BIO EXAM
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/132
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
1
New cards
b
What results from an unequal sharing of electrons between atoms
a) a nonpolar covalent bond
b) a polar covalent bond
c) an ionic bond
d) a hydrogen bond
e) a hydrophobic bond
a) a nonpolar covalent bond
b) a polar covalent bond
c) an ionic bond
d) a hydrogen bond
e) a hydrophobic bond
2
New cards
e
which of the following correctly describes water's unique properties
a)Hydrogen bonds in liquid water form a crystalline structure.
b)Water has a low heat of vaporization resulting in the evaporative cooling effect we experience when we sweat.
c)Water has a low specific heat resulting in a significant amount of heat being released when hydrogen bonds form.
d) Water is a non-polar molecule because oxygen and hydrogen have the same electronegativities.
e)Water molecules like to stick together due to hydrogen bonding.
a)Hydrogen bonds in liquid water form a crystalline structure.
b)Water has a low heat of vaporization resulting in the evaporative cooling effect we experience when we sweat.
c)Water has a low specific heat resulting in a significant amount of heat being released when hydrogen bonds form.
d) Water is a non-polar molecule because oxygen and hydrogen have the same electronegativities.
e)Water molecules like to stick together due to hydrogen bonding.
3
New cards
b
which of the following correctly describes electrons
a) An electron can move from one shell to another only if the energy the electron gains is greater than the difference in energy between the energy levels of the two shells.
b) Electrons are involved in the chemical reactions between atoms.
c) Electrons are neutral.
d) Electrons can move from the nucleus to higher energy levels when they absorb energy.
e) Protons, neutrons and electrons have equal mass.
a) An electron can move from one shell to another only if the energy the electron gains is greater than the difference in energy between the energy levels of the two shells.
b) Electrons are involved in the chemical reactions between atoms.
c) Electrons are neutral.
d) Electrons can move from the nucleus to higher energy levels when they absorb energy.
e) Protons, neutrons and electrons have equal mass.
4
New cards
d
Which or the following correctly describes a cell
a) A cell is not able to perform all the functions of life.
b) Cells may group together to form tissues but are not able to perform a specialized function until higher levels of structure.
c) One example of a specialized tissue is a chloroplast.
d) The cell is the fundamental unit of living organisms.
e) There are 5 different types of molecules within a cell.
a) A cell is not able to perform all the functions of life.
b) Cells may group together to form tissues but are not able to perform a specialized function until higher levels of structure.
c) One example of a specialized tissue is a chloroplast.
d) The cell is the fundamental unit of living organisms.
e) There are 5 different types of molecules within a cell.
5
New cards
b
A compound contains hydroxyl groups as its predominant functional group. Which of the following statements is true concerning this compound?
a) It lacks an asymmetric carbon, and it is probably a fat or lipid.
b)It should dissolve in water.
c)It should dissolve in a nonpolar solvent.
d)It won't form hydrogen bonds with water.
e)It is hydrophobic.
a) It lacks an asymmetric carbon, and it is probably a fat or lipid.
b)It should dissolve in water.
c)It should dissolve in a nonpolar solvent.
d)It won't form hydrogen bonds with water.
e)It is hydrophobic.
6
New cards
b
What does Darwin's proposed mechanism of natural selection require
a)The environments must vary for natural selection to occur.
b)The species' environments selects for certain traits.
c)The environment increases the variation in a species.
d)Natural selection requires equal reproductive success of individuals with different traits.
e)Individuals with new traits always survive for a shorter period of time.
a)The environments must vary for natural selection to occur.
b)The species' environments selects for certain traits.
c)The environment increases the variation in a species.
d)Natural selection requires equal reproductive success of individuals with different traits.
e)Individuals with new traits always survive for a shorter period of time.
7
New cards
e
From its atomic number of 15, it is possible to predict that the phosphorus atom has
a)15 neutrons.
b)15 protons.
c)15 electrons.
d)8 electrons in its outermost electron shell.
e)15 protons and 15 electrons.
a)15 neutrons.
b)15 protons.
c)15 electrons.
d)8 electrons in its outermost electron shell.
e)15 protons and 15 electrons.
8
New cards
b
How is organic chemistry currently defined
a)the study of compounds made only by living cells
b)the study of carbon compounds
c)the study of vital forces
d)the study of natural (as opposed to synthetic) compounds
e)the study of hydrocarbons
a)the study of compounds made only by living cells
b)the study of carbon compounds
c)the study of vital forces
d)the study of natural (as opposed to synthetic) compounds
e)the study of hydrocarbons
9
New cards
d
How many electron pairs does carbon share in order to complete its valence shell?
a)1
b)2
c)3
d)4
e)8
a)1
b)2
c)3
d)4
e)8
10
New cards
b
What does each bondin carbon dioxide represent
a)one resonating electron
b) a pair of shared electrons
c) two pairs of shared electrons
d) a pair of protons
e)a donated electron
a)one resonating electron
b) a pair of shared electrons
c) two pairs of shared electrons
d) a pair of protons
e)a donated electron
11
New cards
c
The atomic number of nitrogen is 7. Nitrogen-15 is heavier than nitrogen-14 because the atomic nucleus of nitrogen-15 contains how many neutrons
a)6
b)7
c)8
d)12
e)14
a)6
b)7
c)8
d)12
e)14
12
New cards
c
One difference between carbon-12 and carbon-14 is that carbon 14 has
a)two more protons than carbon-12.
b)two more electrons than carbon-12.
c)two more neutrons than carbon-12.
d)two more protons and two more neutrons than carbon-12.
e)two more electrons and two more neutrons than carbon-12.
a)two more protons than carbon-12.
b)two more electrons than carbon-12.
c)two more neutrons than carbon-12.
d)two more protons and two more neutrons than carbon-12.
e)two more electrons and two more neutrons than carbon-12.
