Cls 401 final
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
viruses
obligate intracellular parasites
depend on host cell for replication
viruses CANT
make their own energy or substrates
make their own protein
replicate their genome independently (w/o host cell)
classified by
size
genomic material
DNA vs RNA (not both)
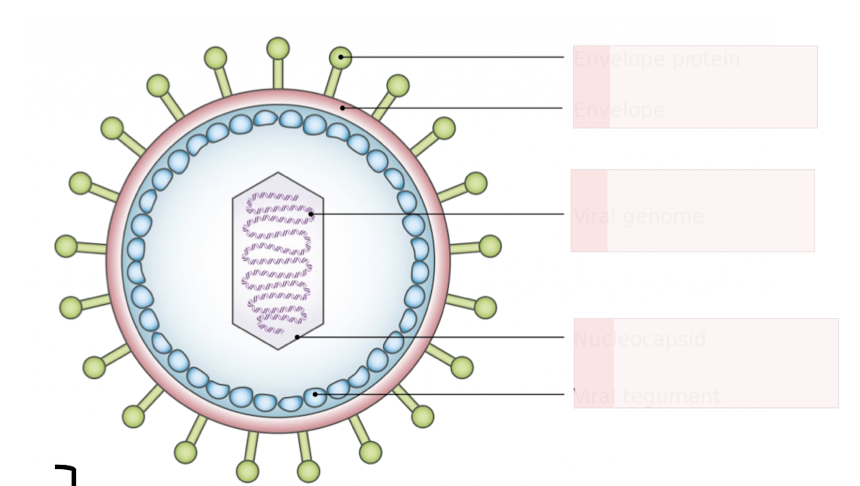
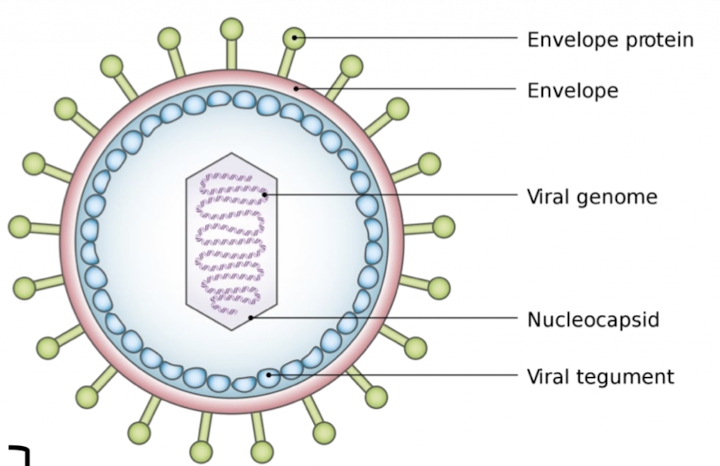
Herpesviridae
DNA viruses
enveloped
DNA vs RNA viruses
stability
infection
location
interaction
Feature | DNA Viruses | RNA Viruses |
|---|
Stability | not transient or labile (stable) | Labile and transient |
Infection | Many establish persistent infections | prone to mutation |
Location of Replication | reside in the nucleus | replicate in the cytoplasm |
Interaction | Viral DNA resembles host DNA for transcription and replication and interact w/ host machinery | Must code for own RNA polymerase
|
enveloped vs nonenveloped
structure
resistance
survival
spread
examples
Feature | Non-enveloped Viruses | Enveloped Viruses |
|---|
Structure | Naked, rigid capsid | Lipid membrane envelope surrounding capsid |
Environmental Resistance | hardier & more resistant to:
| labile (sensitive) to
|
Survival |
