Amino Acids
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
The amino acids that make up human proteins are called essential amino acids
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Which of the following statements concerning amino acids is FALSE?
There are 20 different amino acids that occur naturally in human proteins.
Amino acids are classified by the nature of the side chain R groups that are present.
The amino acids that make up human proteins are called essential amino acids
Except for glycine, where R=H, amino acids are chiral molecules.
C-terminal
What term is used to describe the amino acid that has the free carboxylate group in a peptide?
C’ group
C-terminal
acid end
3º amino acid
1º amino acid
Secondary structure describes the peptide bonds joining the amino acids together in the protein chain.
Which of the statements concerning protein structure is NOT TRUE?
Secondary structure describes the peptide bonds joining the amino acids together in the protein chain.
Hydrogen bonding, disulfide bonds, salt bridges, and van der Waals forces are responsible for maintaining the tertiary structure of a protein.
Tertiary structure describes the overall three-dimensional shape of a protein.
The primary structure of a protein describes the unique sequence of amino acids in the protein chain.
Quaternary structure describes the association of two or more polypeptide chains to form one functioning protein unit.
⍺-helices and β-pleated sheets
What are the two most common types of secondary structures found in proteins?
β-spirals and ⍺-turns
random coils and β-pleated sheets
⍺-helices and β-arrays
double-stranded helices and β-arrays
⍺-helices and β-pleated sheets
Collagen
Which structural protein is found in bone, tendon, and skin?
Collagen
Fibrinogen
Keratin
Insulin
Albumin
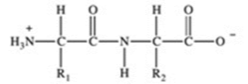
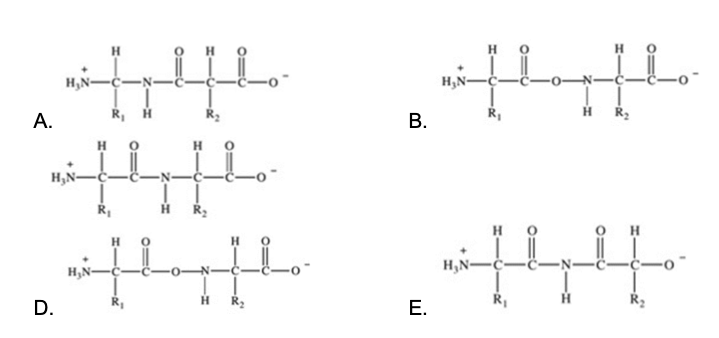
Proteins are long chains of amino acids joined together by peptide bonds. Which of the following properly depicts the peptide bond formed between two generic amino acids?
It describes the overall three-dimensional shape of a protein.
What is meant by the “tertiary structure” of a protein?
It describes the association of two or more polypeptide chains to form one functioning protein unit.
It describes the regular, repeating structures found in the protein chain.
It refers to the peptide bonds that join the amino acids together in the protein chain.
It describes the overall three-dimensional shape of a protein.
It describes the unique sequence of amino acids in the protein chain.
Nonpolar, Hydrophobic
The properties of amino acids and the proteins they compose are based on the nature of their side chain group. Which term best classifies the side chain of the amino acid phenylalanine?
Acidic
Basic
Polar, Hydrophilic
Nonpolar, Hydrophobic
Polar, Neutral
Four amino acids are present, joined together by three peptide bonds.
Tuftsin is a tetrapeptide that stimulates and promotes the destruction of tumor cells. What is meant by the term tetrapeptide?
Four peptide bonds join the amino acids together in their structure.
There are four separate peptide chains in its structure.
Four amino acids are present, joined together by three peptide bonds.
Four different secondary structures are present.
This protein has a quaternary level of structure.
It describes the association of two or more polypeptide chains to form one functioning protein unit.
What is meant by the "quaternary structure" of a protein?
It refers to the four atoms that make up the peptide bonds that join the amino acids together in the protein chain.
It describes the overall three-dimensional shape of a protein.
It describes the four regular, repeating structures found in the protein chain.
It describes the unique sequence of four amino acids in the protein chain.
It describes the association of two or more polypeptide chains to form one functioning protein unit.
denatured
What is the term for the state of a protein when its organized structure has become completely disorganized?
hydrolyzed
isomerized
denatured
globular
fibrous
myoglobin
What protein is the oxygen storage protein of the skeletal muscles?
collagen
hemoglobin
insulin
myoglobin
albumin
trypsin
which of the following is a structural protein?
insulin
myoglobin
albumin
keratin
trypsin
enantiomers
Which term best describes the relationship between L-alanine and D-alanine
identical
enantiomers
diastereomer
constitutional
meso
The peptide contains only hydrophobic amino acid residues
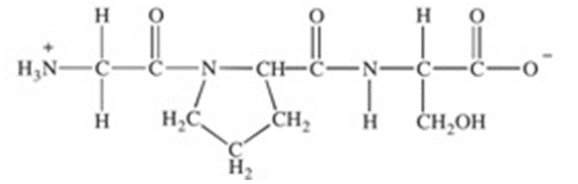
Which of the statements concerning the peptide shown below is FALSE?