13
New cards
d
Which of the following is a correct sequence of level in life's hierarchy proceeding downward from an individual animal
a)brain, organ system, nerve cell, nervous tissue
b)organ system, nervous tissue, brain
c)organism, organ system, tissue, cell, organ
d)nervous system, brain, nervous tissue, nerve cell
e)organ system, tissue, molecule, cell
a)brain, organ system, nerve cell, nervous tissue
b)organ system, nervous tissue, brain
c)organism, organ system, tissue, cell, organ
d)nervous system, brain, nervous tissue, nerve cell
e)organ system, tissue, molecule, cell
14
New cards
d
When two atoms are equally electronegative they will interact to form
a)hydrogen bonds.
b)van der Waals interactions.
c)polar covalent bonds.
d)nonpolar covalent bonds.
e)ionic bonds.
a)hydrogen bonds.
b)van der Waals interactions.
c)polar covalent bonds.
d)nonpolar covalent bonds.
e)ionic bonds.
15
New cards
b
Which of the four classes of biological molecules is not a polymer?
a)carbohydrates
b)lipids
c)proteins
d)nucleic acids
e)All can be considered polymers.
a)carbohydrates
b)lipids
c)proteins
d)nucleic acids
e)All can be considered polymers.
16
New cards
b
Which claa of biological molecules are grouped together because they are hydrophobic
a)carbohydrates
b)lipids
c)proteins
d)nucleic acids
e)This is not a criterion for grouping molecules.
a)carbohydrates
b)lipids
c)proteins
d)nucleic acids
e)This is not a criterion for grouping molecules.
17
New cards
c
what is the covalent bond formed between two monosaccharides by way of dehydration called
a)hydrogen bond
b)sulphide bridge
c)glycosidic linkage
d)glucose bridge
e)disaccharide linkage
a)hydrogen bond
b)sulphide bridge
c)glycosidic linkage
d)glucose bridge
e)disaccharide linkage
18
New cards
d
Which of the following is an example of hydrolysis?
a)the reaction of two monosaccharides joining together to form a disaccharide with the release of water
b)the reaction of two amino acids joining together to form a peptide with the release of water
c)the synthesis of a fat from glycerol and fatty acids with the release of water
d)the breakdown of a fat, forming glycerol and fatty acids with the consumption of water
e)the synthesis of a nucleotide from a phosphate, a pentose sugar, and a nitrogenous base with the production of a molecule of water
a)the reaction of two monosaccharides joining together to form a disaccharide with the release of water
b)the reaction of two amino acids joining together to form a peptide with the release of water
c)the synthesis of a fat from glycerol and fatty acids with the release of water
d)the breakdown of a fat, forming glycerol and fatty acids with the consumption of water
e)the synthesis of a nucleotide from a phosphate, a pentose sugar, and a nitrogenous base with the production of a molecule of water
19
New cards
b
Trans fats resemble saturated fats in that
a)have no carbon-carbon double bonds.
b)stack tightly because of their straight tails.
c)are found only in plants.
d)have only two fatty acid chains.
e)are none of these.
a)have no carbon-carbon double bonds.
b)stack tightly because of their straight tails.
c)are found only in plants.
d)have only two fatty acid chains.
e)are none of these.
20
New cards
c
Why are humans able to digest starch but not cellulose
a)the monomer of starch is glucose, while the monomer of cellulose is galactose
b)humans have enzymes that can hydrolyze the β glycosidic linkages of starch but not the α glycosidic linkages of cellulose
c)humans have enzymes that can hydrolyze the α glycosidic linkages of starch but not the β glycosidic linkages of cellulose
d)humans harbor starch-digesting bacteria in the digestive tract
e)the monomer of starch is glucose, while the monomer of cellulose is glucose with a nitrogen-containing group
a)the monomer of starch is glucose, while the monomer of cellulose is galactose
b)humans have enzymes that can hydrolyze the β glycosidic linkages of starch but not the α glycosidic linkages of cellulose
c)humans have enzymes that can hydrolyze the α glycosidic linkages of starch but not the β glycosidic linkages of cellulose
d)humans harbor starch-digesting bacteria in the digestive tract
e)the monomer of starch is glucose, while the monomer of cellulose is glucose with a nitrogen-containing group
21
New cards
c
There are 20 different amino acids. What makes one amino acid different from another
a)different side chains (R groups) attached to a carboxyl carbon
b)different side chains (R groups) attached to the amino groups
c)different side chains (R groups) attached to an α carbon
d)different structural and optical isomers
different asymmetric carbons
a)different side chains (R groups) attached to a carboxyl carbon
b)different side chains (R groups) attached to the amino groups
c)different side chains (R groups) attached to an α carbon
d)different structural and optical isomers
different asymmetric carbons
22
New cards
a
The enzyme amylase can break glycosidc linkages between glucose monomer only if the monomers are the alpha form. Which of the following molecules could amylase break down
a)glycogen
b)cellulose
c)chitin
d)glycogen and chitin only
e)glycogen, cellulose, and chitin
a)glycogen
b)cellulose
c)chitin
d)glycogen and chitin only
e)glycogen, cellulose, and chitin
23
New cards
c
What is the chemical reaction by which cells make polymers from monomers
a)phosphodiester linkages
b)hydrolysis
c)dehydration reactions
d) ionic bonding of monomers
e)the formation of disulphide bridges between monomers
a)phosphodiester linkages
b)hydrolysis
c)dehydration reactions
d) ionic bonding of monomers
e)the formation of disulphide bridges between monomers
24