hard to kill | Cannot survive GI tract |
Spread | spread easily: Hands, fomites, dust, small droplets super infectious | Large droplets, secretions, organ/tissue transplants, blood transfusions |
Examples | Norovirus, Poliovirus, Rotavirus, Rhinovirus | Measles, Mumps, Rubella, HIV, Rabies, Coronavirus |
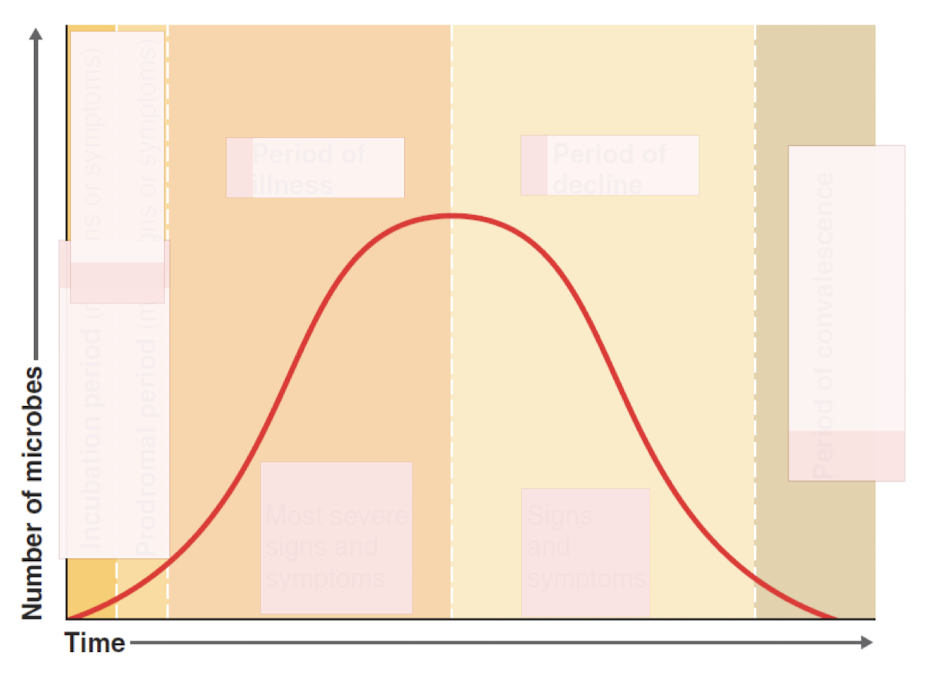
basic steps in viral disease (7)
acquisition : entry into body
infection at primary site : innate reponse activated
incubation period : virus undergoing amplication, may spread to secondary site
replication in target tissue: characteristic disease signs are revealed
host response : immunopathogenesis
viral production in tissue that releases virus to other people
resolution vs persistant/chronic infection : get better or just die
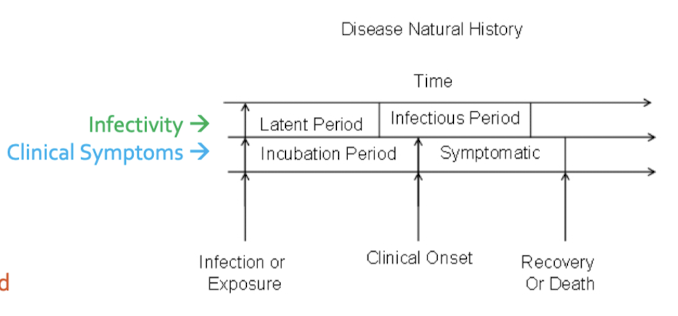
latent period: you have infection but not infectious yet
infectious period: transmit disease to others
incubation period: dont have symptoms
symptomatic period: clinical symptoms
stages of disease
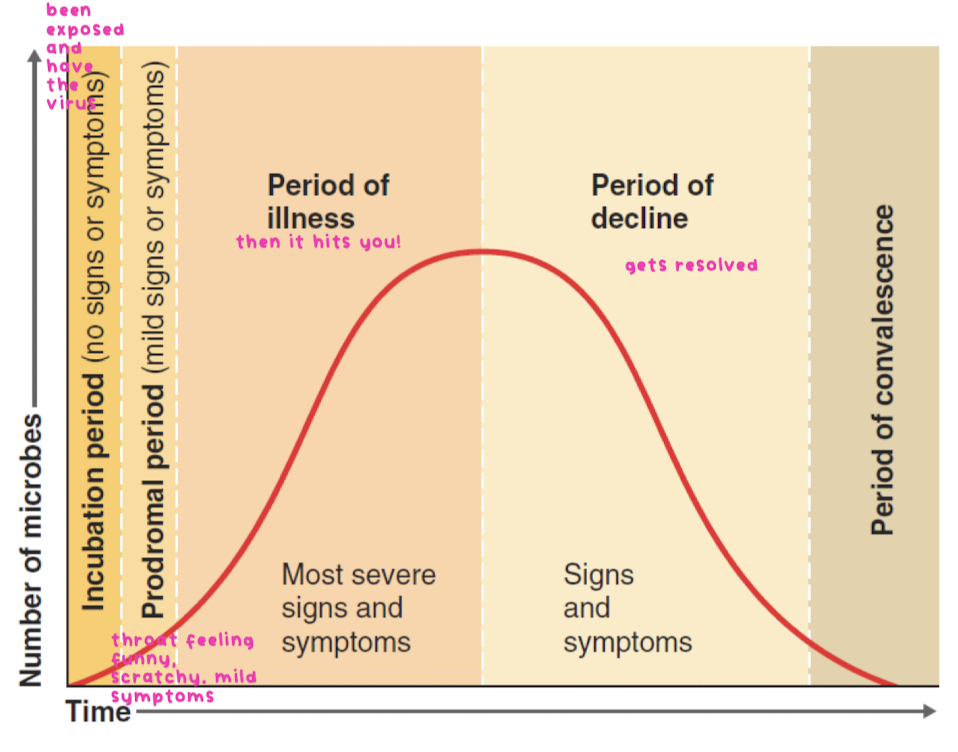
4 potential outcomes of viral infection of a cell
failed/abortive infection: yay!
cell death: cytolytic infection, boo!
replication without cell death: persistant infection
