Lab Practical #1 Study Guide
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Scientific Method
Procedure of scientific investigations:
1. Observation-object of interest
2. Question- curiosity
3. Hypothesis- possible explanation for something that was observed
4. Prediction- make one
5. Test Prediction- design an experiment (should be carried put under controlled conditions and produce an outcome from only one variable). Gather data
6. Result- draw your conclusion from data and see if hypothesis was supported
What variables go on which axis and how do you label the graph?
The independent variables go on the x-axis, and you label the x-axis with that variable and its units of measurement. The dependent variable will label the y-axis and follow same procedure as x-axis.
dependent variable
The variable that changes in reaction to manipulations of the independent variable.
independent variable
The variable being manipulated by the person doing the experiment.
What is a control and what is its purpose in an experiment?
A group in the procedure that does not receive the experimental treatment.
hypertonic
hyper- (higher or greater and sometimes, by extension, too high)
When the solute concentration is described as higher relative to solute concentration of some other solution.
hypotonic
hypo- (lower or less than or sometimes too low)
When a solution has a lower total concentration of solutes relative to another solution.
isotonic
iso- (the same or equal)
When a solution has the same solute concentration relative to another solution.
solute
dissolved substances
solvent def and why is water a good solvent?
substances dissolved in a universal solvent like water
solution
The combination of solvent and dissolved solutes.
diffusion
The spreading of something
The movement of unequally distributed molecules that spreads them out.
Molecules will tend to move from a region of greater concentration to a region of lesser concentration.
osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane from a lower solute concentration to a higher.
What does it mean for a cell membrane to be selectively permeable?
It controls what molecules exit or enter the cell. It does not allow free diffusion. Small molecules can usually get through membranes more easily than larger molecules.
What is the NaCl percentage for an isotonic cell solution (physiological saline)?
A solution of 0.9% sodium chloride.
What happens to RBCs when they are put in a hypertonic solution?
The cytoplasm contracts because of the loss of water (called plasmolysis and the cell becomes crenated)
What happens to RBCs when they are put in a hypotonic solution?
Water leaves the cell and causes the cells to swell and the lyse (burst).
What happens to RBCs when they are put in a isotonic solution?
Nothing
What is the experiment with the dialysis bags and sucrose solutions used to study?
It is used to study the effect of solute concentration on the rate of osmosis.
What are the 4 major groups or organic molecules?
Proteins, Carbs, Nucleic acids, Lipids
What are the subunits of proteins called and what type of bond holds them together?
The subunits of proteins, amino acids, are held together by peptide bonds.
What does the primary structure of a protein look like?
The primary structure of a protein refers to the sequence of amino acids, decided by DNa info, in a polypeptide chain (protein).
What does the secondary structure of a protein look like?
This refers to a protein's natural tendency to fold or coil due to hydrogen bonds that occur along the backbone of the polypeptide chain.
What does the tertiary structure of a protein look like?
This structure occurs when the chain folds and coils even more. The increase in folds is due to interactions between r groups of amino acids (unique to each amino acid). Those interactions cause many more bonds pop up like van der waals and ionic ones.
What does the quaternary structure of a protein look like?
The quaternary structure of a protein occurs in proteins that need this structure for their function. It consists of two or more polypeptide chains that bind together to make a super macromolecule.
What does catalyst mean and what does it have to do with enzymes?
a catalyst is a chemical that lowers the energy activation barrier needed by molecules to react. In doing so, it precipitates reactions. A catalyst is part of the reaction, but is not changed, while the molecules acted upon become new products. An enzyme is a biological catalyst that allows chemical reactions to occur at a temperature compatible with life of the cell.
What is an enzyme?
a substance produced by a living organism that acts as a biological catalyst to bring about a specific biochemical reaction. An enzyme is usually a protein.
What is a substrate and what does it have to do with enzymes?
A substrate is the molecule to be acted upon by an enzyme.
What is an active site and what does it have to do with enzymes?
The active site is the spot on an enzyme that a substrate bonds to get acted upon.
What is denaturation?
Denaturation occurs when pH, salt concentration, temp, or other aspects of a protein's environment are altered. This causes chemical bonds and interactions within the protein to be destroyed, which in turn causes the protein to unravel and lose its natural structure. The function of a protein comes from its structure.
How can enzyme denaturation occur and what are the consequences of it?
It occurs when pH, salt concentration, temp, etc. aren't on par with the level needed for life. The consequence of enzyme denaturation is loss of catalytic activity (substrate can't bind).
Procedure for experiment with gelatinase and kiwi.
kiwi: fruit that contains gelatinase
gelatin: protein
What is the complementary enzyme for the protein gelatin and what does the enzyme do to the gelatin?
The complimentary enzyme for gelatin is gelatinase and it breaks down gelatin (gelatin can no longer set). Gelatinase can be found in kiwi, pineapple, mangoes, etc.
Is agar (carb) a substrate for gelatin's complementary enzyme?
'Tis not.
What is the biuret test used for and what color is the biuret reagent?
It is used to test for the presence of protein. The biuret reagent is blue.
What color does the biuret reagent turn into when the results are positive?
It turns purple.
If the biuret test results are negative what color will the reagent be?
There will be no change, so the reagent will remain blue.
What samples could produce a positive result on the biuret test?
Egg whites and gelatin.
What samples could produce a negative result on the biuret test?
Water, sucrose solution, and juice.
What are the two main types of nucleic acids?
The two main types of nucleic acids are DNA and RNA.
What are the subunits of nucleic acids?
The subunits of nucleic acids are nucleotides.
What are the subunits of nucleic acids made of?
The subunits of nucleic acids consist of a nitrogenous base, a (5-carbon) ribose sugar, and a phosphate group.
What's the difference between the ribose sugar in DNA and the one in RNA?
DNAs sugar is missing a hydroxyl group and RNA isn't (called deoxyribose sugar in DNA).
What's the structural difference between DNA and RNA?
DNA is double-stranded, way longer than RNA, stores genetic information, is self-replicating, has thymine instead of uracil, and has a deoxyribose sugar (is missing an oxygen containing hydroxyl group). RNA is single stranded, codes amino acids, acts a messenger between DNA molecules and the ribosomes, are synthesized by process of transcription, contains nucleotide uracil instead of thymine, and has all its hydroxyl groups.
What nitrogenous bases are found in DNA?
DNA's nitrogenous bases include Adenine (A that pairs with T), Thymine, Guanine (G that pairs with C), and Cytosine.
What nitrogenous bases are found in RNA?
RNA's nitrogenous bases include Adenine (A that pairs with U), Uracil, Guanine (G that pairs with C), and Cytosine.
What is a restriction endonuclease enzyme, where does it originate, and what does it do?
A restriction endonuclease enzyme are naturally made in bacteria to protect themselves from bacterial viruses. They recognize a particular DNA sequence, called a restriction site, and cut both DNA strands at precise points within this restriction site.
What is the substrate of an restriction enzyme?
Foreign DNA
How can agarose gel electrophoresis be used to separate DNA fragments?
Agarose gel is effective in separating DNA fragments because it consists of the movement of particles across a charged field. Seeing as DNA is negatively charged, it migrates from out of the agarose gel and then to the positively charged cathode.
What is a DNA fingerprint?
It is a process that uses restriction to identify the unique genetic makeup of an individual.
How do you interpret the patterns of bands seen on an agarose gel after electrophoresis and what are those bands?
The bands on the agarose gel are referred to as restriction fragments because they are pieces of DNA that were produces by the action of restriction enzymes.
What are the major steps involved in DNA fingerprinting procedure?
1. obtain a sample
2. isolate it
3. cut it with restriction enzymes
4. use gel electrophoresis to separate it
5. analyze it
What is the basic process involved in DNA isolation and what chemical is used to precipitate the DNA?
collect cells, break them open, and condense the DNA. Cold alcohol (95% ethanol) is used to precipitate it into a mass that is big enough to see.
Where is the objective lens located and what does it do?
It is at the lower end of the body tub, nearest to the slide. It forms the primary magnified image of the specimen.
Where is the ocular lens located and what does it do?
The ocular is at the top of the body tube. It gives additional magnification.
Where is the coarse focus located and what does it do?
It is mounted outside of the fine focus knob and it moves the stage up and down.