Its primary structure is Gly-Pro-Ser.
The carboxyl group of Pro is joined to the amino group of Ser.
The peptide contains only hydrophobic amino acid residues.
There are two peptide bonds.
It is a tripeptide.
amino acid sequence of the chain
What determines the primary structure of a protein?
⍺-helix
ionic bonds between the R group of oppositely charged amino acids
hydrogen bonding between amide hydrogens and carboxyl oxygens
amino acid sequence of the chain
None of the choices is correct.
hydrogen bonds between carbonyl and amino groups of peptide bonds
What type of attractive force is responsible for maintaining the secondary structure of a protein?
salt bridges
van der Waals forces between hydrophobic R groups of nonpolar amino acids
S-S bonds between thiol-containing amino acids
hydrogen bonds between carbonyl and amino groups of peptide bonds
None of the choices is correct.
hemoglobin
What protein is an oxygen transport protein found in red blood cells?
fibrinogen
transferrin
myoglobin
hemoglobin
4
How many oxygen molecules can one hemoglobin molecule bind?
1
2
3
4
5
A glutamic acid residue in normal hemoglobin is replaced by a valine residue in sickle cell hemoglobin.
How do the primary structures of normal hemoglobin and sickle cell hemoglobin differ?
A glutamic acid residue in normal hemoglobin is replaced by a valine residue in sickle cell hemoglobin.
There are three heme groups in normal hemoglobin, whereas there are 4 heme groups in sickle cell hemoglobin.
A valine acid residue in normal hemoglobin is replaced by a glutamic acid residue in sickle cell hemoglobin.
There are four heme groups in normal hemoglobin, whereas there are only three heme groups in sickle cell hemoglobin.
Both A and C are correct.
All of the choices
Which of the following can denature a protein?
detergents
drastic change in pH E.
heat
mechanical stress
All of the choices
enzymes
Which of the following kinds of proteins are biochemical catalysts?
enzymes
transport proteins
nutrient proteins
antigens
hormones
in the interior of the folded protein, away from water, due to their hydrophobic nature
Which of the following best describes where the amino acids isoleucine and tryptophan are most likely to be found in the tertiary structure of a protein?
on the exterior surface of the folded protein, where contact with water is greatest, due to their hydrophilic nature
at the C-terminal end of the protein
in the hydrophilic interior of the protein due to their ability to form side-chain hydrogen bonds with each other
at the N-terminal end of the protein
in the interior of the folded protein, away from water, due to their hydrophobic nature
Peptide bonds are broken, and individual amino acids are released.
When a protein undergoes hydrolysis, which of the following can occur?
The protein folds into its functional, three-dimensional shape.
New amino acids are joined to the growing protein chain.
Unsaturation in the side chain R groups is removed.
Peptide bonds are broken, and individual amino acids are released.
Water adds across each double bond that is present to give an alcohol
20
How many different amino acids make up the proteins found in the human body?
125
20
16
4
Not yet determined
alanine
Which amino acid has a methyl group as its R group?
tyrosine
lysine
valine
glycine
alanine
tertiary
What level(s) of protein structure is/are created in part by disulfide bridges?
secondary
primary
tertiary
helical
All of the choices
Secondary, tertiary, or quaternary levels of structure are disrupted.
Denaturation of a protein results in the loss of its native conformation and its biological activity. Which of the following best describes what happens when a protein is denatured?
The primary structure of the protein is altered.
Secondary, tertiary, or quaternary levels of structure are disrupted.
Peptide bonds are broken, and individual amino acids are released.
The N-terminal and C-terminal ends of the protein form their zwitterions.
The N-terminal and C-terminal ends of the protein are hydrolyzed.
tyrosine
Which amino acid contains an aromatic ring in its side chain?
glycine
isoleucine
threonine
alanine
tyrosine
cysteine: cys
Which of the following correctly matches the amino acid with its three-letter abbreviation?
asparagine: asp
tryptophan: try
cysteine: cys
valine: van
isoleucine: iso
The reactant in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is called a cofactor.
Which of the following statements concerning enzymes is FALSE?
Inhibitors are molecules that cause an enzyme to lose its activity.
Enzymes are usually globular proteins with flexible three-dimensional shapes.
Enzymes are the body's biological catalysts, increasing the rate of cellular reactions.
The reactant in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is called a cofactor.
The active site of an enzyme is where substrate binding and catalysis occur.
