Understanding Ultrasound Physics Chapter 4
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Which of the four values for pulse repetition frequency would have the longest pulse repetition?
a. 2kHz
b. 4000 Hz
c. 6 Hz
d. 1 kHz
C. 6 Hz.
Pulse repetition period is the reciprocal of pulse repetition frequency. This choice has the lowest pulse repetition frequency, and thus, the longest pulse repetition.
Four pulses have pulse repetition periods as listed below. Which of the following four waves has the highest pulse repetition frequency?
a. 8 s
b. 80 ms
c. 5 ms
d. 400 ks
c. 5 ms
The pulse with the shortest pulse duration will have the highest pulse repetition frequency.
Which of the four pulses with PRFs listed below has the lowest pulse repetition frequency?
a. 12 kHz
b. 6,000 Hz
c. 20 kHz
d. 1 kHz
C. 20 kHz
Pulse repetition period is the reciprocal of pulse repetition frequency. This answer has the highest pulse repetition frequency, and thus the shortest pulse repetition period.
Four waves have pulse reputation periods as listed below. Which of the following four waves has the lowest pulse repetition frequency?
a. 8 s
b. 80 microseconds (us)
c. 8000 ns
d. 800 ms
a. 8s
The pulse with the longest pulse duration will have the lowest pulse repetition frequency.
True or False: Two waves can have identical pulse repetition frequencies, even if their pulse repetition periods are different?
False.
Two waves can never have identical pulse repetition frequencies if their pulse repetition periods are different.
True or False. Two waves can have identical PRF's, even if their periods are different.
True.
Period and pulse repetition frequencies are unrelated.
True or False : Two waves can have identical pulse repetition frequencies even if their frequencies are different.
True.
Frequency and pulse record frequency unrelated.
True or False. PRF and pulse repetition period are determined only by the imaging depth.
True.
This is a very important concept
If all other factors remain unchanged, what happens to the duty factor (increases, decreases, remains the same) when the pulse repetition frequency increases?
Increases
If all other factors remain unchanged, what happens to the duty factor (increases, decreases, remains the same) when imaging depth increases?
Decreases
If all other factors remain unchanged, what happens to the duty factor (increases, decreases, remains the same) when the pulse repetition period increases?
Decreases
If all other factors remain unchanged, what happens to the duty factor (increases, decreases, remains the same) when the sonographer uses a new transducer with a longer pulse duration?
Increases
What is the duty factor if the pulse duration is 1 microsecond, and the pulse repetition period is 1 ms?
A. 100%
B. 0.1
C. 0.01
D. 0.001
5. D
Which of the following terms does not belong with the others?
A. high duty factor
B. shallow imaging
C. low PRF
D. short pulse repetition period
c. Low PRF
Low pulse repetition frequency is associated with deep imaging. The other three choices are all associated with shallow imaging.
Which of the following terms does not belong with the others?
A. low duty factor
B. shallow imaging
C. low PRF
D. long pulse repetition period
B. Shallow imaging
Shallow imaging does not belong. The other three choices are also associated with deep imaging.
____________ is the time from the start of a pulse to the end of that pulse.
pulse duration
____________ is the time from the start of a pulse to the start of the next pulse.
pulse repetition period
What are the duty factors of the 4 patterns that appear in Fig. 4.13?
a. 100%
b. 33%
c. 0%
d. 50%
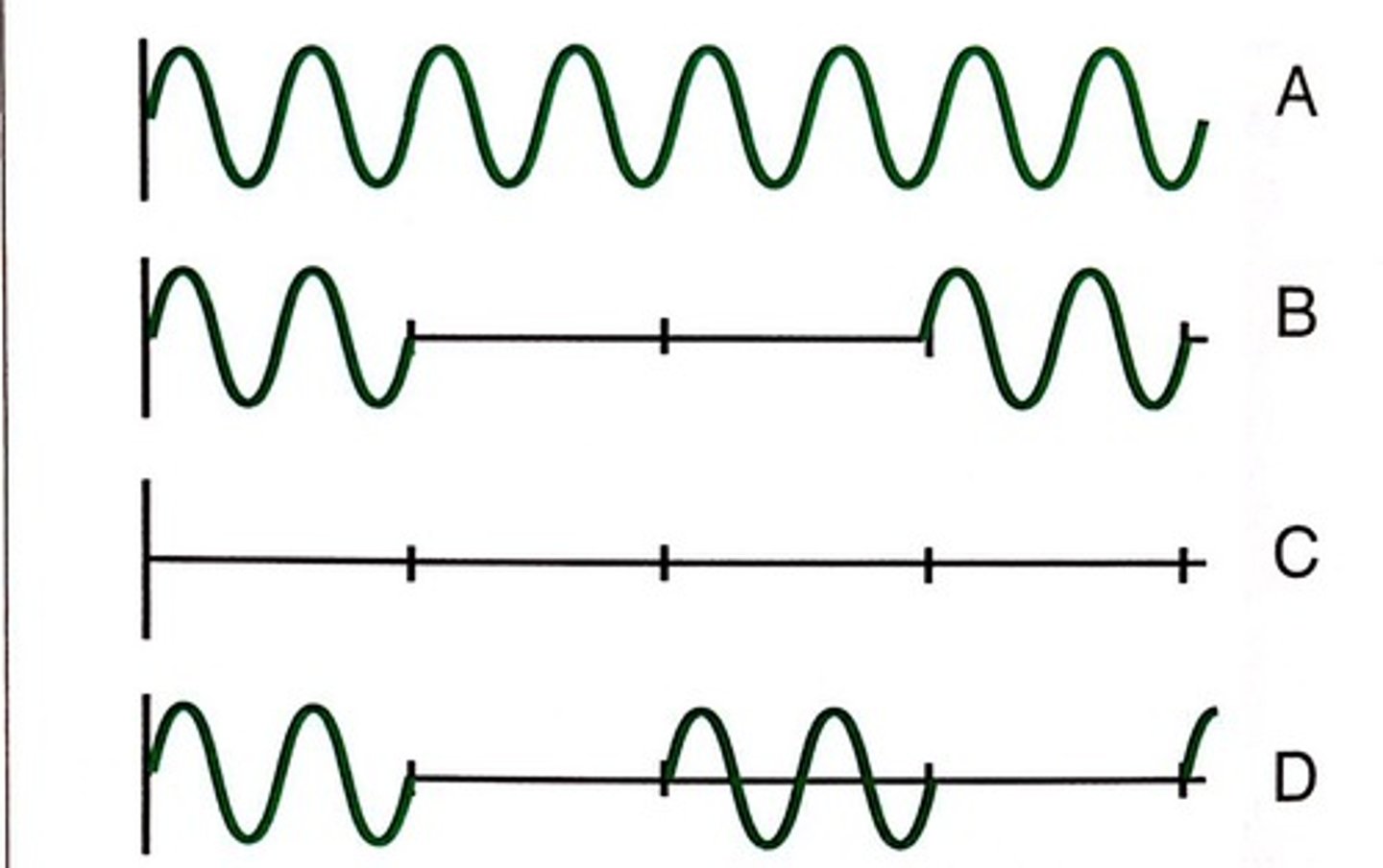
Which of the patterns in Fig. 4.13 indicates a system with a superficial imaging depth?