Where is the fine focus located and what does it do?
The fine focus is adjacent to the coarse focus knob and it allows you to focus precisely on an image.
How do you calculate the total magnification of a microscope?
Multiply the ocular and objective magnifications
What are RBCs shaped like and what is this form called?
RBCs have a biconcave form which means there is a dip in the middle of each one in mammalian blood samples. They have that form in order to carry oxygen.
What are some of the different protozoans we learned about in lab?
Amoeba, paramecium, and euglena
What are the some of the different live species of algae we learned about in class?
Spirogyra, chlamydomonas, micrasterias, oscillatoria, and spirulina
simple squamous epithelium cell (features, where can you find it, and what does it do?)
It's thin, and flat. It's found on the inner layer of blood vessels, and alveoli, abdominal cavity, etc. Since it's flat, it can allow gases too diffuse through it. Features: cell membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus.
simple cuboidal epithelium (features, where can you find it, and what does it do?)
It can be found in the glands (thyroid, adrenal, mammary). It has a cube-ish shape and a large nucleus. it stores hormones in the follicle. Features: cuboidal cell, large nucleus, interior of follicle, and cells between follicles.
simple columnar epithelium + goblet cells (features, where can you find it, and what does it do?)
It can be found in the lining of intestine. The cells are elongated, attached to a basement membrane, nucleus is near the base of the cell. Have microvilli on the top. Some are specialized cells called goblet cells, they secrete mucus of the top of the cell.
Stratified epithelium of mammals (features, where can you find it, and what does it do?)
Found in outermost layer of the skin. Consists of basement membrane, dermis layer, hair follicles, germinal cell layer, dead cells flaking off.
Stratified epithelium of a frog (features, where can you find it, and what does it do?)
Found in the outermost layer of the skin. Features: basement membrane, dermis layer of the skin, skin glands, germinal cells layer.
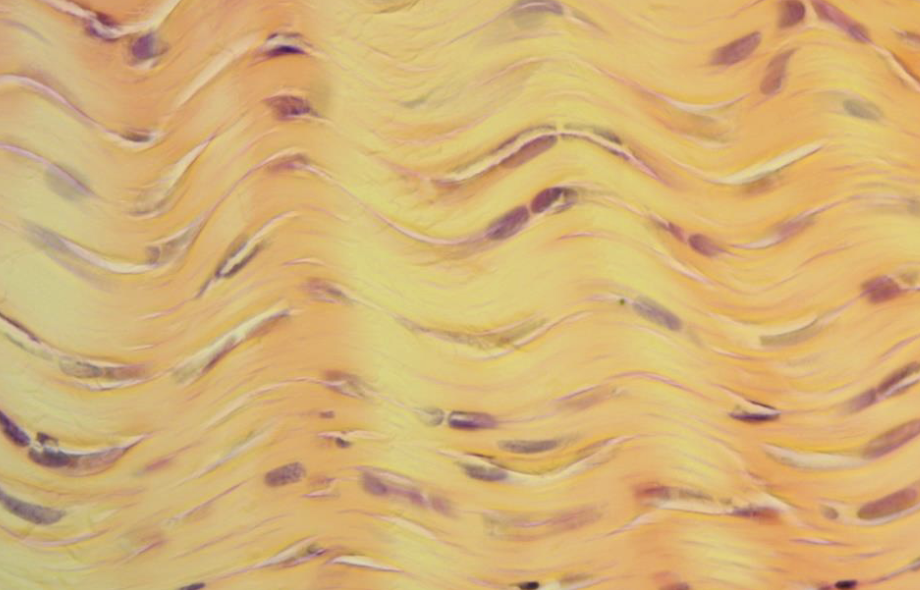
Fibrous connective tissue (features, where can you find it, and what does it do?)
It's very strong. It's cells are called fibroblasts and they secrete collagen (matrix). It has many collagen fibers that form a tough cord. Nuclei are occasionally visible. It can be found in tendons and ligaments.
Cartilage tissue (features, where can you find it, and what does it do?)
Found in the skeletal system where it forms an elastic substance. The cells, chondrocytes, secrete chondrin (matrix), The cells are stuck in the matrix. The cells dwell in holes called lacunae.
Cardiac muscle (features, where can you find it, and what does it do?)
Found in the heart. Distinguishable by the cardiac muscle fibers, the centrally placed nucleus, and the intercalated discs. It is striated, but involuntary. It has branched muscle fibers. Pumps the heart.
Nervous tissue (features, where can you find it, and what does it do?)
Found in the neuron-nervous system (brain and spinal cord). It conducts impulses to the brain. Has a cell body, and neuron processes (dendrites and an axon).
Female reproductive tissue (features, where can you find it, and what does it do?)
It contains and supports the maturation of the ova until they are ready to be released from the ovary during ovulation. Includes Graafian follicle in ovary, developing ova, nurse cells, follicular fluid space, and follicle cells.
Male reproductive tissue (features, where can you find it, and what does it do?)
Found in the testes. Includes seminiferous tubules in testes, sperm in different stages of development (mature sperm vs. spermatogonia, and interstitial cells. Each sperm cell has a flagellum. The opening of the tubule is called the lumen.
Bone tissue (features, where can you find it, and what does it do?)
Cells: osteocytes. Matrix: bone. Located throughout the body along the bone. Within an osteon, canaliculi, osteocytes in lacunae, and the Haversian canal.
Adipose tissue (features, where can you find it, and what does it do?)
cells: adipocytes and it doesn't secrete a matrix. They store fat (energy). Store fat in vacuoles and the fat takes up most of the space in the cell so they nucleus is squished at the edge. Found in clusters.
Blood- liquid tissue (features, where can you find it, and what does it do?)
It transports oxygen. cells: several types like RBCs and WBCs. Matrix: blood plasma --aqueous solution of salt, proteins, glucose, etc. Found in blood vessels. Identify the different cells.
Mammalian: RBCs don't have a nucleus
Frog: RBCs do have a nucleus
Skeletal/striated muscle (features, where can you find it, and what does it do?)
Found in body organs (intestine, blood vessel, uterine). No striations, long and spindle-shaped. one nucleus. Structure: sheets of overlapping cells.
Smooth muscle (features, where can you find it, and what does it do?)
Found in body organs (intestine, blood vessel, uterine). No striations, long and spindle-shaped. one nucleus. Structure: sheets of overlapping cells.
