Learning and memory
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
what is significant about the HM study in memory research
he had anterograde amnesia, which is the inability to form new memories
What brain structures were removed in HM's surgery?
Amygdala, hippocampus, and part of the frontal cortex.
what are some tests of memory
recognition and recall
paired association task
digit span + 1 task
priming tasks
What types of memory tasks did HM perform poorly on?
Recall, paired association, and digit span tasks.
what are recognition and recall tests
given lists of words or images to study, and asked to recall the list
what is paired association task
given pairs of unrelated words to remember
what is digit span +1 task
asked to repeat back numbers, adding a number each time to the sequence after successful recall
what are priming tasks
word stem compeltion
perceptual identification task
what is word stem completion
list of words given to study; the stem of the words are given (app_)
what is perceptual identification task
list of images given to study, an image is flashed quickly and asked to identify image
what are some tests of learning
mirror tracing task
reading mirror-reversed text
familiarity
what is mirror tracing task
trace various shapes using visual guidance via mirror
track errors per trial and track performance over multiple days
what is a typical progression of mirror tracing task
day 1 is improvement across trials
day 2 is baseline improvement
day 3 is mastery of task
what is reading mirror-reversed text
a perceptual task
what is familiarity test
shown images seen before and ask to guess whether the image was seen before
what is a test of association
classical conditioning paradigms
what is classical conditioning
netural stimuli, paired with an unconditioned stimulus that elicits a natural response
what is significant about patient KC
had retrograde amnesia and anterograde amnesia due to damage in frontal cortex and shrinkage of hippocampus from motorcycle accident
what is important about memory
memory is complex
memory is not in one spot (hippocampus)
not all memory is consious
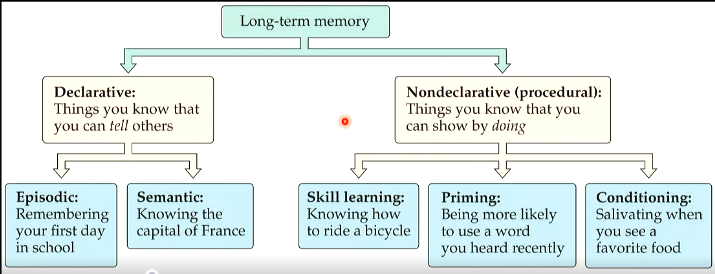
what are the 2 types of long-term memory
declarative
nondeclarative
what is declarative long-term memory
things you know that you can tell others
what is nondeclarative long-term memory
things you know that you can show by doing
describe the proposed flow of information through the brain
sensory processing in cortex → parahippocampal, entorhinal, perirhinal cortex → hippocampus → medial diencephalon including mammillary bodies → declarative memory storage in cortex
describe the long-term memory tree
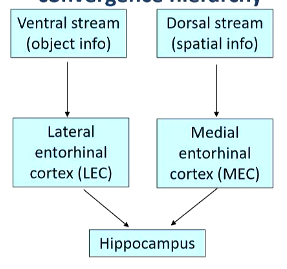
describe the convergence hierarchy into the hippocampus
What are the receptive field properties of lateral entorhinal cortex (LEC) neurons?
LEC neurons respond to non-spatial features such as object identity, odor, or contextual cues—they encode information about what is present.
What are the receptive field properties of medial entorhinal cortex (MEC) neurons?
MEC neurons, including grid cells, encode spatial information—specifically, location, head direction, and movement speed.
What are place cells, and where are they found?
Place cells are neurons in the hippocampus that activate in specific spatial locations, forming a spatial map.
What are grid cells and where are they located?
Grid cells in the medial entorhinal cortex fire in a hexagonal spatial pattern and provide a spatial coordinate system.
What experimental setups are used to infer receptive fields of LEC neurons?
Tasks involving object recognition, novelty detection, or object-in-place associations in arenas with discrete items.
What experimental setups are used to infer receptive fields of MEC neurons?
Open-field exploration tasks with no objects, often testing for grid-like firing patterns during movement through space.
what are border cells
a type of neuron found in the medial entorhinal cortex (MEC) that fire specifically when an animal is near the edge or boundary of its environment
what are head direction cells
cells whose firing pattern depends on head direction
What is a place field in the hippocampus?
It’s the specific location in an environment where a place cell fires most strongly, forming a neural map of space.
What does the Lateral Entorhinal Cortex (LEC) code for?
LEC encodes object-related information, including object identity and position.
what are object cells and where are they found
cells that respond to objects placed within an envrionment that is located in the LEC
what are trace cells and where are they found
encode where an object was and fire when object is removed, located in the LEC
How can animal models of spatial navigation relate to other cognitive functions?
Tasks like maze navigation and context discrimination also model episodic memory, context-dependent learning, and cognitive flexibility relevant to human cognition.
What types of evidence test whether the hippocampus is necessary for memory?
Lesion studies, temporary inactivation, and optogenetics show that disrupting the hippocampus impairs tasks like spatial learning, contextual fear, and episodic memory.
what are the conclusions for lesion studies of LEC and MEC
LEC lesion impairs object memory
MEC lesion impairs contextual memory
what is global remapping
when one spatial map is replaced by another when an entity goes into 2 different environments
what is rate remapping
occurs when nonspatial/less spatial stimuli (local cues, objects, testing chamber) change but main environment remains the same
How is episodic memory formed in the brain?
