Science exam
4.5(2)
4.5(2)
Card Sorting
1/166
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
167 Terms
1
New cards
What is the difference between physical and chemical change (DOE)
Physical change is a change that doesn’t affect the chemical propertieis and chemical does it affects the chemical composition of the substance
2
New cards
What are the five signs of chemical change (DOE)
* colour
* odour
* gas producion
* precipitate
* temperature
* odour
* gas producion
* precipitate
* temperature
3
New cards
What is the relationship between atomic mass and the number of protons and neutrons
protons + neutrons = atomics mass
4
New cards
What is a cation and a anion
Cation is a positively charged ion while an anion is a negatively charged one
5
New cards
How do elements form a negative or positive charge?
If the element loses an electron then it’s postively charged if it gains than it’s negatively charged
6
New cards
What is an ionic bond (DOE) What is a molecular bond
Metal and non metal
non-metal and non-metal
non-metal and non-metal
7
New cards
What are polyatomic ions
They are ions composed of more than one atom (whole atom has a charge)
8
New cards
How many atoms are in this prefix: tetra
4
9
New cards
Formula for Diphosphorus pentoxide (shit like this DOE)
P2O5
10
New cards
Write chemical name of BO3 (DOE)
boron oxide
11
New cards
Law of conservation of mass (DOE)
The law states that matter cannot be created or destroyed and that the mass of the reactants = mass of products
12
New cards
Balance the equation (DOE)
C + H2 = C3H8
C + H2 = C3H8
3C + 4H2 = 1C3H8
13
New cards
Synthesis (all reactions DOE)
2 or more reactants come together and create one product (A+B= AB)
14
New cards
Decomp
A compound breaks down into 2 or more substances (AB = A+B)
15
New cards
Single deplacement
One element displaces another in a compound (AB + X = AX + B)
16
New cards
double displacement
Both switch partners (AB + XY = AX + BY)
17
New cards
complete combustion
Rapid reaction of hydrocarbon and oxygen gas (A + O2 = H2O + CO2)
18
New cards
Neutralization
When products have a neutral pH (acid + base = salt + water)
19
New cards
\
What is an acid
What is a base (DOE)
What is an acid
What is a base (DOE)
An aqueous solution that conducts electricity, sour, turn blue litmus red, and neutralizes base.
\
An aqueous solution that conducts electricity and turns red litmus blue, they feel slippery and taste biter
\
An aqueous solution that conducts electricity and turns red litmus blue, they feel slippery and taste biter
20
New cards
What is a pure substance
a substance where all the particles that make it up are the same
21
New cards
which of the following would be the best conductor of electricity
* pure water
* sea water
* tapa water
* pure water
* sea water
* tapa water
sea water because it has sodium making it ionic bond which re elctroylytes
22
New cards
Name this compound F2O3
difluorine trioxide
23
New cards
What might balance bleach
an acidic compound (lemon juice)
24
New cards
An element that exists as two atom molecules are…
diatomic
25
New cards
What are the 7 diatomic molecules in nature
H O F Br I N Cl
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Fluorin
Bromine
Iodine
Nitrogen
Chlorine
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Fluorin
Bromine
Iodine
Nitrogen
Chlorine
26
New cards
What group is most stable on the periodic table
What group is most reactive
**DOE**
What group is most reactive
**DOE**
noble gases (argon/krypton/etc)
Halogens such as fluroine/bromine/etc
Halogens such as fluroine/bromine/etc
27
New cards
What is an element
Pure substance which can’t be broken down further
28
New cards
What is a period and what is a group on the periodic table
A period refers to the row while a group refers to the columns
29
New cards
Properties of ionic compounds (DOE)
* hard
* high melting point
* electrolytes
* brittle
* high melting point
* electrolytes
* brittle
30
New cards
Properties of molecular compounds (DOE)
* low meltingpoint
* soft
* odour
* soft
* odour
31
New cards
Examples of polyatomic ions in everyday life
* Food additives
* Cleaners
* Fertilizers
* Cleaners
* Fertilizers
32
New cards
What happens in a covalent bond
The outer electrons are being shared
33
New cards
What are reactants and products
Reactants are used up and products are produced ina chemical reaction
34
New cards
What is a skeleton equation
A reaction where products and reactants aren’t balanced
35
New cards
NOTE
Metals rarely appear naturally as pure elements they usually bond with others to form rock deposits called ores
36
New cards
What is incomplete combustion
a combustion reaction of hydrocarbons that may produce carbon monoxide, carbon, carbon dioxide, soot, water, and energy; occurs when the oxygen supply is limited
37
New cards
What is galvanized steel
steel that has been coated with protective layer of zinc, which forms a hard, insoluble oxide
38
New cards
What is corrosion (DOE)
Breakdown of a metal resulting from reactions with chemicals in its environment
39
New cards
What is rust?