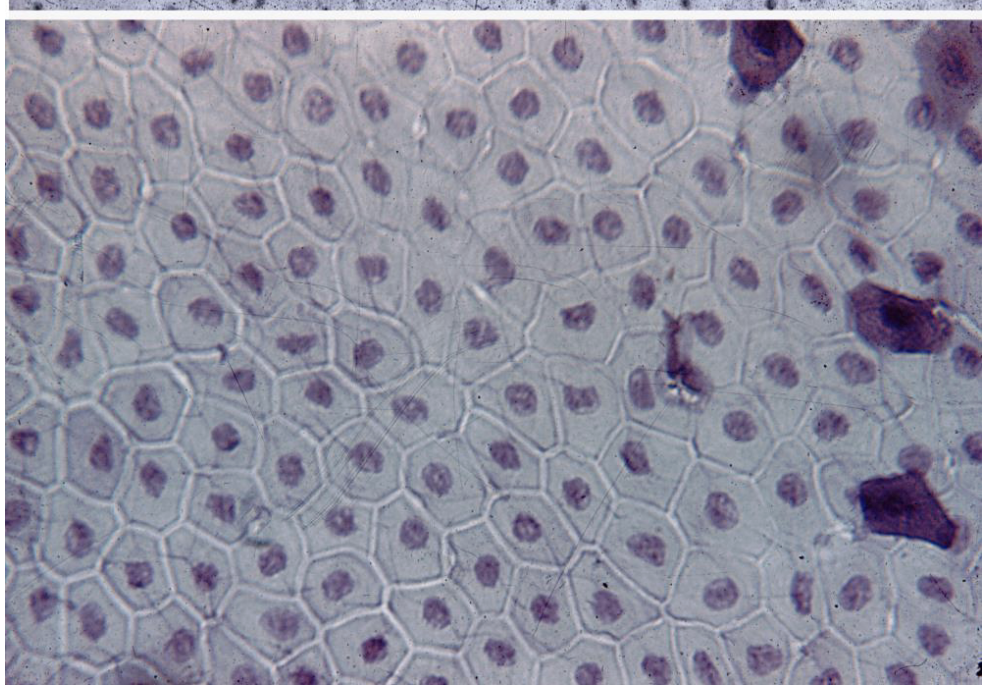
Name the tissue
Simple Squamous Epithelium
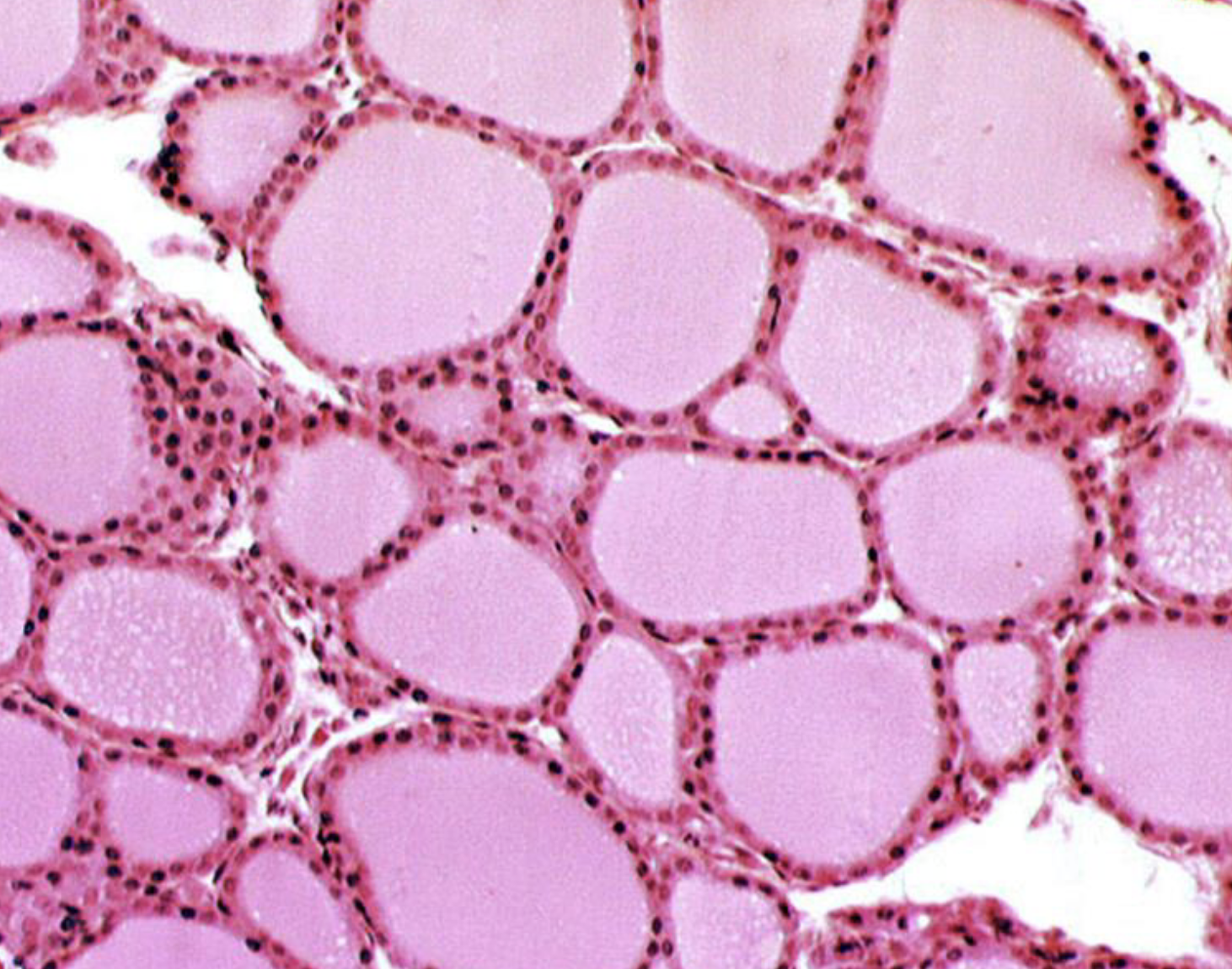
Name the tissue
simple cuboidal epithelium
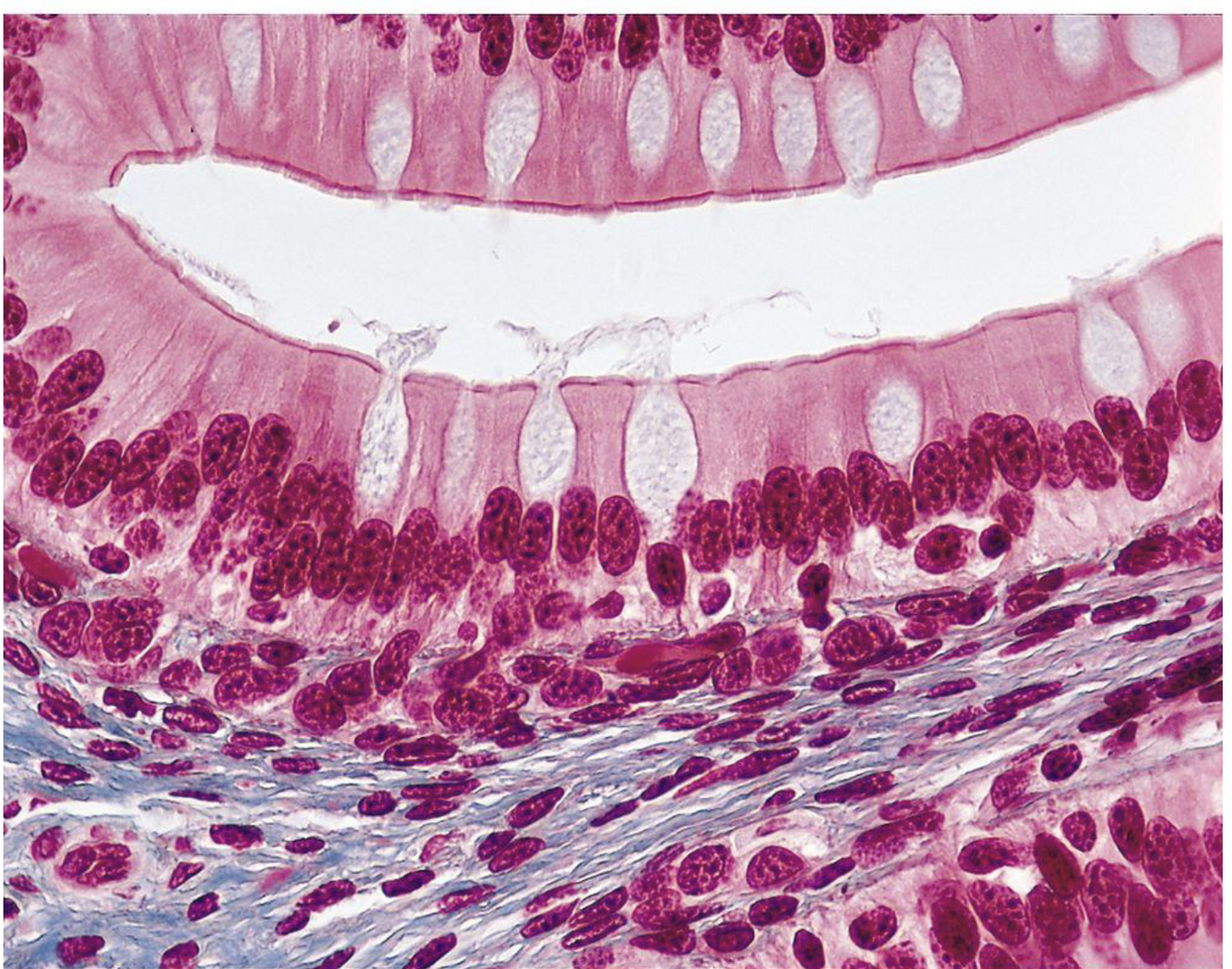
Name the tissue