New cards
c
Which of the following characteristics of protein will remain intact if the protein is denatured
a)the shape of the protein
b)the function of the protein
c)the number of amino acids in the protein
d)the binding properties of the protein
e)All of the answers are correct
a)the shape of the protein
b)the function of the protein
c)the number of amino acids in the protein
d)the binding properties of the protein
e)All of the answers are correct
25
New cards
c
what is the structure in the figure above
a)pentose molecule
b)fatty acid molecule
c)steroid molecule
d)oligosaccharide molecule
e)phospholipid molecule
a)pentose molecule
b)fatty acid molecule
c)steroid molecule
d)oligosaccharide molecule
e)phospholipid molecule
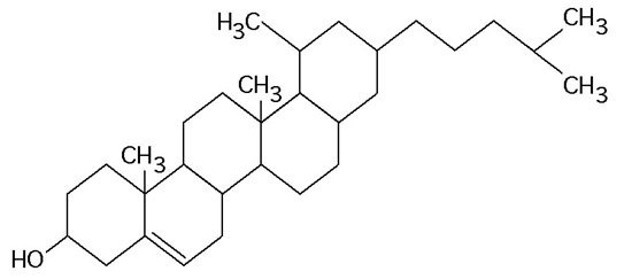
26
New cards
b
What is the likely classification of a molecule with the formula C18H36O2
a) carbohydrate
b) fatty acid
c) protein
d) nucleic acid
e) hydrocarbon
a) carbohydrate
b) fatty acid
c) protein
d) nucleic acid
e) hydrocarbon
27
New cards
c
Which class of biological molecules are grouped together because their monomers are amino acids
a) carbohydrates
b) lipids
c) proteins
d) nucleic acids
a) carbohydrates
b) lipids
c) proteins
d) nucleic acids
28
New cards
c
Which of the following is not a monomer/polymer pairing
a)monosaccharide/polysaccharide
b)amino acid/protein
c)triglyceride/phospholipid bilayer
d)deoxyribonucleotide/DNA
e)ribonucleotide/RNA
a)monosaccharide/polysaccharide
b)amino acid/protein
c)triglyceride/phospholipid bilayer
d)deoxyribonucleotide/DNA
e)ribonucleotide/RNA
29
New cards
c
At hwihc level of proetin structure are intercation vetween the side chain (R groups) most important
a)primary
b)secondary
c)tertiary
d) quaternary
e) all of the above
a)primary
b)secondary
c)tertiary
d) quaternary
e) all of the above
30
New cards
c
Plasmodesmata in plant cells are most similar in function to which of the following structures in animal cells?
a)peroxisomes
b)desmosomes
c)gap junctions
d)extracellular matrix
e)tight junctions
a)peroxisomes
b)desmosomes
c)gap junctions
d)extracellular matrix
e)tight junctions
31
New cards
b
What are the two domains prokaryotes belong to
a)Bacteria and Eukarya
b)Bacteria and Archaea
c)Archaea and Protista
d)Bacteria and Protista
e)Eukarya and Protista
a)Bacteria and Eukarya
b)Bacteria and Archaea
c)Archaea and Protista
d)Bacteria and Protista
e)Eukarya and Protista
32
New cards
phagocytosis
Amoeba engulf bacteria through what process
33
New cards
pinocytosis
an organism non-selectivelu takes in droplets of water and small molecules
34
New cards
b
which of the following organelles contains hydrolytic enzymes in animal cells
a)chloroplast
b)lysosome
c)central vacuole
d)peroxisome
e)glyoxysome
a)chloroplast
b)lysosome
c)central vacuole
d)peroxisome
e)glyoxysome
35
New cards
microtubules; muscle contraction
which structure-function pair is mismatched
a)nucleolus; production of ribosomal subunits
b)lysosome; intracellular digestion
c)ribosome; protein synthesis
d)Golgi; protein trafficking
e)microtubule; muscle contraction
a)nucleolus; production of ribosomal subunits
b)lysosome; intracellular digestion
c)ribosome; protein synthesis
d)Golgi; protein trafficking
e)microtubule; muscle contraction
36
New cards
a
What results from the presence of cholesterol in the plasma membranes of some animals
a)The membrane stays fluid more easily when cell temperature drops.
b)The animal removes hydrogen atoms from saturated phospholipids.
c)The animal adds hydrogen atoms to unsaturated phospholipids.
d)The membrane is less flexible, allowing it to sustain greater pressure from within the cell.
e)The animal is more susceptible to circulatory disorders.
a)The membrane stays fluid more easily when cell temperature drops.
b)The animal removes hydrogen atoms from saturated phospholipids.
c)The animal adds hydrogen atoms to unsaturated phospholipids.
d)The membrane is less flexible, allowing it to sustain greater pressure from within the cell.
e)The animal is more susceptible to circulatory disorders.
37
New cards
a
Which of the following is a reasonable explanation for why unsaturated fatty acids help keep any membrane more fluid at lower temperatures
a)The double bonds form kinks in the fatty acid tails, preventing adjacent lipids from packing tightly.
b)Unsaturated fatty acids have a higher cholesterol content and therefore more cholesterol in membranes.
c)Unsaturated fatty acids are more polar than saturated fatty acids.
d)The double bonds block interaction among the hydrophilic head groups of the lipids.
e)The double bonds result in shorter fatty acid tails and thinner membranes.
a)The double bonds form kinks in the fatty acid tails, preventing adjacent lipids from packing tightly.
b)Unsaturated fatty acids have a higher cholesterol content and therefore more cholesterol in membranes.
c)Unsaturated fatty acids are more polar than saturated fatty acids.
d)The double bonds block interaction among the hydrophilic head groups of the lipids.
e)The double bonds result in shorter fatty acid tails and thinner membranes.
38
New cards
d
How does the cell multiply peroxisomes
a)They bud off from the Golgi.
b)They are brought into the cell from the environment.
c)They are built de novo from cytosol materials.
d)They split in two after they become sufficiently large.
e)The cell synthesizes hydrogen peroxide and encloses it in a membrane.
a)They bud off from the Golgi.
b)They are brought into the cell from the environment.
c)They are built de novo from cytosol materials.
d)They split in two after they become sufficiently large.
e)The cell synthesizes hydrogen peroxide and encloses it in a membrane.
