Chapter 8: T-Cell Mediated Immunity
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
dendritic cell
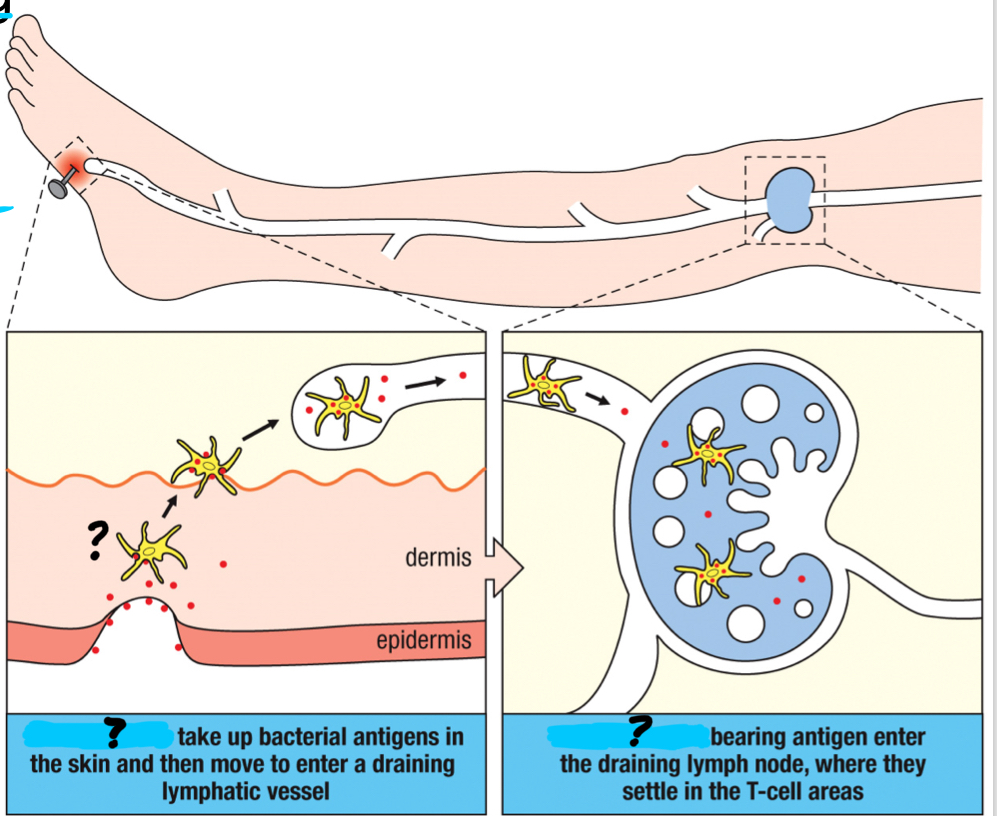
takes up an antigen at the primary infection site and transports it to the draining lymph nodes
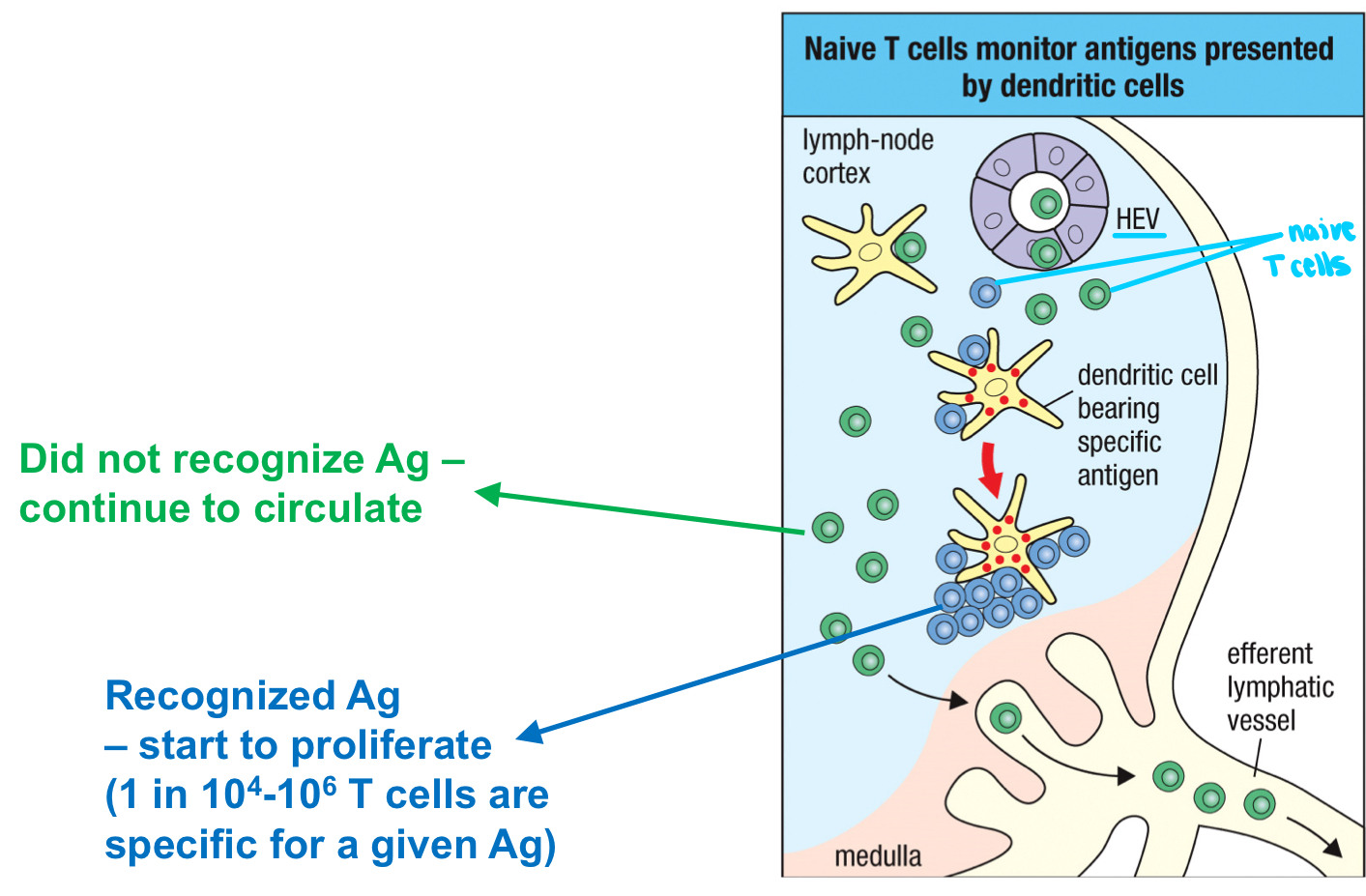
outermost cortex/T cell zone
Where are dendritic cells found in lymphoid tissue?
outermost cortex/T cell zone
Where are naive T cells found in lymphoid tissue?
HEV
small capillaries that dendritic cells use to enter the lymph nodes
lightly
Is MHC class 2 lightly or heavily expressed in the lymphatic circulation?
heavily
Is MHC class 2 lightly or heavily expressed in the lymphoid tissue?
