chapter 9 - architectural patterns of animals
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
homeobox
DNA sequences within developmental genes (like hox genes) that encode the homeodomain, a DNA-binding region of transcription factors
function of homeodomain transcirption factor proteins
regulate gene expression
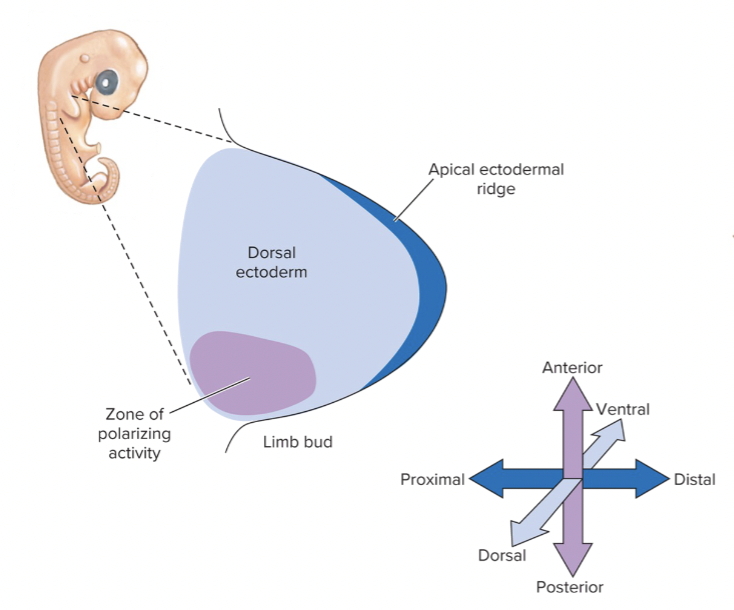
How do Wnt, FGF, and Sonic Hedgehog signaling lead to organogenesis?
Wnt/FGF/Shh activate transcription factors → induce homeobox (HOX) genes → specify cell fate → organogenesis
what tissue gives rise to the neural plate
dorsal ectoderm
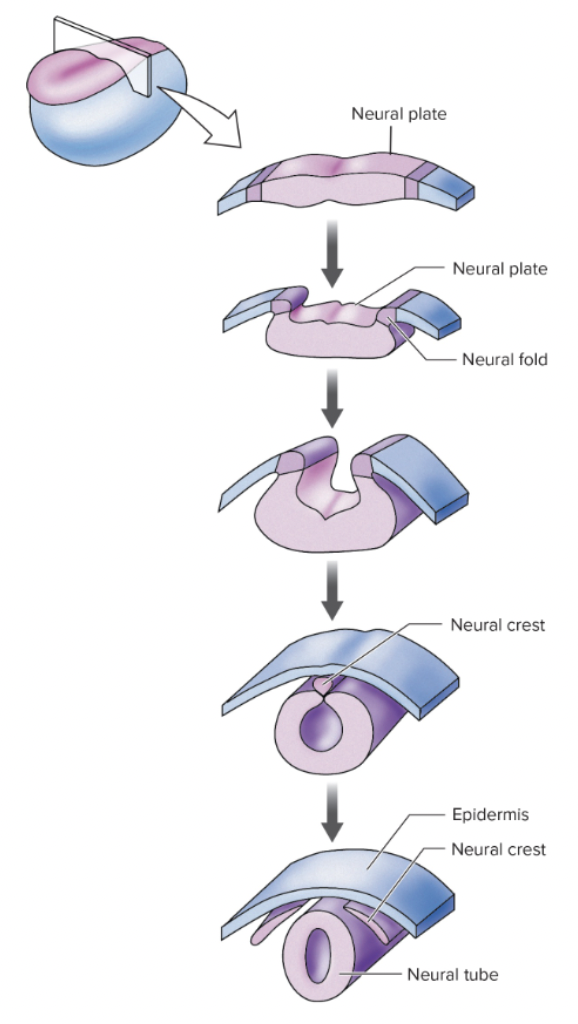
what induces neural plate formation
signals from underlying mesoderm (including the notochord)
what forms from the neural tube
brain and spinal cord
what do neural crest cells do
migrate and form diverse tissues (facial structures, pigment cells)
what happens if homeobox genes are mutated
developmental abnormalities, like the transformation of body parts
how many phyla are recognized in kingdom animalia
32, which appeared during cambrian explosion, and the different phyla represent distinct body plans
age of fossil from cambrian period
500 million years old
5 grades of hierarchical organization of animal complexity
protoplasm, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems
ex of protoplasm complexity
unicellular organisms
ex of cell complexity
sponges
ex of tissue complexity
jellyfishes
ex of organ complexity
flatworms
ex of organ systems complexity
most animal phyla
three main types of animal symmetry