Choice D has the shallowest imaging depth because the pulse repetition period is the shortest.
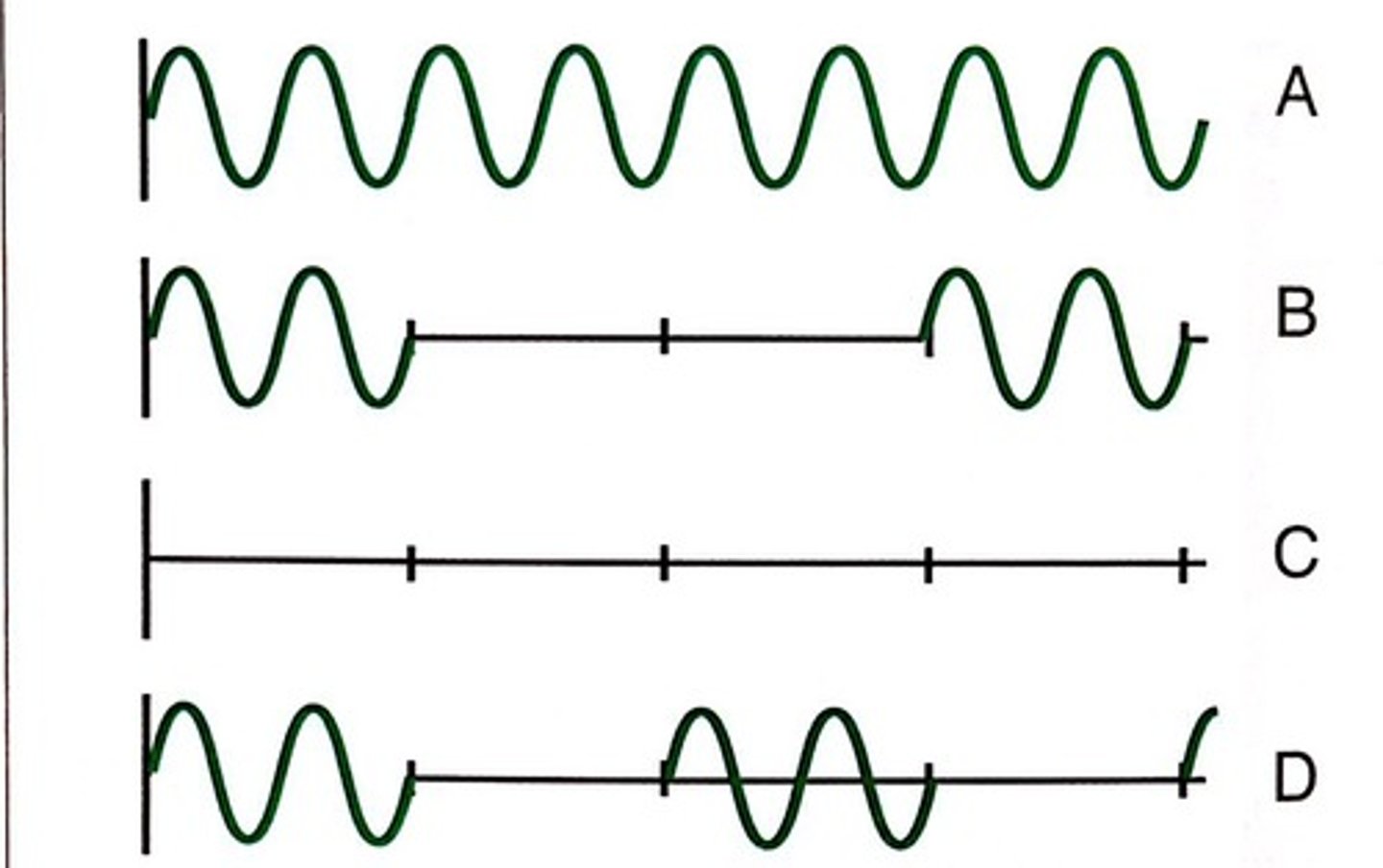
Which of the patterns in Fig. 4.13 indicates a system with a deep imaging depth?
Choice B has the deepest imaging depth because the pulse repetition period is the longest.
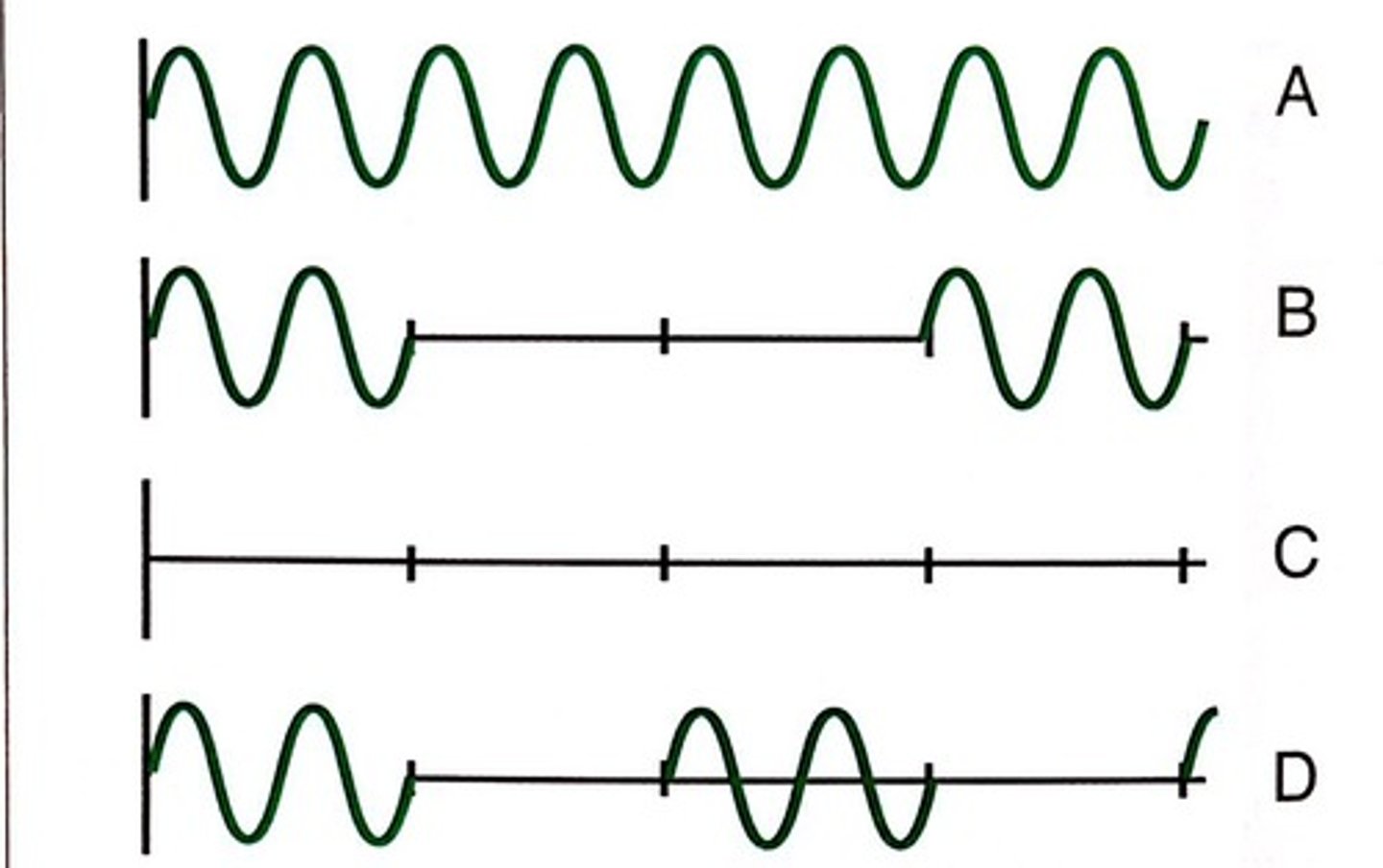
Which two of the patterns in Fig. 4.13 identify an ultrasound system that cannot perform anatomic imaging?
