
The three-phase transformer connection generally used for small, high-voltage transformers.
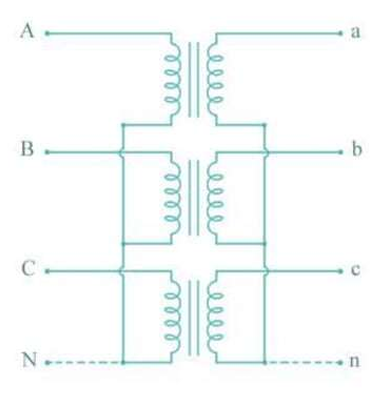
1/sqrt(3)
The amount of insulation required in a Star-Star connection is reduced because the phase voltage is only _ of the line voltage.
In phase or 0 degree shift
In a Star-Star connection, the line voltages on both sides are _ with each other.
Delta-Star
The type of connection mainly used in step-up transformers at the beginning of a transmission line.
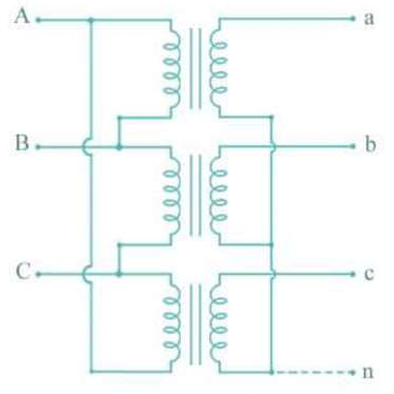
3-phase 4-wire
The Delta-Star connection allows for a _ service.
30 degrees
The phase shift between primary and secondary line voltages in a Delta-Star connection.
30 degrees
The Star-Delta connection has a phase shift of _ between primary and secondary line voltages.
Open Delta
The connection used when one transformer in a Delta-Delta bank is disabled but service must continue.
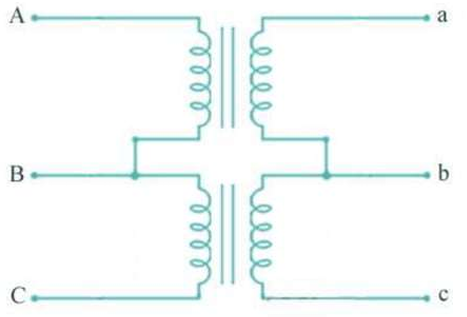
57.70%
The total load carrying capacity of an open delta connection is _ than that of a delta-delta connection.
Scott Connection
The type of connection using two transformers mainly for three-phase to two-phase conversion.

Main Transformer
In a Scott connection, the transformer that has center taps on both primary and secondary windings.
Teaser Transformer
In a Scott connection, the transformer other than the main transformer is called the _.