unit 1 pt 2 psych slides/notes
sleep & dreams
sleep:
state of consciousness
the diff levels of awareness & responsiveness to int. & ext. stimuli
most psychologists define consciousness as our subjective awareness of ourselves & our envmnt
wakefulness
sleeping & dreaming
altered states of consciousness
rhythm of sleep
circadium rhythm
24 hr cycle including sleep & wakefulness
controlled by hypothalamus
receives input from eyes & especially sensitive to light & dark cycles of day & night
one sleep cycle
shown on hypnogram graphs
stages 1-3 of sleep = “quiet sleep”
stage 1
j drifting to sleep
may experience fantastic images &/or auditory hallucinations (hypnagogic sensations)
mix of alpha & theta waves
stage 2
more relaxed
clearly asleep
sleep spindles = short bursts of brain activity
stage 3
deepest sleep
hard to wake from
only occurs during first few sleep cycles of night
large delta waves
REM sleep = paradoxical sleep
rapid eye mvmnt
brain is almost as active as being awake but body is physically paralyzed
dreams
sleep deprivation
teens need 8-10 hrs of sleep
there is no making up on sleep (naps don’t count)
lots of neg effects
REM rebound = incr in sleep duration & intensity
jet lag = maladjustment to circadian rhythms resulting from traveling through several time zones in a short span of time
shift work = work scheduled during swing shift (4pm-12am) or night shift (12am-8am)
sleep theories
sleep protects = sleeping in darkness when predators loom kept our ancestors out of harm’s way
sleep recuperates = sleep helps restore & repair brain & body tissue
sleep helps remembering = sleep stores & rebuilds fading mems; memory consolidation
sleep & growth = pituitary gland releases growth hormones
restoration of resources = brain & body recover & replenish various physical & mental resources during sleep
sleep disorders
insomnia = difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep
narcolepsy = overpowering urge to fall asleep that may occur while talking or standing up; sleep attacks lasting abt 5 mins or less
REM behavior disorder = muscles are not paralyzed as they should be; seen more often in middle age/elderly men & sometimes linked w/ parkinson’s disease
sleep apnea = failure to breathe when asleep
sleep walking = aka somnambulism
dreams:
dream theories
wish fulfillment
sigmund freud
dreams provide a safety value to discharge unconscious wants & desires
manifest content = remembered storyline of dream
latent content = underlying meaning of dream
information processing
dreams may help to sift, sort, & fix day’s experiences in our mems
physiological function
dreams provide sleeping brain w/ periodic stimulation to develop & preserve neural pathways
neural networks of newborns are fast developing & therefore need more sleep
activation-synthesis theory
suggests that brain engages in a lot of random neural activity
dreams make sense of random activity bc brain doesn’t like randomness
dreams are the brain’s interpretations of its own activity & therefore mean nothing
cognitive development
some researchers argue that we dream as a part of brain maturation & cognitive development
consolidation theory
consolidation = stabilization & strengthening of mems over time
non-REM sleep
key for consolidating declarative mems (facts & events) during slow-wave sleep
REM sleep
important for consolidating emotional & procedural mems (skills & habits)
timing
sleep shortly after learning enhances memory consolidation
psychoactive drugs
blood-brain barrier = a border of blood vessels in the brain that don’t allow the blood of the peripheral nervous system to have an effect on the central nervous system
psychoactive drugs = chemical substances that alter perception and mood (effect consciousness)
agonist vs antagonist
agonist = mimics neurotransmitter activity (morphine)