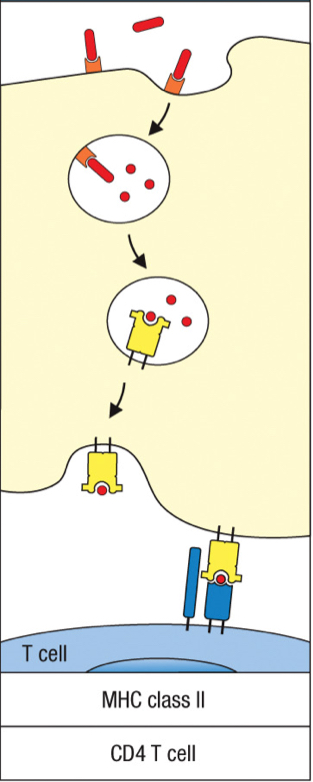
receptor-mediated endocytosis
process that captures bacteria/virus particles in extracellular fluid and send them to lysosome
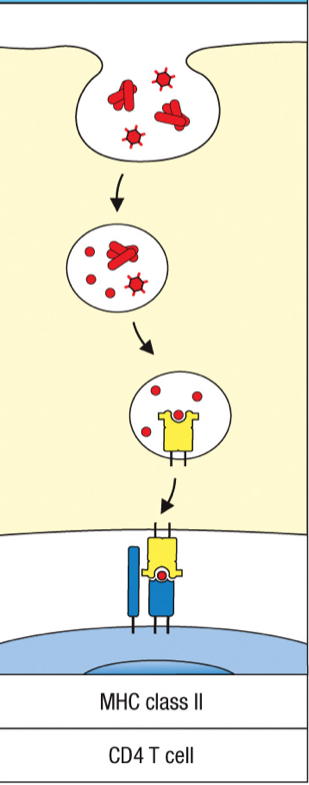
macropinocytosis
process that internalizes a larger volume of extracellular fluid directly without a receptor
true
T/F: dendritic cells can have both classes of MHC
MHC class 2
Which MHC class is used during receptor-mediated endocytosis?
MHC class 2
Which MHC class is used during macropinocytosis?
T cell zone
outermost part of the lymph node cortex where naive T cells meet with mature dendritic cells and respond to specific antigens
increase
The trapping of antigens in the draining lymph node increases or decreases their chance to meet the small population of T cells specific for a particular antigen?
homing