A and C. System A cannot perform anatomic imaging because it is continuous wave. Only pulsed sound creates images. Also, system C cannot perform imaging because it does not produce sound.
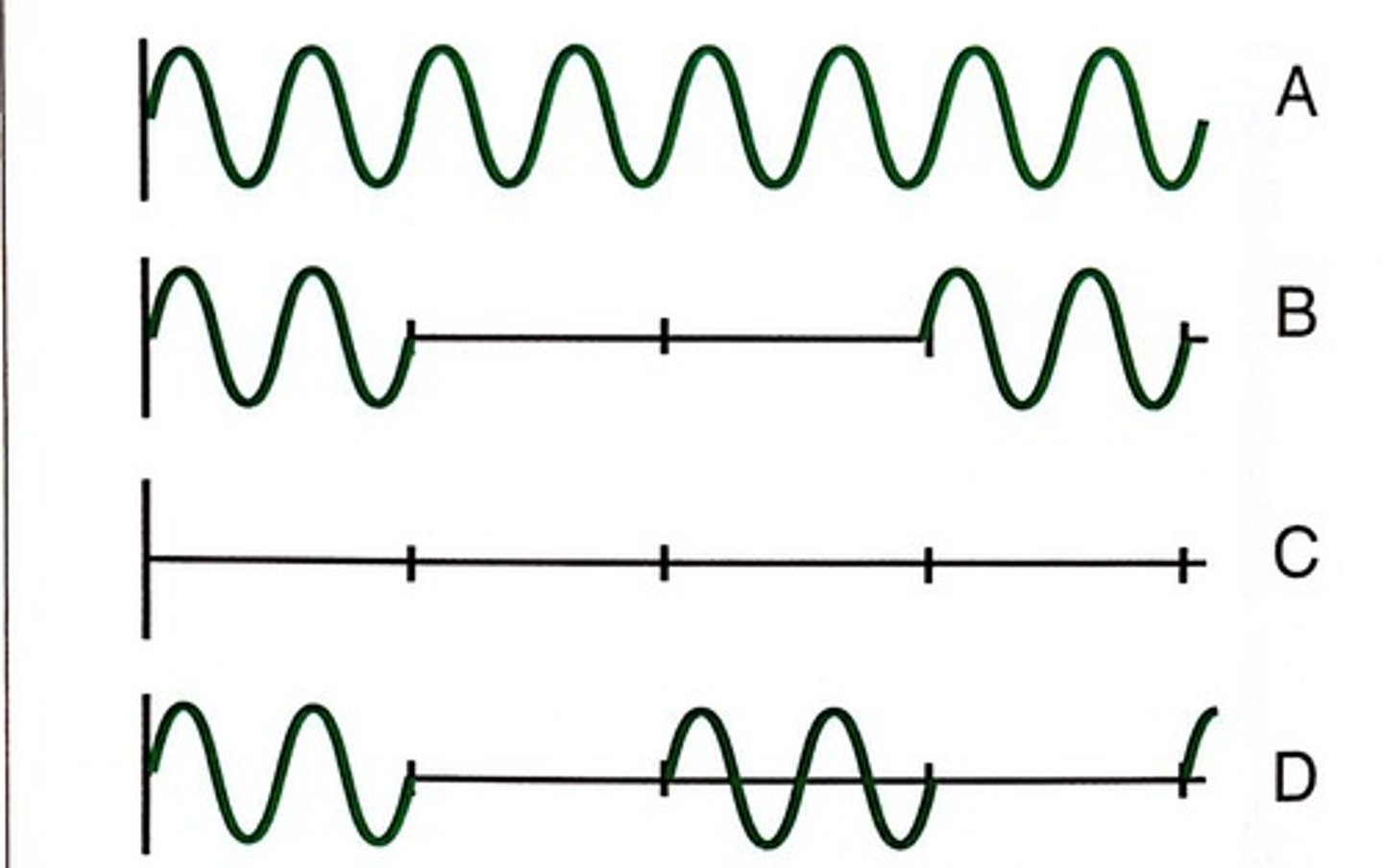
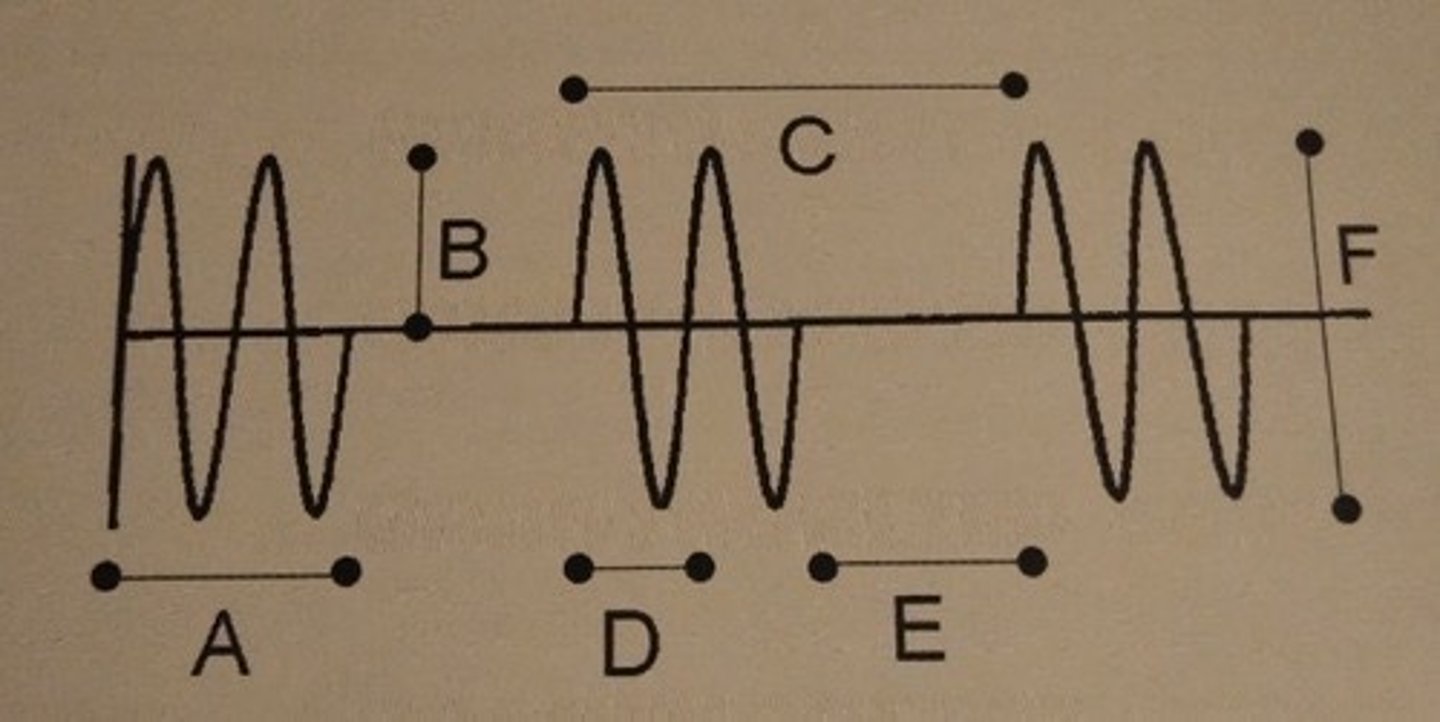
