intro to learning and memory
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
what is memory, and what is it good for?
purpose to influence future actions
modification of structure or behavior
learning/memory often increase fitness, though not always the case
exception to learning and memory increasing fitness: PTSD
mental health condition developing due to shocking/dangerous event
symptoms
flashbacks, bad dreams
avoidance from places that are daily reminders of experience
being easily startled, feeling tense, insomnia
takehome
memory is not always beneficial
understanding brain mechanisms may help treat PTSD and memory-related diseases
memory research in humans vs rodents
humans
clinical cases
psychophysics
fMRI
EEG
rodents
behavioral tasks
lesions
interrupting brain activity
recording brain activity
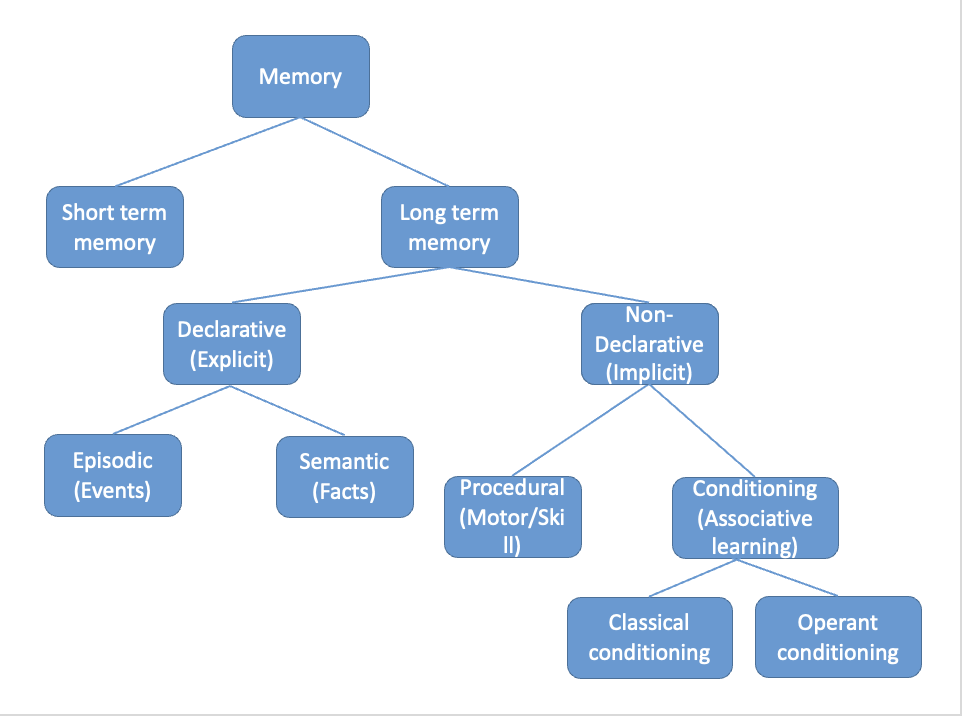
memory types map
short vs long term
short term memory
capacity for storage of small amounts of info in an accessible state for a short period of time (s)
example: remembering a phone number until jotting it down
items short term memory can hold
1956 article by Miller
number of objects a human can hold in short term memory is 7 plus/minus 2
LATER: memory span is not constant as it varies for digits/letters/words; lower for long words than for short words
short term vs working memory
working memory involves temporary storage of info to manipulate it
storage + processing
examples: remembering partial results while calculating
immediate free recall task
presented with sequence of items → asked to report all items in any order
recency effect: then final few items are reported with higher probability
final items are STILL in short term memory
distractor task
immediately after item sequence, perform a distraction task
eliminates the recency effect
by the end of the distraction task, the recent items have been deleted from short term memory
short term memory behavioral test in animals: DMS
delayed-match-to-sample (DMS) task
view object in monitor, delay, another object is presented, detect if a match based on location or object
long term memory
lasting storage of information
general stages: encoding (consolidation) → storage (reconsilidation/extinction) → retrieval
declarative vs non-declarative memory
declarative (explicit)
memory you can consciously recall or declare
non-declarative (implicit)
memory that is expressed through action, not recollection
types of non-declarative memory
procedural: knowledge of how to do something (ex: ride a bike)
conditioning/associative learning: association between items (ex: green light signals to drive)
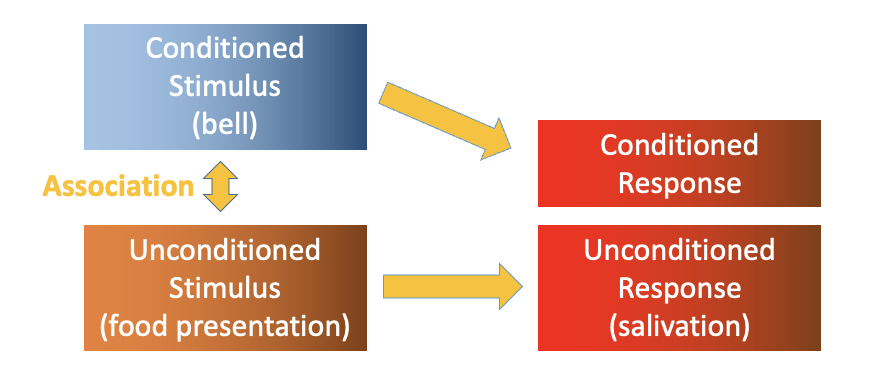
non-declarative classical conditioning (Pavlovian conditioning)
originally studied how NS controls digestion
found that dogs salivate in response to sight of food OR to sound of a bell
common paradigm: fear conditioning
unconditioned stimulus: naturally evokes an unconditioned response
conditioned stimulus: paired with US so that it evokes a response
response to the CS is known as the conditioned response
operant conditioning (instrumental conditioning)
learning through reward and punishment
type of non-declarative memory
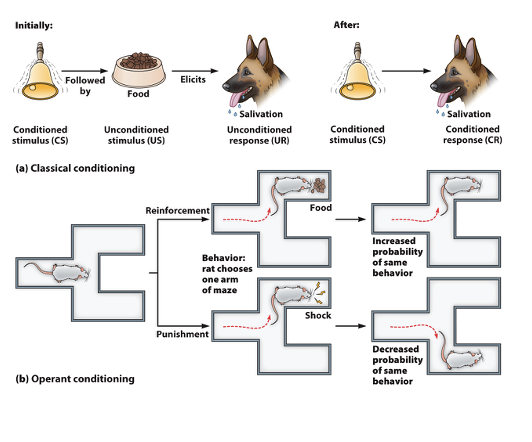
classic vs operant conditioning
classical:
neutral signal before a reflex
non-voluntary behavior
operant:
reinforcement after behavior
voluntary behavior
behaviorism (Watson)
human behavior can be fully accounted for by classical and instrumental conditioning
discounts independent thought, feelings, imagination, creativity
little albert
teaching a boy with classical conditioning
originally not scared of white rates
struck with loud noise and presence of white rats → fear of white rats (acquired fear)
reacted fearfully to similar shaped objects (dog, rabbit)
declarative explicit memory
semantic memories (memories of facts)
episodic memories (memories of events)