When iron or steel corrodes however it doesn’t become a protective oxide rather it begins to chip away
40
New cards
NOTE
Combustion reactions happen faster than corrosion reactions
41
New cards
acid leaching
removing heavy metals from containated soils by adding an acid solution to the soil and catching the solution hat drains through
42
New cards
Dry deposition
Acid-forming pollutants fall directly to earth in the dry state
43
New cards
Prokaryote
Eukaroyte (potentially on exam or POE)
Eukaroyte (potentially on exam or POE)
single celled life forms that don’t contain a nucleus or other membrane bound organelles
\
Cells that contain a nucleus and other organelles (multi-cellular organisms)
\
Cells that contain a nucleus and other organelles (multi-cellular organisms)
44
New cards
Difference between plant an animal cells (DOE)
* Plants have a cell wall
* Plants have chloroplasts
* Plants don’t have centrioles or lysosomes
* Plants have one large vacuole
* Plants have chloroplasts
* Plants don’t have centrioles or lysosomes
* Plants have one large vacuole
45
New cards
3 reasons to cell division
reproduce
regenerate
repair
regenerate
repair
46
New cards
Difference between asexual reproduction and sexual
Asexual reproduction involves one parent and the offspring are exact genetic copies while sexual reproduction involves two parents and the offspring has genetic information of each
47
New cards
Diffusion
When chemicals move in and out of a cell from an area of high concentration to low one
48
New cards
Osmosis
The movement of a liquid (typically water) across a membrane towards an area of high solute concentration
49
New cards
What does a vacuole do? (function of organelles DOE)
a fluid filled sac that stores food and water for the cell
50
New cards
golgi apparatus
an organelle involved in packaging proteins and producing lyosomes
51
New cards
chromosomes
Long twisted strands of DNA in the nucleus
52
New cards
Rough ER
Stores, separates, and serves as the cell’s transport system and it’s covered in ribosomes
53
New cards
Lyosomes
sac like structure full of digestive enzymes
54
New cards
The 3 stages of the cell cycle (DOE)
* interphase
* mitosis
* cytokinesis
* mitosis
* cytokinesis
55
New cards
NOTE
Some cells take 30hrs to divide and certain cells don’t divide like adult nerve cells/cardiac cells
56
New cards
Mitosis (all stages DOE)
the stage where the DNA and nucleus is divided
57
New cards
What is biophotomics
Using light energy to diagnose, monitor, and treat living cells and organisms
58
New cards
Prophase
The chromosomes thicken and become visible and the nuclear membrane disappears
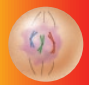
59
New cards
Metaphase
The chromosomes line up at the center with the help of spindle fibers

60
New cards
Anaphase
The sister chromatids separate to opposite ends of the cell
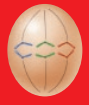
61
New cards
Telophase
The cell starts to separate and a new membrane forms around each cell
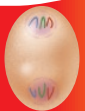
62
New cards
Cytokinesis
Cytoplasm pinches off and there are two new daughter cells

63
New cards
White blood cells (DOE)
fight infection (they make up less than 1% of blood volume)
64
New cards
red blood cells (DOE)
they contain hemoglobin which picks up CO2 and O2 and they make up almost half the body’s blood volume
65
New cards
Platelets
They are cells which help blood clot they also create less than 1% of blood volume
66
New cards
Plasma
Protein rich liquid that carries the blood cells along, makes up over half the blood volume