naive T cells leave the bloodstream to enter the T cell zone of a lymph node
draining lymph node
lymph node nearest to the infection site
HEV
T cells from the bloodstream enter the lymph node through what?
true
T/F: naive T cells enter lymph nodes via blood route or afferent lymph
L-selectin
1; an adhesion molecule that binds to GlyCAM-1 and CD34 on HEVs to attach the T cell to the endothelium to initiate migration of naive T cells into the lymph node
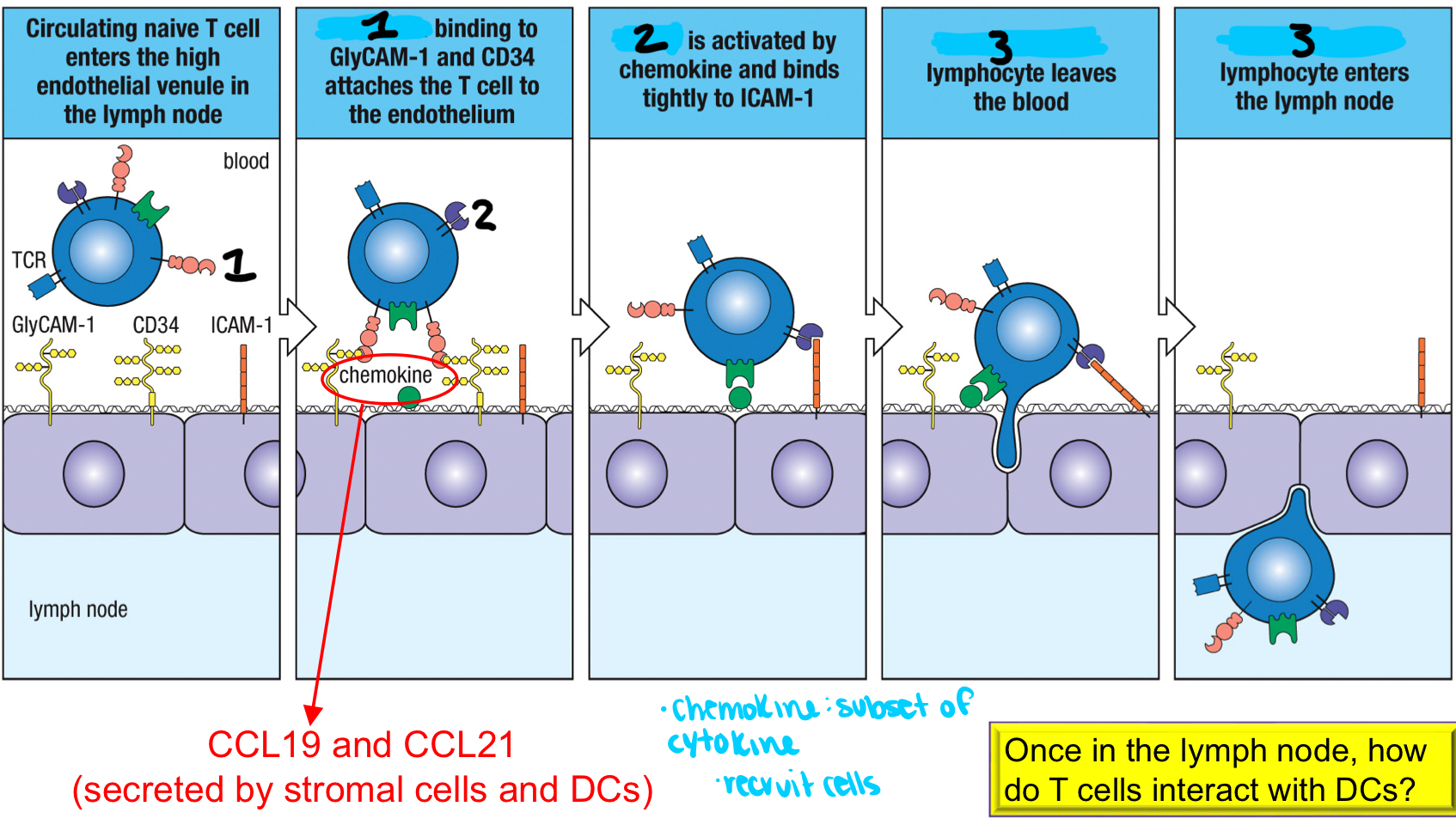
LFA-1
2; activated by chemokine and binds tightly to ICAM-1 to help assist in the naive T cell entering the HEV in the lymph node; part of p-SMAC
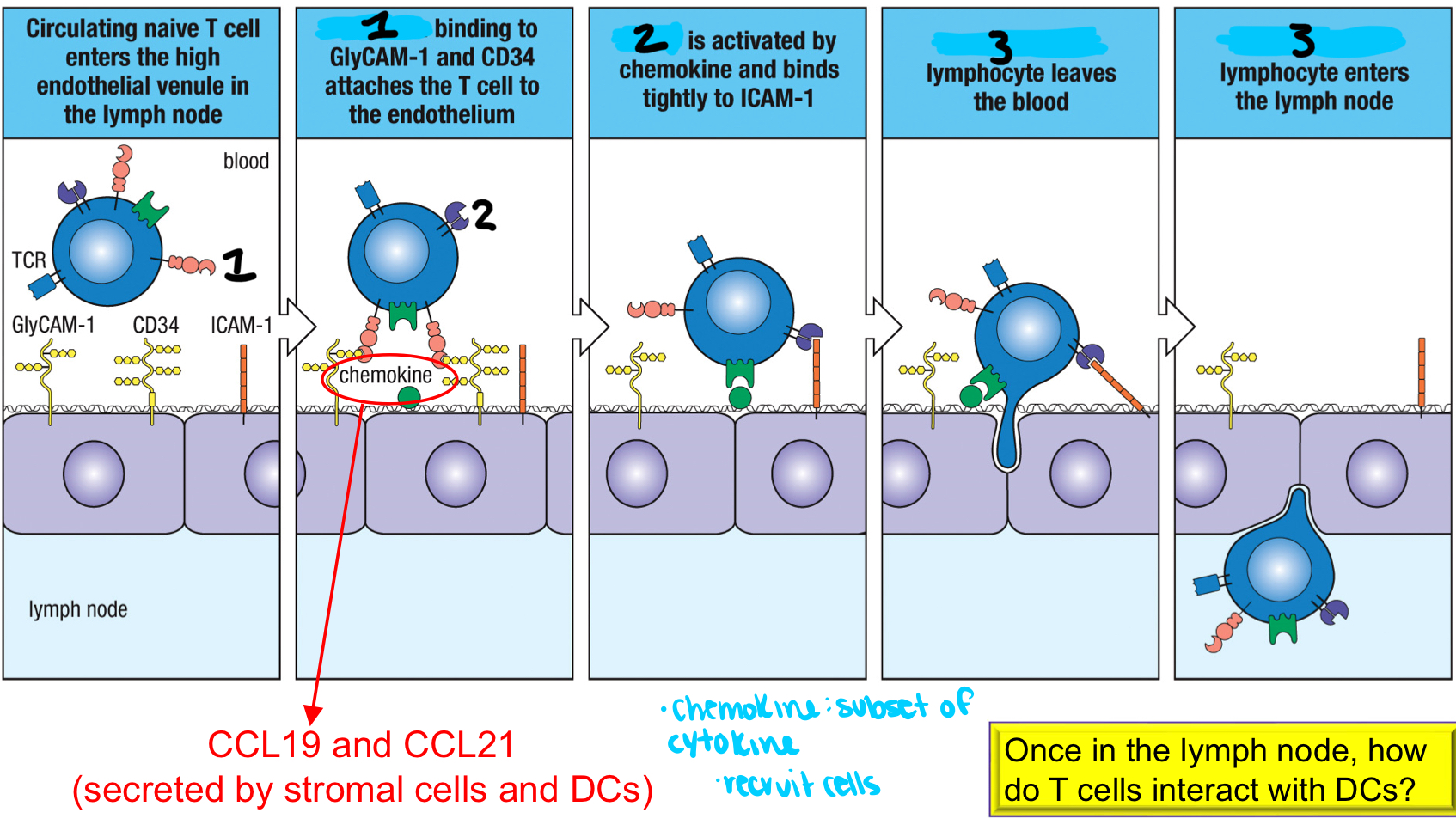
extravasation
3; process where the lymphocyte leaves the blood and enter the lymph node
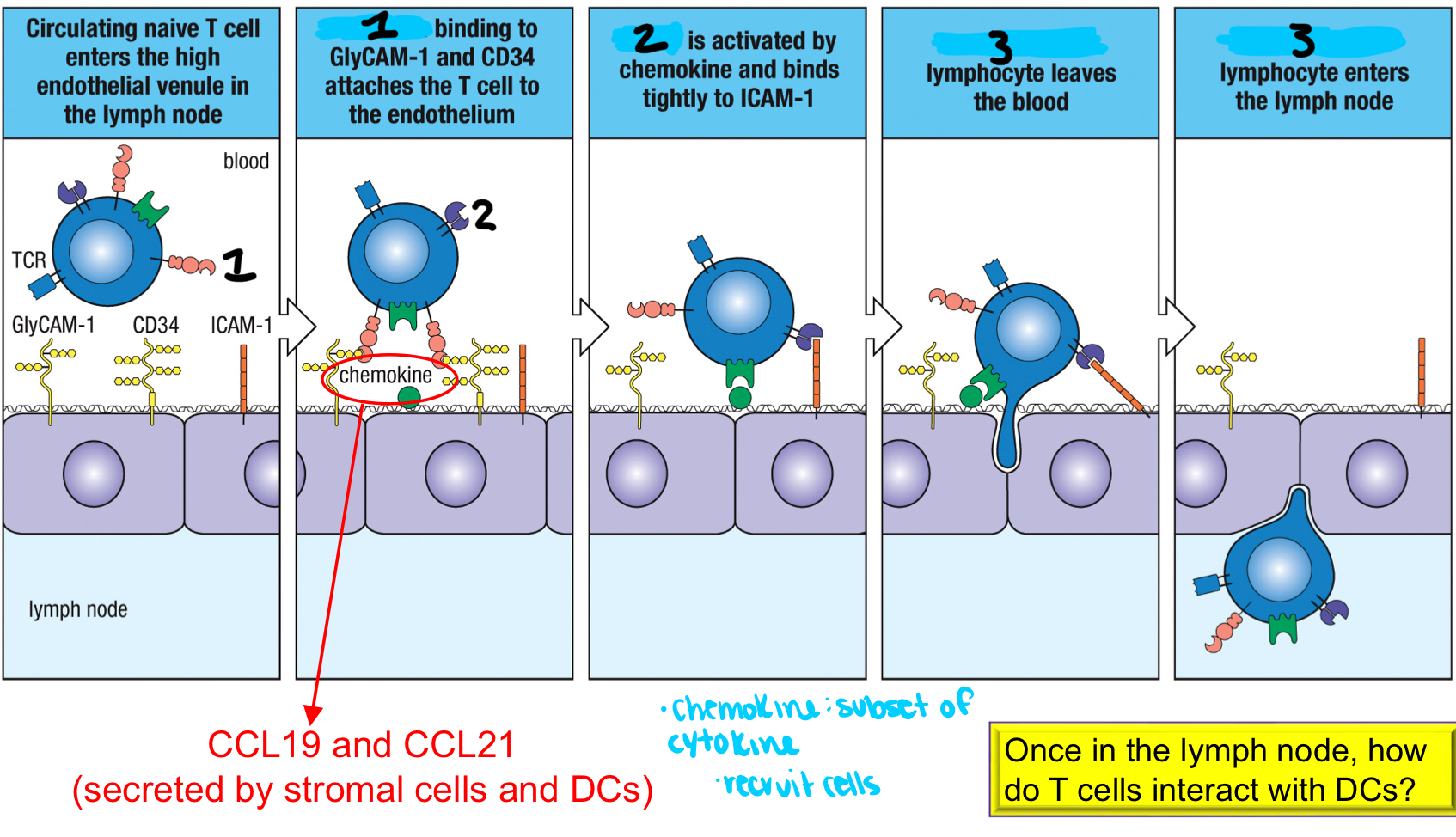
conjugate pair
when 2 cells have multiple receptors required for activation