Simple columnar epithelium and goblet cells
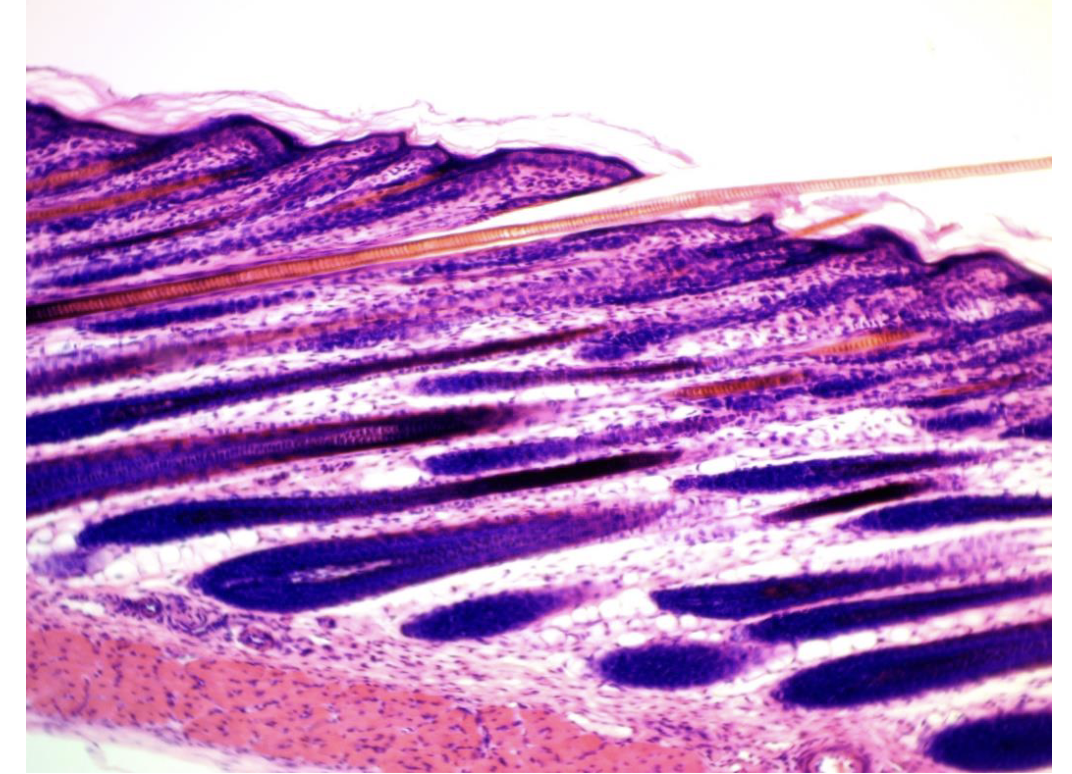
Name the tissue
Stratified epithelium of a mammal
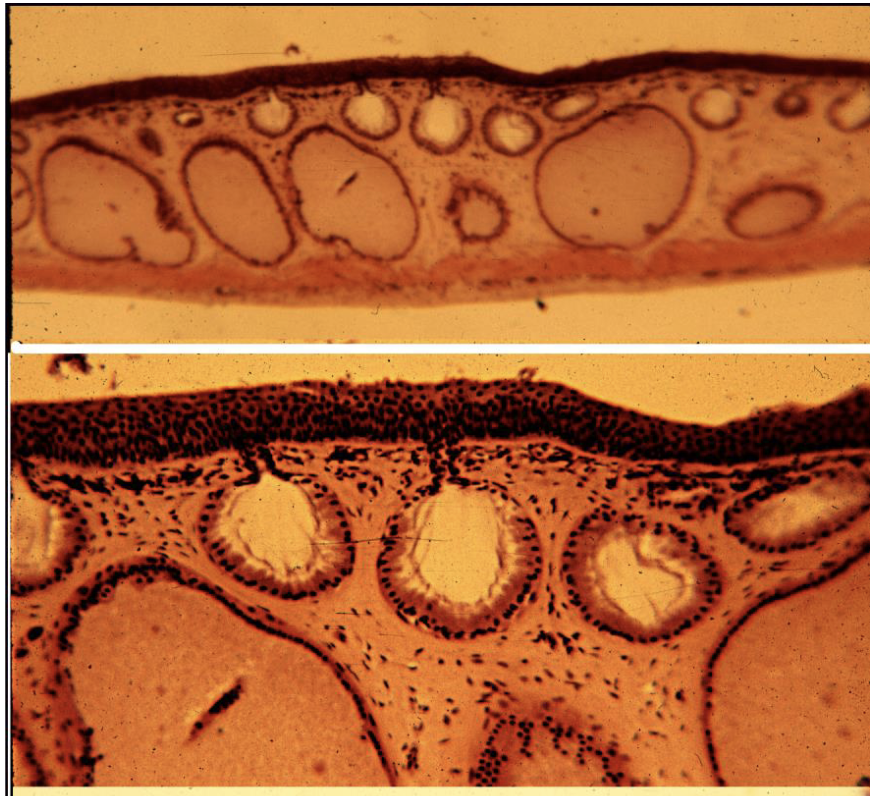
Name the tissue
Stratified epithelium of a Frog
Name the tissue