presence of virus without virus production, but with potential for reactivation: ticking time bomb!
hepatitis types & what do they target/affect?
A,B,C,D,E,G
all target hepatocytes
all affect liver
Hepatitis A Virus (HAV) transmission?
fecal-oral transmission
Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) genetic material?
DNA
only one. the rest of hepatitis is RNA
Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) is known for what?
chronicity 60-85%
highest compared to others
Hepatitis D Virus (HDV) coinfection w/?
exists as co-infection w/ HBV
can replicate only w/ HBV
Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) transmission?
fecal-oral transmission
Hepatitis G Virus (HGV) chronicity and infection?
unknown
which hepatitis virus are bloodborne?
HBV
HCV
HDV
which hepatitis are vaccine preventable?
HAV
HBV
hepatits
inflammation of liver
icterus (jaundice)
yellowing of skin or whites of the eyes
cirrhosis
replacement of liver tissue —> fibrosis, scar tissue
liver function tests (LFT)
ALT/AST
haemolytic : normal
hepatic: increase
cholestatic: normal/mild increase
enzymes going up bc liver cells being destroyed
Hepatitis A Virus
fecal oral
no specific treatment, replacement of fluids
vaccine preventable
VPg
viral (protein genome linked) attached to RNA, acts as a primer to RNA synthesis
Hepatitis B Virus
bloodborne pathogen
vaccine preventable: HbsAg - used to make HBV vaccine
stands for surface antigen
Hepatitis B Virus Structure
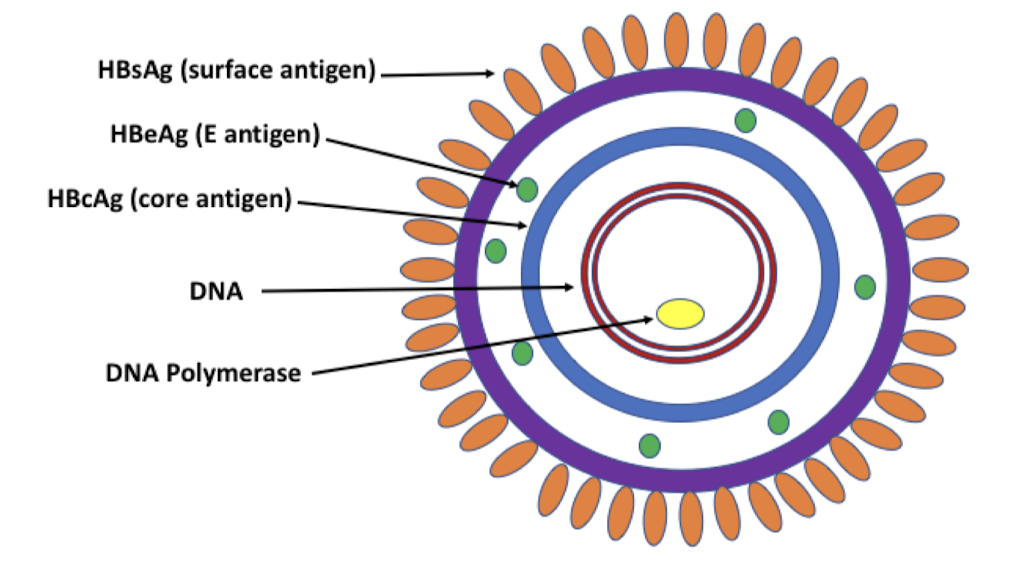
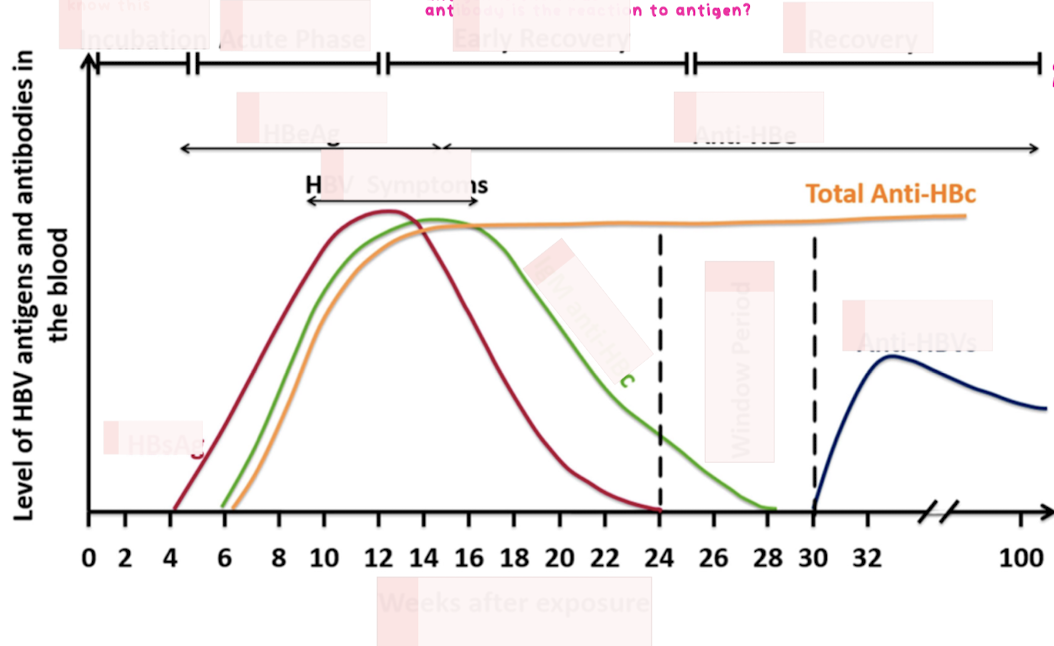
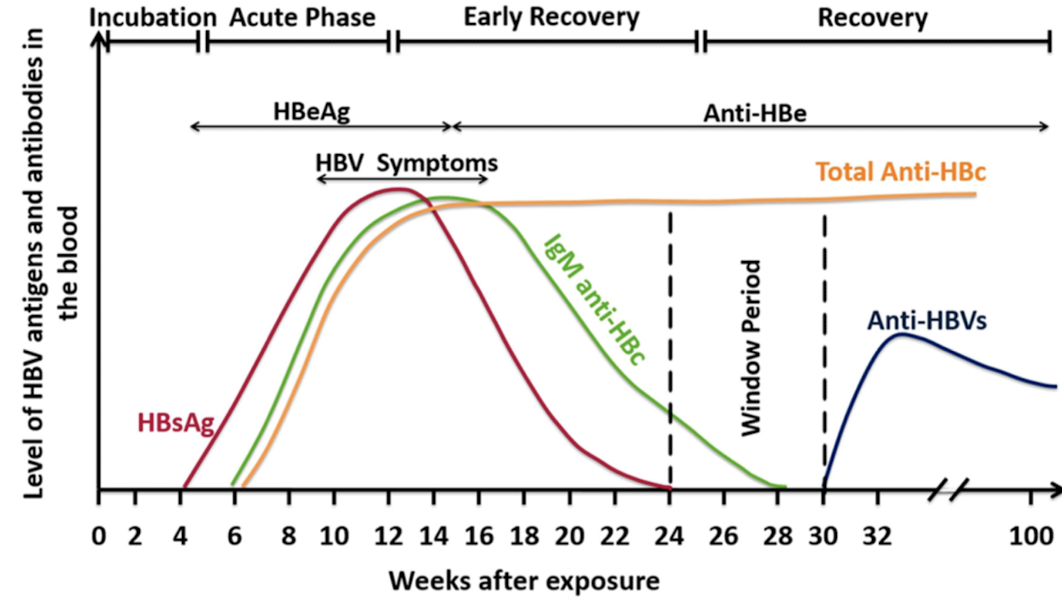
Chronic Hepatitis B
chronic : antigen never goes away
persistance of HBsAg for >6months
interpretation of serologic results
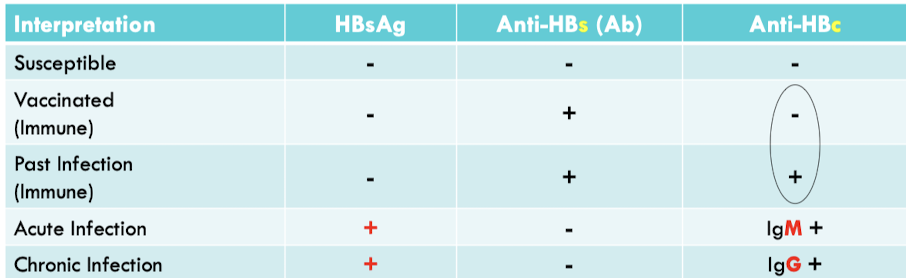
Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)
bloodborne pathogen
chronic
no vaccine
who is at risk:
ppl w/ HIV infections
ppl who use injection drugs
ppl w/ hemodialysis
prior transfusions, transplants
health care
ppl born from 1945-65 ; boomers!
what do you look for in HCV?
RNA
to detect HCV RNA, you need RT-PCR ( reverse transcriptase polymerase chain rxn)
have to first make it into DNA so it can be detected
Hepatitis D Virus (HDV)
bloodborne pathogen
occurs in people who are also infected w/ heptatitis B virus
co-infection: become infected w/ both hepatitis B and heptatitis D at the SAME time
superinfection: get hepatitis D after first being infected with the hepatitis B virus
No vaccine, however, protection against HBV will protect against future HDV infection
who is at risk? ppl chronically infected w/ HBV
diagnostic testing for HDV
serologic: anti-HDV Ab
NAT: HDV RNA
Heptatitis E Virus (HEV)
fecal oral
rare
NO vaccine
HIV is what type of virus?
RNA
requires reverse transcriptase to convert RNA into DNA
HIV infects what cells?
CD4+ cells
CD4+T cells (helper T cells)
proteins associated with HIV
gag, p24: core proteins
pol
env
what is used by HIV strains to enter cells?
CCR5
a chemokine receptor
viruses get immune to it
HIV enters what phase?
latent/asymptomatic
what usually kills patients?
opportuinistic organisms and conditions
first marker for Acute Primary HIV?
p24
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS)
you either have AIDS condition or CD4 count <200 cells/mm3
PrEP: Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis
medication that prevents HIV infection
Gastrointestinal Viruses
what are they?
what do they have in common?
norovirus (Calicivirus)
Hepatitis A : fecal bug
Rotavirus
Poliovirus (enterovirus)
they are all RNA viruses and have NO envelope
which Gastrointestinal Viruses are vaccine preventable?