Through convergence of spatial (MEC) and object (LEC) inputs in the hippocampus, forming rich contextual representations.
What type of memory is the hippocampus most critical for?
Declarative (explicit) memory, especially episodic memory—memory for events tied to specific times and places.
What are three alternate memory systems to the hippocampus and their brain regions?
Striatum: Procedural memory (habits, skills)
Amygdala: Emotional memory (fear conditioning)
Cerebellum: Motor learning (e.g., eyeblink conditioning)
what is the key characteristics of early sensory processing
firing rate increases directly with stimulus intensity
what are the key characteristics of higher-level memory processing
complex, distributed patterns encode specific experiences
What is the function of the dorsal striatum in memory?
It supports habit learning and stimulus-response associations.
How does the amygdala influence memory?
It enhances memory consolidation via emotional arousal and mediates both fear and reward-based conditioning.
What was shown in hippocampal lesion studies using water mazes?
Hippocampal lesions impair flexible spatial navigation but not simple place learning.
what are the subtypes of nondeclarative long-term memory
skill learning
priming
associative learning
what is priming
exposure to a stimulus faciliatates subsequent responses to the same or similar stimulus
what is skill learning
learning to perform a task requiring motor coordination
what is associative learning
the association of two stimuli or of a stimulus and a reponse
what are the different types of skills
sensorimotor skills (mirror drawing task)
perceptual skills (mirror reading task)
cognitive skills (puzzles involving planning and problem solving)
what are the brain areas involved with skill learning
basal ganglia
motor cortex
cerebellum
what are the differences between hippocampal and dorsal striatum memory systems
hippocampal
cognitive/place/detailed/rational memory
dorsal striatum
habit, stimulus-response
what are the advantages of cognitive vs. habit memory
hippocampal memory — flexible
striatum/habit: fast, automated, unconscious
support each other, lead to the same goal/behaviour
what are the tradeoffs of cognitive vs. habit memory
habits can lead to mistakes when a response is applied in the wrong situation
impaired hippocampal function/overactive striatum may contribute to exaggerated habit-like behaviour in addiction, anxiety, autism, tourette’s syndrome
what are the types of associative learning
reflexive conditioning
appetitive/aversive conditioning
what is reflexive conditioning
conditioned automatic reflexive behaviour — cerebellum
what is appetitive/aversive conditioning
an organism learns to associate a neutral stimulus with an emotionally significant outcome — either positive (rewarding) or negative (punishing).
What is the role of the amygdala in fear conditioning?
It forms associations between neutral stimuli and aversive outcomes, producing conditioned fear responses.
What is a 'cell assembly' in Hebbian theory?
A network of neurons with strengthened connections due to repeated simultaneous activation, allowing pattern completion and associative memory.
What is the principle behind Hebbian plasticity?
cells that fire together, wire together. simultaneous activation strengthens synaptic connections
What is long-term potentiation (LTP)?
A long-lasting increase in synaptic strength following high-frequency stimulation of a synapse, often considered a cellular basis for learning and memory.
What is late LTP (L-LTP)?
A longer-lasting form of LTP (hours to days or more), requiring gene expression, protein synthesis, and structural changes at synapses.
What is early LTP (E-LTP)?
A short-lasting form of LTP that lasts minutes to hours and involves post-synaptic modifications without requiring new protein synthesis.
What are three fundamental properties of LTP?
Input specificity – Only the active synapse is strengthened
Cooperativity – Multiple weak inputs can trigger LTP if they co-activate
Associativity – Pairing a weak input with a strong one can strengthen both
What initiates NMDA receptor activity during LTP?
Glutamate binding + postsynaptic depolarization (removes Mg²⁺ block).
What changes occur at the synapse after LTP?
Increased AMPA receptor function and number, and enhanced neurotransmitter release.
What is synaptic tagging and capture?
a mechanism where a weakly stimulated synapse can capture memory proteins made during a nearby strong stimulus, enabling long-term memory formation
what is flashbulb memory
a type of vivid, detailed, and long-lasting memory for the context in which a person first learned about a surprising, emotionally significant, or shocking event.
How have scientists artificially activated specific memories?
Using optogenetics, researchers can label neurons active during learning and later reactivate them with light to trigger recall or behavioral responses.
What is an example of artificial memory activation in rodents?
In one study, rodents formed a memory in context A, but when neurons from A were reactivated in context B using light, the rodents froze—indicating recall of the fear memory.
What are 'engram cells'?
Neurons that store specific memories. Artificial reactivation (e.g., via optogenetics) can induce recall of the encoded memory.
How can false memories be created using optogenetics?
By activating engram cells during an unrelated aversive experience, causing mice to associate fear with a previously safe context.
describe negative to positive memory conversion
session 1: negative memory engram cells labelled with ChR2
session 2: activating those negative engram cells when mice enter a certain place causes mice to avoid that place
session 3: negative engram cells are activated while mice undergo a positive experience
session 4: subsequent activation of those engram cells, when mice visit a certain place, causes mice to prefer that place