Fibrous connective tissue + (another image)

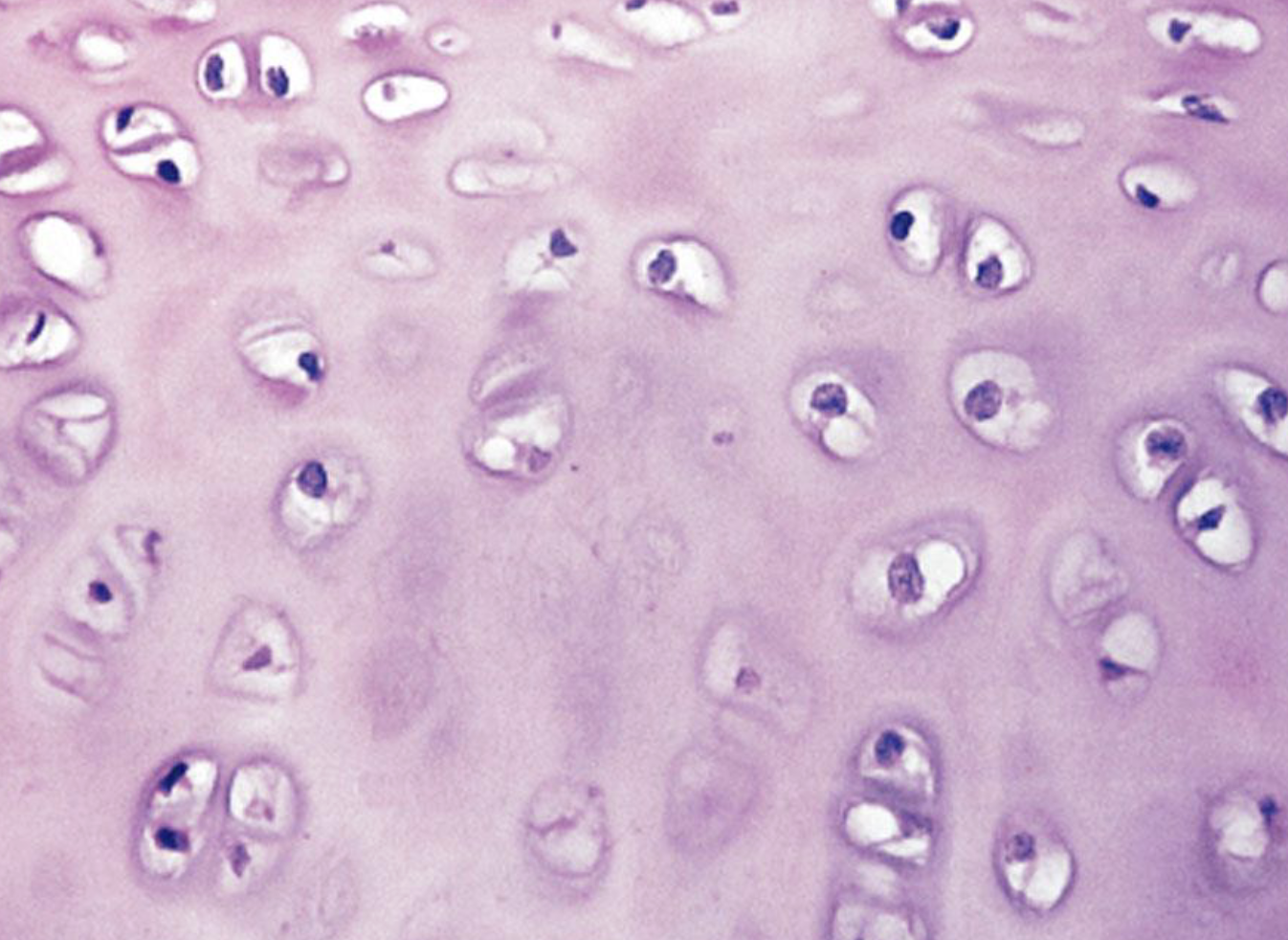
Name the tissue
Cartilage tissue
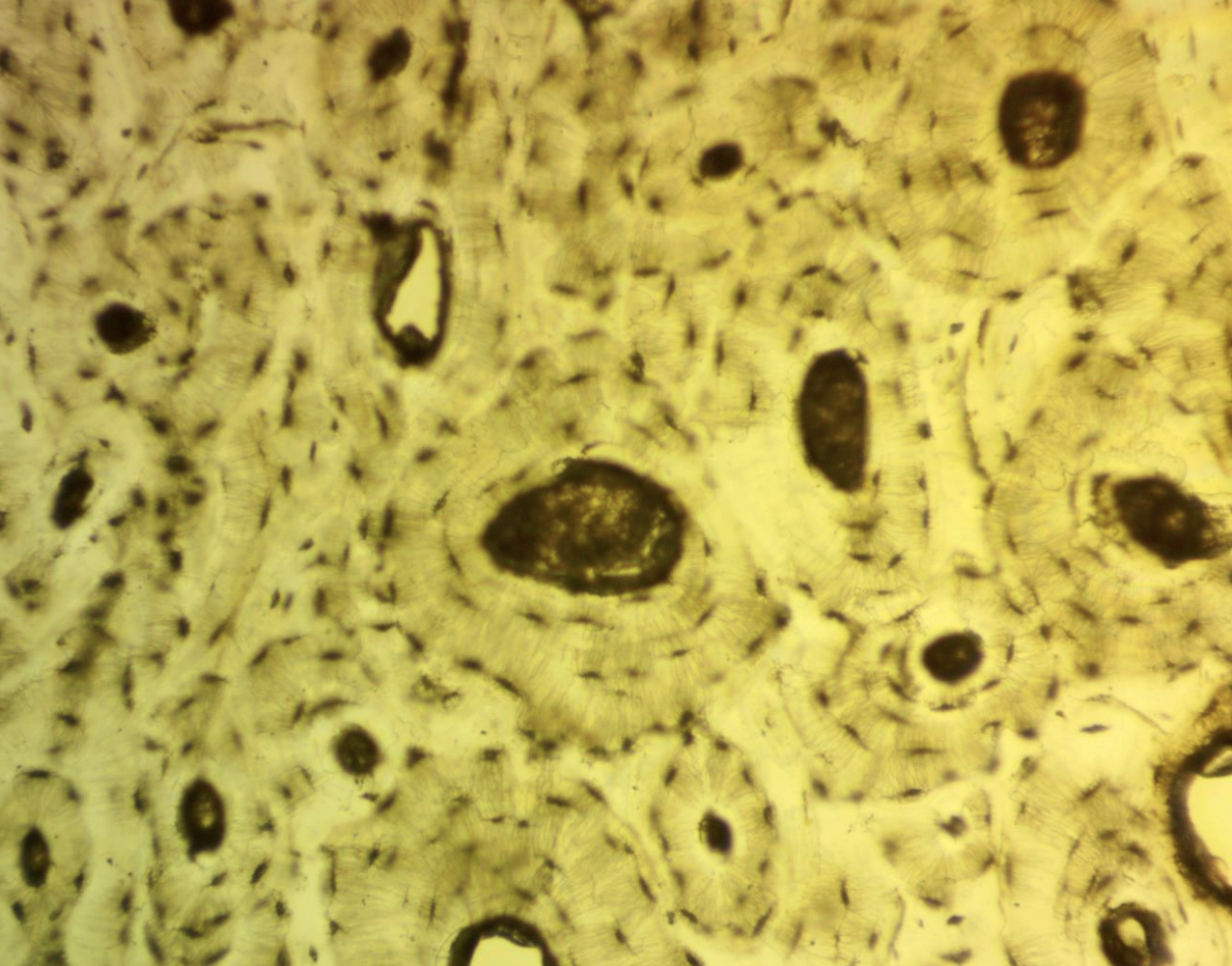
Name the tissue
Bone tissue
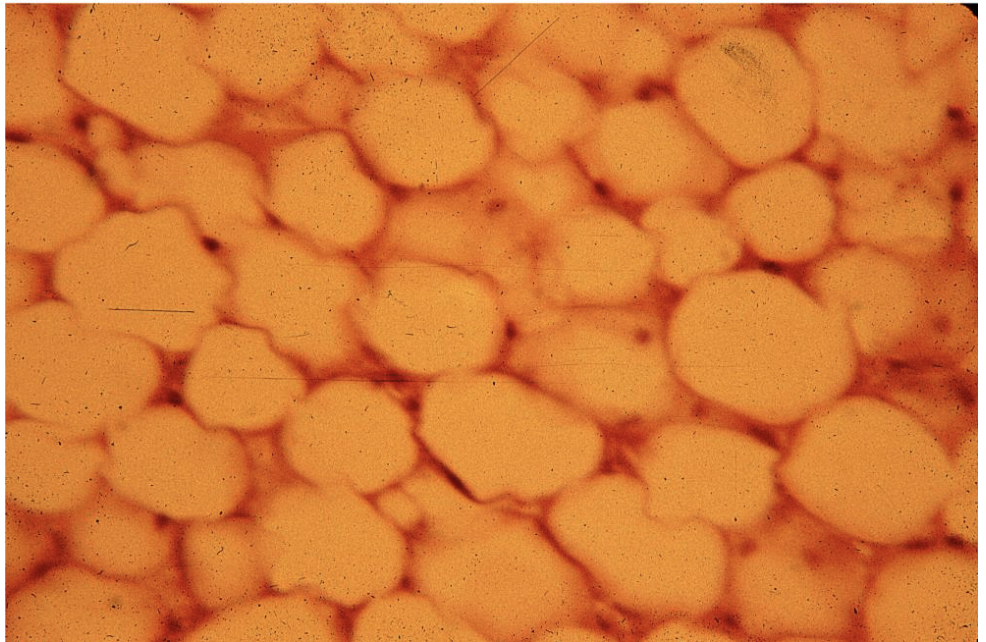