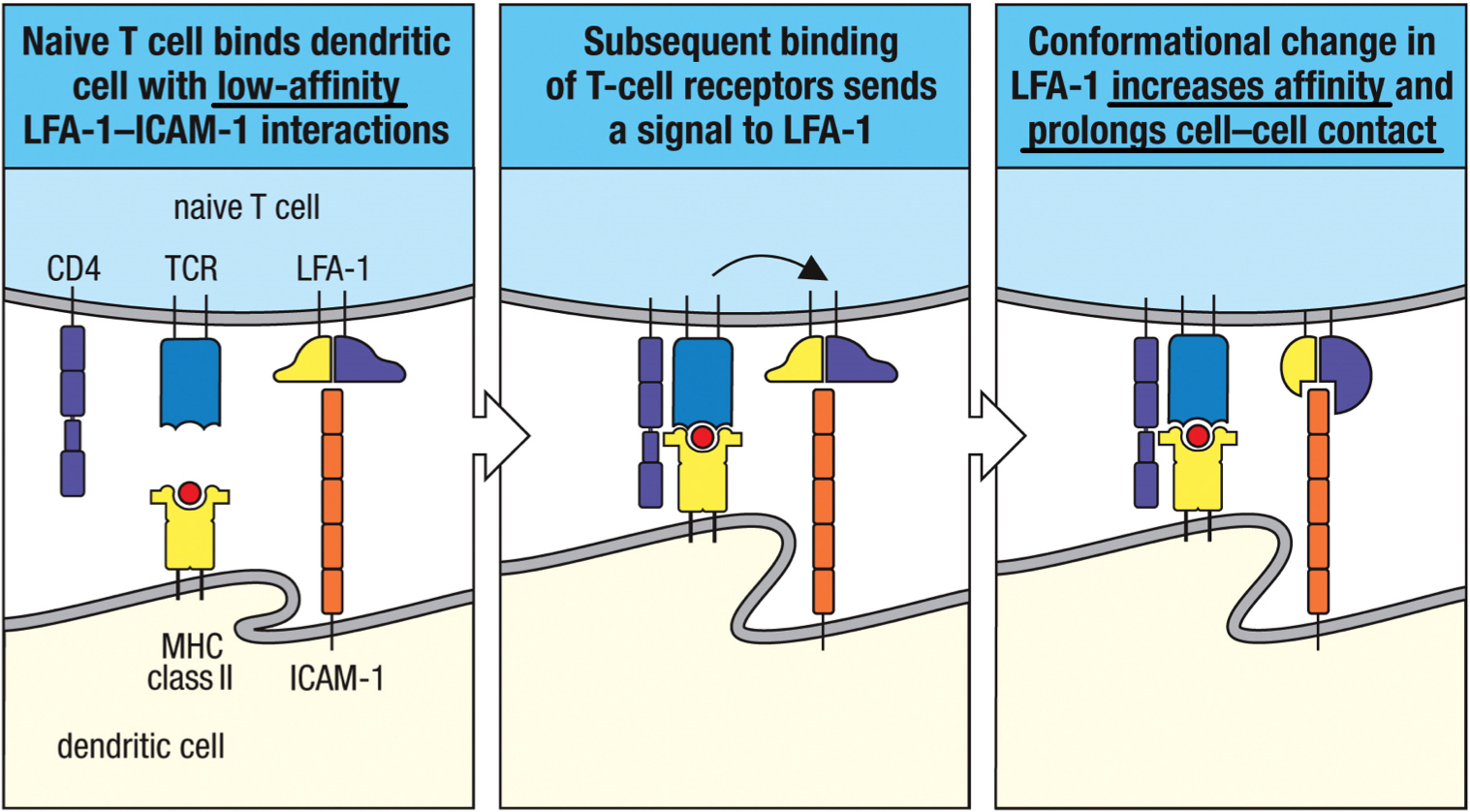
true
T/F: adhesive interactions between a naive T cell and a dendritic cell are transient but provide chances for T cells to scan through the peptide:MHC for specific recognition
true
T/F: when the T cell proliferates into a clone of effector T cells, all the clones are in contact with the dendritic cell in the process
sphingosine-1-phosphate (SIP)
forms a gradient between the T cell area and the efferent lymphatic vessel to control the process of effector T cells leaving the lymph node after the completion of proliferation
co-receptors
CD4 and CD8
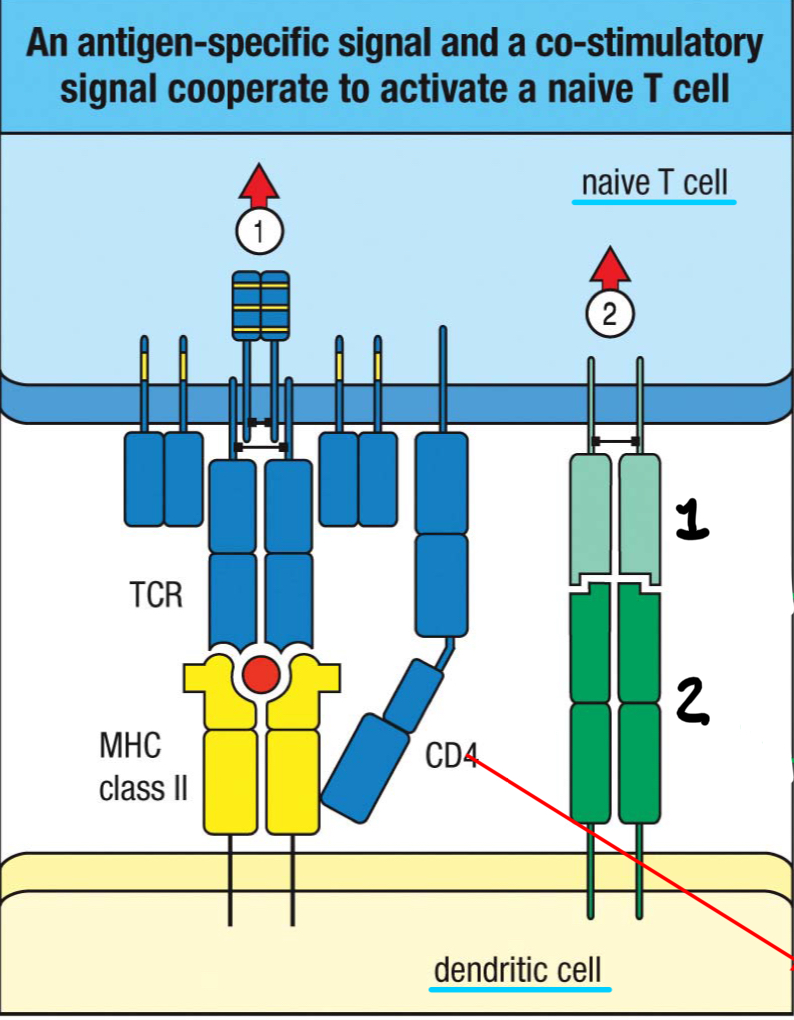
CD28
1; co-stimulatory receptor on T cells that recognizes B7 on the dendritic cell surface and promotes T cell activation
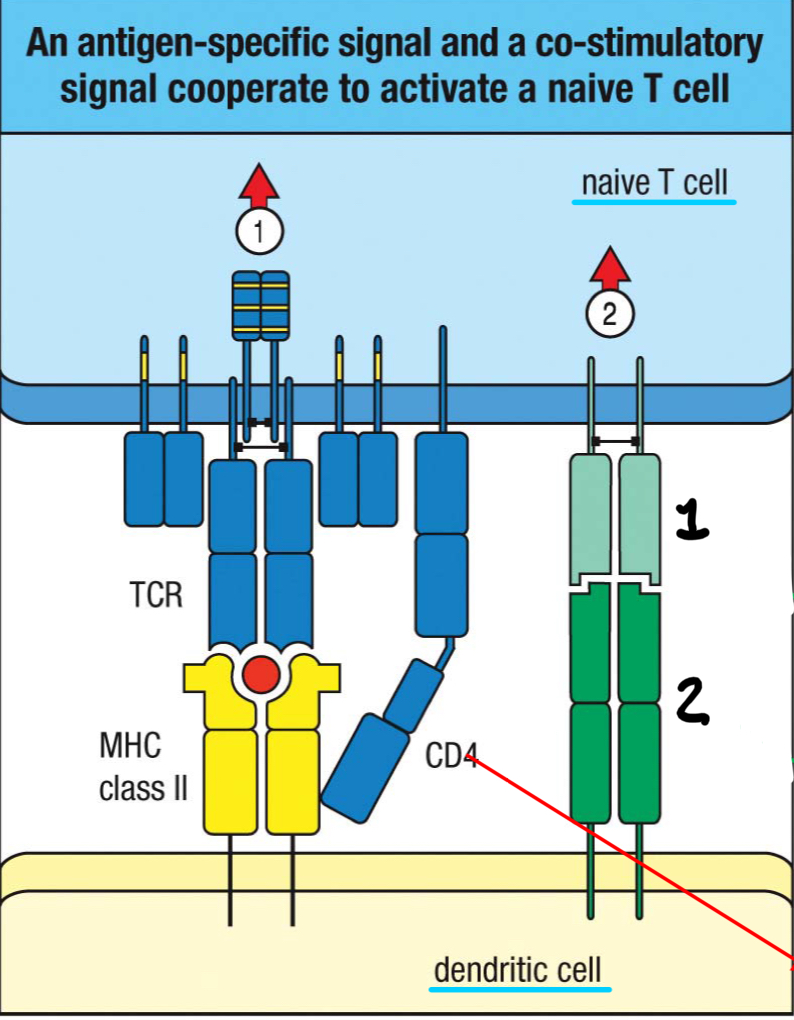
B7
