HEMA2 LAB - CLOT RETRACTION TIME
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
CLOT RETRACTION
Regression in the size of blood clot over a number of days
CLOT RETRACTION
A process that is driven by the outside-in signaling of platelet integrin aIIbβ3 (gp IIb/IIIa)
GP IIb/IIIa
Transmembrane receptor of fibrinogen or vWF
CLOT RETRACTION
Results in the contraction of the fibrin mesh
CLOT RETRACTION
Obsolete method
Measures platelet function
Ability of your blood to clot and to retract/push away your RBC
Contraction of Fibrin Mesh
End result for CLOT RETRACTION
Factors affecting CLOT RETRACTION
Normal numbers of contractile platelets
Presence of Ca & ATP
Normal concentration of fibrinogen
Normal numbers of contractile platelets
Platelets are very important in the clotting or coagulation.
Failure to clot retraction decreases platelet count since platelets aggregates at the sight of injury.
Presence of Ca & ATP
Calcium binds to phospholipids and support granules that leads to secondary platelet activation
Calcium
support granules and activates coagulation factors
Presence of Ca & ATP
Calcium bind to phospholipids and leads to secondary platelet activation that will serve as a surface for coagulation factors
Normal concentration of fibrinogen
Interaction of platelets with fibrinogen and fibrin must also be normal for clot retraction to occur
Normal concentration of fibrinogen
Promotion of stability of clot
Blood vessel patency
blood vessel is not obstructed/blocked
GLANZMANN THROMBASTHENIA
Only disease associated with Clot Retraction
GLANZMANN THROMBASTHENIA
Inherited autosomal recessive disorder
deficiency or abnormality of the platelet membrane glycoprotein (GP) IIb/IIIa complex
GLANZMANN THROMBASTHENIA
Platelet Count
Normal
Platelet Morphology
Normal
Complete Blood Count
Usually Normal
Platelet Aggregation
Abnormal
GLANZMANN THROMBASTHENIA
Bleeding time
Prolonged
Clot retraction time
Diminished
GLANZMANN THROMBASTHENIA
•Rashes
•Bleeding in gums
•Mucocutaneous bleeding
•Epistaxis
•Menorrhagia
•Purpura
QUALITATIVE TEST for CLOT RETRACTION
Hirschboeck Method
Hirschboeck Method
• Known as Castor oil method
• Presence or absence of retraction
1
Hirschboeck Method: Add _ big drop of fresh blood to the test tube with castor oil and
start the timer (both capillary or venipuncture)
3/4 of the tube
Hirschboeck Method: Volume of castor oil
dimpling or Nipple like extrusion or protrusion
Hirschboeck Method: Observe for _______ or extrusion of droplet-like serum on the top portion of the drop of blood
dimpling
Hirschboeck Method: Stop timer as soon as the __________ of serum is observed.
Sally pipette
Hirschboeck Method: : used for Aspiration of blood and to submerge it to castor oil
15-45 minutes
Hirschboeck Method: Reference Value
Normal or Defective/Poor
Hirschboeck Method: REPORTING
Platelet count is
< 100,000 cells/mm3 or
100 x 109 /L
Hirschboeck Method: POOR CLOT RETRACTION
Hemorrhagic Tendency
Hirschboeck Method: > 45 minutes
Thrombotic Tendency
Hirschboeck Method: < 15 minutes
QUANTITATIVE TEST for CLOT RETRACTION
Stefanini Method (Test Tube Method)
MacFarlane Method
Stefanini Method (Test Tube Method)
Venipuncture is done instead of capillary puncture
Begins within 1 hour. Complete within 18-24
hours
Stefanini Method (Test Tube Method): REFERENCE VALUE
Stefanini Method (Test Tube Method)
Clean tube is needed - since it causes false result
ring the clot using a stiff straight wire to
separate it from the wall of the tube
Stefanini Method (Test Tube Method): the clot may adhere to the wall of the tube, what is the course of action
Short retraction time
Stefanini Method (Test Tube Method): NORMAL blood results in
3-5
Stefanini Method (Test Tube Method): Perform venipuncture and place _________ ml of fresh venous blood in a clean tube.
cotton plug
37C
Stefanini Method (Test Tube Method): Close the tube with a _________ and incubate it for 1 hour in a water bath set at _______.
room
Stefanini Method (Test Tube Method): After 1 hour, let the tube stand at _________ temperature and
observe for retraction to take place.