67
New cards
Nerve cells
Conducts electricial impulses to coordinates body activities
68
New cards
Fat cells
large vacuoles that store chemical energy
69
New cards
Skin cells
Tightly packed to reduce water loss
70
New cards
4 types of tissues in human
Epthelial
* Protects from dehydration
* Friction resistant
* Skin
Nerve
* Provie sensory sensations
* Brain to body communication
* Spinal cord cord/ Neurons
Muscle
* Allows the body to move
* 3 types (skeletal/smooth/cardiac)
Connective
* Provides support and insulation
* Blood/Cartilage
* Protects from dehydration
* Friction resistant
* Skin
Nerve
* Provie sensory sensations
* Brain to body communication
* Spinal cord cord/ Neurons
Muscle
* Allows the body to move
* 3 types (skeletal/smooth/cardiac)
Connective
* Provides support and insulation
* Blood/Cartilage
71
New cards
Function of large and small intestine
Large absorbs water from the indigestive waste and small breaks down food further and absorbs nutrients
72
New cards
Pancreas (all key organs **DOE**)
Produces insulin to regulate your glucose levels (digestive system)
73
New cards
Trachea
The airway to your lungs
74
New cards
Alveoli
Tiny air sacs in the lungs surrounded by capillaries and where gas exchange between air and blood occurs
75
New cards
Spinal cord
short cut for our reflexes
76
New cards
Lungs
allows oxygen to move into your blood and CO2 to leave
77
New cards
Digestive system (all key systems DOE)
The system takes food and then digests it and excretes the remaining waste. Involves the following
* Mouth
* Salivary glands
* Esophagus
* Stomach
* Small intestine
* Large intestine (colon)
* Appendix (not sure)
* Rectum then anus
Accesosry organs
* Liver/Gallbladder/Pancreas
* Mouth
* Salivary glands
* Esophagus
* Stomach
* Small intestine
* Large intestine (colon)
* Appendix (not sure)
* Rectum then anus
Accesosry organs
* Liver/Gallbladder/Pancreas
78
New cards
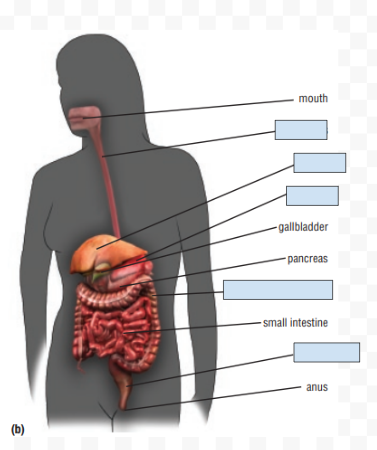
Label the following parts (just go inorder from top to bottom)
Esophagus
Liver
Stomach
Large intestine (colon)
Rectum
Liver
Stomach
Large intestine (colon)
Rectum
79
New cards
Cancer (DOE)
Various diseases which occur from uncontrolled cell division
80
New cards
The three points in the cell theory
* All living things are made up cells
* All cells came from prexisting cells
* The cell is the most basic unit of life
* All cells came from prexisting cells
* The cell is the most basic unit of life
81
New cards
Circulatory system
The system that transports oxygen and nutrients throughout the body and carries away waste
82
New cards
Respiratory system
The system which provides ocygen for the body and allows CO2 to leave. The air travels into your mouth or nose then down the trachea, bronchi and into the alveoli where the gas exchange occurs (this is in the lungs) the lungs and ribcage both expand and contract
83
New cards
Musculoskelteal system
It supports the body/protects delicate organs and allows movement
84
New cards
3 types of connective tissue in skeleton
Bones
* hard and dense
* has nerve and blood vessels
Ligaments
* tough and elastic
* Hold bone together at the joint
Cartilage
* Dense
* strong and flexible
* Found in nose and ear
* hard and dense
* has nerve and blood vessels
Ligaments
* tough and elastic
* Hold bone together at the joint
Cartilage
* Dense
* strong and flexible
* Found in nose and ear
85
New cards
3 types of muscles (POE)
Smooth (involuntary)
skeletal (contrct when signled)
Cardiac (in the heart)