2; co-stimulatory ligand found on the antigen presenting dendritic cell surface that’s recognized by the CD28 co-stimulatory receptor; induced upon activation of professional antigen presenting cells
false
T/F: dendritic cells always express co-stimulatory ligands
true
T/F: dendritic cells only express co-stimulatory ligands upon activation
true
T/F: the stimulation for T cell proliferation and differentiation requires receptor, co-receptor and co-stimulatory interactions
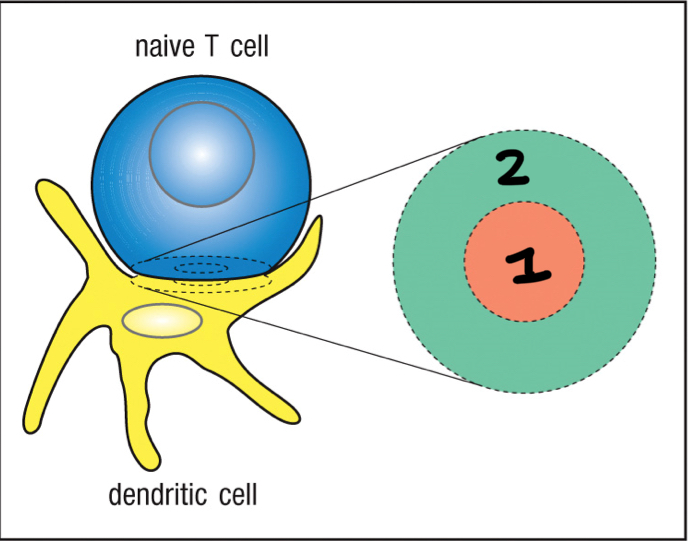
T cell synapse
space between a naive T cell and an antigen specific dendritic cell; includes the c-SMAC and p-SMAC; also space between effector T cells and target cells
central supermolecular activation complex (c-SMAC)
1; part of T cell synapse that includes TCR, CD2, CD4, CD8, and CD28; triggers signal transduction in T cells; includes TCR complex and co-receptors and co-stimulators
