Models and theories
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
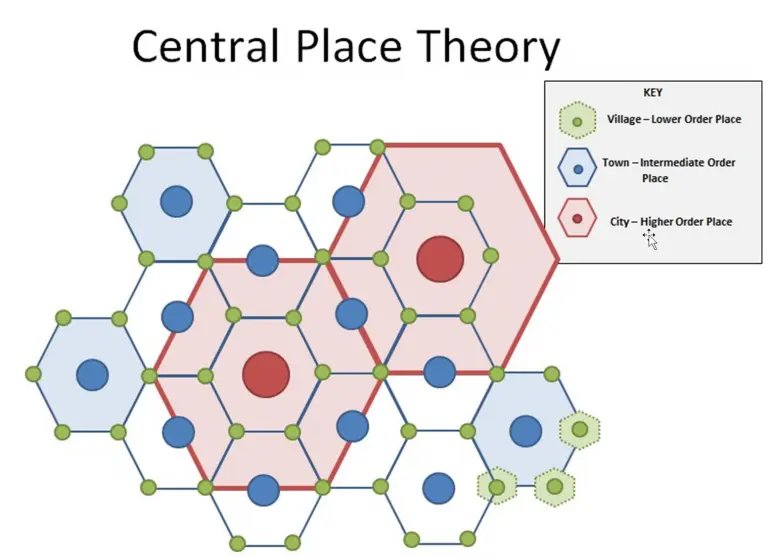
Central Place theory
Explains the spatial arrangement, size, and number of settlements. Larger cities provide more specialized services and are spaced farther apart, while smaller towns are closer together with fewer services. Its based on a hexagonal pattern
Wallersteins world systems theory
divdes the world into core(rich), semi-periphery (middle), and periphery(poor) based on economic roles and dependency.
Von Thunen Model
Shows how farms are arranged around a market based on transportation cost. Perishable goods are the closest, cheaper to move goods are farther.
Rostows stages of economic growth
Five stages of development from traditional economy to modern, wealthy society. Assumes all countries follow the same path.
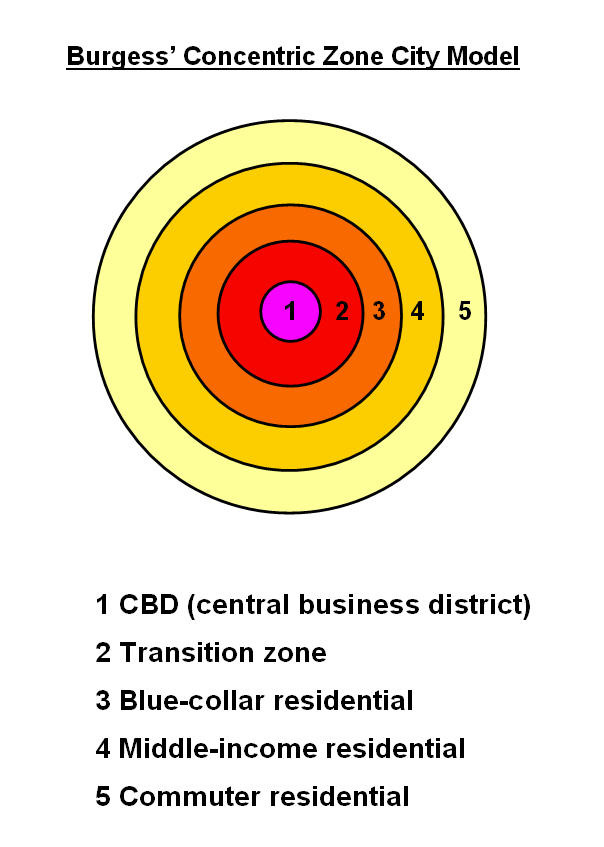
Burgess concentric zone model
City grows in rings: CBD in the center(businesses offices and retail) , then zones of housing and commuting further out. Closer in = denser, less income housing and wealthier housing for commuters farther out.

Hoyt Sector Model
City develops in sectors rather than rings. Sectors extend from the CBD along transportation routes like roads and railways.
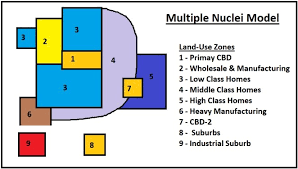
Ullman multiple nuclei model
Cities have several centers (nodes) for different activities (eg. business, industry, housing) not limited to one central business district.