Which of the following describes line A?
A. frequency
B. pulse rep. period
C. period
D. pulse duration
E. duty factor
F. amplitude
D. Pulse duration.
If the units for line A are time, line A is a pulse duration
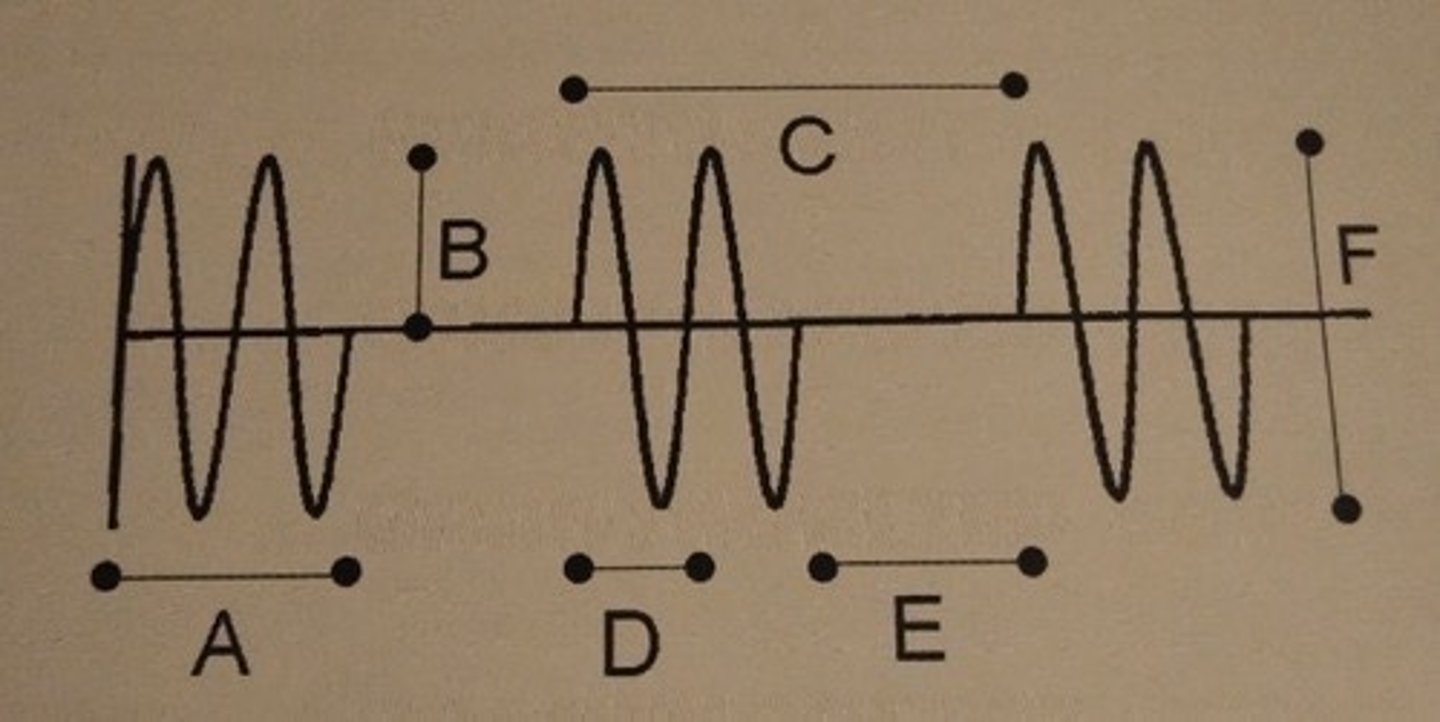
Which of the following describes line A?
