MCAT Uworld Flash Cards biochem peptides and proteins
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
The tertiary structure of a single polypeptide chain (also known as its native structure) is its most energetically favorable three-dimensional folded form. (True or False)
True. The tertiary structure of a single polypeptide chain (also known as its native structure) is its most energetically favorable three-dimensional folded form
A protein's ________ structure is described by the sequence of amino acid residues within the protein.
primary
α-Helices form [right/left]-handed coils that are stabilized by a [covalent/hydrogen/dipole-dipole] bond between the backbone C=O of one residue and the backbone NH of another residue four units away. (Choose one option for each)
right-hand; hydrogen
All proteins require proper quaternary structure to function. (True or False)
False. Not all proteins require proper quaternary structure to function.
Explanation:
Only proteins with multiple subunits have quaternary structure. These multisubunit proteins do require proper quaternary structure to function.
Name the two amino acids that are least likely to be found in an alpha helix.
roline and glycine are least likely to be found in α helices.
Proline is conformationally rigid and cannot contribute a hydrogen bond donor.
Glycine is too conformationally flexible to maintain the features of the alpha helix.
Which two amino acids are most commonly found in β-turns, which link adjacent antiparallel strands?
β-turns, which link adjacent antiparallel strands, commonly contain glycine and/or proline amino acids.
For most soluble proteins, their [hydrophilic/hydrophobic] side chains tend to be buried in the interior of the protein, whereas surface-exposed side chains tend to be [hydrophilic/hydrophobic]. (Choose one option for each)
For most soluble proteins, their hydrophobicside chains tend to be buried in the interior of the protein, whereas surface-exposed side chains tend to by hydrophilic.
Name three examples of noncovalent interactions and one example of a covalent bond between side chains that help stabilize protein tertiary structure.
Noncovalent interactions that stabilize tertiary structure include:
Hydrophobic interactions
Hydrogen bonds
Salt bridges
Ion-dipole interactions
Covalent interactions that stabilize tertiary structure include:
Disulfide bonds
Elements of protein secondary structure, such as -___ and ___-______, arise from interactions within the peptide _________.
Elements of protein secondary structure, such as α-helices and β-sheets, arise from interactions within the peptide backbone.
The average molecular weight of the amino acid residues in a protein is approximately 110 Daltons (Da), where 1 Da = 1 amu. (True or False)
rue. The average molecular weight of the amino acid residues in a protein is approximately 110 Daltons (Da), where 1 Da = 1 amu.
Higher levels of protein structure (secondary, tertiary, and quaternary) are independent of the primary structure. (True or False)
False. Higher levels of protein structure (secondary, tertiary, and quaternary) are dependent on the primary structure.
What is the term for a distinct region within a polypeptide that can fold and function independently of the rest of the polypeptide?
Protein domain -Protein domains are distinct regions within a polypeptide that can fold and function independently of the rest of the polypeptide.
How can one estimate the isoelectric point (pI) of a peptide if given its sequence and all of its pKa values?
The isoelectric point (pI) of a peptide can be estimated by averaging the pKa below which the peptide is positively charged and the pKaabove which the peptide is negatively charged.
n a polypeptide, which amino acid can often participate in both cis and trans peptide bonds?
proline
In biological systems, incoming amino acids are added to which end of a growing peptide chain?
New amino acids are added to the C-terminus of a growing peptide chain.
The only amino acid residues whose predominant forms contribute a negative charge to a peptide at physiological pH are ________ and __________.v
The only amino acid residues whose predominant forms contribute a negative charge to a peptide at physiological pH are aspartate and glutamate.
After two amino acids join together, six atoms—the two atoms of the peptide bond and the four attached to them—all lie in the same plane. (True or False)
True. After two amino acids join together, six atoms—the two atoms of the peptide bond and the four attached to them—all lie in the same plane.
What molecule is lost when a peptide bond forms, and what molecule is used to break a peptide bond?
water
When reading a protein sequence that has been written down, the left end of the sequence is the [N-terminal end/C-terminal end]. (Choose one option)
N-terminal end
Most peptide bonds adopt the [cis/trans] configuration. (Choose one option)
trans
Arginine and lysine residues contribute a [positive/negative] charge to a peptide's net charge at physiological pH (7.4). (Choose one option)
positive
The amino acid residues in a peptide are linked to each other through _______ _______, which form when the ___________ group of one amino acid backbone reacts with the ________ group of another.
The amino acids in a peptide are linked to each other through peptide bonds, which form when the carboxyl group of one amino acid backbone reacts with the amino group of another.
During isoelectric focusing (IEF), as proteins migrate through a gel with a ____ gradient, each protein's ____ ______ changes.
Proteins stop migrating at the point where the pH equals the protein's __________ _______.
During isoelectric focusing, as proteins migrate through a gel with a pH gradient, each protein's net charge changes.
Proteins stop migrating at the point where the pH equals the protein's isoelectric point (pI).
The nitrogen (N) atom in a peptide bond is ____hybridized.
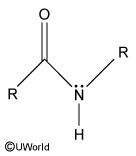
The nitrogen (N) atom in a peptide bond is sp2hybridized.
Explanation:
The nitrogen lone pair participates in resonance with the adjacent carbonyl, giving the peptide bond partial double bond character.
What does it mean for peptide bonds to be kinetically stable?
Although it is thermodynamically favorable for peptides to hydrolyze (break down), peptide bond hydrolysis has a high activation energy.
This means hydrolysis is slow and peptide bonds are unlikely to hydrolyze without a catalyst present.
A peptide's properties depend only on the combination of amino acids used, not on the order in which they are arranged. (True or False)
False. A peptide's properties depend both on the combination of amino acids used and the order in which those amino acids are arranged.
Example:
The following tripeptides have the same amino acid combination but different structures and propertie
Peptide bond formation is thermodynamically [favorable/unfavorable]. (Choose one option)
Peptide bond formation is thermodynamically unfavorable.