1
18-24
Stefanini Method (Test Tube Method): Clot retraction starts within __ hour after blood extraction and it usually complete
within ______ hours (1 hr /2 hrs /16 hrs /18 hrs /24 hrs)
oNormal / Complete Retraction
oPartial Retraction
oPoor Retraction
oVery Poor Retraction
Stefanini Method (Test Tube Method): REPORTING
MacFarlane Method
Determine degree of clot retraction
44% - 67%
MacFarlane Method: REFERENCE VALUE
5 mL
MacFarlane Method: Volume of Blood
MacFarlane Method
Clots which have retracted by the end of the 1st hour of incubation may be freed by carefully passing a fine stiff wire around the inside
of the tube. Tube should then be re-incubated for another hour.
MacFarlane Method
Clot retraction is actually a complicated process that involves the interaction of at least 4 effects
oPresence of platelets
oConcentration of fibrinogen
oNature of tube surface to be used
oRetraction promoting principle in serum
MacFarlane Method: Interaction of the 4 effects
MacFarlane Method: FORMULA
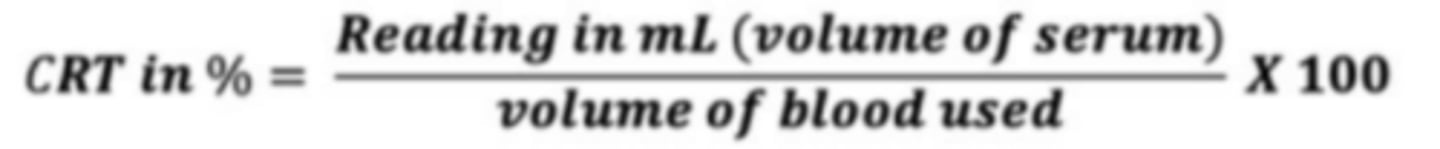
calibrated centrifuge
MacFarlane Method: Fill a ____________ tube with freshly drawn blood up to the 5ml mark
glass rod
MacFarlane Method: Place a __________ inside the tube with the expansion immersed
in the column of blood.
cork
MacFarlane Method: Fit a ________ into place over the projecting end of the glass rod.
coagulation
5 - 10
MacFarlane Method: Place the tube in a water bath set at 37C and examine the
blood for evidence of _________ at ________ minutes.
one hour
MacFarlane Method: Remove the tube from the water bath ______ after a firm clot
has formed.
shrink
MacFarlane Method: If retraction has taken place, the clot will ________ and attach to
the glass rod.
graduated scale
MacFarlane Method: •
Pull the glass rod and the clot will be removed together with
the rod.
Read the volume of the serum directly in the __________ of the tube.
Red top tube also known as
in MacFarlane Method: blood is collected in what tube?
Cork
used to stabilize the glass rod thus will avoid disturbance
that may be caused by the glass rod due to its movement from the boils in the water bath.
cause false results while the remaining serum may get mixed (serum may contain RBCs)
in MacFarlane Method: What is the effect if glass rod disturbed the clot formation while performing incubation at a water bath?
MacFarlane Method
Observe 5 to 10 minutes first for evidence of coagulation or any clot formation before starting the 1-hour timer
MacFarlane Method
After 1 hour, the remaining serum is measured firstly by removing the Para film and glass rod or applicator stick with solid clot. The
remaining serum is transferred to the graduated cylinder using Pasteur pipette.
soft clot
solid clot
In MacFarlane Method, Quality of clot formed must be noted as
soft clot
there are remaining RBCs at
the bottom
solid clot
serum remains at the bottom
solid clot
target quality of clot at the end of the activity to obtain the correct measurement of the serum.