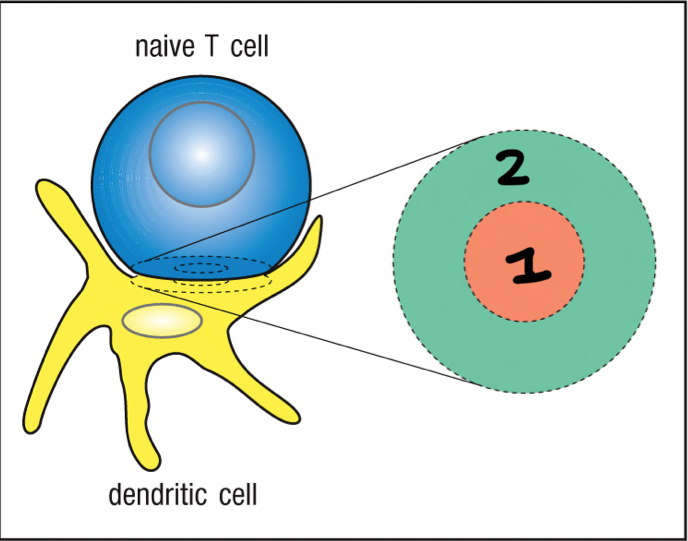
peripheral supermolecular activation complex (p-SMAC)
2; part of T cell synapse that includes LFA-1, ICAM-1; triggers signal transduction in T cells
true
T/F: the clustered interactions trigger signal transduction via several tyrosine phosphorylation reactions, which lead to T cell differentiation
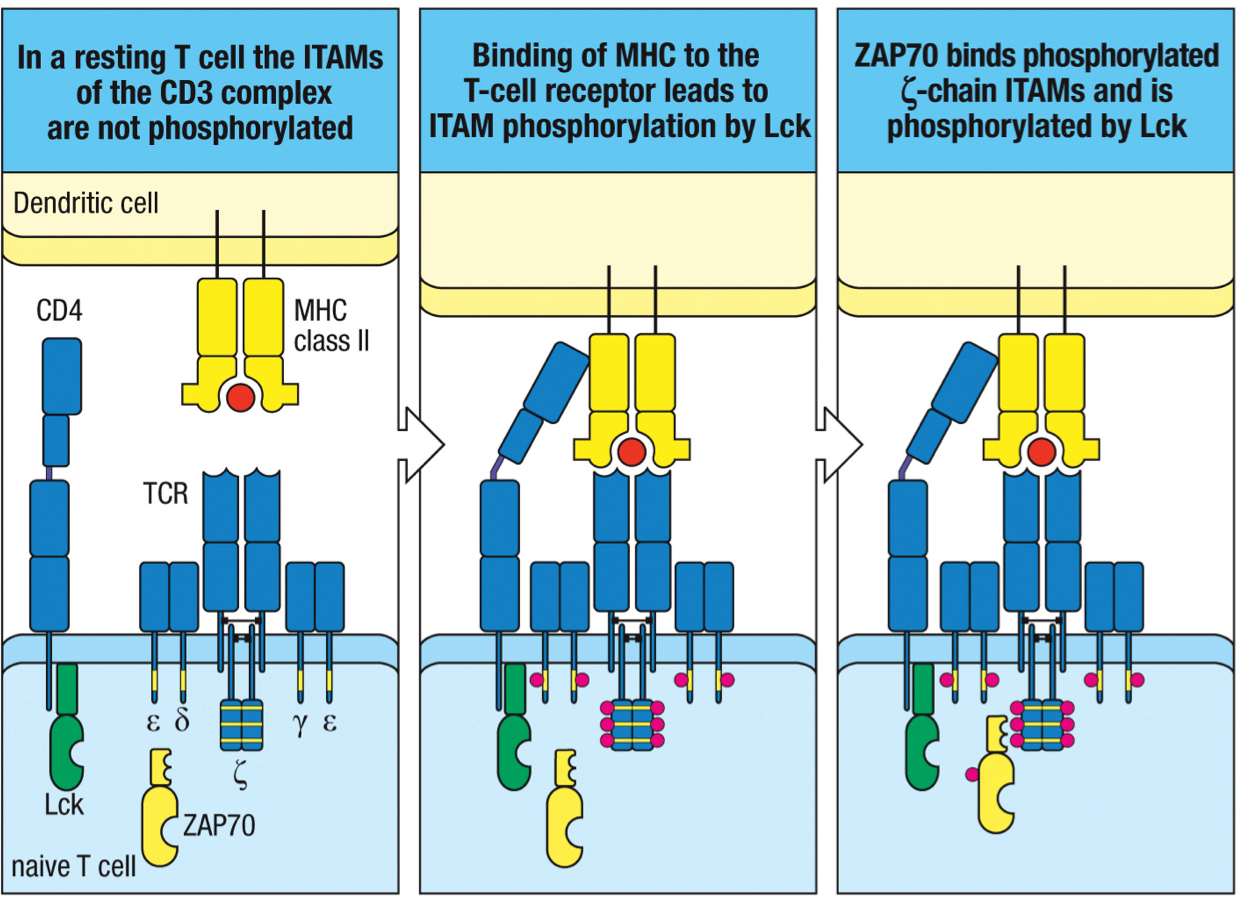
interleukin-2 (IL-2)
cytokine that acts on the activated T cell in an autocrine fashion; produced by activated T cells and is essential for the proliferation of activated T cells
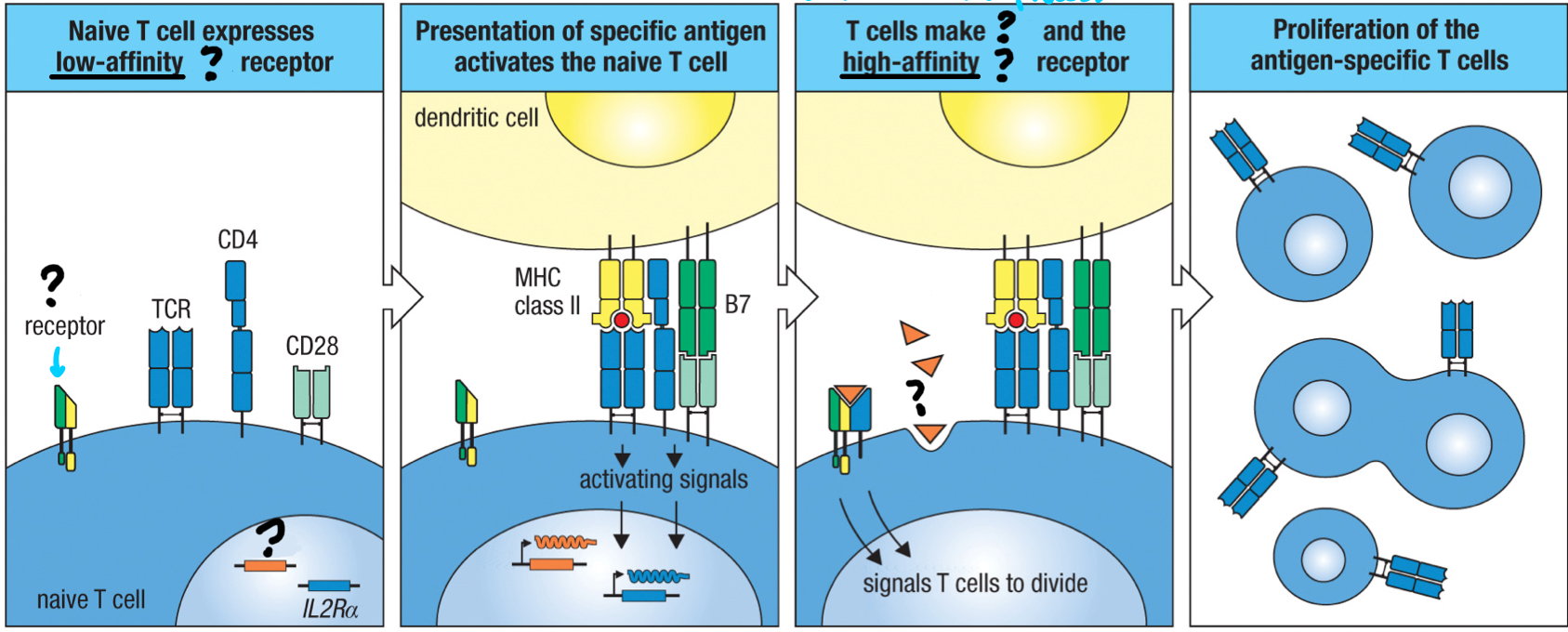
false
T/F: naive T cells and activated T cells have the same forms of IL-2 receptors
lower
Naive T cells have a higher or lower affinity to IL-2?
higher
Activated T cells have a higher or lower affinity to IL-2?