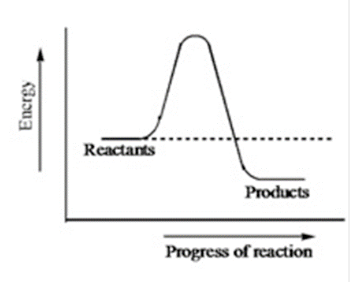
The activation energy decreases.
The diagram below shows the energy pathway of an uncatalyzed reaction. How does the energy diagram change when an enzyme is used in the same reaction?
The energy of the reactants decreases.
The energy of the products decreases.
The energy of the reactants becomes equal to the energy of the products.
The energy of the reactants increases.
The activation energy decreases.
pH optimum
What term describes the pH at which an individual enzyme functions best?
neutral pH
pH optimum
isoelectric pH
zwitterion
physiological pH
proenzyme
Proteolytic digestive enzymes are often produced in an inactive form. What is the name that refers to the inactive form of an enzyme?
inhibitor
isozyme
zwitterion
allele
proenzyme
E
The protease enzyme chymotrypsin cleaves peptide bonds on the carbonyl side of aromatic amino acids. Which labeled bond in the peptide below would be cleaved by chymotrypsin?
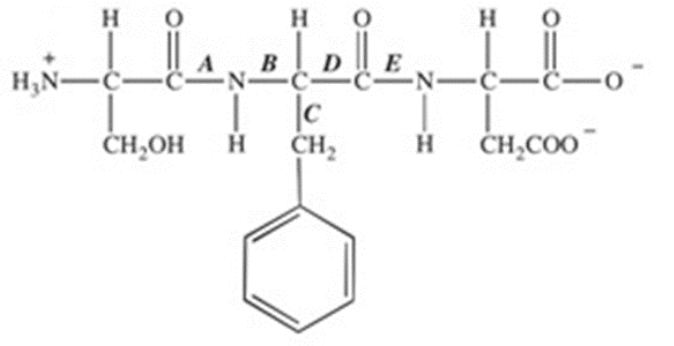
in the interior of the folded protein
About half of the 223 amino acids in the enzyme trypsin are hydrophobic. Where in the tertiary structure of this globular protein are these amino acids most likely to be found?
at the C-terminal end of the protein chain
on the exterior surface of the folded protein
in the interior of the folded protein
in the active site of the enzyme
at the N-terminal end of the protein chain
isomerases
To which class of enzymes does an enzyme belong if it catalyzes the rearrangement of functional groups within a molecule?
lyases
isomerases
oxidoreductases
ligases
both A and D
The rate increases until it reaches a maximum, constant value.
For enzyme-catalyzed reactions, what happens as the concentration of the substrate is increased?
The rate increases until it reaches a maximum, constant value.
The rate decreases until it reaches a minimum, constant value.
The rate increases until it reaches a maximum, then the rate decreases.
The rate continues to increase as substrate concentration increases.
The rate decreases with increasing concentration of the substrate.
formation of an enzyme-substrate complex
What is the first step in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction?
A. catalysis of enzyme
B. formation of an enzyme-substrate complex
C. dimerizing the substrate
D. ionization of enzyme
E. decrease of pH
active site
What portion of an enzyme is in direct contact with the substrate?
inert site
beta site
alpha site
active site
delta site
ligase
What is the classification of an enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules?
transferase
ligase
hydrolase
oxidoreductase
kinase
transferase
An enzyme catalyzes the removal of an amino group from one substrate and its addition to another compound. To what class of enzymes does it belong?
hydrolase
transferase
kinase
oxidoreductase
lyase
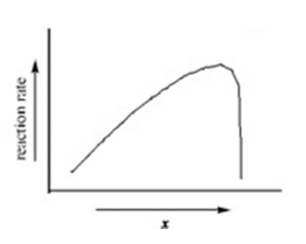
temperature
The graph illustrates how the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction varies with the variable x. Which of the following quantities could x most likely represent?
substrate concentration
enzyme concentration
progress of the reaction
energy
temperature
True
[BONUS ITEM]
Hydrogen bonding, disulfide bonds, salt bridges, and van der Waals forces are responsible for maintaining the tertiary structure of a protein
True or False
Tertiary Structure
[BONUS ITEM]
The _________ describes the overall three-dimensional shape of a protein
Primary Structure
[BONUS ITEM]
The _________ of a protein describes the unique sequence of amino acids in the protein chain
Quaternary Structure
[BONUS ITEM]
The _________ describes the association of two or more polypeptide chains to form one functioning protein unit
Secondary Structure
[BONUS ITEM]
The ________ describes the regular, repetitive folding patterns of the polypeptide backbone, which are stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the backbone atoms.