no symmetry, radial symmetry, and bilateral symmetry
ex of no symmetry
poriferia (a sponge)
ex of radial symmetry
cnidaria/jellyfish
ex of bilateral symmetry
most animal phyla
what is cephalization and which type of symmetry is it associated with
cephalization = differentiation of a head with a concentration of sensory organs and feeding apparatus - associated w/ bilateral symmetry
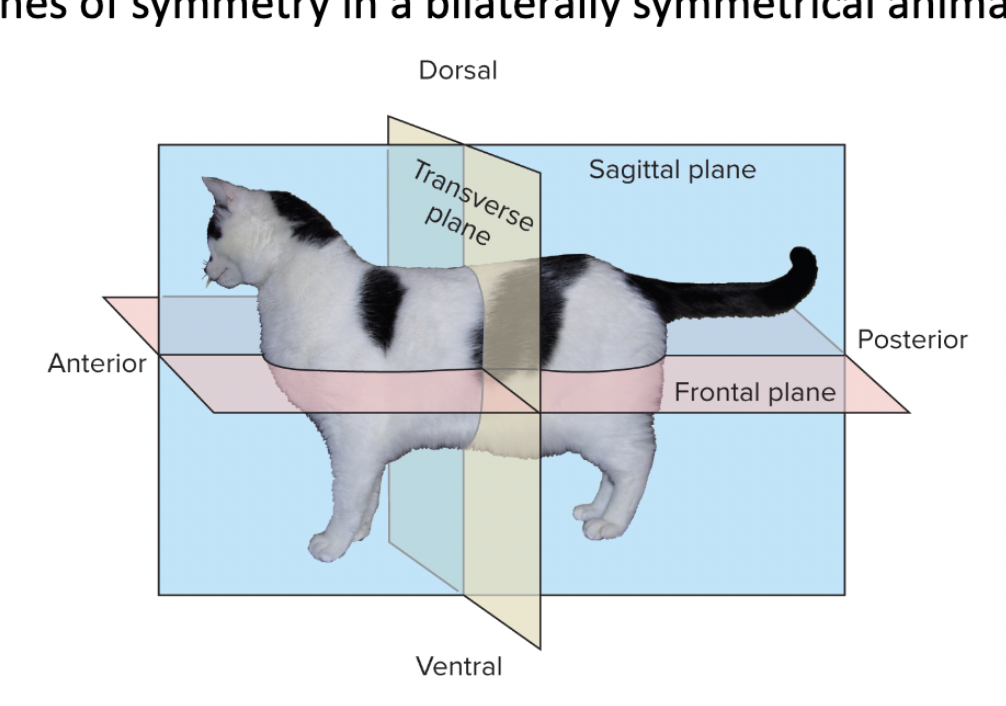
planes of symmetry
sagittal plane - Divides the body into left and right
SAG = Side (left vs right)
frontoal (coronal) plane - Divides the body into front (anterior) and back (posterior)
FRONT-al = Front
transverse plane - Divides the body into upper (superior) and lower (inferior)
TRANS = Across (across the body)
parenchyma
Spongy, space-filling tissue
PARENCHYMA = PADDING
→ fills space like a sponge
acoelomate
lacks a body cavity
A = Absent coelom
→ all solid, no space
pseudocoelom
is a “fake” coelom not completely lined w/ mesoderm
PSEUDO = Pretend
→ looks like a cavity but isn’t proper
pseudocoelomate
Body cavity from blastocoel
Partly mesoderm-lined
-ate = has it
coelom
true body cavity lined with mesoderm
COELOM = Complete lining
eucoelomate
Animal with a true coelom
“Eu-” = true
diploblasts
animals w/ 2 germ layers (ectoderm and endoderm)
ex) cnidaria (jelly fish, sea anemone)
triploblasts
animals w/ 3 germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm)
ex) most animals
segmentation
segmentation - metamerism
repetition of similar body segments along the body axis
each segment = metamere