39
New cards
d
Which of the following statements correctly describes the normal tonicity condition for a typical plant and animal cells
a)The animal cell is in a hypotonic solution, and the plant cell is in an isotonic solution.
b)The animal cell is in an isotonic solution, and the plant cell is in a hypertonic solution.
c)The animal cell is in a hypertonic solution, and the plant cell is in an isotonic solution.
d)The animal cell is in an isotonic solution, and the plant cell is in a hypotonic solution.
e)The animal cell is in a hypertonic solution, and the plant cell is in a hypotonic solution.
a)The animal cell is in a hypotonic solution, and the plant cell is in an isotonic solution.
b)The animal cell is in an isotonic solution, and the plant cell is in a hypertonic solution.
c)The animal cell is in a hypertonic solution, and the plant cell is in an isotonic solution.
d)The animal cell is in an isotonic solution, and the plant cell is in a hypotonic solution.
e)The animal cell is in a hypertonic solution, and the plant cell is in a hypotonic solution.
40
New cards
chloroplast
Thylakoids, DNA and ribosomes are all components in which organelle
41
New cards
c
which of the following is true of osmosis
a)Osmosis only occurs in red blood cells.
b)Osmosis is an energy-demanding or active process.
c)In osmosis, water moves across a membrane from areas of lower solute concentration to areas of higher solute concentration.
d)In osmosis, solutes move across a membrane from areas of lower water concentration to areas of higher water concentration.
e)Osmosis only occurs in eukaryotes.
a)Osmosis only occurs in red blood cells.
b)Osmosis is an energy-demanding or active process.
c)In osmosis, water moves across a membrane from areas of lower solute concentration to areas of higher solute concentration.
d)In osmosis, solutes move across a membrane from areas of lower water concentration to areas of higher water concentration.
e)Osmosis only occurs in eukaryotes.
42
New cards
c
A cell has the following molecules and structures: enzymes, DNA, ribosomes, plasma membrane and mitochondria. What kind of cell might it be
a)a bacterium
b)an animal, but not a plant
c)nearly any eukaryotic organism
d)any multicellular organism, like a plant or an animal
e) any kind of organism
a)a bacterium
b)an animal, but not a plant
c)nearly any eukaryotic organism
d)any multicellular organism, like a plant or an animal
e) any kind of organism
43
New cards
b
which or the following is present in a prokaryotic cell
a)mitochondrion
b)ribosome
c)nuclear envelope
d)chloroplast
e)ER
a)mitochondrion
b)ribosome
c)nuclear envelope
d)chloroplast
e)ER
44
New cards
e
Which of the following is not part of prokaryotic cell
a)DNA
b)a cell wall
c)a plasma membrane
d)ribosomes
e) an endoplasmic reticulum
a)DNA
b)a cell wall
c)a plasma membrane
d)ribosomes
e) an endoplasmic reticulum
45
New cards
a
which of the following statements is true about enzyme-catalyzed reactions
a)The reaction is faster than the same reaction in the absence of the enzyme.
b)The free energy change of the reaction is opposite from the reaction that occurs in the absence of the enzyme.
c)The reaction always goes in the direction toward chemical equilibrium.
d)Enzyme-catalyzed reactions require energy to activate the enzyme.
e)Enzyme-catalyzed reactions release more free energy than noncatalyzed reactions.
a)The reaction is faster than the same reaction in the absence of the enzyme.
b)The free energy change of the reaction is opposite from the reaction that occurs in the absence of the enzyme.
c)The reaction always goes in the direction toward chemical equilibrium.
d)Enzyme-catalyzed reactions require energy to activate the enzyme.
e)Enzyme-catalyzed reactions release more free energy than noncatalyzed reactions.
46
New cards
e
what is a chemical agent that speeds up a reaction without being consumed during the reaction
a)an enhancer
b)a substrate
c)a co-enzyme
d)a reactant
e)a catalyst
a)an enhancer
b)a substrate
c)a co-enzyme
d)a reactant
e)a catalyst
47
New cards
b
How does a noncompetitive inhibitor decrease the rate of an enzyme reaction
a)by binding at the active site of the enzyme
b)by changing the shape of the enzyme's active site
c)by changing the free energy change of the reaction
d)by acting as a coenzyme for the reaction
e)by decreasing the activation energy of the reaction
a)by binding at the active site of the enzyme
b)by changing the shape of the enzyme's active site
c)by changing the free energy change of the reaction
d)by acting as a coenzyme for the reaction
e)by decreasing the activation energy of the reaction
48
New cards
a
Biological evolution of life on Earth, from simple prokaryote-like cells to large multicellular eukaryotic organisms
a)has occurred in accordance with the laws of thermodynamics.
b)has caused an increase in the entropy of the planet.
c)has been made possible by expending Earth's energy resources.
d)has occurred in accordance with the laws of thermodynamics, by expending Earth's energy resources and causing an increase in the entropy of the planet.
e)violates the laws of thermodynamics because Earth is a closed system.
a)has occurred in accordance with the laws of thermodynamics.
b)has caused an increase in the entropy of the planet.
c)has been made possible by expending Earth's energy resources.
d)has occurred in accordance with the laws of thermodynamics, by expending Earth's energy resources and causing an increase in the entropy of the planet.
e)violates the laws of thermodynamics because Earth is a closed system.
49
New cards
c
why are some bacteria metabolically active in hot springs
a)They are able to maintain a lower internal temperature.
b)High temperatures make catalysis unnecessary.
c)Their enzymes have high optimal temperatures.
d)Their enzymes are completely insensitive to temperature.
e)They use molecules other than proteins or RNAs as their main catalysts.
a)They are able to maintain a lower internal temperature.
b)High temperatures make catalysis unnecessary.
c)Their enzymes have high optimal temperatures.
d)Their enzymes are completely insensitive to temperature.
e)They use molecules other than proteins or RNAs as their main catalysts.
