Vertebrate Zoology Exam 1
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
Zoology
The study of animals
What things do vertebrates have?
A backbone
Bilateral symmetry
A true body cavity
An enlarged brain cavity/cranium
An internal skeleton
Gills/lungs
Separate sexes
Precambrian Era
The first era of life on Earth that lasted 4,600 mya-570 mya, but vertebrates did not exist yet
Paleozoic Era
The second era of life on Earth that lasted 570 mya-245 mya that contained 6 periods
What were the periods of the Paleozoic Era in order?
Cambrian (with algae and invertebrates)
Ordovician (jawless fishes)
Silurian (jawed fishes)
Devonian (first amphibians)
Carboniferous (first reptiles)
Permian (diversity spike before a mass extinction)
(Pneumonic device: Carrie’s onions smelled dank, crude, and putrid)
Mesozoic Era
The third era of life on Earth that lasted 245 mya-65 mya that contained 3 periods
What were the periods of the Mesozoic Era?
Triassic
Jurassic
Cretaceous
(Pneumonic device: Three jumpy creatures)
Cenozoic Era
The fourth and current era of life on Earth that started 65 mya and has 2 periods
What are the periods of the Cenozoic Era?
Paleogene
Neogene
(Remember that neo means new)
How did Native Americans view vertebrates?
In a practical sense where they weren’t “scientific” but didn’t overexploit organisms
How did European settlers impact vertebrate populations?
They were pragmatic at first, but became very harmful to them and their habitats in the mid 1700s (and realized their faults in the late 1800s)
Who were some of the earliest American naturalists?
Lewis and Clark
Audubon
Wilson
Bachman
What did the New York Sportsman Club accomplish?
It established game laws and penalized poachers
What did Theodore Roosevelt do to conserve vertebrates?
Helped form national forests and refuges, encouraged scientific research and policing, and gained hunters’ support
What did the Lacey Act do?
Declared that taking illegal game across state lines would count as a federal offense
What did the Migratory Bird Act do?
Restricted hunting of migratory bird species
What did the Pittman-Robertson Act do?
Designated federal funds (the majority being from hunting/trapping/fishing fees) for the production and reintroduction of wildlife
What did the Endangered Species Act do?
Established criteria for identifying or protecting threatened and endangered species
What’s the difference between ventral and dorsal?
Ventral is along the front/belly side/underside of an organism, dorsal is along the back side of an organism
What’s the difference between anterior and posterior?
Anterior is towards the head and posterior is towards the tail end of an organism
What’s the difference between medial and lateral?
Medial is along the midline (separating the body into two halves) and lateral is away from the midline of an organism
What’s the difference between proximal and distal?
Proximal is closer to a reference point and distal is farther from a reference point of an organism
What’s the difference between a sagittal, a transverse, and a frontal section?
A sagittal section divides into left and right portions, a transverse divides into anterior and posterior portions, and a frontal divides into dorsal and ventral sections
Taxonomy
The study of naming and classifying living organisms
Who was Linnaeus?
The “father of taxonomy” who developed the current classification system
Taxonomic Hierarchy
A system classifying organisms using 8 categories going from domain to species
What do prefixes do for the hierarchy?
Allow for further subdivisions in established categories
Binomial Nomenclature
A system assigning a 2-name (scientific name) combo to an organism
What is the biological species concept?
The concept that states organisms are species if they’re reproductively isolated
What is the evolutionary species concept?
The concept stating that organisms are species if they retain a distinct evolutionary identity
What are 4 characteristics of an organism in phylum chordata?
Having a notochord
Having a nerve cord
Having pharyngeal slits/pouches
Having a postanal tail
What describes organisms in subphylum urochordata?
Marine filter feeders that aren’t “chordate-like”; tunicates/sea squirts
What describes organisms in subphylum cephalochordata?
Small, marine filter feeders, usually with their posterior end buried in sediment; lancelets, amphioxus
What is the food path in a lancelet?
Mouth
Pharynx
Stomach
Intestine
Anus
What is the water path in a lancelet?