Name the tissue
Adipose tissue
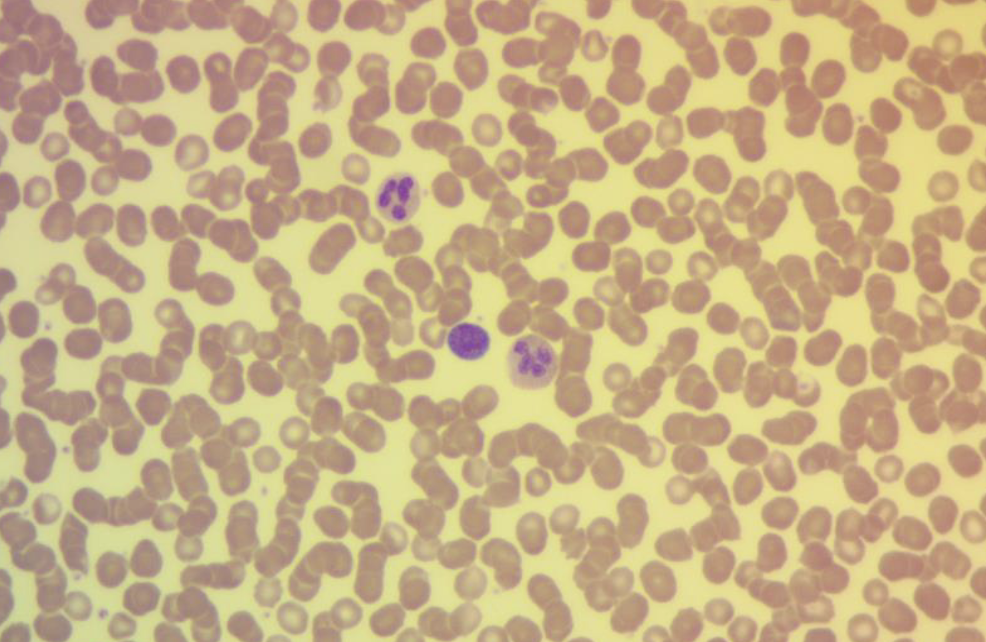
Name the tissue
Mammal blood
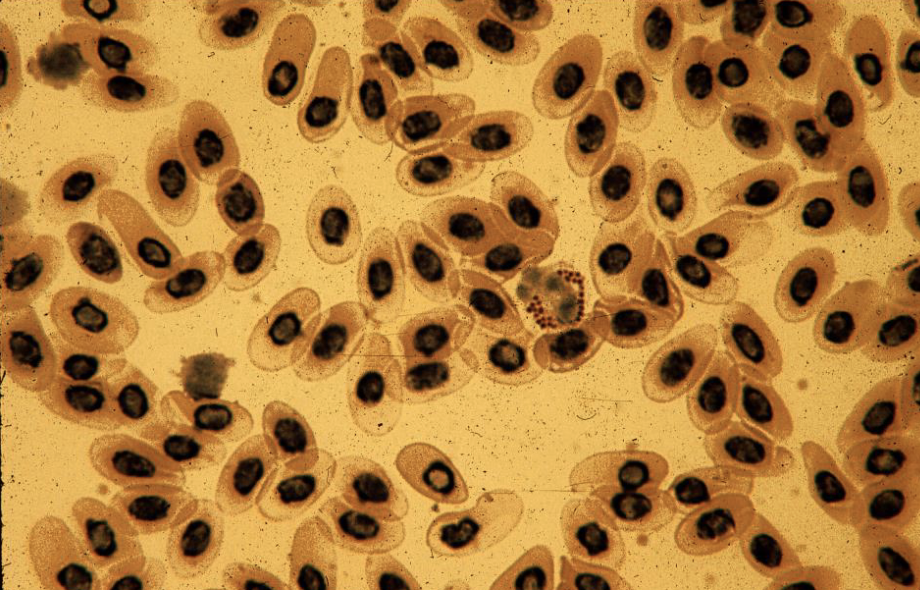
Name the tissue
Non-mammal blood
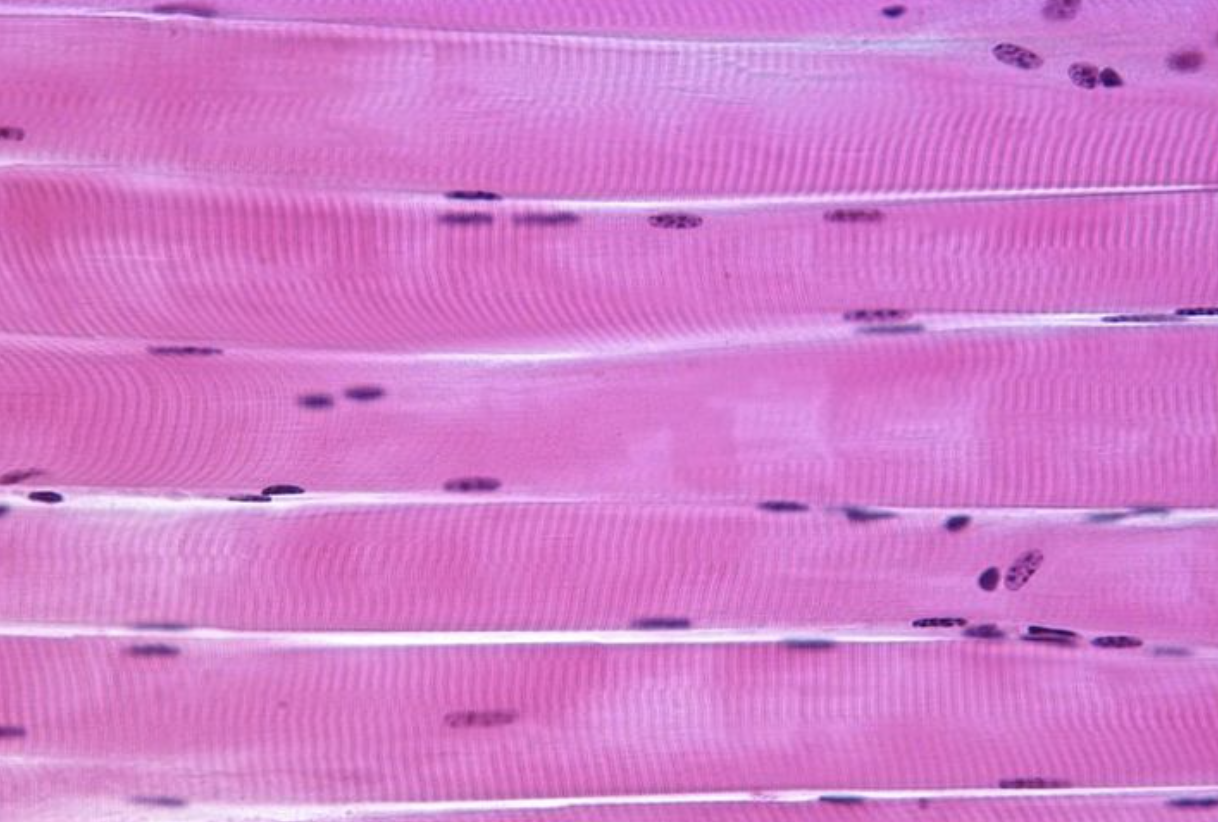