50
New cards
d
What is the kinetic energy associated with the random movement of atoms
a)entropy
d)work
c)chemical energy
d)thermal energy
e)heat
a)entropy
d)work
c)chemical energy
d)thermal energy
e)heat
51
New cards
a
How is a chemical reaction that has a positive delta G correctly described
a)endergonic
b)endothermic
c)enthalpic
d)spontaneous
e)exothermic
a)endergonic
b)endothermic
c)enthalpic
d)spontaneous
e)exothermic
52
New cards
b
a molecule binds between two subunits and stabilizes the active form of an enzyme. What does this describe
a)allosteric inhibition
b)allosteric activation
c)cooperativity
d)competitive activation
e)feedback activation
a)allosteric inhibition
b)allosteric activation
c)cooperativity
d)competitive activation
e)feedback activation
53
New cards
d
What is allosteric enzyme regulation usually associated with
a)lack of cooperativity
b)feedback inhibition
c)activating activity
d)an enzyme with more than one subunit
e)the need for cofactors
a)lack of cooperativity
b)feedback inhibition
c)activating activity
d)an enzyme with more than one subunit
e)the need for cofactors
54
New cards
b
which of the following statements is true concerning catabolic pathways
a)They combine molecules into more energy-rich molecules.
b)They supply energy, primarily in the form of ATP, for the cell's work.
c)They are endergonic.
d)They are spontaneous and do not need enzyme catalysis.
e)They build up complex molecules such as protein from simpler compounds.
a)They combine molecules into more energy-rich molecules.
b)They supply energy, primarily in the form of ATP, for the cell's work.
c)They are endergonic.
d)They are spontaneous and do not need enzyme catalysis.
e)They build up complex molecules such as protein from simpler compounds.
55
New cards
b
Why is ATP an important molecule in metabolism
a)Its hydrolysis provides an input of free energy for exergonic reactions.
b)It provides energy coupling between exergonic and endergonic reactions.
c)Its terminal phosphate group contains a strong covalent bond that, when hydrolyzed, releases free energy.
d)Its terminal phosphate bond has higher energy than the other two.
e)It is one of the four building blocks for DNA synthesis.
a)Its hydrolysis provides an input of free energy for exergonic reactions.
b)It provides energy coupling between exergonic and endergonic reactions.
c)Its terminal phosphate group contains a strong covalent bond that, when hydrolyzed, releases free energy.
d)Its terminal phosphate bond has higher energy than the other two.
e)It is one of the four building blocks for DNA synthesis.
56
New cards
d
What type of reaction absorbs free energy from its surroundings
a)spontaneous
b)endothermic
c)exothermic
d)endergonic
e)exergonic
exergonic
a)spontaneous
b)endothermic
c)exothermic
d)endergonic
e)exergonic
exergonic
57
New cards
b
Reactants capable of interacting form products in a chemical reaction must first overcome a thermodynamic barrier
a)The reaction's entropy.
b)The reaction's activation energy.
c)The reaction's endothermic level.
d)The reaction's equilibrium point.
e)The reaction's free-energy content.
a)The reaction's entropy.
b)The reaction's activation energy.
c)The reaction's endothermic level.
d)The reaction's equilibrium point.
e)The reaction's free-energy content.
58
New cards
b
which of the following precisely describes the mechanism where and end product of a metabolic pathway inhibits an earlier step in the pathway
a)metabolic inhibition
b)feedback inhibition
c)allosteric inhibition
d)noncooperative inhibition
e)reversible inhibition
a)metabolic inhibition
b)feedback inhibition
c)allosteric inhibition
d)noncooperative inhibition
e)reversible inhibition
59
New cards
b
which of the following statements regarding enzymes is true
a)Enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by making the reaction more exergonic.
b)Enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering the activation energy barrier.
c)Enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by reducing the rate of reverse reactions.
d)Enzymes change the equilibrium point of the reactions they catalyze.
e)Enzymes make the rate of a reaction independent of substrate concentrations.
a)Enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by making the reaction more exergonic.
b)Enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering the activation energy barrier.
c)Enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by reducing the rate of reverse reactions.
d)Enzymes change the equilibrium point of the reactions they catalyze.
e)Enzymes make the rate of a reaction independent of substrate concentrations.
60
New cards
b
During aerobic respiration, electrons travel downhill in which sequence
a)food → citric acid cycle → ATP → NAD+
b)food → NADH → electron transport chain → oxygen
c)glucose → pyruvate → ATP → oxygen
d)glucose → ATP → electron transport chain → NADH
e)food → glycolysis → citric acid cycle → NADH → ATP
a)food → citric acid cycle → ATP → NAD+
b)food → NADH → electron transport chain → oxygen
c)glucose → pyruvate → ATP → oxygen
d)glucose → ATP → electron transport chain → NADH
e)food → glycolysis → citric acid cycle → NADH → ATP
61
New cards
e
Where does glycolysis take place in eucaryote cells
a)mitochondrial matrix
b)mitochondrial outer membrane
c)mitochondrial inner membrane
d)mitochondrial intermembrane space
e)cytosol
a)mitochondrial matrix
b)mitochondrial outer membrane
c)mitochondrial inner membrane
d)mitochondrial intermembrane space
e)cytosol
62
New cards
b
Which process in eukaryotic cells will proceed normally whether oxygen (O) is present or absent
a)electron transport
b)glycolysis
c)the citric acid cycle
d)oxidative phosphorylation
e)chemiosmosis
a)electron transport
b)glycolysis
c)the citric acid cycle
d)oxidative phosphorylation
e)chemiosmosis
63
New cards
c
Where are the proteins of the electron transport chain located
a)cytosol
b)mitochondrial outer membrane
c)mitochondrial inner membrane
d)mitochondrial intermembrane space
e)mitochondrial matrix
a)cytosol
b)mitochondrial outer membrane
c)mitochondrial inner membrane
d)mitochondrial intermembrane space
e)mitochondrial matrix
64
New cards
a
Which of the following statements describes NAD+
a)NAD+ is reduced to NADH during glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, and the citric acid cycle.
b)NAD+ has more chemical energy than NADH.
c)NAD+ is oxidized by the action of hydrogenases.
d)NAD+ can donate electrons for use in oxidative phosphorylation.
e)In the absence of NAD+, glycolysis can still function.
a)NAD+ is reduced to NADH during glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, and the citric acid cycle.
b)NAD+ has more chemical energy than NADH.
c)NAD+ is oxidized by the action of hydrogenases.
d)NAD+ can donate electrons for use in oxidative phosphorylation.
e)In the absence of NAD+, glycolysis can still function.