Mouth
Pharynx
Gills
Gill bars
Atrium
Atriopore
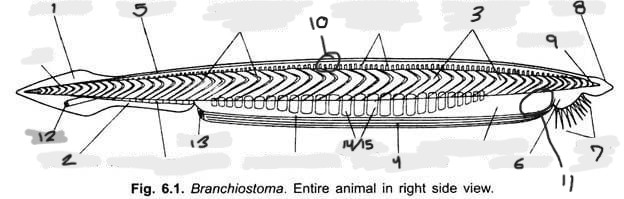
Name structure 1
Caudal fin
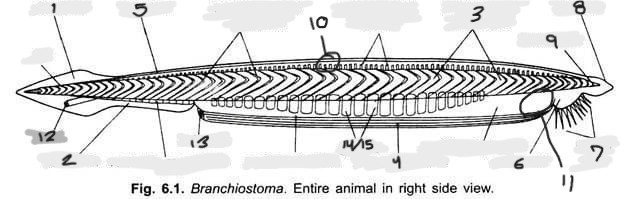
Name structure 2
Ventral fin
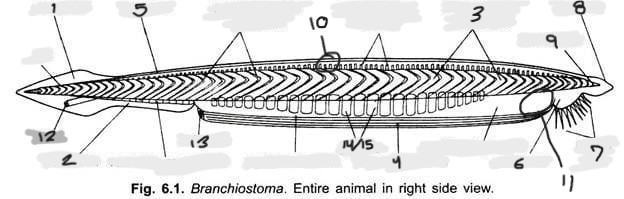
Name structure 3
Myomere(s)
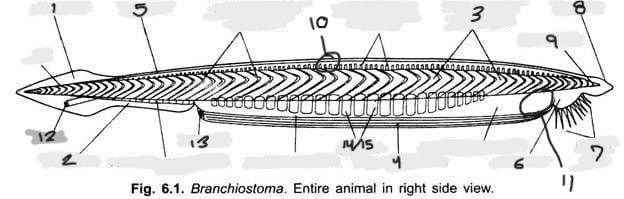
Name structure 4
Metapleural folds
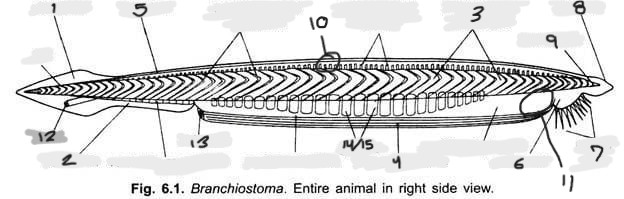
Name structure 5
Dorsal fin
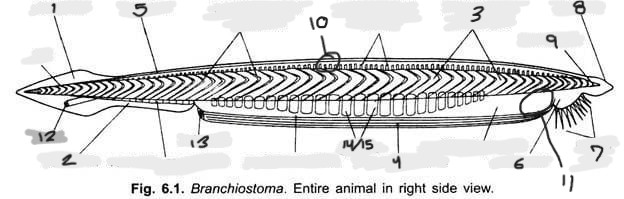
Name structure 6
Oral hood
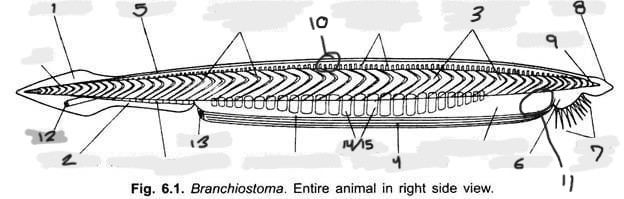
Name structure 7
Cirri
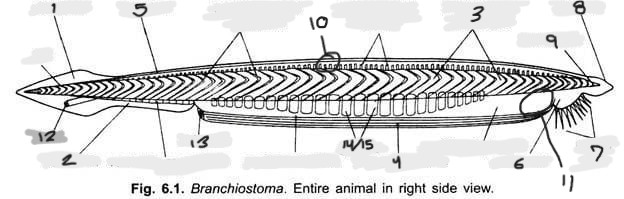
Name structure 8
Rostrum
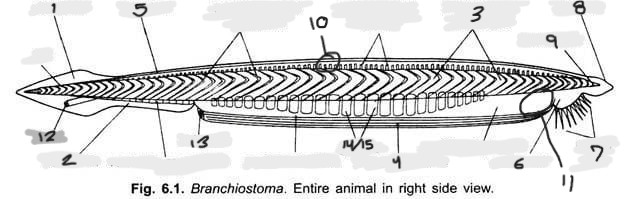
Name structure 9
Notochord
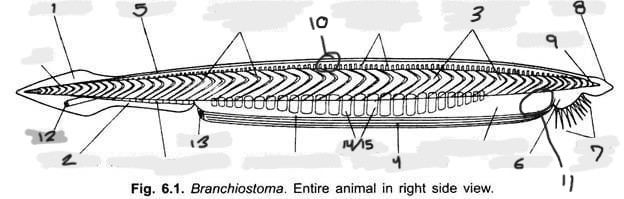
Name structure 10
Nerve cord
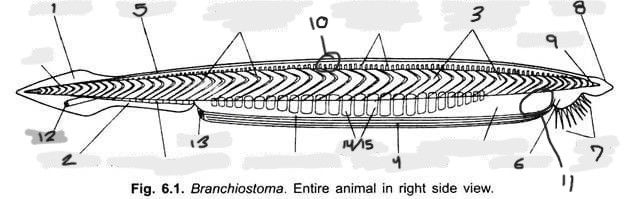
Name structure 11
Wheel organ (roughly)
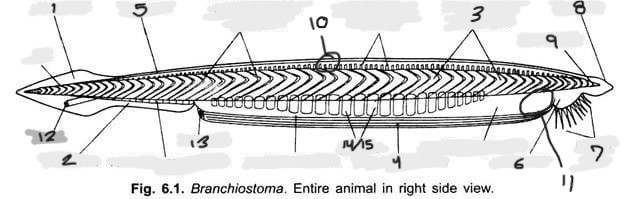
Name structure 12
Anus
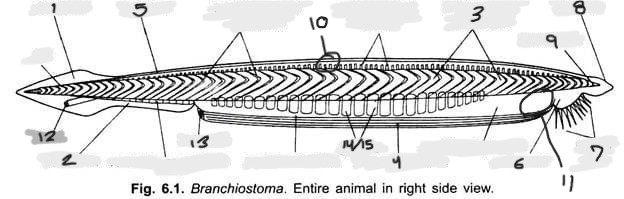
Name structure 13
Atriopore
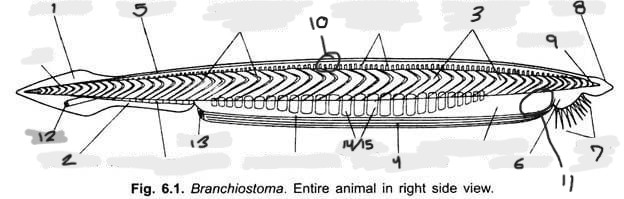
Name structures 14 and 15
Gill slits and gill bars
What is the anguilliform body type?