Name the tissue
Skeletal (striated) muscle
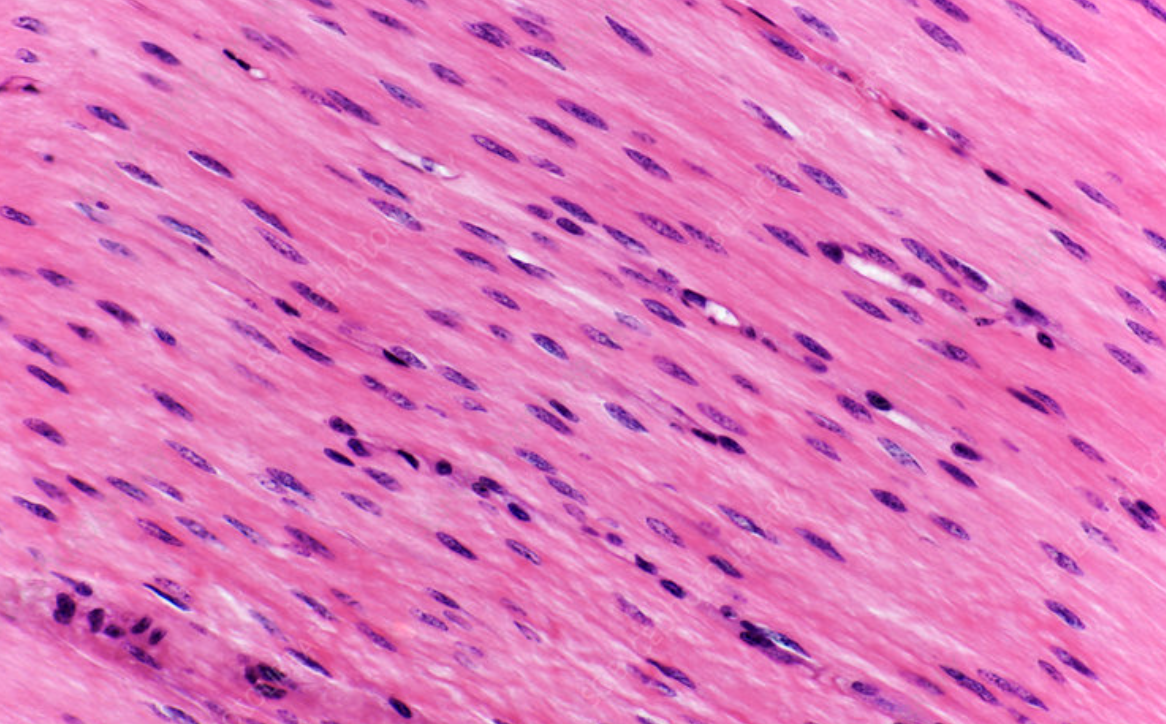
Name the tissue
Smooth muscle
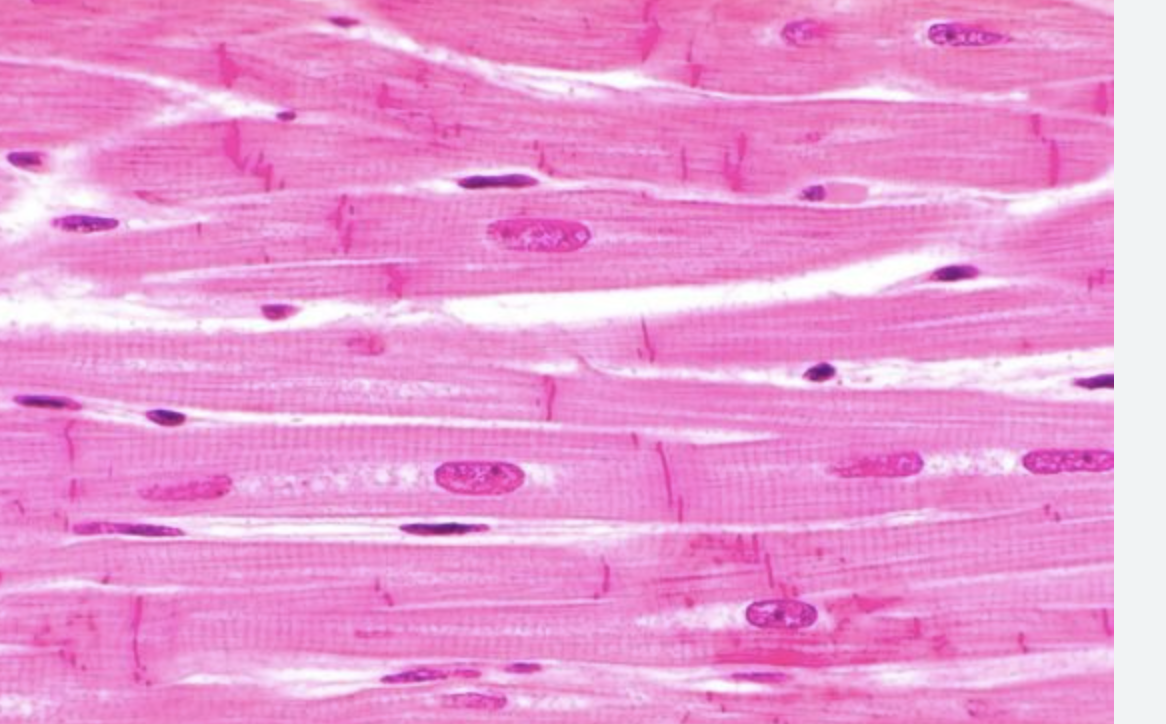
Name the tissue
Cardiac muscle
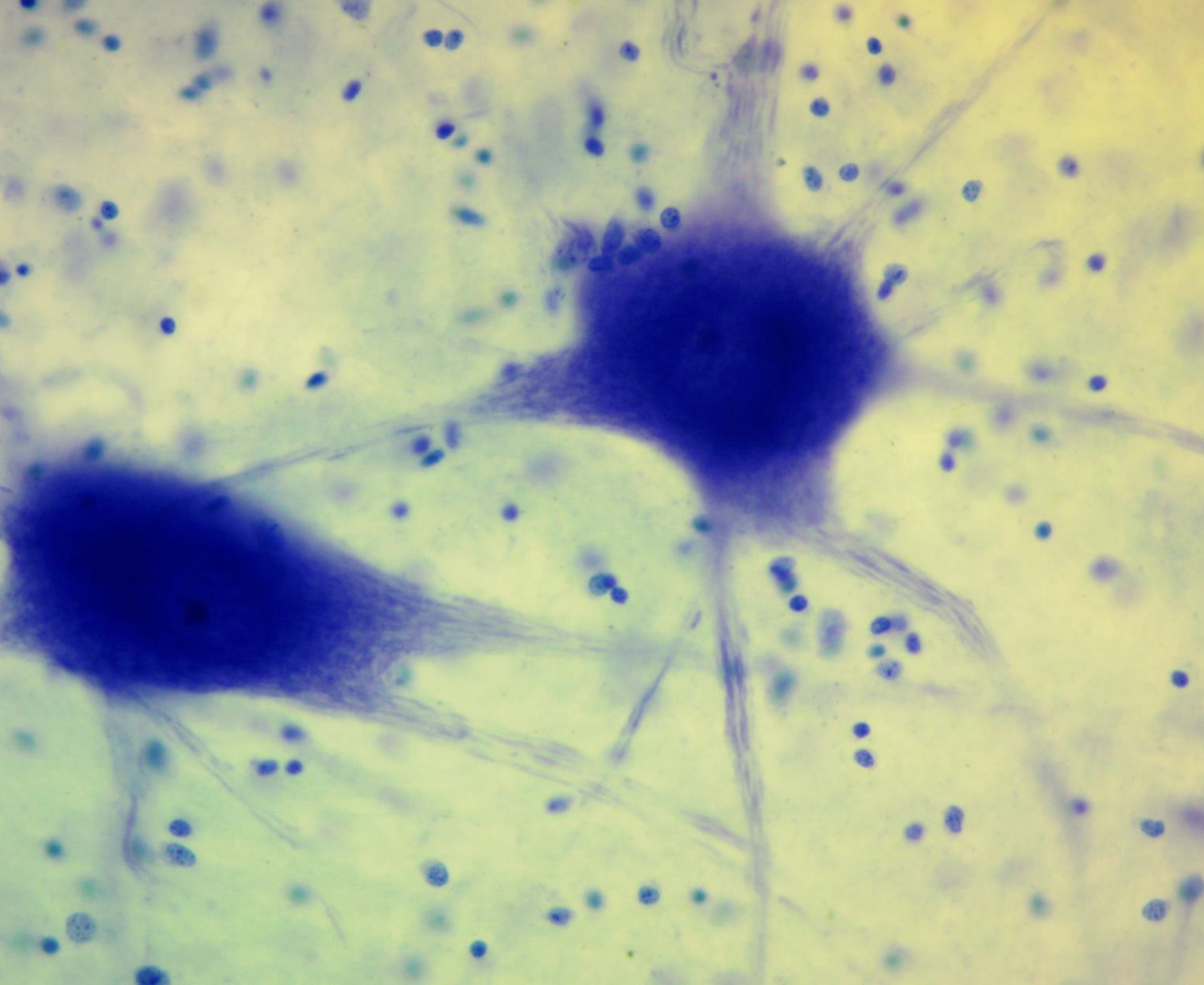
