SET 2 biology chapter 3 enzymes
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
enzymes def.
proteins that act as biological catalysts to speed up biological reactions by lowering activation energy required to initiate a given reaction
enzyme features
reusable
have an active site specific to substrate
speed up not create
are proteins (most??)
all enzymes are catalysts but not all catalysts are enzymes
can influence entire biochemical pathways
often end in ‘ase’
above the arrow in a reaction (not a reactant or product)
the enzyme active site and substrate are…
complementary in shape
how an enzyme works
substrate bind to specific complementary enzyme active site → together they form enzyme-substrate complex → active site conformationally changes to accomodate substrate → substrate small change → reaction occurs → products leave enzyme active site → enzyme can be reused
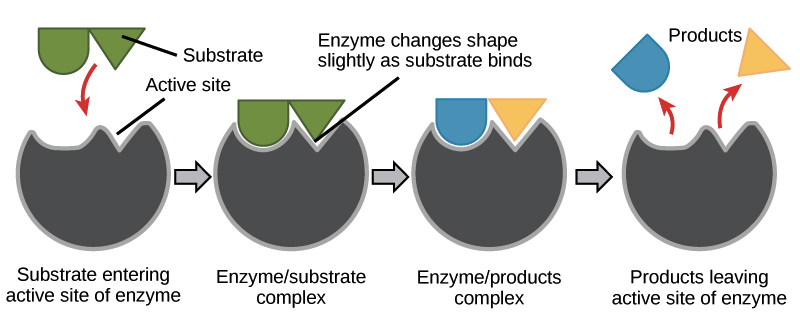
activation energy
minimum energy amount required to energise atoms to state where they can undergo chem. transformation