true
T/F: naive T cells can be activated by different types of cytokines leading to differentiation into distinct effector subsets that participate in different immunological processes
TH1, TH2, TH17, TFH and Treg
activation of naive CD4 T cells can trigger these 5 types of effector CD4 T cells
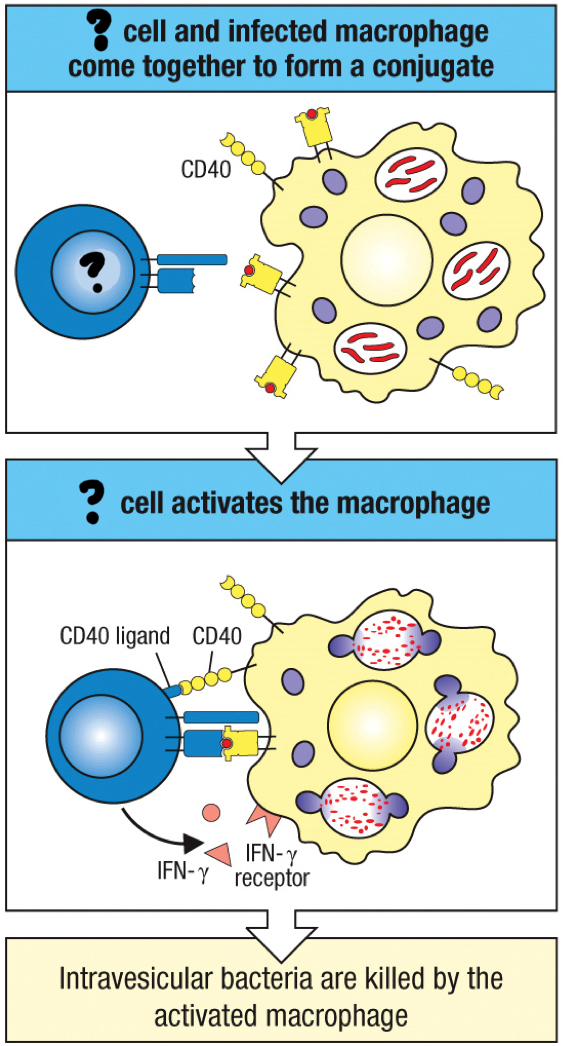
TH1 cells
effector CD4 T cell that activates macrophages to suppress intracellular infections by fusing phagosomes more efficiently with lysosomes and increasing the synthesis of microbicidal molecules, such as oxygen radicals and nitric oxide; produces inflammatory cytokines
TH2 cells
effector CD4 T cell that activates cellular and antibody response to parasites; helps basophils, mast cells, eosinophils and B cells; produce non-inflammatory cytokines that promote the production of IgE antibodies
TH17 cells
effector CD4 T cell that enhances neutrophil response to fungal and extracellular bacterial infections’ promote inflammation and are associated with autoimmune conditions
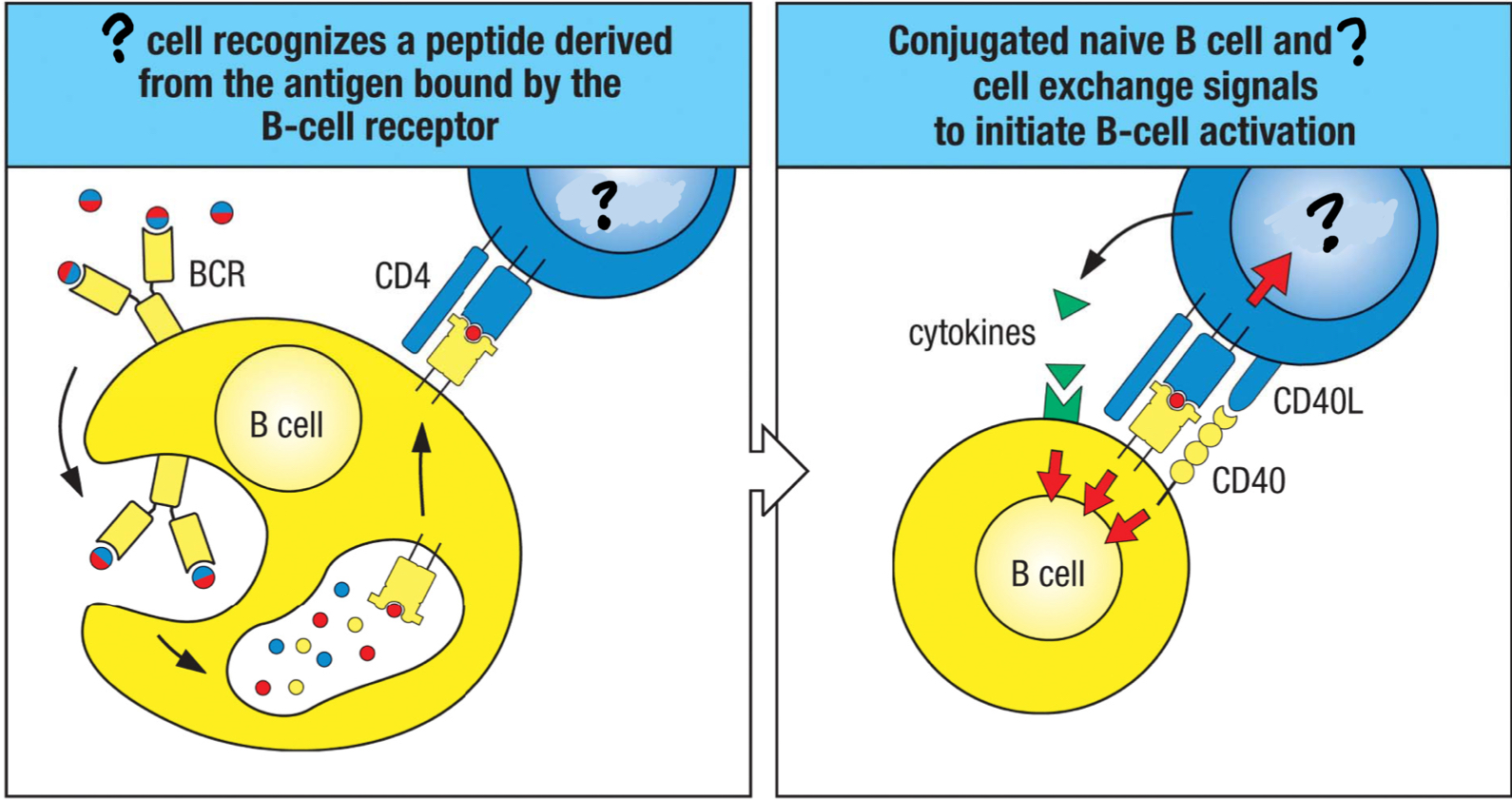
TFH cells
effector CD4 T cell that activates B cells to refine the antibody response; follicular helper T cell; helps switch isotype and increase antibody affinity; moves from the T cell area in the lymph nodes to B cell area where they interact with naive B cells in afferent lymph that have been exposed to the antigen at the site of infection
Treg cell`
effector CD4 T cell that suppresses other effector T cells
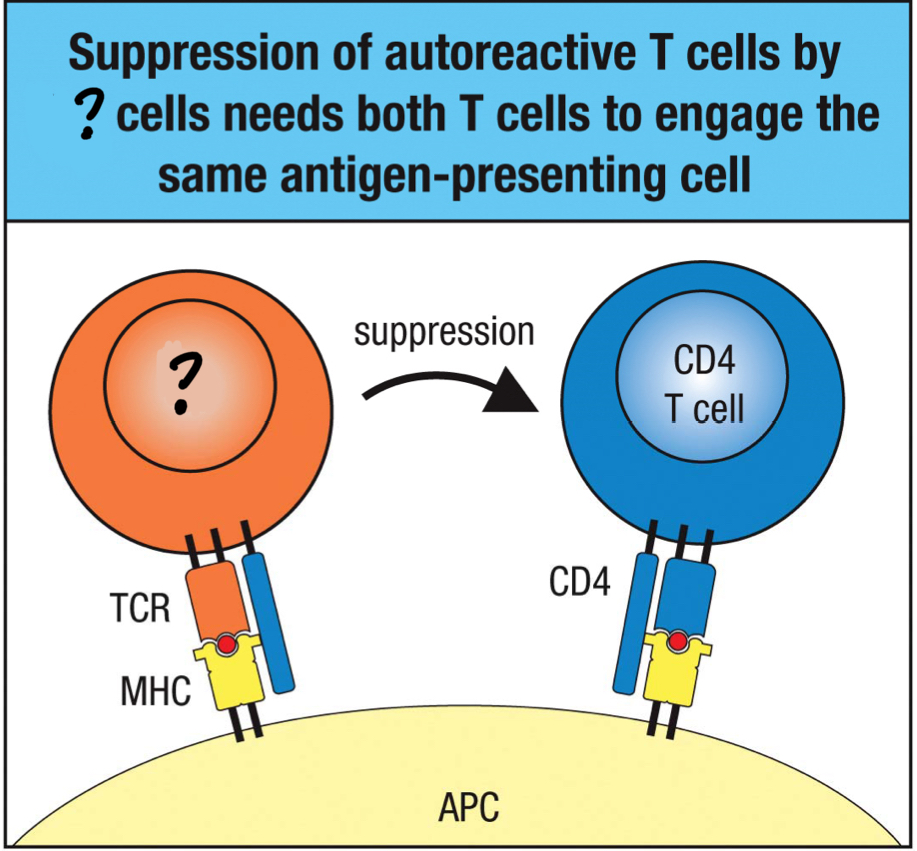
true
T/F: IL-2 production is important in CD8 T cell proliferation
true
T/F: a naive CD8 T cell can be activated directly by a virus-infected dendritic cell
true
T/F: a dendritic cell that induces insufficient co-stimulation can be helped by IL-2 secreted by the CD4 T cells to boost the activation of CD8 T cells
true
T/F: naive CD8 T cell activation requires a co-stimulatory signal
false
T/F: effector CD8 T cells/cytotoxic T cells require a co-stimulatory signal
cytokine
protein that alters the behavior of the target cell via gene regulation
cytotoxin
protein secreted by cytotoxic T cells that kills the target cell
cytotoxin
Does CD8 mainly produce cytokines or cytotoxins?
cytokines
Does CD4 only produce cytokines or cytotoxins?
helper T cell
What type of T cell is CD4?
cytotoxic T cell
What type of T cell is CD8?
granzyme
protease cytotoxin stored in lytic granules of CD8 T cells
perforin
membrane disrupting cytotoxin stored in lytic granules of CD8 T cells; forms pores in the target cell membrane