A. frequency
B. pulse rep. period
C. period
D. Spatial pulse length
E. duty factor
F. amplitude
D. Spatial pulse length
If the units for line A are distance, line A is a spatial pulse length. Both spatial pulse length and pulse duration describe a pulse
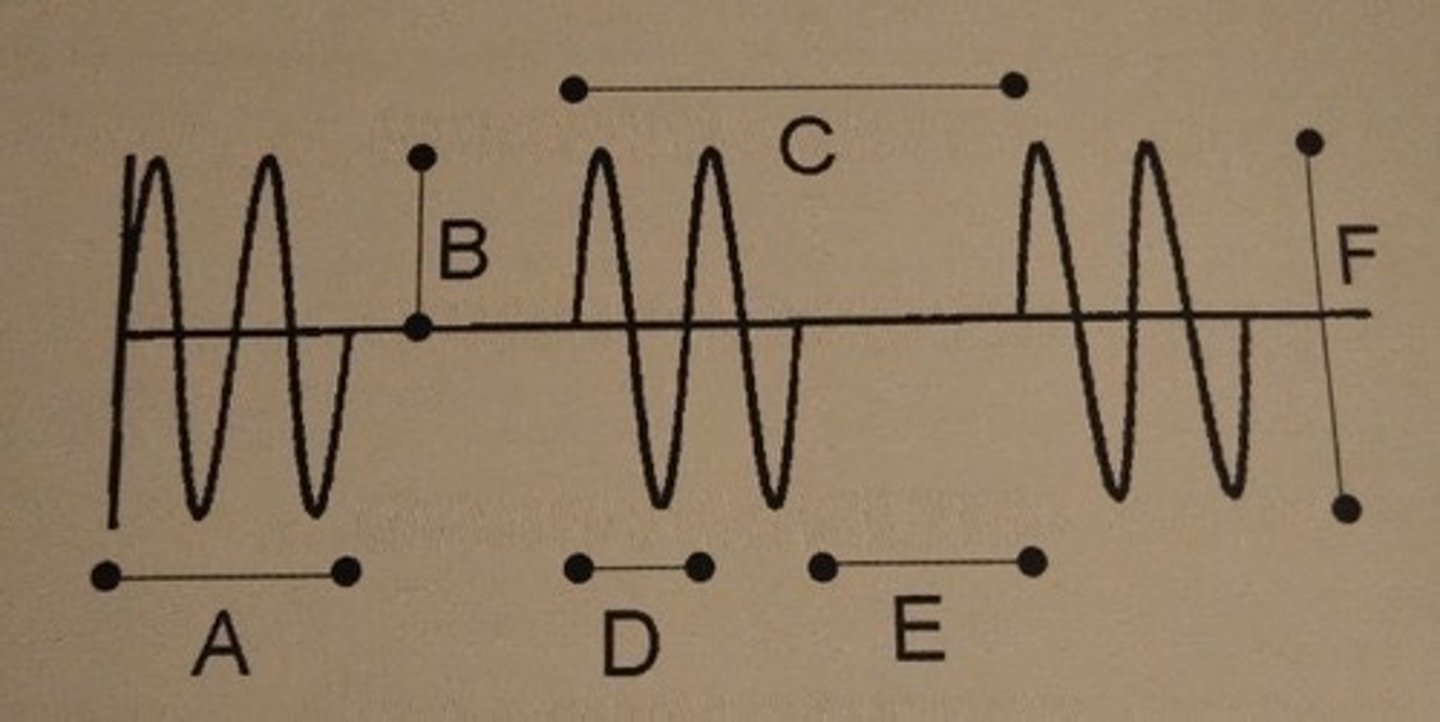
Which of the following describes line B?
A. frequency
B. pulse rep. period
C. period
D. pulse duration
E. duty factor
F. amplitude
F. Amplitude
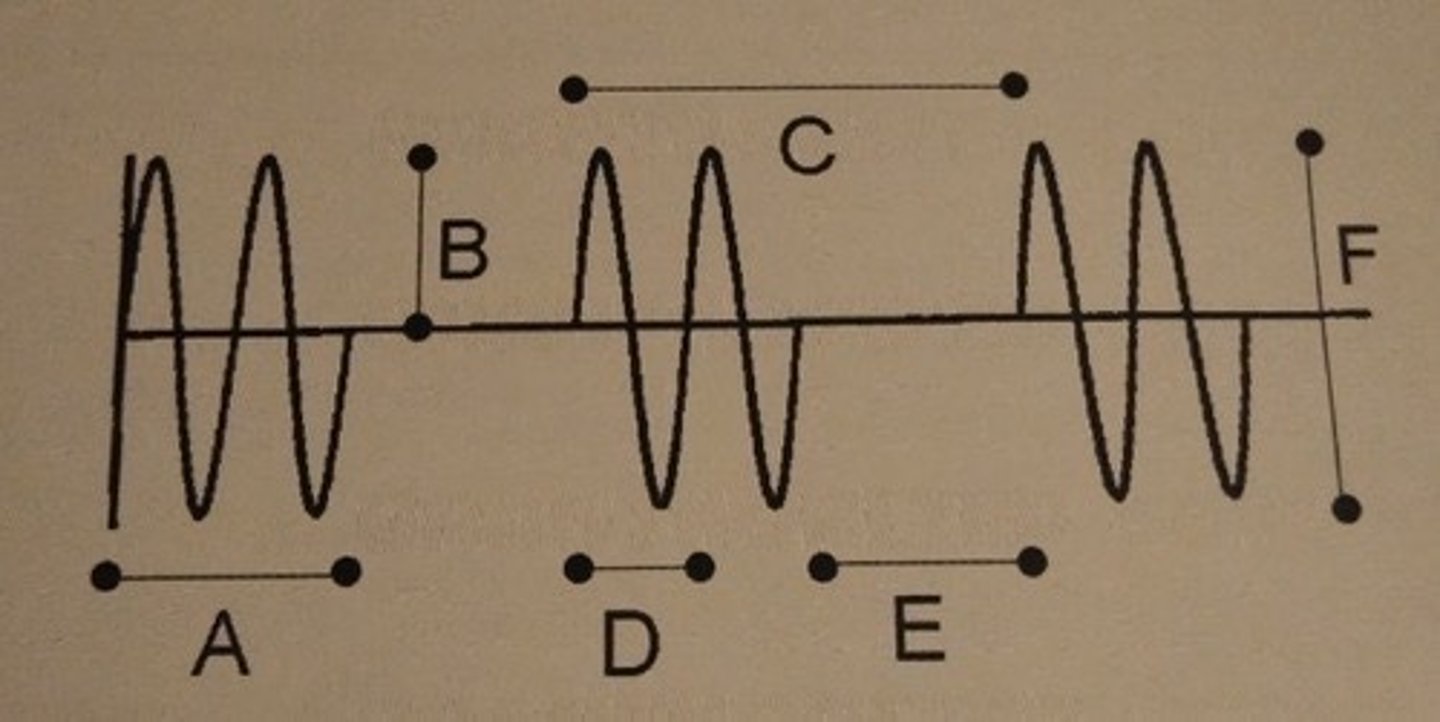
Which of the following describes line C?