Name the tissue
Nervous tissue
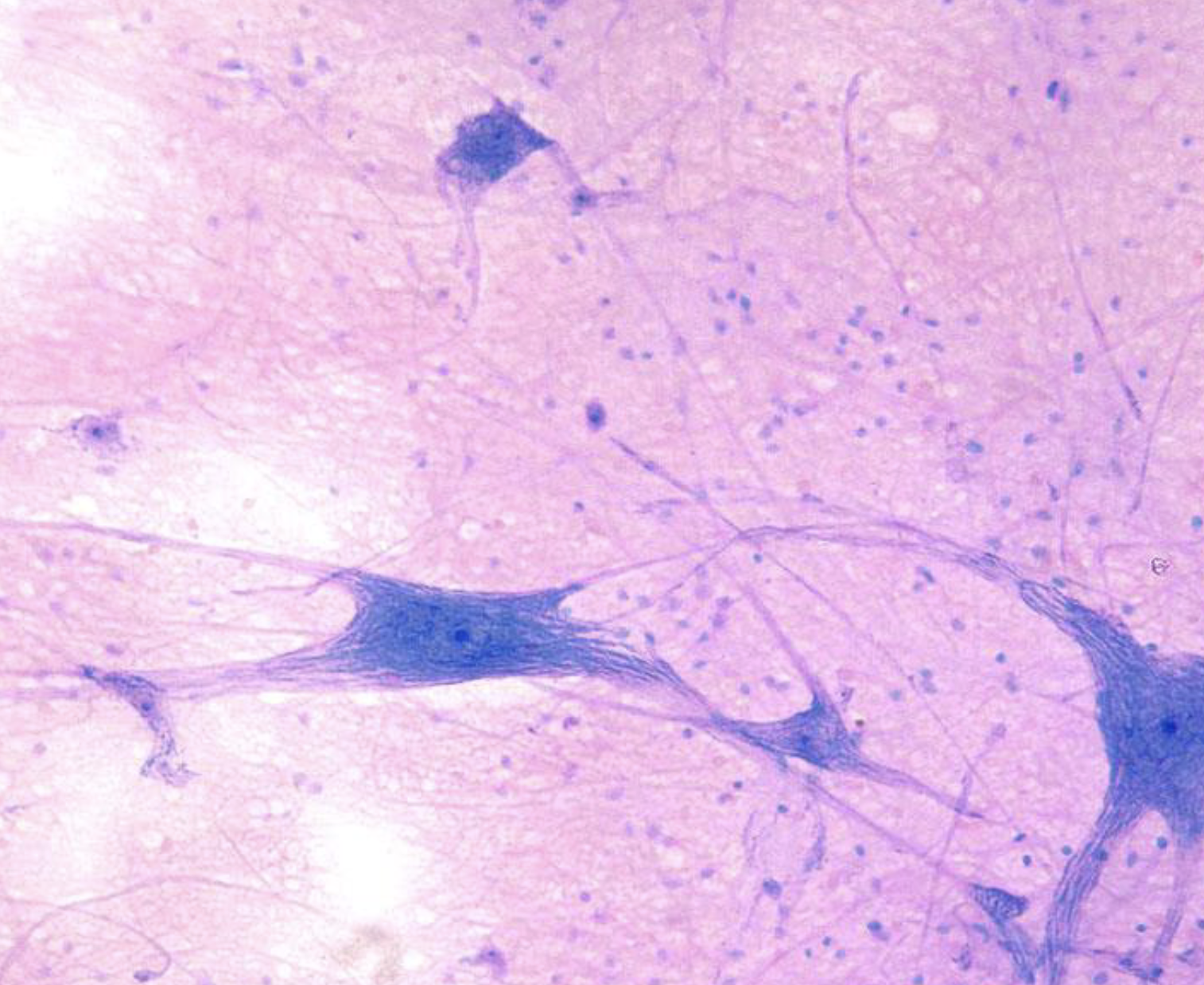
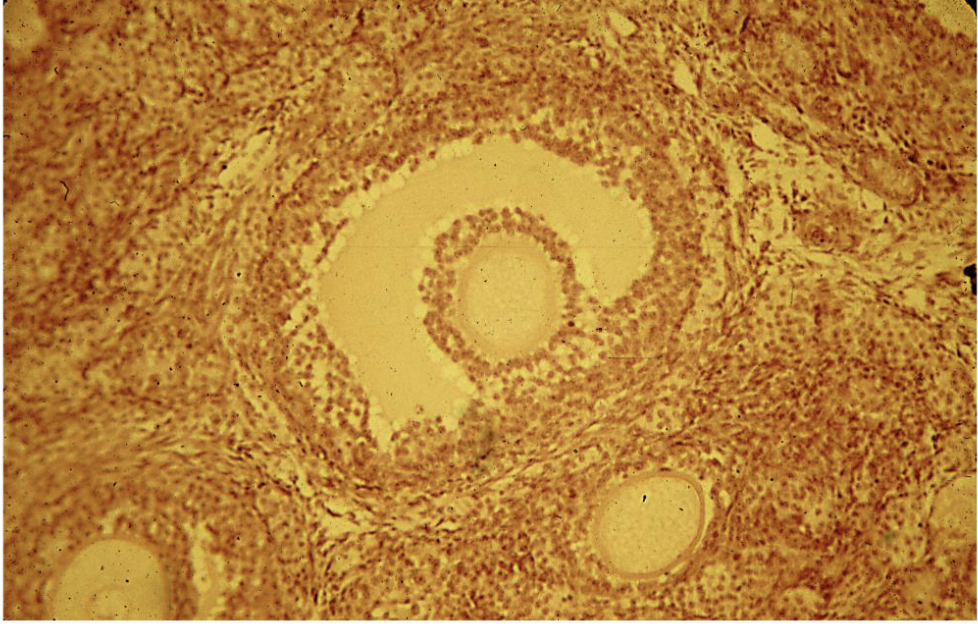
Name the tissue
Female reproductive tissue
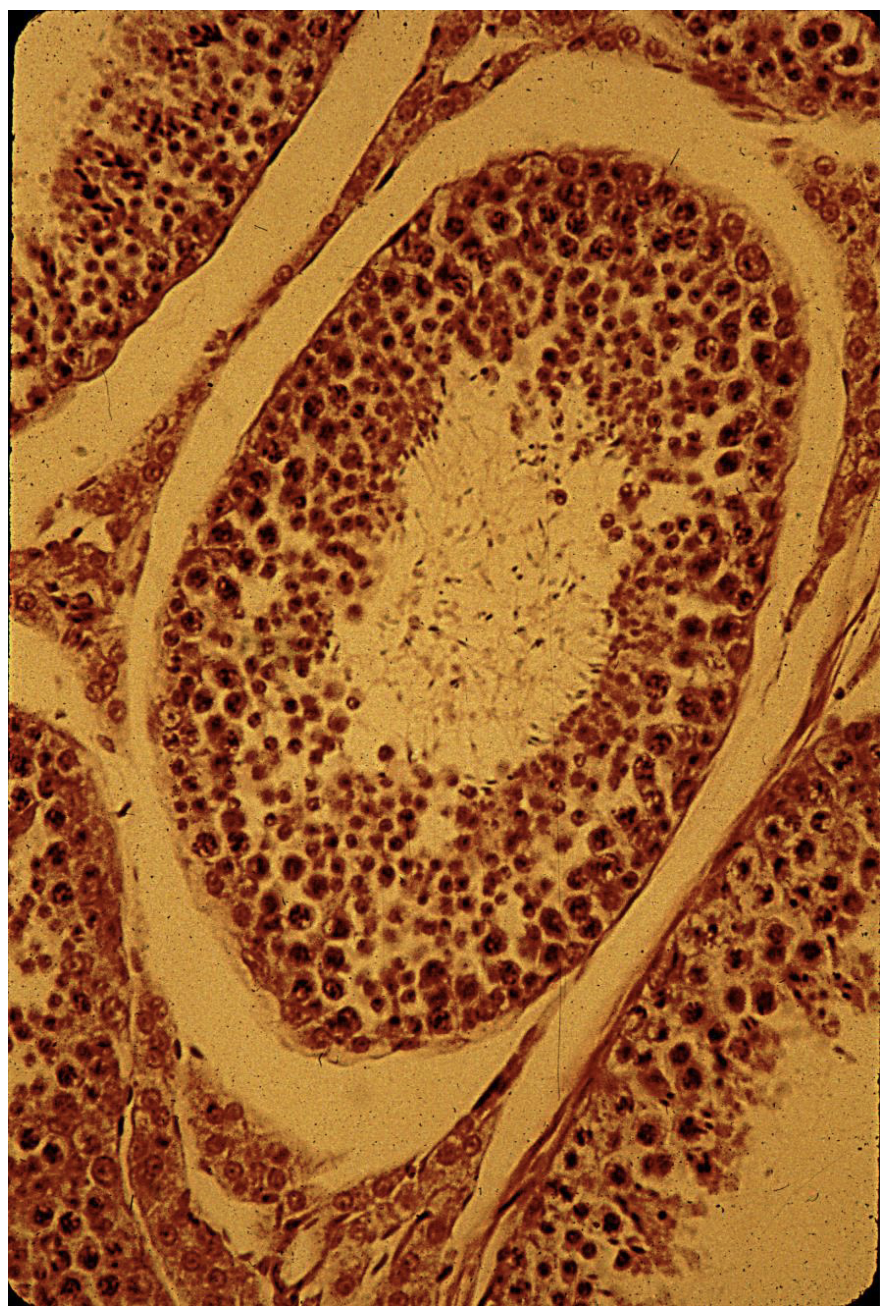
Name the tissue
Male reproductive tissue