65
New cards
a
Why does glucose oxidation occur in a series of steps
a)One step wouldn't allow the energy released to be harnessed efficiently.
b)It doesn't have to; it just happens to be that way.
c)Glycolysis evolved first and steps were just added over time.
d)Glucose cannot pass into the mitochondria and oxygen cannot enter the cytosol.
e)Glucose is reduced, not oxidized.
a)One step wouldn't allow the energy released to be harnessed efficiently.
b)It doesn't have to; it just happens to be that way.
c)Glycolysis evolved first and steps were just added over time.
d)Glucose cannot pass into the mitochondria and oxygen cannot enter the cytosol.
e)Glucose is reduced, not oxidized.
66
New cards
a
What is the electron transport chain
a)a series of redox reactions
b)a series of substitution reactions
c)reactions driven by ATP consumption
d)reactions occurring in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells
e)a series of condensation reactions
a)a series of redox reactions
b)a series of substitution reactions
c)reactions driven by ATP consumption
d)reactions occurring in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells
e)a series of condensation reactions
67
New cards
\
c
c
Which of the following events takes place in the electron transport chain
a)the breakdown of glucose into two pyruvate molecules
b)the breakdown of an acetyl group to carbon dioxide
c)the extraction of energy from high-energy electrons remaining from glycolysis and the citric acid cycle
d)substrate-level phosphorylation
e)reduction ADP to ATP
a)the breakdown of glucose into two pyruvate molecules
b)the breakdown of an acetyl group to carbon dioxide
c)the extraction of energy from high-energy electrons remaining from glycolysis and the citric acid cycle
d)substrate-level phosphorylation
e)reduction ADP to ATP
68
New cards
a
**C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy**
Which of the following statements describes the results of this reaction?
a)C6H12O6 is oxidized and O2 is reduced.
b)O2 is oxidized and H2O is reduced.
c)CO2 is reduced and O2 is oxidized.
d)C6H12O6 is reduced and CO2 is oxidized.
e)O2 is reduced and CO2 is oxidized.
Which of the following statements describes the results of this reaction?
a)C6H12O6 is oxidized and O2 is reduced.
b)O2 is oxidized and H2O is reduced.
c)CO2 is reduced and O2 is oxidized.
d)C6H12O6 is reduced and CO2 is oxidized.
e)O2 is reduced and CO2 is oxidized.
69
New cards
a
In alcohol fermentation NAD+ is regenerated from NADH by which of the following
a)reduction of acetaldehyde to ethanol (ethyl alcohol)
b)oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
c)reduction of pyruvate to form lactate
d)oxidation of ethanol to acetyl CoA
e)reduction of ethanol to pyruvate
a)reduction of acetaldehyde to ethanol (ethyl alcohol)
b)oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
c)reduction of pyruvate to form lactate
d)oxidation of ethanol to acetyl CoA
e)reduction of ethanol to pyruvate
70
New cards
d
WHich of the following intermediary metabolites enters the citric acid cycle and is formed, in part by the removal of a carbon CO from one molecule of pyruvate
a)lactate
b)glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate
c)oxaloacetate
d)acetyl CoA
e)citrate
a)lactate
b)glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate
c)oxaloacetate
d)acetyl CoA
e)citrate
71
New cards
c
How many oxygen molecules are required each time a molecule of glucose is completely oxidized to carbon dioxide and water via aerobic respiration
a) 1
b) 3
c) 6
d) 12
e) 30
a) 1
b) 3
c) 6
d) 12
e) 30
72
New cards
d
when hydrogen ions are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix across the inner membrane and into the inter-membrane space what is the result
a)formation of ATP
b)reduction of NAD+
c)restoration of the Na+/K+ balance across the membrane
d)creation of a proton-motive force
e)lowering of pH in the mitochondrial matrix
a)formation of ATP
b)reduction of NAD+
c)restoration of the Na+/K+ balance across the membrane
d)creation of a proton-motive force
e)lowering of pH in the mitochondrial matrix
73
New cards
c
when a molecule of NAD+ gains a hydrogen atom what happens to NAD+
a)NAD+ is dehydrogenated.
b)NAD+ is oxidized.
c)NAD+ is reduced.
d)NAD+ is redoxed.
e)NAD+ is hydrolyzed.
a)NAD+ is dehydrogenated.
b)NAD+ is oxidized.
c)NAD+ is reduced.
d)NAD+ is redoxed.
e)NAD+ is hydrolyzed.
74
New cards
100%
Substrate-level phosphorylation accounts for approximately what percentage of the ATP formed by the reactions of glycolysis
75
New cards
c
Chloroplasts contain disk-like membranous sacs arranged in stacks called
a)cristae.
b)thylakoids.
c)grana.
d)vacuoles.
e)plasmodesmata.
a)cristae.
b)thylakoids.
c)grana.
d)vacuoles.
e)plasmodesmata.
76
New cards
d
What event accompanies energy absorption by chlorophyll
a)ATP is synthesized from the energy absorbed.
b)A carboxylation reaction of the Calvin cycle occurs.
c)Electrons are stripped from NADPH.
d)An electron is excited.
e)A proton is sent to the thylakoid space.
a)ATP is synthesized from the energy absorbed.
b)A carboxylation reaction of the Calvin cycle occurs.
c)Electrons are stripped from NADPH.
d)An electron is excited.
e)A proton is sent to the thylakoid space.