Rotavirus
Poliovirus
Norovirus
non-enveloped
highly infectious
acute fluid, severe dehydration
difficult to kill
transmission for Norovirus?
fecal-oral
common outbreak for Norovirus ?
cruise ships
clinical presentation for Norovirus?
nausea, vomitting
watery diarrhea
poo and puke all at once
Rotavirus
wheel
highly infectious
vaccine preventable
transmission of Rotavirus ?
fecal-oral
who is at risk for Rotavirus?
children 4-36 months; toddlers
a lot of the problems w/ Rotavirus is due to what?
its a toxin : enterotoxin
and killing cells
causes secretory diarrhea
Poliovirus (Enterovirus)
non-enveloped
super resistant !
no cure but vaccine preventable
transmission for Poliovirus (Enterovirus)
fecal-oral
Poliovirus Pathogenesis
how it gets there
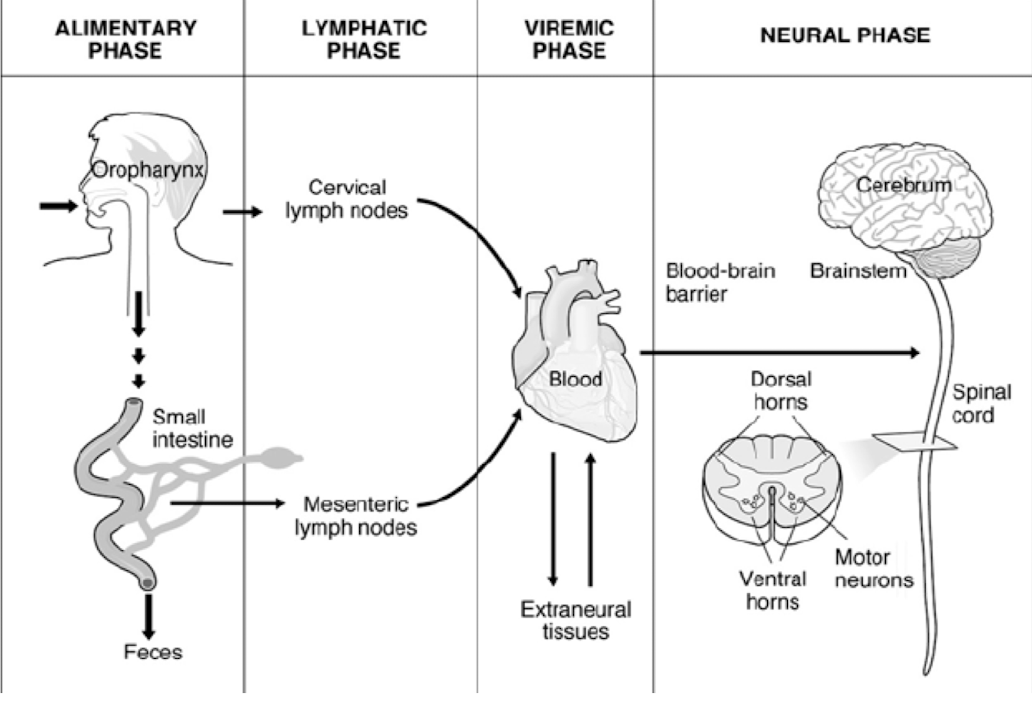
eat it, gets to lymph nodes, goes to blood, then BBB
when it passes BBB, it is an issue
neurologic phase: PARALYSIS
clinical symptoms of Poliovirus in severe cases?
paralytic polio
for Poliovirus, before vaccine this was used to help patient recover and breathe on their own
Iron Lung
inventor of Polio Vaccine?
Jonas Salk
Oral Polio Vaccine is __
Inactivated Polio Vaccine is ___
cVDPV
alive
new strains, vaccines now, but a risk to regain virulence
dead
circulating vaccine derive poliovirus
Influenza
which ones are seasonal epidemic?
which ones are flu pandemics?
A, B: seasonal epidemic
A : the only one that causes flu pandemic
C: mild, not any epidemics
D : infect cattle
which respiratory viruses are vaccine preventable?
measles
rubella
mumps
Innate Immune Response
Good and Bad
too much or too little immune response is a problem
want just the right amount
proteins associated with Flu
HA: hemagglutinin
NA: neuraminidase
Antigenic Drift vs Shift
drift: small genetic mutations
change NA and HA
shift: abrubt, major change in Flu A virus
new HA and/or NA
Influenza Diagnosis
rapid antigen testing
RT-PCR
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
there are new vaccines for adults: moms, older ppl
babies get more of the passive immunoglobulin
what are we worried about? infants and young children, and older ppl (65+)
fatal
Human Parainfluenza Virus (HPV)
respiratory virus
4 types: 1,2,3,4
croups is associated with what virus?