anabolic vs catabolic
anabolic = smaller molecs. combine, form bigger molecule (think assemble)
catabolic = large molecule breaks down, form smaller molecs.
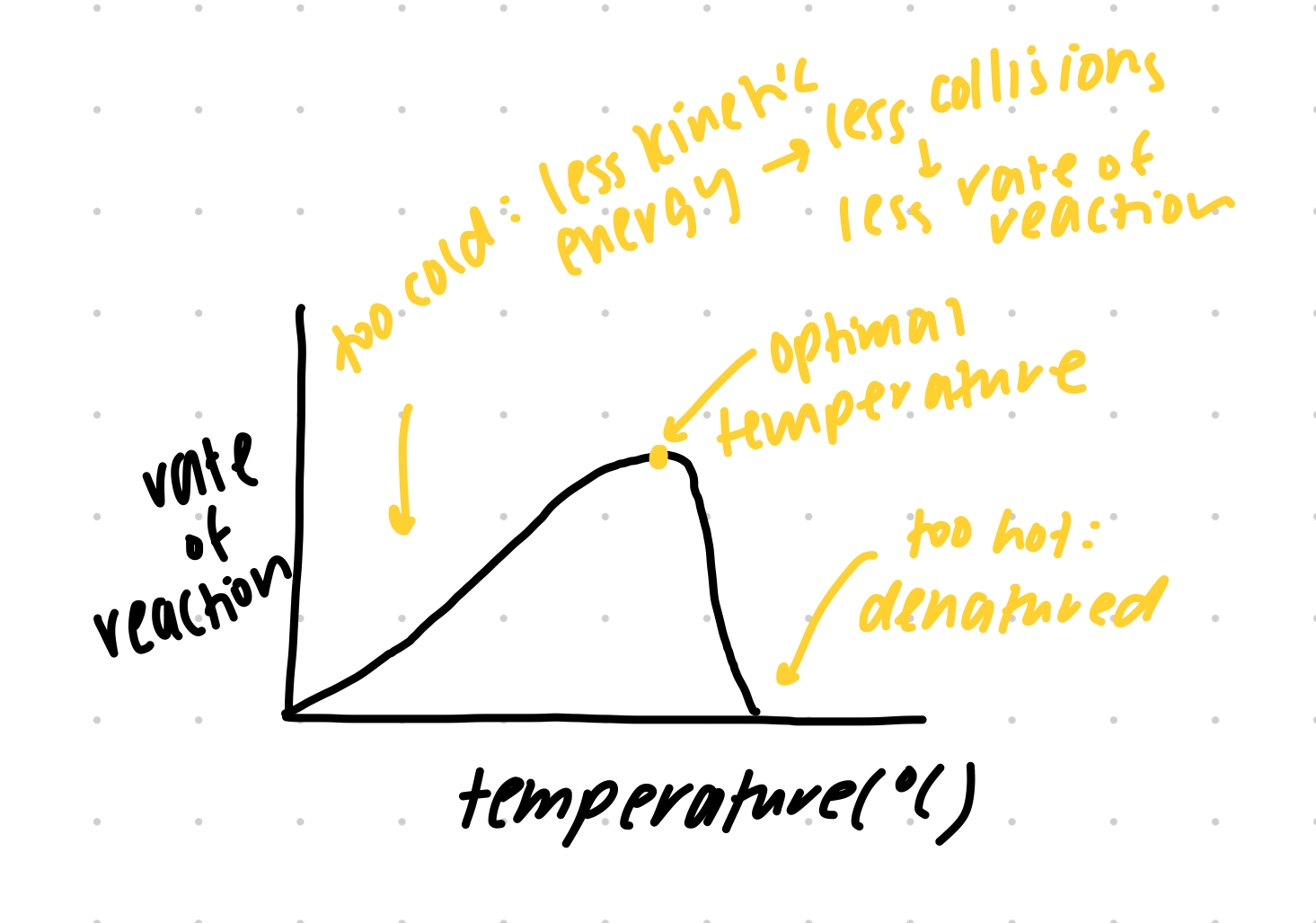
factors on enzyme activity — TEMPERATURE
too cold: less kinetic energy → less enzyme active site and substrate collision → lowered enzyme activity
BUT can regain functionality by heating
too hot: causes enzyme denaturation → active site conformationally change → substrate cannot fit, reduced enzyme activity
this is irreversible
factors on enzyme activity — TEMPERATURE graph
factors on enzyme activity — pH
optimal level varies between dif. enzymes based on their location
too acidic or too basic → enzyme denaturation → active site conformationally change → substrate cannot fit, reduced enzyme activity
factors on enzyme activity — pH graph
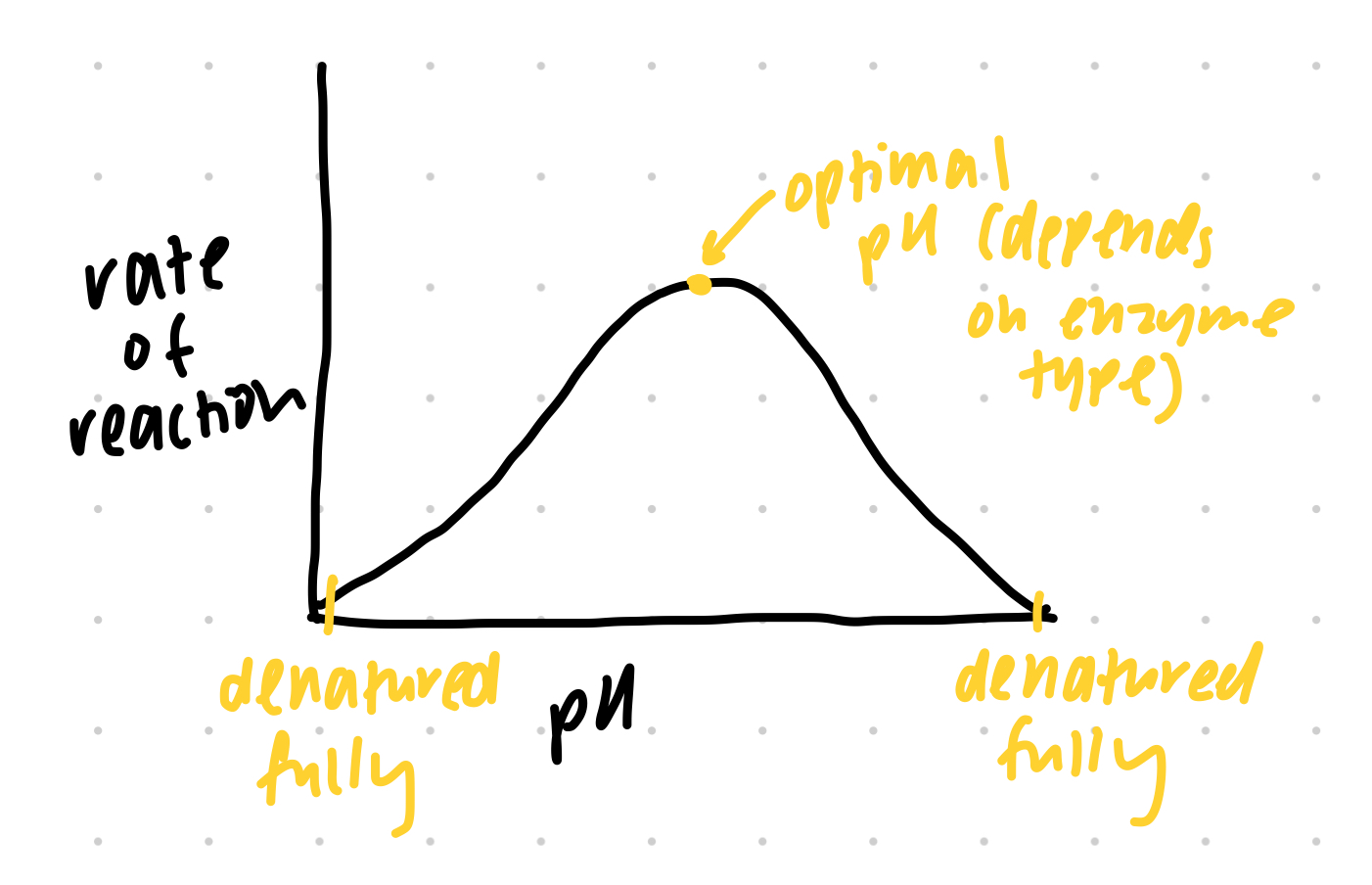
optimal def. and tolerance range def.
optimal level = point for a given condition where max. function of enzyme occurs
tolerance range = wider range of given condition that an enzyme can function under