77
New cards
c
What compound provides the reducing power for Calvin cycle reactions
a)ATP
b)NADP+
c)NADPH
d)NAD+
e)NADH
a)ATP
b)NADP+
c)NADPH
d)NAD+
e)NADH
78
New cards
e
Which of the following are products of the light reactions of photosynthesis that are utilized in the Calvin cycle?
a)CO2 and glucose
b)H2O and O2
c)ADP, Pi, and NADP+
d)electrons and H+
e)ATP and NADPH
a)CO2 and glucose
b)H2O and O2
c)ADP, Pi, and NADP+
d)electrons and H+
e)ATP and NADPH
79
New cards
b
In C3 photosynthesis, where do the reactions that require ATP take place?
a)only in the light reactions
b)only in the Calvin cycle
c)in both the light reactions and the Calvin cycle
d)in neither the light reactions nor the Calvin cycle
e)n the chloroplast, but they are not part of photosynthesis
a)only in the light reactions
b)only in the Calvin cycle
c)in both the light reactions and the Calvin cycle
d)in neither the light reactions nor the Calvin cycle
e)n the chloroplast, but they are not part of photosynthesis
80
New cards
b
In the thylakoid membranes, what is the main role of the antenna pigment molecules?
a)split water and release oxygen to the reaction-centre chlorophyll
b)harvest photons and transfer light energy to the reaction-centre chlorophyll
c)synthesize ATP from ADP and Pi
d)transfer electrons to ferredoxin and then NADPH
e)concentrate photons within the stroma
a)split water and release oxygen to the reaction-centre chlorophyll
b)harvest photons and transfer light energy to the reaction-centre chlorophyll
c)synthesize ATP from ADP and Pi
d)transfer electrons to ferredoxin and then NADPH
e)concentrate photons within the stroma
81
New cards
b
Which of the following are directly associated with photosytem 1
a)harvesting of light energy by ATP
b)receiving electrons from the thylakoid membrane electron transport chain
c)generation of molecular oxygen
d)extraction of hydrogen electrons from the splitting of water
e)passing electrons to the thylakoid membrane electron transport chain
a)harvesting of light energy by ATP
b)receiving electrons from the thylakoid membrane electron transport chain
c)generation of molecular oxygen
d)extraction of hydrogen electrons from the splitting of water
e)passing electrons to the thylakoid membrane electron transport chain
82
New cards
b
Why are C4 plants able to photosynthesize with no apparent photorespiration?
a)They do not participate in the Calvin cycle.
b)They use PEP carboxylase to initially fix CO2.
c)They are adapted to cold, wet climates.
d)They conserve water more efficiently.
e)They exclude oxygen from their tissues.
a)They do not participate in the Calvin cycle.
b)They use PEP carboxylase to initially fix CO2.
c)They are adapted to cold, wet climates.
d)They conserve water more efficiently.
e)They exclude oxygen from their tissues.
83
New cards
c
The electrons of photosystem II are excited and transferred to electron carriers. From which molecule or structure do the photosystem II replacement electrons come?
a)the electron carrier, plastocyanin
b)photosystem I
c)water
d)oxygen
e)carbon dioxide
a)the electron carrier, plastocyanin
b)photosystem I
c)water
d)oxygen
e)carbon dioxide
84
New cards
d
In a plant cell, where are the ATP synthase complexes located?
a)thylakoid membrane only
b)plasma membrane only
c)inner mitochondrial membrane only
d)thylakoid membrane and inner mitochondrial membrane
e)thylakoid membrane and plasma membrane
a)thylakoid membrane only
b)plasma membrane only
c)inner mitochondrial membrane only
d)thylakoid membrane and inner mitochondrial membrane
e)thylakoid membrane and plasma membrane
85
New cards
d
Where does photosynthesis occur in plants?
a)leaves
b)leaves and green stems
c)leaves, green stems, and unripened fruit
d)mostly in the leaves, but also in all plant tissues
e)all plant tissues, as all plant tissues need the carbohydrate produced by photosynthesis
a)leaves
b)leaves and green stems
c)leaves, green stems, and unripened fruit
d)mostly in the leaves, but also in all plant tissues
e)all plant tissues, as all plant tissues need the carbohydrate produced by photosynthesis
86
New cards
b
Where do reactions that require CO2 take place?
a)only in the light reactions
b)only in the Calvin cycle
c)in both the light reactions and the Calvin cycle
d)in neither the light reactions nor the Calvin cycle
e)in the chloroplast, but they are not part of photosynthesis
a)only in the light reactions
b)only in the Calvin cycle
c)in both the light reactions and the Calvin cycle
d)in neither the light reactions nor the Calvin cycle
e)in the chloroplast, but they are not part of photosynthesis
87
New cards
a
CAM plants keep stomata closed in daytime, thus reducing loss of water. Why can they can do this?
a)They fix CO2 into organic acids during the night.
b)They fix CO2 into sugars in the bundle-sheath cells.
c)They fix CO2 into pyruvate in the mesophyll cells.
d)They use the enzyme phosphofructokinase, which outcompetes rubisco for CO2.
e)They use photosystem I and photosystem II at night.
a)They fix CO2 into organic acids during the night.
b)They fix CO2 into sugars in the bundle-sheath cells.
c)They fix CO2 into pyruvate in the mesophyll cells.
d)They use the enzyme phosphofructokinase, which outcompetes rubisco for CO2.
e)They use photosystem I and photosystem II at night.