A. frequency
B. pulse rep. period
C. period
D. pulse duration
E. duty factor
F. amplitude
B. Pulse repetition period
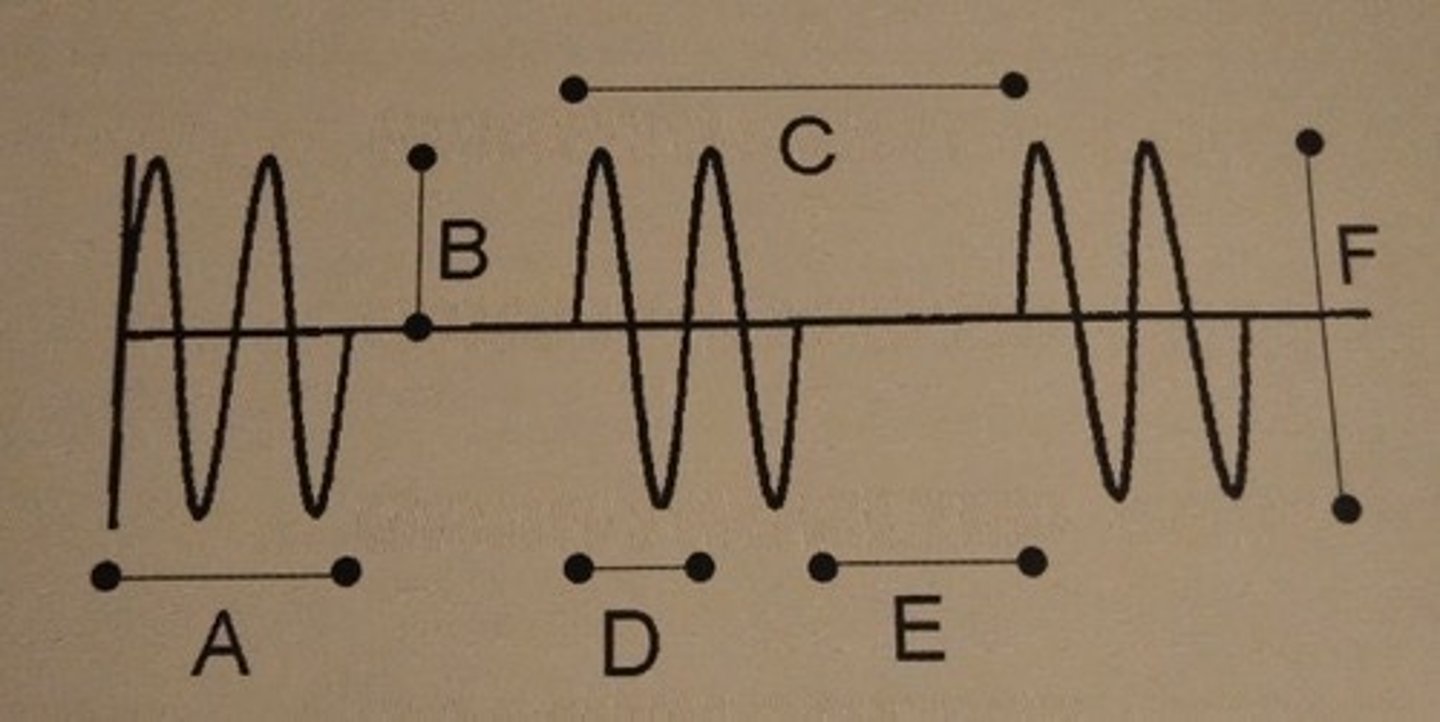
Which of the following describes line D ?
A. frequency
B. pulse rep. period
C. period
D. pulse duration
E. duty factor
F. amplitude
C. Period
If the units for line D are time, D is a period
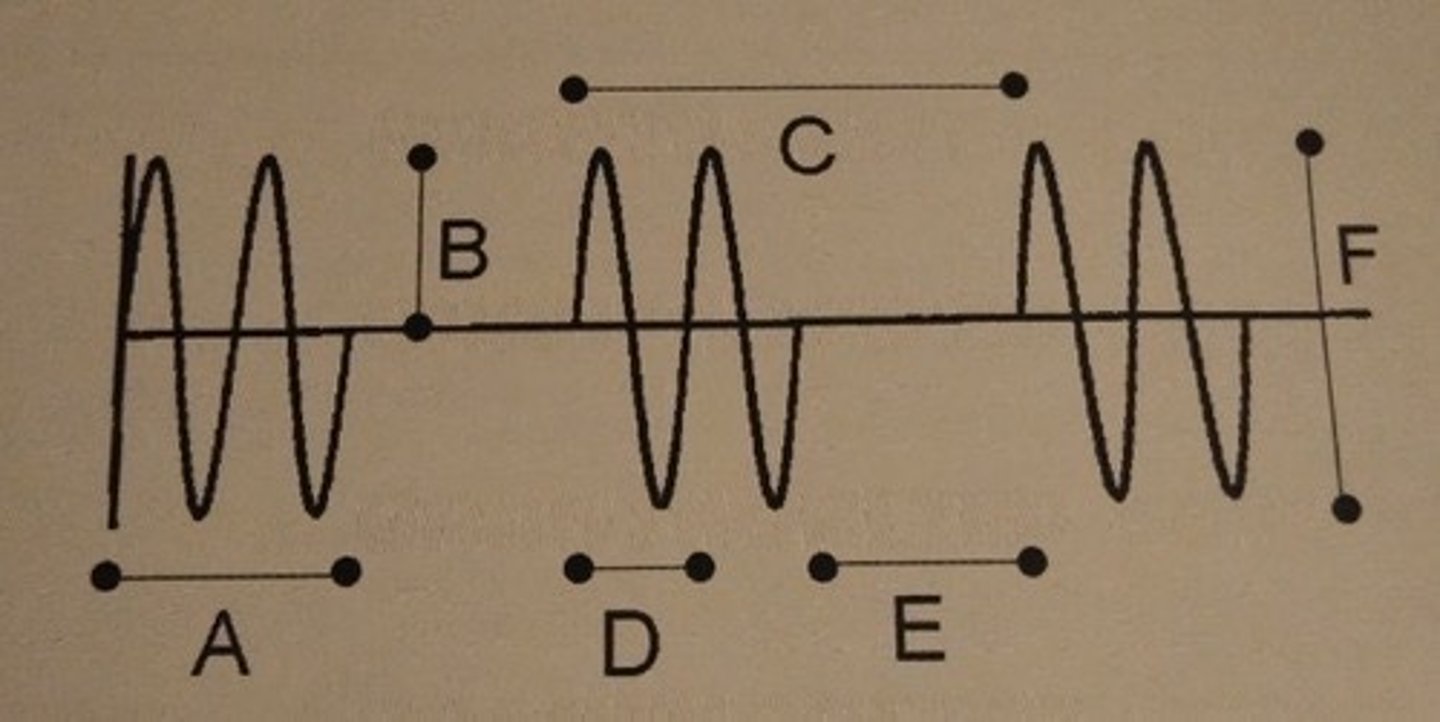
Which of the following describes line D ?