skeletal (contrct when signled)
Cardiac (in the heart)
86
New cards
Nervous system
System which senses the environment and coordinates appropriate responses
87
New cards
Central nervous system (CNS)
consists of brain and spinal cord and it carry signlas between the CNS and the PNS
88
New cards
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
it relays info about the internal and external environment to the brain and connects the rest of the body to the CNS
89
New cards
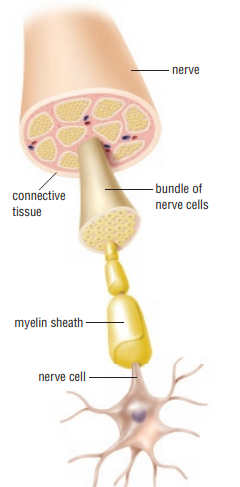
Why is the structure of a neuron important (POE)
They send signals from one area of the body to another (axons are neurons covered in myelin and it acts as insulation on an electrical wire making sure it passes in the right way)
90
New cards
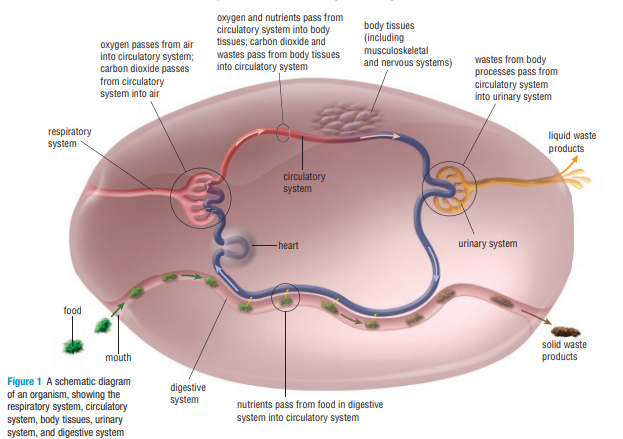
How do the circulatory and urinary system work together (system network DOE)
The urinary system has to get rid of waste the way this happens is if the blood travels there from the circulatory system and absorbs the waste and then transport it back out
91
New cards
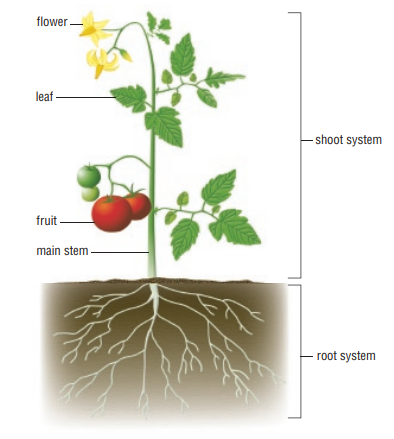
What is shoot and root system (DOE)
Shoot system contains the stem ,leaves and flower it is there to conduct photosynthesis and create flowers for sexual reproduction and the root system just contains the various roots which absorbs water and minerals and bring them to the various plant parts
92
New cards
Explain the 3 types of tissue in plants (DOE)
Dermal
* Outer layer
* Epidermal is outer layer on non-woody plants and periderm is the opposite
Vascular Tissue
* Specialized tissues
* Transporting water and minerla s and nutrients throughout the plant
* 2 types (xylem and phloem)
Ground
* Makes up everything that the other two don’t
* Manufactured nutrients by the process of photosynthesis; in the roots, they store carbohydrates; and in the stems, they provide storage and support
* Outer layer
* Epidermal is outer layer on non-woody plants and periderm is the opposite
Vascular Tissue
* Specialized tissues
* Transporting water and minerla s and nutrients throughout the plant
* 2 types (xylem and phloem)
Ground
* Makes up everything that the other two don’t
* Manufactured nutrients by the process of photosynthesis; in the roots, they store carbohydrates; and in the stems, they provide storage and support
93
New cards
What is xyelm and pholem (DOE)
The two types of vascular tissues. Xylem transport water and dissolved minerals upwards from the root while pholem transports sugar solutions from photosynthesis and hormones
94
New cards
What are meristematic cells
undifferentiated plant cells that can divide and become specalized
95
New cards
Palisade layer and spongy mesophyll
The first is near the top and it is packed cells while the other is loosely packaged cells
96
New cards
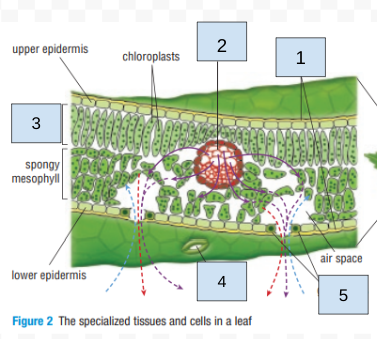
Label the leaf diagram (off of test)
1. cuticle
2. vascular bundle
3. palisade layer/mesophyll
4. stomate
5. guard cells
97
New cards
Apical meristem and lateral meristem
Apical are undifferentiated cells at the tip of plant roots and shoots and hey allow them to grow longer and lateral are undifferentiated cells in the bark they allow the plant to grow wider
98
New cards
Medium
Phsyical substance through which energy can be transferred
99
New cards
Radiation
a method of energy transfer that does not require a medium
100
New cards
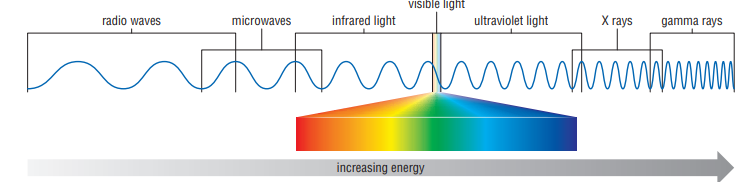
Electromagnetic wave (DOE)
A wave that has both electric and magnetic parts does not require a medium