88
New cards
b
Where is the Calvin cycle located in a C4 plant?
a)stems
b)bundle sheath cells
c)mesophyll cells
d)stomata
e)the chloroplasts in leaves
a)stems
b)bundle sheath cells
c)mesophyll cells
d)stomata
e)the chloroplasts in leaves
89
New cards
b
Where did the process of photosynthesis probably originate?
a)plants
b)prokaryotes
c)fungi
d)three separate times during evolution
e)protists
a)plants
b)prokaryotes
c)fungi
d)three separate times during evolution
e)protists
90
New cards
c
Why do neurons and some other specialized cells divide infrequently?
a)They no longer have active nuclei.
b)They no longer carry receptors for signal molecules.
c)They have been shunted into G0.
d)They can no longer bind Cdk to cyclin.
e)They show a drop in MPF concentration.
a)They no longer have active nuclei.
b)They no longer carry receptors for signal molecules.
c)They have been shunted into G0.
d)They can no longer bind Cdk to cyclin.
e)They show a drop in MPF concentration.
91
New cards
E
The lettered circle in the figure shows a diploid nucleus with four chromosomes. There are two pairs of homologous chromosomes, one long and the other short. One haploid set is symbolized as black and the other haploid set is grey. The chromosomes in the unlettered circle have not yet replicated. What is the correct chromosomal condition for one daughter nucleus at telophase of mitosis?
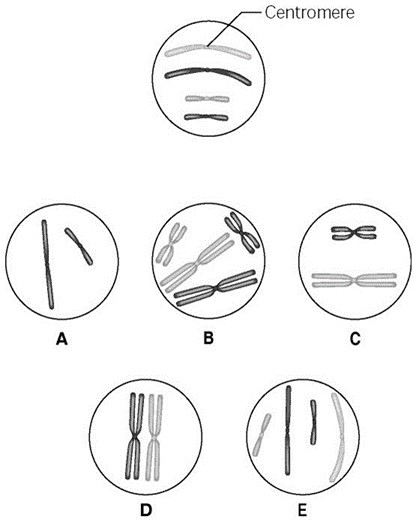
92
New cards
c)
What is a cleavage furrow?
a)a ring of vesicles forming a cell plate
b)the separation of divided prokaryotes
c)a groove in the plasma membrane between daughter nuclei
d)the metaphase plate where chromosomes attach to the spindle
e)the space that is created between two chromatids during anaphase
a)a ring of vesicles forming a cell plate
b)the separation of divided prokaryotes
c)a groove in the plasma membrane between daughter nuclei
d)the metaphase plate where chromosomes attach to the spindle
e)the space that is created between two chromatids during anaphase
93
New cards
b
What is the microtubule-organizing center known as?
a)microtubulere
b)centrosome
c)centromere
d)kinetochore
e)chromatid
a)microtubulere
b)centrosome
c)centromere
d)kinetochore
e)chromatid
94
New cards
d
Which of the following most accurately describes a cyclin?
a)It is present in similar concentrations throughout the cell cycle.
b)It is activated to phosphorylate by complexing with a Cdk.
c)It decreases in concentration when MPF activity increases.
d)It activates a Cdk molecule when it is in sufficient concentration.
e)It activates a Cdk when its concentration is decreased.
a)It is present in similar concentrations throughout the cell cycle.
b)It is activated to phosphorylate by complexing with a Cdk.
c)It decreases in concentration when MPF activity increases.
d)It activates a Cdk molecule when it is in sufficient concentration.
e)It activates a Cdk when its concentration is decreased.
95
New cards
d)
Which of the following is a protein synthesized at specific times during the cell cycle that associates with a kinase to form a catalytically active complex?
a)PDGF
b)MPF
c)protein kinase
d)cyclin
e)Cdk
a)PDGF
b)MPF
c)protein kinase
d)cyclin
e)Cdk
96
New cards
e
Which of the following is a protein maintained at constant levels throughout the cell cycle that requires cyclin to become catalytically active?
a)PDGF
b)MPF
c)protein kinase
d)cyclin
e)Cdk
a)PDGF
b)MPF
c)protein kinase
d)cyclin
e)Cdk
97
New cards
b
What will proceed only after all kinetochores are attached to spindle microtubules?
a)metaphase
b)anaphase
c)synthesis
d)MPF
e)G0
a)metaphase
b)anaphase
c)synthesis
d)MPF
e)G0
98
New cards
b
How is plant cell cytokinesis different from animal cell cytokinesis?
a)The contractile filaments found in plant cells are structures composed of carbohydrates; the cleavage furrow in animal cells is composed of contractile phospholipids.
b)Plant cells deposit vesicles containing cell-wall building blocks on the metaphase plate; animal cells form a cleavage furrow.
c)The structural proteins of plant cells separate the two cells; in animal cells, a cell membrane separates the two daughter cells.
d)Plant cells divide after metaphase but before anaphase; animal cells divide after anaphase.
e)Plant cells undertake cytokinesis during anaphase; animal cells undertake cytokinesis during telophase.
a)The contractile filaments found in plant cells are structures composed of carbohydrates; the cleavage furrow in animal cells is composed of contractile phospholipids.
b)Plant cells deposit vesicles containing cell-wall building blocks on the metaphase plate; animal cells form a cleavage furrow.
c)The structural proteins of plant cells separate the two cells; in animal cells, a cell membrane separates the two daughter cells.
d)Plant cells divide after metaphase but before anaphase; animal cells divide after anaphase.
e)Plant cells undertake cytokinesis during anaphase; animal cells undertake cytokinesis during telophase.
99
New cards
c
Once a cell completes mitosis, molecular division triggers must be turned off. What happens to MPF during mitosis?
a)It is completely degraded.
b)It is exported from the cell.
c)The cyclin component of MPF is degraded.
d)The Cdk component of MPF is degraded and exported from the cell.
e)It is phosphorylated.
a)It is completely degraded.
b)It is exported from the cell.
c)The cyclin component of MPF is degraded.
d)The Cdk component of MPF is degraded and exported from the cell.
e)It is phosphorylated.
100
New cards
e
Which of the following is part of the mitotic phase?
a)G0
b)G1
c)G2
d)S
e)prophase
a)G0
b)G1
c)G2
d)S
e)prophase