antagonist = blocks neurotransmitter activity (botox)
tolerance = effects of a psychoactive drug lessens with repeated exposure
addiction
physical = physical condition caused by chronic use of a tolerance-forming drug in which abrupt withdrawal causes unpleasant physical symptoms
a state that involves emotional-motivational withdrawal symptoms upon cessation of drug use
withdrawal
physical symptoms = fatigue, headaches, tremors, sweating, vomiting, & many other varying symptoms
psychological symptoms = dysphoria, depression, anxiety, agitation, anhedonia
sensation
sensation = the process of constructing mental representations of the external world by detecting physical stimulus & converting it into neural signals
vs perception = when we select, organize, & interpret sensations
bottom-up processing = analysis of the stimulus begins w/ the sense receptors & works up to the level of the brain & mind (ex: which flag is american flag)
top-down processing = info processing guided by high level mental processes as we construct perceptions drawing on our experience & expectations (being able to read a sentence despite letters missing)
transduction = the process by which sensory info is converted into neural signals that the brain can interpret & is crucial for how we perceive & interact w/ the world around us
absolute threshold = minimum stimulation needed to detect a particular stimulus 50% of the time
difference threshold = minimum difference between two stimuli required for detection 50% of the time, also called just noticeable difference (JND)
weber’s law = jnd is proportional to intensity of stimulus
sensory adaptation = diminshed sensitivity as a consequence of constant stimulation
sensory interaction = one sense affects the perception of another (taste & smell)
synesthesia = one sensory stimulation stimulates an automatic & involuntary experiences in another sensory pathway
vision
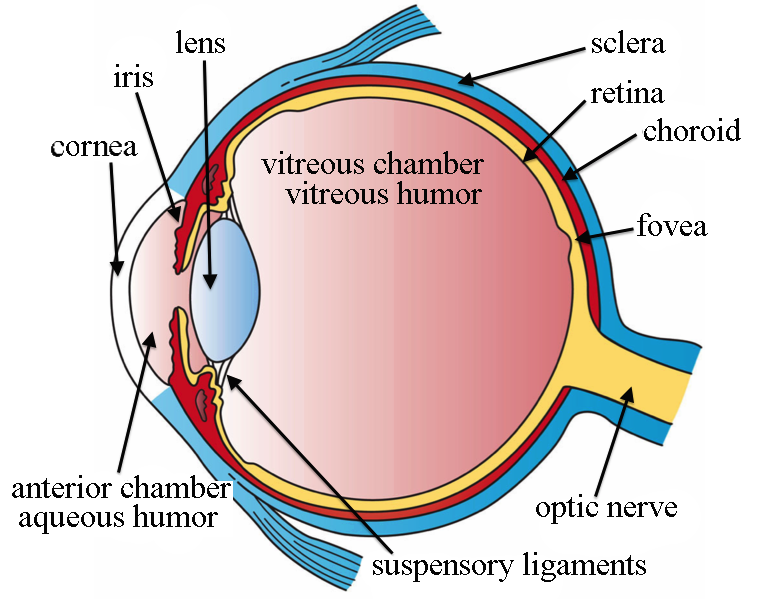
optic/visual nerve = bundle of nerve fibers that transmits visual info from retina to brain
primary function is to bring message from eye to brain
sensation —> perception once enters brain
wavelength = distance from one peak of one wave to the peak of the next
intensity of color = how high each wave is
amplitude = how high each wave is
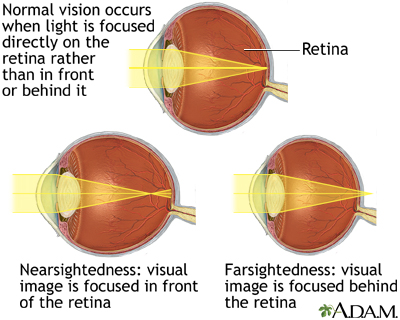
nearsightedness = can see near better but not far
farsightedness = can see far better but not near
retina = light-sensitive inner surface of eye & contains rods & cones
rods = sensitive to light
cones = color & fine detail
feature detectors = nerve cells in the visual cortex that respond to specific features (edges, angles, length, mvmnt)
visual info processing = processing several aspects of the stimulus simultaneously = parallel processing
monochromatism = grey-scale
dichromatism = a person is missing either a red or green cone
trichromatic theory = rbg cones
opponent process theory = four primary colors opposed in pairs of red-green, blue-yellow, and black-white
afterimages = supports opponent process theory
prosopagnosia = ppl can’t recognize the faces of friends and family, and even their own face sometimes
blindsight = response to visual stimuli w/o conscious awareness of seeing
chemical senses
gustation/taste = a chemical sense bc a substance is what is detected (not j energy like in sight & hearing)
super-tasters = more taste buds
medium tasters = 15-35 taste buds
non-tasters = 15 or less taste buds
sweet = donut
sour = lemon
salty = salt
bitter = coffee
umami = meat
oleogustus = oils
astringent = cranberries
olfaction/smell = relayed directly to brain region associated w/ mems & emotional processes
sensory interaction = when one sense affects another sense
pheromones = chem signals that provide info to members of the same species & marks territories