factors on enzyme activity - CONCENTRATION
substrate conc. = enzyme conc. constant while substrate conc. increases → increase in enzyme activity until saturation point → here all enzyme active sites occupied hence plateau
enzyme conc. = substrate conc. constant while enzyme conc. increases → more active sites hence increase in activity until saturation point → here all substrates used up hence plateau
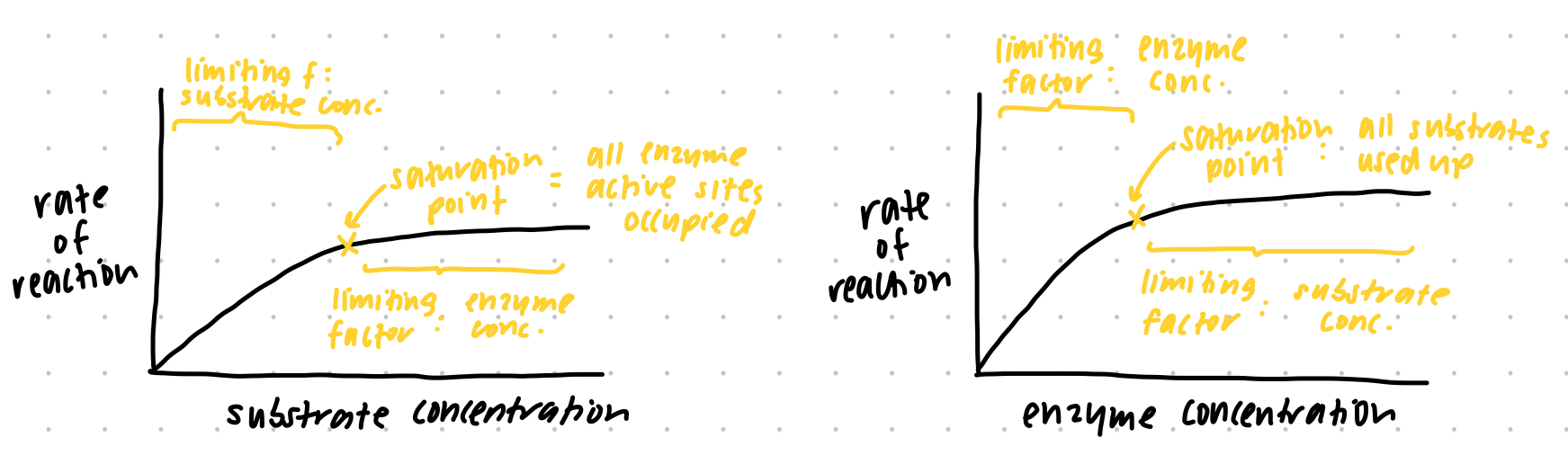
factors on enzyme activity - CONCENTRATION graphs (substrate and enzyme concentration)
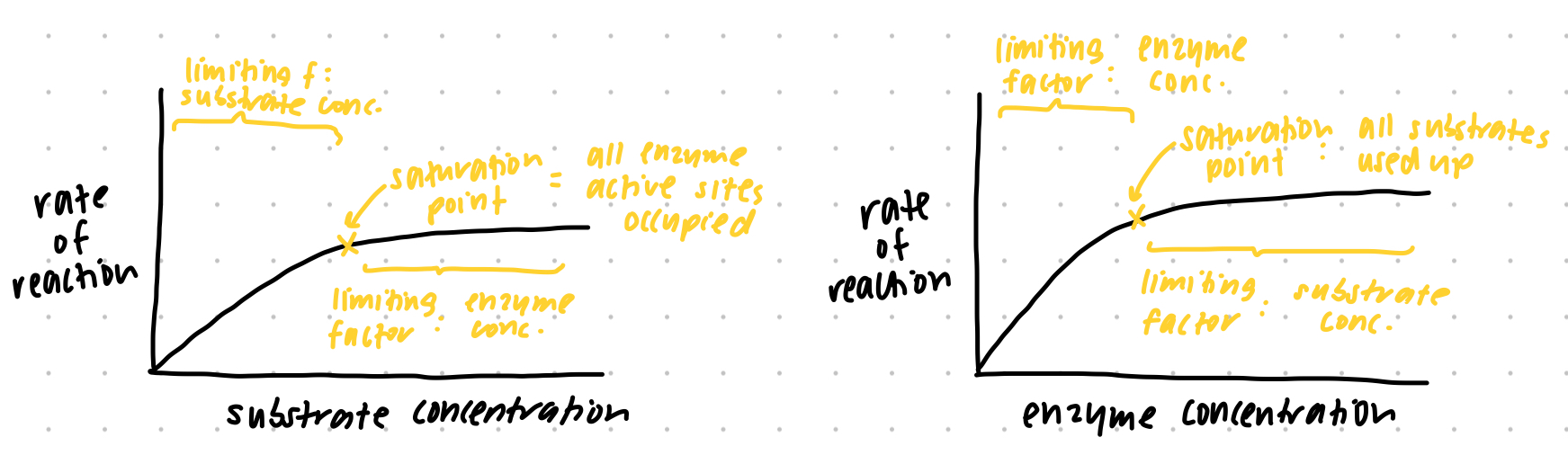
saturation point def.
point where substance cannot receive more of another substance → plateau of graph here
limiting factor def.
factor that prevents rate of reaction from increasing
inhibitors def.
molecs. bind to enzyme and prevent its functioning
competitive and non-competitive inhibition
competitive inhibition = inhibitor bind to enzyme active site → blocks substrate from binding → inhibitor shape is complementary to active site enzyme hence inhibitor shape similar to substrate shape (as they both complement to same active site)
influenced by substrate conc.
non-competitive inhibition = inhibitor binds to site on enzyme other than active site (allosteric site) → causes conformational change to active site → substrate cannot bind to it
not influenced by substrate conc.
reversible and irreversible inhibition
reversible inhibition = bonds formed between inhibitor and enzyme are weak → can be broken → slows rate of reaction not stops
can be competitive and non-competitive
irreversible inhibition = bonds formed between inhibitor and enzyme strong → can‘t be broken easily → reaction never occurs with enzyme
generally competitive
biochemical pathway inhibition
when end product (of pathway) inhibits enzymes in the pathway → halts pathway → so production is regulated
coenzyme def.
organic non-protein that assists enzyme function (releases energy, recyclable)
e.g. ATP
cofactor def.
organic or inorganic molecule that assists enzyme function
coenzymes are a subset of cofactors