A long and tubular body type; seen in eels
What is a fusiform body type?
The most common body type shaped like a torpedo, stream lined, and allows for strong swimming; seen in sharks and tuna
What is a compressiform body type?
A laterally flattened body that’s ideal for slipping in/out of cover; usually seen in flounders and sunfish
What is a depressiform body type?
A dorsoventrally flattened body usually associated with bottom dwellers; seen in skates and rays
What is a globiform body type?
A spherically shaped body type that causes slow swimming; seen in pufferfish
What is a protocercal tail type?
A tail where the notochord extends to the posterior tail tip
What is a heterocercal tail type?
A tail type where the tail lobe sizes are uneven and (typically) the notochord extends into the larger lobe; the most primitive tail type
What is a homocercal tail type?
A tail type where the tail lobe sizes are even; the most common tail type
Agnatha
A superclass meaning “lacking jaws”; previously called cyclostomata (“round mouth”)
What were ostracoderms?
Organisms that shared an ancestor of agnathans; they had shell-like skin, were possibly scavengers or filter feeders, and lived from the Ordovician to the Devonian period
What are agnathans’ skin like?
Smooth and covered by a mucus covering; hagfish produce thick slime in defense and their “hide” are sold as eel-skin
What are agnathans’ skeletal systems like?
Cartilaginous, poorly developed with no paired fins; they have a cranium but no true vertebral column
What are myomeres?
Series of muscles that laterally undulate to help agnathans move
What direction does blood flow in an agnathan?
Posterior to anterior; going from the sinus venosus → atrium → ventricle → conus arteriosus
What parts of the heart act as pumps?
The atrium and the ventricle
What kind of gills do agnathans have?
Pouch-like gills
How many gill slit pairs do lampreys have? Hagfish?
7 pairs and a median nostril
Up to 15 pairs and a median nostril
What kind of metabolism do agnathans have?
They’re “cold-blooded”/poikilothermic so their body temp fluctuates with their environment
Buccal funnel
A round and suctorial mouth lined with horny teeth to scrape through scales and skin; a characteristic of lampreys (1/2 of all adults are parasitic)
How do hagfish eat?
They scavenge after seeking things out with their 3 pairs of barbels; they display knotting behaviors for leverage

Name structure 1
Olfactory lobe

Name structure 2
Pineal organ

Name structure 3
Cerebrum

Name structure 4
Medulla
What sense is the best-used and developed of agnathans?
Olfaction/smell
What is a lateral line system?
A linear series of pores full of neuromast cells that detect vibrations in water
Where can lamprey live? Hagfish?
Salt and freshwater (due to salt-secreting cells in gills)
Saltwater only (body fluids are the same salt concentration as ocean water)
What is a pronephros kidney?
The most primitive type of kidney that’s elongated and least efficient; seen only in adult hagfish
What is an opisthonephros kidney?
A decently advanced and slightly more efficient kidney form; seen in adult lampreys
What is a metanephros kidney?
The most advanced and efficient kidney type
What do agnathan reproductive systems look like?
They have one functioning gonad and are oviparous (eggs laid and develop outside; fertilized externally)
Milt
The term used for when male fish release sperm to fertilize an egg
What characteristic do hagfish eggs have that lampreys don’t?
Filaments to attach to other eggs or substrate
Redd
A term meaning a fish’s nest; seen in lampreys (made of gravel)
Where do lampreys need to spawn?
Only in freshwater, where the parents were born (upstream and tracked by smell)
How do lamprey young develop?
They filter feed after burrowing in substrate; they live in this larval stage for 3-7 years
How long do adult lampreys live for?
5-6 months if not parasitic, ~2 years if parasitic
What is the class and order of hagfish?
Class myxini, order myxiniformes
What is the class and order of lampreys?
Class petromyzontida, order petromyzontiformes
When were lampreys first found in North America?
1829, after the Welland Canal was built to bypass Niagara Falls