HPV: human parainfluenza viruses
barky cough
infection of vocal cords Larynx, windpipe Trachea, bronchial tubes Bronchi
Rhinovirus
a common cold
no vaccine
Measles (Rubeola)
highly contangious
vaccine preventable
Measles (Rubeola) Clinical Presentation
Symptoms:
rash
Koplik Spots
complications:
Encephalitis leads to deafness bc it can go to your brain
Death
weird response:
immune amnesia - makes you forget
Mumps
highly contagious
vaccine preventable
Mumps Clinical Presentation
swollen salivary glands
swelling
meningitis: swelling of meninges
Rubella (German Measles)
vaccine preventable
who are we worried about getting Rubella (German Measles)?
pregnant ladies
we are trying to prevent Congenital Rubella Syndrome (CRS)
Enterovirus symptoms
Severe Cases
acute flaccid paralysis
enterovirus D68
which ones belong to the Herpesviridae?
Herpes Simplex (HSV 1,2)
Varicella zoster virus (VZV)
Epstein Barr Virus (EBV)
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
which Herpesviridae are vaccine preventable?
Varicella Zoster Virus (VZV)
chickenpox
shingles aka “zoster”
what does Herpesviridae cause?
latent and lytic
go away but they are never really gone, they come back and destroy your cells
Herpes Simplex 1 (HSV-1) vs Herpes Simplex 2 (HSV-2)
Herpes Simplex 1 (HSV-1) : oral
Herpes Simplex 2 (HSV-2) : genital
Non-Genital Herpes Infection
Primary Infection
Oral HSV-1 Infection
Herpes simplex encephalitis (HSE) is the most common cause for what?
Sporadic non-seasonal encephalitis
attacks the brain
Ocular (eye) Herpes Simplex
is reccurent : it follows the optic nerve pathway
Genital Herpes
hides out and comes back
increase risk of HIV/ STDs
Neonatal Herpes
when thinking of congenital problems, think of what?
TORCH
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) Diagnostics
looks like “owl eye”
Varicella Zoster Virus (VZV)
chicken pox: primary exposure
shingles: secondary, reactivation
vaccine preventable
chickenpox
itchy, painful
complications: pneumonia, encephalitis
has different stages
waiting for Stage 3: crusting
vaccine preventable
Shingles (Zoster)
a reactivation
where it shows up depends on which nerve pathway
dermatones
what is dermatone?
nerve pathway from spinal cord then feed into certain area of skin, this is where you see it
if it shows up on more than one dermatone, its disseminated, NOT localized
localized = contact isolation
disseminated = airborne
Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) associated w/ what?
Infectious Mononucleosis
Cancers:
B-lymphocytes
Epithelial Cells
Natural Killer T cells
Infectious Mononucleosis (IM) symptoms
swollen lymph nodes
enlarged spleen
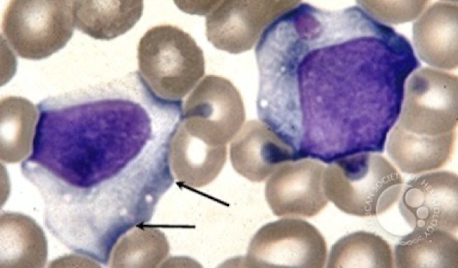
Peripheral Blood smear of Infectious Mononucleosis (IM)
activated, big
ballerina skirt, scalloped margins
vacuolated cytoplasm
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
its primary then its hiding out
recurrent CMV: transplant patients
congenital CMV: most common infectious cause of birth defects in US
virus passed to fetus from moms blood through placenta
TORCH
infectious acquired utero or during birth process that are associated w/ miscarriage and/or congenital abnormalities
T = toxoplasmosis
O = other
Syphilis
Parvovirus
VZV
Listeria
R = Rubella
C = CMV
H = HSV
Most Common Cause of Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)?
sepsis
serotypes of Dengue
DENV-1
DENV-2
DENV-3
DENV-4
you can be infected up to 4 times in your life
AB to one serotype increases likelihood you will have more severe infection the next time
for Zika Virus, what are we worried about?
Congenital Zika Syndrome
microcephaly
Where is West Nile Virus (WNV) transmitted?
mosquito
birds
what disease is involved w/ West Nile Virus (WNV)?
CNS involvement