A. frequency
B. pulse rep. period
C. wavelength
D. pulse duration
E. duty factor
F. amplitude
C. Wavelength.
If the units for line D are distance, line D is a wavelength. Both wavelength and period describe a single cycle.
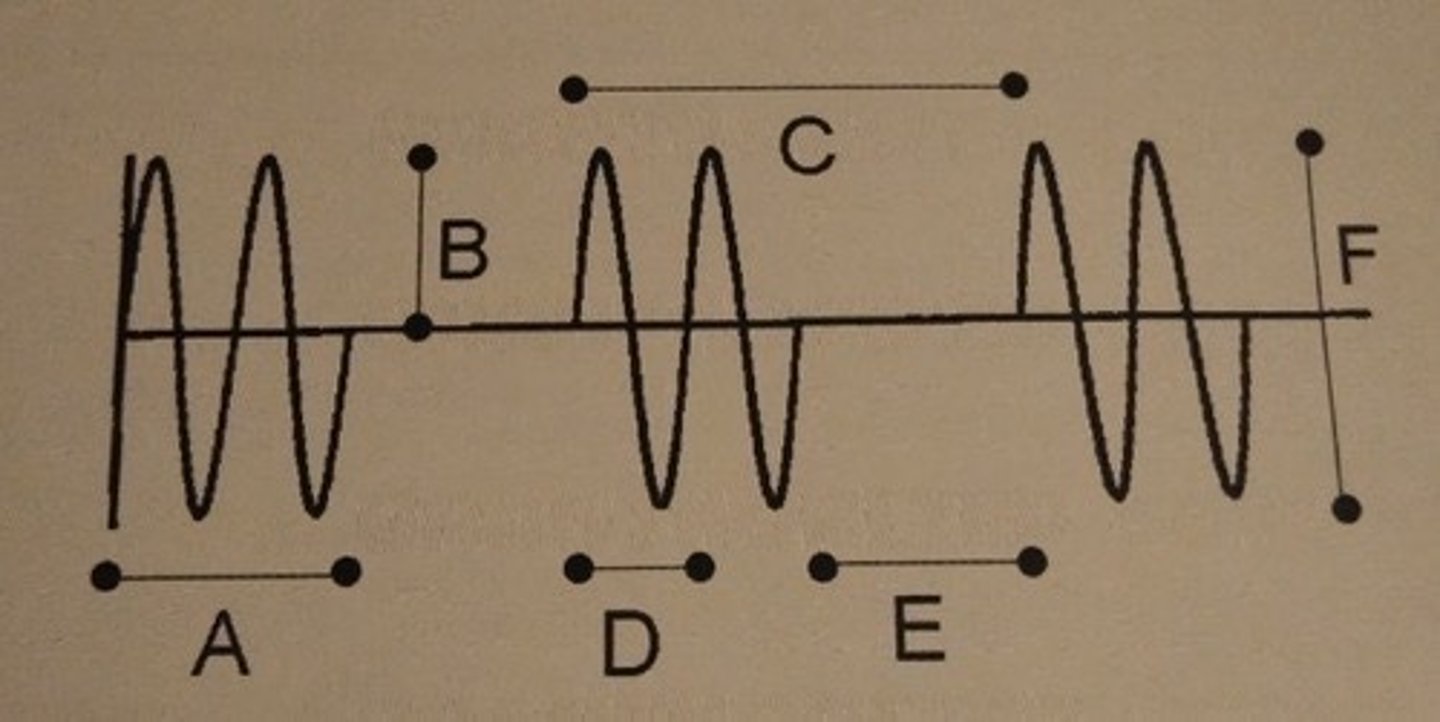
Which of the following describes line E?
A. frequency
B. pulse rep. period
C. period
D. pulse duration
E. duty factor
F. none of the above
F. None of the above.
Line E represents only the listening time
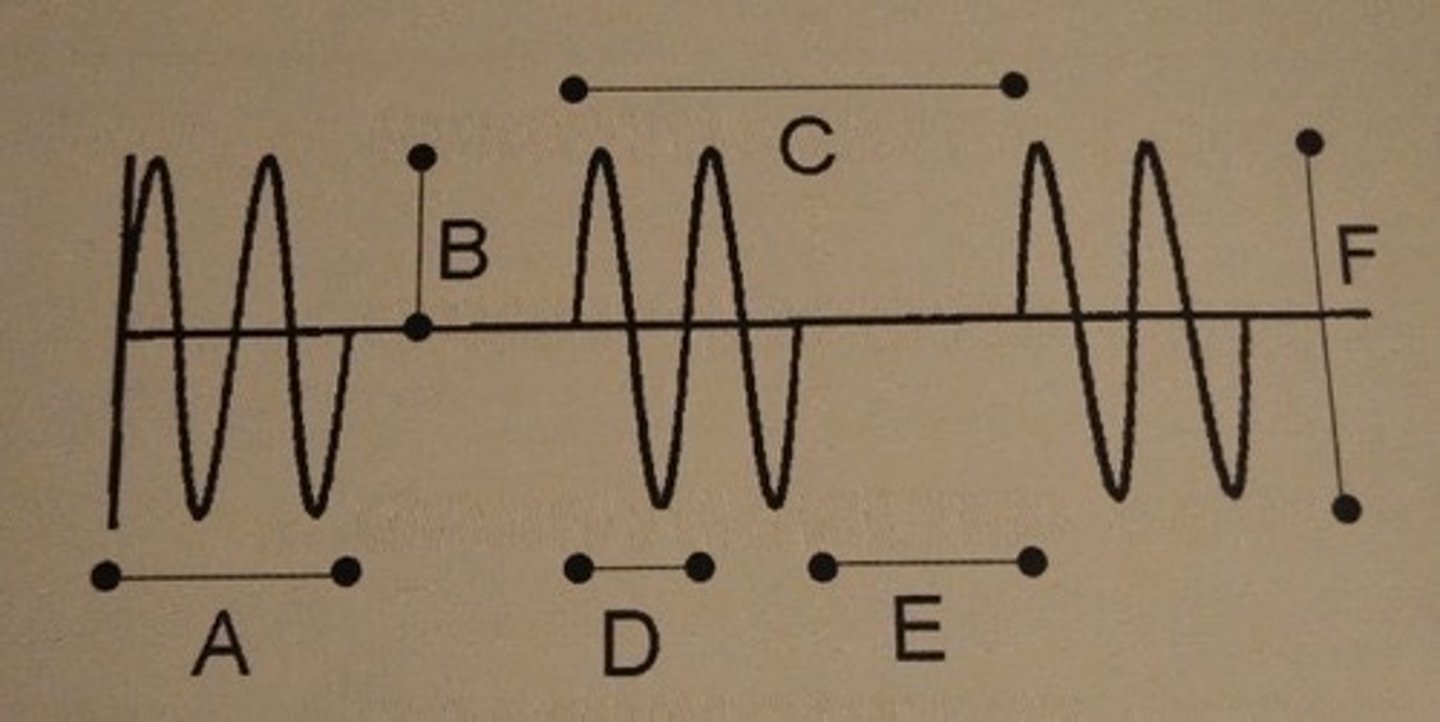
Which of the following describes line F?