granulysin
detergent-like cytotoxin stored in lytic granules of CD8 T cells; makes pores in the target cell membrane
serglycin
proteoglycan cytotoxin stored in lytic granules of CD8 T cells
true
T/F: the targeted release of cytotoxins allows cytotoxic T cells not to attack healthy neighboring cells or the T cell itself
true
T/F: once the target cell is dying, the cytotoxic T cells can detach from the target, make a new set of lytic granules and move onto the next target cell
lytic granules
intracellular storage granule of where cytotoxins of CD8 T cells are stored
IFN-γ
cytokine secreted by activated CD8 T cells to inhibit viral replication, enhance MHC expression and activate macrophages to dispose of dead/dying infected cells
macrophage activation
the overall enhancement of macrophages by the cytokines secreted by TH1 cells
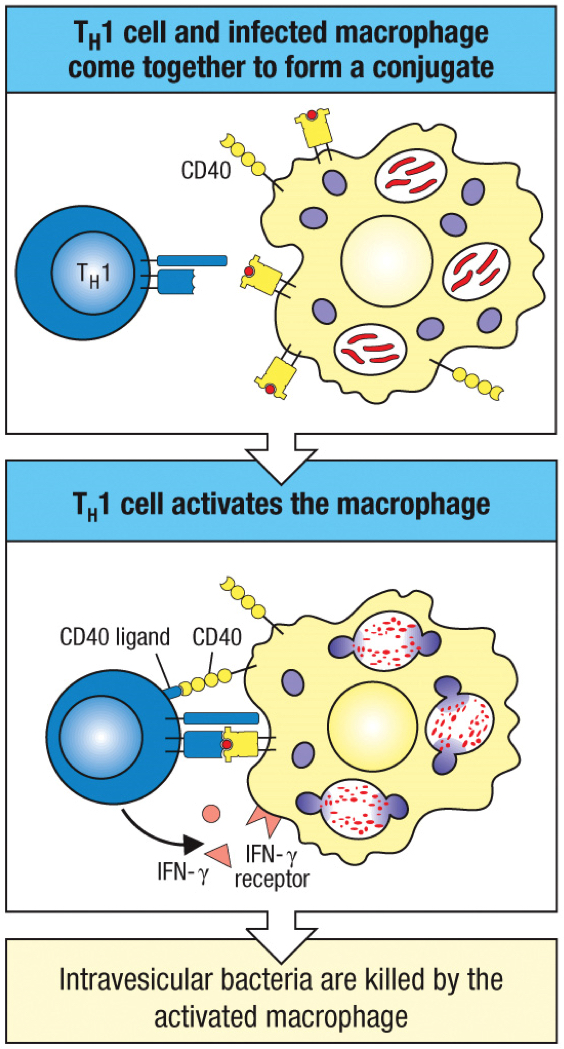
IFN-γ and CD40 ligand
two cytokines from TH1 cells that activate macrophages
true
T/F: TH2 and Treg cytokines suppress macrophage activation and limit damage to healthy cells
MHC class 2
Which MHC class goes with CD4 T cells?
MHC class 1
Which MHC class goes with CD8 T cells?
T cell anergy
state of nonresponsiveness that’s induced in naive T cells if their antigen receptor is engaged in the absence of co-stimulation
CD40 ligand
transmembrane protein on T cells that’s the ligand for CD40 on B cells and triggers their proliferation and differentiation and their ability to switch isotypes
true
T/F: only mature dendritic cells can activate naive T cells
true
T/F: naive T cells can only be activated in secondary lymphoid tissues
false
T/F: naive T cells are activated in both the cortex and the medulla of lymph nodes
true
T/F: naive T cells express LFA-1 molecules that change their conformation after encountering a specific peptide:MHC complex
true
T/F: naive T cells exit from lymph nodes using the same route as effector T cells
true
T/F: naive T cells express S1P receptors on their surface, which allows them to reenter the circulation
false
T/F: Once T cells are activated by specific antigens, they cease to secrete and respond to IL-2
true
T/F: Once T cells are activated by specific antigens, they suppress expression of the S1P receptor
true
T/F: dendritic cells upregulate B7 after engaging innate immunity receptors at sites of infection
__ cells remain in, rather than leave, the secondary lymphoid organs in which they differentiated.
CD4 TFH cells