A. frequency
B. pulse rep. period
C. period
D. pulse duration
E. peak-to-peak amplitude
E. peak-to-peak amplitude
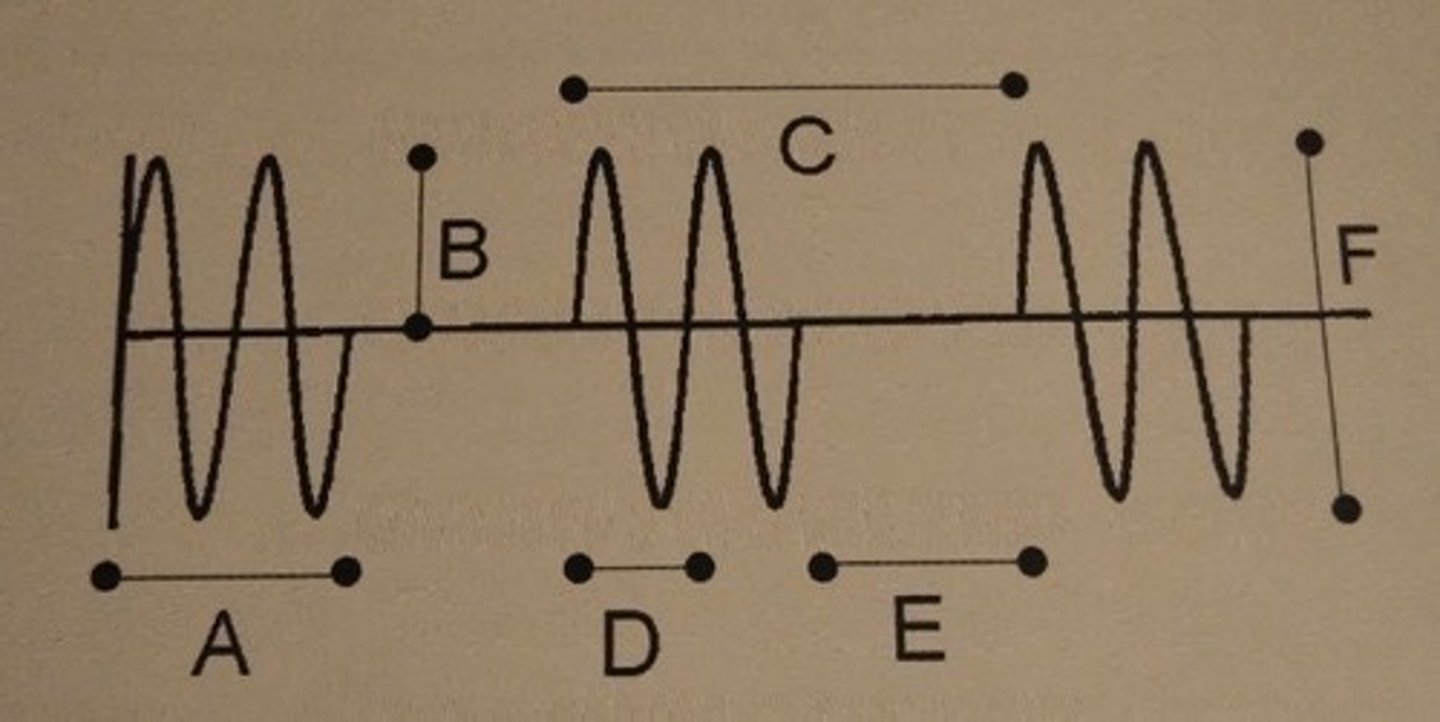
Which of the following best describes the duty factor?
A. A x B
B. A/E
C. D/E
D. A/C
E. E x F
F. (A + B)/C
D. A/C
To determine the duty factor, divide pulse duration by pulse repetition period. This is choice D
Pulse repetition frequency is the reciprocal of _________.
Pulse repetition period
By changing the imaging depth, which of the following does the operator also change (more than 1 may be correct)?
A. pulse repetition frequency
B. duty factor
C. propagation speed
D. pulse repetition period
E. amplitude
F. spatial pulse length
A. pulse repetition frequency
B. Duty factor
D. Pulse repetition period
The speed of a 5 MHz CW is 1.8 km/sec. The wave is then pulsed with a duty factor of 0.5. Calculate the new propagation speed.
The propagation speed for pulse and continuous wave sound is the same; in this case, 1.8 km/s. It depends upon the medium through which the sound travels.
What is the duty factor if the pulse duration is 1 microsecond, and the pulse repetition period is 1 ms?
The duty factor is 0.001 or 10^-3.
10^-6 divided by 10^3 = 10^-3, or 0.001.
What is the duty factor if the pulse duration is 1 millisecond, and the pulse repetition period is 1 second?
The duty factor is 0.001 or 0.1%
0.001 divided by 1.0 =0.001
A sonographer adjusts the depth from 8 cm to 16 cm. Would each of the following parameters increase, decrease, or remain the same?
A) Period
B) Frequency
C) Wavelength
D) Speed
E) Amplitude (initial)
F) Pulse Duration
G) PRF
H) Duty Factor
I) SPL
J) PRP
A. Remains the same
B. Remains the same
C. Remains the same
D. Remains the same
E. Remains the same
F. Remains the same
G. Decreases
H. Decreases
I. Remains the same
J. Increases
A sonographer is using a 3 MHz transducer and changes to a 6 MHz transducer. The imaging depth remains unchanged. Would each of the following parameters increase, decrease, or remain the same?
A. period
B. frequency
C. wavelength
D. speed
E. intensity (initial)
F. PRF
G. pulse repetition period
A. decreases
b. increases
c. decreases
D. Remains the same
E. Remains the same
F. Remains the same
G. Remains the same
A sonographer is using a 3 MHz transducer and increases the output power to visualize structures that are positioned deeper in the patient. No other controls are adjusted. Would each of the following parameters increase, decrease, or remain the same?
A. period
B. frequency
C. wavelength
D. speed
E. power (initial)
F. intensity (initial)
G. pulse duration
H. PRF
I. duty factor
J. spatial pulse length
K. pulse repetition period
A. Remains the same
B. Remains the same
C. Remains the same
D. Remains the same
E. Increases
F. Increases
G. Remains the same
H. Remains the same
I. Remains the same
J. Remains the same
K. Remains the same